Computer-Aided Planning in Orthognathic Surgery: A Comparative Study with the Establishment of Burstone Analysis-Derived 3D Norms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Three-Dimensional Image Acquisition and Processing
2.2. Three-Dimensional Burstone Cephalometric Analysis
2.3. Three-Dimensional Versus 2D Norms
2.4. Outcome of Computer-Assisted Simulation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reliability Analysis
3.2. Three-Dimensional Facial Bone Norms
3.3. Three-Dimensional Facial Soft-Tissue Norms
3.4. Three-Dimensional Versus 2D Norms
3.5. Outcome of Computer-Assisted Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, J.J.; Shevchenko, L.; Gateno, J.; Teichgraeber, J.F.; Taylor, T.D.; Lasky, R.E.; English, J.D.; Kau, C.H.; McGrory, K.R. Outcome study of computer-aided surgical simulation in the treatment of patients with craniomaxillofacial deformities. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 2014–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gateno, J.; Xia, J.J.; Teichgraeber, J.F.; Christensen, A.M.; Lemoine, J.J.; Liebschner, M.A.; Gliddon, M.J.; Briggs, M.E. Clinical feasibility of computer-aided surgical simulation (CASS) in the treatment of complex cranio-maxillofacial deformities. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonic, D.; Pai, B.C.J.; Yamaguchi, K.; Chortrakarnkij, P.; Lin, H.H.; Lo, L.J. Computer-assisted orthognathic surgery for patients with cleft lip/palate: From traditional planning to three-dimensional surgical simulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denadai, R.; Chou, P.Y.; Pai, B.C.J.; Chen, C.; Lin, C.C.H.; Huang, C.S.; Chen, Y.R.; Lo, L.J. Skeletofacial reconstruction for cleft-related deformities: Four decades of evolving cleft care. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1760. [Google Scholar]
- Bayome, M.; Park, J.H.; Kook, Y.A. New three-dimensional cephalometric analyses among adults with a skeletal Class I pattern and normal occlusion. Korean J. Orthod. 2013, 43, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z. Norms of McNamara’s cephalometric analysis on lateral view of 3D CT imaging in adults from Northeast China. J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2014, 23, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, L.K.; Chan, Y.M.; Jayaratne, Y.S.; Lo, J. Three-dimensional cephalometric norms of Chinese adults in Hong Kong with balanced facial profile. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2011, 112, e56–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Ho, C.T.; Lin, H.H.; Lo, L.J. Three-dimensional cephalometry for orthognathic planning: Normative data and analyses. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdettin, L.; Aksoy, S.; Öz, U.; Orhan, K. Three-dimensional cephalometric norms of Turkish Cypriots using CBCT images reconstructed from a volumetric rendering program in vivo. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.W.; Chau, A.C.; Hägg, U. 3D CBCT McNamaras cephalometric analysis in an adult southern Chinese population. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstone, C.J.; James, R.B.; Legan, H.; Murphy, G.A.; Norton, L.A. Cephalometrics for orthognathic surgery. J. Oral Surg. 1978, 36, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Legan, H.L.; Burstone, C.J. Soft tissue cephalometric analysis for orthognathic surgery. J Oral Surg. 1980, 38, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al Taki, A.; Yaqoub, S.; Hassan, M. Legan-burstone soft tissue profile values in a Circassian adult sample. J. Orthod. Sci. 2018, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perović, T.; Blažej, Z. Male and Female Characteristics of facial soft tissue thickness in different orthodontic malocclusions evaluated by cephalometric radiography. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3415–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, R.; Alexander, M. “Are we similar to caucasians”: Orthognathic surgery for north Indians. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2015, 14, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebi, A.A.; Tan, E.; Gelgor, I.E.; Colak, T.; Ayyildiz, E. Comparison of soft tissue cephalometric norms between Turkish and European-American adults. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 806203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, T.; Baysal, A.; Yagci, A.; Sigler, L.M.; McNamara, J.A., Jr. Ethnic differences in the soft tissue profiles of Turkish and European-American young adults with normal occlusions and well-balanced faces. Eur. J. Orthod. 2012, 34, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokić, D.; Jokić, D.; Uglešić, V.; Macan, D.; Knežević, P. Soft tissue changes after mandibular setback and bimaxillary surgery in Class III patients. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarakati, S.F.; Baidas, L.F. Orthognathic surgical norms for a sample of Saudi adults: Hard tissue measurements. Saudi Dent. J. 2010, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Kalra, J.P. Soft tissue cephalometric norms for a North Indian population group using Legan and Burstone analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.O.; Walia, C.S.; Borle, R.M.; Chaoji, K.H.; Rajan, R.; Datarkar, A.N. Cephalometric norms for Central Indian population using Burstone and Legan analysis. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2011, 22, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, K.V.; Reddy, V.V.; Tauro, D.P. Establishment of Cephalometric Norms for the South Indian (Karnataka) Population Based on Burstone’s Analysis. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2010, 9, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcalde, R.E.; Jinno, T.; Pogrel, M.A.; Matsumura, T. Cephalometric norms in Japanese adults. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1998, 56, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, K.K.; Ho, K.K.; Keng, S.B.; Ho, K.H. Soft-tissue cephalometric norms in Chinese adults with esthetic facial profiles. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1992, 50, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Niddam, J.; Noel, W.; Hersant, B.; Meningaud, J.P. Comparison of aesthetic facial criteria between Caucasian and East Asian female populations: An esthetic surgeon’s perspective. Asian J. Surg. 2018, 41, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ludlow, J.B.; Mol, A.; Cevidanes, L. Comparison of conventional and cone beam CT synthesized cephalograms. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2007, 36, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vlijmen, O.J.C.; Maal, T.; Bergé, S.J.; Bron-khorst, E.M.; Katsaros, C.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. A comparison between two-dimensional and three-dimensional cephalometry on frontal radiographs and on cone beam computed tomography scans of human skulls. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2009, 117, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlijmen, O.J.C.; Maal, T.; Bergé, S.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Katsaros, C.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. A comparison between 2D and 3D cephalometry on CBCT scans of human skulls. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Y.; Lin, H.H.; Lo, L.J.; Ho, C.T. Postoperative outcomes of two- and three-dimensional planning in orthognathic surgery: A comparative study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2017, 70, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.T.; Lin, H.H.; Liou, E.J.; Lo, L.J. Three-dimensional surgical simulation improves the planning for correction of facial prognathism and asymmetry: A qualitative and quantitative study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Y.; Denadai, R.; Lin, H.H.; Ho, C.T.; Lo, L.J. The outcome of skeletofacial reconstruction with mandibular rotation for management of asymmetric skeletal class III deformity: A three-dimensional computer-assisted investigation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.H.; Chang, H.W.; Wang, C.H.; Kim, S.G.; Lo, L.J. Three-dimensional computer-assisted orthognathic surgery: Experience of 37 patients. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2015, 74, S118–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swennen, G.R.J.; Schutyser, F.A.C.; Hausamen, J.E. Three-Dimensional Cephalometry: A Color Atlas and Manual; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, L.G. Anthropometry of the Head and Face; Raven Pr: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.H.; Chuang, Y.F.; Weng, J.L.; Lo, L.J. Comparative validity and reproducibility study of various landmark-oriented reference planes in 3-dimensional computed tomographic analysis for patients receiving orthognathic surgery. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samizadeh, S.; Wu, W. Ideals of Facial Beauty amongst the Chinese Population: Results from a Large National Survey. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2018, 42, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samizadeh, S. The Ideals of Facial Beauty among Chinese Aesthetic Practitioners: Results from a Large National Survey. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Denadai, R.; Ho, C.T.; Lai, B.R.; Lo, L.J. Measuring patient-reported outcomes in orthognathic surgery: Linguistic and psychometric validation of the Mandarin Chinese version of FACE-Q instrument. Biomed. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, M.; Wall, G.; Greiff, L.; Rasmusson, L. Treatment outcome in orthognathic surgery—A prospective randomized blinded case-controlled comparison of planning accuracy in computer-assisted two- and three-dimensional planning techniques (part II). J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, M.; Wall, G.; Miranda-Burgos, P.; Rasmusson, L. Treatment outcome in orthognathic surgery—A prospective comparison of accuracy in computer assisted two and three-dimensional prediction techniques. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomlarptham, N.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Ko, E.W. Does two-dimensional vs. three-dimensional surgical simulation produce better surgical outcomes among patients with class III facial asymmetry? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.; Perry, S.; Liao, C.; Yang, Y. The relationship between the cranial base and jaw base in a Chinese population. Head Face Med. 2014, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Ko, E.W. Dentoskeletal parameters related to visual perception of facial asymmetry in patients with skeletal class III malocclusion after orthognathic surgery. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Son, W.; Kim, S.S. Hard-and soft-tissue profiles of the midface region in patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion using cone-beam computed tomography multiplanar-reconstructed image analysis. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moate, S.J.; Darendeliler, M.A. Cephalometric norms for the Chinese: A compilation of existing data. Aust. Orthod. J. 2002, 18, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooke, M.S.; Wei, S.H. A comparative study of southern Chinese and British Caucasian cephalometric standards. Angle Orhtod. 1989, 59, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Hagg, U.; Wu, J.; Yeung, S. Differences in dentofacial characteristics between southern versus northern Chinese adolescents. Aust. Orthod. J. 2011, 27, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; McNamara, J.A., Jr.; Sigler, L.M.; Baccetti, T. Comparison of craniofacial characteristics of typical Chinese and Caucasian young adults. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.F.; Chen, Y.F.; Yao, C.F.; Chen, Y.A.; Chen, Y.R. Long-term outcomes of bimaxillary surgery for treatment of asymmetric skeletal class III deformity using surgery-first approach. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.F.; Chiu, Y.T.; Huang, C.S.; Ko, E.W.; Chen, Y.R. Presurgical orthodontics versus no presurgical orthodontics: Treatment outcome of surgical-orthodontic correction for skeletal class III open bite. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 2074–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, E.J.W.; Chen, P.H.; Wang, U.C.; Yu, C.C.; Huang, C.S.; Chen, Y.R. Surgery-First Accelerated orthognathic surgery: Postoperative rapid orthodontic tooth movement. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Landmarks | Abbreviations | Definitions |
|---|---|---|
| Skeletal Landmark | ||
| Cranium | ||
| Orbitale | Or | The most inferior point of each infra-orbital rim |
| Porion | Po | The most superior point of each external acoustic meatus |
| Sella turcica | S | The center of the sella turcica on the midsagittal plane |
| Nasion | N | The junction between the nasal and frontonasal sutures |
| Basion | Ba | The most anterior point of the foramen magnum |
| Maxilla | ||
| Anterior nasal spine | ANS | The most anterior midpoint of the anterior nasal spine of the maxilla |
| Posterior nasal spine | PNS | The most posterior midpoint of the posterior nasal spine of the palatine bone |
| A point | A | The point of maximum concavity in the mid-line of the alveolar process of the maxilla |
| Posterior maxillary point | PMP | The point of maximum concavity of the posterior border of the palatine bone in the horizontal plane at both sides |
| Mandible | ||
| B point | B | The point of maximum concavity in the mid-line of the alveolar process of the mandible |
| Pogonion | Pog | The most anterior midpoint of the chin on the outline of the mandibular symphysis |
| Menton | Me | The most inferior midpoint of the chin on the outline of the mandibular symphysis |
| Gnathion | Gn | The most anterior and inferior point on the anterior margin of symphysis on the sagittal plane |
| Gonion | Go | Dropping a perpendicular from the intersection point of the tangent lines to the posterior margin of the mandibular vertical ramus and inferior margin of the mandibular body or horizontal ramus |
| Condylion | Co | The most postero-superior point of each mandibular condyle in the sagittal plane |
| Dentoalveolar Landmarks | ||
| U1 incisal tip | U1 | The midpoint between the crowns of the maxillary central incisors tip |
| U1 incisal apex | U1A | The incisor apex of the upper central incisor |
| L1 incisal tip | L1 | The incisal tip of the crown of lower central incisor |
| L1 incisor apex | L1A | The midpoint between the crowns of the mandibular central incisors tip |
| U6 cusp | UR6, UL6 | The most inferior point of the mesial cusp of the crown of each first upper molar in the profile plane |
| L6 cusp | LR6, LL6 | The most superior point of the mesial cusp of the crown of each first lower molar in the profile plane |
| Soft tissue Landmarks | ||
| Glabella | G | The most anterior midpoint on the front-to-orbital soft tissue contour |
| Columella | Cm | The point on each columella crest, level with the top of the corresponding nostril |
| Subnasale | Sn | The midpoint on the nasolabial soft tissue contour between the columella crest and the upper lip |
| Labiale superius | Ls | The midpoint of the vermilion line of the upper lip |
| Stomion | Stm (Stms, Stmi) | The midpoint of the horizontal labial fissure (Stms, upper lip; Stmi, lower lip) |
