Unique MicroRNA and mRNA Interactions in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. EGFR Mutation
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Expression Analysis of MicroRNAs
2.5. Expression Analysis of Messenger RNAs
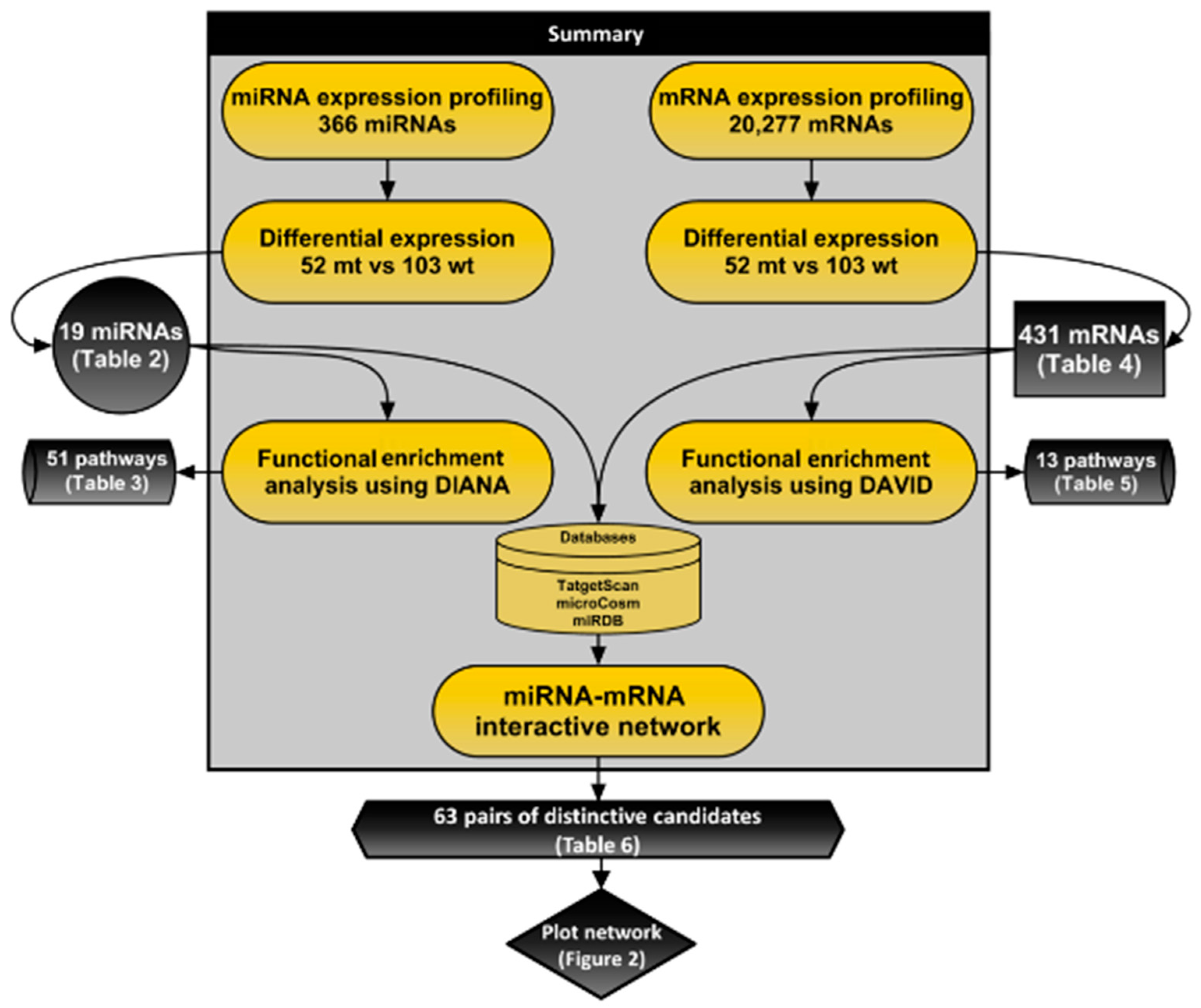
2.6. Integrative Analysis
2.7. Functional Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design of the Study and Clinicopathological Characteristics
3.2. Expression Profiling and Functional Analysis of MicroRNAs
3.3. Expression Profiling and Functional Enrichment Analysis of Messenger RNAs
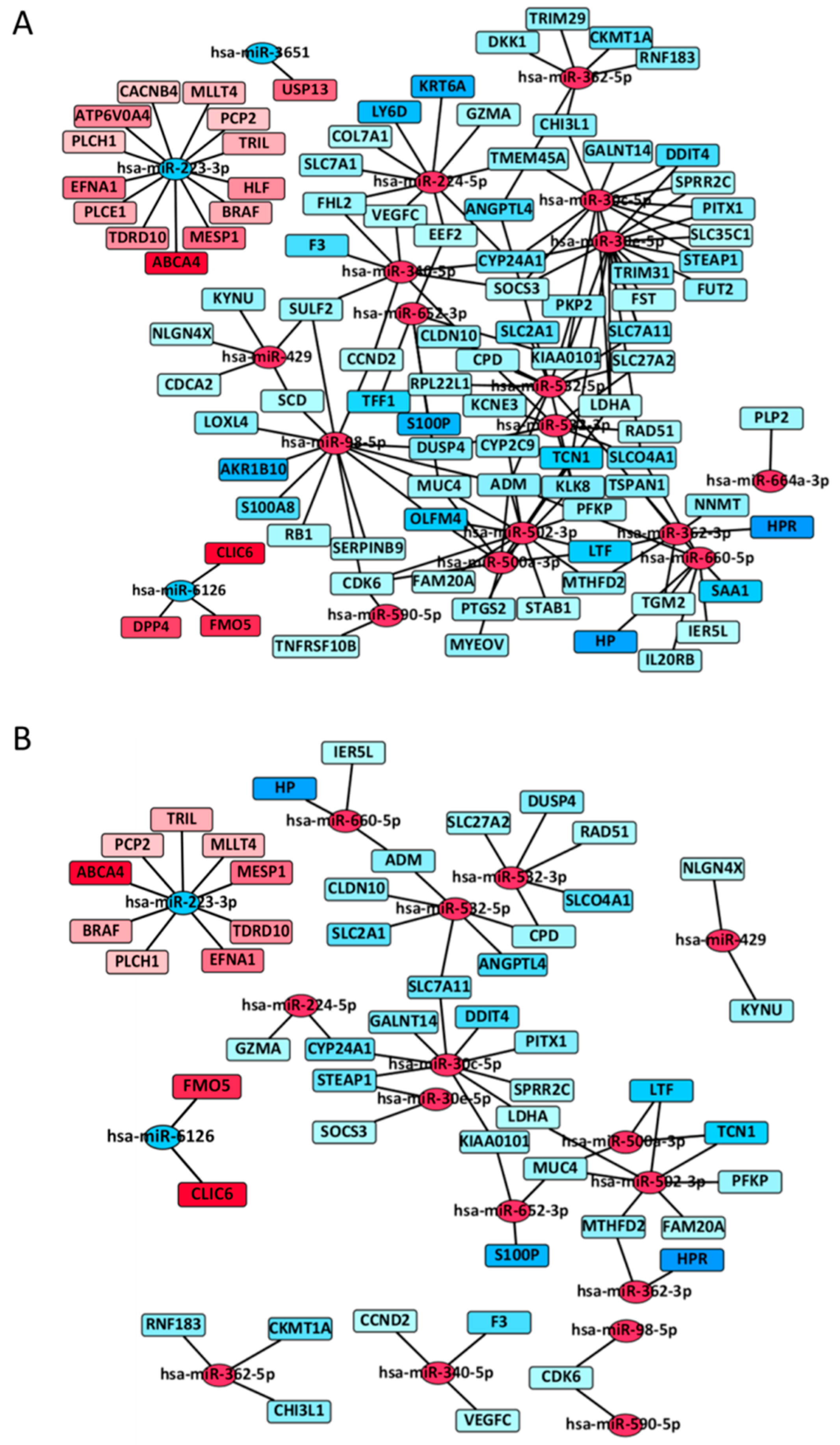
3.4. MiRNA-mRNA Interactive Network
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K. Lung cancer: Understanding its molecular pathology and the 2015 WHO classification. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.G.; Jänne, P.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Hsu, P.P.; Awad, M.M.; Engelman, J.A. Tyrosine kinase gene rearrangements in epithelial malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 772–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. Mechanistic insight into ALK receptor tyrosine kinase in human cancer biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K.; Soda, M.; Togashi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Sakata, S.; Hatano, S.; Asaka, R.; Hamanaka, W.; Ninomiya, H.; Uehara, H.; et al. RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.I.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun Ha, S.; Choi, S.-J.; Ho Cho, J.; Joo Choi, H.; Lee, J.; Jung, K.; Irwin, D.; Liu, X.; Lira, M.E.; Mao, M.; et al. Lung cancer in never-smoker Asian females is driven by oncogenic mutations, most often involving EGFR. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5465–5474. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Inamura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Matsubara, O. Is the epidermal growth factor receptor status in lung cancers reflected in clinicopathologic features? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veale, D.; Ashcroft, T.; Marsh, C.; Gibson, G.J.; Harris, A.L. Epidermal growth factor receptors in non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1987, 55, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.V.; Bell, D.W.; Settleman, J.; Haber, D.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, E.; Gazdar, A. Pathogenesis of lung cancer signalling pathways: Roadmap for therapies. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2009, 4, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.; Peruzzi, P.P.; Lawler, S. MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajewsky, N. MicroRNA target predictions in animals. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Ishikawa, Y. MicroRNA in lung cancer: Novel biomarkers and potential tools for treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.W.; Mendell, J.T. