Proenkephalin 119–159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
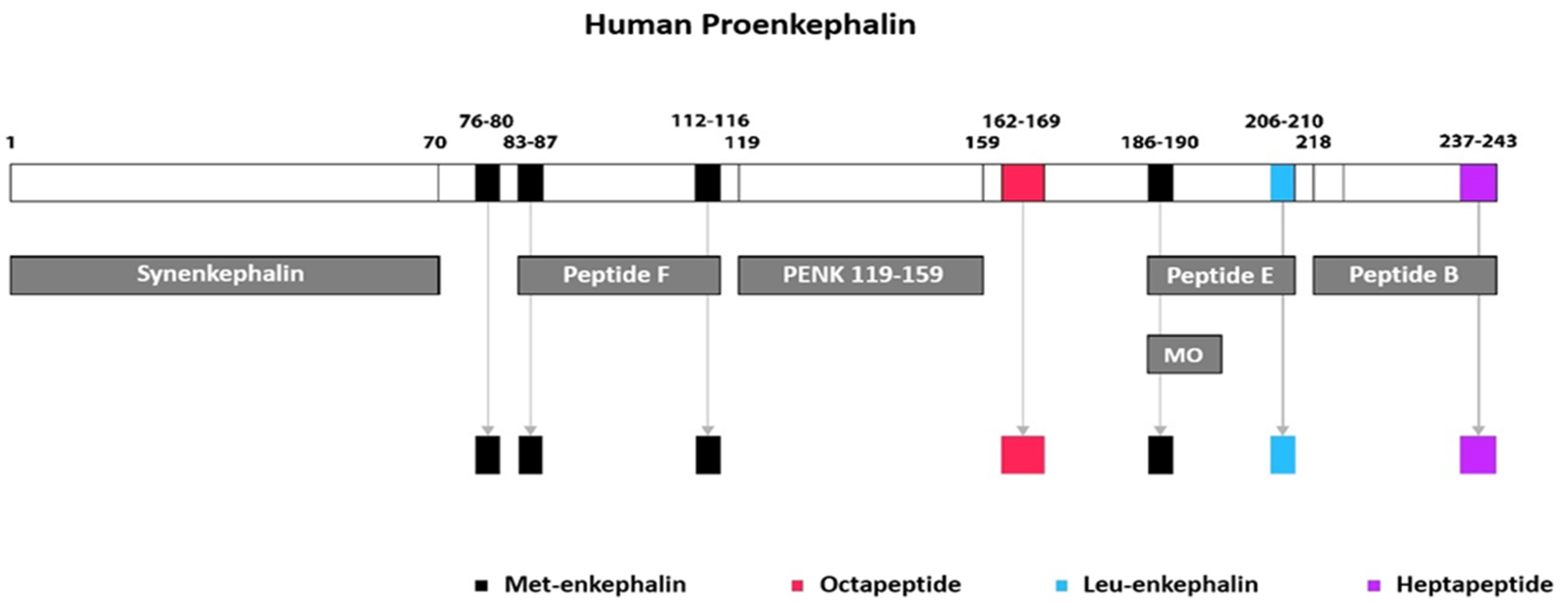
2. Enkephalins
2.1. Endogenous Opioid Peptides
2.2. Enkephalin Peptides
2.3. Opioid Peptide Receptors in Myocardium
2.4. Enkephalins in Myocardial Tissue
2.5. Enkephalins in Adrenal Tissue
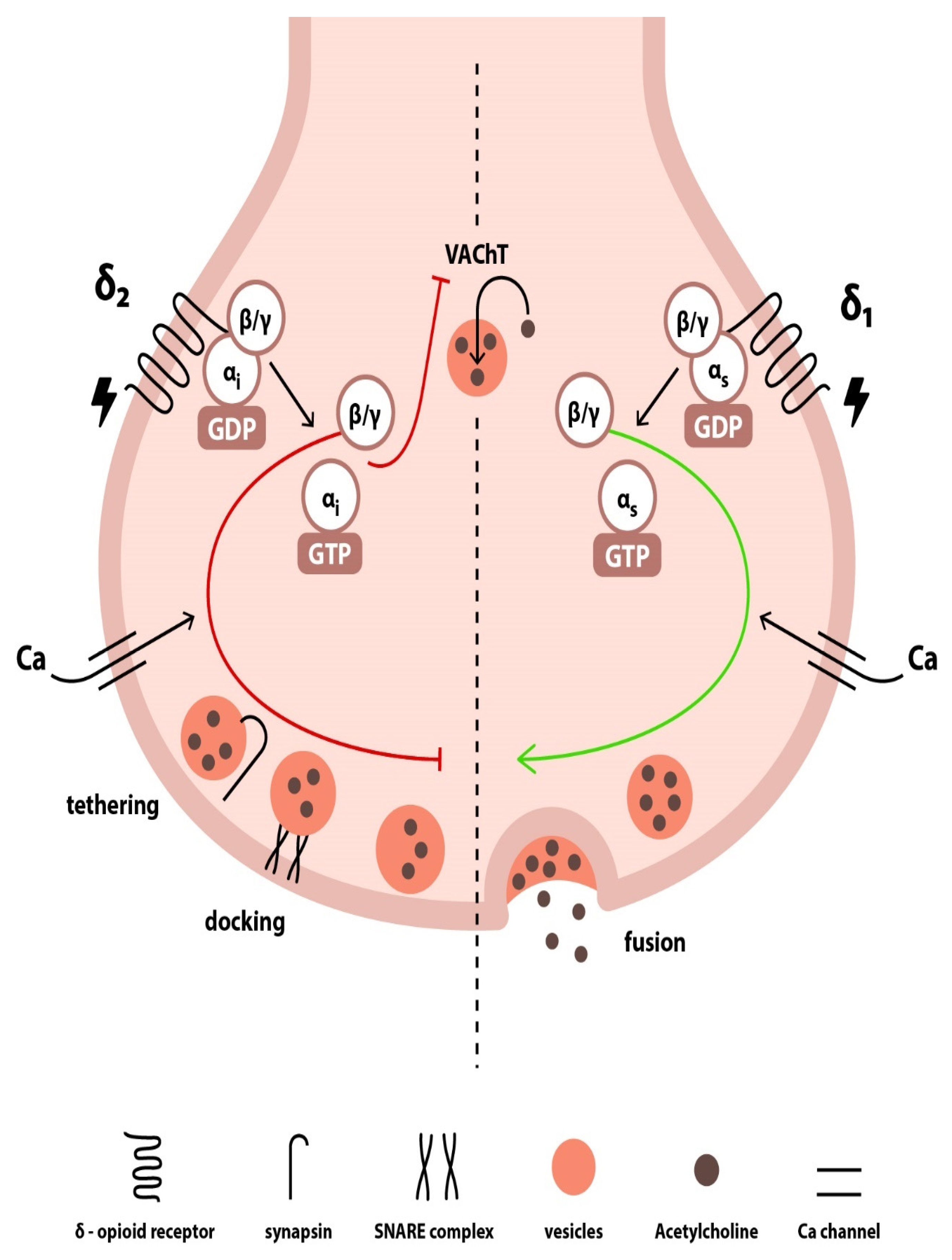
3. Enkephalin-Mediated Cardiovascular Regulation
3.1. CNS-Mediated Regulation
3.2. Presynaptic Modulation
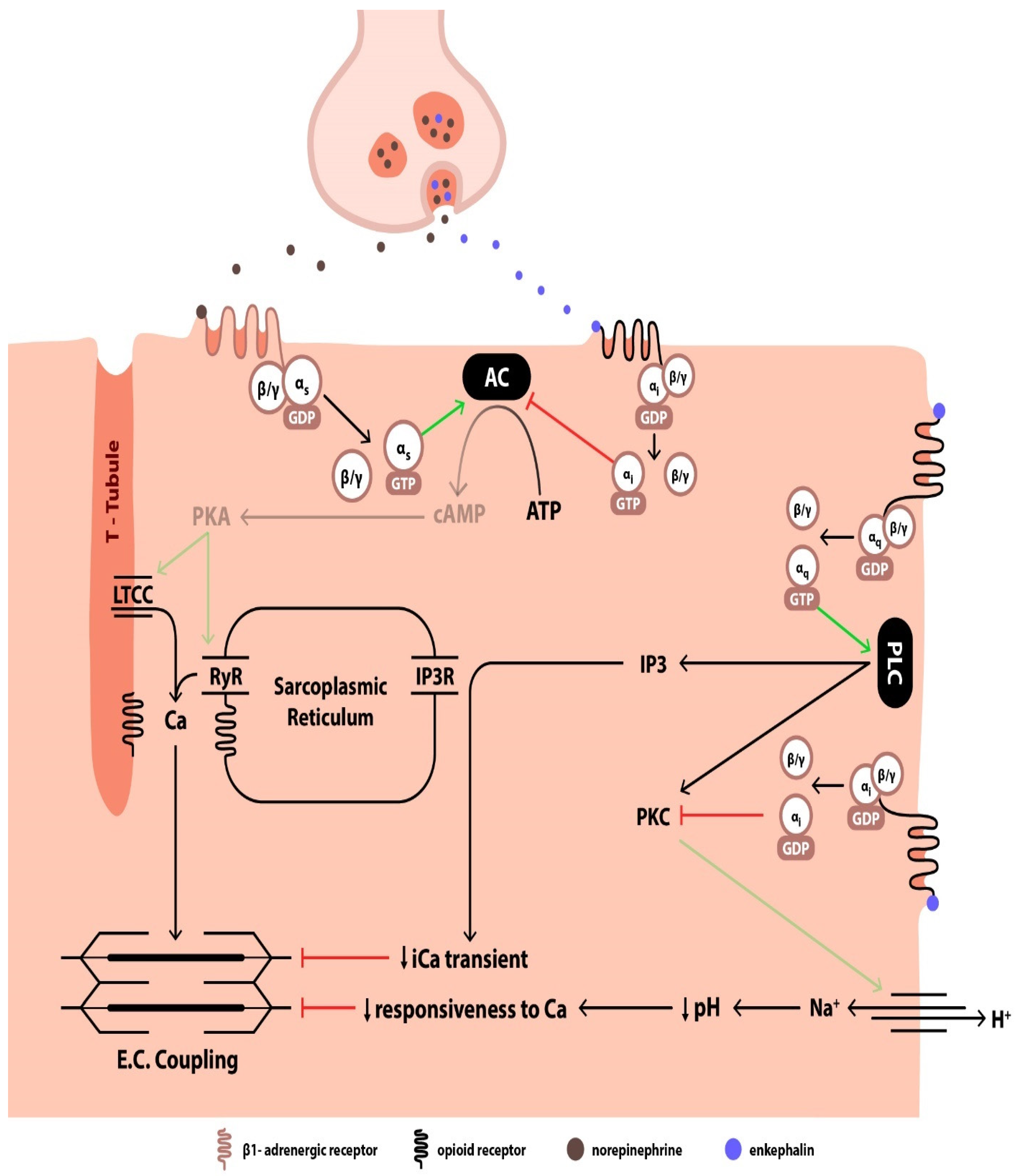
3.3. Postsynaptic Effects
4. Enkephalin-Mediated Regulation of Renal Function
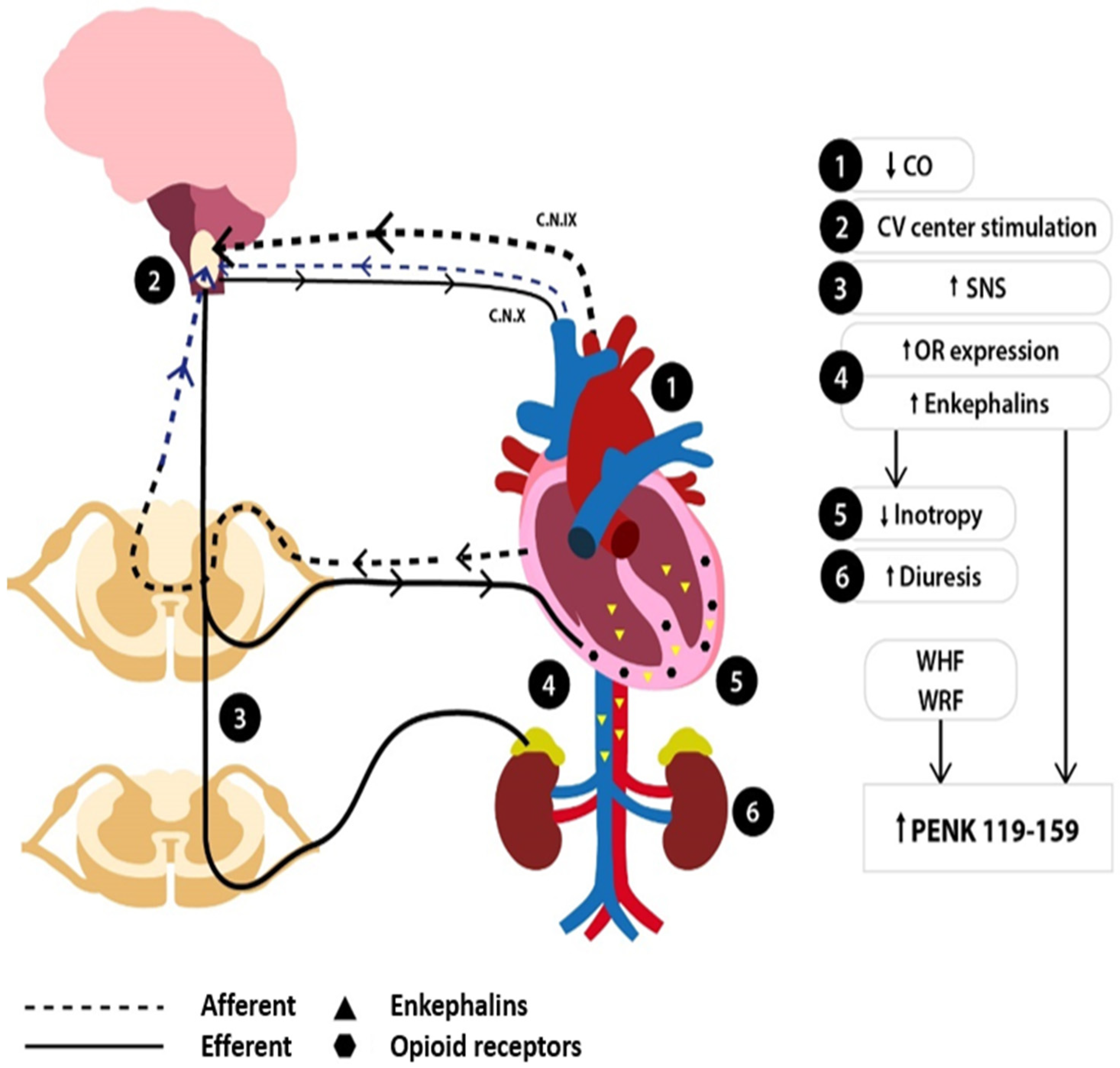
5. Changes in the Enkephalin System in HF
6. Modulation of the Endogenous Opioid System in HF
7. PENK119–159 in HF
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaudhry, S.-P.; Stewart, G.C. Advanced Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Clin. 2016, 12, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siranart, N.; Laohasurayotin, K.; Phanthong, T.; Sowalertrat, W.; Ariyachaipanich, A.; Chokesuwattanaskul, R. Proenkephalin as a Novel Prognostic Marker in Heart Failure Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, A.; Köhrle, J.; Bergmann, A. Proenkephalin A 119–159, a Stable Proenkephalin A Precursor Fragment Identified in Human Circulation. Peptides 2006, 27, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.-A.; Christensson, A.; Ericson, U.; Almgren, P.; Hindy, G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Melander, O.; Orho-Melander, M. High Level of Fasting Plasma Proenkephalin-A Predicts Deterioration of Kidney Function and Incidence of CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treskatsch, S.; Feldheiser, A.; Shaqura, M.; Dehe, L.; Habazettl, H.; Röpke, T.K.; Shakibaei, M.; Schäfer, M.; Spies, C.D.; Mousa, S.A. Cellular Localization and Adaptive Changes of the Cardiac Delta Opioid Receptor System in an Experimental Model of Heart Failure in Rats. Heart Vessels 2016, 31, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treskatsch, S.; Shaqura, M.; Dehe, L.; Feldheiser, A.; Roepke, T.K.; Shakibaei, M.; Spies, C.D.; Schäfer, M.; Mousa, S.A. Upregulation of the Kappa Opioidergic System in Left Ventricular Rat Myocardium in Response to Volume Overload: Adaptive Changes of the Cardiac Kappa Opioid System in Heart Failure. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 102, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobanski, P.; Krajnik, M.; Shaqura, M.; Bloch-Boguslawska, E.; Schäfer, M.; Mousa, S.A. The Presence of Mu-, Delta-, and Kappa-Opioid Receptors in Human Heart Tissue. Heart Vessels 2014, 29, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerstein, G. The Opioid System and Central Cardiovascular Control: Analysis of Controversies. Peptides 1985, 6, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricker, L.D.; Margolis, E.B.; Gomes, I.; Devi, L.A. Five Decades of Research on Opioid Peptides: Current Knowledge and Unanswered