Hyperreflective Retinal Foci (HRF): Definition and Role of an Invaluable OCT Sign
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
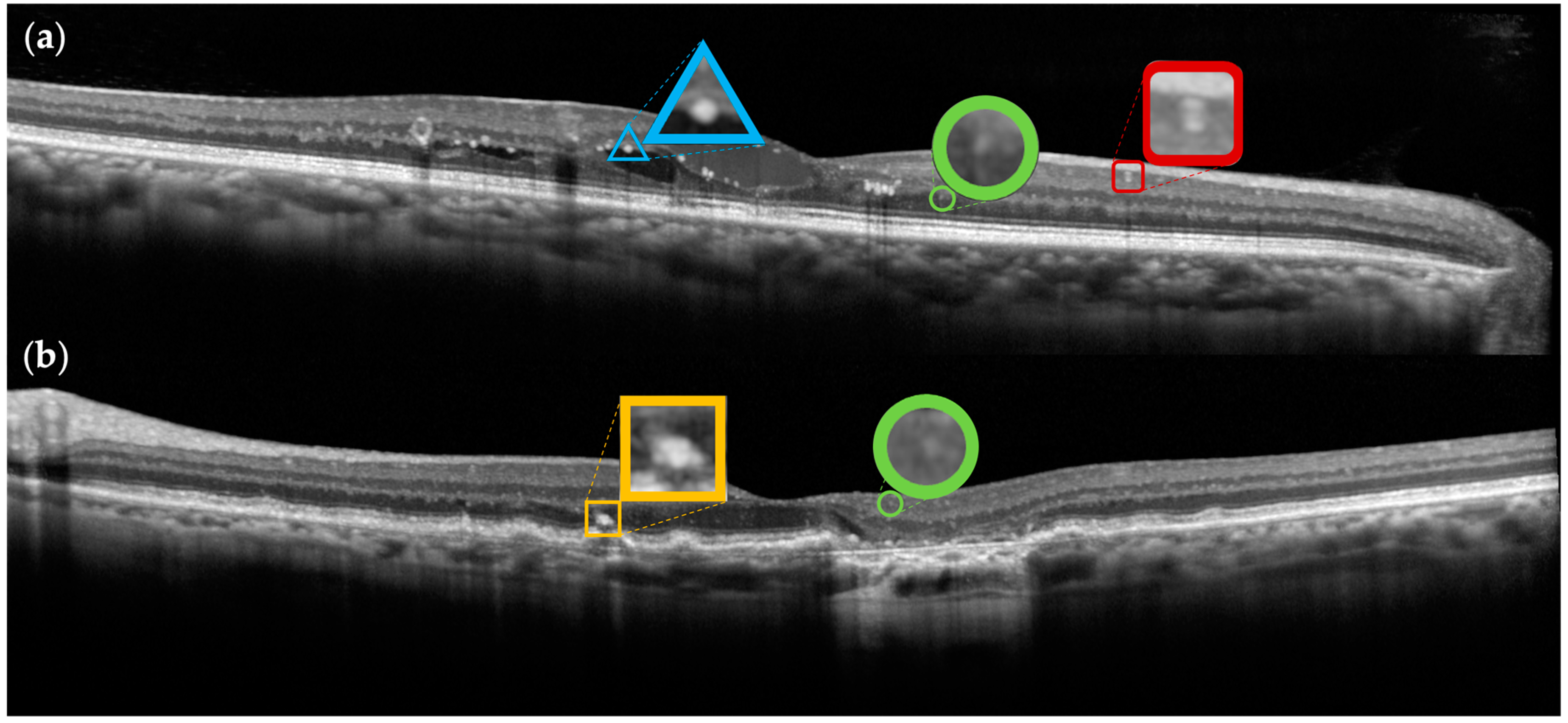
3.1. Biomarkers
3.1.1. Definition of Biomarker
3.1.2. The Use of Biomarkers in Retinal Disorders
3.1.3. Nomenclature
3.2. Vessels and Vascular Abnormalities
3.3. Retinal Neuroinflammation
3.4. Exudation
3.5. Degeneration
3.6. Artificial Intelligence Application
4. Discussion and Final Proposal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMD | Age-related macular degeneration |
| DME | Diabetic macular edema |
| DR | Diabetic retinopathy |
| ELM | External limiting membrane |
| GA | Geographic atrophy |
| HRD | Hyperreflective dots |
| HRF | Hyperreflective retinal foci |
| HRS | Hyperreflective retinal spots |
| OCT | Optical coherence tomography |
| ONL | Outer nuclear layer |
| OPL | Outer plexiform layer |
| PED | Pigment epithelium detachment |
| RPE | Retinal pigment epithelium |
| SRD | Serous retinal detachment |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelium growth factor |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What are biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, B.B.; Morley, M.G.; Bernstein, P.S.; Maddess, T. Severity of age-related macular degeneration at first presentation in Bhutan: A 3-year national study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022, 22, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, B.U.; Grinton, M.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Felfeli, T. Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging Biomarkers: A Review of the Literature. Retina 2024, 44, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO International Programme on Chemical Safety. Biomarkers and Risk Assessment: Concepts and Principles. 1993. Available online: http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc155.htm (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGillivray, T.J.; Trucco, E.; Cameron, J.R.; Dhillon, B.; Houston, J.G.; van Beek, E.J. Retinal imaging as a source of biomarkers for diagnosis, characterization and prognosis of chronic illness or long-term conditions. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscas, G.; De Benedetto, U.; Coscas, F.; Li Calzi, C.I.; Vismara, S.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Bandello, F.; Souied, E. Hyperreflective dots: A new spectral-domain optical coherence tomography entity for follow-up and prognosis in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica 2013, 229, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanifar, A.A.; Koreishi, A.F.; Izatt, J.A.; Toth, C.A. Drusen Ultrastructure Imaging with Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Age-related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, C.G.; Witkin, A.J.; Ko, T.H.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Chan, A.; Schuman, J.S.; Ishikawa, H.; Reichel, E.; Duker, J.S. Ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography in non-exudative age related macular degeneration. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Bini, S.; Midena, G.; Berton, M.; Pilotto, E.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective intraretinal spots in diabetics without and with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: An in vivo study using spectral domain OCT. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 491835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolz, M.