Stress and Displacement Dynamics in Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion: A Comprehensive Finite Element Analysis of Various Osteotomy Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Facial Skeleton Models for Finite Element Analysis
2.2. Types of Osteotomies Used on the Models
2.3. Loading and Boundary Conditions
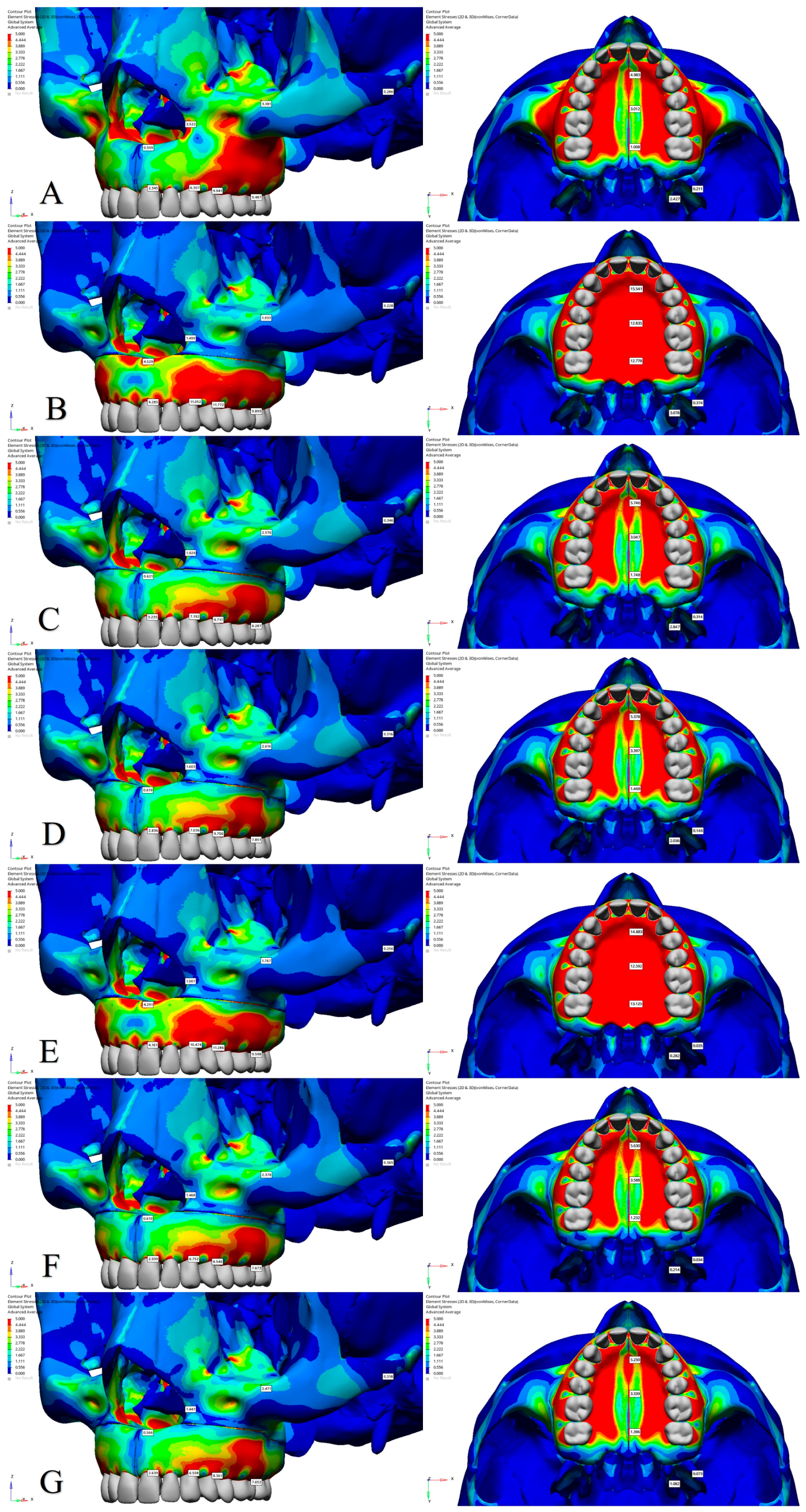
3. Results
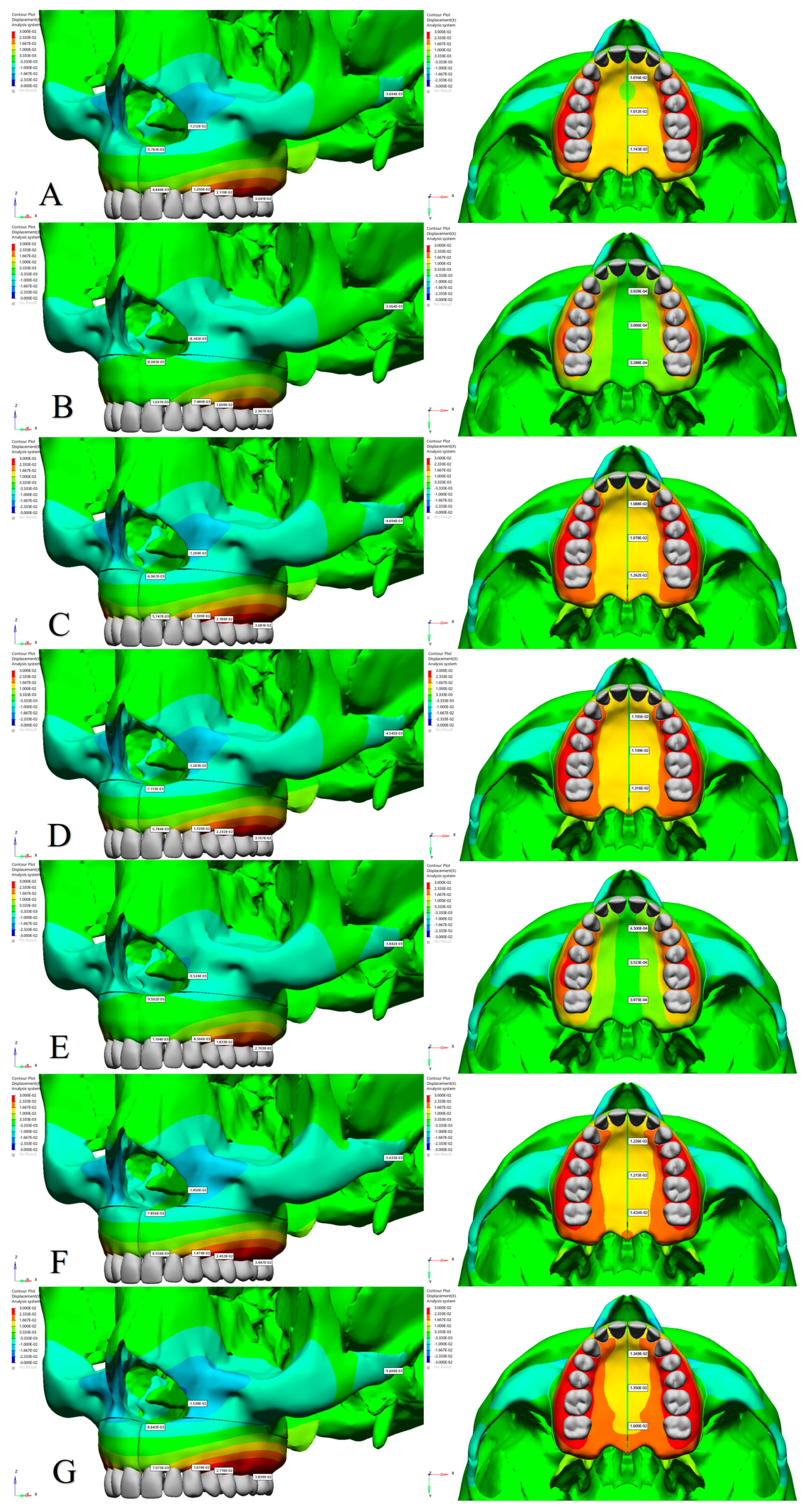
3.1. Amount of Displacement
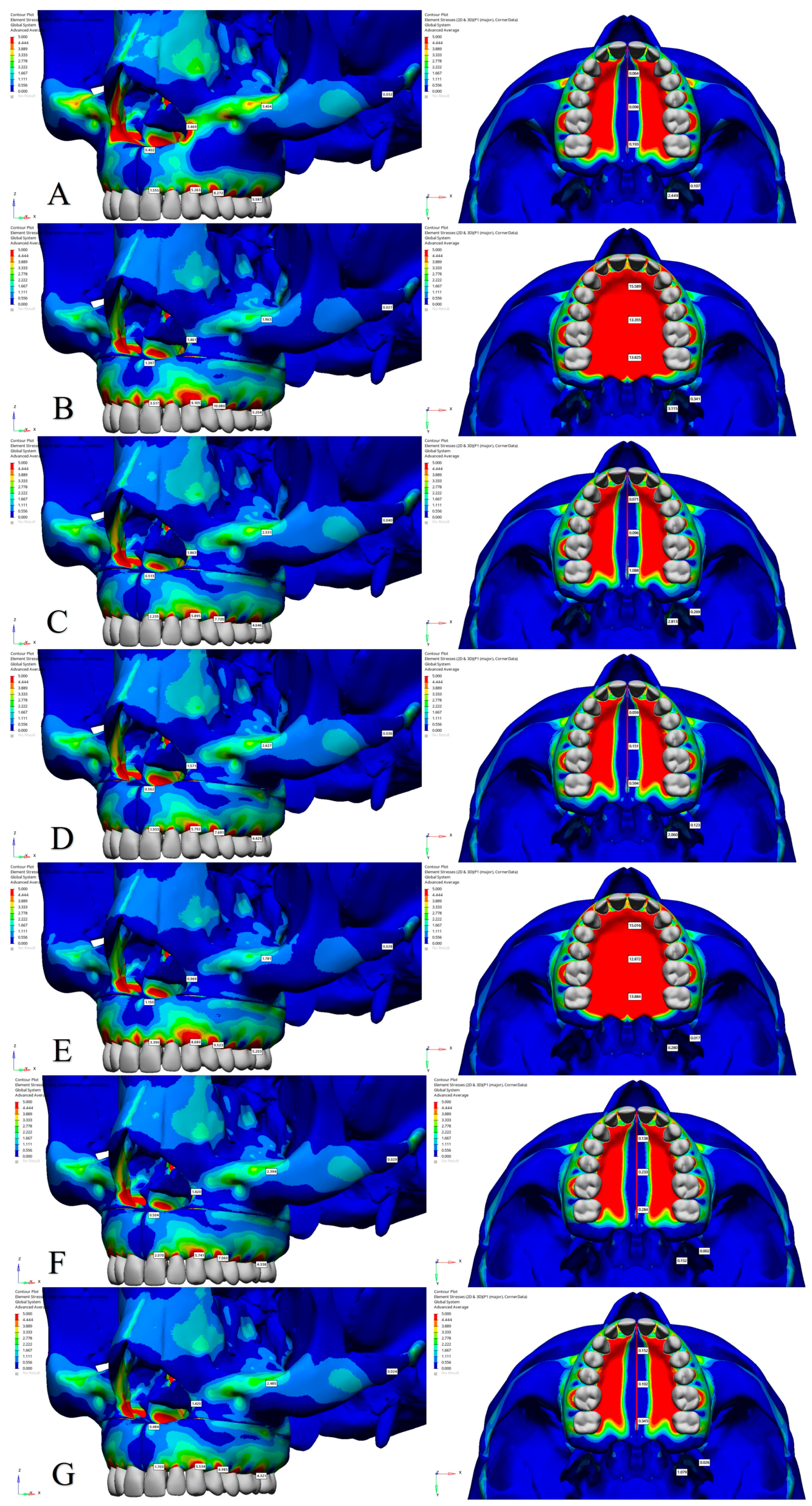
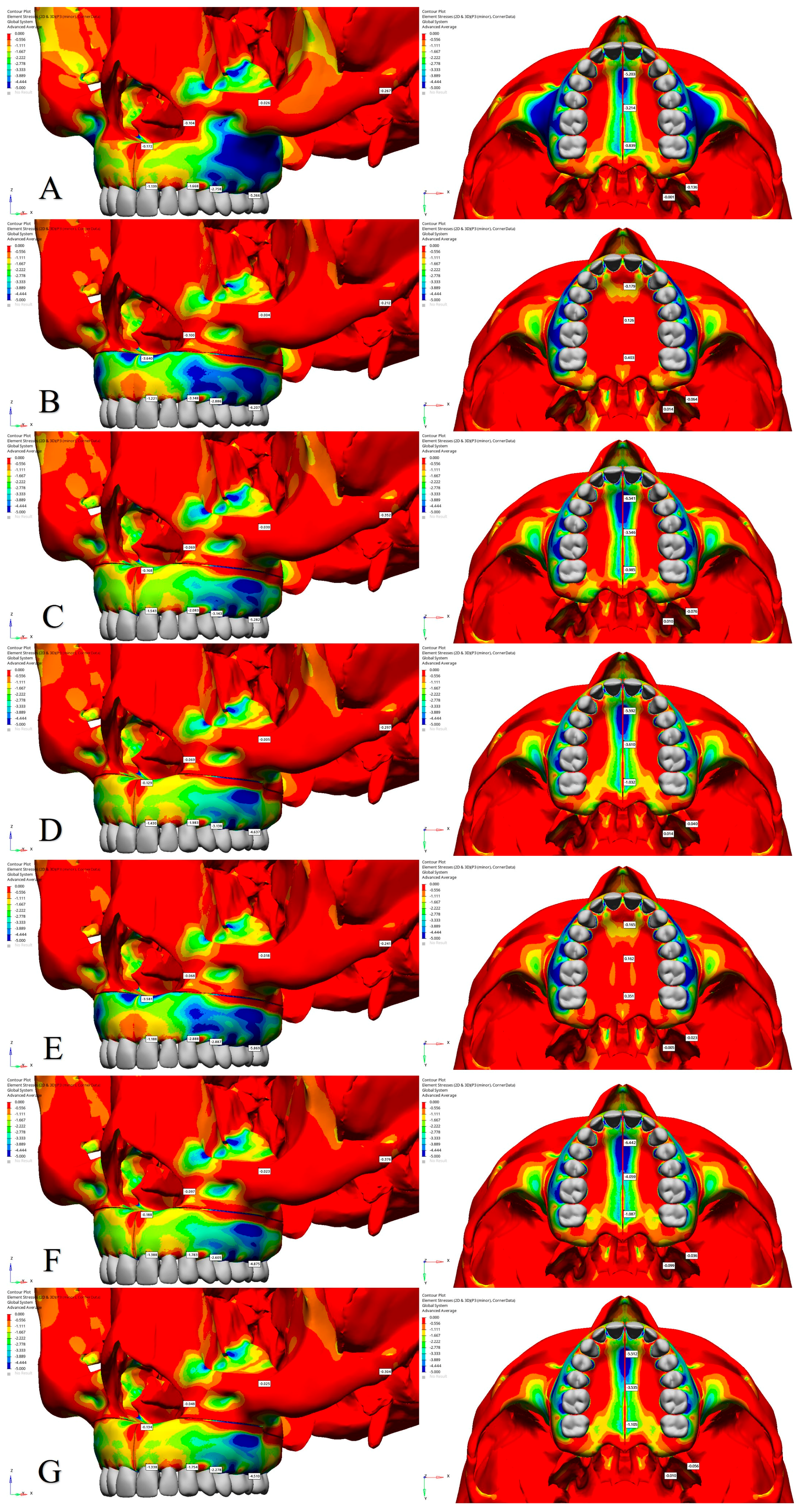
3.2. Stress Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McNamaraa, J.A. Maxillary transverse deficiency. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2000, 117, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishara, S.E.; Staley, R.N. Maxillary expansion: Clinical implications. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1987, 91, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvold, E.P.; Chierici, G.; Vargervik, K. Experiments on the development of dental malocclusions. Am. J. Orthod. 1972, 61, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.D.; Prado, G.P.R.; Abramoff, M.M.F.; Aloise, A.C.; Ferreira, L.M. Classification of midpalatal suture opening after surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion using computed tomography. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2010, 110, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proffit, W.R.; Fields, H.; Msd, D.M.; Larson, B.; Sarver, D.M. Contemporary Orthodontics, 6th ed.; Elsevier South Asia Edition-E-Book: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 430–440. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, A.J. The treatment of maxillary deficiency by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1965, 35, 200–217. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, A.J. Palatal expansion: Just the beginning of dentofacial orthopedics. Am. J. Orthod. 1970, 57, 219–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, L.; Taneja, P. Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: A literature review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Alfaro, F.; Bueno, J.M.; Diaz, A.; Pagés, C.M. Minimally invasive surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion with limited approach under sedation: A report of 283 consecutive cases. J .Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2154–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.K.; Yethadka, M.; Madhur, V. Surgically Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (SARPE): A Literature Review. Sch. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 8, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.V.I. The Surgery of Oral and Facial Diseases and Malformations: Their Diagnosis and Treatment Including Plastic Surgical Reconstruction, 4th ed.; Lea & Febiger: London, UK, 1938; pp. 308–507. [Google Scholar]
