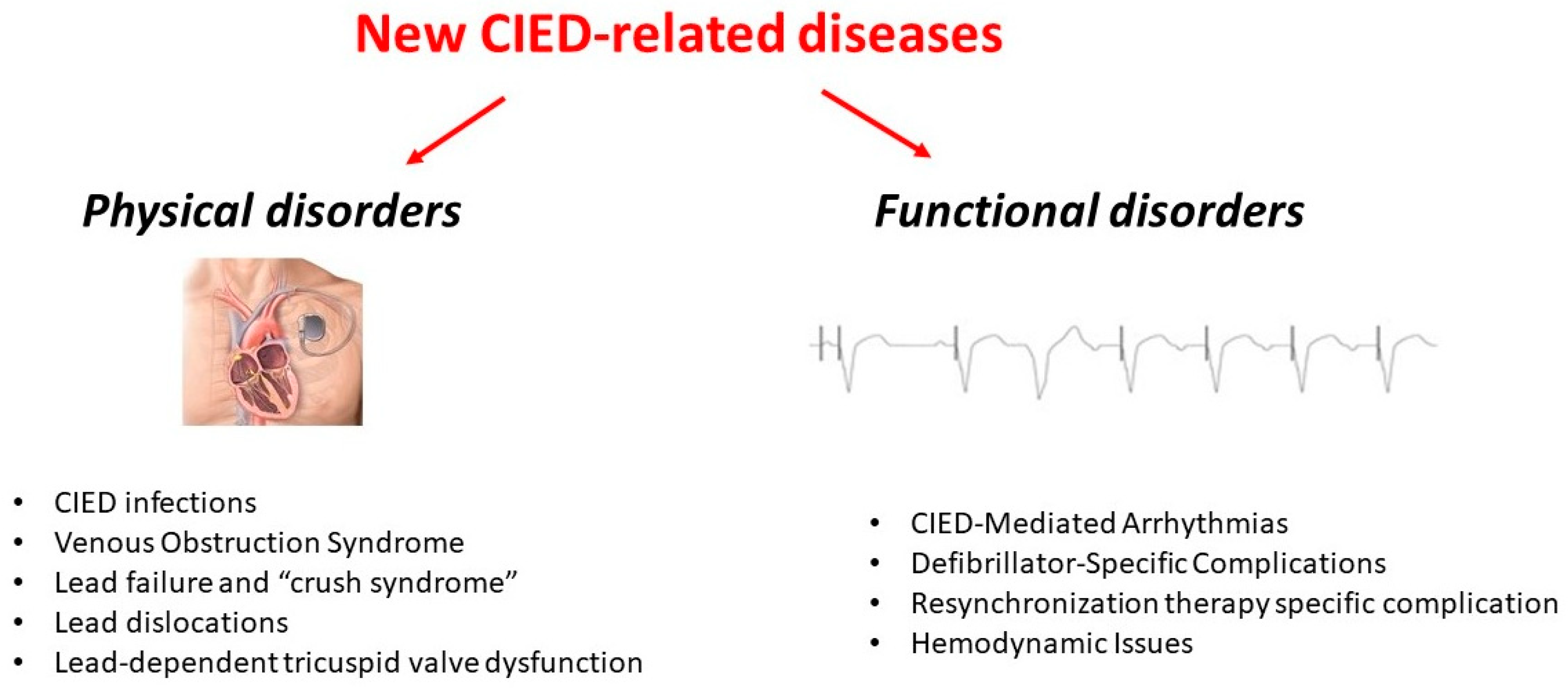
New Diseases Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (CIEDs): An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physical Disorders
2.1. CIED Infections
2.2. Venous Obstruction Syndrome
2.3. Lead Failure and “Crush Syndrome”
- -
- Insulation breach: associated with lead exposure. Characterized by electrical parameter alteration such as abrupt drop of impedance (<200 Ohm) and noise generation.
- -
- Fracture lead: associated with electrical parameters changes such as noise, sudden impedance rise (>2000 Ohm) and abrupt pacing threshold increase [29]. Spontaneous lead fracture is a serious complication that may result in the proximal migration of the broken lead segment within the cardiovascular system. This can lead to embolization, vascular obstruction, arrhythmias, or even end-organ damage, necessitating prompt detection and intervention, often through percutaneous retrieval techniques or surgical extraction.
2.4. Lead Dislocations
2.4.1. Right Heart
2.4.2. Left Heart
2.4.3. Perforation
2.4.4. Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Displacement
2.5. Lead-Dependent Tricuspid Valve Dysfunction
3. Functional Disorders
3.1. CIED-Mediated Arrhythmias
3.1.1. Endless Loop Tachycardia (ELT)
3.1.2. Repetitive Non-Reentrant Ventriculoatrial Synchrony
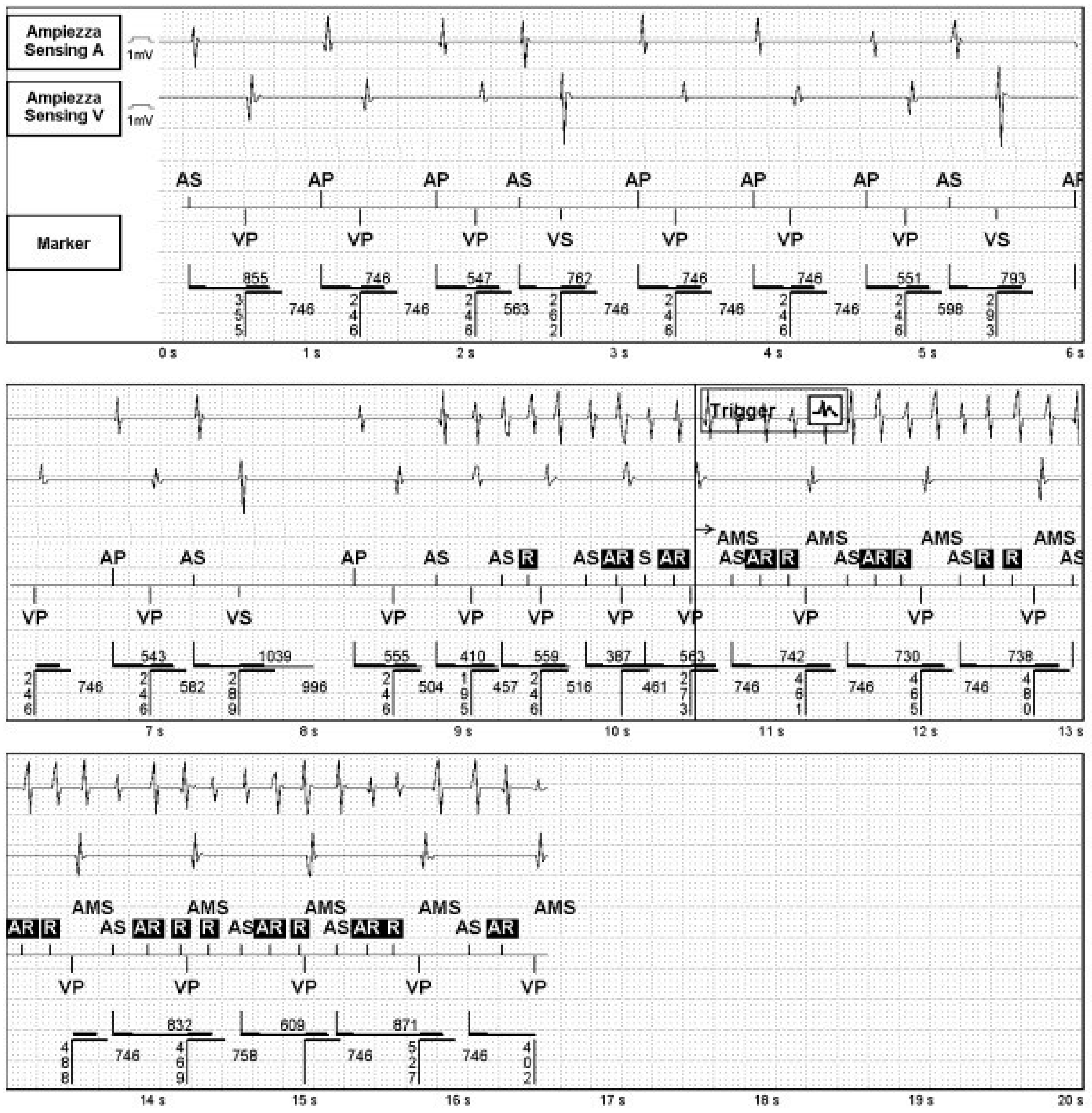
3.1.3. The 2:1 Lock-In—Mode Switching Failure During Atrial Flutter
3.1.4. Short-Long-Short Sequences Promoting Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias
3.2. Defibrillator-Specific Complications
3.2.1. Inappropriate Shocks
3.2.2. Phantom Shocks
3.2.3. Arrhythmic Storms
3.3. Resynchronization Therapy Specific Complication
3.3.1. Arrhythmogenic Potential from Coronary Sinus Pacing
3.3.2. Phrenic Nerve Stimulation in LV Epicardial Pacing
3.4. Hemodynamic Issues
3.4.1. Pacemaker Syndrome
3.4.2. Left Ventricular Dysfunction from Right Ventricular Pacing
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarakji, K.G.; Krahn, A.D.; Poole, J.E.; Mittal, S.; Kennergren, C.; Biffi, M.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Dallaglio, P.D.; Lexcen, D.R.; Lande, J.D.; et al. Risk Factors for CIED Infection After Secondary Procedures: Insights From the WRAP-IT Trial. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 8, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Traykov, V.; Erba, P.A.; Burri, H.; Nielsen, J.C.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Poole, J.; Boriani, G.; Costa, R.; Deharo, J.-C.; et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) international consensus document on how to prevent, diagnose, and treat cardiac implantable electronic device infections—Endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), the Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS), International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases (ISCVID), and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2012–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, V.; Shah, K.; Ferraro, B.; Gasimli-Gamache, L.; Nanda, S.; Stevens, S.; Shirani, J. Cardiac implantable electronic device implantation and device-related infection. Europace 2023, 25, euad208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriello, F.; Saviano, M.; Faggiano, A.; Gentile, D.; Provenzale, G.; Pollina, A.V.; Gherbesi, E.; Barbieri, L.; Carugo, S. Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices Infection Assessment, Diagnosis and Management: A Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeri, N.O.; Kramer, D.B.; Karchmer, A.W.; Zimetbaum, P.J. A Review of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infections for the Practicing Electrophysiologist. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSimone, D.C.; Sohail, M.R. Infection Management. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2018, 10, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, L.M.; Esquer Garrigos, Z.; Rizwan Sohail, M.; Havers-Borgersen, E.; Krahn, A.D.; Chu, V.H.; Radke, C.S.; Avari-Silva, J.; El-Chami, M.F.; Miro, J.M.; et al. Update on cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections and their prevention, diagnosis, and management: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 149, e201–e216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Delgado, V.; Marsan, N.A.; Marsan, N.A.; de Waha, S.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Brida, M.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, J.; Hutt, E.; Jaber, W.A. Imaging of Cardiac Device-Related Infection. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 729786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, C.T.; Tarakji, K.G. Cardiac implantable electronic device infection. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glikson, M.; Nielsen, J.C.; Kronborg, M.B.; Michowitz, Y.; Auricchio, A.; Barbash, I.M.; Barrabés, J.A.; Boriani, G.; Braunschweig, F.; Brignole, M.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Europace 2022, 24, 71–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahn, A.D.; Longtin, Y.; Philippon, F.; Birnie, D.H.; Manlucu, J.; Angaran, P.; Rinne, C.; Coutu, B.; Low, R.A.; Essebag, V.; et al. Prevention of Arrhythmia Device Infection Trial: The PADIT Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 3098–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essebag, V.; Verma, A.; Healey, J.S.; Krahn, A.D.; Kalfon, E.; Coutu, B.; Ayala-Paredes, F.; Tang, A.S.; Sapp, J.; Sturmer, M.; et al. Clinically significant pocket hematoma increases long-term risk of device infection: BRUISE CONTROL INFECTION study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Healey, J.S.; A Wells, G.; Ayala-Paredes, F.; Coutu, B.; Sumner, G.L.; Becker, G.; Verma, A.; Philippon, F.; Kalfon, E.; et al. Continued vs. interrupted direct oral anticoagulants at the time of device surgery, in patients with moderate to high risk of arterial thrombo-embolic events (BRUISE CONTROL-2). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3973–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarakji, K.G.; Mittal, S.; Kennergren, C.; Corey, R.; Poole, J.; Stromberg, K.; Lexcen, D.R.; Wilkoff, B.L. Worldwide Randomized Antibiotic EnveloPe Infection PrevenTion Trial (WRAP-IT). Am. Heart J. 2016, 180, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspon, A.J.; Eby, E.L.; Petrilla, A.A.; Sohail, M.R. Treatment patterns, costs, and mortality among Medicare beneficiaries with CIED infection. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaz, M.; Chorin, E.; Schwartz, A.L.; Hochstadt, A.; Shotan, A.; Ashkenazi, I.; Kazatsker, M.; Carmel, N.-N.; Topaz, G.; Oron, Y.; et al. Regional Antibiotic Delivery for Implanted Cardiovascular Electronic Device Infections. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, K.; Ihlemann, N.; Gill, S.U.; Madsen, T.; Elming, H.; Jensen, K.T.; Bruun, N.E.; Høfsten, D.E.; Fursted, K.; Christensen, J.J.; et al. Partial Oral versus Intravenous Antibiotic Treatment of Endocarditis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetta, G.; Parlavecchio, A.; Magnocavallo, M.; Valente, D.; Caminiti, R.; Polselli, M.; Vetta, F.; Cirone, D.; Cauti, F.M.; Crea, P.; et al. Subcutaneous versus transvenous implantable cardioverter defibrillators in children and young adults: A meta-analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 45, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, M.; Di Fusco, S.A.; Santini, A.; Magris, B.; Pignalberi, C.; Aquilani, S.; Colivicchi, F.; Gargaro, A.; Ricci, R.P. Prevalence and predictor factors of severe venous obstruction after cardiovascular electronic device implantation. Europace 2016, 18, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkeila, P.; Nyman, K.; Ylitalo, A.; Koistinen, J.; Karjalainen, P.; Lund, J.; Airaksinen, K.J. Venous Obstruction After Pacemaker Implantation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2007, 30, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czajkowski, M.; Polewczyk, A.; Jacheć, W.; Kosior, J.; Nowosielecka, D.; Tułecki, Ł.; Stefańczyk, P.; Kutarski, A. Multilevel Venous Obstruction in Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices. Medicina 2024, 60, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimetbaum, P.; Carroll, B.J.; Locke, A.H.; Secemsky, E.; Schermerhorn, M. Lead-Related Venous Obstruction in Patients with Implanted Cardiac Devices: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czajkowski, M.; Polewczyk, A.; Jacheć, W.; Nowosielecka, D.; Tułecki, Ł.; Stefańczyk, P.; Kutarski, A. How does a CIED presence influence chances and safety of haemodialysis access? Conclusions from over 3000 thoracic venografies. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2023, 43, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriels, J.; Chang, D.; Maytin, M.; Tadros, T.; John, R.M.; Sobieszczyk, P.; Eisenhauer, A.; Epstein, L.M. Percutaneous management of superior vena cava syndrome in patients with cardiovascular implantable electronic devices. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, A.; Shim, D.; Burr, J.; Mehegan, T.; Murphy, K.; D’Avila, A.; Schermerhorn, M.; Zimetbaum, P. Lead-associated Superior Vena Cava Syndrome. J. Innov. Card. Rhythm. Manag. 2021, 12, 4459–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakawa, H.; Suzuki, T.; Terata, K.; Watanabe, H. Successful treatment of lead-related superior vena cava syndrome in combination with transvenous lead extraction and venous stenting. J. Arrhythmia 2023, 39, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumoto, F.M.; Schoenfeld, M.H.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Berul, C.I.; Birgersdotter-Green, U.M.; Carrillo, R.; Cha, Y.-M.; Clancy, J.; Deharo, J.-C.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; et al. 2017 HRS expert consensus statement on cardiovascular implantable electronic device lead management and extraction. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, e503–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeberlin, A.; Anwander, M.-T.; Kueffer, T.; Tholl, M.; Baldinger, S.; Servatius, H.; Lam, A.; Franzeck, F.; Asatryan, B.; Zurbuchen, A.; et al. Unexpected high failure rate of a specific MicroPort/LivaNova/Sorin pacing lead. Heart Rhythm 2020, 18, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borleffs, C.J.W.; van Erven, L.; van Bommel, R.J.; van der Velde, E.T.; van der Wall, E.E.; Bax, J.J.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Schalij, M.J. Risk of Failure of Transvenous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Leads. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizal, A.; Ruspiono, E.; Putri, D.H. Intermittent Pacemaker Malfunction Caused by Continuous Compression of the Lead by the Clavicle (Subclavian Crush Syndrome). Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2020, 7, 001684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterns, L.D. Pacemaker lead surveillance and failure: Is there a signal in the noise? Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 579–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbhaiya, C.R.; Niazi, O.; Bostrom, J.; Patil, S.; Jankelson, L.; Bernstein, S.; Park, D.; Holmes, D.; Aizer, A.; Chinitz, L.A. Early ICD lead failure in defibrillator systems with multiple leads via cephalic access. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetta, G.; Magnocavallo, M.; Parlavecchio, A.; Caminiti, R.; Polselli, M.; Sorgente, A.; Cauti, F.M.; Crea, P.; Pannone, L.; Marcon, L.; et al. Axillary vein puncture versus cephalic vein cutdown for cardiac implantable electronic device implantation: A meta-analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 46, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Filippaios, A.; Murphy, J.; Berg, M.; Lampert, R.; Schloss, E.J.; Noone, M.; Mela, T. Short- and Long-Term Risk of Lead Dislodgement Events: Real-World Experience from Product Surveillance Registry. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e011029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, W.; Zhou, C.; Yin, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, G.; Duan, C.; Cao, M.; Li, M.; Toft, E.S.; et al. Meta-analysis of the incidence of lead dislodgement with conventional and leadless pacemaker systems. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.; Wang, Y.; Curtis, J.P.; Varosy, P.D. Acute Lead Dislodgements and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients Enrolled in the National Cardiovascular Data Registry Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynarski, R.; Mlynarska, A.; Joniec, M.; Gladysz-Wanha, S.; Honkowicz, M.; Stachanczyk, J.; Golba, K.S. Predictors of Early Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Lead Dislodgement in the Elderly. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruya, Y.; Yamaura, T.; Mine, H.; Suzuki, H. Successful pericardial repair and coverage for late pacemaker lead-related atrial perforation and pneumothorax: A case report. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. Cases 2023, 2, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, B.; Bigdeli, A.K.; Beiras-Fernandez, R.; Kaczmarek, I.; Kowalski, C.; Schmoeckel, M.; Reichart, B. Successful management of late right ventricular perforation after pacemaker implantation. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2010, 6, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, B.M.; Verberkmoes, N.; Nathoe, R.; Bracke, F.A. Late asymptomatic atrial lead perforation, a fortuitous finding during lead extraction using thoracoscopic surveillance: A case report and review of the literature. Europace 2016, 18, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, H.; Funatsu, T.; Taniguchi, K. Late Left Ventricular Perforation by Active Fixation Pacemaker Lead Implanted in the Right Ventricular Septum. J. Card. Surg. 2012, 27, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merla, R.; Reddy, N.K.; Kunapuli, S.; Rosanio, S.; Schwarz, E.; Vitarelli, A. Late Right Ventricular Perforation and Hemothorax After Transvenous Defibrillator Lead Implantation. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 334, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, P.; Parlavecchio, A.; Vetta, G.; Crea, P.; Carerj, S.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Guido, A.; Accogli, M.; Coluccia, G. Spontaneous Sinus Rhythm Restoration in Patients with Refractory, Permanent Atrial Fibrillation Who Underwent Conduction System Pacing and Atrioventricular Junction Ablation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 209, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, P.; Parlavecchio, A.; Crea, P.; Guido, A.; Accogli, M.; Coluccia, G. Superior approach from the pocket for atrioventricular junction ablation performed at the time of conduction system pacing implantation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 46, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlavecchio, A.; Vetta, G.; Coluccia, G.; Pistelli, L.; Caminiti, R.; Crea, P.; Ajello, M.; Magnocavallo, M.; Dattilo, G.; Foti, R.; et al. Success and complication rates of conduction system pacing: A meta-analytical observational comparison of left bundle branch area pacing and His bundle pacing. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2024, 67, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlavecchio, A.; Vetta, G.; Caminiti, R.; Coluccia, G.; Magnocavallo, M.; Ajello, M.; Pistelli, L.; Dattilo, G.; Foti, R.; Carerj, S.; et al. Left bundle branch pacing versus biventricular pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 46, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzębski, M.; Kiełbasa, G.; Cano, O.; Curila, K.; Heckman, L.; De Pooter, J.; Chovanec, M.; Rademakers, L.; Huybrechts, W.; Grieco, D.; et al. Left bundle branch area pacing outcomes: The multicentre European MELOS study. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4161–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, H.; Jastrzebski, M.; Cano, Ó.; Čurila, K.; de Pooter, J.; Huang, W.; Israel, C.; Joza, J.; Romero, J.; Vernooy, K.; et al. EHRA clinical consensus statement on conduction system pacing implantation: Endorsed by the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), Canadian Heart Rhythm Society (CHRS), and Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS). Europace 2023, 25, 1208–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Subzposh, F.A.; Naperkowski, A.; Panikkath, R.; John, K.; Mascarenhas, V.; Bauch, T.D.; Huang, W. Prospective evaluation of feasibility and electrophysiologic and echocardiographic characteristics of left bundle branch area pacing. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pooter, J.; Ozpak, E.; Calle, S.; Peytchev, P.; Heggermont, W.; Marchandise, S.; Provenier, F.; Francois, B.; Anné, W.; Pollet, P.; et al. Initial experience of left bundle branch area pacing using stylet-driven pacing leads: A multicenter study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnusamy, S.S.; Vijayaraman, P. Aborted ST-elevation myocardial infarction—An unusual complication of left bundle branch pacing. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2020, 6, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wei, L.; Bai, J.; Wang, W.; Qin, S.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Su, Y.; Ge, J. Procedure-Related Complications of Left Bundle Branch Pacing: A Single-Center Experience. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 645947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.C.; Sauer, W.H.; Duque, M.; Koplan, B.A.; Braunstein, E.D.; Marín, J.E.; Aristizabal, J.; Niño, C.D.; Bastidas, O.; Martinez, J.M.; et al. Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Versus Biventricular Pacing as Initial Strategy for Cardiac Resynchronization. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 1568–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polewczyk, A.; Jacheć, W.; Nowosielecka, D.; Tomaszewski, A.; Brzozowski, W.; Szczęśniak-Stańczyk, D.; Duda, K.; Kutarski, A. Lead Dependent Tricuspid Valve Dysfunction-Risk Factors, Improvement after Transvenous Lead Extraction and Long-Term Prognosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, D.; Aldrich, H.R.; Lieberman, E.H.; Lamas, G.A.; Agatston, A.S. Increased prevalence of significant tricuspid re-gurgitation in patients with transvenous pacemakers leads. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 82, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klutstein, M.; Balkin, J.; Butnaru, A.; Ilan, M.; Lahad, A.; Rosenmann, D. Tricuspid Incompetence Following Permanent Pacemaker Implantation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2009, 32 (Suppl. S1), S135–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Iannaccone, A.; Kaye, G.; Negishi, K.; Kosmala, W.; Marwick, T.H.; PROTECT-PACE Investigator. Effect of Right Ventricular Pacing on Right Ventricular Mechanics and Tricuspid Regurgitation in Patients with High-Grade Atrioventricular Block and Sinus Rhythm (from the Protection of Left Ventricular Function During Right Ventricular Pacing Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crea, P.; Picciolo, G.; Crea, T.; Luzza, F. Spike on T wave! What went wrong? J. Electrocardiol. 2017, 50, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crea, P.; Crea, T.; Picciolo, G.; Luzza, F. SafeR and escape junctional rhythm: A singular trigger for pacemaker-mediated tachycardia. J. Electrocardiol. 2017, 50, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savio, A.L.; Crea, B.; Dattilo, G.; Crea, P. Risks of inappropriate use of an algorithm favouring intrinsic conduction. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 45, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumin, H.; Furman, S. Endless loop tachycardia started by an atrial premature complex in a patient with a dual chamber pacemaker. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985, 5, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strik, M.; Frontera, A.; Eschalier, R.; Defaye, P.; Mondoly, P.; Ritter, P.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Ploux, S.; Bordachar, P. Accuracy of the pacemaker-mediated tachycardia algorithm in Boston Scientific devices. J. Electrocardiol. 2016, 49, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Kaszala, K.; Tan, A.Y.; Koneru, J.N.; Shepard, R.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Huizar, J.F. Repetitive Non-Reentrant Ventriculo-Atrial Synchrony: An Under-Recognized Cause of Pacemaker Related Arrhythmia. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethals, M.; Timmermans, W.; Geelen, P.; Backers, J.; Brugada, P. Mode switching failure during atrial flutter: The ’2:1 lock-in’ phenomenon. Europace 2003, 5, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, N.d.A.; Sampaio, S.M.V.; de Castro, R.L. Atrioventricular hysteresis pacemaker mode promoting a short-long-short sequence at the onset of ventricular tachycardia. Heart Rhythm Case Rep. 2018, 4, 564–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Takatsuki, S.; Messali, A.; Milliez, P.; Extramiana, F.; Leenhardt, A. Short-long-short sequence caused by ventricular safety pacing inducing ventricular tachycardia in a patient with a dual-chamber implantable cardioverter defibrillator. Europace 2008, 10, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.O.; Ruetz, L.L.; Belk, P.; Mullen, T.J.; Johnson, J.W.; Sheldon, T. Bradycardia Pacing-Induced Short-Long-Short Sequences at the Onset of Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias: A possible mechanism of proarrhythmia? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, T.; Hochadel, M.; Strauss, M.; Skarlos, A.; Seidl, K.; Zahn, R. Comparison Between Atrial Fibrillation-Triggered Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) Shocks and Inappropriate Shocks Caused by Lead Failure: Different Impact on Prognosis in Clinical Practice. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubert, J.P.; Zareba, W.; Cannom, D.S.; McNitt, S.; Rosero, S.Z.; Wang, P.; Schuger, C.; Steinberg, J.S.; Higgins, S.L.; Wilber, D.J.; et al. Inappropriate Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Shocks in MADIT II: Frequency; mechanisms; predictors; and survival impact. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rees, J.B.; Borleffs, C.J.; de Bie, M.K.; Stijnen, T.; van Erven, L.; Bax, J.J.; Schalij, M.J. Inappropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks: Incidence; predictors; and impact on mortality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.O.; Wathen, M.S.; Volosin, K.; Abdalla, I.; DeGroot, P.J.; Otterness, M.F.; Stark, A.J. Appropriate and Inappropriate Ventricular Therapies, Quality of Life, and Mortality Among Primary and Secondary Prevention Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Patients: Results from the Pacing Fast VT REduces Shock ThErapies (PainFREE Rx II) trial. Circulation 2005, 111, 2898–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knops, R.E.; van der Stuijt, W.; Delnoy, P.P.H.; Boersma, L.V.; Kuschyk, J.; El-Chami, M.F.; Bonnemeier, H.; Behr, E.R.; Brouwer, T.F.; Kaab, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Appropriate Shocks and Antitachycardia Pacing in Transvenous and Subcutaneous Implantable Defibrillators: Analysis of All Appropriate Therapy in the PRAETORIAN Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichtl, W.; De Sousa, J.; Lopez, J.M.R.; Campo, E.G.; Gutleben, K.