Feasibility Study for Multimodal Image-Based Assessment of Patient-Specific Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation Hemodynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient and Image Data
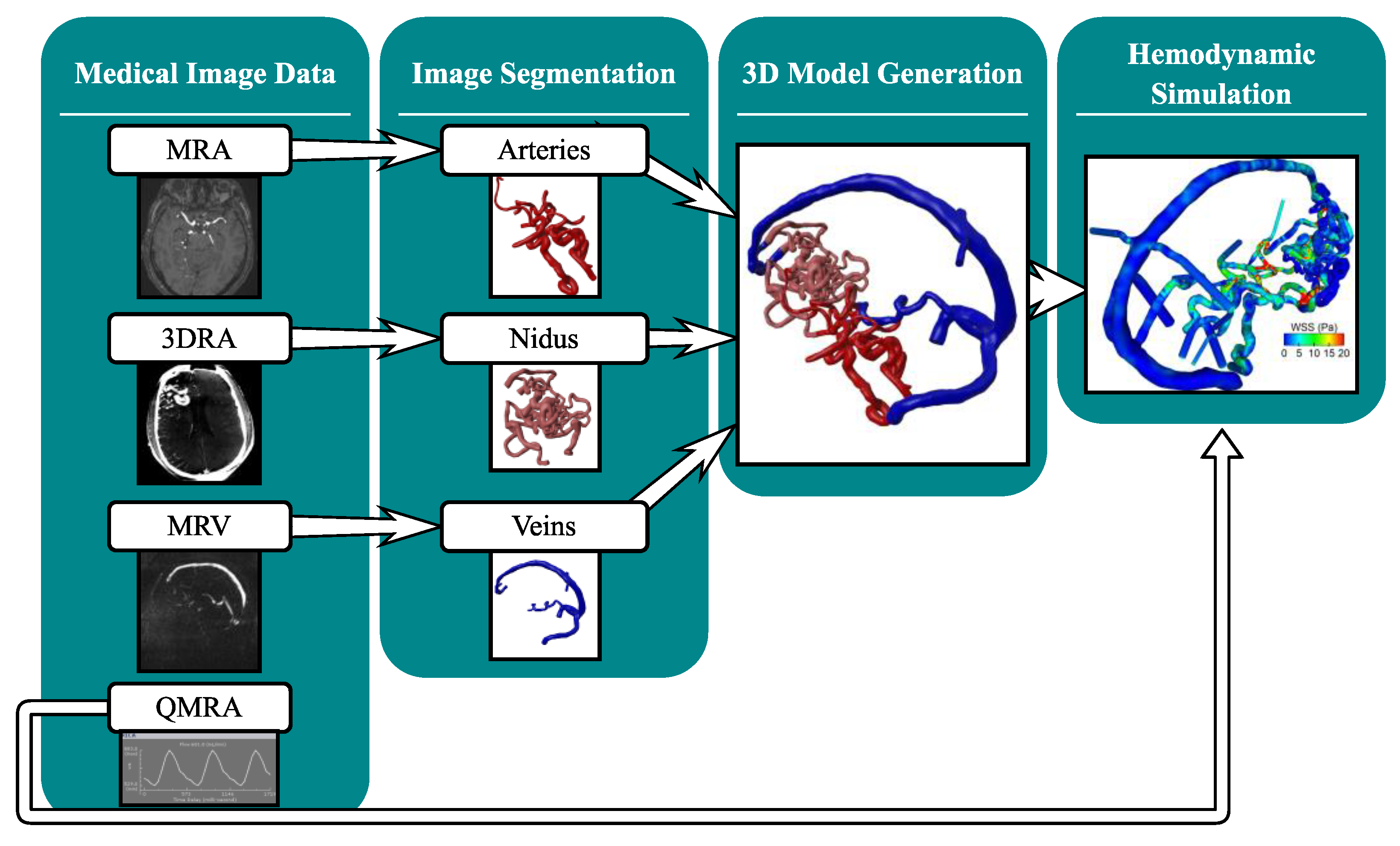
2.2. Multimodal Image Segmentation and 3D Model Generation
2.3. Hemodynamic Simulation
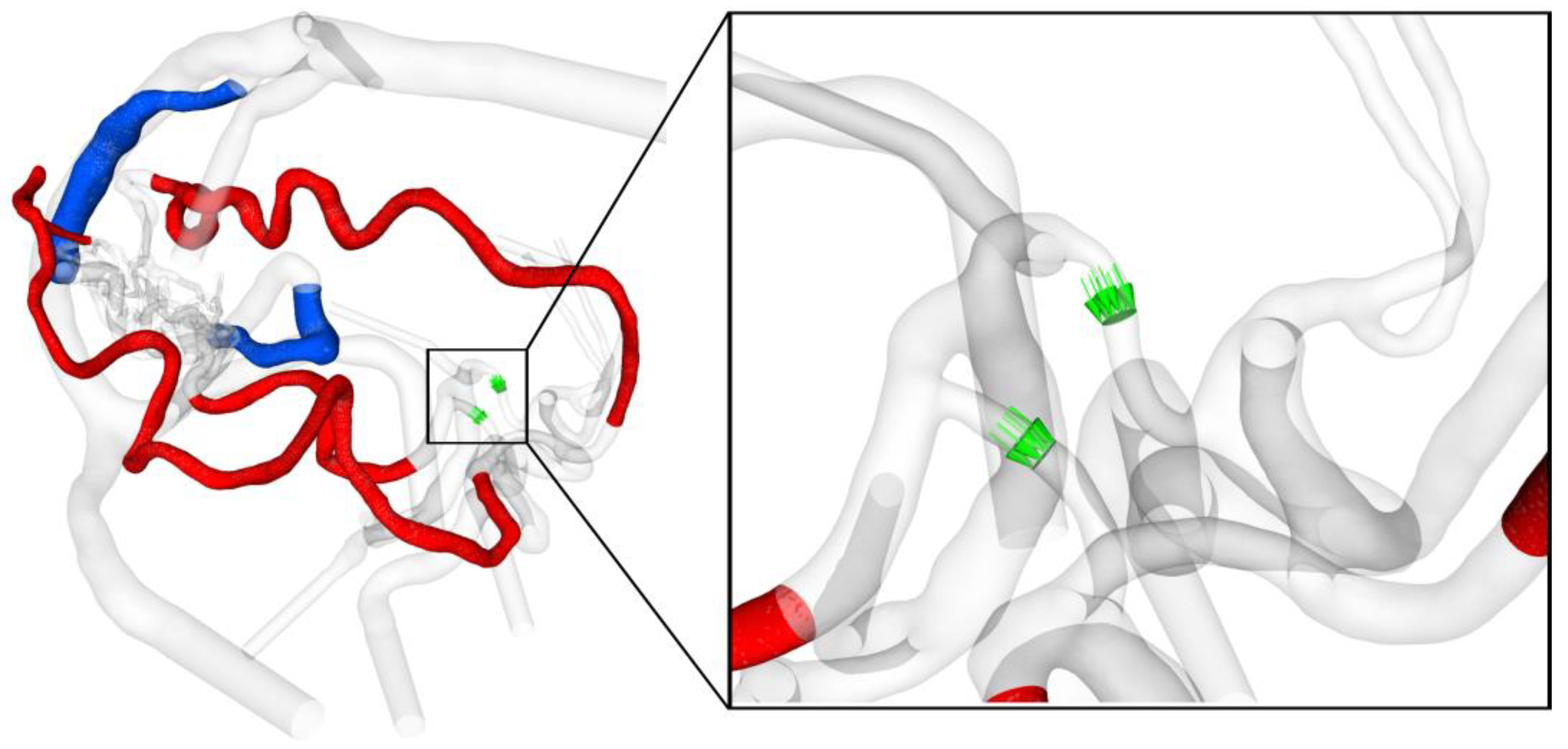
2.4. Analysis of Hemodynamic Parameter
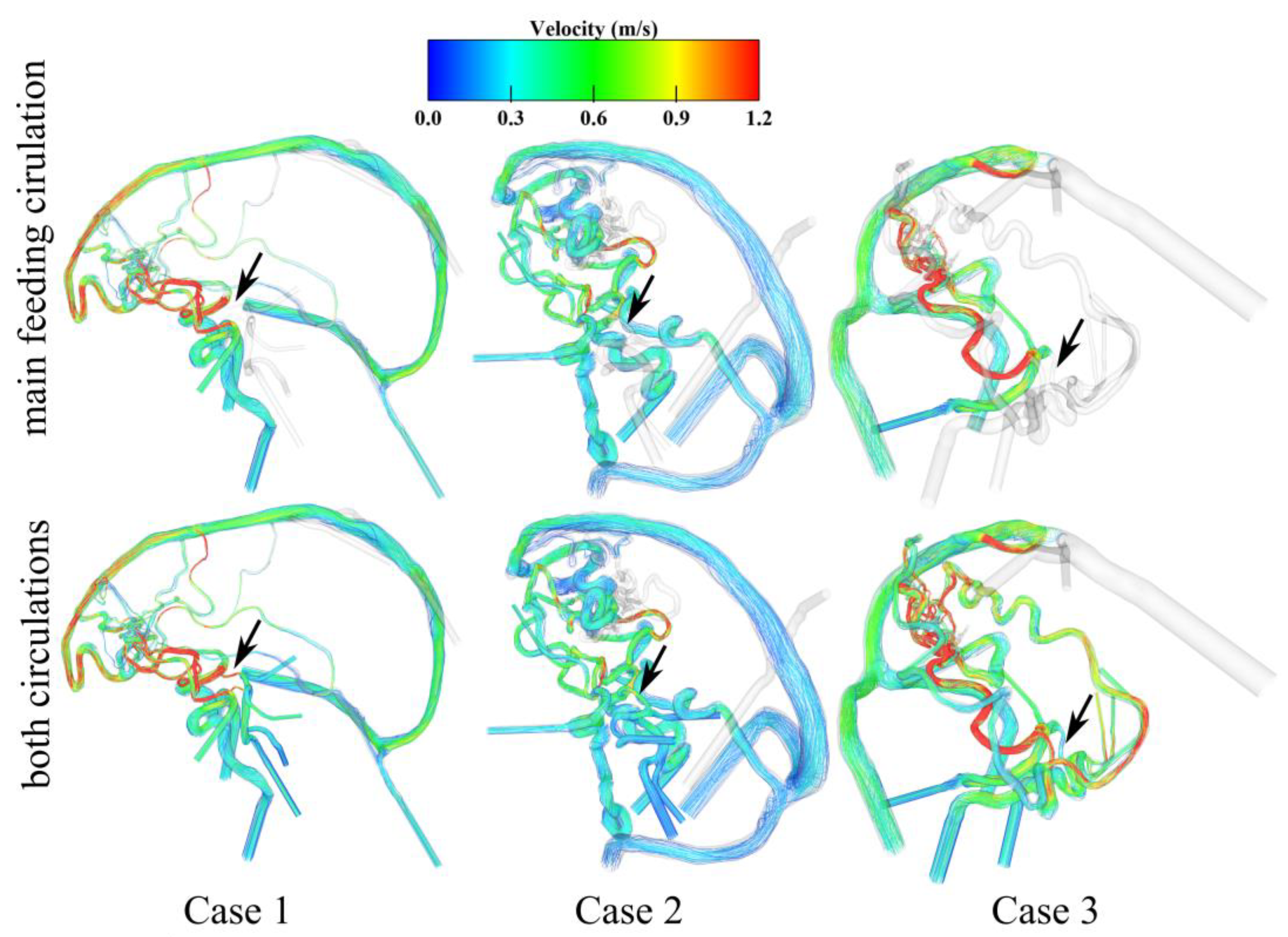
3. Results
3.1. Three-Dimensional Modeling Results
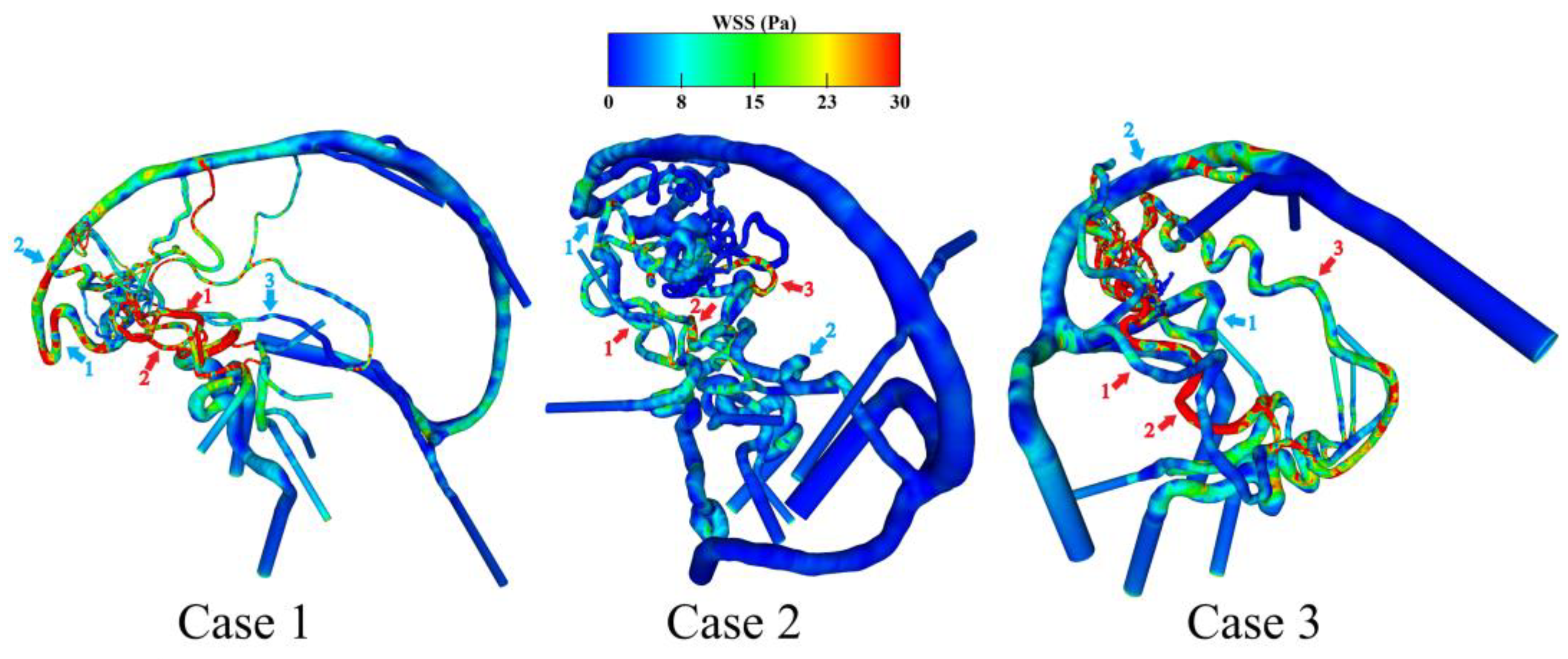
3.2. Hemodynamic Investigation of Shear-Related Phenomena
3.3. Analysis of the AVM-Related Blood-Drawing Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3DRA | 3D rotational angiography |
| AVM | arteriovenous malformations |
| DICOM | Digital imaging and communications in medicine |
| CFD | computational fluid dynamics |
| LPcom | Left posterior communicating artery |
| MRA | magnetic resonance angiography |
| MRV | magnetic resonance venography |
| NOVA | non-invasive optimized vessel analysis |
| QMRA | phase-contrast quantitative magnetic resonance imaging |
| RPcom | Right posterior communicating artery |
| WSS | wall shear stress |
References
- Choi, J.H.; Mast, H.; Sciacca, R.R.; Hartmann, A.; Khaw, A.V.; Mohr, J.P.; Sacco, R.L.; Stapf, C. Clinical outcome after first and recurrent hemorrhage in patients with untreated brain arteriovenous malformation. Stroke 2006, 37, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, K.; Leschke, J.; Lazzaro, M.A. Cerebral arteriovenous malformation diagnosis and management. Semin. Neurol. 2013, 33, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozpinar, A.; Mendez, G.; Abla, A.A. Epidemiology, genetics, pathophysiology, and prognostic classifications of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Can, A.; Gross, B.A.; Du, R. The natural history of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ajiboye, N.; Chalouhi, N.; Starke, R.M.; Zanaty, M.; Bell, R. Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: Evaluation and management. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 649036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.A.A.; Shuib, A.S.; Mohyi, M.H.H. A review of hemodynamic parameters in cerebral aneurysm. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2020, 22, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, M.R.; McGah, P.M.; Aliseda, A.; Mourad, P.D.; Nerva, J.D.; Vaidya, S.S.; Morton, R.P.; Ghodke, B.V.; Kim, L.J. Cerebral aneurysms treated with flow-diverting stents: Computational models with intravascular blood flow measurements. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, J.; Marsh, L.M.M.; Thormann, M.; Ding, A.; Saalfeld, S.; Behme, D.; Berg, P. Assessment of the flow-diverter efficacy for intracranial aneurysm treatment considering pre- and post-interventional hemodynamics. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 156, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidzik, F.; Korte, J.; Saalfeld, S.; Janiga, G.; Berg, P. Image-based hemodynamic simulations for intracranial aneurysms: The impact of complex vasculature. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2024, 19, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lylyk, P.; Lylyk, I.; Bleise, C.; Scrivano, E.; Lylyk, P.N.; Beneduce, B.; Heilman, C.B.; Malek, A.M. First-in-human endovascular treatment of hydrocephalus with a miniature biomimetic transdural shunt. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 14, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, D.A.; Gounis, M.J.; Levitt, M.R. You’re so vein, you probably think this model’s about you: Opportunities and challenges for computational fluid dynamics in cerebral venous disease. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, E.; Fick, T.; Esposito, G.; Germans, M.; Regli, L.; van Doormaal, T. Segmentation techniques of brain arteriovenous malformations for 3D visualization: A systematic review. La Radiol. Medica 2022, 127, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.S.; Do, H.M.; Wintermark, M.; Massoud, T.F. Large-scale ensemble simulations of biomathematical brain arteriovenous malformation models using graphics processing unit computation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 113, 103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, G.; Bonfanti, M.; Tanade, C.; Lim, C.S.; Tsui, J.; Hamilton, G.; Díaz-Zuccarini, V.; Balabani, S. A Computational Framework for Pre-Interventional Planning of Peripheral Arteriovenous Malformations. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2022, 13, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, N.; Ullman, H.; Ali, F.; Berg, P.; Ooi, Y.C.; Tateshima, S.; Colby, G.P.; Komuro, Y.; Hu, P.; Khatibi, K.; et al. In Vitro Modeling of Human Brain Arteriovenous Malformation for Endovascular Simulation and Flow Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, e873–e879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Voß, S.; Saalfeld, S.; Janiga, G.; Bergersen, A.W.; Valen-Sendstad, K.; Bruening, J.; Goubergrits, L.; Spuler, A.; Cancelliere, N.M.; et al. Multiple Aneurysms AnaTomy CHallenge 2018 (MATCH): Phase I: Segmentation. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.M.; Brina, O.; Marcos Gonzales, A.; Narata, A.P.; Bijlenga, P.; Schaller, K.; Lovblad, K.O.; Ouared, R. Evaluation of the influence of inlet boundary conditions on computational fluid dynamics for intracranial aneurysms: A virtual experiment. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodis, S.; Kargar, S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Dragomir-Daescu, D. Artery length sensitivity in patient-specific cerebral aneurysm simulations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Saalfeld, S.; Voß, S.; Beuing, O.; Janiga, G. A review on the reliability of hemodynamic modeling in intracranial aneurysms: Why computational fluid dynamics alone cannot solve the equation. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lian, J.; Luo, F.; Han, H.; Deng, X. Flow Dynamics of Cerebral Bridging Veins Entering Superior Sagittal Sinus by Color-Coded Duplex Sonography. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2017, 7, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chau, N.; Ho, H. Patient-Specific Blood Flow Analysis for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation Based on Digital Subtraction Angiography Images. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Tutino, V.M.; Snyder, K.V.; Meng, H. CFD: Computational fluid dynamics or confounding factor dissemination? The role of hemodynamics in intracranial aneurysm rupture risk assessment. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Cebral, J.R.; Mut, F.; Weir, J.; Putman, C.M. Association of hemodynamic characteristics and cerebral aneurysm rupture. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, L.; Li, M.-T.; Chen, X.-L.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y.-L.; et al. Hemodynamic changes in superficial arteriovenous malformation surgery measured by intraoperative ICG fluorescence videoangiography with FLOW 800 software. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2020, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Loecher, M.W.; Wu, Y.; Niemann, D.B.; Ciske, B.; Aagaard-Kienitz, B.; Kecskemeti, S.; Johnson, K.M.; Wieben, O.; Mistretta, C.; et al. Hemodynamic Changes in Patients with Arteriovenous Malformations Assessed Using High-Resolution 3D Radial Phase-Contrast MR Angiography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, J.; McGuire, L.S.; Rizko, M.; Saalfeld, S.; Berg, P.; Alaraj, A. Are hemodynamics responsible for inflammatory changes in venous vessel walls? A quantitative study of wall-enhancing intracranial arteriovenous malformation draining veins. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 141, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, G.; Yu, J.; Hou, K.; Yu, J. Regression of a symptomatic varix after transarterial embolization of a brain arteriovenous malformation: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2019, 98, e18418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, G.; Ge, L.; Wang, S. Computational modeling and simulation for endovascular embolization of cerebral arteriovenous malformations with liquid embolic agents. Acta Mech. Sin. 2024, 40, 623042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, M.; Mosimann, P.J.; Nordmeyer, H.; Heddier, M.; Krause, J.; Narata, A.-P.; Serwi, A.E.; Stracke, C.P.; Chapot, R. The transvenous retrograde pressure cooker technique for the curative embolization of high-grade brain arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2021, 13, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammirati, M. Augmented reality in brain tumor surgery using the microscope focal point as the virtual pointer. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Condino, S.; Carbone, M.; Cattari, N.; D’Amato, R.; Cutolo, F.; Ferrari, V. Brain Tumor and Augmented Reality: New Technologies for the Future. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, V.M.; Lylyk, P.; Cancelliere, N.; Lylyk, P.N.; Lylyk, I.; Anagnostakou, V.; Bleise, C.; Nishi, H.; Epshtein, M.; King, R.M.; et al. Volumetric microscopy of cerebral arteries with a miniaturized optical coherence tomography imaging probe. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadl4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, H.G.; Larrabide, I.; Geers, A.J.; Aguilar, M.L.; Frangi, A.F. Newtonian and non-Newtonian blood flow in coiled cerebral aneurysms. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.O.; Steinman, D.A.; Valen-Sendstad, K. Non-Newtonian versus numerical rheology: Practical impact of shear-thinning on the prediction of stable and unstable flows in intracranial aneurysms. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voß, S.; Niemann, U.; Saalfeld, S.; Janiga, G.; Berg, P. Impact of workflow variability on image-based intracranial aneurysm hemodynamics. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 190, 110018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A. Accounting for residence-time in blood rheology models: Do we really need non-Newtonian blood flow modelling in large arteries? J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


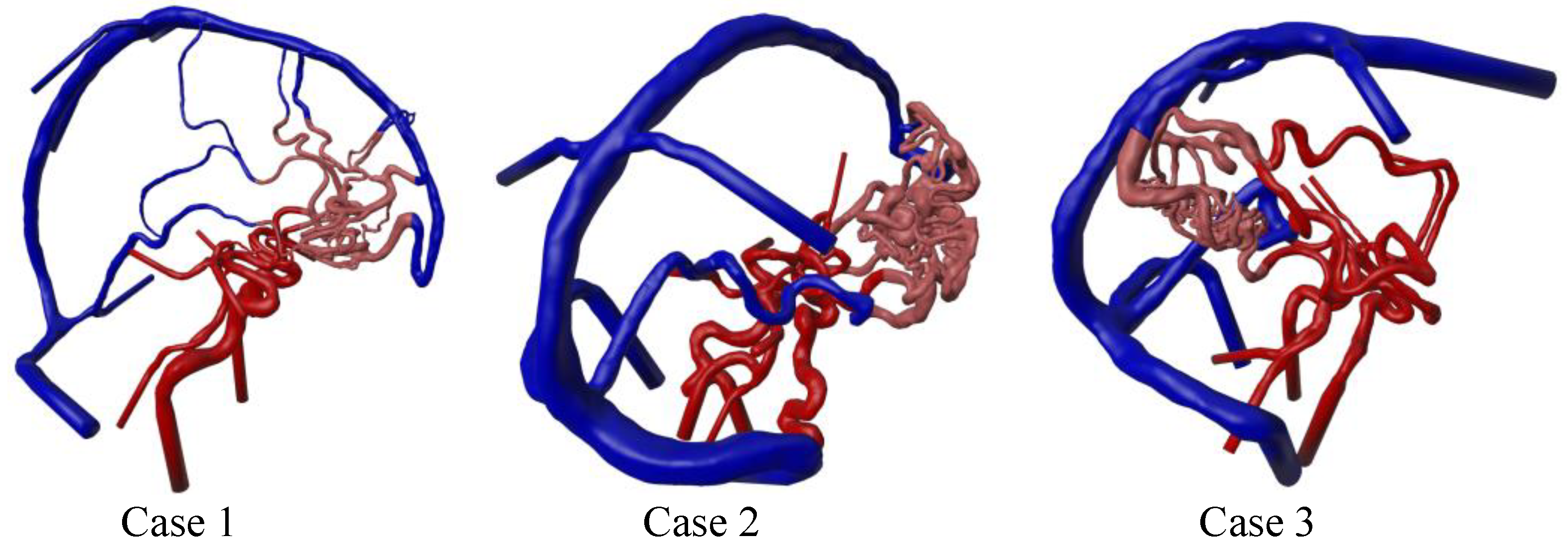
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nidus location | right frontal | right frontal | right occipital |
| Number of feeding arteries | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Number of draining veins | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WSS feeding artery 1 in Pa | 52.6 | 7.7 | 5.1 |
| WSS feeding artery 2 in Pa | 17.0 | 7.1 | 46.2 |
| WSS feeding artery 3 in Pa | n/a | 12.8 | 12.5 |
