Rare Earth Elements in Human Calcified Aortic Valves and Epicardial Adipose Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Mineralization
2.4. Determination of Rare Earth Elements
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Studied Patients
3.2. Levels of Rare Earth Elements in Aortic Valves and Epicardial Tissue
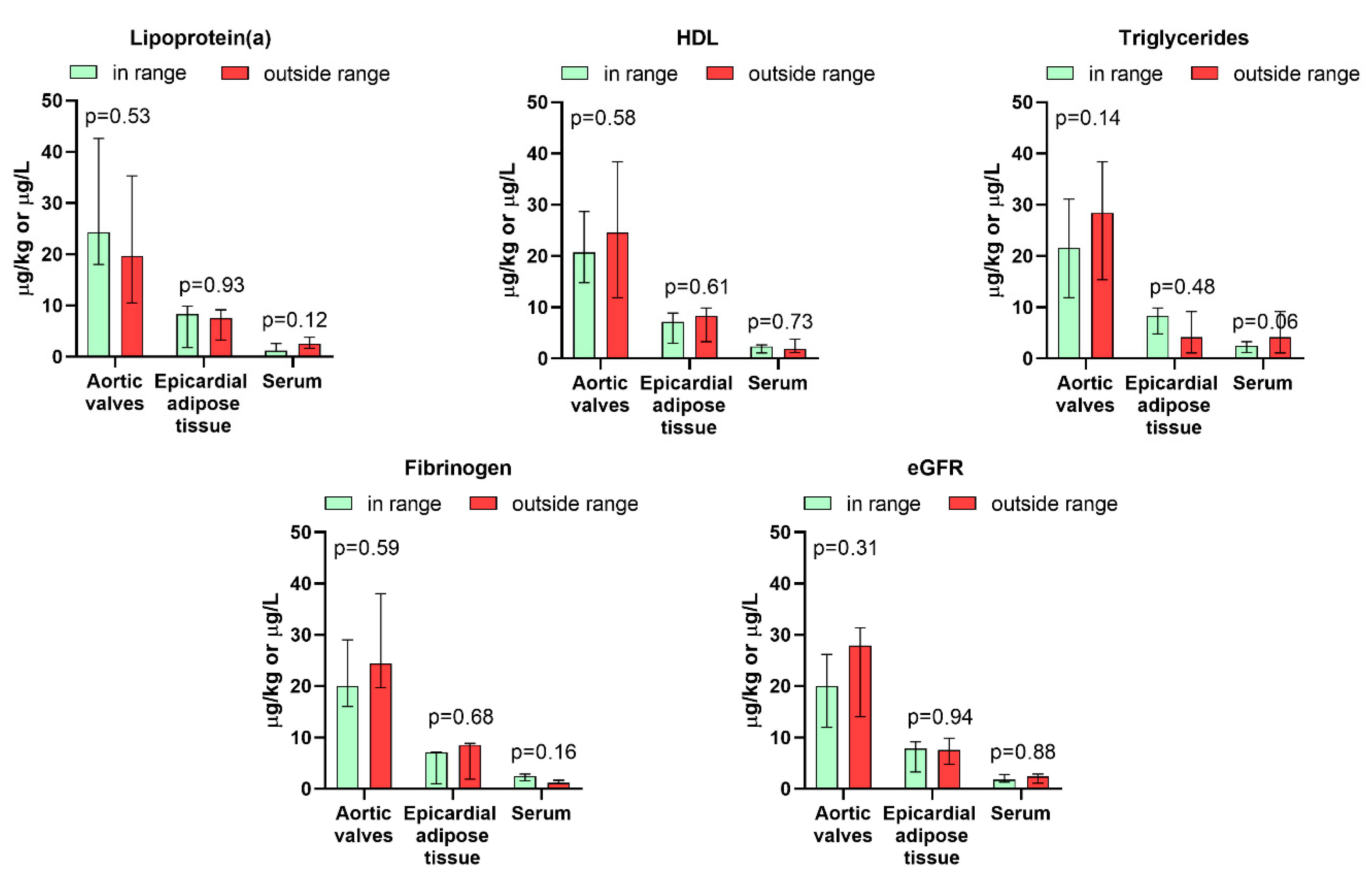
3.3. Association Between Rare Earth Elements Levels and Demographic, Biochemical, and Clinical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gwenzi, W.; Makuvara, Z.; Marumure, J. Rare Earth Elements: Human Exposure, Risk Factors, and Health Risks. In Emerging Contaminants in the Terrestrial-Aquatic-Atmosphere Continuum; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Balaram, V. Rare Earth Elements: A Review of Applications, Occurrence, Exploration, Analysis, Recycling, and Environmental Impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egler, S.G.; Niemeyer, J.C.; Correia, F.V.; Saggioro, E.M. Effects of Rare Earth Elements (REE) on Terrestrial Organisms: Current Status and Future Directions. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.M.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Bakar, A.F.A.; Ashraf, M.A. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in the Ecosystem: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 22764–22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwulski, M.; Budka, A.; Rzymski, P.; Mleczek, P.; Budzyńska, S.; Gąsecka, M.; Szostek, M.; Kalač, P.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Niedzielski, P.; et al. Multiannual Monitoring (1974–2019) of Rare Earth Elements in Wild Growing Edible Mushroom Species in Polish Forests. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marginson, H.; MacMillan, G.A.; Grant, E.; Gérin-Lajoie, J.; Amyot, M. Rare Earth Element Bioaccumulation and Cerium Anomalies in Biota from the Eastern Canadian Subarctic (Nunavik). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, K.; Dia, A.; Marques, R.; Prudêncio, M.I.; Diamantino, C.; Carvalho, E.; Russo, D.; Dionisio, I.; Davranche, M.; Bouhnik-Le-Coz, M.; et al. Bioconcentration and Translocation of Rare Earth Elements in Plants Collected from Three Legacy Mine Sites in Portugal. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1191909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Klimaszyk, P.; Niedzielski, P.; Marszelewski, W.; Borowiak, D.; Nowiński, K.; Baikenzheyeva, A.; Kurmanbayev, R.; Aladin, N. Pollution with Trace Elements and Rare-Earth Metals in the Lower Course of Syr Darya River and Small Aral Sea, Kazakhstan. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.T.; Ottosen, L. Recovering Rare Earth Elements from Contaminated Soils: Critical Overview of Current Remediation Technologies. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Domingo, J.L. Levels of Rare Earth Elements in Food and Human Dietary Exposure: A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 203, 2240–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, W.; Zheng, H. Hazard Profiles, Distribution Trends, and Sources Tracing of Rare Earth Elements in Dust of Kindergartens in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 358, 124374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez-Hernández, L.A.; Boada, L.D.; Carranza, C.; Pérez-Arellano, J.L.; González-Antuña, A.; Camacho, M.; Almeida-González, M.; Zumbado, M.; Luzardo, O.P. Blood Levels of Toxic Metals and Rare Earth Elements Commonly Found in E-Waste May Exert Subtle Effects on Hemoglobin Concentration in Sub-Saharan Immigrants. Environ. Int. 2017, 109, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, N.; Xu, M.; Gao, J.