| Labiale inferius | Li | The midpoint of the vermilion line of the lower lip |
| Sublabiale | Si | The most posterior midpoint on the labiomental soft tissue contour that defines the border between the lower lip and the chin |
| Soft tissue pogonion | Pg’ | The most anterior point of the soft tissue chin in the centerline |
| Soft tissue gnathion | Gn’ | The most inferior point of the soft tissue chin in the centerline |
| Cervical point | C | The junction of the submental, the submandibular regions and the neck in the midline |
| Menton’ | Me’ | The most inferior midpoint of the chin on the outline of the soft tissue over mandible |
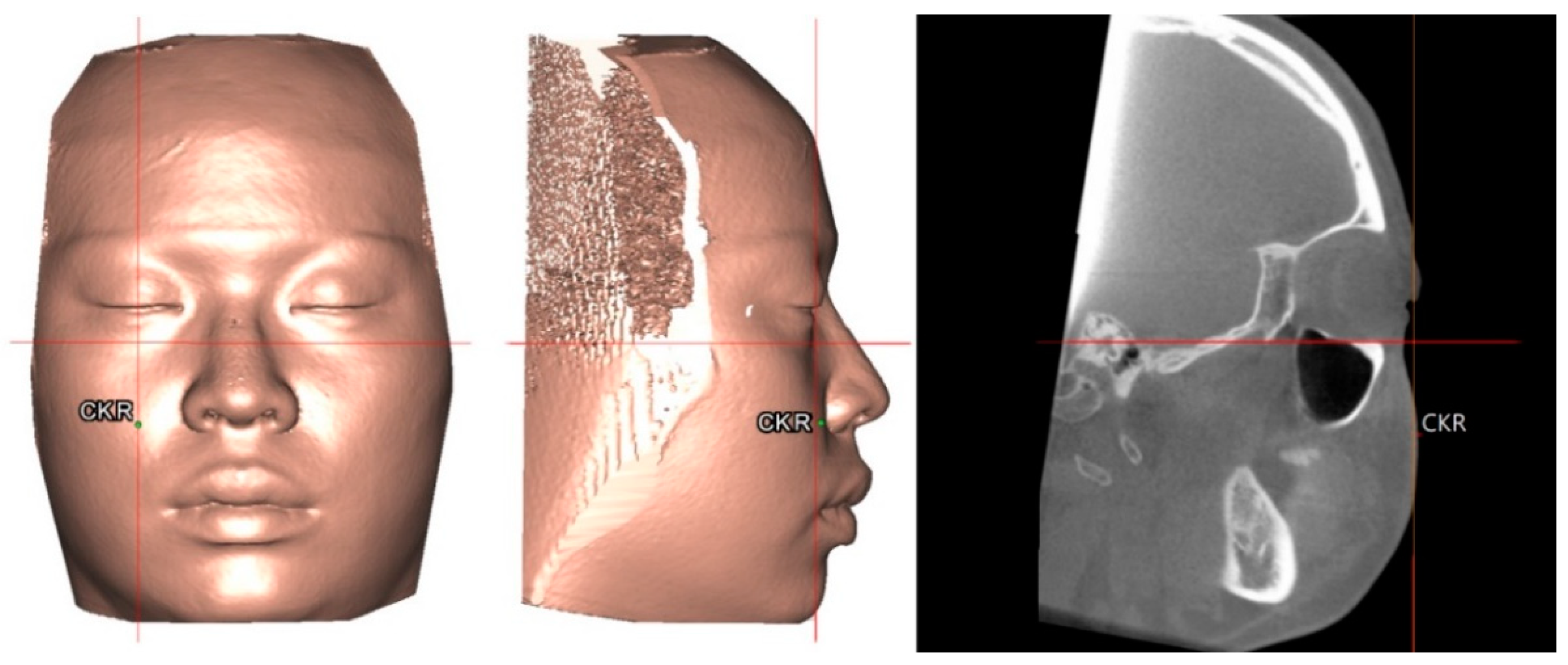
| Cheek mass | CK | The most convex point under infraorbital area relative to the perpendicular line from midpoint of upper eyelid to FH plane |
| Cornea | CL, CR | The most anterior point of the cornea |
| Planes | Definition |
|---|---|
| Frankfort horizontal plane (FH) | A plane through landmarks Orbitale (Or) on both sides and the midpoint of Porion (Po) of both sides |
| Midsagittal plane (MS) | A plane formed by basion (Ba), nasion (N), and perpendicular to FH plan |
| Palatal plane (PP) | A plane through landmarks ANS and PMP on both sides |
| Occlusal plane (OP) | A plane through the mean of landmarks upper incisor tip and lower incisor tip on both sides (U1Tip & L1 Tip), through the means of landmarks upper and lower molar buccal cusp of both sides |
| Mandibular plane (MP) | A plane through landmark Menton (Me) and Gonion (Go) of both sides |
| Anterior facial plane (N-vert) | A plane through landmark of Nasion (N) and perpendicular to FH plane and MS plane |
| Soft tissue anterior facial plane (G-vert) | A plane through landmark of Glabella (G) and perpendicular to FH plane and MS plane |
| Mid-pupillary plane | A plane through Cornea point (C) and perpendicular to FH plane and coronal plane |
| Parameters | Mean Difference (mm) | SD | Median | Q1 | Q3 | r | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basion (Ba) | 0.32 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 0.004 |
| Nasion (N) | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.48 | 0.93 | 0.009 |
| Sella turcica (S) | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.65 | 0.58 | 0.71 | 0.89 | 0.001 |
| Porion (Po) | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.71 | 0.52 | 1.03 | 0.88 | 0.008 |
| Orbitale (Or) | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.73 | 0.40 | 1.14 | 0.96 | 0.003 |
| Posterior maxillary point (PMP) | 0.43 | 0.15 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.54 | 0.99 | 0.008 |
| Anterior nasal spine (ANS) | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.29 | 0.59 | 0.99 | 0.009 |
| Posterior nasal spine (PNS) | 0.50 | 0.219 | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.63 | 0.92 | 0.004 |
| A point (A) | 0.35 | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.24 | 0.64 | 0.91 | 0.007 |
| B point (B) | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.41 | 0.19 | 0.48 | 0.88 | 0.004 |
| Pogonion (Pog) | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.63 | 0.93 | 0.006 |
| Gnathion (Gn) | 0.49 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 0.003 |
| Menton (Me) | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.006 |
| Gonion (Go) | 0.49 | 0.61 | 0.77 | 0.45 | 1.09 | 0.89 | 0.006 |
| Condylion (Co) | 0.46 | 0.62 | 0.79 | 0.36 | 1.37 | 0.90 | 0.003 |
| U1 incisal tip (U1T) | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.98 | 0.003 |
| U1 incisal apex (U1A) | 0.46 | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.64 | 0.91 | 0.006 |
| L1 incisal tip (L1T) | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.99 | 0.001 |
| L1 incisor apex (L1A) | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.99 | 0.001 |
| U6 cusp (UR6C, UL6C) | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.99 | 0.007 |