- Anttila, A.; Finne, K.; Keski-Nisula, K.; Somppi, M.; Panula, K.; Peltomäki, T. Feasibility and long-term stability of surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion with lateral osteotomy. Eur. J. Orthod. 2004, 26, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, A.S.; Nahigian, S.J.; Medway, J.M.; Aronowitz, H.I. Conservative surgical orthodontic adult rapid palatal expansion: Sixteen cases. Am. J. Orthod. 1984, 86, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timms, D.J.; Vero, D. The relationship of rapid maxillary expansion to surgery with special reference to midpalatal synostosis. Br. J. Oral. Surg. 1981, 19, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northway, W.M.; Meade, J.B., Jr. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: A comparison of technique, response, and stability. Angle Orthod. 1997, 67, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Bays, R.A.; Greco, J.M. Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: An outpatient technique with long-term stability. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1992, 50, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangsari, A.H.; Sadr-Eshkevari, P.; Al-Dam, A.; Friedrich, R.E.; Freymiller, E.; Rashad, A. Surgically assisted rapid palatomaxillary expansion with or without pterygomaxillary disjunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhlhenrich, S.C.; Modabber, A.; Kamal, M.; Fritz, U.; Prescher, A.; Hölzle, F. Three-dimensional effects of pterygomaxillary disconnection during surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: A cadaveric study. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2016, 121, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, V.; Caridad, J.; Caputo, A.A.; Chaconas, S.J. Biomechanical rationale for surgical-orthodontic expansion of the adult maxilla. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1994, 52, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sygouros, A.; Motro, M.; Ugurlu, F.; Acar, A. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of different surgical techniques and their effects on the maxillary dentoskeletal complex. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2014, 146, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Işeri, H.; Tekkaya, A.E.; Öztan, Ö.; Bilgic, S. Biomechanical effects of rapid maxillary expansion on the craniofacial skeleton, studied by the finite element method. Eur. J. Orthod. 1998, 20, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.P.; Tan, K.B.; Liu, G.R. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: A review of the literature. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes de Oliveira, S.; Seraidarian, P.I.; Landre Jr, J.; Oliveira, D.D.; Cavalcanti, B.N. Tooth displacement due to occlusal contacts: A three-dimensional finite element study. