His Bundle Pacing Improves Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Bradyarrhythmia or Tachy-Brady Syndrome and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
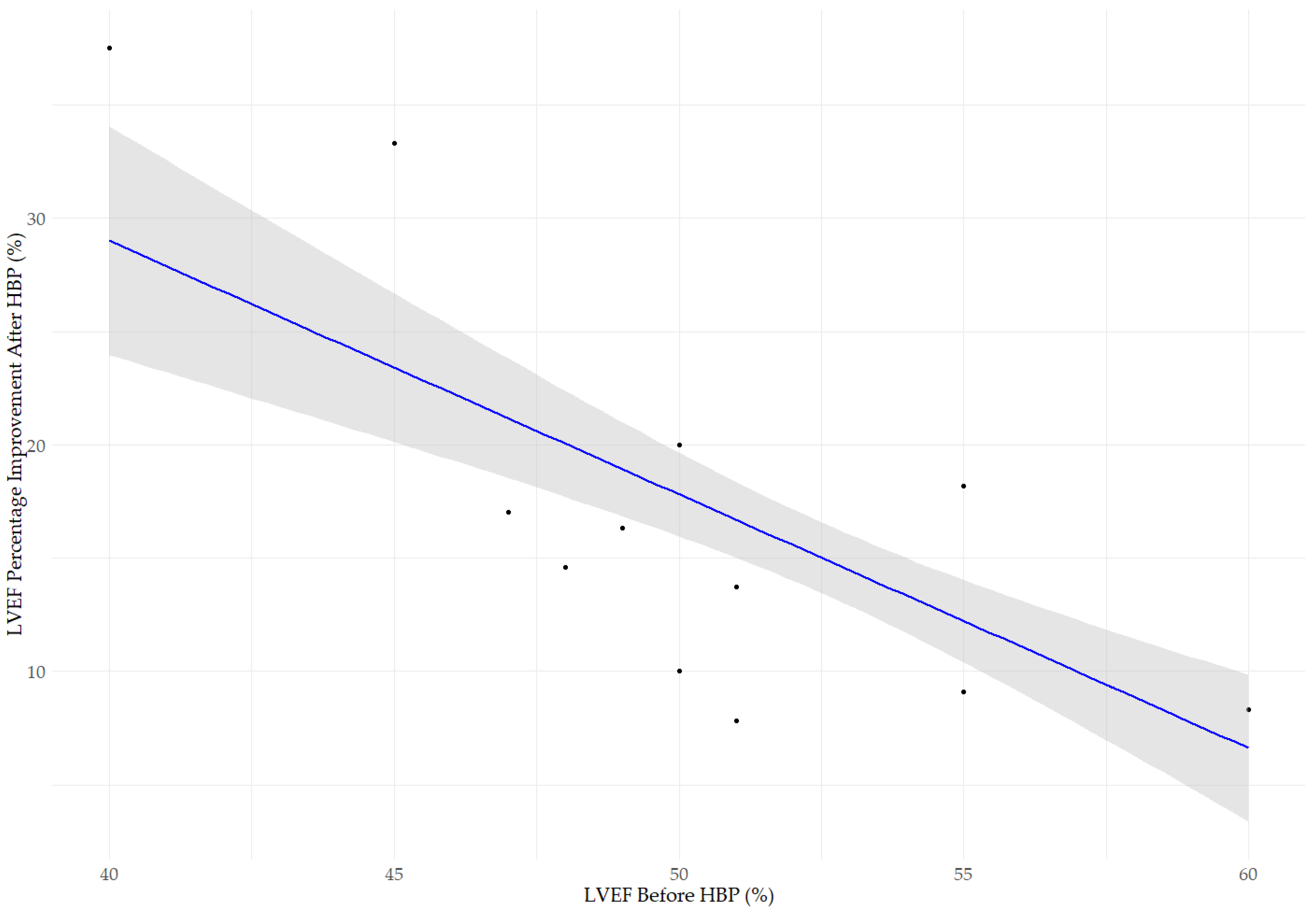
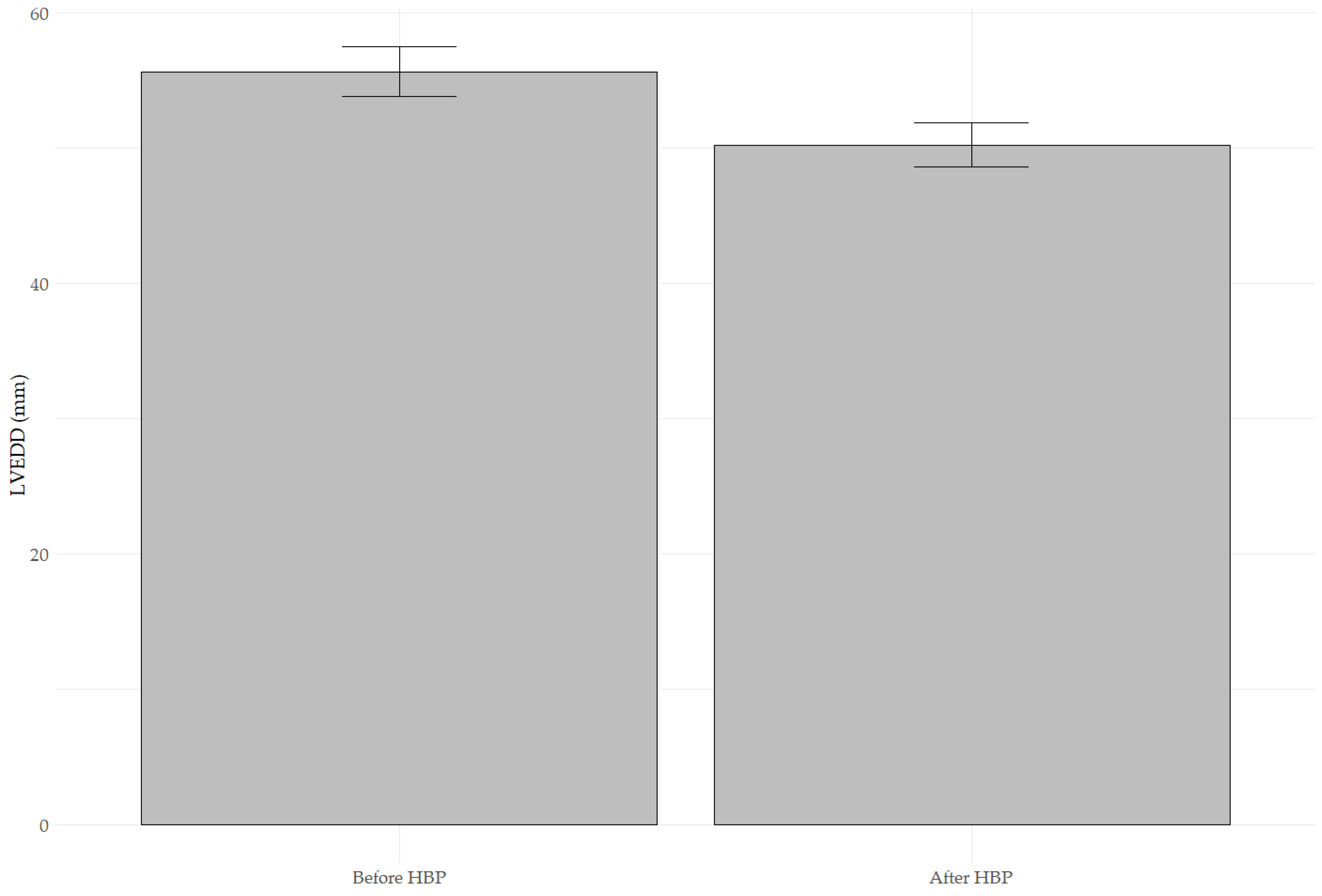
3.1. Changes in LVEF, LVEDD, and MR After His Bundle Pacing
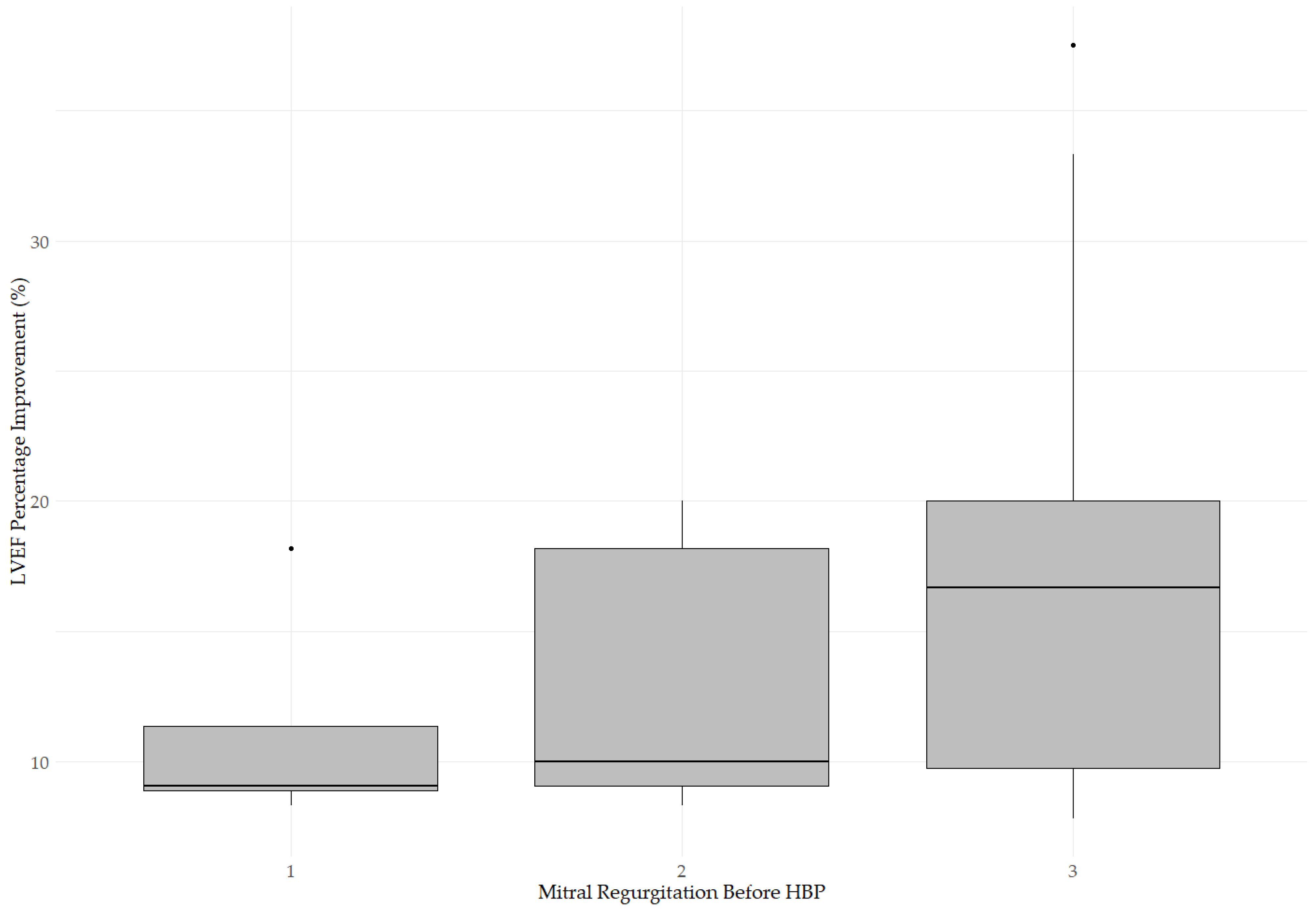
3.2. Impact of Medications and Comorbidities on Changes in Echocardiographic Parameters After Pacing
3.3. Minimum Sample Size
3.4. Summary of Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| AFMR | Atrial functional mitral regurgitation |
| AV | Atrioventricular |
| AVNA | Atrioventricular node ablation |
| BVP | Biventricular Pacing |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CS | Coronary sinus |
| CRT | Cardiac resynchronization therapy |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HFH | Heart-failure-related hospitalization |
| HBP | His-bundle pacing |
| HFmrEF | Heart failure with mildly reduced |
| HFpEF | Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction |
| HFrEF | Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction |
| HT | Hypertension |
| IHD | Ischemic heart disease |
| K+ | Potassium |
| LBBB | Left bundle branch block |
| LVEDD | Left ventricular end-diastolic diameter |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| MI | Myocardial infarction |
| MR | Mitral regurgitation |
| MRA | Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist |
| PICM | Pacing-induced cardiomyopathy |
| RVP | Right ventricular pacing |
| SND | Sinus node dysfunction |
References
- Kotecha, D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Voors, A.A.; Rienstra, M. Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2217–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espnes, H.; Wilsgaard, T.; Ball, J.; Løchen, M.-L.; Njølstad, I.; Schnabel, R.B.; Gerdts, E.; Sharashova, E. Heart Failure in Atrial Fibrillation Subtypes in Women and Men in the Tromsø Study. JACC Adv. 2025, 4, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.D.; O’Meara, E.; Böhm, M.; Savarese, G.; Kelly, P.R.; Vardeny, O.; Allen, L.A.; Lancellotti, P.; Gottlieb, S.S.; Samad, Z.; et al. Implications of Atrial Fibrillation for Guideline-Directed Therapy in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 932–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, A.; Li, N.; Hansen, B.J.; Zhao, J.; Fedorov, V.V. Canine and Human Sinoatrial Node: Differences and Similarities in the Structure, Function, Molecular Profiles, and Arrhythmia. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2019, 22, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Silvestry, F.E. Mechanistic Insights into Mitral Regurgitation Due to Atrial Fibrillation: “Atrial Functional Mitral Regurgitation”. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 26, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghbi, W.A.; Levine, R.A.; Flachskampf, F.; Grayburn, P.; Gillam, L.; Leipsic, J.; Thomas, J.D.; Kwong, R.Y.; Vandervoort, P.; Chandrashekhar, Y. Atrial Functional Mitral Regurgitation. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, P.; Farinha, J.M.; Gupta, D.; Kahn, M.; Proietti, R.; Lip, G.Y.H. A Comparison of Medical Therapy and Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Heart Failure. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2022, 20, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkash, R.; Wells, G.A.; Rouleau, J.; Talajic, M.; Essebag, V.; Skanes, A.; Wilton, S.B.; Verma, A.; Healey, J.S.; Sterns, L.; et al. Randomized Ablation-Based Rhythm-Control Versus Rate-Control Trial in Patients with Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: Results from the RAFT-AF Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. A Conversion CRT Strategy Combined with AVJA May Be a Perspective Alternative for Heart Failure Patients with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glikson, M.; Nielsen, J.C.; Kronborg, M.B.; Michowitz, Y.; Auricchio, A.; Barbash, I.M.; Barrabés, J.A.; Boriani, G.; Braunschweig, F.; Brignole, M.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on Cardiac Pacing and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3427–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, A.; Boczar, K.; Siekiera, M.; Gajek, J.; Sławuta, A. The Clinical Utility of Direct His-Bundle Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation. Acta Cardiol. 