| L6 cusp (LR6C, LL6C) | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.48 | 0.34 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 0.006 |
| Glabella (G) | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.69 | 0.99 | 0.009 |
| Columella (Cm) | 0.43 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.99 | 0.003 |
| Subnasale (Sn) | 0.44 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.66 | 0.97 | 0.009 |
| Labiale superius (Ls) | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.99 | 0.007 |
| Stomion (Stm) | 0.28 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.99 | 0.005 |
| Labiale inferius (Li) | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.56 | 0.90 | 0.003 |
| Soft tissue pogonion (Pog’) | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.63 | 0.91 | 0.006 |
| Soft tissue gnathion (Gn’) | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 0.99 | 0.001 |
| Cervical point (C’) | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.71 | 0.96 | 0.008 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.40 ± 0.06 |
| Parameters | Male (n = 30) | Female (n = 30) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Cranial Base | |||||
| S-N mm | 67.941 | 1.911 | 62.563 | 3.191 | 0.006 |
| Horizontal (Skeletal) | |||||
| N-A-Pg (angle) ° | 6.506 | 2.987 | 5.850 | 2.945 | 0.610 |
| N-A (//HP) mm | 2.552 | 1.588 | 2.124 | 1.263 | 0.493 |
| N-B (//HP) mm | −1.791 | 4.434 | −2.517 | 3.991 | 0.691 |
| N-Pg (//HP) mm | −1.062 | 4.521 | −1.731 | 4.438 | 0.731 |
| Vertical (Skeletal, Dental) | |||||
| N-ANS (PHP) mm | 55.457 | 4.299 | 51.052 | 1.293 | 0.007 |
| ANS-Gn (PHP) mm | 65.093 | 5.043 | 63.744 | 2.803 | 0.449 |
| PNS-N (PHP) mm | 54.195 | 2.143 | 50.569 | 2.097 | 0.001 |
| MP-HP (angle) ° | 23.939 | 4.134 | 25.321 | 1.820 | 0.307 |
| U1-NF (PNF) mm | 28.240 | 3.599 | 28.101 | 1.148 | 0.905 |
| U6-NF (PNF) mm | 24.818 | 2.754 | 24.490 | 2.777 | 0.784 |
| L6-MP (PMP) mm | 35.418 | 2.865 | 32.368 | 2.388 | 0.014 |
| L1-MP (PMP) mm | 42.056 | 2.710 | 41.430 | 1.972 | 0.543 |
| Maxilla, Mandible | |||||
| PNS-ANS (//HP) mm | 53.431 | 2.726 | 48.240 | 3.200 | 0.001 |
| Co-Go (linear) mm | 65.866 | 6.482 | 57.665 | 3.064 | 0.002 |
| Go-Pg (linear) mm | 92.061 | 4.793 | 88.908 | 4.582 | 0.130 |
| B-Pg (//MP) mm | 5.415 | 0.985 | 5.361 | 3.461 | 0.740 |
| Dental | |||||
| OP upper-HP (angle) ° | 8.915 | 2.286 | 9.139 | 2.444 | 0.827 |
| U1-NF (angle) ° | 115.272 | 5.951 | 112.090 | 7.175 | 0.272 |
| L1-MP (angle) ° | 96.685 | 9.558 | 92.932 | 2.906 | 0.236 |
| A-B (//OP) mm | −1.742 | 1.177 | −2.456 | 1.497 | 0.228 |
| Parameters | Male (n = 30) | Female (n = 30) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Facial Form | |||||
| Facial convexity angle: G′-Sn′-Pg′ | 12.245 | 3.415 | 10.572 | 2.642 | 0.214 |
| Maxillary projection: G-Sn (//HP) | 6.920 | 2.168 | 6.489 | 2.428 | 0.665 |
| Mandibular projection: G-Pg′ (//HP) | 1.445 | 3.579 | 2.843 | 3.362 | 0.378 |
| Vertical height ratio: G-Sn/Sn-Me (PHP) | 1.114 | 0.095 | 1.126 | 0.102 | 0.775 |
| Lower face throat angle: Sn-Gn′-C | 100.818 | 7.319 | 100.501 | 3.375 | 0.899 |
| Cheek mass (cheek contour): CK | 2.105 | 1.028 | 2.186 | 1.312 | 0.257 |
| Lip Position and Form | |||||
| Nasolabial angle: Cm-Sn-Ls | 98.651 | 8.694 | 99.796 | 8.279 | 0.755 |
| Upper lip protrusion: Ls to (Sn-Pg′) | 6.426 | 1.846 | 5.472 | 1.717 | 0.224 |
| Lower lip protrusion: Li to (Sn-Pg′) | 4.475 | 1.455 | 3.771 | 1.847 | 0.333 |
| Mentolabial sulcus: Si to (Li-Pg′) | 3.923 | 0.832 | 3.672 | 0.763 | 0.469 |
| Vertical lip chin ratio: Sn-Stm/Stm-Me′ (PHP) | 0.521 | 0.053 | 0.488 | 0.043 | 0.131 |
| Maxillary incisor exposure: Stm-1 | 1.182 | 1.079 | 1.455 | 1.128 | 0.569 |
| Interlabial gap: Stms-Stmi (PHP) | 1.273 | 0.647 | 1.182 | 0.603 | 0.737 |