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; et al. Urine Is Better for Rare Earth Elements Bimonitoring in Long-Term Exposed Population: An Exposure-Response Relationship Study. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasull, M.; Camargo, J.; Pumarega, J.; Henríquez-Hernández, L.A.; Campi, L.; Zumbado, M.; Contreras-Llanes, M.; Oliveras, L.; González-Marín, P.; Luzardo, O.P.; et al. Blood Concentrations of Metals, Essential Trace Elements, Rare Earth Elements and Other Chemicals in the General Adult Population of Barcelona: Distribution and Associated Sociodemographic Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec-Wróblewska, U.; Kamiński, P.; Łakota, P.; Ludwikowski, G.; Szymański, M.; Wasilow, K.; Stuczyński, T.; Buciński, A.; Jerzak, L. Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Human Sperm and Association with Semen Quality. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniedziałek, B.; Rzymski, P.; Pięt, M.; Niedzielski, P.; Mleczek, M.; Wilczak, M.; Rzymski, P. Rare-Earth Elements in Human Colostrum Milk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 26148–26154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Ye, B.; Liang, T. Rare Earth Elements in Human Hair from a Mining Area of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 96, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, X.; Zhang, N.; Su, X.; Pang, H.; Li, W.; Wang, F.; Pu, Y.; et al. A Human Health Risk Assessment of Rare Earth Elements through Daily Diet Consumption from Bayan Obo Mining Area, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira Pereira, W.V.; Ramos, S.J.; Melo, L.C.A.; Dias, Y.N.; Martins, G.C.; Ferreira, L.C.G.; Fernandes, A.R. Human and Environmental Exposure to Rare Earth Elements in Gold Mining Areas in the Northeastern Amazon. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouziotis, A.A.; Giarra, A.; Libralato, G.; Pagano, G.; Guida, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Toxicity of Rare Earth Elements: An Overview on Human Health Impact. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 948041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, L.; Huo, W.; Lu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Rare Earth Elements and Hypertension Risk among Housewives: A Pilot Study in Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Aracena, J.; Riemersma, R.A.; Gutiérrez-Bedmar, M.; Bode, P.; Kark, J.D.; Garcia-Rodríguez, A.; Gorgojo, L.; Van’t Veer, P.; Fernández-Crehuet, J.; Kok, F.J.; et al. Toenail Cerium Levels and Risk of a First Acute Myocardial Infarction: The EURAMIC and Heavy Metals Study. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, G.; Lan, C.; Yan, L.; Liang, R.; Hao, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Q.; et al. Association between Exposure of Light Rare Earth Elements and Outcomes of in Vitro Fertilization-Embryo Transfer in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, F.E.C.M.; Meex, S.J.R.; Dweck, M.R.; Aikawa, E.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Schurgers, L.J.; Kietselaer, B.L.J.H. Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis: Hard Disease in the Heart: A Biomolecular Approach towards Diagnosis and Treatment. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, J.A. Cellular Mechanisms of Aortic Valve Calcification. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 5, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomášek, A.; Maňoušek, J.; Kuta, J.; Hlásenský, J.; Křen, L.; Šindler, M.; Zelený, M.; Kala, P.; Němec, P. Metals and Trace Elements in Calcified Valves in Patients with Acquired Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis: Is There a Connection with the Degeneration Process? J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniedziałek, B.; Perek, B.; Proch, A.; Komosa, A.; Niedzielski, P.; Buczkowski, P.; Jemielity, M.; Rzymski, P. Mineral Composition and Ratios in Aortic Valves, Serum, and Epicardial Fat among Patients with Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Aortic Valve Replacement. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, G. Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Contemporary Cardiology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, G.; Barbaro, G. The Double Role of Epicardial Adipose Tissue as Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Organ. Horm. Metab. Res. 2008, 40, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Généreux, P.; Sharma, R.P.; Cubeddu, R.J.; Aaron, L.; Abdelfattah, O.M.; Koulogiannis, K.P.; Marcoff, L.; Naguib, M.; Kapadia, S.R.; Makkar, R.R.; et al. The Mortality Burden of Untreated Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Afoakwah, C.; Chan, Y.-K.; Strom, J.B.; Playford, D.; Strange, G.A. Counting the Cost of Premature Mortality with Progressively Worse Aortic Stenosis in Australia: A Clinical Cohort Study. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022, 3, e599–e606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, R.Q.; Raja, S.G. Surgical Pericardial Heart Valves: 50 Years of Evolution. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 94, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Czlapka-Matyasik, M.; Wojciechowska, Z.; Proch, J.; Kowalski, R.; Niedzielski, P. Rare Earth Elements Accumulation in the Hair of Malagasy Children and Adolescents in Relation to Their Age and Nutritional Status. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Taesh, H.; Çelekli, A.; Sucu, M.; Taysi, S. Trace Elements in Patients with Aortic Valve Sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 15, 1753944720985985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olcay, A.; Albayrak, S.B.; Yolay, O.; Ozturk, V.; Canturk, E.; Tezcan, E.; Karaoglu, H.; Kucuk, C.; Serbest, N.G.; Umihanic, A. Stenotic Aortic Valves Have High Metal and Lack Selenium: A New Toxic Inflammation Hypothesis? Atherosclerosis 2022, 355, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coady, M.A.; Sellke, F.W. Metallothionein Link to Bicuspid Aortic Valve-Associated Ascending Aortic Dilatation. Circulation 2009, 119, 2423–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takyi, S.A.; Basu, N.; Arko-Mensah, J.; Dwomoh, D.; Houessionon, K.G.; Fobil, J.N. Biomonitoring of Metals in Blood and Urine of Electronic Waste (E-Waste) Recyclers at Agbogbloshie, Ghana. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, B.; Liao, X.; Liang, T.; Yu, J. Levels of Rare Earth Elements, Heavy Metals and Uranium in a Population Living in Baiyun Obo, Inner Mongolia, China: A Pilot Study. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Ge, J.; Wang, L.; Wan, X.; Guo, G.; Liang, T.; Bolan, N.; Rennert, T.; Rinklebe, J. Hair-Biomonitoring Assessment of Rare-Earth-Element Exposure in Residents of the Largest Rare-Earth Mining and Smelting Area of China. Environ. Int. 2023, 179, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirtiu, C.M.; Valcke, M.; Gagné, M.; Bourgault, M.-H.; Narame, C.; Gadio, S.; Poulin, P.; Ayotte, P. Biological Monitoring of Exposure to Rare Earth Elements and Selected Metals in the Inuit Population of Nunavik, Canada. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Niedzielski, P.; Rzymski, P.; Tomczyk, K.; Kozak, L.; Poniedziałek, B. Metal Accumulation in the Human Uterus Varies by Pathology and Smoking Status. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 105, 1511–1518.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, J.Q.; Dranikov, A.; Iannucci, A.; Wagner, W.P.; LoBello, J.; Allen, J.; Weiss, G.J. Heavy Metal Content in Thoracic Tissue Samples from Patients with and without NSCLC. Lung Cancer Int. 2014, 2014, 853158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, C.; Vrhovnik, P.; Fiket, Ž.; Salcedo-Bellido, I.; Echeverría, R.; Martín-Olmedo, P.; Kniewald, G.; Fernández, M.F.; Arrebola, J.P. Adipose Tissue Concentrations of Arsenic, Nickel, Lead, Tin, and Titanium in Adults from GraMo Cohort in Southern Spain: An Exploratory Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamphlett, R.; Bishop, D.P.; Kum Jew, S.; Doble, P.A. Age-Related Accumulation of Toxic Metals in the Human Locus Ceruleus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, N.K.; Ramanujam, V.M.S.; Kalariya, N.; Lewis, J.R.; van Kuijk, F.J.G.M. Copper and Zinc Distribution in the Human Retina: Relationship to Cadmium Accumulation, Age, and Gender. Exp. Eye Res. 2008, 87, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichick, S.; Zaichick, V.; Karandashev, V.; Nosenko, S. Accumulation of Rare Earth Elements in Human Bone within the Lifespan. Metallomics 2011, 3, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumbado, M.; Luzardo, O.P.; Rodríguez-Hernández, Á.; Boada, L.D.; Henríquez-Hernández, L.A. Differential Exposure to 33 Toxic Elements through Cigarette Smoking, Based on the Type of Tobacco and Rolling Paper Used. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlandt, A.; Schierl, R.; Diemer, J.; Koch, C.; Bolte, G.; Kiranoglu, M.; Fromme, H.; Nowak, D. High Concentrations of Cadmium, Cerium and Lanthanum in Indoor Air Due to Environmental Tobacco Smoke. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, M.; Luzardo, O.P.; González-Antuña, A.; Zumbado, M.; Rogozea, L.; Floroian, L.; Alexandrescu, D.; Moga, M.; Gaman, L.; Radoi, M.; et al. Body Burden of Toxic Metals and Rare Earth Elements in Non-Smokers, Cigarette Smokers and Electronic Cigarette Users. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, S.; Pai, A.M.; Gill, K.S.; Pai, R.G. New Insights into the Progression of Aortic Stenosis: Implications for Secondary Prevention. Circulation 2000, 101, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A.; Bäck, M. Alcohol Consumption, Cigarette Smoking and Incidence of Aortic Valve Stenosis. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Shimaya, M.; Tomita, Y.; Fukaya, T.; Yoshida, K. Impact of Cumulative Smoking Exposure on Subclinical Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease in Apparently Healthy Male Workers. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e008901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mleczek, M.; Niedzielski, P.; Kalač, P.; Siwulski, M.; Rzymski, P.; Gąsecka, M. Levels of Platinum Group Elements and Rare-Earth Elements in Wild Mushroom Species Growing in Poland. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzymski, P.; Budzulak, J.; Niedzielski, P.; Klimaszyk, P.; Proch, J.; Kozak, L.; Poniedziałek, B. Essential and Toxic Elements in Commercial Microalgal Food Supplements. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3567–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiket, Ž.; Medunić, G. Dataset of Rare Earth Elements Distribution in Soils and Vegetables. Results Earth Sci. 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency Air Quality in Europe 2021. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2021 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Shen, Y.-W.; Zhao, C.-X.; Zhao, H.; Dong, S.-F.; Guo, Q.; Xie, J.-J.; Lv, M.-L.; Yuan, C.-G. Insight Study of Rare Earth Elements in PM2.5 during Five Years in a Chinese Inland City: Composition Variations, Sources, and Exposure Assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, C.; Xu, S.; Shao, P.; Wu, D.; Yang, W.; Gu, J. Chronic Toxicity of Rare-Earth Elements on Human Beings: Implications of Blood Biochemical Indices in REE-High Regions, South Jiangxi. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2000, 73, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelouzou, A.; Tsourelis, L.; Kaklamanis, L.; Degiannis, D.; Kogerakis, N.; Cokkinos, D.V. Serum and Tissue Biomarkers in Aortic Stenosis. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2015, 2015, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfors, B.; Furer, A.; Lindman, B.R.; Burkhoff, D.; Marquis-Gravel, G.; Francese, D.P.; Ben-Yehuda, O.; Pibarot, P.; Gillam, L.D.; Leon, M.B.; et al. Biomarkers in Aortic Stenosis: A Systematic Review. Struct. Heart 2017, 1, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, J.; Meng, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhen, H.; Zheng, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, X.; Zu, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Rare Earth Elements Lanthanum and Praseodymium Adversely Affect Neural and Cardiovascular Development in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, L. Toxic Effects of Rare Earth Elements on Human Health: A Review. Toxics 2024, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Demographic Data | Mean ± SD or % (n) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.9 ± 7.4 |
| <70 years | 50 (10) |
| ≥70 years | 50 (10) |
| Male/Female | 70/30 (14/6) |
| Body Mass Index (BMI, kg/m2) | 29.4 ± 4.6 |
| Obesity, BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 45 (9) |
| Rural/urban inhabitants | 30/70 (6/14) |
| Current smokers (within last year) | 15 (3) |
| Past smokers (cessation within 1–10 years) | 25 (5) |
| Biochemical parameters | mean ± SD |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) in reference range—≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2 (%, (n)) | 86.4 ± 25.9 50 (10) |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) in reference range—53–115 µmol/L (%, (n)) | 85.6 ± 17.3 90 (18) |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) in reference range—5.0 mmol/L (%, (n)) | 3.7 ± 1.1 85 (17) |
| Low-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) in reference range, <2.6 mmol/L, (%, (n)) | 1.9 ± 0.9 80 (16) |
| High-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) in reference range—≥1.3 mmol/L, (%, (n)) | 1.4 ± 0.4 60 (12) |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) in reference range, <1.7 mmol/L (%, (n)) | 1.1 ± 0.4 75 (15) |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) in reference range—200–400 mg/dL (%, (n)) | 356.5 ± 84.0 70 (14) |
| Lipoprotein (mg/dL) in reference range, <30 mg/dL (%, (n)) | 40.8 ± 51.1 55 (11) |
| Preoperative Echocardiographic Findings (M+2D+Doppler) | mean ± SD or % (n) |
| Mean systolic pressure gradient (mmHg) >50 mmHg (%, (n)) | 53.9 ± 15.9 35.0 (7) |
| Peak systolic pressure gradient (mmHg) | 82.3 ± 23.9 |
| Bicuspid aortic valve (%, (n)) | 10.0 (2) |
| Element | Aortic Valves [µg/kg] | Epicardial Fat [µg/kg] | SERUM [µg/L] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >LOD (n) | Mean ± SD (max) | >LOD (n) | Mean ± SD (max) | >LOD (n) | Mean ± SD (max) | |
| Ce | 20 | 12.9 ± 12.4 (55.1) | 15 | 5.9 ± 8.5 (35.9) | 18 | 0.9 ± 0.03 (1.5) |