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2006, 33, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Shetty, K.S.; Kumar, M. Study of stress distribution and displacement of various craniofacial structures following application of transverse orthopedic forces—A three-dimensional FEM study. Angle Orthod. 2003, 73, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.L. Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 3rd ed.; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 103–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zemann, W.; Schanbacher, M.; Feichtinger, M.; Linecker, A.; Kärcher, H. Dentoalveolar changes after surgically assisted maxillary expansion: A three-dimensional evaluation. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2009, 107, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.H.; Goldman, A.M. Dental tipping and rotation immediately after surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. Eur. J. Orthod. 2003, 25, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro-Bezerra, M.; Tavares, R.N.; de Medeiros, J.R.; Nogueira, A.S.; Avelar, R.L.; Studart Soares, E.C. Effects of Pterygomaxillary Seperation on Skeletal and Dental Changes After Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion: A Single-Center, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzani, M.; Nucci, L.; Lupini, D.; Tripodi, D.; Noori, N.; Hasani, M.; Jamilian, A. Two different designs of mini-screw assisted maxillary expanders, using FEM to analyse stress distribution in craniofacial structures and anchor teeth. Int. Orthod. 2022, 20, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihaner, D.; Karabulut, D.; Dogan Onur, O.; Cansiz, E.; Arslan, Y.Z. Evaluation of Treatment Protocols in Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion by Finite Element Analysis. Medicina 2024, 60, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Assis, D.S.F.R.; Xavier, T.A.; Noritomi, P.Y.; Gonçales, A.G.B.; Ferreira Jr, O.; De Carvalho, P.C.P.; Gonçales, E.S. Finite element analysis of stress distribution in anchor teeth in surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlin, D.; Vukicevic, D. Mechanical reactions of facial skeleton to maxillary expansion determined by laser holography. Am. J. Orthod. 1984, 85, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiślak, E.; Olejnik, A.; Frątczak, R.; Nowak, R. Impact of osteotomy in surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion using tooth-borne appliance on the formation of stresses and displacement patterns in the facial skeleton—A study using finite element analysis (fea). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, U.A.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.U. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution and displacement of the maxilla following surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion. J. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009, 37, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Yi, F.; Lu, Y. Displacement and stress distribution of the craniomaxillofacial complex under different surgical conditions: A three-dimensional finite element analysis of fracture mechanics. BMC Oral. Health 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhlhenrich, S.C.; Modabber, A.; Kniha, K.; Peters, F.; Steiner, T.; Hölzle, F.; Raith, S. Simulation of three surgical techniques combined with two different bone-borne forces for surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion of the maxillofacial complex: A finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalband, M.; Kashani, J.; Hashemzehi, H. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution and displacement of the maxilla following surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion with tooth-and bone-borne devices. J. Dent. 2015, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Lanigan, D.T.; Mintz, S.M. Complications of surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: Review of the literature and report of a case. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 60, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro Jr, J.T.; Paschoal, E.H.A.; Carreira, A.S.D.; Real, R.P.V. Carotid cavernous fistula after surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion with a bone anchored appliance. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newhouse, R.F.; Schow, S.R.; Kraut, R.A.; Price, J.C. Life-threatening hemorrhage from a Le Fort I osteotomy. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1982, 40, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dergin, G.; Aktop, S.; Varol, A.; Ugurlu, F.; Garip, H. Complications related to surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2015, 119, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Meara, J.G.; Rubin, P.A. Orbital compartment syndrome following orthognathic surgery. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1995, 53, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, R.; Olejnik, A.; Gerber, H.; Frątczak, R.; Zawiślak, E. Comparison of tooth-and bone-borne appliances on the stress distributions and displacement patterns in the facial skeleton in surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion—A finite element analysis (FEA) study. Materials 2021, 14, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holberg, C.; Steinhäuser, S.; Rudzki, I. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: Midfacial and cranial stress distribution. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2007, 132, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, M.; Miresmaeili, A.; Heidari, A.; Lamei, A. The necessity of pterygomaxillary disjunction in surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: A short-term, double-blind, historical controlled clinical trial. J. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016, 44, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, E.; Kilic, B.; Kurt, G.; Sakin, C.; Alkan, A. Effects of surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion with and without pterygomaxillary disjunction on dental and skeletal structures: A retrospective review. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2013, 115, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moga, R.A.; Olteanu, C.D.; Buru, S.M.; Botez, M.D.; Delean, A.G. Cortical and Trabecular Bone Stress Assessment during Periodontal Breakdown–A Comparative Finite Element Analysis of Multiple Failure Criteria. Medicina 2023, 59, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shash, Y.H.; El-Wakad, M.T.; Eldosoky, M.A.; Dohiem, M.M. Finite-Element Analysis of the Effect of Utilizing Various Material Assemblies in “All on Four” on the Stresses on Mandible Bone and Prosthetic Parts. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, H. Ductility and brittleness of bone. Int. J. Fract. 2006, 139, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askerbeyli, Ö.S.; Küçükkaya, E.S. Effects of different treatment modalities on biomechanical behavior of maxillary incisors with external invasive cervical resorption at different progression levels. Dent. Traumatol. 2023, 39, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplanken, T.; Vanroose, R.; Ureel, M.; Coupman, R.; Van Paepegem, W. Numerical study of the impact of osteotomies and distractor location in surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion for transverse maxillary deficiency. J. Stomatol. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 125, 101916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koudstaal, M.J.; Wolvius, E.B.; Schulten, A.J.M.; Hop, W.C.J.; van der Wal, K.G.H. Stability, tipping and relapse of bone-borne versus tooth-borne surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion; a prospective randomized patient trial. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrick, S.; Hothan, T.; Hietschold, V.; Schneider, M.; Harzer, W.; Tausche, E. Bone density of the midpalatal suture 7 months after surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion in adults. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 139, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsu, M.; Şimşek, M.B. Impact of different osteotomy techniques on SARPE: Bone displacement. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 74, S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