Questions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, G.M.; Ackermann, L.W.; Barna, T.J.; Armstrong, J.G.; Stoll, L.L.; Weintraub, N.L.; Dickson, E.W. Proenkephalin Expression and Enkephalin Release Are Widely Observed in Non-Neuronal Tissues. Peptides 2008, 29, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comb, M.; Rosen, H.; Seeburg, P.; Adelman, J.; Herbert, E. Primary Structure of the Human Proenkephalin Gene. DNA 1983, 2, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.V.; Erickson, B.W. Evolution of Proenkephalin and Prodynorphin. Am. Zool. 1986, 26, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boarder, M.R.; Contractor, H.; Marriott, D.; McArdle, W. Metorphamide, a C-Terminally Amidated Opioid Peptide, in Human Adrenal and Human Phaeochromocytoma. Regul. Pept. 1985, 12, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stell, W.K.; Chaminade, M.; Metters, K.M.; Rougeot, C.; Dray, F.; Rossier, J. Detection of Synenkephalin, the Amino-Terminal Portion of Proenkephalin, by Antisera Directed Against Its Carboxyl Terminus. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement-Jones, V.; Lowry, P.J.; Rees, L.H.; Besser, G.M. Met-Enkephalin Circulates in Human Plasma. Nature 1980, 283, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Sarkar, S.; Chang, S.L. Opioid Receptor Expression in Human Brain and Peripheral Tissues Using Absolute Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2012, 124, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treskatsch, S.; Shaqura, M.; Dehe, L.; Roepke, T.K.; Shakibaei, M.; Schäfer, M.; Mousa, S.A. Evidence for MOR on Cell Membrane, Sarcoplasmatic Reticulum and Mitochondria in Left Ventricular Myocardium in Rats. Heart Vessels 2016, 31, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.E.; Hermann, K.; Dietz, R.; Gaida, W.; Ganten, D.; Kraft, K.; Unger, T. Evidence for the Presence of Enkephalins in the Heart. Life Sci. 1983, 32, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechardt, L.; Aalto-Setälä, K.; Purjeranta, M.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Kyösola, K. Peptidergic Innervation of Human Atrial Myocardium: An Electron Microscopical and Immunocytochemical Study. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1986, 17, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, B.A. Opioid Peptides and the Heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 43, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younès, A.; Pepe, S.; Barron, B.A.; Spurgeon, H.A.; Lakatta, E.G.; Caffrey, J.L. Cardiac Synthesis, Processing, and Coronary Release of Enkephalin-Related Peptides. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H1989–H1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viveros, O.H.; Diliberto, E.J.; Hazum, E.; Chang, K.J. Opiate-Like Materials in the Adrenal Medulla: Evidence for Storage and Secretion with Catecholamines. Mol. Pharmacol. 