Stable Yet Destabilised: Towards Understanding Brain Network Dynamics in Psychogenic Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Deriving Time-Evolving Functional Brain Networks from EEG Recordings
2.3. Characterising Evolving Functional Brain Networks on Global and Local Scales
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
- A total of 30 individuals without any history of neurological disorders (12 females, 18 males; age range: 19–88 yrs; median age: 37 yrs; control group G1);
- A total of 22 individuals with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (11 females, 11 males; age range: 21–82 yrs; median age: 29 yrs; group G2);
- A total of 33 individuals with focal epilepsy (19 females, 14 males; age range: 19–81 yrs; median age: 35 yrs; group G3).
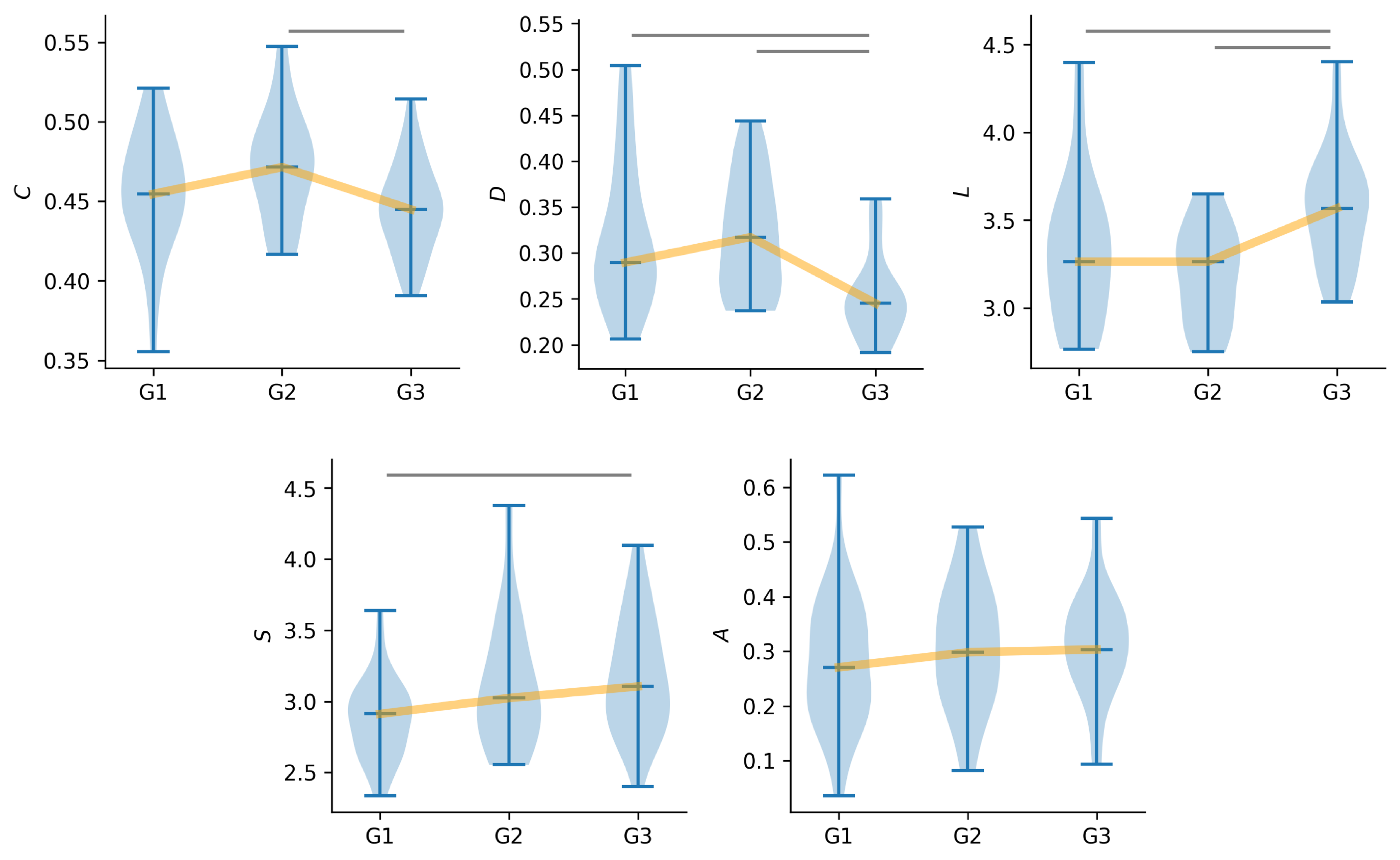
3.1. Global Characteristics of Time-Evolving Functional Brain Networks
3.2. Local Characteristics of Time-Evolving Functional Brain Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fobian, A.D.; Elliott, L. A review of functional neurological symptom disorder etiology and the integrated etiological summary model. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2019, 44, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, D.L.; LaFrance, W.C. Nonepileptic seizures: An updated review. CNS Spectr. 2016, 21, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, K.; Stransky, A.D.; Miller, G. Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: Diagnosis, management, and bioethics. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 62, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuber, M.; Fernandez, G.; Bauer, J.; Helmstaedter, C. Delays in the diagnosis of psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. (ABN Abstracts). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 224–225. [Google Scholar]
- Reuber, M.; Fernández, G.; Bauer, J.; Helmstaedter, C.; Elger, C.E. Diagnostic delay in psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Neurology 2002, 58, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmanesh, M.; Jalili, M.; Kozlowska, K. Activation of functional brain networks in children with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.; Razvi, S.; Mulhern, S. Newly presenting psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: Incidence, population characteristics, and early outcome from a prospective audit of a first seizure clinic. Epilepsy Behav. 2011, 20, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaadi, T.M.; Marquez, A.V. Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Bodde, N.; Brooks, J.; Baker, G.; Boon, P.; Hendriksen, J.; Mulder, O.; Aldenkamp, A. Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures—Definition, etiology, treatment and prognostic issues: A critical review. Seizure 2009, 18, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keynejad, R.C.; Frodl, T.; Kanaan, R.; Pariante, C.; Reuber, M.; Nicholson, T.R. Stress and functional neurological disorders: Mechanistic insights. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Bühler, J.; Vanini, G.; Loukas, S.; Bruckmaier, R.; Aybek, S. Identification of biopsychological trait markers in functional neurological disorders. Brain 2023, 146, 2627–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.J.; Reuber, M. Towards an integrative theory of psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES). Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 47, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopp, J.L. Nonepileptic episodic events. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2019, 25, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedzelman, E.R.; LaRoche, S.M. Long-term video EEG monitoring for diagnosis of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C.; Gilliam, F.G.; Kilgore, M.; Faught, E.; Kuzniecky, R. Improved health care resource utilization following video-EEG-confirmed diagnosis of nonepileptic psychogenic seizures. Seizure 1998, 7, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigo, F.; Igwe, S.C.; Erro, R.; Bongiovanni, L.G.; Marangi, A.; Nardone, R.; Tinazzi, M.; Trinka, E. Postictal serum creatine kinase for the differential diagnosis of epileptic seizures and psychogenic non-epileptic seizures: A systematic review. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gledhill, J.M.; Brand, E.J.; Pollard, J.R.; St. Clair, R.D.; Wallach, T.M.; Crino, P.B. Association of epileptic and nonepileptic seizures and changes in circulating plasma proteins linked to neuroinflammation. Neurology 2021, 96, e1443–e1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, C.J. Modern network science of neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaflarski, J.P.; LaFrance, W.C., Jr. Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) as a network disorder–evidence from neuroimaging of functional (psychogenic) neurological disorders. Epilepsy Curr. 2018, 18, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S. Neural networks in human epilepsy: Evidence of and implications for treatment. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, M. Current themes in neuroimaging of epilepsy: Brain networks, dynamic phenomena, and clinical relevance. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 1153–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnertz, K.; Ansmann, G.; Bialonski, S.; Dickten, H.; Geier, C.; Porz, S. Evolving networks in the human epileptic brain. Physica D 2014, 267, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnertz, K.; Bröhl, T.; von Wrede, R. Epileptic-network-based prediction and control of seizures in humans. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 181, 106098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröhl, T.; Rings, T.; Pukropski, J.; von Wrede, R.; Lehnertz, K. The time-evolving epileptic brain network: Concepts, definitions, accomplishments, perspectives. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2024, 3, 1338864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegaran, E.; Joudaki, A.; Jalili, M.; Rossetti, A.O.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Knyazeva, M.G. Properties of functional brain networks correlate with frequency of psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, N.; Pei, Y.; Carrette, E.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; Pechenizkiy, M. EEG-based classification of epilepsy and PNES: EEG microstate and functional brain network features. Brain Inform. 2020, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnertz, K.; Rings, T.; Bröhl, T. Time in Brain: How Biological Rhythms Impact on EEG Signals and on EEG-Derived Brain Networks. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2021, 1, 755016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormann, F.; Lehnertz, K.; David, P.; Elger, C.E. Mean phase coherence as a measure for phase synchronization and its application to the EEG of epilepsy patients. Physica D 2000, 144, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnert, M.T.; Elger, C.E.; Lehnertz, K. Long-term variability of global statistical properties of epileptic brain networks. Chaos 2010, 20, 043126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickten, H.; Porz, S.; Elger, C.E.; Lehnertz, K. Weighted and directed interactions in evolving large-scale epileptic brain networks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, C.; Lehnertz, K. Long-term variability of importance of brain regions in evolving epileptic brain networks. Chaos 2017, 27, 043112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Wrede, R.; Bröhl, T.; Rings, T.; Pukropski, J.; Helmstaedter, C.; Lehnertz, K. Modifications of Functional Human Brain Networks by Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Impact of Time of Day. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rings, T.; von Wrede, R.; Bröhl, T.; Schach, S.; Helmstaedter, C.; Lehnertz, K. Impact of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on large-scale functional brain networks: From local to global. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 700261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wrede, R.; Rings, T.; Bröhl, T.; Pukropski, J.; Schach, S.; Helmstaedter, C.; Lehnertz, K. Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Differently Modifies Functional Brain Networks of Subjects With Different Epilepsy Types. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 867563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tononi, G.; Sporns, O.; Edelman, G.M. A measure for brain complexity: Relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5033–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M. Networks; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L. Master stability functions for synchronized coupled systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 2109–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahona, M.; Pecora, L.M. Synchronization in small-world systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 054101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröhl, T.; Lehnertz, K. Centrality-based identification of important edges in complex networks. Chaos 2019, 29, 033115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröhl, T.; Lehnertz, K. A straightforward edge centrality concept derived from generalizing degree and strength. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnertz, H.; Broehl, T.; Rings, T.; Von Wrede, R.; Lehnertz, K. Modifying functional brain networks in focal epilepsy by manual visceral-osteopathic stimulation of the vagus nerve at the abdomen. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2023, 3, 1205476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeck, M.; Koessler, L.; Bast, T.; Leijten, F.; Michel, C.; Baumgartner, C.; He, B.; Beniczky, S. The standardized EEG electrode array of the IFCN. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuber, M.; Jamnadas-Khoda, J.; Broadhurst, M.; Grunewald, R.; Howell, S.; Koepp, M.; Sisodiya, S.; Walker, M. Psychogenic nonepileptic seizure manifestations reported by patients and witnesses. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 2028–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFrance, W.C., Jr.; Devinsky, O. Treatment of nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2002, 3, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kruijs, S.J.; Bodde, N.M.; Vaessen, M.J.; Lazeron, R.H.; Vonck, K.; Boon, P.; Hofman, P.A.; Backes, W.H.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; Jansen, J.F. Functional connectivity of dissociation in patients with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiruska, P.; de Curtis, M.; Jefferys, J.G.R.; Schevon, C.A.; Schiff, S.J.; Schindler, K. Synchronization and desynchronization in epilepsy: Controversies and hypotheses. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elger, C.E.; Helmstaedter, C.; Kurthen, M. Chronic epilepsy and cognition. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J., Jr.; Thompson, P.M.; Stern, J.M.; Staba, R.J.; Bragin, A.; Mody, I. Connectomics and epilepsy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Bonilha, L.; Gross, D.W. Network analysis for a network disorder: The emerging role of graph theory in the study of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 50, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O.; Bassett, D.S. New trends in connectomics. Netw. Neurosci. 2018, 2, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. The economy of brain network organization. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröhl, T.; Von Wrede, R.; Lehnertz, K. Impact of biological rhythms on the importance hierarchy of constituents in time-dependent functional brain networks. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2023, 3, 1237004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichle, M.E. The brain’s default mode network. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 38, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, F.A.; Woldman, W.; FitzGerald, T.H.; Elwes, R.D.; Nashef, L.; Terry, J.R.; Richardson, M.P. Revealing a brain network endophenotype in families with idiopathic generalised epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegaran, E.; Carmeli, C.; Rossetti, A.O.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Knyazeva, M.G. Weakened functional connectivity in patients with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES) converges on basal ganglia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höller, Y.; Helmstaedter, C.; Lehnertz, K. Quantitative pharmaco-electroencephalography in antiepileptic drug research. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badr, M.; Bröhl, T.; Dissouky, N.; Helmstaedter, C.; Lehnertz, K. Stable Yet Destabilised: Towards Understanding Brain Network Dynamics in Psychogenic Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030666
Badr M, Bröhl T, Dissouky N, Helmstaedter C, Lehnertz K. Stable Yet Destabilised: Towards Understanding Brain Network Dynamics in Psychogenic Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(3):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030666
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadr, Mostafa, Timo Bröhl, Nayrin Dissouky, Christoph Helmstaedter, and Klaus Lehnertz. 2025. "Stable Yet Destabilised: Towards Understanding Brain Network Dynamics in Psychogenic Disorders" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 3: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030666
APA StyleBadr, M., Bröhl, T., Dissouky, N., Helmstaedter, C., & Lehnertz, K. (2025). Stable Yet Destabilised: Towards Understanding Brain Network Dynamics in Psychogenic Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(3), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030666