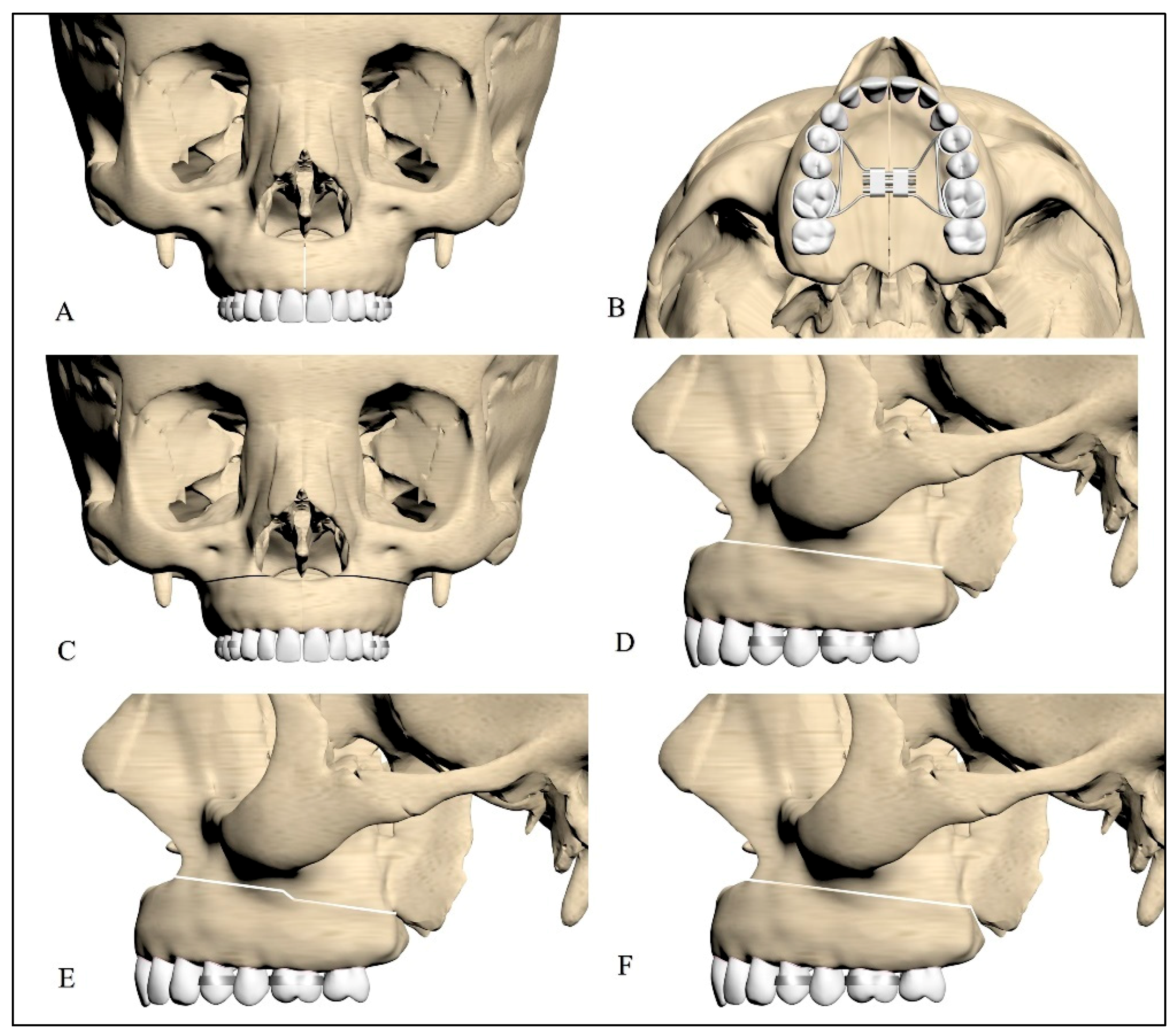

| Models | Number of Nodes | Number of Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 1,314,093 | 5,397,257 |
| Model 2 | 1,317,030 | 5,420,606 |
| Model 3 | 1,322,605 | 5,420,048 |
| Model 4 | 1,331,596 | 5,457,519 |
| Model 5 | 1,321,567 | 5,423,891 |
| Model 6 | 1,326,902 | 5,446,452 |
| Model 7 | 1,331,933 | 5,483,917 |
| Elastic Modulus [MPa] | Poisson Ratio | |
|---|---|---|
| Cortical bone | 13,700 | 0.30 |
| Cancellous bone | 1370 | 0.30 |
| Teeth | 18,600 | 0.31 |
| Periodontal ligament | 69 | 0.45 |
| Stainless steel (tooth-borne appliance) | 200,000 | 0.30 |
| Models | Appliance | Osteotomy Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Tooth-borne | Midpalatal osteotomy |
| Model 2 | Tooth-borne | Lateral osteotomy |
| Model 3 | Tooth-borne | Midpalatal and lateral osteotomy |
| Model 4 | Tooth-borne | Midpalatal osteotomy and stepped lateral osteotomy |
| Model 5 | Tooth-borne | Lateral osteotomy with pterygomaxillary junction (PMJ) separation |
| Model 6 | Tooth-borne | Midpalatal osteotomy and lateral osteotomy with PMJ separation |
| Model 7 | Tooth-borne | Midpalatal osteotomy and stepped lateral osteotomy with PMJ separation |
| Anatomical Structure | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | |
| Central Incisor | 0.01783 | 0.01069 | −0.02418 | 0.004140 | 0.01296 | −0.02368 | 0.02069 | 0.01075 | −0.02942 | 0.02049 | 0.01171 | −0.02966 | 0.004189 | 0.01010 | −0.02201 | 0.02101 | 0.007598 | −0.02791 | 0.02055 | 0.01096 | −0.02926 |
| Canine Cusp | 0.05640 | −0.003056 | −0.004805 | 0.05593 | −0.002874 | −0.005458 | 0.05799 | −0.002047 | −0.006200 | 0.05785 | −0.001356 | −0.006336 | 0.05609 | −0.005288 | −0.004487 | 0.05824 | −0.004553 | −0.005334 | 0.05789 | −0.001956 | −0.006106 |
| First Premolar Buccal Tubercle | 0.06667 | −0.006613 | 0.005785 | 0.06792 | −0.007314 | 0.006767 | 0.06706 | −0.005258 | 0.005218 | 0.06702 | −0.004589 | 0.005205 | 0.06796 | −0.009684 | 0.007267 | 0.06711 | −0.007692 | 0.005617 | 0.06702 | −0.005173 | 0.005324 |
| First Molar Mesiobuccal Tubercle | 0.06354 | 0.001799 | 0.006254 | 0.06535 | 0.001564 | 0.008392 | 0.06414 | 0.001860 | 0.007051 | 0.06403 | 0.002514 | 0.007204 | 0.06553 | −0.001047 | 0.008062 | 0.06439 | −0.0007814 | 0.006672 | 0.06408 | 0.001900 | 0.007142 |
| Anatomical Structure | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | |
| Central Incisor Alveolar Ridge | 0.004844 | 0.01022 | −0.02146 | 0.001037 | 0.007736 | −0.01776 | 0.005747 | 0.009773 | −0.02589 | 0.005784 | 0.01057 | −0.02672 | 0.001194 | 0.007304 | −0.01857 | 0.006556 | 0.008960 | −0.02715 | 0.007073 | 0.01232 | −0.03200 |
| Canine Alveolar Ridge | 0.01200 | 0.002844 | −0.006453 | 0.007489 | 0.002740 | −0.007208 | 0.01309 | 0.003036 | −0.007885 | 0.01329 | 0.003561 | −0.008301 | 0.008566 | 0.001735 | −0.007164 | 0.01474 | 0.001660 | −0.007645 | 0.01619 | 0.003864 | −0.009760 |