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Fabbri, M.; Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, Z.; Jaiswal, B.S.; Stinson, J.; Janakiraman, V.; Bhatt, D.; Stern, H.M.; Yue, P.; Haverty, P.M.; Bourgon, R.; Zheng, J.; et al. Diverse somatic mutation patterns and pathway alterations in human cancers. Nature 2010, 466, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—MicroRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, B.M.; Robles, A.I.; Harris, C.C. Genetic variation in microRNA networks: The implications for cancer research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 10, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.M.; Liu, K.Q.; Zhu, G.; He, F.; Duval, B.; Richer, J.M.; Huang, D.S.; Jiang, C.J.; Hao, J.K.; Chen, L. Identifying cancer-related microRNAs based on gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Nomura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Hiramatsu, M.; Okui, M.; Satoh, Y.; Okumura, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Tsuchiya, E.; et al. Up-regulation of PTEN at the transcriptional level is an adverse prognostic factor in female lung adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer 2007, 57, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Romero, P. Pre-processing and differential expression analysis of Agilent microRNA arrays using the AgiMicroRNA Bioconductor library. BMC Genomics 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, G.K. Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2004, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, G.K. Limma: Linear Models for Microarray Data; Springer: New York, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 397–420. [Google Scholar]
- Vila-casadesús, M.; Gironella, M. MiRComb: An R package to analyse miRNA-mRNA interactions. Package‘miRComb’. 2016. Available online: http://mircomb.sourceforge.net (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- Rehmsmeier, M.; Steffen, P.; Höchsmann, M.; Giegerich, R.; Ho, M. Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. Spring 2004, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.; Wang, X. MiRDB: An online resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Kir, J.; Liu, D.; Bryant, D.; Guo, Y.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R. A DAVID bioinformatics resources: Expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjaanæs, M.M.; Halvorsen, A.R.; Solberg, S.; Jørgensen, L.; Dragani, T.A.; Galvan, A.; Colombo, F.; Anderlini, M.; Pastorino, U.; Kure, E.; et al. Unique microRNA-profiles in EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouelle, D.E.; Zindy, F.; Ashmun, R.A.; Sherr, C.J. Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell 1995, 83, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Getz, G.; Wheeler, D.A.; Mardis, E.R.; McLellan, M.D.; Cibulskis, K.; Sougnez, C.; Greulich, H.; Muzny, D.M.; Morgan, M.B.; et al. Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2008, 455, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hida, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Achiwa, H.; Muramatsu, H.; Kozaki, K.; Nakamura, S.; Ogawa, M.; Mitsudomi, T.; Sugiura, T.; Takahashi, T. Increased expression of cyclooxygenase 2 occurs frequently in human lung cancers, specifically in adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998, 3761–3764. [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik, A.; Rosen, L.S.; Tolaney, S.M.; Tolcher, A.W.; Goldman, J.W.; Gandhi, L.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Beeram, M.; Rasco, D.W.; Hilton, J.F.