2022, 77, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Kong, N.W.; Beaser, A.; Aziz, Z.; Yeshwant, S.; Ozcan, C.; Tung, R.; Upadhyay, G.A. Clinical Outcomes of Conduction System Pacing Compared to Biventricular Pacing in Patients with Mid-Range Ejection Fraction. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2024, 68, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, D.J.; Krishnan, K. Patient Selection for Biventricular Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy, His Bundle Pacing, and Left Bundle Branch Pacing. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 2021, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotwiner, D.J.; Raitt, M.H.; Del-Carpio Munoz, F.; Mulpuru, S.K.; Nasser, N.; Peterson, P.N. Impact of Physiologic Pacing versus Right Ventricular Pacing among Patients with Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Greater than 35%: A Systematic Review for the 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients with Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, e280–e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, D.; Shun-Shin, M.J.; Arnold, A.D.; March, K.; Qureshi, N.; Ng, F.S.; Tanner, M.; Linton, N.; Lim, P.B.; Lefroy, D.; et al. Within-patient Comparison of His-bundle Pacing, Right Ventricular Pacing, and Right Ventricular Pacing Avoidance Algorithms in Patients with PR Prolongation: Acute Hemodynamic Study. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 2964–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Yang, Y.; Dai, B.; Zhang, R.; Wang, N.; Li, D.; Yin, X.; Gao, L.; Xia, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Brady-arrhythmias in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure of Reduced Ejection Fraction: Is His-bundle Pacing Superior to Biventricular Pacing? Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 44, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardas, R.; Golba, K.S.; Loboda, D.; Biernat, J.; Soral, T.; Kulesza, P.; Sajdok, M.; Zub, K. The Usefulness of His Bundle Pacing in a Heterogeneous Population of Patients with Impaired Left Ventricular Systolic Function. Cardiol. J. 2024, 31, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, G.; Fastner, C.; Hetjens, S.; Toepel, M.; Schmiel, G.; Yazdani, B.; Husain-Syed, F.; Liebe, V.; Rudic, B.; Akin, I.; et al. Impact of Baseline Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction on Long-term Outcomes in Cardiac Contractility Modulation Therapy. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 45, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deferm, S.; Bertrand, P.B.; Verbrugge, F.H.; Verhaert, D.; Rega, F.; Thomas, J.D.; Vandervoort, P.M. Atrial Functional Mitral Regurgitation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, S.; Silbiger, J.J.; Halperin, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Vogel, B.; Kini, A.; Sharma, S.; Lerakis, S. Pathophysiology, Echocardiographic Diagnosis, and Treatment of Atrial Functional Mitral Regurgitation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2314–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouris, N.T.; Kostakou, P.M.; Tryfou, E.S.; Olympios, C.D. Incidence and Causal Association of Functional Atrial Mitral Regurgitation in HFpEF. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2023, 69, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, G.A.; Henry, M.; Genovese, D.; Desai, P.; Lattell, J.; Wey, H.; Besser, S.A.; Aziz, Z.; Beaser, A.D.; Ozcan, C.; et al. Impact of Physiological Pacing on Functional Mitral Regurgitation in Systolic Dysfunction: Initial Echocardiographic Remodeling Findings after His Bundle Pacing. Heart Rhythm O2 2021, 2, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kan, J.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Wang, R. His-Purkinje Conduction System Pacing: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis in Bradycardia and Conduction Disorders. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 3245–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.; Garlitski, A.C.; Weinstock, J.; Homoud, M.; Madias, C.; Estes, N.A.M. His Bundle Pacing. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2018, 52, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashida, Y.; Mori, F.; Arashi, H.; Hosaka, F.; Itai, T.; Ohnishi, S. Improvement of Left Ventricular Function by Permanent Direct His-Bundle Pacing in a Case with Dilated Cardiomyopathy. J. Arrhythmia 2006, 22, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soral, T.; Gardas, R.; Gołba, K.S.; Kulesza, P.; Biernat, J.; Łoboda, D. His Bundle Pacing Is Continually Relevant