1979, 16, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, H.K.; Waqar, F.; Gerson, M.C. Cardiac Autonomic Innervation. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Dusting, H.K.; Rand, M.J. Effect of [D-Ala2,Met5]Enkephalinamide and [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]Enkephalin on Cholinergic and Noradrenergic Neurotransmission in Isolated Atria. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 111, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanfill, A.A.; Jackson, K.; Farias, M.; Barlow, M.; Deo, S.; Johnson, S.; Caffrey, J.L. Leucine-Enkephalin Interrupts Sympathetically Mediated Tachycardia Prejunctionally in the Canine Sinoatrial Node. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 228, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musha, T.; Satoh, E.; Koyanagawa, H.; Kimura, T.; Satoh, S. Effects of Opioid Agonists on Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Transmission to the Dog Heart. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989, 250, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, M.; Jackson, K.; Yoshishige, D.; Caffrey, J.L. Bimodal Delta-Opioid Receptors Regulate Vagal Bradycardia in Canine Sinoatrial Node. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 285, H1332–H1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, S.M.; Shen, K.-F. After Chronic Opioid Exposure Sensory Neurons Become Supersensitive to the Excitatory Effects of Opioid Agonists and Antagonists as Occurs after Acute Elevation of GM1 Ganglioside. Brain Res. 1992, 575, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, S.H.; Barlow, M.A.; Gonzalez, L.; Yoshishige, D.; Caffrey, J.L. Cholinergic Location of Delta-Opioid Receptors in Canine Atria and SA Node. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H829–H838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrovatkina, V.; Alegre, K.O.; Dey, R.; Huang, X.-Y. Regulation, Signaling, and Physiological Functions of G-Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3850–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutens, B.; Ingram, S.L. Key Differences in Regulation of Opioid Receptors Localized to Presynaptic Terminals Compared to Somas: Relevance for Novel Therapeutics. Neuropharmacology 2023, 226, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurawski, Z.; Page, B.; Chicka, M.C.; Brindley, R.L.; Wells, C.A.; Preininger, A.M.; Hyde, K.; Gilbert, J.A.; Cruz-Rodriguez, O.; Currie, K.P.M.; et al. Gβγ Directly Modulates Vesicle Fusion by Competing with Synaptotagmin for Binding to Neuronal SNARE Proteins Embedded in Membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12165–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, S.; Hamm, H.; Rodriguez, S.; Zurawski, Z. Gβγ SNARE Interactions and Their Behavioral Effects. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesca, F.; Baldelli, P.; Valtorta, F.; Benfenati, F. The Synapsins: Key Actors of Synapse Function and Plasticity. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 313–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, B.M.; de Jaeger, X.; Martins-Silva, C.; Lima, R.D.F.; Amaral, E.; Menezes, C.; Lima, P.; Neves, C.M.L.; Pires, R.G.; Gould, T.W.; et al. The Vesicular Acetylcholine Transporter Is Required for Neuromuscular Development and Function. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 5238–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuder, H.; Buder, M.; Riers, H.-D.; Rothacher, G. On the Opioid Receptor Subtype Inhibiting the Evoked Release of 3H-Noradrenaline from Guinea-Pig Atria in Vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1986, 332, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jullié, D.; Benitez, C.; Knight, T.A.; Simic, M.S.; von Zastrow, M. Endocytic Trafficking Determines Cellular Tolerance of Presynaptic Opioid Signaling. Elife 2022, 11, e81298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crain, S.M.; Shen, K.-F. Modulation of Opioid Analgesia, Tolerance and Dependence by Gs-Coupled, GM1 Ganglioside-Regulated Opioid Receptor Functions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1998, 19, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C. Opioid Receptors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, S.; Xiao, R.-P.; Hohl, C.; Altschuld, R.; Lakatta, E.G. ‘Cross Talk’ Between Opioid Peptide and Adrenergic Receptor Signaling in Isolated Rat Heart. Circulation 1997, 95, 2122–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.P.; Pepe, S.; Spurgeon, H.A.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Lakatta, E.G. Opioid Peptide Receptor Stimulation Reverses Beta-Adrenergic Effects in Rat Heart Cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, H797–H805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. The Molecular Basis of G Protein–Coupled Receptor Activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, C.; Brette, F. T-Tubules and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Function in Cardiac Ventricular Myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 77, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, C.; Spurgeon, H.; Lakatta, E.G.; Guarnieri, C.; Capogrossi, M.C. Kappa and Delta Opioid Receptor Stimulation Affects Cardiac Myocyte Function and Ca2+ Release from an Intracellular Pool in Myocytes and Neurons. Circ. Res. 1992, 70, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ela, C.; Barg, J.; Vogel, Z.; Hasin, Y.; Eilam, Y. Distinct Components of Morphine Effects on Cardiac Myocytes Are Mediated by the Kappa and Delta Opioid Receptors. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1997, 29, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ela, C.; Hasin, Y.; Eilam, Y. Opioid Effects on Contractility, Ca2+-Transients and Intracellular pH in Cultured Cardiac Myocytes. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1993, 25, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanai, E.; Frantz, S. Pathophysiology of Heart Failure. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 6, 187–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, D.R. Opioid Mechanisms Controlling Renal Function. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1995, 22, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownell, J.; del Pozo, E.; Donatsch, P. Inhibition of Vasopressin Secretion by a Met-Enkephalin (FK 33-824) in Humans. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1980, 94, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, A.; Besser, G.M.; Milles, J.J.; Baylis, P.H. Inhibition of Vasopressin Release in Man by an Opiate Peptide. Lancet 1980, 2, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, P.A.; Sedman, A.J.; Rose, S.; Wright, D.S.; Dawkins, R.; Rajagopalan, R. Diuretic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, and Safety of a New Centrally Acting Kappa-Opioid Agonist (CI-977) in Humans. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 34, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, F.; Bernardi, P.; Pich, E.M.; Capelli, M.; Bortoluzzi, L.; Spampinato, S.; Canossa, M. Relationship between Plasma Atrial Natriuretic Factor and Opioid Peptide Levels in Healthy Subjects and in Patients with Acute Congestive Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 1993, 14, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, C.; Bastagli, L.; Bernardi, P.; Caldarera, C.M.; Guarnieri, C. Opioid Receptors in Rat Cardiac Sarcolemma: Effect of Phenylephrine and Isoproterenol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 987, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.M. Modulation of Adrenergic Receptors and G-Transduction Proteins in Failing Human Ventricular Myocardium. Circulation 1993, 87, IV27–IV34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maslov, L.N.; Khaliulin, I.; Oeltgen, P.R.; Naryzhnaya, N.V.; Pei, J.; Brown, S.A.; Lishmanov, Y.B.; Downey, J.M. Prospects for Creation of Cardioprotective and Antiarrhythmic Drugs Based on Opioid Receptor Agonists. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 871–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugsley, M.K.; Saint, D.A.; Penz, M.P.; Walker, M.J.A. Electrophysiological and Antiarrhythmic Actions of the Kappa Agonist PD 129290, and Its R,R (+)-Enantiomer, PD 129289. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naryzhnaia, N.V.; Krylatov, A.V.; Maslov, L.N.; Lishmanov, I.B.; Gross, G.J.; Stephano, J.B. Role of Delta Opioid Receptors and Their Ligands in the Development of Adaptive Heart Protection against Arrhythmogenesis. Ross. Fiziol. Zhurnal Im. IM. Sechenova 2001, 87, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.-C.; Wang, H.-X.; Pei, J.-M.; Wong, T.M. Anti-Arrhythmic Effect of Kappa-Opioid Receptor Stimulation in the Perfused Rat Heart: Involvement of a cAMP-Dependent Pathway. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1999, 31, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtchanova-Matchouganska, A.; Missankov, A.; Ojewole, J.A. Evaluation of the Antidysrhythmic Effects of Delta- And Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonists and Antagonists on Calcium Chloride-, Adrenaline- and Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Arrhythmias in Rats. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 26, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lishmanov, A.Y.; Maslov, L.N.; Lasukova, T.V.; Crawford, D.; Wong, T.M. Activation of Kappa-Opioid Receptor as a Method for Prevention of Ischemic and Reperfusion Arrhythmias: Role of Protein Kinase C and K(ATP) Channels. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 143, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugsley, M.K. The Diverse Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for the Actions of Opioids on the Cardiovascular System. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 93, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolte, C.; Newman, G.; Schultz, J.E.J. Kappa and Delta Opioid Receptor Signaling Is Augmented in the Failing Heart. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2009, 47, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.S.; Imai, N.; Stone, C.K.; Woolf, P.D.; Kawashima, S.; Tuttle, R.R. The Role of Endogenous Opioids in Congestive Heart Failure: Effects of Nalmefene on Systemic and Regional Hemodynamics in Dogs. Circulation 1987, 75, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himura, Y.; Liang, C.-S.; Imai, N.; Delehanty, J.M.; Woolf, P.D.; Hood, W.B., Jr. Short-Term Effects of Naloxone Hemodynamics and Baroreflex Function in Conscious Dogs with Pacing-Induced Congestive Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1994, 23, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, N.; Kashiki, M.; Woolf, P.D.; Liang, C.S. Comparison of Cardiovascular Effects of Mu- and Delta-Opioid Receptor Antagonists in Dogs with Congestive Heart Failure. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, H912–H917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldroyd, K.G.; Gray, C.E.; Carter, R.; Harvey, K.; Borland, W.; Beastall, G.; Cobbe, S.M. Activation and Inhibition of the Endogenous Opioid System in Human Heart Failure. Br. Heart J. 1995, 73, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ng, L.L.; Sandhu, J.K.; Narayan, H.; Quinn, P.A.; Squire, I.B.; Davies, J.E.; Bergmann, A.; Maisel, A.; Jones, D.J.L. Proenkephalin and Prognosis after Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbit, B.; Marston, N.; Shah, K.; Lee, E.L.; Aramin, H.; Clopton, P.; Maisel, A.S. Prognostic Usefulness of Proenkephalin in Stable Ambulatory Patients with Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsue, Y.