Hemoperfusion Using the Oxiris Membrane in Septic Shock Patients with Preserved Kidney Function: A Case Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Population
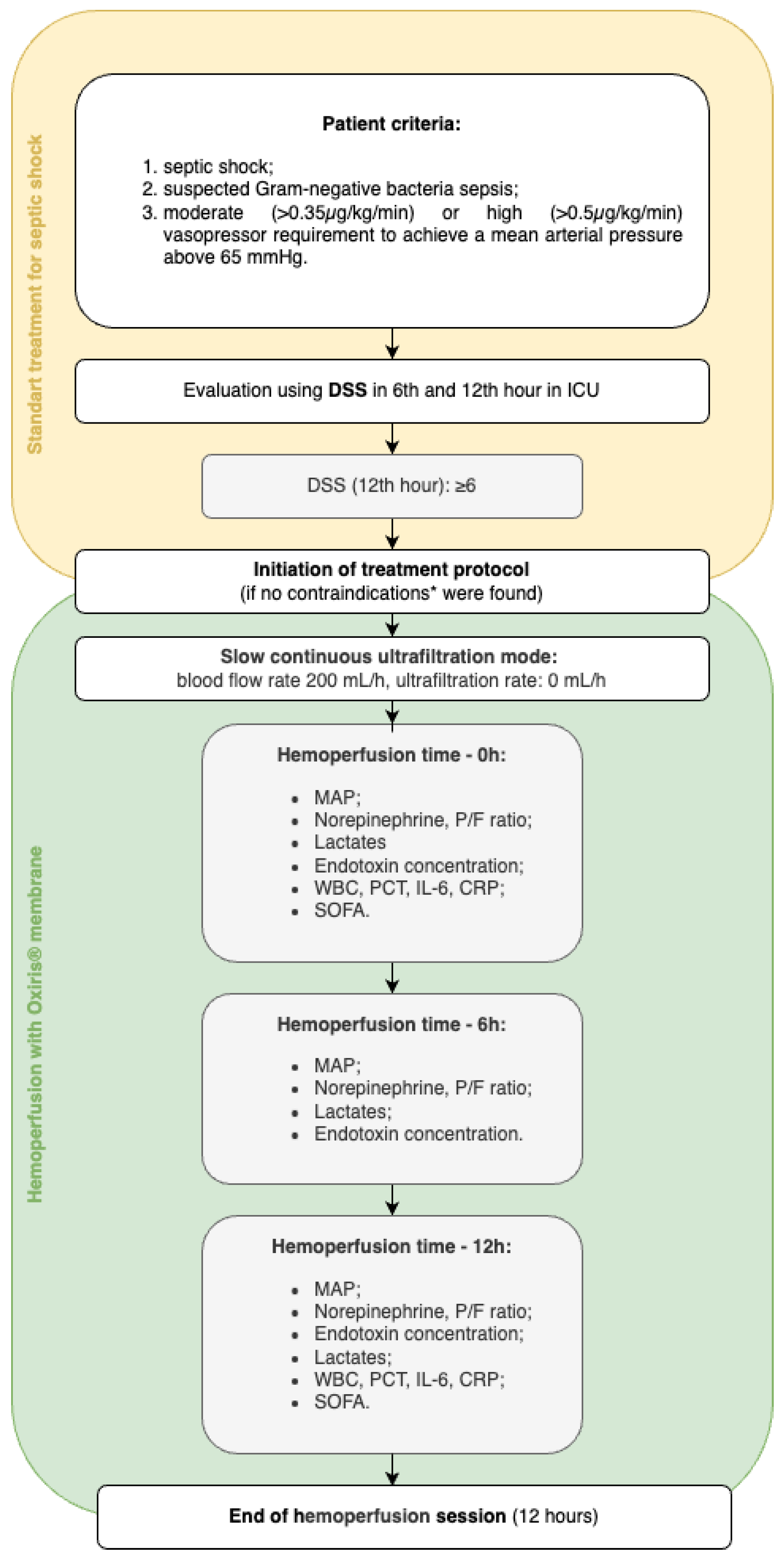
2.2. Description of the Treatment Protocol and Technical Considerations for Hemoperfusion
2.3. Data Collection and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Case Presentation and Description
3.1. Clinical Case 1 (Patient A)
3.2. Clinical Case 2 (Patient B)
3.3. Clinical Case 3 (Patient C)
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Main Findings
4.2. Reflection on Previous Studies
4.3. Strength and Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CRRT | Continuous renal replacement therapy |
| CVVH | Continuous venovenous hemofiltration |
| DSS | Dynamic Score System |
| EAA | Endotoxin activity assay |
| EDTA | Ethylene-tetra-acetic acid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ET | Endotoxin |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| Lac | Lactate |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| MSSA | Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus |
| NE | Norepinephrine |
| OD | Optical density |
| P/F | Ratio of partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood to the fraction of inspiratory oxygen concentration |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| SCUF | Slow continuous ultrafiltration |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| WBC | White blood cell |
Appendix A
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payen, D.; Dupuis, C.; Deckert, V.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Rérole, A.L.; Lukaszewicz, A.C.; Coudroy, R.; Robert, R.; Lagrost, L. Endotoxin mass concentration in plasma is associated with mortality in a multicentric cohort of peritonitis-induced shock. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 749405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, C.W.; Kennedy, J.N.; Wang, S.; Chang, C.H.; Elliott, C.F.; Xu, Z.; Berry, S.; Clermont, G.; Cooper, G.; Gomez, H.; et al. Derivation, validation, and potential treatment implications of novel clinical phenotypes for sepsis. JAMA 2019, 321, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.C. Endotoxemia and Gram-negative bacteremia as predictors of outcome in sepsis: A meta-analysis using ROC curves. J. Endotoxin Res. 2003, 9, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, B.; Lambert, C.; Kellum, J.A. In Vitro comparison of the adsorption of inflammatory mediators by blood purification devices. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siew, L.Y.; Lee, Z.Y.; Yunos, N.M.; Atan, R.; Cove, M.E.; Lumlertgul, N.; Srisawat, N.; Hasan, M.S. Outcomes of extracorporeal blood purification with oXiris® membrane in critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2024, 83, 154844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, M.E.; Hansson, F.; Vincent, J.L.; Bodelsson, M. Endotoxin and cytokine reducing properties of the oXiris membrane in patients with septic shock: A randomized crossover