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Abemaciclib, an inhibitor of CDK4 and CDK6, for patients with breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and other solid tumors. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitale, D.; Gong, Y.; Taylor, B.S.; Broderick, S.; Brennan, C.; Somwar, R.; Golas, B.; Wang, L.; Motoi, N.; Szoke, J.; et al. An integrated genomic analysis of lung cancer reveals loss of DUSP4 in EGFR-mutant tumors. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Rong, X.; Chen, J.; Zheng, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Luo, R.; Zhao, P.; Ruan, J. MiR-661 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by directly inhibiting RB1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila-Casadesús, M.; Gironella, M.; Lozano, J.J. MiRComb: An R package to analyse miRNA–mRNA interactions. Examples across five digestive cancers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokutan-Kurata, M.; Yoshizawa, A.; Sumiyoshi, S.; Sonobe, M.; Menju, T.; Momose, M.; Koyama, M.; Shigeto, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Lung adenocarcinoma with MUC4 expression is associated with smoking status, HER2 protein expression, and poor prognosis: Clinicopathologic analysis of 338 cases. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.-G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pak, M.G.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, W.J.; Shin, D.H.; Roh, M.S. Unique microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma groups according to major TKI sensitive EGFR mutation status. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Kamoto, Y.; Sakai, A.; Sasai, K.; Hayashi, T.; Toyooka, S.; Katayama, H. Unique circulating microRNAs in relation to EGFR mutation status in Japanese smoker male with lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114685–114697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, G.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Yuan, A.; Cheng, C.L.; Wang, C.H.; Terng, H.J.; Kao, S.F.; et al. A five-gene signature and clinical outcome in non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z. MiR-223 reverses the resistance of EGFR-TKIs through IGF1R/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Meng, W.; Sun, H.-L.; Kim, T.; Ye, Z.; Fassan, M.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Li, B.; Vicentini, C.; Peng, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-224 promotes tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4288–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A.; Di Maria, M.V.; Veve, R.; Bremnes, R.M.; Barón, A.E.; Zeng, C.; Franklin, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: Correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethune, G.; Bethune, D.; Ridgway, N.; Xu, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in lung cancer: An overview and update. J. Thorac. Dis. 2010, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rikova, K.; Guo, A.; Zeng, Q.; Possemato, A.; Yu, J.; Haack, H.; Nardone, J.; Lee, K.; Reeves, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 2007, 131, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chaib, I.; Karachaliou, N.; Pilotto, S.; Codony Servat, J.; Cai, X.; Li, X.