Problems in Diagnosis and Treatment of Soleus Muscle Injuries—Narrative Review and Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Muscle Anatomy
1.2. Causes of Injuries
1.3. Analysis of Diagnostic Challenges in Soleus Muscle Injuries
| Type of Damage | Symptoms | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Soleus muscle | Pain is felt most in the posterolateral calf. Pain during passive ankle dorsiflexion or resisted ankle plantarflexion with the knee bent [4]. | Ultrasound may not confirm morphological changes; it is necessary to perform MRI [6]. |
| Tennis leg | Patients often report immediate, intense pain in the calf, typically during activities like running or jumping. Localized swelling and tenderness around the medial gastrocnemius muscle are joint, often accompanied by difficulty in weight-bearing. Increased pain during dorsiflexion of the foot, both actively and passively, is frequently observed, Clinicians may find palpable defects in the muscle, indicating the severity of the injury [6]. | In this case, an ultrasound examination is an excellent diagnostic tool. MRI examinations are not always necessary [23]. |
| Neuropathy | Tibial nerve Sensory Symptoms Patients often report abnormal sensations, such as burning or tingling, particularly in the sole of the foot and the medial malleolus. Pain: Chronic pain can occur, especially in the calf and sole, and is often exacerbated at night. Motor Symptoms Weakness: There may be noticeable weakness in foot flexors, leading to difficulty in plantar flexion and inversion of the ankle Muscle Atrophy: Prolonged nerve damage can result in muscle denervation and atrophy in the affected areas [24] Personal nerve Inability to bend the foot in the dorsum of the foot, difficulty bending the toes. Bird gait (bending the leg at the knee and lifting it, placing the foot on the toes, then on the side of the foot, and finally on the heel [25]. | The most common findings in pathologies of the peroneal nerve were hypoechoic thickenings. In inflammation, the extended segment of the nerve is affected by edema, and ultrasound examination shows hypoechoic thickening of the involved segment of the nerve, with loss of intraneural hypoechoic tissue peripherally surrounded by interfascicular epineurium. On ultrasound examination, small fascicles may appear as a single undifferentiated structure and indistinguishable from the surrounding interfascicular epineurium or a cluster of fascicles. Electrodiagnostic testing is essential for identifying the type and severity of neuropathy [25]. |
| Achilles tendon | Performing palpation tests and muscle power tests with Thompson’s sign and Matles’ test [17]. | High-resolution ultrasonography is effective in diagnosing Achilles tendon lesions. It shows comparable results to MRI for tendinopathy and full-thickness tears while excelling in early enthesitis detection [26]. |