double-blind study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; He, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Deng, K.; et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy with the adsorptive oXiris filter may be associated with lower 28-day mortality in sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalenka, A.; Arens, P.; Müllenbach, R.M.; Weigand, M.A.; Brune, M.; Fiedler-Kalenka, M.O. Effects of Oxiris® therapy on cytokine elimination after a LPS infusion—An experimental animal study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Fernández, X.; Ulsamer, A.; Cámara-Rosell, M.; Sbraga, F.; Boza-Hernández, E.; Moret-Ruíz, E.; Plata-Menchaca, E.; Santiago-Bautista, D.; Boronat-García, P.; SIRAKI02 Study Group; et al. Extracorporeal blood purification and acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery: The SIRAKI02 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Inter. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kogelmann, K.; Hübner, T.; Schwameis, F.; Drüner, M.; Scheller, M.; Jarczak, D. First evaluation of a new dynamic scoring system intended to support prescription of adjuvant CytoSorb hemoadsorption therapy in patients with septic shock. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, M.E.; Bodelsson, M. Analysis of endotoxin adsorption in two Swedish patients with septic shock. Blood Purif. 2019, 47 (Suppl. S3), 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Chung, Y.J.; Lee, G.R.; Kim, E.Y. The clinical efficacy and suitable implementation of two extracorporeal blood purification therapies: AN69-oXiris versus PMX-HP. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1344893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cove, M.; Nguyen, B.G.; Lumlertgul, N.; Ganesh, K.; Chan, A.; Bui, G.T.H.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; et al. Adsorptive hemofiltration for sepsis management: Expert recommendations based on the Asia Pacific experience. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 2258–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vriese, A.S.; Colardyn, F.A.; Philippé, J.J.; Vanholder, R.C.; De Sutter, J.H.; Lameire, N.H. Cytokine removal during continuous hemofiltration in septic patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, E.T.; Ong, V.; Remani, D.; Wong, W.K.; Haroon, S.; Lau, T.; Nyeo, H.Q.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Tan, B.H.; Chua, H.R. Filter life and safety of heparin-grafted membrane for continuous renal replacement therapy—A randomized controlled trial. Semin. Dial. 2021, 34, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretkalniņš, D.N.; Smirnova, D.; Klibus, M.; Šķesters, A.; Freijs, Ģ.; Liguts, V.; Sabeļņikovs, O. Clinical Efficacy of the Oxiris® Membrane in Patients with Refractory Septic Shock: Comparison Between Isolated Hemadsorption and Continuous Veno-Venous Hemofiltration Modalities. In Proceedings of the RSU Research Week 2025, Riga, Latvia, 26–28 March 2025; Available online: https://rw2025.rsu.lv (accessed on 16 March 2025).