| First Premolar Alveolar Ridge | 0.02119 | 0.0001255 | 0.0009165 | 0.01609 | 0.0004928 | 0.0006400 | 0.02189 | 0.0006594 | 0.001427 | 0.02232 | 0.001088 | 0.001265 | 0.01833 | −0.0008134 | 0.001361 | 0.02453 | −0.0009506 | 0.002302 | 0.02716 | 0.0008673 | 0.001753 |
| First Molar Alveolar Ridge | 0.03041 | 0.001940 | 0.003802 | 0.02367 | 0.002042 | 0.005226 | 0.03081 | 0.002126 | 0.006461 | 0.03157 | 0.002663 | 0.006769 | 0.02703 | 0.0009805 | 0.005824 | 0.03447 | 0.0007857 | 0.006988 | 0.03839 | 0.002827 | 0.008189 |
| Nasal Base | −0.00576 | 0.008583 | −0.02547 | −0.00008083 | 0.002814 | −0.01729 | −0.006967 | 0.007483 | −0.03049 | −0.007113 | 0.007969 | −0.03135 | −0.00009502 | 0.002855 | −0.01840 | −0.007856 | 0.007789 | −0.03284 | −0.008643 | 0.009494 | −0.03773 |
| Lateral Nasal Wall | −0.01212 | 0.006087 | −0.005516 | −0.008142 | 0.003612 | −0.004369 | −0.01269 | 0.005879 | −0.005802 | −0.01263 | 0.006035 | −0.005438 | −0.009524 | 0.004038 | −0.004645 | −0.01450 | 0.006482 | −0.006141 | −0.01538 | 0.007301 | −0.006506 |
| Zygomatic Arch | −0.00369 | −0.002437 | 0.001004 | −0.003064 | −0.001685 | −0.001156 | −0.004694 | −0.002756 | −0.0009965 | −0.004545 | −0.002727 | −0.0006058 | −0.003842 | −0.001968 | −0.001424 | −0.005633 | −0.003066 | −0.001365 | −0.005600 | −0.003301 | −0.0007841 |
| Anterior Intermaxillary Suture | 0.01016 | 0.01007 | −0.02927 | 0.0003928 | 0.005842 | −0.01879 | 0.01088 | 0.009330 | −0.03408 | 0.01105 | 0.01017 | −0.03472 | 0.0004500 | 0.005123 | −0.02068 | 0.01226 | 0.008401 | −0.03754 | 0.01348 | 0.01182 | −0.04203 |
| Posterior Intermaxillary Suture | 0.01143 | 0.004844 | −0.02417 | 0.0003288 | 0.0008733 | −0.01570 | 0.01262 | 0.004059 | −0.03415 | 0.01316 | 0.004272 | −0.03417 | 0.0003973 | −0.001495 | −0.02158 | 0.01424 | 0.001146 | −0.04353 | 0.01600 | 0.004253 | −0.04272 |
| Anatomical Structure | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmax | Pmin | VonMises | Pmax | Pmin | VonMises | Pmax | Pmin | VonMises | Pmax | Pmin | VonMises | Pmax | Pmin | VonMises | Pmax | Pmin | VonMises | Pmax | Pmin | VonMises | |
| Central Incisor Alveolar Ridge | 1.555 | −1.139 | 2.345 | 3.517 | −1.221 | 4.285 | 2.235 | −1.543 | 3.235 | 1.933 | −1.430 | 2.836 | 3.390 | −1.188 | 4.161 | 2.070 | −1.388 | 2.939 | 1.703 | −1.138 | 2.639 |
| Canine Alveolar Ridge | 5.263 | −1.668 | 6.307 | 9.105 | −3.148 | 11.052 | 5.895 | −2.083 | 7.192 | 5.792 | −1.983 | 7.036 | 8.680 | −2.888 | 10.474 | 5.741 | −1.783 | 6.752 | 5.534 | −1.754 | 6.508 |
| First Premolar Alveolar Ridge | 8.272 | −2.758 | 9.941 | 10.080 | −2.886 | 11.772 | 7.720 | −3.143 | 9.717 | 7.691 | −3.138 | 9.706 | 9.523 | −2.887 | 11.286 | 7.060 | −2.605 | 8.546 | 6.985 | −2.278 | 8.361 |