| Venous diseases | Cyanosis occurs, Homans and Mayr symptoms, we perform the Wells scale and Virchow’s triad [27]. | The basic examination is a power Doppler of the veins, which can confirm venous thrombosis and a blood d-dimer test. It should be remembered that d-dimers are not specific markers and may also be elevated, for example, in injuries and inflammations [27]. |
| Arterial diseases | Intermittent claudication and pain occur, which are worse on walking and subside with rest. There may be abnormal peripheral pulses and arterial bruits [28]. | We examine using Doppler examination, ankle-brachial index, and angiography [28]. |
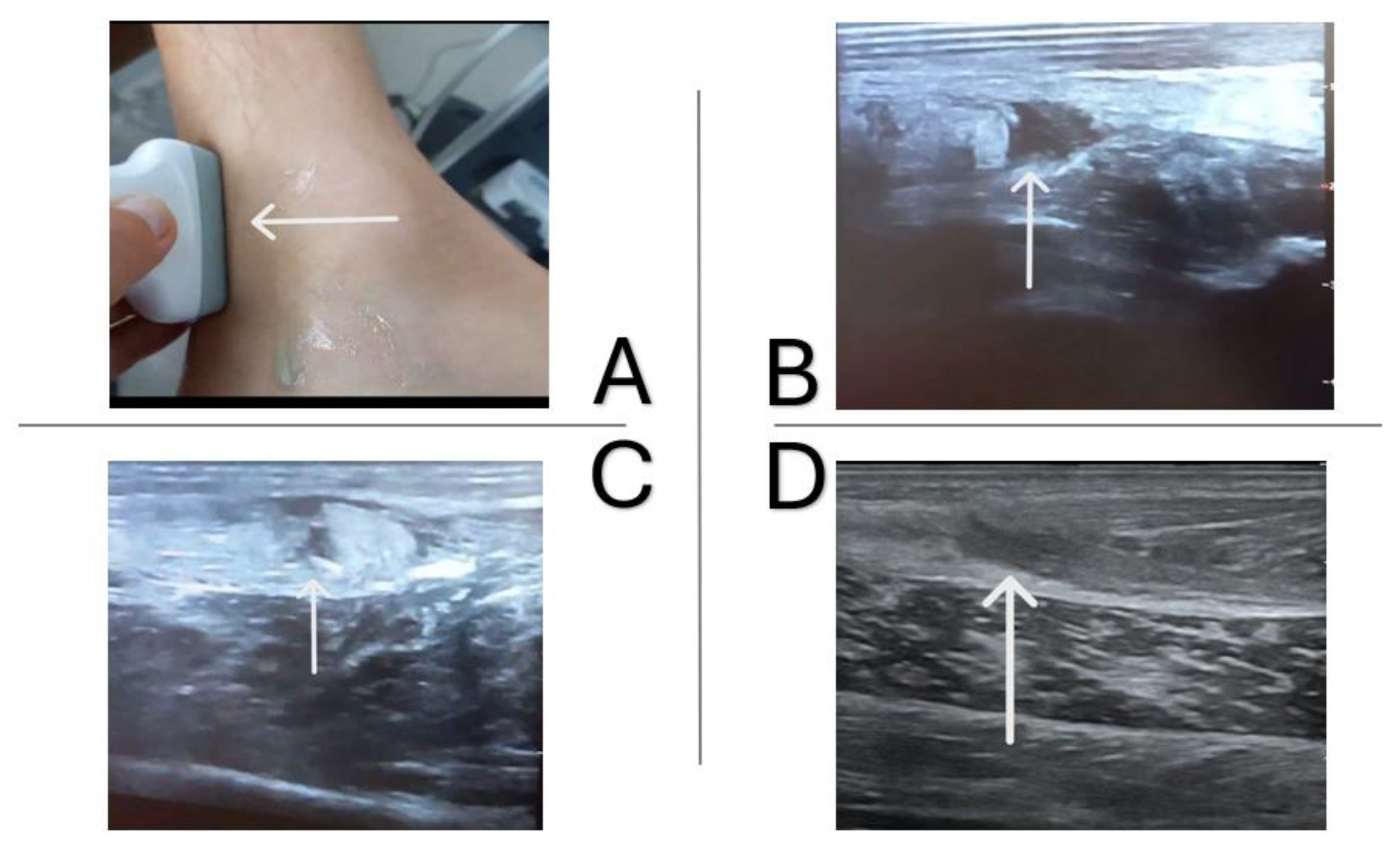
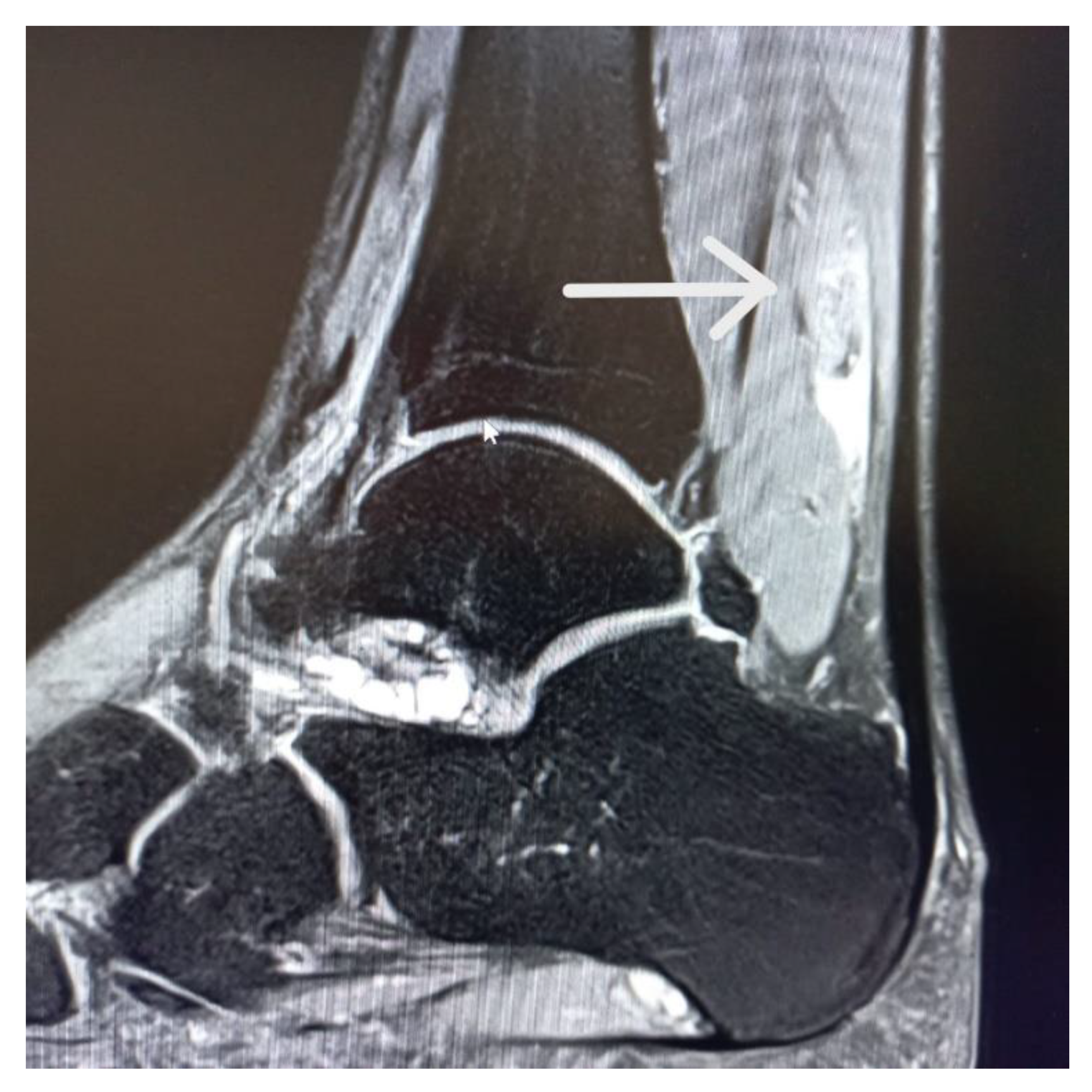
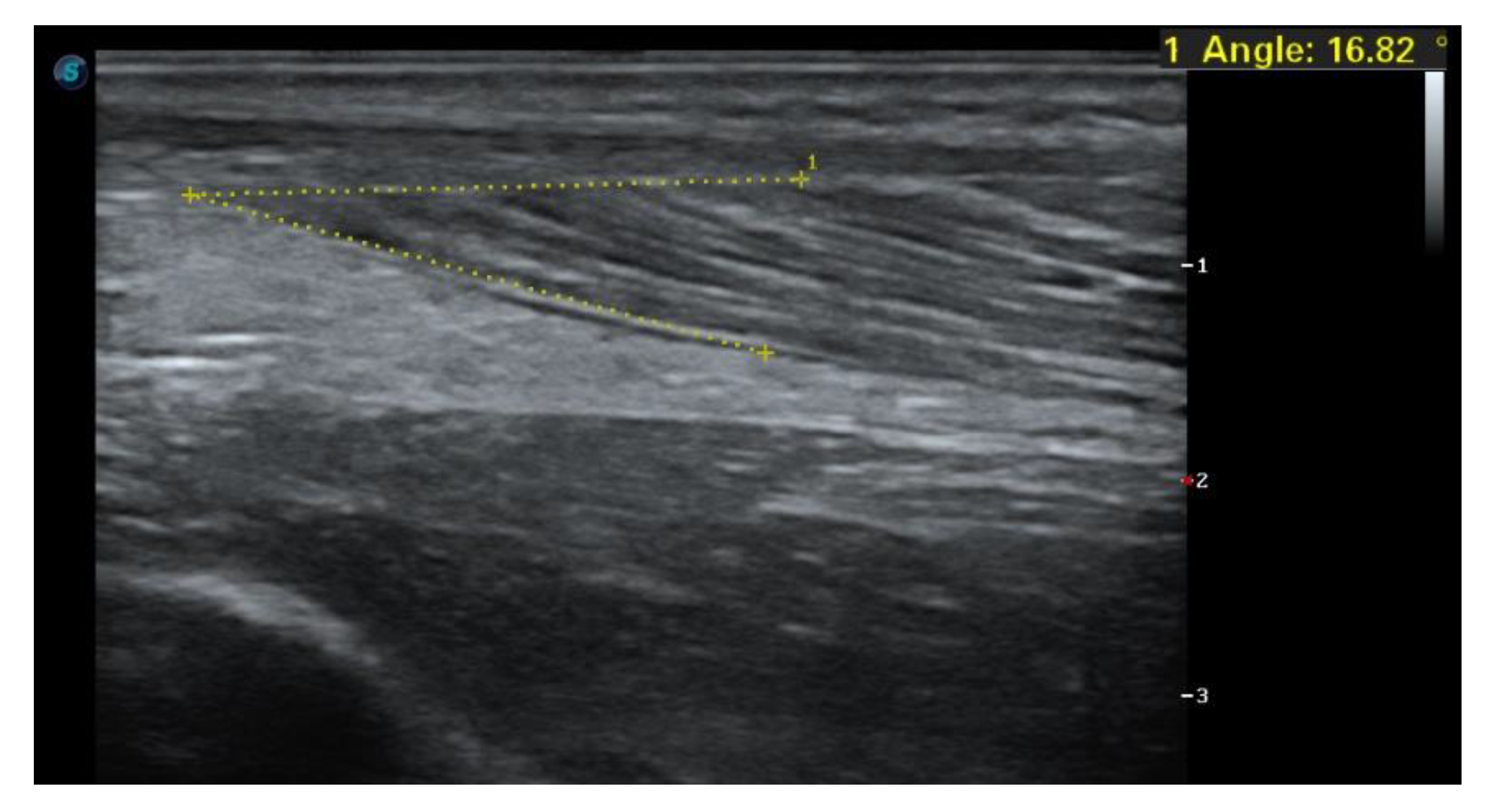
1.4. Case Report
1.5. Imaging Tests
2. Physiotherapy Protocol
Principles of Load Selection Based on Objective Data
3. Discussion
4. Limitations of the Current Studies and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siedi, A.F.; Rolon, A.U.; Bernard, N.; Bernasconi, J.; Palmas, M.; Couto, D.A.; Pascual, T.A. Posterior Leg Pain: Understanding Soleus Muscle Injuries. Radiographics 2022, 42, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, A.; Entwisle, T.; Schneider, M.; Brukner, P.; Connell, D. Connective tissue injury in calf muscle tears and return to play: MRI correlation. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.D.; Finni, T.; Hodgson, J.A.; Lai, A.M.; Edgerton, V.R.; Sinha, S. Soleus aponeurosis strain distribution following chronic unloading in humans: An in vivo MR phase-contrast study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 2004–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draghi, F.; Bortolotto, C.; Ferrozzi, G. Soleus strain: An underestimated injury? J. Ultrasound 2021, 24, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Hume, P.A.; Maxwell, L. Delayed onset muscle soreness: Treatment strategies and performance factors. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balius, R.; Rodas, G.; Pedret, C.; Capdevila, L.; Alomar, X.; Bong, D.A. Soleus muscle injury: Sensitivity of ultrasound patterns. Skeletal Radiol. 2014, 43, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau-Pastor, M.; Fargues-Polo, B.; Casanova-Martínez, D.; Vega, J.; Golanó, P. Anatomy of the triceps surae: A pictorial essay. Foot Ankle Clin. 2014, 19, 603–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruse, M.; Trappe, S.; Trappe, T.A. Human skeletal muscle-specific atrophy with aging: A comprehensive review. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 134, 900–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döner, R.S.; Keleş, P.; Karip, B. Presence of Accessory Soleus Muscle in Cadaver: Case Report. Duzce Med. J. 2023, 25, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobalt, K.; Turk, M.; Kalu, G.; Steele, R.; Withnell, C.B. Morphological variation of the soleus muscle: Determining general patterns and characteristics of the connective tissue architecture. Transl. Res. Anat. 2024, 37, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balius, R.; Alomar, X.; Rodas, G.; Miguel-Pérez, M.; Pedret, C.; Dobado, M.C.; Blasi, J.; Koulouris, G. The soleus muscle: MRI, anatomic and histologic findings in cadavers with clinical correlation of strain injury distribution. Skeletal Radiol. 2013, 42, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.R.; Eng, C.M.; Smallwood, L.H.; Lieber, R.L. Are current measurements of lower extremity muscle architecture accurate? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemello, F.; Bean, C.; Cancellara, P.; Laveder, P.; Reggiani, C.; Lanfranchi, G. Microgenomic analysis in skeletal muscle: Expression signatures of individual fast and slow myofibers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e0016807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finni, T.; Hodgson, J.A.; Lai, A.M.; Edgerton, V.R.; Sinha, S. Nonuniform strain of human soleus aponeurosis-tendon complex during submaximal voluntary contractions in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 95, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolsterlee, B.; Finni, T.; D’Souza, A.; Eguchi, J.; Clarke, E.C.; Herbert, R.D. Three-dimensional architecture of the whole human soleus muscle in vivo. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Choe, M.A. Effects of unilateral sciatic nerve injury on unaffected hindlimb muscles of rats. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2009, 39, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trybulski, R.; Muracki, J.; Podleśny, M.; Vovkanych, A.; Kużdżał, A. Effectiveness of Kinesiotherapy in the Treatment of Achilles Tendinopathy—A Narrative Review. Sports 2024, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedret, C.; Rodas, G.; Balius, R.; Capdevila, L.; Bossy, M.; Vernooij, R.W.; Alomar, X. Return to Play After Soleus Muscle Injuries. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2015, 3, 2325967115595802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secondulfo, L. Diffusion-Tensor MRI Methods to Study and Evaluate Muscle Architecture. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Flux, E.; van der Krogt, M.M.; Harlaar, J.; Buizer, A.I.; Sloot, L.H. Functional assessment of stretch hyperreflexia in children with cerebral palsy using treadmill perturbations. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Morales, C.; López-López, D.; Almazán-Polo, J.; Mogedano-Cruz, S.; Sosa-Reina, M.D.; García-Pérez-De-Sevilla, G.; Martín-Pérez, S.; González-De-La-Flor, Á. Prevalence, diagnosis and management of musculoskeletal disorders in elite athletes: A mini-review. Dis. Mon. 2023, 70, 101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Morales, C.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Navarro-Flores, E.; Mazoteras-Pardo, V.; García-Bermejo, P.; López-López, D.; Martínez-Jiménez, E.M.; De-la-Cruz-Torres, B. M-Mode Ultrasound Examination of Soleus Muscle in Healthy Subjects: Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability Study. Healthcare 2020, 8, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, C.; Orgenc, Y.; Ergenc, R.; Erkan, N. Rupture of the medial gastrocnemius muscle during namaz praying: An unusual cause of tennis leg. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2008, 32, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecher, G.; Chompoopong, P.; Litchy, W.J.; Boon, A.J. Distal Tibial Mononeuropathy From Compression by the Posterior Tibial Artery: Clinical-Electrophysiological-Ultrasonographic Correlations. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2023, 40, E17–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, B.J.; Pobre, T. Electrodiagnostic Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy; StatPearls: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, A.M. High-Resolution Ultrasonography Versus MRI in the Diagnosis of Achilles Tendon Lesions. Am. J. Med. Sci. Innov. 2024, 3, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behling-Kelly, E.; Goggs, R. Thrombotic Disorders. In Schalm’s Veterinary Hematology, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trybulski, R.; Biolik, G.; Kuczmik, W.; Ivasyk, N.; Tyravska, O. Application of Deep Oscillation Therapy in The Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases. Medicni Perspekt. 2023, 28, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleakley, C.M.; Glasgow, P.; MacAuley, D.C. PRICE needs updating, should we call the POLICE? Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Louis, M.S.; Fournier, M. Vibration and pressure wave therapy for calf strains: A proposed treatment. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2013, 3, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trybulski, R.; Kużdżał, A.; Bichowska-Pawęska, M.; Vovkanych, A.; Kawczyński, A.; Biolik, G.; Muracki, J. Immediate Effect of Cryo-Compression Therapy on Biomechanical Properties and Perfusion of Forearm Muscles in Mixed Martial Arts Fighters. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trybulski, R.; Vovkanych, A.; Bas, O.; Tyravska, O. The low-temperature effect on sports regeneration. Fisioter. Em Mov. 2023, 36, e36204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Application of blood flow restriction training in lower limb rehabilitation. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2024, 50, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, T.W.; Schache, A.G.; Pandy, M.G. Muscular strategy shift in human running: Dependence of running speed on hip and ankle muscle performance. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babtan, A.; Ilea, A.; Feurdean, C.; Ceci, S.; Pula, B.; Candrea, S.; Azzollini, D.; Piras, F.; Curatoli, L.; Corriero, A.; et al. Biostimulation with low-level laser therapy and its effects on soft and hard tissue regeneration. Literature review. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2022, 9, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, A.; DeMarees, M.; Grau, M.; Hollinger, A.; Seeger, B.; Schiffer, T.; Bloch, W.; Gehlert, S. Superimposed whole-body electrostimulation augments strength adaptations and type ii myofiber growth in soccer players during a competitive season. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 463187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, P.; Soroko, M.; Zwyrzykowska, A.; Kiełbowicz, Z. The use of laser biostimulation in human and animal physiotherapy—A review. Acta Vet. Brno 2017, 86, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliario, M.; Yerra, P.; Gino, S.; Sabbatini, M.; Renò, F. Laser Biostimulation Induces Wound Healing-Promoter β2-Defensin Expression in Human Keratinocytes via Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivkov, R.; Mihaylova, M.; Yankov, T. An overview of the more significant therapeutic effects of TECAR therapy. Varna Med. Forum 2023, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastra, J.C.R.; Mendez, E.P.; Lastra, J.C.R.; Mendez, E.P. Use of an Evolution in Tecartherapy for Muscle Improvement and Treatment of Sports Injuries. In Contemporary Advances in Sports Science; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, P.S.; Cardoso, K.R.d.S.; Vieira, R.d.P.; Ruiz-Silva, C.; Coelho, C.d.F.; Martins, P.S.L.L.; Lopes-Martins, R.A.B. Applications of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy in Skeletal-Muscle System: An Integrative Review. Man. Ther. Posturology Rehabil. J. 2023, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, R.C.; Eisenmann, J.; Glass, N.A.; Petrachaianan, K.; Wilz, L. Platelet-Poor vs Platelet-Rich Plasma For The Treatment Of Acute Thigh Muscle Injuries. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 104, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourugeon, Y.; Yonai, Y.; Berkovich, Y.; Laver, L. Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for Muscle Injuries. In Musculoskeletal Injections Manual; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, J.B.; Penner, L.C.; Galarneau, J.-M.; Josafatow, N.; Cooper, J.; Ghodsi, M.; Huang, J.; Fraser, D.D.; Smirl, J.; Esser, M.J.; et al. Plasma Biomarkers of Traumatic Brain Injury in Adolescents with Sport-Related Concussion. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2431959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, E.M.; Draskovits, T.; Praschak, M.; Quittan, M.; Graf, A. Association between ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness, pennation angle, echogenicity and skeletal muscle strength in the elderly. Age 2013, 35, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manal, K.; Roberts, D.P.; Buchanan, T.S. Optimal Pennation Angle of the Primary Ankle Plantar and Dorsiflexors: Variations with Sex, Contraction Intensity, and Limb. J. Appl. Biomech. 2006, 22, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwah, L.K.; Pinto, R.Z.; Diong, J.; Herbert, R.D. Reliability and validity of ultrasound measurements of muscle fascicle length and pennation in humans: A systematic review. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minuti, T.; Cigni, P.; Costagli, M.; Cucini, A.; Cione, E.; Melotto, S.; Rapetti, S.; Ricotti, L.; Cannataro, R. Reliability of a Custom Device Used to Measure Isometric Knee Flexor and Extensor Strength in Standing Position. Life 2023, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.B.; Oliveira, C.; Ornelas, G.; Soares, T.; Souto, J.; Póvoa, A.R.; Ferreira, L.M.A.; Ricci-Vitor, A.L. Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability of the Kinvent Hand-Held Dynamometer in Young Adults. Med. Sci. Forum 2023, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Suga, T.; Terada, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kusagawa, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Nagano, A.; Isaka, T. Relationship of the knee extensor strength but not the quadriceps femoris muscularity with sprint performance in sprinters: A reexamination and extension. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.S.; Yi, Y.G.; Shin, H.I. Reliability and validity of knee extensor strength measurements using a portable dynamometer anchoring system in a supine position. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, M.; McLaine, S.; Magni, N. Validity and Reliability of the Kinvent Handheld Dynamometer in the Athletic Shoulder Test. J. Sport. Rehabil. 2023, 32, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Goto, K.; Kojima, A.; Akema, T.; Uehara, K.; Aoki, H.; Sugiura, T.; Ohira, Y.; Yoshioka, T. Possible role of calcineurin in heating-related increase of rat muscle mass. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannoy, J.; Crowley, S.; Jarratt, A.; Werts, K.L.; Osborne, K.; Park, S.; English, A.W. Upslope treadmill exercise enhances motor axon regeneration but not functional recovery following peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 116, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Palma, M.; Ambrogini, P.; Lattanzi, D.; Brocca, L.; Bottinelli, R.; Cuppini, R.; Pellegrino, M.A.; Sartini, S. The impact of different exercise protocols on rat soleus muscle reinnervation and recovery following peripheral nerve lesion and regeneration. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 948985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.V.; Yetter, T.R.; Somerson, J.S. Surgical repair of distal triceps rupture: A systematic review of outcomes and complications. JSES Rev. Rep. Tech. 2022, 2, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schemitsch, C.; Nauth, A. Psychological factors and recovery from trauma. Injury 2020, 51, S64–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K. Rehabilitation Nutrition for Injury Recovery of Athletes: The Role of Macronutrient Intake. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Jia, W. Food-derived bioactive peptides as momentous food components: Can functional peptides passed through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and NF-κB pathway to repair and protect the skeletal muscle injury. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 9210–9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipton, K.D. Nutritional Support for Exercise-Induced Injuries. Sports Med. 2015, 45 (Suppl. S1), 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzucchi, I.; Patrizio, F.; Ceci, R.; Duranti, G.; Sabatini, S.; Sgrò, P.; Di Luigi, L.; Sacchetti, M. Quercetin Supplementation Improves Neuromuscular Function Recovery from Muscle Damage. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Rincon, M.; Gelabert-Rebato, M.; Galvan-Alvarez, V.; Gallego-Selles, A.; Martinez-Canton, M.; Lopez-Rios, L.; Wiebe, J.C.; Martin-Rodriguez, S.; Arteaga-Ortiz, R.; Dorado, C.; et al. Supplementation with a Mango Leaf Extract (Zynamite®) in Combination with Quercetin Attenuates Muscle Damage and Pain and Accelerates Recovery after Strenuous Damaging Exercise. Nutrients 2020, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Calleja-González, J.; Refoyo, I.; León-Guereño, P.; Cordova, A.; Del Coso, J. Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Cardiac Stress During a Marathon Could be Associated with Dietary Intake During the Week Before the Race. Nutrients 2020, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Zwetsloot, K.A.; Simonson, A.J.; Hoyle, A.T.; Wang, X.; Nelson, H.K.; Lefranc-Millot, C.; Guérin-Deremaux, L. Effects of Whey and Pea Protein Supplementation on Post-Eccentric Exercise Muscle Damage: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracino, P.G.; Saylor, H.E.; Hanna, B.R.; Hickner, R.C.; Kim, J.S.; Ormsbee, M.J. Effects of Pre-Sleep Whey vs. Plant-Based Protein Consumption on Muscle Recovery Following Damaging Morning Exercise. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van’t Veld, R.C.; Rosu, A.C.; van der Kooij, H.; van Asseldonk, E.H.F. Down-Conditioning of Soleus Reflex Activity using Mechanical Stimuli and EMG Biofeedback. In Proceedings of the Summer School on Neurorehabilitation 2018—Parador de Baiona, Baiona, Spain, 16–21 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De-La-Cruz-Torres, B.; Barrera-Garciá-Martín, I.; Valera-Garrido, F.; Minaya-Munõz, F.; Romero-Morales, C. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Needle Electrolysis in Dancers with Chronic Soleus Injury: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 4156258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, Y.; Joginder, Y.; Sheetal, K. A Comparative Study of Effectiveness between Myofascial Release and Pressure Release on Pain and Ankle Range of Motion in Adults with Soleus Myofascial Trigger Points. Int. J. Orthop. Rehabil. 2022, 1, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Injury Type | Prevalence (%) | Common Cause | Typical Recovery Time (Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soleus Strain | 15 | Overuse or sudden increase in activity | 2 |
| Soleus Tear | 10 | Trauma or high-force contraction | 4 |
| Soleus Tendinopathy | 5 | Repetitive stress and improper biomechanics | 6 |
| Partial Tear | 8 | Acute injury with swelling | 3 |
| Complete Tear | 2 | Severe trauma or sudden excessive force | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trybulski, R.; Gałęziok, K.; Matuszczyk, F.; Halski, T.; Muracki, J. Problems in Diagnosis and Treatment of Soleus Muscle Injuries—Narrative Review and Case Report. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061955
Trybulski R, Gałęziok K, Matuszczyk F, Halski T, Muracki J. Problems in Diagnosis and Treatment of Soleus Muscle Injuries—Narrative Review and Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061955
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrybulski, Robert, Kamil Gałęziok, Filip Matuszczyk, Tomasz Halski, and Jarosław Muracki. 2025. "Problems in Diagnosis and Treatment of Soleus Muscle Injuries—Narrative Review and Case Report" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061955
APA StyleTrybulski, R., Gałęziok, K., Matuszczyk, F., Halski, T., & Muracki, J. (2025). Problems in Diagnosis and Treatment of Soleus Muscle Injuries—Narrative Review and Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061955