| Patient | Gender | Age, Years | BMI, kg/m² | Sepsis Cause | Bacteriology Result | Intrahospital Days | ICU Days | Norepinephrine Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Male | 61 | 24.5 | Pleural empyema | A. baumannii 1 | 76 | 23 | 7 |
| B | Female | 53 | 17.9 | Mediastinitis | S. anginosus 2 | 34 | 4 | 4 |
| C | Female | 73 | 20.2 | Pneumonia | MSSA, E. coli 3 | 28 | 10 | 5 |
| Patient | Marker/Parameter | Hemoperfusion Time | Absolute Change, Δ | Relative Change, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 12 h | ||||
| A | WBC, ×109/L | 15.3 | 11.8 | −3.5 | −22.88 |
| CRP, mg/L | 587.95 | 369.39 | −218.56 | −37.17 | |
| PCT, ng/mL | 11.09 | 6.48 | −4.61 | −41.57 | |
| IL-6, pg/mL | 398.6 | 232.9 | −165.7 | −41.57 | |
| SOFA | 10 | 9 | - | - | |
| B | WBC, ×109/L | 10.2 | 8.1 | −2.1 | −20.59 |
| CRP, mg/L | 411.55 | 370.04 | −41.51 | −10.09 | |
| PCT, ng/mL | 22.17 | 15.68 | −6.49 | −29.27 | |
| IL-6, pg/mL | 162.2 | 34.5 | −127.7 | −78.73 | |
| SOFA | 7 | 5 | - | - | |
| C 1 | WBC, ×109/L | 9.4 | 14.0 | +4.6 | +48.94 |
| CRP, mg/L | 288.62 | 302.12 | +13.5 | +4.68 | |
| PCT, ng/mL | 359.59 | 181.47 | −178.12 | −49.53 | |
| IL-6, pg/mL | 1270.1 | 76.8 | −1193.3 | −93.95 | |
| SOFA | 10 | 9 | - | - | |
| C 2 | WBC, ×109/L | 14.0 | 10.1 | −3.9 | −27.86 |
| CRP, mg/L | 301.75 | 257.75 | −44.00 | −14.58 | |
| PCT, ng/mL | 122.11 | 68.76 | −53.35 | −43.69 | |
| IL-6, pg/mL | 133.3 | 69.5 | −63.8 | −47.86 | |
| SOFA | 10 | 9 | - | - | |
| Patient | Parameter | Hemoperfusion Time | Absolute Change, Δ | Relative Change, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 6 h | 12 h | ||||
| A | NE, µg/kg/min | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.14 | −0.21 | −56.25 |
| MAP, mmHg | 83 | 98 | 81 | −2 | −2.41 | |
| P/F ratio | 206.7 | 247.3 | 228.0 | +21.3 | +10.30 | |
| Lac, mmol/L | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.3 | +0.1 | +8.33 | |
| ET, EU/mL | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.19 | −0.31 | −62.00 | |
| B | NE, µg/kg/min | 0.5 | 0.48 | 0.43 | −0.07 | −14.00 |
| MAP, mmHg | 72 | 72 | 81 | +9 | +12.50 | |
| P/F ratio | 387.5 | 395.2 | 428.6 | +41.1 | +10.61 | |
| Lac, mmol/L | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.2 | −0.6 | −33.33 | |
| ET, EU/mL | 1.55 | 1.52 | 1.34 | −0.21 | −13.55 | |
| C 1 | NE, µg/kg/min | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.87 | −0.1 | −10.31 |
| MAP, mmHg | 73 | 72 | 94 | +11 | +15.07 | |
| P/F ratio | 268.0 | 201.0 | 332.0 | +64 | +23.88 | |
| Lac, mmol/L | 2.6 | 2.7 | 3.0 | +0.4 | +15.38 | |
| ET, EU/mL | 1.50 | 1.70 | 1.60 | +0.1 | +6.67 | |
| C 2 | NE, µg/kg/min | 0.50 | 0.19 | 0.15 | −0.35 | −70.00 |
| MAP, mmHg | 95 | 98 | 92 | −3 | −3.16 | |
| P/F ratio | 357.1 | 306.7 | 363.3 | +6.20 | +1.74 | |
| Lac, mmol/L | 2.1 | 3.1 | 2.3 | +0.2 | +9.52 | |
| ET, EU/mL | 1.55 | 1.71 | 1.50 | −0.05 | −3.22 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smirnova, D.; Serzans, R.; Klibus, M.; Liguts, V.; Lece, A.; Skesters, A.; Villa, G.; Sabelnikovs, O. Hemoperfusion Using the Oxiris Membrane in Septic Shock Patients with Preserved Kidney Function: A Case Series. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062113
Smirnova D, Serzans R, Klibus M, Liguts V, Lece A, Skesters A, Villa G, Sabelnikovs O. Hemoperfusion Using the Oxiris Membrane in Septic Shock Patients with Preserved Kidney Function: A Case Series. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062113
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmirnova, Darja, Rihards Serzans, Mara Klibus, Valdis Liguts, Anna Lece, Andrejs Skesters, Gianluca Villa, and Olegs Sabelnikovs. 2025. "Hemoperfusion Using the Oxiris Membrane in Septic Shock Patients with Preserved Kidney Function: A Case Series" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062113
APA StyleSmirnova, D., Serzans, R., Klibus, M., Liguts, V., Lece, A., Skesters, A., Villa, G., & Sabelnikovs, O. (2025). Hemoperfusion Using the Oxiris Membrane in Septic Shock Patients with Preserved Kidney Function: A Case Series. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062113