-J.; Poezevara, Y.; Probst, V. Low rates of inappropriate shocks in contemporary real-world implantable cardioverter defibrillator patients: The CARAT observational study. Europace 2023, 25, euad186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterwerff, E.; Adiyaman, A.; Elvan, A.; Ghani, A.; Hoek, L.; Breeman, K.; Smit, J.J.; Misier, A.R.; Delnoy, P.P. Significantly less inappropriate shocks in ischemic patients compared to non-ischemic patients: The S-ICD experience of a high volume single-center. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 44, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safak, E.; Eckardt, L.; Jung, W.; Ince, H.; Senges, J.; Hochadel, M.; Perings, C.; Spitzer, S.; Brachmann, J.; Seidl, K.; et al. Determinants of inappropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks: The German Device Registry perspective. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2019, 56, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkoff, B.L.; Williamson, B.D.; Stern, R.S.; Moore, S.L.; Lu, F.; Lee, S.W.; Birgersdotter-Green, U.M.; Wathen, M.S.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Heubner, B.M.; et al. Strategic Programming of Detection and Therapy Parameters in Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators Reduces Shocks in Primary Prevention Patients: Results from the PREPARE (Primary Prevention Parameters Evaluation) study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, M.; Friedman, P.A. Optimal Programming of Implantable Cardiac-Defibrillators. Circulation 2013, 128, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donna, P.D.; Petrovic, L.; Nasir, U.; Ahmed, A.; Suero-Abreu, G.A. Phantom Shocks Associated with a Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator. J. Med. Cases 2021, 12, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenizi, K.; Alharthi, R. Incidence, Risk Factors and Predictors of Phantom Shocks in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators: State-of-the-art Review. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2024, 13, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, S.; Geller, J.C.; Ohlow, M.-A. Phantom shocks in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator recipients: Impact of education level, anxiety, and depression. Herzschrittmachertherapie + Elektrophysiologie 2019, 30, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Panaich, S.S.; Zalawadiya, S.K.; McKelvey, G.; Abraham, G.; Aravindhakshan, R.; Sears, S.F.; Conti, J.B.; Marsh, H.M. Phantom shocks unmasked: Clinical data and proposed mechanism of memory reactivation of past traumatic shocks in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2011, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.L.; Hamilton, G.A.; McGovern, B.A. Changes in health status and quality of life and the impact of uncertainty in patients who survive life-threatening arrhythmias. Heart Lung 1999, 28, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilanovic, A.; Irvine, J.; Kovacs, A.H.; Hill, A.; Cameron, D.; Katz, J. Uncovering Phantom Shocks in Cardiac Patients with an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, S.K.; Moons, P.; Zwisler, A.-D.; Winkel, P.; Pedersen, B.D.; Pedersen, P.U.; Svendsen, J.H. Phantom shocks in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillator: Results from a randomized rehabilitation trial (COPE-ICD). Europace 2013, 15, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, R.J.; Coulton, S.; Frizelle, D.J.; Kaye, G.; Cox, H. A brief cognitive behavioural preimplantation and rehabilitation programme for patients receiving an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator improves physical health and reduces psychological morbidity and unplanned readmissions. Heart 2008, 95, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Sapp, J.L. Electrical storm: Definitions; clinical importance; and treatment. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2013, 28, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exner, D.V.; Pinski, S.L.; Wyse, D.G.; Renfroe, E.G.; Follmann, D.; Gold, M.; Beckman, K.J.; Coromilas, J.; Lancaster, S.; Hallstrom, A.P.; et al. Electrical Storm Presages Nonsudden Death. Circulation 2001, 103, 2066–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bänsch, D.; Böcker, D.; Brunn, J.; Weber, M.; Breithardt, G.; Block, M. Clusters of ventricular tachycardias signify impaired survival in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and implantable cardioverter defibrillators. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatzoulis, K.A.; Andrikopoulos, G.K.; Apostolopoulos, T.; Sotiropoulos, E.; Zervopoulos, G.; Antoniou, J.; Brili, S.; Stefanadis, C.I. Electrical storm is an independent predictor of adverse long-term outcome in the era of implantable defibrillator therapy. Europace 2005, 7, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, S.F.; Conti, J.B. Understanding implantable cardioverter defibrillator shocks and storms: Medical and psychosocial considerations for research and clinical care. Clin. Cardiol. 2003, 26, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savastano, S.; Baldi, E.; Compagnoni, S.; Rordorf, R.; Sanzo, A.; Gentile, F.R.; Dusi, V.; Frea, S.; Gravinese, C.; Cauti, F.M.; et al. Electrical storm treatment by percutaneous stellate ganglion block: The STAR study. Europace Heart J. 2024, 45, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, E.; Baldi, E.; Dusi, V.; Dusi, V.; Rordorf, R.; Rordorf, R.; Currao, A.; Currao, A.; Compagnoni, S.; Compagnoni, S.; et al. Efficacy of early use of percutaneous stellate ganglion block for electrical storms. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc Care 2024, 13, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi, E.; Rordorf, R.; Compagnoni, S.; Dusi, V.; Sanzo, A.; Gentile, F.R.; Frea, S.; Gravinese, C.; Cauti, F.M.; Iannopollo, G.; et al. Efficacy of percutaneous stellate ganglion block according to ventricular arrhythmia cycle length: A post hoc subanalysis of the STAR study. Heart Rhythm 2024. In Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adduci, C.; Semprini, L.; Palano, F.; Musumeci, M.B.; Volpe, M.; Autore, C.; Francia, P. Safety and efficacy of anti-tachycardia pacing in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy implanted with an ICD. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 42, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf-Dabbagh, G.; Siontis, K.C.; Latchamsetty, R.; Jongnarangsin, K.; Yokokawa, M.; Lathkar-Pradhan, S.; Morady, F.; Bogun, F. Significance of clinical ventricular tachycardias induced by antitachycardia pacing in patients with prior myocardial infarction. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crea, P.; Andò, G.; Zagari, D.; Giordano, A.; Picciolo, G.; Oreto, G. Do patients with heart failure and right bundle branch block need biventricular pacing? A case of significant QRS narrowing by right ventricular pacing alone. J. Electrocardiol. 2015, 48, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, M.; Correale, M.; Laterra, G.; Vaccaro, V.; Morabito, C.; Crea, P.; Signorelli, S.S.; Katsiki, N.; Luzza, F.; de Gregorio, C.; et al. Effects of Sacubitril/Valsartan in Patients with High Arrhythmic Risk and an ICD: A Longitudinal Study. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.T.; Fisher, W.G.; Smith, A.L.; Delurgio, D.B.; Leon, A.R.; Loh, E.; Kocovic, D.Z.; Packer, M.; Clavell, A.L.; Hayes, D.L.; et al. Cardiac Resynchronization in Chronic Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, J.G.; Daubert, J.-C.; Erdmann, E.; Freemantle, N.; Gras, D.; Kappenberger, L.; Tavazzi, L.; Cardiac Resynchronization-Heart Failure (CARE-HF) Study Investigators. The Effect of Cardiac Resynchronization on Morbidity and Mortality in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Hall, W.J.; Cannom, D.S.; Klein, H.; Brown, M.W.; Daubert, J.P.; Estes, N.A.M., III; Foster, E.; Greenberg, H.; Higgins, S.L.; et al. Cardiac-Resynchronization Therapy for the Prevention of Heart-Failure Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, M.R.; Saxon, L.A.; Boehmer, J.; Krueger, S.; Kass, D.A.; De Marco, T.; Carson, P.; DiCarlo, L.; DeMets, D.; White, B.G.; et al. Cardiac-Resynchronization Therapy with or without an Implantable Defibrillator in Advanced Chronic Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparini, M.; Lunati, M.; Landolina, M.; Santini, M.; Padeletti, L.; Perego, G.; Vincenti, A.; Curnis, A.; Carboni, A.; Denaro, A.; et al. Electrical storm in patients with biventricular implantable cardioverter defibrillator: Incidence, predictors, and prognostic implications. Am. Heart J. 2008, 156, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, J.M.; Wu, J.; Miller, J.M.; Groh, W.J. Increase in Ventricular Tachycardia Frequency After Biventricular Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Upgrade. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, 1245–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Ayerza, M.; Vanderheyden, M.; Verstreken, S.; de Zutter, M.; Geelen, P.; Brugada, P. Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Induced by Left Ventricular Pacing. Circulation 2004, 109, 2924–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mykytsey, A.; Maheshwari, P.; Dhar, G.; Razminia, M.; Zheutlin, T.; Wang, T.; Kehoe, R. Ventricular Tachycardia Induced by Biventricular Pacing in Patient with Severe Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, L.; Russo, V.; Ammendola, E.; Cavallaro, C.; Vecchione, F.; Garofalo, S.; D’Onofrio, A.; Minnini, N.; Calabrò, R. Biventricular pacing and heterogeneity of ventricular repolarization in heart failure patients. Heart Int. 2006, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberlin, A.; Ploux, S.; Noel, A.; Chauvel, R.; Welte, N.; Marchand, H.; Haissaguerre, M.; Ritter, P.; Bordachar, P. Left ventricular sensing in cardiac resynchronization devices—Opportunities and pitfalls for device programming. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, O.; Farouk, W.; ElAzab, A.; Khald, H.; Curnis, A. Potential pro-arrhythmic effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2013, 25, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, M.; Arai, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Gokan, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ochi, A.; Onishi, Y.; Munetsugu, Y.; Ito, H.; Onuki, T.; et al. Association left ventricular lead and ventricular arrhythmias after upgrade to cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. Clin. Cardiol. 2019, 42, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, C.; Abraham, W.T.; Gold, M.R.; Sutton, M.S.J.; Ghio, S.; Daubert, C.; REVERSE (REsynchronization reVErses Remodeling in Systolic left vEntricular dysfunction) Study Group. Randomized Trial of Cardiac Resynchronization in Mildly Symptomatic Heart Failure Patients and in Asymptomatic Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Previous Heart Failure Symptoms. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.S.; Wells, G.A.; Talajic, M.; Arnold, M.O.; Sheldon, R.; Connolly, S.