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Deak, G.; Mylonas, G.; Kriechbaum, K.; Scholda, C.; Diabetic Retinopathy Research Group Vienna. Optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci: A morphologic sign of lipid extravasation in diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, S.K.; Freund, K.B.; Shah, V.P.; Sarraf, D. The pearl necklace sign: A novel spectral domain optical coherence tomography finding in exudative macular disease. Retina 2014, 34, 2088–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujosevic, S.; Bini, S.; Torresin, T.; Berton, M.; Midena, G.; Parrozzani, R.; Martini, F.; Pucci, P.; Daniele, A.R.; Cavarzeran, F.; et al. Hyperreflective Retinal Spots in Normal and Diabetic Eyes: B-Scan and En Face Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Evaluation. Retina 2017, 37, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merriam-Webster: America’s Most Trusted Dictionary. Available online: https://www.merriam-webster.com (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Oxford Dictionary, Oxford University Press. Available online: https://www.oed.com/?tl=true (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Reche, J.; Stocker, A.B.; Henchoz, V.; Habra, O.; Escher, P.; Wolf, S.; Zinkernagel, M.S. High-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography in Healthy Individuals Provides Resolution at the Cellular and Subcellular Levels. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midena, E.; Bini, S. Multimodal retinal imaging of diabetic macular edema: Toward new paradigms of pathophysiology. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parravano, M.; De Geronimo, D.; Scarinci, F.; Querques, L.; Virgili, G.; Simonett, J.M.; Varano, M.; Bandello, F.; Querques, G. Diabetic Microaneurysms Internal Reflectivity on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography and Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Detection. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 179, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Hwang, T.S.; Bailey, S.T.; Wilson, D.J.; Jia, Y.; Huang, D. Detailed Vascular Anatomy of the Human Retina by Projection-Resolved Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, E.; Leonardi, F.; Stefanon, G.; Longhin, E.; Torresin, T.; Deganello, D.; Cavarzeran, F.; Miglionico, G.; Parrozzani, R.; Midena, E. Early retinal and choroidal OCT and OCT angiography signs of inflammation after uncomplicated cataract surgery. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Eter, N.; Heiduschka, P. The microglia in healthy and diseased retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 136, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigsby, J.G.; Cardona, S.M.; Pouw, C.E.; Muniz, A.; Mendiola, A.S.; Tsin, A.T.; Allen, D.M.; Cardona, A.E. The Role of Microglia in Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 2014, 705783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, U.K.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia: Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmann, T. Microglia activation in retinal degeneration. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joussen, A.M.; Poulaki, V.; Le, M.L.; Koizumi, K.; Esser, C.; Janicki, H.; Schraermeyer, U.; Kociok, N.; Fauser, S.; Kirchhof, B.; et al. A central role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1450–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Micera, A.; Bini, S.; Berton, M.; Esposito, G.; Midena, E. Proteome analysis of retinal glia cells-related inflammatory cytokines in the aqueous humour of diabetic patients. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016, 94, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.Y.; Green, W.R.; Tso, M.O. Microglial activation in human diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujosevic, S.; Torresin, T.; Berton, M.; Bini, S.; Convento, E.; Midena, E. Diabetic Macular Edema With and Without Subfoveal Neuroretinal Detachment: Two Different Morphologic and Functional Entities. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 181, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paques, M.; Simonutti, M.; Augustin, S.; Goupille, O.; El Mathari, B.; Sahel, J.A. In vivo observation of the locomotion of microglial cells in the Retina. Glia 2010, 58, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetto, U.; Sacconi, R.; Pierro, L.; Lattanzio, R.; Bandello, F. Optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci in early stages of diabetic retinopathy. Retina 2015, 35, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, B.; Yildirim, H. The causes of hyperreflective dots in optical coherence tomography excluding diabetic macular edema and retinal venous occlusion§. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2015, 9, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Torresin, T.; Bini, S.; Convento, E.; Pilotto, E.; Parrozzani, R.; Midena, E. Imaging retinal inflammatory biomarkers after intravitreal steroid and anti-VEGF treatment in diabetic macular oedema. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Yamashita, T.; Shirasawa, M.; Otsuka, H.; Sonoda, Y. Retinal morphologic changes and concentrations of cytokines in eyes with diabetic macular edema. Retina 2014, 34, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dolz-Marco, R.; Messinger, J.D.; Wang, L.; Feist, R.M.; Girkin, C.A.; Gattoussi, S.; Ferrara, D.; Curcio, C.A.; Freund, K.B. Clinicopathologic Correlation of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Treated Type 3 Neovascularization in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, C.A.; Zanzottera, E.C.; Ach, T.; Balaratnasingam, C.; Freund, K.B. Activated Retinal Pigment Epithelium, an Optical Coherence Tomography Biomarker for Progression in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, BIO211–BIO226. [Google Scholar]
- Pilotto, E.; Parolini, F.; Midena, G.; Cosmo, E.; Midena, E. Small Hyperreflective Retinal Foci as in vivo imaging feature of resident microglia activation in geographic atrophy. Exp. Eye Res. 2024, 248, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Nor, M.N.; Guo, C.X.; Green, C.R.; Squirrell, D.; Acosta, M.L. Hyper-reflective dots in optical coherence tomography imaging and inflammation markers in diabetic retinopathy. J. Anat. 2023, 243, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiotta, S.; Rossi, T.; Cutini, A.; Grenga, P.L.; Vingolo, E.M. Predictive Factors for Development of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Study. Retina 2018, 38, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Suzuma, K.; Dodo, Y.; Yoshitake, T.; Yasukura, S.; Nakanishi, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Oishi, M.; Tsujikawa, A. Decorrelation Signal of Diabetic Hyperreflective Foci on Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Berton, M.; Bini, S.; Casciano, M.; Cavarzeran, F.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective Retinal Spots and Visual Function After Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment in Center-Involving Diabetic Macular Edema. Retina 2016, 36, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.W.; Chung, H.; Chan Kim, H. Correlation of Optical Coherence Tomographic Hyperreflective Foci with Visual Outcomes in Different Patterns of Diabetic Macular Edema. Retina 2016, 36, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, B.; Zhou, H.Y.; Jiao, X.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of hyperreflective foci as a prognostic factor of visual outcome in retinal vein occlusion. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Chatziralli, I.P.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Sivaprasad, S. Hyperreflective Foci as An Independent Visual Outcome Predictor in Macular Edema Due to Retinal Vascular Diseases Treated with Intravitreal Dexamethasone or Ranibizumab. Retina 2016, 36, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berasategui, B.; Fonollosa, A.; Artaraz, J.; Ruiz-Arruza, I.; Ríos, J.; Matas, J.; Llorenç, V.; Diaz-Valle, D.; Sastre-Ibañez, M.; Arriola-Villalobos, P.; et al. Behavior of hyperreflective foci in non-infectious uveitic macular edema, a 12-month follow-up prospective study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizziero, L.; Parrozzani, R.; Midena, G.; Miglionico, G.; Vujosevic, S.; Pilotto, E.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective Intraretinal Spots in Radiation Macular Edema on Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. Retina 2016, 36, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrozzani, R.; Midena, G.; Frizziero, L.; Marchione, G.; Midena, E. Radiation Maculopathy is Anticipated by Oct Hyperreflective Retinal Foci: A Large, Prospective, Confirmation Study. Retina 2022, 42, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, E.; Miante, S.; Torresin, T.; Puthenparampil, M.; Frizziero, L.; Federle, L.; Gallo, P.