for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Bradycardia without Prior Atrioventricular Nodal Ablation, Data from Mid-Term Follow-Up. Pol. Heart J. 2024, 82, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.C.; Knijnik, L.; Lopez, J.; Rivera, M.; Fernandes, A.; Lambrakos, L.K.; Myerburg, R.J.; Mitrani, R.D.; Goldberger, J.J. Network Meta-analysis of His Bundle, Biventricular, or Right Ventricular Pacing as a Primary Strategy for Advanced Atrioventricular Conduction Disease with Normal or Mildly Reduced Ejection Fraction. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonieczny, B.; Gajek, A.; Strózik, P.; Zawadzki, J.; Adamowicz, J.; Gajek, J.; Sławuta, A. The Optimal Management of Patient with Permanent Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction—The Permanent His-Bundle Pacing Is a Solution. A Case Report. J. Electrocardiol. 2018, 51, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J. β Blockers, Atrial Fibrillation, and Heart Failure. Lancet 2014, 384, 2181–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, D.; Holmes, J.; Krum, H.; Altman, D.G.; Manzano, L.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Coats, A.J.S.; Andersson, B.; Kirchhof, P.; et al. Efficacy of β Blockers in Patients with Heart Failure plus Atrial Fibrillation: An Individual-Patient Data Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienstra, M.; Damman, K.; Mulder, B.A.; Van Gelder, I.C.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J. Beta-Blockers and Outcome in Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Heart Fail. 2013, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareev, Y.; Cleland, J.G.F. Should β-Blockers Be Used in Patients With Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation? Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullington, D.; Goode, K.M.; Zhang, J.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Clark, A.L. Is Heart Rate Important for Patients With Heart Failure in Atrial Fibrillation? JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajah, A.; Lau, D.H.; Sanders, P. Atrial Fibrillation and Conduction System Disease: The Roles of Catheter Ablation and Permanent Pacing. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2018, 52, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, T.; Ilan, M.; Fishman, E.; Michowitz, Y.; Khalameizer, V.; Katz, A.; Glikson, M.; Medina, A.; Rav Acha, M. “Preventive” Pacing in Patients with Tachy-brady Syndrome (TBS): Confirming a Common Practice. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Female a | 27/68.85 |