| Eu | 18 | 0.6 ± 0.3 (1.1) | 12 | 0.4 ± 0.1 (0.6) | 10 | 0.2 ± 0.01 (0.2) |
| Er | 18 | 0.8 ± 0.6 (2.7) | 15 | 0.5 ± 0.2 (1.0) | 18 | 0.2 ± 0.1 (0.3) |
| La | 0 | - | 1 | 23.4 | 1 | 4.3 |
| Gd | 19 | 10.6 ± 15.9 (66.6) | 15 | 1.9 ± 1.4 (6.6) | 13 | 0.4 ± 0.2 (0.7) |
| Nd | 16 | 3.5 ± 2.0 (9.2) | 4 | 6.9 ± 6.5 (16.4) | 3 | 1.1 ± 0.1 (1.1) |
| Pr | 18 | 2.3 ± 2.8 (9.7) | 7 | 1.2 ± 1.5 (4.5) | 6 | 0.2 ± 0.1 (0.3) |
| Sm | 15 | 1.3 ± 1.4 (5.9) | 10 | 1.5 ± 0.5 (2.5) | 9 | 0.4 ± 0.1 (0.7) |
| Dy | 4 | 0.9 ± 0.6 (1.8) | 6 | 0.7 ± 0.2 (1.1) | 3 | 0.2 ± 0.1 (0.3) |
| Ho | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Lu | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Tb | 6 | 1.3 ± 0.8 (2.6) | 5 | 1.6 ± 0.1 (1.7) | 6 | 0.8 ± 0.3 (1.1) |
| Tm | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Yb | 5 | 0.1 ± 0.2 (0.7) | 7 | 0.7 ± 0.2 (1.0) | 1 | 0.2 |
| Σ Light REEs | 20 | 29.5 ± 24.7 (90.1) | 20 | 9.8 ± 18.2 (84.3) | 20 | 1.8 ± 1.4 (6.3) |
| Σ Heavy REEs | 20 | 1.4 ± 0.8 (3.3) | 20 | 1.2 ± 1.1 (3.7) | 20 | 0.5 ± 0.4 (1.5) |
| Σ Total REEs | 20 | 30.9 ± 24.8 (90.9) | 20 | 11.0 ± 18.0 (84.6) | 20 | 2.3 ± 1.6 (7.4) |
| Total REEs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Epicardial adipose tissue | Serum | |
| Aortic valves | 0.31 (p = 0.19) | −0.32 (p = 0.16) |
| Epicardial adipose tissue | - | −0.16 (p = 0.49) |
| Light REEs | ||
| Epicardial adipose tissue | Serum | |
| Aortic valves | 0.33 (p = 0.14) | −0.33 (p = 0.15) |
| Epicardial adipose tissue | - | 0.02 (p = 0.92) |
| Heavy REEs | ||
| Epicardial adipose tissue | Serum | |
| Aortic valves | −0.25 (p = 0.29) | 0.08 (p = 0.75) |
| Epicardial adipose tissue | - | −0.22 (p = 0.36) |
| Parameter | Aortic Valves | Epicardial Adipose Tissue | Serum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs | p | Rs | p | Rs | p | |
| Age | −0.04 | 0.88 | −0.11 | 0.64 | −0.13 | 0.60 |
| BMI | 0.06 | 0.81 | 0.05 | 0.83 | −0.21 | 0.81 |
| Creatinine | −0.22 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.91 | −0.04 | 0.85 |
| Total cholesterol | −0.01 | 0.95 | −0.08 | 0.74 | −0.28 | 0.24 |
| LDL | −0.06 | 0.81 | −0.08 | 0.74 | −0.31 | 0.19 |
| HDL | −0.08 | 0.75 | −0.12 | 0.61 | −0.00 | 0.99 |
| Triglycerides | 0.32 | 0.18 | −0.12 | 0.63 | −0.29 | 0.23 |
| Lipoprotein(a) | −0.07 | 0.77 | −0.05 | 0.85 | 0.00 | 0.99 |
| Fibrinogen | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.93 | −0.24 | 0.30 |
| eGFR | 0.13 | 0.59 | −0.02 | 0.93 | −0.13 | 0.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poniedziałek, B.; Perek, B.; Proch, A.; Misterski, M.; Komosa, A.; Niedzielski, P.; Fal, A.; Jemielity, M.; Rzymski, P. Rare Earth Elements in Human Calcified Aortic Valves and Epicardial Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092891
Poniedziałek B, Perek B, Proch A, Misterski M, Komosa A, Niedzielski P, Fal A, Jemielity M, Rzymski P. Rare Earth Elements in Human Calcified Aortic Valves and Epicardial Adipose Tissue. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092891
Chicago/Turabian StylePoniedziałek, Barbara, Bartłomiej Perek, Aleksandra Proch, Marcin Misterski, Anna Komosa, Przemysław Niedzielski, Andrzej Fal, Marek Jemielity, and Piotr Rzymski. 2025. "Rare Earth Elements in Human Calcified Aortic Valves and Epicardial Adipose Tissue" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092891
APA StylePoniedziałek, B., Perek, B., Proch, A., Misterski, M., Komosa, A., Niedzielski, P., Fal, A., Jemielity, M., & Rzymski, P. (2025). Rare Earth Elements in Human Calcified Aortic Valves and Epicardial Adipose Tissue. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092891