| Parameters | Taiwanese Male (n = 30) | Caucasian Male (n = 14) | p-Value | Taiwanese Female (n = 30) | Caucasian Female (n = 16) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| Horizontal (Skeletal) | ||||||||||
| N-A-Pg (angle) | 6.506 | 2.987 | 3.9 | 6.4 | 0.161 | 5.850 | 2.945 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 0.056 |
| N-A (//HP) | 2.552 | 1.588 | 0.0 | 3.7 | 0.022 | 2.124 | 1.263 | −2.0 | 3.7 | 0.001 |
| N-B (//HP) | −1.791 | 4.434 | −5.3 | 6.7 | 0.086 | −2.517 | 3.991 | −6.9 | 4.3 | 0.007 |
| N-Pg (//HP) | −1.062 | 4.521 | −4.3 | 8.5 | 0.198 | −1.731 | 4.438 | −6.5 | 5.1 | 0.011 |
| Vertical (Skeletal, Dental) | ||||||||||
| N-ANS (PHP) | 55.457 | 4.299 | 54.7 | 3.2 | 0.576 | 51.052 | 1.293 | 50.0 | 2.4 | 0.016 |
| ANS-Gn (PHP) | 65.093 | 5.043 | 68.6 | 3.8 | 0.034 | 63.744 | 2.803 | 61.3 | 3.3 | 0.001 |
| PNS-N (PHP) | 54.195 | 2.143 | 53.9 | 1.7 | 0.671 | 50.569 | 2.097 | 50.6 | 2.2 | 0.968 |
| MP-HP (angle) | 23.939 | 4.134 | 23.0 | 5.9 | 0.601 | 25.321 | 1.820 | 24.2 | 5.0 | 0.433 |
| U1-NF (PNF) | 28.240 | 3.599 | 30.5 | 2.1 | 0.047 | 28.101 | 1.148 | 27.5 | 1.7 | 0.260 |
| U6-NF (PNF) | 24.818 | 2.754 | 26.2 | 2.0 | 0.119 | 24.490 | 2.777 | 23.0 | 1.3 | 0.076 |
| L6-MP (PMP) | 35.418 | 2.865 | 35.8 | 2.6 | 0.696 | 32.368 | 2.388 | 32.1 | 1.9 | 0.738 |
| L1-MP (PMP) | 42.056 | 2.710 | 45.0 | 2.1 | 0.002 | 41.430 | 1.972 | 40.8 | 1.8 | 0.371 |
| Maxilla, Mandible | ||||||||||
| PNS-ANS (//HP) | 53.431 | 2.726 | 57.7 | 2.5 | <0.001 | 48.240 | 3.200 | 52.6 | 3.5 | 0.001 |
| Go-Pg (linear) | 92.061 | 4.793 | 83.7 | 4.6 | <0.001 | 88.908 | 4.582 | 74.3 | 5.8 | <0.001 |
| B-Pg (//MP) | 5.415 | 0.985 | 8.9 | 1.7 | <0.001 | 5.361 | 3.461 | 7.2 | 1.9 | 0.084 |
| Dental | ||||||||||
| OP upper-HP (angle) | 8.915 | 2.286 | 6.2 | 5.1 | 0.007 | 9.139 | 2.444 | 7.1 | 2.5 | 0.032 |
| U1-NF (angle) | 115.272 | 5.951 | 111.1 | 4.7 | 0.040 | 112.090 | 7.175 | 112.5 | 5.3 | 0.864 |
| L1-MP (angle) | 96.685 | 9.558 | 95.9 | 5.2 | 0.776 | 92.932 | 2.906 | 95.9 | 5.7 | 0.101 |
| A-B (//OP) | −1.742 | 1.177 | −1.1 | 2.0 | 0.285 | −2.456 | 1.497 | −0.4 | 2.5 | 0.017 |
| Parameters | Taiwanese (n = 60) * | Caucasian (n = 40) ** | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Facial Form | |||||
| Facial convexity angle: G′-Sn′-Pg′ | 11.409 | 3.100 | 12 | 4.0 | 0.482 |
| Maxillary projection: G-Sn (//HP) | 6.705 | 2.257 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 0.263 |
| Mandibular projection: G-Pg′ (//HP) | 2.144 | 3.626 | 0 | 3.0 | 0.005 |
| Vertical height ratio: G-Sn/Sn-Me (PHP) | 1.130 | 0.088 | 1.0 | – | – |
| Lower face throat angle: Sn-Gn′-C | 100.660 | 5.881 | 100 | 7.0 | 0.660 |
| Lip Position and Form | |||||
| Nasolabial angle: Cm-Sn-Ls | 99.224 | 8.305 | 102 | 8.0 | 0.134 |
| Upper lip protrusion: Ls to (Sn-Pg′) | 5.949 | 1.807 | 3.0 | 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Lower lip protrusion: Li to (Sn-Pg′) | 4.122 | 1.662 | 2.0 | 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Mentolabial sulcus: Si to (Li-Pg′) | 3.797 | 0.789 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 0.595 |
| Vertical lip chin ratio: Sn-Stm/Stm-Me′(PHP) | 0.505 | 0.050 | 0.5 | – | – |
| Maxillary incisor exposure: Stm-1 | 1.319 | 1.044 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.088 |
| Interlabial gap: Stms-Stmi (PHP) | 1.227 | 0.571 | 2.0 | 2.0 | – |
| Parameters | Taiwanese (n = 60) * | Singaporean (n = 72) ** | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Facial Form | |||||
| Facial convexity angle: G′-Sn′-Pg′ | 11.409 | 3.100 | 10.5 | 3.5 | 0.164 |
| Maxillary projection: G-Sn (//HP) | 6.705 | 2.257 | 2.5 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Mandibular projection: G-Pg′ (//HP) | 2.144 | 3.626 | – | – | – |
| Vertical height ratio: G-Sn/Sn-Me (PHP) | 1.130 | 0.088 | 1.0 | 0.1 | <0.001 |
| Lower face throat angle: Sn-Gn′-C | 100.660 | 5.881 | 96 | 4 | <0.001 |
