Mapping the Epileptogenic Brain Using Low-Frequency Stimulation: Two Decades of Advances and Uncertainties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Do specific response patterns differentiate epileptogenic tissues from healthy regions?
- (2)
- How do epileptogenic regions interact with and influence the broader network of functionally connected brain regions?
- (3)
- How do stimulation-induced seizures relate to spontaneous seizures?
- (4)
- Can LFS guide emerging stimulation-based therapies such as responsive neurostimulation (RNS)?
2. Basic Principles of Low-Frequency Stimulation
3. Do Specific Response Patterns Differentiate Epileptogenic Tissues from Healthy Regions?
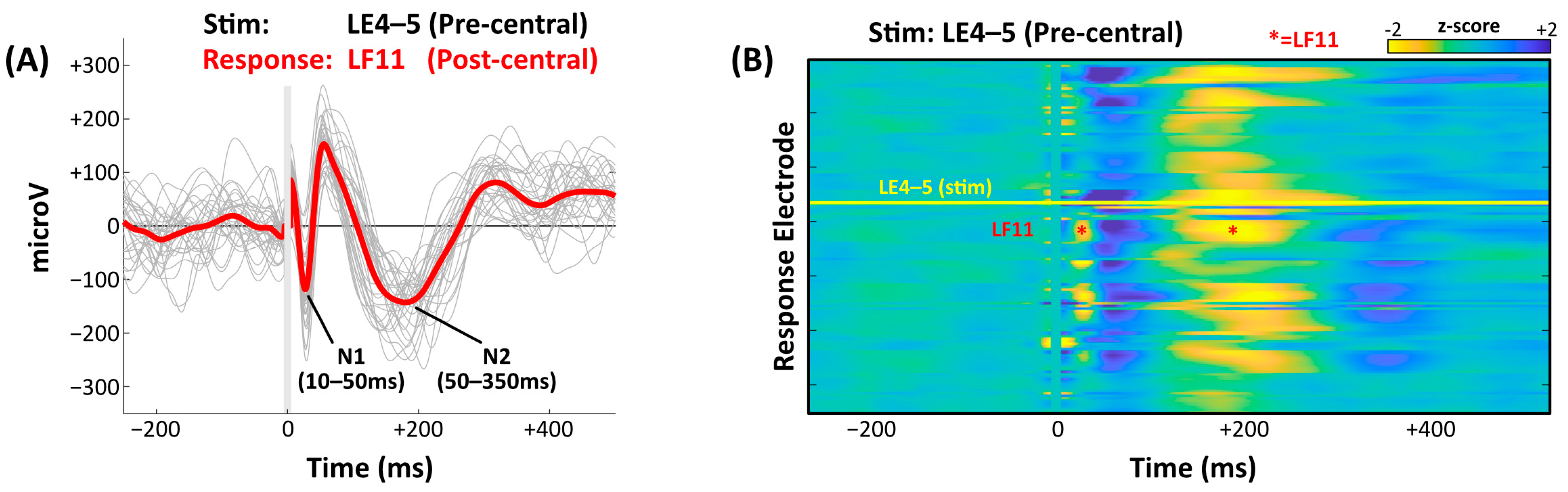
3.1. Early Response, Late Response, and CCEP Amplitude
3.2. Evoked High-Frequency Oscillations
3.3. CCEPs and Interictal Spikes
3.4. CCEP Variability
4. How Do Epileptogenic Regions Interact with and Influence the Broader Network of Functionally Connected Brain Regions?
4.1. Effective Connectivity Measures and SOZ Localization
4.2. CCEPs and Other Connectivity Measures
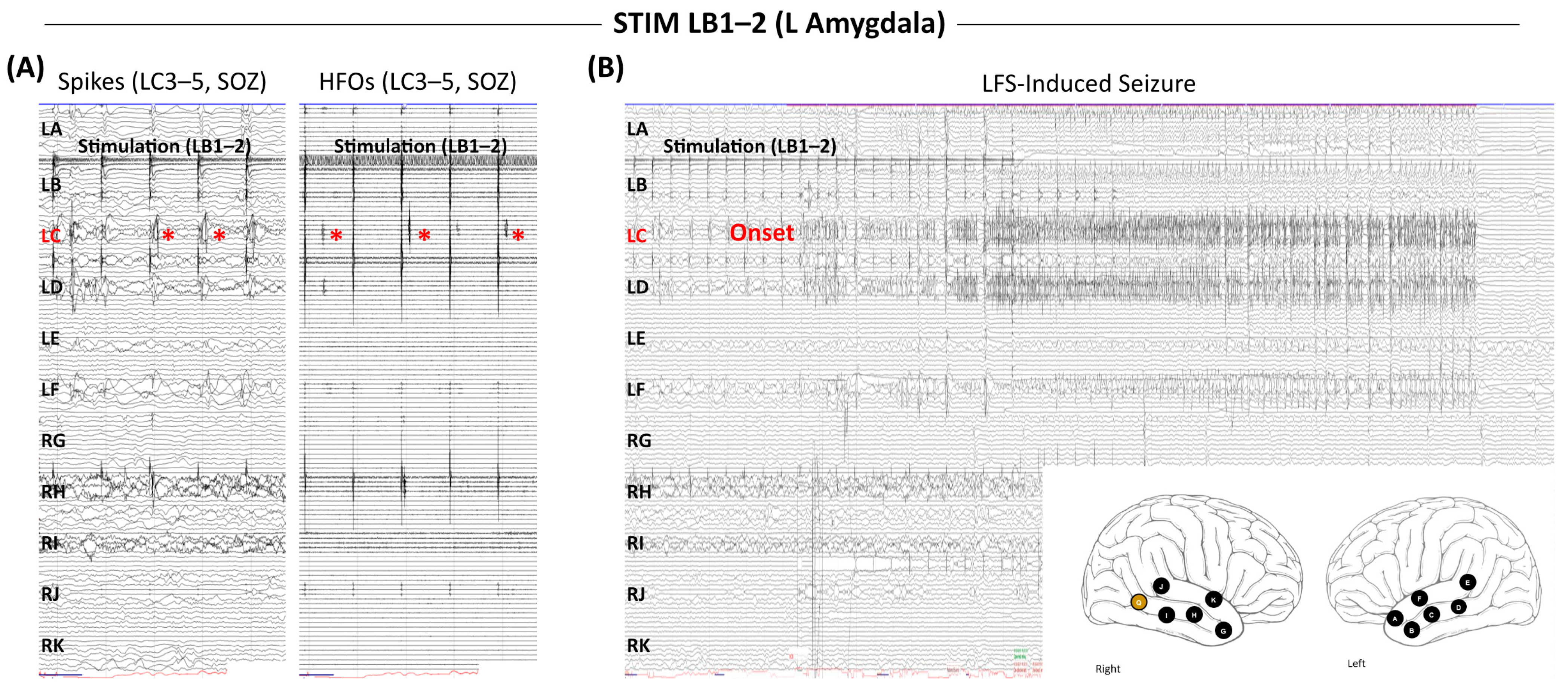
5. How Do Stimulation-Induced Seizures Relate to Spontaneous Seizures?
6. Can LFS Guide Emerging Stimulation-Based Therapies?
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCEPs | Cortico-cortical evoked potentials |
| DRE | Drug-resistant epilepsy |
| DR | Delayed response |
| DTI | Diffusion tensor imaging |
| EMU | Epilepsy monitoring unit |
| ER | Early response |
| EZ | Epileptogenic zone |
| FRs | Fast ripples |
| HFOs | High-frequency oscillations |
| HFS | High-frequency stimulation |
| LFS | Low-frequency stimulation |
| MEG | Magnetoencephalography |
| MTL | Mesial temporal lobe |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| RNS | Responsive neurostimulation |
| SEEG | Stereoelectroencephalography |
| SOZ | Seizure onset zone |
| SPES | Single-pulse electrical stimulation |
| SPECT | Single-photon emission computed tomography |
References
- Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Ryvlin, P.; Tomson, T. Epilepsy: New advances. Lancet 2015, 385, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.; Huh, L. Outcomes of epilepsy surgery in adults and children. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüders, H.O.; Najm, I.; Nair, D.; Widdess-Walsh, P.; Bingman, W. The epileptogenic zone: General principles. Epileptic Disord. 2006, 8 (Suppl. S2), S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.A.; Cash, S.S. Epilepsy as a disorder of cortical network organization. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diessen, E.; Diederen, S.J.; Braun, K.P.; Jansen, F.E.; Stam, C.J. Functional and structural brain networks in epilepsy: What have we learned? Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramantani, G.; Westover, M.B.; Gliske, S.; Sarnthein, J.; Sarma, S.; Wang, Y.; Baud, M.O.; Stacey, W.C.; Conrad, E.C. Passive and active markers of cortical excitability in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2023, 64 (Suppl. S3), S25–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, O.; Bastin, J.; Chabardès, S.; Minotti, L.; Kahane, P. Studying network mechanisms using intracranial stimulation in epileptic patients. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.S.; Clayden, J.D.; Cardoso, M.J.; Rodionov, R.; Duncan, J.S.; Scott, C.; Diehl, B.; Ourselin, S. Structural and effective connectivity in focal epilepsy. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 17, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novitskaya, Y.; Dümpelmann, M.; Schulze-Bonhage, A. Physiological and pathological neuronal connectivity in the living human brain based on intracranial EEG signals: The current state of research. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2023, 3, 1297345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, W.; Jasper, H. Epilepsy and the Functional Anatomy of the Human Brain. AMA Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1954, 72, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, R.; Nair, D.R.; LaPresto, E.; Bingaman, W.; Shibasaki, H.; Lüders, H.O. Functional connectivity in human cortical motor system: A cortico-cortical evoked potential study. Brain 2007, 130, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, R.; Nair, D.R.; LaPresto, E.; Najm, I.; Bingaman, W.; Shibasaki, H.; Lüders, H.O. Functional connectivity in the human language system: A cortico-cortical evoked potential study. Brain 2004, 127, 2316–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenoix, H.; Magnin, M.; Mauguière, F.; Ryvlin, P. Evoked potential study of hippocampal efferent projections in the human brain. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 2488–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenoix, H.; Magnin, M.; Guénot, M.; Isnard, J.; Mauguière, F.; Ryvlin, P. Hippocampal-orbitofrontal connectivity in human: An electrical stimulation study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enatsu, R.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Bulacio, J.; Kubota, Y.; Mosher, J.; Burgess, R.C.; Najm, I.; Nair, D.R. Connections of the limbic network: A corticocortical evoked potentials study. Cortex 2015, 62, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, R.; Kunieda, T.; Nair, D. Single pulse electrical stimulation to probe functional and pathological connectivity in epilepsy. Seizure 2017, 44, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.L.; Isokawa, M.; Babb, T.L.; Crandall, P.H. Functional connections in the human temporal lobe. I. Analysis of limbic system pathways using neuronal responses evoked by electrical stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 1990, 82, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.L.; Isokawa, M.; Babb, T.L.; Crandall, P.H.; Levesque, M.F.; Engel, J., Jr. Functional connections in the human temporal lobe. II. Evidence for a loss of functional linkage between contralateral limbic structures. Exp. Brain Res. 1991, 85, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, A.; Anderson, M.; Alarcón, G.; Seoane, J.J.; Selway, R.; Binnie, C.D.; Polkey, C.E. Responses to single pulse electrical stimulation identify epileptogenesis in the human brain in vivo. Brain 2002, 125, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, A.; Alarcón, G.; García-Seoane, J.J.; Lacruz, M.E.; Nayak, S.D.; Honavar, M.; Selway, R.P.; Binnie, C.D.; Polkey, C.E. Single-pulse electrical stimulation identifies epileptogenic frontal cortex in the human brain. Neurology 2005, 65, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, A.; Alarcón, G.; Honavar, M.; García Seoane, J.J.; Selway, R.P.; Polkey, C.E.; Binnie, C.D. Single pulse electrical stimulation for identification of structural abnormalities and prediction of seizure outcome after epilepsy surgery: A prospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huiskamp, G.; van Blooijs, D.; van der Stoel, M. Harvesting responses to single pulse electrical stimulation for presurgical evaluation in epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 2444–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Kunii, N.; Shimada, S.; Saito, N. Utilizing Excitatory and Inhibitory Activity Derived from Interictal Intracranial Electroencephalography as Potential Biomarkers for Epileptogenicity. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2024, 64, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauscher, B.; Bartolomei, F.; Baud, M.O.; Smith, R.J.; Worrell, G.; Lundstrom, B.N. Stimulation to probe, excite, and inhibit the epileptic brain. Epilepsia 2023, 64 (Suppl. S3), S49–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, B.; Ostrowski, L.; Williams, Z.M.; Dougherty, D.D.; Eskandar, E.N.; Widge, A.S.; Chu, C.J.; Cash, S.S.; Paulk, A.C. Local and distant responses to single pulse electrical stimulation reflect different forms of connectivity. NeuroImage 2021, 237, 118094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.S.; Sinha, S.R.; Gordon, B.; Lesser, R.P.; Thakor, N.V. Determination of current density distributions generated by electrical stimulation of the human cerebral cortex. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1993, 86, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prime, D.; Rowlands, D.; O’Keefe, S.; Dionisio, S. Considerations in performing and analyzing the responses of cortico-cortical evoked potentials in stereo-EEG. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, D.; Valentín, A.; García Seoane, J.J.; Alarcón, G.; Boyd, S.G. Single-pulse electrical stimulation helps to identify epileptogenic cortex in children. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Blooijs, D.; Blok, S.; Huiskamp, G.J.M.; van Eijsden, P.; Meijer, H.G.E.; Leijten, F.S.S. The effect of propofol on effective brain networks. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2024, 161, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamao, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Kunieda, T.; Nakae, T.; Nishida, S.; Inano, R.; Shibata, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Arakawa, Y.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Effects of propofol on cortico-cortical evoked potentials in the dorsal language white matter pathway. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Enatsu, R.; Kanno, A.; Yokoyama, R.; Suzuki, H.; Tachibana, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Mikami, T.; Ochi, S.; Yamakage, M.; et al. The Influence of Anesthesia on Corticocortical Evoked Potential Monitoring Network Between Frontal and Temporoparietal Cortices. World Neurosurg. 2019, 123, e685–e692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbune, A.A.; Popa, I.; Mindruta, I.; Beniczky, S.; Donos, C.; Daneasa, A.; Mălîia, M.D.; Băjenaru, O.A.; Ciurea, J.; Barborica, A. Sleep modulates effective connectivity: A study using intracranial stimulation and recording. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usami, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Hitomi, T.; Shimotake, A.; Kikuchi, T.; Matsuhashi, M.; Kunieda, T.; Mikuni, N.; Miyamoto, S.; et al. Sleep modulates cortical connectivity and excitability in humans: Direct evidence from neural activity induced by single-pulse electrical stimulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 4714–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Usami, K.; Matsuhashi, M.; Shimotake, A.; Kikuchi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Kunieda, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Takahashi, R.; et al. Cortico-cortical evoked potential by single-pulse electrical stimulation is a generally safe procedure. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, L.J.; Brunner, P.; Kapeller, C.; Guger, C.; Kamada, K.; Bunch, M.E.; Frawley, B.K.; Lynch, T.M.; Ritaccio, A.L.; Schalk, G. A quantitative method for evaluating cortical responses to electrical stimulation. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 311, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, M.A.; Kamali, G.; Koubeissi, M.Z.; Sarma, S.V.; Crone, N.E.; Smith, R.J.; Kang, J.Y. Towards optimizing single pulse electrical stimulation: High current intensity, short pulse width stimulation most effectively elicits evoked potentials. Brain Stimul. 2023, 16, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, M.A.; Smith, R.J.; Haridas, B.; Coogan, C.; Crone, N.E.; Kang, J.Y. Effects of stimulation intensity on intracranial cortico-cortical evoked potentials: A titration study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 2766–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Davis, T.S.; Philip, B.; Smith, E.H.; Arain, A.; Peters, A.; Newman, B.; Butson, C.R.; Rolston, J.D. A systematic exploration of parameters affecting evoked intracranial potentials in patients with epilepsy. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, L.H.; Sun, S.; Paschall, C.J.; Perks, K.M.; Weaver, K.E.; Perlmutter, S.I.; Ko, A.L.; Ojemann, J.G.; Herron, J.A. Data processing techniques impact quantification of cortico-cortical evoked potentials. J. Neurosci. Methods 2024, 408, 110130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donos, C.; Mîndruţă, I.; Ciurea, J.; Mălîia, M.D.; Barborica, A. A comparative study of the effects of pulse parameters for intracranial direct electrical stimulation in epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Kunii, N.; Kawai, K.; Matsuo, T.; Ishishita, Y.; Ibayashi, K.; Saito, N. Impact of volume-conducted potential in interpretation of cortico-cortical evoked potential: Detailed analysis of high-resolution electrocorticography using two mathematical approaches. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prime, D.; Woolfe, M.; O’Keefe, S.; Rowlands, D.; Dionisio, S. Quantifying volume conducted potential using stimulation artefact in cortico-cortical evoked potentials. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 337, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L. MRIES: A Matlab Toolbox for Mapping the Responses to Intracranial Electrical Stimulation. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 652841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prime, D.; Woolfe, M.; Rowlands, D.; O’Keefe, S.; Dionisio, S. Comparing connectivity metrics in cortico-cortical evoked potentials using synthetic cortical response patterns. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 334, 108559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajnal, B.; Szabó, J.P.; Tóth, E.; Keller, C.J.; Wittner, L.; Mehta, A.D.; Erőss, L.; Ulbert, I.; Fabó, D.; Entz, L. Intracortical mechanisms of single pulse electrical stimulation (SPES) evoked excitations and inhibitions in humans. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.J.; Honey, C.J.; Mégevand, P.; Entz, L.; Ulbert, I.; Mehta, A.D. Mapping human brain networks with cortico-cortical evoked potentials. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novitskaya, Y.; Dümpelmann, M.; Vlachos, A.; Reinacher, P.C.; Schulze-Bonhage, A. In vivo-assessment of the human temporal network: Evidence for asymmetrical effective connectivity. NeuroImage 2020, 214, 116769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.J.; Honey, C.J.; Entz, L.; Bickel, S.; Groppe, D.M.; Toth, E.; Ulbert, I.; Lado, F.A.; Mehta, A.D. Corticocortical evoked potentials reveal projectors and integrators in human brain networks. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 9152–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entz, L.; Tóth, E.; Keller, C.J.; Bickel, S.; Groppe, D.M.; Fabó, D.; Kozák, L.R.; Erőss, L.; Ulbert, I.; Mehta, A.D. Evoked effective connectivity of the human neocortex. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 5736–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaréchal, J.D.; Jedynak, M.; Trebaul, L.; Boyer, A.; Tadel, F.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Deman, P.; Tuyisenge, V.; Ayoubian, L.; Hugues, E.; et al. A brain atlas of axonal and synaptic delays based on modelling of cortico-cortical evoked potentials. Brain 2022, 145, 1653–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, K.; Milsap, G.W.; Korzeniewska, A.; Collard, M.J.; Wang, Y.; Lesser, R.P.; Anderson, W.S.; Crone, N.E. Cortical Responses to Input from Distant Areas are Modulated by Local Spontaneous Alpha/Beta Oscillations. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón, G.; Martinez, J.; Kerai, S.V.; Lacruz, M.E.; Quiroga, R.Q.; Selway, R.P.; Richardson, M.P.; García Seoane, J.J.; Valentín, A. In vivo neuronal firing patterns during human epileptiform discharges replicated by electrical stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, A.; Alarcón, G. Single pulse electrical stimulation and high-frequency oscillations, a complicated marriage. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1026–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, A.; Alarcón, G.; Barrington, S.F.; García Seoane, J.J.; Martín-Miguel, M.C.; Selway, R.P.; Koutroumanidis, M. Interictal estimation of intracranial seizure onset in temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentín, A.; Morris, R.; Honavar, M.; Bodi, I.; Teijeira-Azcona, A.; Lázaro, M.; Selway, R.; Alarcón, G.; Richardson, M.P. Single Pulse Electrical Stimulation Identifies Epileptogenicity in a Case with Subcortical Nodular Heterotopia and MRI Negative Epilepsy. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouthaan, B.E.; van ’t Klooster, M.A.; Keizer, D.; Hebbink, G.J.; Leijten, F.S.S.; Ferrier, C.H.; van Putten, M.; Zijlmans, M.; Huiskamp, G.J.M. Single Pulse Electrical Stimulation to identify epileptogenic cortex: Clinical information obtained from early evoked responses. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enatsu, R.; Jin, K.; Elwan, S.; Kubota, Y.; Piao, Z.; O’Connor, T.; Horning, K.; Burgess, R.C.; Bingaman, W.; Nair, D.R. Correlations between ictal propagation and response to electrical cortical stimulation: A cortico-cortical evoked potential study. Epilepsy Res. 2012, 101, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lega, B.; Dionisio, S.; Flanigan, P.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.; Nair, D.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J. Cortico-cortical evoked potentials for sites of early versus late seizure spread in stereoelectroencephalography. Epilepsy Res. 2015, 115, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousseyn, S.; Krishnan, B.; Wang, Z.I.; Wongwiangjunt, S.; Nayak, C.S.; Mosher, J.C.; Wu, G.; Van Paesschen, W.; Leahy, R.M.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.A.; et al. Connectivity in ictal single photon emission computed tomography perfusion: A cortico-cortical evoked potential study. Brain 2017, 140, 1872–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Enatsu, R.; Matsumoto, R.; Novak, E.; Thankappen, B.; Piao, Z.; O’Connor, T.; Horning, K.; Bingaman, W.; Nair, D. Accentuated cortico-cortical evoked potentials in neocortical epilepsy in areas of ictal onset. Epileptic Disord. 2010, 12, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, B.; Rajah, G.B.; Geng, X.; Singh, R.; Yang, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, W.; Ding, Y.; et al. The effectiveness of cortico-cortical evoked potential in detecting seizure onset zones. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enatsu, R.; Piao, Z.; O’Connor, T.; Horning, K.; Mosher, J.; Burgess, R.; Bingaman, W.; Nair, D. Cortical excitability varies upon ictal onset patterns in neocortical epilepsy: A cortico-cortical evoked potential study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, M.A.; Smith, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Coogan, C.; Sarma, S.V.; Crone, N.E.; Kang, J.Y. Cortico-cortical evoked potentials in response to varying stimulation intensity improves seizure localization. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2023, 145, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Xia, J.; Fu, M.; Cai, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhan, Y. Identification of epileptic networks with graph convolutional network incorporating oscillatory activities and evoked synaptic responses. NeuroImage 2023, 284, 120439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.W.; Cai, L.Y.; Doss, D.J.; Jiang, J.W.; Negi, A.S.; Narasimhan, S.; Paulo, D.L.; González, H.F.J.; Williams Roberson, S.; Bick, S.K.; et al. Localizing seizure onset zones in surgical epilepsy with neurostimulation deep learning. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 138, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.; Kamali, G.; Hays, M.; Coogan, C.G.; Crone, N.E.; Sarma, S.V.; Kang, J.Y. State-space models of evoked potentials to localize the seizure onset zone. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 2528–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, S.; Valentin, A.; Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. Localization of Epileptic Brain Responses to Single-Pulse Electrical Stimulation by Developing an Adaptive Iterative Linearly Constrained Minimum Variance Beamformer. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2023, 33, 2350050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauscher, B.; Bartolomei, F.; Kobayashi, K.; Cimbalnik, J.; van ’t Klooster, M.A.; Rampp, S.; Otsubo, H.; Höller, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Asano, E.; et al. High-frequency oscillations: The state of clinical research. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlmans, M.; Jiruska, P.; Zelmann, R.; Leijten, F.S.; Jefferys, J.G.; Gotman, J. High-frequency oscillations as a new biomarker in epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Gotman, J. High-frequency changes during interictal spikes detected by time-frequency analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; van ’t Klooster, M.; Hoogteijling, S.; Jacobs, J.; Zijlmans, M. Prognostic Value of Complete Resection of the High-Frequency Oscillation Area in Intracranial EEG: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurology 2024, 102, e209216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van ’t Klooster, M.A.; Zijlmans, M.; Leijten, F.S.; Ferrier, C.H.; van Putten, M.J.; Huiskamp, G.J. Time-frequency analysis of single pulse electrical stimulation to assist delineation of epileptogenic cortex. Brain 2011, 134, 2855–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van ’t Klooster, M.A.; van Klink, N.E.C.; van Blooijs, D.; Ferrier, C.H.; Braun, K.P.J.; Leijten, F.S.S.; Huiskamp, G.J.M.; Zijlmans, M. Evoked versus spontaneous high frequency oscillations in the chronic electrocorticogram in focal epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Zijlmans, M.; Zelmann, R.; Olivier, A.; Hall, J.; Gotman, J.; Dubeau, F. Value of electrical stimulation and high frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) in identifying epileptogenic areas during intracranial EEG recordings. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donos, C.; Mîndruţă, I.; Malîia, M.D.; Raşină, A.; Ciurea, J.; Barborica, A. Co-occurrence of high-frequency oscillations and delayed responses evoked by intracranial electrical stimulation in stereo-EEG studies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Matsuhashi, M.; Usami, K.; Shimotake, A.; Kunieda, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Mikuni, N.; Miyamoto, S.; et al. High frequency activity overriding cortico-cortical evoked potentials reflects altered excitability in the human epileptic focus. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.S.; Rolston, J.D.; Bollo, R.J.; House, P.A. Delayed high-frequency suppression after automated single-pulse electrical stimulation identifies the seizure onset zone in patients with refractory epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mălîia, M.D.; Donos, C.; Barborica, A.; Mindruta, I.; Popa, I.; Ene, M.; Beniczky, S. High frequency spectral changes induced by single-pulse electric stimulation: Comparison between physiologic and pathologic networks. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstl, J.V.E.; Kiseleva, A.; Imbach, L.; Sarnthein, J.; Fedele, T. High frequency oscillations in relation to interictal spikes in predicting postsurgical seizure freedom. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, K.J.; White, A.; Dudek, F.E. Interictal spikes: Harbingers or causes of epilepsy? Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 497, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoly, P.J.; Freestone, D.R.; Boston, R.; Grayden, D.B.; Himes, D.; Leyde, K.; Seneviratne, U.; Berkovic, S.; O’Brien, T.; Cook, M.J. Interictal spikes and epileptic seizures: Their relationship and underlying rhythmicity. Brain 2016, 139, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, E.D.; Peltzer, B.; Brown, M.W., 3rd; Wusthoff, C.; Storm, P.B., Jr.; Litt, B.; Porter, B.E. Interictal EEG spikes identify the region of electrographic seizure onset in some, but not all, pediatric epilepsy patients. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, D.; Valentín, A.; Selway, R.P.; Alarcón, G. Can single pulse electrical stimulation provoke responses similar to spontaneous interictal epileptiform discharges? Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedynak, M.; Boyer, A.; Chanteloup-Forêt, B.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Saubat, C.; Tadel, F.; Kahane, P.; David, O. Variability of Single Pulse Electrical Stimulation Responses Recorded with Intracranial Electroencephalography in Epileptic Patients. Brain Topogr. 2023, 36, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feys, O.; Wens, V.; Schuind, S.; Rikir, E.; Legros, B.; De Tiège, X.; Gaspard, N. Variability of cortico-cortical evoked potentials in the epileptogenic zone is related to seizure occurrence. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2024, 11, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornblath, E.J.; Lucas, A.; Armstrong, C.; Greenblatt, A.S.; Stein, J.M.; Hadar, P.N.; Raghupathi, R.; Marsh, E.; Litt, B.; Davis, K.A.; et al. Quantifying trial-by-trial variability during cortico-cortical evoked potential mapping of epileptogenic tissue. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, K.; Wu, C. Epilepsy Networks and Their Surgical Relevance. Brain Sci. 2023, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Bonilha, L.; Gross, D.W. Network analysis for a network disorder: The emerging role of graph theory in the study of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 50, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulogne, S.; Pizzo, F.; Chatard, B.; Roehri, N.; Catenoix, H.; Ostrowsky-Coste, K.; Giusiano, B.; Guenot, M.; Carron, R.; Bartolomei, F.; et al. Functional connectivity and epileptogenicity of nodular heterotopias: A single-pulse stimulation study. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, H.; Taylor, K.; Hirfanoglu, T.; Koneru, S.; Bingaman, W.; Kobayashi, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Joshi, A.; Leahy, R.M.; Mosher, J.C.; et al. Effective connectivity differs between focal cortical dysplasia types I and II. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Blooijs, D.; Leijten, F.S.S.; van Rijen, P.C.; Meijer, H.G.E.; Huiskamp, G.J.M. Evoked directional network characteristics of epileptogenic tissue derived from single pulse electrical stimulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 4611–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.H.; Zhao, B.T.; Toprani, S.; Hu, W.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Sang, L.; Ma, Y.S.; Shao, X.Q.; Razavi, B.; et al. Epileptogenic network of focal epilepsies mapped with cortico-cortical evoked potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boido, D.; Kapetis, D.; Gnatkovsky, V.; Pastori, C.; Galbardi, B.; Sartori, I.; Tassi, L.; Cardinale, F.; Francione, S.; de Curtis, M. Stimulus-evoked potentials contribute to map the epileptogenic zone during stereo-EEG presurgical monitoring. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 4267–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Gaspard, N.; Zaveri, H.P.; Blumenfeld, H.; Hirsch, L.J.; Spencer, D.D.; Alkawadri, R. The connectivity index: An effective metric for grading epileptogenicity. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 133, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, M.A.; Daraie, A.H.; Smith, R.J.; Sarma, S.V.; Crone, N.E.; Kang, J.Y. Network excitability of stimulation-induced spectral responses helps localize the seizure onset zone. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2024, 166, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hays, M.A.; Coogan, C.; Crone, N.E.; Kang, J.Y. Graph theoretical analysis of evoked potentials shows network influence of epileptogenic mesial temporal region. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 4173–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, B.H.; Asano, E.; Sugiura, A.; Sonoda, M.; Lee, M.H.; Jeong, J.W. Dynamic tractography: Integrating cortico-cortical evoked potentials and diffusion imaging. NeuroImage 2020, 215, 116763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbink, J.; van Blooijs, D.; Huiskamp, G.; Leijten, F.S.S.; van Gils, S.A.; Meijer, H.G.E. A Comparison of Evoked and Non-evoked Functional Networks. Brain Topogr. 2019, 32, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilioti, M.; Winston, J.S.; Centeno, M.; Scott, C.; Chowdhury, F.; Diehl, B. The nature, frequency and value of stimulation induced seizures during extraoperative cortical stimulation for functional mapping. Seizure 2020, 81, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvel, P.; Landré, E.; Trottier, S.; Vignel, J.P.; Biraben, A.; Devaux, B.; Bancaud, J. Electrical stimulation with intracerebral electrodes to evoke seizures. Adv. Neurol. 