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Servat, C.C.; Yang, J.; Hu, C.; et al. Co-activation of STAT3 and YES-associated protein 1 (YAP1) pathway in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D. The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Mao, D.; Hua, G.; Lv, X.; Chen, X.; Angeletti, P.C.; Dong, J.; Remmenga, S.W.; Rodabaugh, K.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1426–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yatabe, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Mitsudomi, T. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene amplification is acquired in association with tumor progression of EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2106–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.P.; Lau, N.C.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Grimson, A.; Schelter, J.M.; Castle, J.; Bartel, D.P.; Linsley, P.S.; Johnson, J.M. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 2005, 433, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Tang, W.; Du, P.; Wang, G.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, J.; Cui, L. Identifying microRNA–mRNA regulatory network in colorectal cancer by a combination of expression profile and bioinformatics analysis. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. An integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expressions in non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e0026502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, A.J.; Thorsson, V.; Shmulevich, I.; Reynolds, S.M.; Miller, M.; Bernard, B.; Hinoue, T.; Laird, P.W.; Curtis, C.; Shen, H.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 513, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, X.; Luo, G.; Zhou, X.; Luo, W.; Wu, X.; Zhong, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, J. Rad51 in regulating the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer with different epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status. Thorac. Cancer 2016, 7, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Number of Patients (%) | EGFR | p Values 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation 52 (34%) | Wild-Type 103 (66%) | |||
| Age (years) | 0.30 | |||
| <65 | 96 (62%) | 29 (56%) | 67 (65%) | |
| ≥65 | 59 (38%) | 23 (44%) | 36 (35%) | |
| Gender | 0.13 | |||
| Males | 77 (50%) | 21 (40%) | 56 (54%) | |
| Females | 78 (50%) | 31 (60%) | 47 (46%) | |
| Smoking status | 0.40 | |||
| Never | 81 (52%) | 30 (58%) | 51 (50%) | |
| Ever | 74 (48%) | 22 (42%) | 52 (50%) | |
| Cumulative smoking | 0.02 | |||
| Pack-years < 40 | 123 (79%) | 47 (90%) | 76 (74%) | |
| Pack-years ≥ 40 | 32 (21%) | 5 (10%) | 24 (26%) | |
| Size (mm) | 0.23 | |||
| <30 | 91 (59%) | 27 (52%) | 64 (62%) | |
| ≥30 | 64 (41%) | 25 (48%) | 39 (38%) | |
| Tumor differentiation | <0.0001 | |||
| Well | 60 (39%) | 37 (72%) | 23 (22%) | |
| Moderate–poor | 95 (61%) | 15 (29%) | 80 (78%) | |
| Pathological stage | 0.39 | |||
| I | 93 (60%) | 34 (65%) | 59 (57%) | |
| II–IV | 62 (40%) | 18 (35%) | 44 (43%) | |
| miRNA | FC 1 | p Values 2 | Up or Down |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-532-3p | 3.52 | 1.32E–04 | Up |
| miR-362-3p | 3.29 | 1.02E–04 | Up |