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Nichol, G.; Birnie, D.H.; Sapp, J.L.; et al. Cardiac-Resynchronization Therapy for Mild-to-Moderate Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deif, B.; Ballantyne, B.; Almehmadi, F.; Mikhail, M.; McIntyre, W.F.; Manlucu, J.; Yee, R.; Sapp, J.L.; Roberts, J.D.; Healey, J.S.; et al. Cardiac resynchronization is pro-arrhythmic in the absence of reverse ventricular remodelling: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Yoshida, A.; Fukuzawa, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Imamura, K.; Fujiwara, R.; Suzuki, A.; Nakanishi, T.; Yamashita, S.; Matsumoto, A.; et al. Time-dependent effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy on ventricular repolarization and ventricular arrhythmias. Europace 2013, 15, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzmeister, J.; Leclercq, C. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators and cardiac resynchronisation therapy. Lancet 2011, 378, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, M.; Moschini, C.; Bertini, M.; Saporito, D.; Ziacchi, M.; Diemberger, I.; Valzania, C.; Domenichini, G.; Cervi, E.; Martignani, C.; et al. Phrenic Stimulation: A challenge for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, J.; Healey, J.S.; Krahn, A.D.; Philippon, F.; Gurevitz, O.; Swearingen, A.; Glikson, M.; on behalf of the ELECTION Investigators. The effect of electronic repositioning on left ventricular pacing and phrenic nerve stimulation. Europace 2011, 13, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, M.; Schau, T.; Moeller, V.; Neuss, M.; Meyhoefer, J.; Butter, C. Influence of pacing configurations, body mass index, and position of coronary sinus lead on frequency of phrenic nerve stimulation and pacing thresholds under cardiac resynchronization therapy. Europace 2010, 12, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.H.; Goff, R.P.; Iaizzo, P.A. Left phrenic nerve anatomy relative to the coronary venous system: Implications for phrenic nerve stimulation during cardiac resynchronization therapy. Clin. Anat. 2015, 28, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetze, S.; on behalf of the ERACE study investigators; Defaye, P.; Bauer, A.; Merkel, M.; Bizeau, O.; Treusch, S.; Contzen, K.; Juenger, C.; Winter, J. Phrenic nerve stimulation in CRT patients and benefits of electronic lead repositioning: The ERACE trial. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2013, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, J.M.; Bostock, J.; Li, A.P.Z.; Chin, H.M.S.; Jubb, S.; Lent, E.; Gamble, J.; Foley, P.W.X.; Betts, T.R.; Rinaldi, C.A.; et al. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Delivered Via a Multipolar Left Ventricular Lead is Associated with Reduced Mortality and Elimination of Phrenic Nerve Stimulation: Long-Term Follow-Up from a Multicenter Registry. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, H.; Asbach, S.; Köbe, J.; Weglage, H.; Schulte-Pitzke, B.; Brachmann, J. Effectiveness and Reliability of Selected Site Pacing for Avoidance of Phrenic Nerve Stimulation in CRT Patients with Quadripolar LV Leads: The EffaceQ Study. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 38, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Regibus, V.; Biffi, M.; Infusino, T.; Savastano, S.; Landolina, M.; Palmisano, P.; Foti, R.; Facchin, D.; Russo, A.D.; Urraro, F.; et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with a quadripolar active fixation left ventricular lead: An Italian multicenter experience. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, M.; Mezzetti, M.; De Fazio, M.G.; Caccamo, L.; Busacca, P.; Dattilo, G. Novel active fixation lead guided by electrical delay can improve response to cardiac resynchronization therapy in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, G.A.; Orav, E.J.; Stambler, B.S.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Sgarbossa, E.B.; Huang, S.K.S.; Marinchak, R.A.; Estes, N.M.; Mitchell, G.F.; Lieberman, E.H.; et al. Quality of Life and Clinical Outcomes in Elderly Patients Treated with Ventricular Pacing as Compared with Dual-Chamber Pacing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, M.S.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Estes, N.; Orav, E.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Ibrahim, B.; Greenspon, A.; Rizo-Patron, C.; Goldman, L.; Lee, K.L.; et al. High incidence of pacemaker syndrome in patients with sinus node dysfunction treated with ventricular-based pacing in the Mode Selection Trial (MOST). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2066–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldman, D.; Mulvihill, D.; Nguyen, H.; Messenger, J.C.; Rylaarsdam, A.; Evans, K.; Castellanet, M.J. True Incidence of Pacemaker Syndrome. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1990, 13, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Ross, R.; A Kenny, R. Pacemaker syndrome in older people. Age and Ageing 2000, 29, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanagala, T.; Johnston, S.L.; Groot, G.D.; Rhine, D.K.; Varma, N. Left Atrial Mechanical Responses to Right Ventricular Pacing in Heart Failure Patients: Implications for Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2011, 22, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.C.; Kristensen, L.; Andersen, H.R.; Mortensen, P.T.; Pedersen, O.L.; Pedersen, A.K. A randomized comparison ofatrial and dual-chamber pacing in177 consecutive patients with sick sinus syndrome: Echocardiographic and clinical outcome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutalek, S.P.; Sharma, A.D.; McWilliams, M.J.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Leonen, A.; Hallstrom, A.P.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; the DAVID Investigators. Effect of Pacing for Soft Indications on Mortality and Heart Failure in the Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator (DAVID) Trial. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2008, 31, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.D.; Rizo-Patron, C.; Hallstrom, A.P.; O’neill, G.P.; Rothbart, S.; Martins, J.B.; Roelke, M.; Steinberg, J.S.; Greene, H.L.; DAVID Investigators. Percent right ventricular pacing predicts outcomes in the DAVID trial. Heart Rhythm 2005, 2, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.O.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Greenspon, A.J.; Freedman, R.A.; Lee, K.L.; Lamas, G.A.; MOde Selection Trial Investigators. Adverse Effect of Ventricular Pacing on Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation Among Patients with Normal Baseline QRS Duration in a Clinical Trial of Pacemaker Therapy for Sinus Node Dysfunction. Circulation 2003, 107, 2932–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkoff, B.L.; Cook, J.R.; Epstein, A.E.; Greene, H.L.; Hallstrom, A.P.; Hsia, H.; Kutalek, S.P.; Sharma, A.; Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator Trial Investigators. Dual-chamber pacing or ventricular backup pacing in patients with an implantable defibrillator: The Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator (DAVID) Trial. JAMA 2002, 288, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsheshet, A.; Moss, A.J.; McNitt, S.; Jons, C.; Glikson, M.; Klein, H.U.; Huang, D.T.; Steinberg, J.S.; Brown, M.W.; Zareba, W.; et al. Long-term implications of cumulative right ventricular pacing among patients with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm 2010, 8, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.C.; Bøttcher, M.; Nielsen, T.T.; Pedersen, A.K.; Andersen, H.R. Regional myocardial blood flow in patients with sick sinus syndrome randomized to long-term single chamber atrial or dual chamber pacing—Effect of pacing mode and rate. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkoff, B.L.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; Buxton, A.E.; Sharma, A.; Cook, J.R.; Bhandari, A.K.; Biehl, M.; Tomassoni, G.; Leonen, A.; Klevan, L.R.; et al. The DAVID (Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator) II Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-H.; Chen, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Guo, B.-F.; Pan, K.-L.; Yang, C.-H.; Chang, H.-W. Right Ventricular Apical Pacing Acutely Impairs Left Ventricular Function and Induces Mechanical Dyssynchrony in Patients with Sick Sinus Syndrome: A Real-time Three-dimensional Echocardiographic Study. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2008, 21, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, R.; Padeletti, L.; Schreuder, J.; Jackson, K.; Michelucci, A.; Colella, A.; Eastman, W.; Valsecchi, S.; Hettrick, D.A. Ventricular Pacing Lead Location Alters Systemic Hemodynamics and Left Ventricular Function in Patients with and Without Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, C.; Gras, D.; Le Helloco, A.; Nicol, L.; Mabo, P.; Daubert, C. Hemodynamic importance of preserving the normal sequence of ventricular activation in permanent cardiac pacing. Am. Heart J. 1995, 129, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenqvist, M.; Isaaz, K.; Botvinick, E.H.; Dae, M.W.; Cockrell, J.; Abbott, J.A.; Schiller, N.B.; Griffin, J.C. Relative importance of activation sequence compared to atrioventricular synchrony in left ventricular function. Am. J. Cardiol. 1991, 67, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Tops, L.F.; Trines, S.A.; Zeppenfeld, K.; Marsan, N.A.; Bertini, M.; Holman, E.R.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J. Acute Effects of Right Ventricular Apical Pacing on Left Ventricular Synchrony and Mechanics. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorger, J.; Wyman, B.; Faris, O.; Hunter, W.; McVeigh, E. Torsion of the Left Ventricle During Pacing with MRI Tagging. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2003, 5, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.O.; Bank, A.J.; Nsah, E.; Koullick, M.; Zeng, Q.C.; Hettrick, D.; Sheldon, T.; Lamas, G.A.; Search AV Extension and Managed Ventricular Pacing for Promoting Atrioventricular Conduction (SAVE PACe) Trial. Minimizing Ventricular Pacing to Reduce Atrial Fibrillation in Sinus-Node Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olshansky, B.; Day, J.D.; Moore, S.; Gering, L.; Rosenbaum, M.; McGuire, M.; Brown, S.; Lerew, D.R. Is Dual-Chamber Programming Inferior to Single-Chamber Programming in an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator? Results of the INTRINSIC RV (Inhibition of Unnecessary RV Pacing with AVSH in ICDs) study. Circulation 2007, 115, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crea, P.; Cocuzza, F.; Bonanno, S.; Ferrara, N.; Teresi, L.; La Maestra, D.; Bellocchi, P.; Micari, A.; Moncada, A.; Micari, A.; et al. New Diseases Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (CIEDs): An Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041322
Crea P, Cocuzza F, Bonanno S, Ferrara N, Teresi L, La Maestra D, Bellocchi P, Micari A, Moncada A, Micari A, et al. New Diseases Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (CIEDs): An Overview. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041322
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrea, Pasquale, Federica Cocuzza, Salvatore Bonanno, Nicola Ferrara, Lucio Teresi, Diego La Maestra, Paolo Bellocchi, Antonino Micari, Alice Moncada, Antonio Micari, and et al. 2025. "New Diseases Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (CIEDs): An Overview" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041322
APA StyleCrea, P., Cocuzza, F., Bonanno, S., Ferrara, N., Teresi, L., La Maestra, D., Bellocchi, P., Micari, A., Moncada, A., Micari, A., Di Bella, G., & Dattilo, G. (2025). New Diseases Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (CIEDs): An Overview. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041322