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective Foci in the Retina of Active Relapse-Onset Multiple Sclerosis. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 1774–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, M.; Miante, S.; Franciotta, S.; Ponzano, M.; Torresin, T.; Bovis, F.; Rinaldi, F.; Perini, P.; Saiani, M.; Margoni, M.; et al. Retinal Hyperreflecting Foci Associate With Cortical Pathology in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2022, 9, e1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthenparampil, M.; Basili, E.; Ponzano, M.; Mauceri, V.A.; Miscioscia, A.; Pilotto, E.; Perini, P.; Rinaldi, F.; Bovis, F.; Gallo, P. Hyper-reflective foci changes in RRMS under natalizumab therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1421755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthenparampil, M.; Torresin, T.; Franciotta, S.; Marin, A.; De Napoli, F.; Mauceri, V.A.; Miante, S.; Pilotto, E.; Midena, E.; Gallo, P. Hyper-Reflecting Foci in Multiple Sclerosis Retina Associate With Macrophage/Microglia-Derived Cytokines in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 85218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midena, G.; Danieli, L.; Pilotto, E.; Frizziero, L.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective choroidal foci in diabetic eyes with and without macular edema: Novel insights on diabetic choroidopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2024, 247, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Saurabh, K.; Shah, D.; Chowdhury, M.; Goel, S. Choroidal Hyperreflective Foci: A Novel Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Biomarker in Eyes With Diabetic Macular Edema. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, M.; Nishijima, K.; Sakamoto, A.; Murakami, T.; Takayama, K.; Horii, T.; Yoshimura, N. Optical coherence tomographic evaluation of foveal hard exudates in patients with diabetic maculopathy accompanying macular detachment. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Framme, C.; Schweizer, P.; Imesch, M.; Wolf, S.; Wolf-Schnurrbusch, U. Behavior of SD-OCT-detected hyperreflective foci in the retina of anti-VEGF-treated patients with diabetic macular edema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5814–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Framme, C.; Wolf, S.; Wolf-Schnurrbusch, U. Small dense particles in the retina observable by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5965–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, K.; Murakami, T.; Tsujikawa, A.; Miyamoto, K.; Sakamoto, A.; Ota, M.; Yoshimura, N. Characteristics of optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci in retinal vein occlusion. Retina 2012, 32, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, T.; Tsujikawa, A.; Murakami, T.; Ogino, K.; Muraoka, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Akagi-Kurashige, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Yoshimura, N. Subfoveal serous retinal detachment associated with extramacular branch retinal vein occlusion. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 7, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Midena, E.; Frizziero, L. Letter to the Editor Regarding “Intraretinal Hyper-Reflective Foci Are Almost Universally Present and Co-Localize With Intraretinal Fluid in Diabetic Macular Edema”. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2025, 66, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.E.; Messinger, J.D.; Zanzottera, E.C.; Freund, K.B.; Curcio, C.A. The Onion Sign in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Represents Cholesterol Crystals. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2316–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi-Kurashige, Y.; Tsujikawa, A.; Oishi, A.; Ooto, S.; Yamashiro, K.; Tamura, H.; Nakata, I.; Ueda-Arakawa, N.; Yoshimura, N. Relationship between retinal morphological findings and visual function in age-related macular degeneration. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 250, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaratnasingam, C.; Messinger, J.D.; Sloan, K.R.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Freund, K.B.; Curcio, C.A. Histologic and Optical Coherence Tomographic Correlates in Drusenoid Pigment Epithelium Detachment in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Heussen, F.M.; Hariri, A.; Keane, P.A.; Sadda, S.R. Optical coherence tomography-based observation of the natural history of drusenoid lesion in eyes with dry age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Jung, J.J.; Curcio, C.A.; Balaratnasingam, C.; Gallego-Pinazo, R.; Dolz-Marco, R.; Freund, K.B.; Yannuzzi, L.A. Intraretinal Hyperreflective Foci in Acquired Vitelliform Lesions of the Macula: Clinical and Histologic Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 164, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uji, A.; Murakami, T.; Nishijima, K.; Akagi, T.; Horii, T.; Arakawa, N.; Muraoka, Y.; Ellabban, A.A.; Yoshimura, N. Association between hyperreflective foci in the outer retina, status of photoreceptor layer, and visual acuity in diabetic macular edema. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 153, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumüller, S.; Issa, P.C.; Scholl, H.P.N.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Holz, F.G. Outer retinal hyperreflective spots on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in macular telangiectasia type 2. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Leong, B.; Messinger, J.D.; Kar, D.; Ach, T.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Freund, K.B.; Curcio, C.A. Hyperreflective Foci, Optical Coherence Tomography Progression Indicators in Age-Related Macular Degeneration, Include Transdifferentiated Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Sadeghipour, A.; Gerendas, B.S.; Waldstein, S.M.; Bogunović, H. Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 67, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegl, T.; Bogunovic, H.; Klimscha, S.; Seeböck, P.; Sadeghipour, A.; Gerendas, B.; Waldstein, S.M.; Langs, G.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Fully Automated Segmentation of Hyperreflective Foci in Optical Coherence Tomography Images. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.03278. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Jansonius, N.M.; Chen, H.; Los, L.I. Hyperreflective Dots on OCT as a Predictor of Treatment Outcome in Diabetic Macular Edema: A Systematic Review. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2022, 6, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Kwapong, W.R.; Ying, J.; Lu, J.; Ma, S.; Yan, Q.; Yi, Q.; Zhao, Y. Automated evaluation of retinal hyperreflective foci changes in diabetic macular edema patients before and after intravitreal injection. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1280714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuwobi, I.P.; Ji, Z.; Fan, W.; Yuan, S.; Bekalo, L.; Chen, Q. Automated Quantification of Hyperreflective Foci in SD-OCT With Diabetic Retinopathy. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midena, E.; Toto, L.; Frizziero, L.; Covello, G.; Torresin, T.; Midena, G.; Danieli, L.; Pilotto, E.; Figus, M.; Mariotti, C.; et al. Validation of an Automated Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for the Quantification of Major OCT Parameters in Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xie, S.; Niu, S.; Ji, Z.; Fan, W.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q. Hyper-reflective foci segmentation in SD-OCT retinal images with diabetic retinopathy using deep convolutional neural networks. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 4502–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciu, C.I.; Marginean, A.; Suciu, V.I.; Muntean, G.A.; Nicoară, S.D. Diabetic Macular Edema Optical Coherence Tomography Biomarkers Detected with EfficientNetV2B1 and ConvNeXt. Diagnostics 2023, 14, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midena, E.; Torresin, T.; Velotta, E.; Pilotto, E.; Parrozzani, R.; Frizziero, L. OCT Hyperreflective Retinal Foci in Diabetic Retinopathy: A Semi-Automatic Detection Comparative Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 613051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, L.; Kovács, A.; Grósz, T.; Thury, G.; Hadarits, F.; Dégi, R.; Dombi, J. Automatic segmentation of hyperreflective foci in OCT images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 178, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monemian, M.; Daneshmand, P.G.; Rakhshani, S.; Rabbani, H. A new texture-based labeling framework for hyper-reflective foci identification in retinal optical coherence tomography images. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toto, L.; Romano, A.; Pavan, M.; Degl’Innocenti, D.; Olivotto, V.; Formenti, F.; Viggiano, P.; Midena, E.; Mastropasqua, R. A deep learning approach to hard exudates detection and disorganization of retinal inner layers identification on OCT images. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunovic, H.; Montuoro, A.; Baratsits, M.; Karantonis, M.G.; Waldstein, S.M.; Schlanitz, F.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Machine Learning of the Progression of Intermediate Age-Related Macular Degeneration Based on OCT Imaging. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, BIO141–BIO150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schulthess, E.L.; Maunz, A.; Chakravarthy, U.; Holekamp, N.; Pauleikhoff, D.; Patel, K.; Bachmeier, I.; Yu, S.; Cohen, Y.; Scherb, M.P.; et al. Intraretinal Hyper-Reflective Foci Are Almost Universally Present and Co-Localize With Intraretinal Fluid in Diabetic Macular Edema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Bogunovic, H.; Grechenig, C.; Bui, P.; Fabianska, M.; Waldstein, S.; Reiter, G.S. Role of Deep Learning-Quantified Hyperreflective Foci for the Prediction of Geographic Atrophy Progression. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 216, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, W.; Lin, T.; Los, L.I.; Yao, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. Algorithm for Detection and Quantification of Hyperreflective Dots on Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Macular Edema. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 688986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Kumar, P.; Tulsani, A.; Chakrapani, P.K.; Maiya, G.; Bhandary, S.V.; Mayya, V.; Pathan, S.; Achar, R.; Acharya, U.R. Fuzzy Logic-Based System for Identifying the Severity of Diabetic Macular Edema from OCT B-Scan Images Using DRIL, HRF, and Cystoids. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreur, V.; Altay, L.; van Asten, F.; Groenewoud, J.M.M.; Fauser, S.; Klevering, B.J.; Hoyng, C.B.; de Jong, E.K. Hyperreflective foci on optical coherence tomography associate with treatment outcome for anti-VEGF in patients with diabetic macular edema. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, F.; Zhang, X. Hyperreflective foci in OCT image as a biomarker of poor prognosis in diabetic macular edema patients treating with Conbercept in China. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019, 19, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Yang, C.H.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Yang, C.M.; Ho, T.C.; Lai, T.T. Hyperreflective foci in predicting the treatment outcomes of diabetic macular oedema after anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Kim, D.Y.; Chae, J.B. Association between Hyperreflective Foci on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography and Early Recurrence of Diabetic Macular Edema after Intravitreal Dexamethasone Implantation. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 3459164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.R.; Park, S.J.; Shin, J.P.; Park, D.H. Assessment of Hyperreflective Foci After Bevacizumab or Dexamethasone Treatment According to Duration of Macular Edema in Patients With Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion. Retina 2021, 41, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, K.; Reiter, G.S.; Steiner, I.; Deák, G.; Mohamed, H.; Schürer-Waldheim, S.; Gumpinger, M.; Bogunović, H.