| Lip Position and Form | |||||
| Nasolabial angle: Cm-Sn-Ls | 99.224 | 8.305 | 95 | 3 | 0.001 |
| Upper lip protrusion: Ls to (Sn-Pg′) | 5.949 | 1.807 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.002 |
| Lower lip protrusion: Li to (Sn-Pg′) | 4.122 | 1.662 | – | – | – |
| Mentolabial sulcus: Si to (Li-Pg′) | 3.797 | 0.789 | 3.5 | 2 | 0.336 |
| Vertical lip chin ratio: Sn-Stm/Stm-Me′ (PHP) | 0.505 | 0.050 | 0.5 | – | – |
| Maxillary incisor exposure: Stm-1 | 1.319 | 1.044 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.481 |
| Interlabial gap: Stms-Stmi (PHP) | 1.227 | 0.571 | 1 | 1 | 0.167 |
| Parameters | 3D Simulation (n = 30) | 3D Norms (n = 60) * | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Horizontal (Skeletal) | |||||
| N-A-Pg angle | 4.750 | 2.873 | 6.178 | 2.914 | 0.111 |
| N-A (//HP) | 1.114 | 3.284 | 2.338 | 1.417 | 0.119 |
| N-B (//HP) | −2.773 | 4.618 | −2.154 | 4.133 | 0.673 |
| N-Pg (//HP) | −1.764 | 4.066 | −1.396 | 4.385 | 0.716 |
| Vertical (Skeletal, Dental) | |||||
| N-ANS/ANS-Gn | 0.831 | 0.066 | 0.826 | 0.097 | 0.614 |
| MP-HP (angle) | 25.001 | 2.637 | 24.636 | 3.156 | 0.446 |
| U1-NF/L1-MP | 0.675 | 0.062 | 0.677 | 0.046 | 0.919 |
| Dental | |||||
| OP upper-HP (angle) | 12.341 | 2.337 | 9.027 | 2.312 | <0.001 |
| U1-NF (angle) | 112.818 | 4.992 | 113.68 | 6.483 | 0.491 |
| L1-MP (angle) | 88.318 | 2.495 | 94.809 | 7.156 | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Initial | Surgical Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal (Skeletal) | ||
| N-A-Pg | −14.23 | 2.69 |
| Nvert-A | 1.43 | 4.09 |
| Nvert-B | 12.63 | 2.97 |
| Nvert-Pg | 17.37 | 7.14 |
| Vertical (Skeletal, Dental) | ||
| N-ANS | 48.95 | 48.19 |
| ANS-Gn | 66.89 | 65.62 |
| N-ANS/ANS-Gn (ratio) | 0.73 | 0.73 |
| U1-NF | 27.00 | 26.97 |
| L1-MP | 38.24 | 38.13 |
| U1-NF/L1-MP | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| Dental | ||
| OP-FH | 2.81 | 9.49 |
| UR6-NP | 47.68 | 44.63 |
| UL6-NP | 49.04 | 46.36 |
| Parameters | Treatment Plan in 3 Dimension (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| X Axis (Left, Right) | Y Axis (Anterior, Posterior) | Z Axis (Up−Down) | |
| N | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ANS | 0 | 2.75 | 0.76 |
| A point | 0 | 2.37 | 1.03 |
| B point | 0 | −10.35 | 2.11 |
| Pog | 0 | −10.92 | 1.96 |
| Gn | 0 | −10.66 | 2.03 |
| Me | 0 | −10.93 | 2.14 |
| U1 mid | 0 | 0 | 0.01 |
| L1 mid | 0 | −9.00 | 2.01 |
| U6R | 0 | 0.40 | 2.94 |
| U6L | 0 | 0.20 | 2.70 |
| Right (+) Left (−) | Anterior (+) Posterior (−) | Up (+) Down (−) | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, C.-T.; Denadai, R.; Lai, H.-C.; Lo, L.-J.; Lin, H.-H. Computer-Aided Planning in Orthognathic Surgery: A Comparative Study with the Establishment of Burstone Analysis-Derived 3D Norms. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122106
Ho C-T, Denadai R, Lai H-C, Lo L-J, Lin H-H. Computer-Aided Planning in Orthognathic Surgery: A Comparative Study with the Establishment of Burstone Analysis-Derived 3D Norms. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(12):2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122106
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Cheng-Ting, Rafael Denadai, Hsin-Chih Lai, Lun-Jou Lo, and Hsiu-Hsia Lin. 2019. "Computer-Aided Planning in Orthognathic Surgery: A Comparative Study with the Establishment of Burstone Analysis-Derived 3D Norms" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 12: 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122106
APA StyleHo, C.-T., Denadai, R., Lai, H.-C., Lo, L.-J., & Lin, H.-H. (2019). Computer-Aided Planning in Orthognathic Surgery: A Comparative Study with the Establishment of Burstone Analysis-Derived 3D Norms. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(12), 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122106