| First Molar Alveolar Ridge | 5.587 | −5.366 | 9.487 | 5.204 | −6.207 | 9.899 | 4.646 | −5.282 | 8.287 | 4.425 | −4.637 | 7.851 | 5.203 | −5.869 | 9.598 | 4.338 | −4.875 | 7.673 | 4.321 | −4.510 | 7.652 |
| Nasal Base | 0.402 | −0.172 | 0.509 | 1.397 | −3.640 | 4.529 | 0.513 | −0.168 | 0.621 | 0.562 | −0.129 | 0.619 | 1.150 | −3.581 | 4.291 | 0.504 | −0.188 | 0.610 | 0.484 | −0.134 | 0.566 |
| Lateral Nasal Wall | 3.469 | −0.104 | 3.522 | 1.461 | −0.100 | 1.499 | 1.863 | −0.069 | 1.929 | 1.571 | −0.069 | 1.603 | 0.969 | −0.068 | 1.007 | 1.420 | −0.097 | 1.468 | 1.420 | −0.048 | 1.447 |
| Infraorbital Rim | 3.404 | −0.026 | 3.381 | 1.963 | −0.004 | 1.933 | 2.531 | −0.030 | 2.576 | 2.627 | −0.005 | 2.616 | 1.781 | −0.018 | 1.767 | 2.394 | −0.023 | 2.378 | 2.485 | −0.025 | 2.471 |
| Zygomatic Arch | 0.032 | −0.267 | 0.286 | 0.027 | −0.212 | 0.228 | 0.040 | −0.352 | 0.346 | 0.036 | −0.297 | 0.316 | 0.028 | −0.241 | 0.256 | 0.029 | −0.376 | 0.365 | 0.024 | −0.304 | 0.318 |
| Anterior Intermaxillary Suture | 0.064 | −5.203 | 4.983 | 15.589 | −0.179 | 15.541 | 0.071 | −6.541 | 5.746 | 0.059 | −5.592 | 5.378 | 15.016 | −0.165 | 14.883 | 0.138 | −6.442 | 5.630 | 0.152 | −5.512 | 5.250 |
| Posterior Intermaxillary Suture | 0.193 | −0.839 | 1.008 | 13.825 | 0.403 | 12.778 | 1.088 | −0.985 | 1.748 | 0.594 | −1.032 | 1.469 | 13.884 | 0.351 | 13.125 | 0.284 | −1.087 | 1.232 | 0.345 | −1.105 | 1.396 |
| Lateral Pterygoid | 0.107 | −0.136 | 0.211 | 0.341 | −0.064 | 0.374 | 0.269 | −0.076 | 0.314 | 0.123 | −0.040 | 0.146 | 0.017 | −0.023 | 0.035 | 0.002 | −0.036 | 0.034 | 0.026 | −0.056 | 0.073 |
| Medial Pterygoid | 2.449 | −0.001 | 2.427 | 3.115 | 0.014 | 3.078 | 2.813 | 0.010 | 2.847 | 2.060 | 0.014 | 2.036 | 0.280 | −0.005 | 0.282 | 0.152 | −0.099 | 0.214 | 1.079 | −0.010 | 1.082 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gürsu, M.; Şimşek, M.B. Stress and Displacement Dynamics in Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion: A Comprehensive Finite Element Analysis of Various Osteotomy Techniques. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020449
Gürsu M, Şimşek MB. Stress and Displacement Dynamics in Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion: A Comprehensive Finite Element Analysis of Various Osteotomy Techniques. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020449
Chicago/Turabian StyleGürsu, Müjde, and Mehmet Barış Şimşek. 2025. "Stress and Displacement Dynamics in Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion: A Comprehensive Finite Element Analysis of Various Osteotomy Techniques" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020449
APA StyleGürsu, M., & Şimşek, M. B. (2025). Stress and Displacement Dynamics in Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion: A Comprehensive Finite Element Analysis of Various Osteotomy Techniques. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020449