| Age [years] c | 71 (68–75) |
| Medications a | |
| Digoxin usage | 18/43.90 |
| Dose of metoprolol: | |
| 12.5 mg | 1/2.44 |
| 25.0 mg | 5/12.20 |
| 50.0 mg | 8/19.51 |
| 100.0 mg | 17/41.46 |
| 150.0 mg | 2/4.88 |
| 200.0 mg | 8/19.51 |
| Dose of MRA: | |
| without | 25/60.98 |
| 12.5 mg | 1/2.44 |
| 25.0 mg | 12/29.27 |
| 50.0 mg | 3/7.31 |
| Laboratory parameters | |
| Hb [g/dL] b | 14.19 ± 1.05 |
| K+ [mmol/L] b | 4.46 ± 0.38 |
| Glucose [mmol/L] c | 115.00 (102.00–137.00) |
| Creatinine [mg/dL] c | 0.90 (0.80–1.10) |
| Comorbidities a | |
| HT | 36/87.80 |
| DM | 13/31.71 |
| CKD | 3/7.32 |
| IHD | 10/24.39 |
| MI | 5/12.20 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | |
| Baseline LVEDD [mm] b | 55.63 ± 1.81 |
| Baseline LVEF [%] c | 55.00 (50.00–55.00) |
| Baseline MR: a | |
| without | 0/0 |
| mild | 4/9.76 |
| moderate | 21/51.22 |
| severe | 16/39.02 |
| Population (P) | 41 patients with heart failure, bradyarrhythmia, or tachy-brady syndrome in the course of persistent AF with indications for pacemaker implantation. |
| Intervention (I) | Application of HBP. |
| Comparison (C) | Same patients before HBP. |
| Outcome (O) | LVEF, LVEDD, and degree of MR. |
| Echocardiographic Parameters | Before HBP | After HBP | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LVEDD [mm] b | 55.63 ± 1.81 | 50.22 ± 1.60 | <0.001 |
| LVEF [%] c | 55.00 (50.00–55.00) | 60.00 (60.00–65.00) | <0.001 |
| LVEF increase [%] c | – | 14.58 (9.09–20.00) | – |
| MR: a | <0.001 | ||
| without | 0/0 | 1/2.44 | |
| mild | 4/9.76 | 28/68.29 | |
| moderate | 21/51.22 | 10/24.39 | |
| severe | 16/39.02 | 2/4.88 |
| MR 0 After a | MR 1 After b | MR 2 After c | MR 3 After d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR 1 before b | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| MR 2 before c | 0 | 19 | 2 | 0 |
| MR 3 before d | 0 | 6 | 8 | 2 |
