Managing Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Literature Review of Current Non-Surgical Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
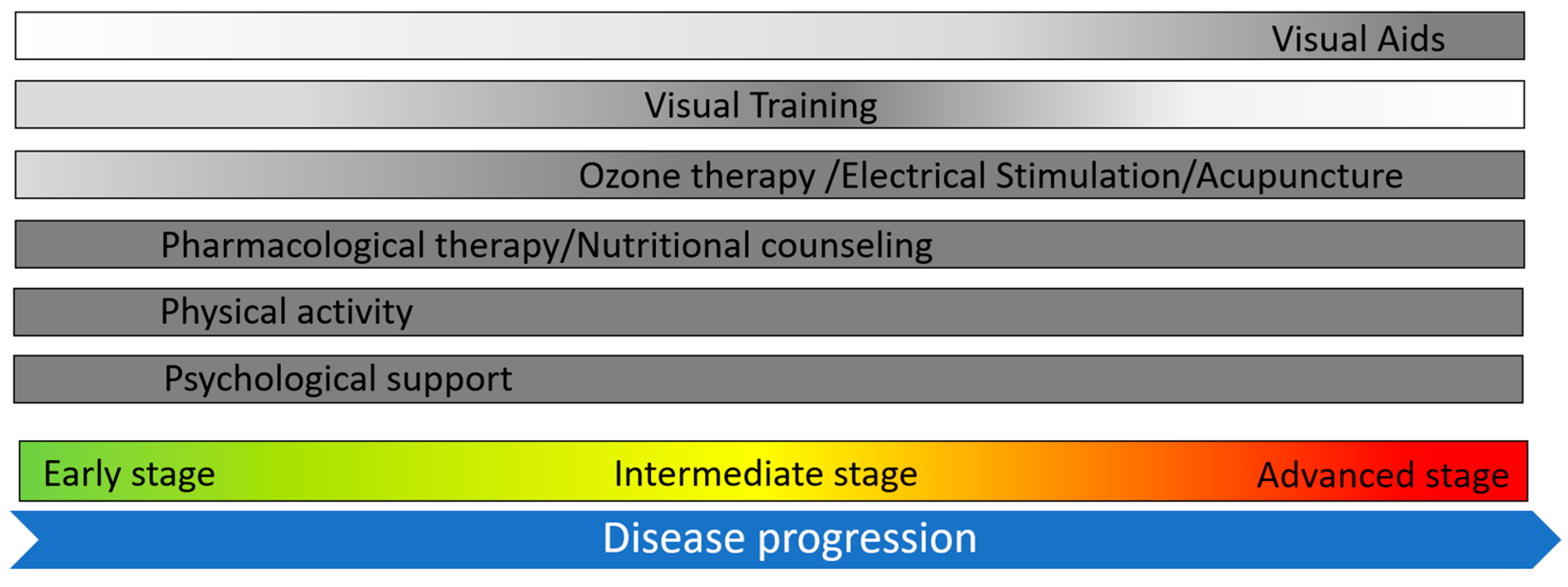
2. Enhancing Vision in Retinitis Pigmentosa
2.1. Visual Training
2.2. Visual Aids: From Traditional Magnifiers to Advanced Digital Solutions
2.3. Photoprotection
3. Complementary Therapies
3.1. Electrical Stimulation
3.2. Acupuncture
3.3. Oxygen and Ozone Therapy
4. Pharmacological Therapies
5. Lifestyle and Nutrients
5.1. Physical Activity and Smoking
5.2. Fatty Acids
5.3. Antioxidants
5.4. Lutein
5.5. Curcumin
6. Psychological Approach
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neal, T.B.; Tripathy, K.; Luther, E.E. Retinitis Pigmentosa. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Daiger, S.P.; Sullivan, L.S.; Bowne, S.J. Genes and mutations causing retinitis pigmentosa. Clin. Genet. 2013, 84, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, K.R.; Barnes, C.S.; Fishman, G.A. Deficits in temporal integration for contrast processing in retinitis pigmentosa. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alexander, K.R.; Rajagopalan, A.S.; Seiple, W.; Zemon, V.M.; Fishman, G.A. Contrast response properties of magnocellular and parvocellular pathways in retinitis pigmentosa assessed by the visual evoked potential. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madreperla, S.A.; Palmer, R.W.; Massof, R.W.; Finkelstein, D. Visual acuity loss in retinitis pigmentosa: Relationship to visual field loss. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1990, 108, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeo, K.; Hiida, Y.; Saga, M.; Inoue, R.; Oguchi, Y. Correlation between contrast sensitivity and visual acuity in retinitis pigmentosa patients. Ophthalmologica 2002, 216, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbakel, S.K.; van Huet, R.A.C.; Boon, C.J.F.; den Hollander, A.I.; Collin, R.W.J.; Klaver, C.C.W.; Hoyng, C.B.; Roepman, R.; Klevering, B.J. Non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 66, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, A.; Bowman, L.; Nguyen, T.; So, J.; Duff, M.; Grover, S.; Chen, J. Quality of Life Analysis in Patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa. Ophthalmic Res. 2024, 67, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, A.M.; Simonelli, F.; Pierce, E.A.; Pugh, E.N., Jr.; Mingozzi, F.; Bennicelli, J.; Banfi, S.; Marshall, K.A.; Testa, F.; Surace, E.M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of gene transfer for Leber’s congenital amaurosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turano, K.A.; Geruschat, D.R.; Baker, F.H.; Stahl, J.W.; Shapiro, M.D. Direction of gaze while walking a simple route: Persons with normal vision and persons with retinitis pigmentosa. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2001, 78, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turano, K.A.; Geruschat, D.R.; Stahl, J.W. Mental effort required for walking: Effects of retinitis pigmentosa. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1998, 75, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geruschat, D.R.; Turano, K.A.; Stahl, J.W. Traditional measures of mobility performance and retinitis pigmentosa. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1998, 75, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmis, M.A.; Allsop, J.; Baranian, M.; Baker, J.; Basevitch, I.; Latham, K.; Pardhan, S.; van Paridon, K.N. Visual Search Behavior in Individuals with Retinitis Pigmentosa During Level Walking and Obstacle Crossing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 4737–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Martin, F.; Peli, E. Eye movements of patients with tunnel vision while walking. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5295–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peli, E.; Apfelbaum, H.; Berson, E.L.; Goldstein, R.B. The risk of pedestrian collisions with peripheral visual field loss. J. Vis. 2016, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.V.; Mackeben, M.; Vollmer, A.; Martus, P.; Nguyen, N.X.; Trauzettel-Klosinski, S. Eye Movement Training and Suggested Gaze Strategies in Tunnel Vision—A Randomized and Controlled Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Lopez, H.; Pelayo, F.J.; Lopez-Justicia, M.D.; Morillas, C.A. Visual training and emotional state of people with retinitis pigmentosa. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2013, 50, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgili, G.; Pierrottet, C.; Parmeggiani, F.; Pennino, M.; Giacomelli, G.; Steindler, P.; Menchini, U.; Orzalesi, N.; MNREAD Charts. Reading performance in patients with retinitis pigmentosa: A study using the MNREAD charts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3418–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, M.A.; Gaudio, A.R. Reading speed of patients with advanced retinitis pigmentosa or choroideremia. Retina 2006, 26, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, F.E.; Sutton, J.; Yuen, H.M.; Green, D.; Van Dorn, S.; Braun, T.; Cree, A.J.; Russell, S.R.; Lotery, A.J. A novel, wearable, electronic visual aid to assist those with reduced peripheral vision. PLoS ONE 2019, 15, e0223755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliney, D.H. What is light? The visible spectrum and beyond. Eye 2016, 30, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, K.R.; Fishman, G.A.; Derlacki, D.J. Intraocular light scatter in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Vision Res. 1996, 36, 3703–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, L.; Melardi, E.; Ferri, P.; Montesano, G.; Samir Attaalla, S.; Patelli, F.; De Cilla, S.; Savaresi, G.; Rossetti, L. Visual function improvement using photocromic and selective blue-violet light filtering spectacle lenses in patients affected by retinal diseases. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, Y.; Oishi, A.; Miyata, M.; Oishi, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Numa, S.; Ikeda, H.O.; Tsujikawa, A. Wavelength of light and photophobia in inherited retinal dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedrun-Sanchez, J.E.; Chamorro, E.; Bonnin-Arias, C.; Aguirre-Vilacoro, V.; Castro, J.J.; Sanchez-Ramos, C. Visual Discrimination Increase by Yellow Filters in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2016, 93, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, A.U.; James, L.M.; Schlangen, L.J.; Dijk, D.J. Blue-enriched white light in the workplace improves self-reported alertness, performance and sleep quality. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2008, 34, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, A.K.; Deschler, E.K.; Dagnelie, G. Visual function and performance with blue-light blocking filters in age-related macular degeneration. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 36, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, M.; Rozanowska, M.; Rozanowski, B. Retinal photodamage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2001, 64, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, R.S.; Lawwill, T. Oxygen dependence of damage by 435 nm light in cultured retinal epithelium. Curr. Eye Res. 1984, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, J.D.; Walston, S.T.; Humayun, M.S. Electrical Stimulation of the Retina to Produce Artificial Vision. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2016, 2, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, A.K.H.; So, K.F.; Lee, V.W.H.; Chiu, K. Mechanisms of electrical stimulation in eye diseases: A narrative review. Adv. Ophthalmol. Pract. Res. 2022, 2, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehic, A.; Guo, S.; Cho, K.S.; Corraya, R.M.; Chen, D.F.; Utheim, T.P. Electrical Stimulation as a Means for Improving Vision. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2783–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.Y.; Chow, V.Y.; Packo, K.H.; Pollack, J.S.; Peyman, G.A.; Schuchard, R. The artificial silicon retina microchip for the treatment of vision loss from retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.Q.; Gan, D.K.; Xu, H.D.; Xu, G.Z.; Da, C.D. Neuroprotective effect of transcorneal electrical stimulation on light-induced photoreceptor degeneration. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 219, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, T.; Kanda, H.; Kondo, M.; Terasaki, H.; Nishida, K.; Fujikado, T. Transcorneal electrical stimulation promotes survival of photoreceptors and improves retinal function in rhodopsin P347L transgenic rabbits. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4254–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Xu, W.W.; Qin, L.M.; Peng, G.H.; Yi-Fei, H. Topographic Quantification of the Transcorneal Electrical Stimulation (TES)-Induced Protective Effects on N-Methyl-N-Nitrosourea-Treated Retinas. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 4614–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agadagba, S.K.; Li, X.; Chan, L.L.H. Excitation of the Pre-frontal and Primary Visual Cortex in Response to Transcorneal Electrical Stimulation in Retinal Degeneration Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 572299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, L.; Caretti, A.; Dei Cas, M.; Luciano, F.; Romano, D.; Paroni, R.; Patelli, F.; Ghidoni, R.; Rossetti, L. Vitreous composition modification after transpalpebral electrical stimulation of the eye: Biochemical analysis. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 207, 108601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, A.; Rock, T.; Naycheva, L.; Willmann, G.; Wilhelm, B.; Peters, T.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Zrenner, E.; Messias, A.; Gekeler, F. Transcorneal electrical stimulation for patients with retinitis pigmentosa: A prospective, randomized, sham-controlled exploratory study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 4485–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, A.; Pach, J.; Gosheva, M.; Naycheva, L.; Willmann, G.; Wilhelm, B.; Peters, T.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Zrenner, E.; Messias, A.; et al. Transcorneal Electrical Stimulation for Patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Prospective, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Follow-up Study Over 1 Year. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinim Kahraman, N.; Oner, A. Effect of Transcorneal Electrical Stimulation on Patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 36, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, A.K.; Seger, K. Longevity of visual improvements following transcorneal electrical stimulation and efficacy of retreatment in three individuals with retinitis pigmentosa. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.; Maslim, J.; Valter-Kocsi, K.; Mervin, K.; Bowers, F.; Chu, Y.; Barnett, N.; Provis, J.; Lewis, G.; Fisher, S.K.; et al. Mechanisms of photoreceptor death and survival in mammalian retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1999, 18, 689–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, M.G.; Turksever, C.; Schorderet, D.F.; Valmaggia, C. Retinal vessel oxygen saturation in patients suffering from inherited diseases of the retina. Klin. Monbl Augenheilkd. 2014, 231, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornfield, T.E.; Newman, E.A. Regulation of blood flow in the retinal trilaminar vascular network. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11504–11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, A.K.; Seger, K.; Salveson, R.; Kayser, S.; Morrison, N.; Vargas, P.; Mendelsohn, D.; Han, J.; Bi, H.; Dagnelie, G.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of electro-stimulation therapies to modulate retinal blood flow and visual function in retinitis pigmentosa. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, e366–e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Volpe-Waizel, M.; Zuche, H.C.; Muller, U.; Rickmann, A.; Scholl, H.P.N.; Todorova, M.G. Metabolic monitoring of transcorneal electrical stimulation in retinitis pigmentosa. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meral, N.; Zabek, O.; Camenzind Zuche, H.; Muller, U.; Pretot, D.; Rickmann, A.; Scholl, H.P.N.; Della Volpe Waizel, M. Metabolic Long-Term Monitoring of Transcorneal Electrical Stimulation in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Ophthalmic Res. 2022, 65, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.K.; Jolly, J.K.; Pefkianaki, M.; Gekeler, F.; Webster, A.R.; Downes, S.M.; Maclaren, R.E. Transcorneal electrical stimulation for the treatment of retinitis pigmentosa: Results from the TESOLAUK trial. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2017, 2, e000096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, J.K.; Wagner, S.K.; Martus, P.; MacLaren, R.E.; Wilhelm, B.; Webster, A.R.; Downes, S.M.; Charbel Issa, P.; Kellner, U.; Jagle, H.; et al. Transcorneal Electrical Stimulation for the Treatment of Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Multicenter Safety Study of the OkuStim(R) System (TESOLA-Study). Ophthalmic Res. 2020, 63, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wahner-Roedler, D.L.; Zhou, X.; Johnson, L.A.; Do, A.; Pachman, D.R.; Chon, T.Y.; Salinas, M.; Millstine, D.; Bauer, B.A. Acupuncture for palliative cancer pain management: Systematic review. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2021, 11, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, A.K.; Dagnelie, G. Reported effects of non-traditional treatments and complementary and alternative medicine by retinitis pigmentosa patients. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2008, 91, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wong, S.; Ching, R. The use of acupuncture in ophthalmology. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1980, 8, 104–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabov, S.; Goutoranov, G.; Ivanova, R.; Petkova, N. Clinical application of acupuncture in ophthalmology. Acupunct. Electrother. Res. 1985, 10, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, A.K.; Gould, J.M.; Rosenfarb, A.; Rozanski, C.; Dagnelie, G. A pilot study of an acupuncture protocol to improve visual function in retinitis pigmentosa patients. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2014, 97, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereydouni, F.; Qasemi, V.; Moradian, S.; Tabatabaee, S. Can acupuncture therapy help patients with retinitis-pigmentosa? J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2017, 29, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, L.; Manni, L.; Aloe, L. Effects of electroacupuncture on retinal nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in a rat model of retinitis pigmentosa. Brain Res. 2006, 1092, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qin, W.; Bai, L.; Tian, J. Exploring vision-related acupuncture point specificity with multivoxel pattern analysis. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 28, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Akiyama, M.; Fujiwara, K.; Yoshida, N.; Nakatake, S.; Notomi, S.; Nabeshima, T.; Hisatomi, T.; Enaida, H.; et al. Correlation between macular blood flow and central visual sensitivity in retinitis pigmentosa. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e644–e648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingolo, E.M.; Pelaia, P.; Forte, R.; Rocco, M.; Giusti, C.; Rispoli, E. Does hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) delivery rescue retinal photoreceptors in retinitis pigmentosa? Doc. Ophthalmol. 1998, 97, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingolo, E.M.; Rocco, M.; Grenga, P.; Salvatore, S.; Pelaia, P. Slowing the degenerative process, long lasting effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in retinitis pigmentosa. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Pelluz, J.; Arango-Gonzalez, B.; Kustermann, S.; Romero, F.J.; van Veen, T.; Zrenner, E.; Ekström, P.; Paquet-Durand, F. Photoreceptor cell death mechanisms in inherited retinal degeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 38, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocci, V.A. Scientific and medical aspects of ozone therapy. State of the art. Arch. Med. Res. 2006, 37, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copello, M.; Menéndez, S.; Hernández, F. Ozone Therapy in Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients: Clinical Evolution and Oxidative Stress Behavior in Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients Treated with Ozone Therapy over 20 Years. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2012, 34, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Shinoda, K.; Tanino, T.; Ohtake, Y.; Mashima, Y. Effect of topical unoprostone isopropyl on optic nerve head circulation in controls and in normal-tension glaucoma patients. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 49, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polska, E.; Doelemeyer, A.; Luksch, A.; Ehrlich, P.; Kaehler, N.; Percicot, C.L.; Lambrou, G.N.; Schmetterer, L. Partial antagonism of endothelin 1-induced vasoconstriction in the human choroid by topical unoprostone isopropyl. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tawada, A.; Sugawara, T.; Ogata, K.; Hagiwara, A.; Yamamoto, S. Improvement of central retinal sensitivity six months after topical isopropyl unoprostone in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 61, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Notomi, S.; Murakami, Y.; Hisatomi, T.; Enaida, H.; Ishibashi, T. Therapeutic efficacy of topical unoprostone isopropyl in retinitis pigmentosa. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, e229–e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Ito, T.; Metoki, T.; Kudo, T.; Ohguro, H. Long-term effects of nilvadipine against progression of the central visual field defect in retinitis pigmentosa: An extended study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 585729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Valproate Information. 2015. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/valproate-information (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- Chen, P.S.; Wang, C.C.; Bortner, C.D.; Peng, G.S.; Wu, X.; Pang, H.; Lu, R.B.; Gean, P.W.; Chuang, D.M.; Hong, J.S. Valproic acid and other histone deacetylase inhibitors induce microglial apoptosis and attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Nishida, K.; Nakashima, K.; Tano, Y. Conversion of mammalian Muller glial cells into a neuronal lineage by in vitro aggregate-culture. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suuronen, T.; Nuutinen, T.; Ryhanen, T.; Kaarniranta, K.; Salminen, A. Epigenetic regulation of clusterin/apolipoprotein J expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, S.; Liang, M.H.; Marinova, Z.; Yahyavi, A.; Chuang, D.M. The mood stabilizers lithium and valproate selectively activate the promoter IV of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurons. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Midha, N.; Gogia, V.; Gupta, S.; Sehra, S.; Chohan, A. Efficacy of oral valproic acid in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 30, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, D.G.; Bernstein, P.S.; Iannacone, A.; Pennesi, M.E.; Lam, B.L.; Heckenlively, J.; Csaky, K.; Hartnett, M.E.; Winthrop, K.L.; Jayasundera, T.; et al. Effect of Oral Valproic Acid vs Placebo for Vision Loss in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Randomized Phase 2 Multicenter Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryja, T.P.; Li, T. Molecular genetics of retinitis pigmentosa. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Falsini, B.; Iarossi, G.; Chiaretti, A.; Ruggiero, A.; Manni, L.; Galli-Resta, L.; Corbo, G.; Abed, E. NGF eye-drops topical administration in patients with retinitis pigmentosa, a pilot study. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liang, Q.; Meng, X.; Duan, P.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.Q. Intravenous Infusion of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Maintains and Partially Improves Visual Function in Patients with Advanced Retinitis Pigmentosa. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Bennett, J.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; McCague, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu-Tan, J.A.; Kirkby, M.; Natoli, R. Running to save sight: The effects of exercise on retinal health and function. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 50, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Girardot, P.E.; Sellers, J.T.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Chrenek, M.A.; Wu, W.; Skelton, H.; Nickerson, J.M.; Pardue, M.T.; et al. Wheel running exercise protects against retinal degeneration in the I307N rhodopsin mouse model of inducible autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Mol. Vis. 2019, 25, 462–476. [Google Scholar]
- Levinson, J.D.; Joseph, E.; Ward, L.A.; Nocera, J.R.; Pardue, M.T.; Bruce, B.B.; Yan, J. Physical Activity and Quality of Life in Retinitis Pigmentosa. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 2017, 6950642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, A.; Noda, K.; Birtel, J.; Miyake, M.; Sato, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Miyata, M.; Numa, S.; Charbel Issa, P.; Tsujikawa, A. Effect of smoking on macular function and retinal structure in retinitis pigmentosa. Brain Commun. 2020, 2, fcaa117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinkels, D.; Baes, M. The essential role of docosahexaenoic acid and its derivatives for retinal integrity. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 247, 108440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komeima, K.; Rogers, B.S.; Lu, L.; Campochiaro, P.A. Antioxidants reduce cone cell death in a model of retinitis pigmentosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11300–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeima, K.; Rogers, B.S.; Campochiaro, P.A. Antioxidants slow photoreceptor cell death in mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 213, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.D.; Almeida, M.C.; Lopes, N.P.; de Souza, G.E. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities of the natural polyphenol chlorogenic acid. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Yu, H.G. Chlorogenic acid supplementation improves multifocal electroretinography in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.H.; Lam, H.I.; Choi, K.Y.; Li, S.Z.; Lakshmanan, Y.; Yu, W.Y.; Chang, R.C.; Lai, J.S.; So, K.F. Delay of cone degeneration in retinitis pigmentosa using a 12-month treatment with Lycium barbarum supplement. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 236, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, P.; Mas-Sanchez, A.; Garriga, P. Polyphenols and Visual Health: Potential Effects on Degenerative Retinal Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosner, B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Hayes, K.C.; Nicholson, B.W.; Weigel-DiFrano, C.; Willett, W. Vitamin A supplementation for retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1993, 111, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosner, B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Moser, A.; Brockhurst, R.J.; Hayes, K.C.; Johnson, C.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Gaudio, A.R.; et al. Clinical trial of docosahexaenoic acid in patients with retinitis pigmentosa receiving vitamin A treatment. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berson, E.L.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Rosner, B.; Gaudio, A.R.; Sandberg, M.A. Association of Vitamin A Supplementation with Disease Course in Children with Retinitis Pigmentosa. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.G.; Wang, X.; Chavis, P.; Kuriyan, A.E.; Abariga, S.A. Vitamin A and fish oils for preventing the progression of retinitis pigmentosa. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD008428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rotenstreich, Y.; Belkin, M.; Sadetzki, S.; Chetrit, A.; Ferman-Attar, G.; Sher, I.; Harari, A.; Shaish, A.; Harats, D. Treatment with 9-cis beta-carotene-rich powder in patients with retinitis pigmentosa: A randomized crossover trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yan, W.; Beight, C. Lutein and Zeaxanthin Isomers Reduce Photoreceptor Degeneration in the Pde6b (rd10) Mouse Model of Retinitis Pigmentosa. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4374087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Liu, X.B.; Chen, X.M.; Kong, Q.H.; Liu, Y.S.; So, K.F.; Chen, J.S.; Xu, Y.; Mi, X.S.; Tang, S.B. Lutein delays photoreceptor degeneration in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosner, B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Brockhurst, R.J.; Hayes, K.C.; Johnson, E.J.; Anderson, E.J.; Johnson, C.A.; Gaudio, A.R.; et al. Clinical trial of lutein in patients with retinitis pigmentosa receiving vitamin A. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2010, 128, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Franzone, F.; Nebbioso, M.; Pergolizzi, T.; Attanasio, G.; Musacchio, A.; Greco, A.; Limoli, P.G.; Artico, M.; Spandidos, D.A.; Taurone, S.; et al. Anti-inflammatory role of curcumin in retinal disorders (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherani, I.Z.; Andrews, C.; Pereira, J.A.; Moniz, L.S.; Qian, C.X. Impact of inherited retinal diseases on Canadian patients and families: A mixed-methods study. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 58, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, N.; van Steen, C.; Zegaoui, Y.; Satherley, A.; Angelillo, L. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Burden of Disease and Current Unmet Needs. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 1993–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Aouadj, C.; Hiratsuka, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Murakami, A. Quality of Life and Economic Impacts of Retinitis Pigmentosa on Japanese Patients: A Non-interventional Cross-sectional Study. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 2375–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Shin, D.W.; An, A.R.; Lee, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Oh, M.K.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Cho, B.; et al. Mental health of people with retinitis pigmentosa. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, P.; Nguyen, M.; Vu, T.; Dao, D.P.; Olson, D.; Zhang, A.Y. Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa. J. Vitreoretin. Dis. 2021, 5, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Geng, Z.; Khattak, S.; Ji, X.; Wu, D.; Dang, Y. Role of Oxidative Stress in Retinal Disease and the Early Intervention Strategies: A Review. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 7836828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, L.; Chaumet-Riffaud, P.; Jaron, S.; Roux, C.; Sancho, S.; Berdugo, N.; Audo, I.; Sahel, J.A.; Mohand-Said, S. Threshold levels of visual field and acuity loss related to significant decreases in the quality of life and emotional states of patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmic Res. 2015, 54, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colombo, L.; Baldesi, J.; Martella, S.; Quisisana, C.; Antico, A.; Mapelli, L.; Montagner, S.; Primon, A.; Rossetti, L. Managing Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Literature Review of Current Non-Surgical Approaches. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020330
Colombo L, Baldesi J, Martella S, Quisisana C, Antico A, Mapelli L, Montagner S, Primon A, Rossetti L. Managing Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Literature Review of Current Non-Surgical Approaches. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020330
Chicago/Turabian StyleColombo, Leonardo, Jacopo Baldesi, Salvatore Martella, Chiara Quisisana, Aleksei Antico, Luca Mapelli, Stefania Montagner, Alberto Primon, and Luca Rossetti. 2025. "Managing Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Literature Review of Current Non-Surgical Approaches" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020330
APA StyleColombo, L., Baldesi, J., Martella, S., Quisisana, C., Antico, A., Mapelli, L., Montagner, S., Primon, A., & Rossetti, L. (2025). Managing Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Literature Review of Current Non-Surgical Approaches. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020330