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Struck, J.; Metra, M.; O’Connor, C.M.; Ponikowski, P.; Teerlink, J.R.; Cotter, G.; Davison, B.; Cleland, J.G.; et al. Clinical Correlates and Prognostic Value of Proenkephalin in Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.L.; Squire, I.B.; Jones, D.J.L.; Cao, T.H.; Chan, D.C.S.; Sandhu, J.K.; Quinn, P.A.; Davies, J.E.; Struck, J.; Hartmann, O.; et al. Proenkephalin, Renal Dysfunction, and Prognosis in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagala, P.; Squire, I.B.; Jones, D.J.L.; Cao, T.H.; Chan, D.C.S.; McCann, G.; Sandhu, J.K.; Quinn, P.A.; McAdam, J.; Marsh, A.M.; et al. Proenkephalin and Prognosis in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A GREAT Network Study. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2019, 108, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmens, J.E.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Brouwers, F.P.; Kieneker, L.M.; Damman, K.; Hartmann, O.; Schulte, J.; Bakker, S.J.L.; de Boer, R.A.; Voors, A.A. Proenkephalin and the Risk of New-Onset Heart Failure: Data from Prevention of Renal and Vascular End-Stage Disease. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäntti, T.; Tarvasmäki, T.; Harjola, V.-P.; Pulkki, K.; Turkia, H.; Sabell, T.; Tolppanen, H.; Jurkko, R.; Hongisto, M.; Kataja, A.; et al. Predictive Value of Plasma Proenkephalin and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Cardiogenic Shock. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molvin, J.; Jujic, A.; Navarin, S.; Melander, O.; Zoccoli, G.; Hartmann, O.; Bergmann, A.; Struck, J.; Bachus, E.; Di Somma, S.; et al. Bioactive Adrenomedullin, Proenkephalin A and Clinical Outcomes in an Acute Heart Failure Setting. Open Heart 2019, 6, e001048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmens, J.E.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Damman, K.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; de Boer, R.A.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Sama, I.E.; Streng, K.W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Proenkephalin, an Opioid System Surrogate, as a Novel Comprehensive Renal Marker in Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2019, 12, e005544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.-L.; Hu, H.-J.; Zhao, X.-J.; Chi, W.-W.; Liu, D.-M.; Wang, Q.; Cui, W. Urine N-Terminal pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and Plasma Proenkephalin Are Promising Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1 in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Prospective, Double-Center, Observational Study in Real-World. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grycuk, W.; Jakubowska, Z.; Małyszko, J. Proenkephalin Levels and Its Determinants in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease Treated with Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinger, R.H.G. Pathophysiology of Heart Failure. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 11, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnart, S.E.; Wehrens, X.H.T.; Kushnir, A.; Marks, A.R. Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor Function and Regulation in Heart Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1015, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshansky, B.; Sabbah, H.N.; Hauptman, P.J.; Colucci, W.S. Parasympathetic Nervous System and Heart Failure: Pathophysiology and Potential Implications for Therapy. Circulation 2008, 118, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Zarbock, A.; Goldstein, S.; Kashani, K.; Macedo, E.; Murugan, R.; Bell, M.; Forni, L.; Guzzi, L.; Joannidis, M.; et al. Recommendations on Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers from the Acute Disease Quality Initiative Consensus Conference: A Consensus Statement. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2019209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavalle, C.; Mariani, M.V.; Severino, P.; Palombi, M.; Trivigno, S.; D’Amato, A.; Silvetti, G.; Pierucci, N.; Di Lullo, L.; Chimenti, C.; et al. Efficacy of Modern Therapies for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Specific Population Subgroups: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cardiorenal Med. 2024, 14, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfsten, H.; Goliasch, G.; Bartko, P.E.; Prausmüller, S.; Spinka, G.; Cho, A.; Novak, J.; Mascherbauer, J.; Haslacher, H.; Strunk, G.; et al. Neprilysin Inhibition Does Not Alter Dynamic of Proenkephalin-A 119-159 and Pro-Substance P in Heart Failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lai, W.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Hong, K. The Safety of Morphine in Patients with Acute Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, J.; Szczesna, K.; Schulze, A.; Ngo, H.; Doyle, M.; Do, T.; Vu, M.; Nguyen, J.; Löffler, J.; Borshchivska, M.; et al. Proenkephalin A 119–159 (PenKid)—A Novel Biomarker and Its Quantification on the Nexus IB10 POC System for Assessing Kidney Function. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, e121–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsiras, D.; Ventoulis, I.; Verras, C.; Bistola, V.; Bezati, S.; Fyntanidou, B.; Polyzogopoulou, E.; Parissis, J.T. Proenkephalin 119–159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082657
Matsiras D, Ventoulis I, Verras C, Bistola V, Bezati S, Fyntanidou B, Polyzogopoulou E, Parissis JT. Proenkephalin 119–159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082657
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsiras, Dionysis, Ioannis Ventoulis, Christos Verras, Vasiliki Bistola, Sofia Bezati, Barbara Fyntanidou, Effie Polyzogopoulou, and John T. Parissis. 2025. "Proenkephalin 119–159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082657
APA StyleMatsiras, D., Ventoulis, I., Verras, C., Bistola, V., Bezati, S., Fyntanidou, B., Polyzogopoulou, E., & Parissis, J. T. (2025). Proenkephalin 119–159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082657