| Mean value (standard dev.) in Pa | 34.8 (17.8) | 9.2 (2.6) | 21.3 (17.9) |
| WSS draining vein 1 in Pa | 19.0 | 2.6 | 9.5 |
| WSS draining vein 2 in Pa | 15.5 | 3.3 | 9.5 |
| WSS draining vein 3 in Pa | 3.4 | n/a | n/a |
| Mean value (standard dev.) in Pa | 12.6 (6.7) | 2.9 (0.3) | 9.5 (0.01) |
| Rel. dev. of feeding arteries to draining veins | 63.7% | 68.2% | 55.5% |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RPcom volume flow rate in mL/min | 70.8 | 122.4 | −255.5 |
| LPcom volume flow rate in mL/min | 40.2 | n/a | −40.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stahl, J.; McGuire, L.S.; Abou-Mrad, T.; Saalfeld, S.; Behme, D.; Alaraj, A.; Berg, P. Feasibility Study for Multimodal Image-Based Assessment of Patient-Specific Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation Hemodynamics. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082638
Stahl J, McGuire LS, Abou-Mrad T, Saalfeld S, Behme D, Alaraj A, Berg P. Feasibility Study for Multimodal Image-Based Assessment of Patient-Specific Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation Hemodynamics. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082638
Chicago/Turabian StyleStahl, Janneck, Laura Stone McGuire, Tatiana Abou-Mrad, Sylvia Saalfeld, Daniel Behme, Ali Alaraj, and Philipp Berg. 2025. "Feasibility Study for Multimodal Image-Based Assessment of Patient-Specific Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation Hemodynamics" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082638
APA StyleStahl, J., McGuire, L. S., Abou-Mrad, T., Saalfeld, S., Behme, D., Alaraj, A., & Berg, P. (2025). Feasibility Study for Multimodal Image-Based Assessment of Patient-Specific Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation Hemodynamics. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082638