| miR-340-5p | 3.25 | 3.44E–03 | Up |
| miR-500a-3p | 2.93 | 1.32E–04 | Up |
| miR-224-5p | 2.83 | 1.49E–02 | Up |
| miR-362-5p | 2.82 | 1.04E–03 | Up |
| miR-502-3p | 2.65 | 1.66E–03 | Up |
| miR-590-5p | 2.37 | 1.33E–02 | Up |
| miR-664a-3p | 2.31 | 4.86E–02 | Up |
| miR-652-3p | 2.12 | 1.37E–02 | Up |
| miR-532-5p | 2.05 | 1.91E–03 | Up |
| miR-429 | 1.92 | 1.68E–02 | Up |
| miR-660-5p | 1.70 | 1.14E–02 | Up |
| miR-30e-5p | 1.38 | 3.44E–03 | Up |
| miR-30c-5p | 1.34 | 3.09E–02 | Up |
| miR-98-5p | 1.34 | 3.27E–02 | Up |
| miR-6126 | −1.25 | 4.86E–02 | Down |
| miR-3651 | −1.36 | 4.57E–02 | Down |
| miR-223-3p | −1.66 | 1.37E–02 | Down |
| KEGG Pathway | p Values | n1 of miRNAs |
|---|---|---|
| Hippo signaling pathway | 2.38E–08 | 18 |
| Pathways in cancer | 4.33E–05 | 18 |
| FoxO signaling pathway | 2.38E–08 | 17 |
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | 3.84E–07 | 17 |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 2.44E–04 | 17 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 4.43E–04 | 17 |
| Glioma | 9.11E–04 | 17 |
| T-cell receptor signaling pathway | 1.42E–03 | 17 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 1.70E–03 | 17 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 2.80E–03 | 17 |
| Prolactin signaling pathway | 3.26E–03 | 17 |
| Viral carcinogenesis | 3.26E–03 | 17 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 3.50E–03 | 17 |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | 3.75E–03 | 17 |
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 3.79E–03 | 17 |
| cAMP signaling pathway | 4.95E–03 | 17 |
| Melanoma | 7.01E–03 | 17 |
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | 7.40E–03 | 17 |
| Dorsoventral axis formation | 1.99E–02 | 17 |
| Wnt signaling pathway | 2.59E–02 | 17 |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | 2.80E–02 | 17 |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | 2.82E–02 | 17 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | 8.42E–08 | 16 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | 1.36E–07 | 16 |
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | 3.26E–07 | 16 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 3.34E–05 | 16 |
| Ras signaling pathway | 8.22E–05 | 16 |
| ErbB signaling pathway | 1.12E–04 | 16 |
| GABAergic synapse | 3.59E–04 | 16 |
| Focal adhesion | 8.84E–04 | 16 |
| mRNA | FC 1 | p Values 2 | Up or Down |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRRC75B | 2.35 | 2.77E–13 | Up |
| EGFR | 1.88 | 1.78E–11 | Up |
| KIAA0319L | 1.65 | 2.08E–10 | Up |
| CA10 | 2.75 | 2.31E–10 | Up |
| USP13 | 1.82 | 2.31E–10 | Up |
| CECR2 | 1.65 | 2.31E–10 | Up |
| TBXT | 1.63 | 2.54E–10 | Up |
| LCT | 1.83 | 5.56E–09 | Up |
| MYBPHL | 3.44 | 6.00E–09 | Up |
| GGTLC2 | 2.15 | 9.00E–09 | Up |
| GGTLC1 | 2.77 | 1.47E–08 | Up |
| FNDC10 | 2.51 | 1.74E–08 | Up |
| ATP13A4 | 3.10 | 1.86E–08 | Up |
| DDX21 | −1.60 | 2.41E–08 | Down |
| SCUBE2 | 2.38 | 2.67E–08 | Up |
| APOH | 3.24 | 1.40E–07 | Up |
| SERPINA3 | −3.89 | 1.49E–07 | Down |
| GFRA3 | 2.85 | 1.58E–07 | Up |
| MEGF6 | 1.88 | 1.58E–07 | Up |
| SLC41A1 | 1.67 | 1.95E–07 | Up |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | p Values | n1 | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pathways in cancer | 4.70E–03 | 19 | COL4A4,FZD9,EGFR,CEBPA,COL4A3,FGFR3,PTGS2,BRAF,EGLN3,CDK6,RB1,BIRC3,DAPK2,RAD51,VEGFC,CBLC,FZD10,WNT3,SLC2A1 |