1993, 63, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kahane, P.; Tassi, L.; Francione, S.; Hoffmann, D.; Lo Russo, G.; Munari, C. Electroclinical manifestations elicited by intracerebral electric stimulation “shocks” in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurophysiol. Clin. 1993, 23, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, S.; Kahane, P.; Diehl, B. Seizures induced by direct electrical cortical stimulation--Mechanisms and clinical considerations. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, C.; Kahane, P.; Tassi, L.; Francione, S.; Hoffmann, D.; Lo Russo, G.; Benabid, A.L. Intracerebral low frequency electrical stimulation: A new tool for the definition of the “epileptogenic area”? Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1993, 58, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuello Oderiz, C.; von Ellenrieder, N.; Dubeau, F.; Eisenberg, A.; Gotman, J.; Hall, J.; Hincapié, A.S.; Hoffmann, D.; Job, A.S.; Khoo, H.M.; et al. Association of Cortical Stimulation-Induced Seizure with Surgical Outcome in Patients with Focal Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manokaran, R.K.; Ochi, A.; Weiss, S.; Yau, I.; Sharma, R.; Otsubo, H.; Ibrahim, G.M.; Donner, E.J.; Jain, P. Stimulation-Induced Seizures in Children Undergoing Stereo-EEG Evaluation. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2024, 42, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraju, A.; Quraishi, I.; Collins, E.; McGrath, H.; Ramos, A.; Turk-Browne, N.B.; Zaveri, H.; Damisah, E.; Spencer, D.D.; Hirsch, L.J. Systematic 1 Hz direct electrical stimulation for seizure induction: A reliable method for localizing seizure onset zone and predicting seizure freedom. Brain Stimul. 2024, 17, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Nitsche, M.A.; Rotter, S.; Focke, N.K.; Rao, V.R. Neurostimulation targeting the epileptic focus: Current understanding and perspectives for treatment. Seizure 2024, 117, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, R.J.; Richardson, R.M.; Worrell, G.; Carmichael, D.W.; Baldeweg, T.; Litt, B.; Denison, T.; Tisdall, M.M. Towards network-guided neuromodulation for epilepsy. Brain 2022, 145, 3347–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.M.; Lee, A.T.; Kudo, K.; Ranasinghe, K.G.; Morise, H.; Findlay, A.M.; Kirsch, H.E.; Chang, E.F.; Nagarajan, S.S.; Rao, V.R. Network connectivity predicts effectiveness of responsive neurostimulation in focal epilepsy. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, B.H.; Bernabei, J.M.; Khambhati, A.N.; Mouchtaris, S.; Jeschke, J.; Bassett, D.S.; Becker, D.; Davis, K.A.; Lucas, T.; Doyle, W.; et al. Intracranial electroencephalographic biomarker predicts effective responsive neurostimulation for epilepsy prior to treatment. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Taylor, K.N.; Shahabi, H.; Krishnan, B.; Joshi, A.; Mackow, M.J.; Feldman, L.; Zamzam, O.; Medani, T.; Bulacio, J.; et al. Effective connectivity relates seizure outcome to electrode placement in responsive neurostimulation. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomlinson, S.B.; Baumgartner, M.E.; Darlington, T.R.; Marsh, E.D.; Kennedy, B.C. Mapping the Epileptogenic Brain Using Low-Frequency Stimulation: Two Decades of Advances and Uncertainties. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061956
Tomlinson SB, Baumgartner ME, Darlington TR, Marsh ED, Kennedy BC. Mapping the Epileptogenic Brain Using Low-Frequency Stimulation: Two Decades of Advances and Uncertainties. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061956
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomlinson, Samuel B., Michael E. Baumgartner, Timothy R. Darlington, Eric D. Marsh, and Benjamin C. Kennedy. 2025. "Mapping the Epileptogenic Brain Using Low-Frequency Stimulation: Two Decades of Advances and Uncertainties" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061956
APA StyleTomlinson, S. B., Baumgartner, M. E., Darlington, T. R., Marsh, E. D., & Kennedy, B. C. (2025). Mapping the Epileptogenic Brain Using Low-Frequency Stimulation: Two Decades of Advances and Uncertainties. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061956