| Factor | Median LVEF Improvement (%) [IQR] | p-Value a | Change in Mean LVEDD (mm) ± SD | p-Value b | Mean Change in MR [IQR] | p-Value c | Effect on MR Improvement (β) | p-Value d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digoxin (yes vs. no) | 14.6 [9.1–20.0] vs. 14.9 [9.1–20.0] | 0.1495 | 55.6 ± 1.8 vs. 55.6 ± 1.8 | 0.9831 | 1 [0–2] vs. 1 [0–2] | 0.5846 | 2.33 | 0.3145 |
| Metoprolol (dose) | – | ρ = 0.25, p = 0.1091 e | – | r = 0.19, p = 0.2437 e | – | ρ = 0.02, p = 0.9021 e | −0.01 | 0.3392 |
| MRA (yes vs. no) | 14.6 [9.1–20.0] vs. 14.9 [9.1–20.0] | 0.7662 | 55.6 ± 1.8 vs. 55.6 ± 1.8 | 0.9308 | 1 [0–2] vs. 1 [0–2] | 0.9308 | −0.03 | 0.2105 |
| IHD (yes vs. no) | 10.0 [7.8–14.6] vs. 14.9 [9.1–20.0] | 0.1053 | 55.5 ± 1.8 vs. 55.7 ± 1.8 | 0.8175 | 1 [0–2] vs. 1 [0–2] | 0.1634 | −0.40 | 0.7512 |
| DM (yes vs. no) | 14.6 [9.1–20.0] vs. 14.9 [9.1–20.0] | 0.6184 | 56.1 ± 1.8 vs. 55.4 ± 1.8 | 0.3022 | 1 [0–2] vs. 1 [0–2] | 0.7187 | 1.02 | 0.4786 |
| CKD (yes vs. no) | 14.6 [9.1–20.0] vs. 14.9 [9.1–20.0] | 0.9190 | 55.7 ± 1.8 vs. 55.6 ± 1.8 | 0.9831 | 1 [0–2] vs. 1 [0–2] | 0.6024 | −4.18 | 0.0486 |
| HT (yes vs. no) | 14.6 [9.1–20.0] vs. 14.9 [9.1–20.0] | 0.4662 | 55.8 ± 1.8 vs. 54.8 ± 1.8 | 0.4141 | 1 [0–2] vs. 1 [0–2] | 0.6785 | −16.79 | 0.9951 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paluszkiewicz, P.; Martuszewski, A.; Smereka, J.; Gajek, J. His Bundle Pacing Improves Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Bradyarrhythmia or Tachy-Brady Syndrome and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092860
Paluszkiewicz P, Martuszewski A, Smereka J, Gajek J. His Bundle Pacing Improves Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Bradyarrhythmia or Tachy-Brady Syndrome and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092860
Chicago/Turabian StylePaluszkiewicz, Patrycja, Adrian Martuszewski, Jacek Smereka, and Jacek Gajek. 2025. "His Bundle Pacing Improves Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Bradyarrhythmia or Tachy-Brady Syndrome and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092860
APA StylePaluszkiewicz, P., Martuszewski, A., Smereka, J., & Gajek, J. (2025). His Bundle Pacing Improves Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Bradyarrhythmia or Tachy-Brady Syndrome and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092860