| Protein digestion and absorption | 1.00E–03 | 9 | COL4A4,COL4A3,COL21A1,COL7A1,KCNK5,PRSS3,PRSS1,DPP4,KCNE3 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | 5.69E–04 | 8 | AKR1C3,GPX2,PTGS2,CYP2B6,CYP2C9,ALOX15B,PLA2G1B,GGT1 |
| Hepatitis C | 3.64E–02 | 8 | EGFR,OCLN,BRAF,CLDN3,SOCS3,CLDN2,CLDN10,OAS1 |
| Wnt signaling pathway | 4.30E–02 | 8 | FZD9,FZD10,WNT3,DKK1,CCND2,VANGL2,BAMBI,DAAM2 |
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 3.69E–03 | 7 | GLS2,EGFR,FGFR3,GLS,SLC2A1,PFKP,PGAM2 |
| Small-cell lung cancer | 4.88E–02 | 6 | COL4A4,COL4A3,PTGS2,CDK6,RB1,BIRC3 |
| Bladder cancer | 1.50E–02 | 5 | EGFR,FGFR3,BRAF,RB1,DAPK2 |
| Non-small-cell lung cancer | 4.17E–02 | 5 | EGFR,BRAF,CDK6,RB1,ALK |
| Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 2.96E–02 | 4 | NT5M,ENPP3,QPRT,NNMT |
| Galactose metabolism | 3.23E–02 | 4 | AKR1B10,AKR1B1,PFKP,LCT |
| Fructose and mannose metabolism | 3.82E–02 | 4 | GMPPB,AKR1B10,AKR1B1,PFKP |
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 4.79E–02 | 4 | GLS2,GLS,CPS1,RIMKLA |
| miRNA | FC_miRNA 1 | mRNA | FC_mRNA 1 | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-502-3p | Up | MTHFD2 | Down | 1.00E–09 |
| miR-502-3p | Up | LTF | Down | 1.20E–07 |
| miR-502-3p | Up | PFKP | Down | 2.11E–07 |
| miR-30c-5p | Up | GALNT14 | Down | 5.85E–07 |
| miR-30c-5p | Up | STEAP1 | Down | 6.07E–07 |
| miR-532-3p | Up | CPD | Down | 7.25E–07 |
| miR-502-3p | Up | LDHA | Down | 9.39E–07 |
| miR-223-3p | Down | BRAF | Up | 1.36E–06 |
| miR-6126 | Down | CLIC6 | Up | 1.92E–06 |
| miR-30c-5p | Up | KIAA0101 | Down | 3.04E–06 |
| miR-532-5p | Up | CPD | Down | 3.19E–06 |
| miR-532-3p | Up | RAD51 | Down | 5.83E–06 |
| miR-532-3p | Up | DUSP4 | Down | 6.70E–06 |
| miR-500a-3p | Up | LTF | Down | 1.17E–05 |
| miR-502-3p | Up | MUC4 | Down | 1.71E–05 |
| miR-223-3p | Down | PLCH1 | Up | 1.79E–05 |
| miR-532-5p | Up | ANGPTL4 | Down | 1.83E–05 |
| miR-532-5p | Up | CLDN10 | Down | 2.02E–05 |
| miR-6126 | Down | FMO5 | Up | 2.57E–05 |
| miR-660-5p | Up | IER5L | Down | 3.69E–05 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subat, S.; Inamura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Nagano, H.; Okumura, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Unique MicroRNA and mRNA Interactions in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110419
Subat S, Inamura K, Ninomiya H, Nagano H, Okumura S, Ishikawa Y. Unique MicroRNA and mRNA Interactions in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(11):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110419
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubat, Sophia, Kentaro Inamura, Hironori Ninomiya, Hiroko Nagano, Sakae Okumura, and Yuichi Ishikawa. 2018. "Unique MicroRNA and mRNA Interactions in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 11: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110419
APA StyleSubat, S., Inamura, K., Ninomiya, H., Nagano, H., Okumura, S., & Ishikawa, Y. (2018). Unique MicroRNA and mRNA Interactions in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(11), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110419