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Topographic and quantitative correlation of structure and function using deep learning in subclinical biomarkers of intermediate age-related macular degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, G.S.; Bogunovic, H.; Schlanitz, F.; Vogl, W.D.; Seeböck, P.; Ramazanova, D.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Point-to-point associations of drusen and hyperreflective foci volumes with retinal sensitivity in non-exudative age-related macular degeneration. Eye 2023, 37, 3582–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenbury, J.G.; Folgar, F.A.; O’Connell, R.V.; Chiu, S.J.; Farsiu, S.; Toth, C.A. Progression of intermediate age-related macular degeneration with proliferation and inner retinal migration of hyperreflective foci. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitnilska, V.; Kersten, E.; Altay, L.; Schick, T.; Enders, P.; de Jong, E.K.; Langmann, T.; Hoyng, C.B.; den Hollander, A.I.; Fauser, S. Major Predictive Factors for Progression of Early to Late Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmologica 2020, 243, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, O.; Barayev, E.; Nemet, A.Y.; Geffen, N.; Vainer, I.; Mimouni, M. Prognostic Value of Hyperreflective Foci in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Treated with Bevacizumab. Retina 2016, 36, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, T.; Murakami, T.; Suzuma, K.; Dodo, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Tsujikawa, A. Hyperreflective Foci in the Outer Retinal Layers as a Predictor of the Functional Efficacy of Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.Y.; Jee, D.; Kwon, J.W. Characteristics of diabetic macular edema patients refractory to anti-VEGF treatments and a dexamethasone implant. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meduri, A.; Oliverio, G.W.; Trombetta, L.; Giordano, M.; Inferrera, L.; Trombetta, C.J. Optical Coherence Tomography Predictors of Favorable Functional Response in Naïve Diabetic Macular Edema Eyes Treated with Dexamethasone Implants as a First-Line Agent. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 2021, 6639418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zur, D.; Iglicki, M.; Busch, C.; Invernizzi, A.; Mariussi, M.; Loewenstein, A.; International Retina Group. OCT Biomarkers as Functional Outcome Predictors in Diabetic Macular Edema Treated with Dexamethasone Implant. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziralli, I.; Theodossiadis, P.; Parikakis, E.; Dimitriou, E.; Xirou, T.; Theodossiadis, G.; Kabanarou, S.A. Dexamethasone Intravitreal Implant in Diabetic Macular Edema: Real-Life Data from a Prospective Study and Predictive Factors for Visual Outcome. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.S.; Chae, J.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y. Association Between Hyperreflective Dots on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Macular Edema and Response to Treatment. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 5958–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, A.; Wiedemann, P. Müller glial cells in retinal disease. Ophthalmologica 2012, 227, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatsu, H.; Yamashita, H.; Noma, H.; Mimura, T.; Yamashita, T.; Hori, S. Increased levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6 in the aqueous humor of diabetics with macular edema. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 133, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatsu, H.; Noma, H.; Mimura, T.; Eguchi, S.; Hori, S. Association of vitreous inflammatory factors with diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midena, E.; Frizziero, L.; Midena, G.; Pilotto, E. Intraocular fluid biomarkers (liquid biopsy) in human diabetic retinopathy. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 3549–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsaygili, C.; Duru, N. Comparison of Intravitreal Dexamethasone Implant and Aflibercept in Patients with Treatment-Naive Diabetic Macular Edema with Serous Retinal Detachment. Retina 2020, 40, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weingessel, B.; Miháltz, K.; Gleiss, A.; Sulzbacher, F.; Schütze, C.; Vécsei-Marlovits, P.V. Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema with Intravitreal Antivascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Prompt versus Deferred Focal Laser during Long-Term Follow-Up and Identification of Prognostic Retinal Markers. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2018, 3082560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuschen, J.N.; Schuman, S.G.; Winter, K.P.; McCall, M.N.; Wong, W.T.; Chew, E.Y.; Hwang, T.; Srivastava, S.; Sarin, N.; Clemons, T.; et al. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography characteristics of intermediate age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Witkin, A.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Schuman, J.S.; Duker, J.S. Documentation of intraretinal retinal pigment epithelium migration via high-speed ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodjikian, L.; Bellocq, D.; Bandello, F.; Loewenstein, A.; Chakravarthy, U.; Koh, A.; Augustin, A.; de Smet, M.D.; Chhablani, J.; Tufail, A.; et al. First-line treatment algorithm and guidelines in center-involving diabetic macular edema. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 29, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassisi, M.; Fan, W.; Shi, Y.; Lei, J.; Borrelli, E.; Ip, M.; Sadda, S.R. Quantity of Intraretinal Hyperreflective Foci in Patients With Intermediate Age-Related Macular Degeneration Correlates with 1-Year Progression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuwobi, I.P.; Shen, Y.; Li, M.; Fan, W.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Q. Hyperreflective Foci Enhancement in a Combined Spatial-Transform Domain for SD-OCT Images. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Denomination | Origin | Dimension | Reflectivity | Back-Shadowing | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vascular V-HRF | Vascular structures | >30 µm | Intermediate, similar to RNFL | Yes | Inner retina |
| Exudative E-HRF | Exudation/extravasated lipoproteins and/or proteins | >30 µm | High, similar to RPE | Yes | Non-uniform distribution, particularly pronounced around the outer plexiform layer and also observed along the cyst walls |
| Pigmentary P-HRF | Degeneration/RPE- derived cells | Variable dimension and conformation | High, similar to RPE | Yes | Predominantly in the outer retinal layers, especially overlying drusen |
| Inflammatory I-HRF | Neuroinflammation/microglia cells | <30 µm | Intermediate, similar to RNFL | No | Throughout all retinal layers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frizziero, L.; Midena, G.; Danieli, L.; Torresin, T.; Perfetto, A.; Parrozzani, R.; Pilotto, E.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective Retinal Foci (HRF): Definition and Role of an Invaluable OCT Sign. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093021
Frizziero L, Midena G, Danieli L, Torresin T, Perfetto A, Parrozzani R, Pilotto E, Midena E. Hyperreflective Retinal Foci (HRF): Definition and Role of an Invaluable OCT Sign. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093021
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrizziero, Luisa, Giulia Midena, Luca Danieli, Tommaso Torresin, Antonio Perfetto, Raffaele Parrozzani, Elisabetta Pilotto, and Edoardo Midena. 2025. "Hyperreflective Retinal Foci (HRF): Definition and Role of an Invaluable OCT Sign" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093021
APA StyleFrizziero, L., Midena, G., Danieli, L., Torresin, T., Perfetto, A., Parrozzani, R., Pilotto, E., & Midena, E. (2025). Hyperreflective Retinal Foci (HRF): Definition and Role of an Invaluable OCT Sign. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093021









