Investigation of Risk Factors for Pain Chronification in Patients Suffering from Infections of the Spine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
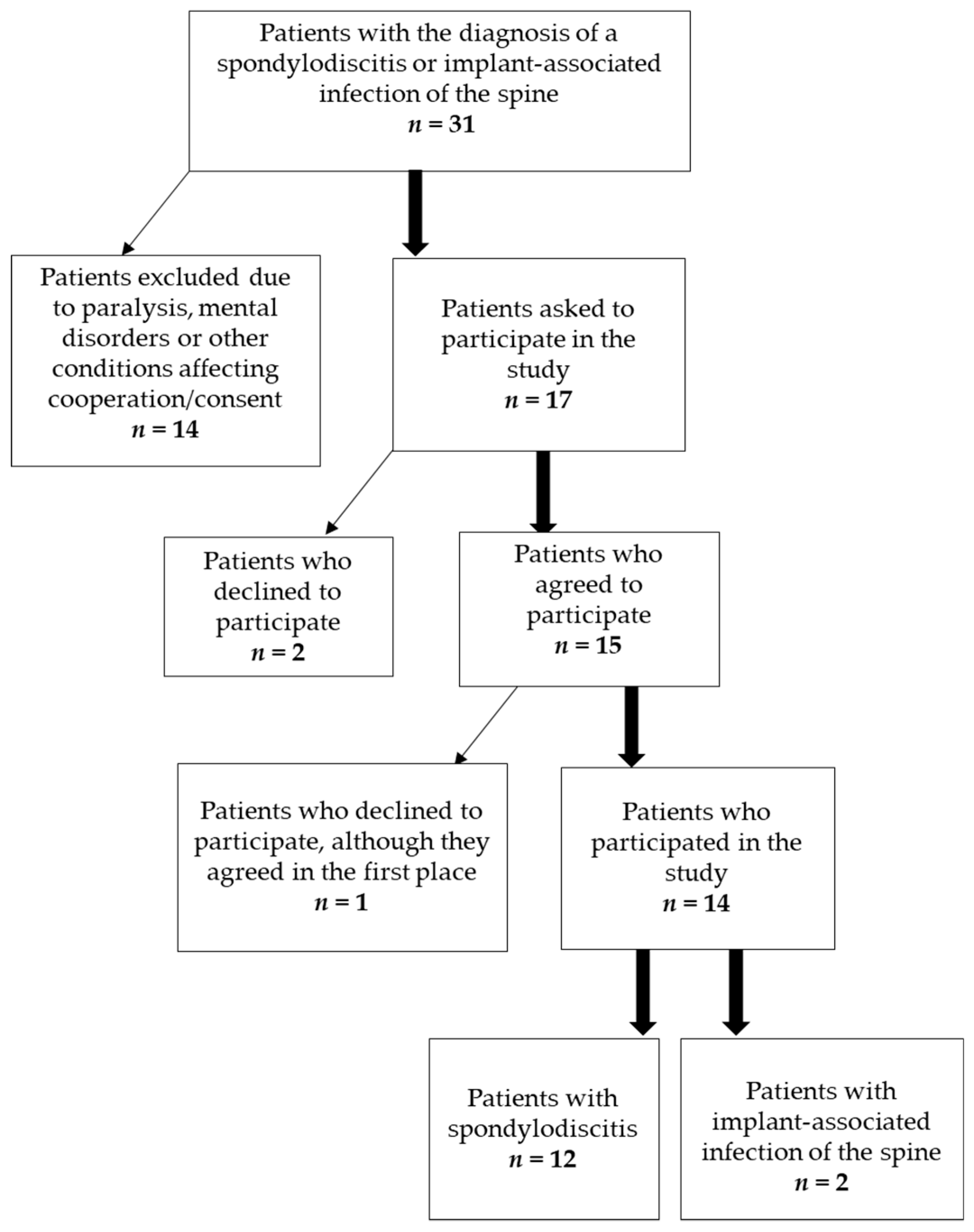
2.1. Patients
2.2. Questionnaires
2.3. Quantitative Sensory Testing (QST)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Clinical Data
3.2. Questionnaires
3.3. Quantitative Sensory Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregori, F.; Grasso, G.; Iaiani, G.; Marotta, N.; Torregrossa, F.; Landi, A. Treatment algorithm for spontaneous spinal infections: A review of the literature. J. Craniovertebr. Junction Spine 2019, 10, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapunt, U.; Bürkle, C.; Günther, F.; Pepke, W.; Hemmer, S.; Akbar, M. Surgical site infections following instrumented stabilization of the spine. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aagaard, T.; Roed, C.; Dragsted, C.; Skinhøj, P. Microbiological and therapeutic challenges in infectious spondylodiscitis: A cohort study of 100 cases, 2006–2011. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 45, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, D.P.; Waldvogel, F.A. Osteomyelitis. Lancet 2004, 364, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Ochsner, P.E. Prosthetic-Joint Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grunewald, T.; Ruf, B.R. Musculoskeletal infections in the era of multiresistant pathogens. Der Unfallchirurg 2012, 115, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, A.G.; Costerton, J.W. Bacterial adherence and the glycocalyx and their role in musculoskeletal infection. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1984, 15, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mückley, T.; Boszczyk, B.; Hofmann, G.O. Spinale und paraspinale Infektionen. In Infektionen der Knochen und Gelenke in Traumatologie und Orthopädie; Elsevier, Urban & Fischer Verlag: München, Gertmany, 2004; pp. 131–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, P.M.; Fleming, J.L. Vertebral Body Osteomyelitis: Spectrum and Natural History: A Retrospective Analysis of 37 Cases. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1976, 118, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Colmenero, J.D.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Sánchez-Lora, F.J.; Reguera, J.M.; Palomino-Nicás, J.; Martos, F.; Heras, J.G.d.l.; Pachón, J. Pyogenic, tuberculous, and brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis: A descriptive and comparative study of 219 cases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, B.; Brinkschmidt, T.; Casser, H.-R.; Diezemann, A.; Gralow, I.; Irnich, D.; Kaiser, U.; Klasen, B.; Klimczyk, K.; Lutz, J. Multimodale Schmerztherapie für die Behandlung chronischer Schmerzsyndrome. Der Schmerz 2014, 28, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häuser, W.; Bernardy, K.; Arnold, B.; Offenbächer, M.; Schiltenwolf, M. Efficacy of multicomponent treatment in fibromyalgia syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Arthr. Rheum 2009, 61, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merle, C.; Brendle, S.; Wang, H.; Streit, M.R.; Gotterbarm, T.; Schiltenwolf, M. Multidisciplinary treatment in patients with persistent pain following total hip and knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Simonsen, O.; Wilder-Smith, O.; Laursen, M.B. Presurgical assessment of temporal summation of pain predicts the development of chronic postoperative pain 12 months after total knee replacement. Pain 2015, 156, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebbeck, T.; Moloney, N.; Azoory, R.; Hübscher, M.; Waller, R.; Gibbons, R.; Beales, D. Clinical ratings of pain sensitivity correlate with quantitative measures in people with chronic neck pain and healthy controls: Cross-sectional study. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latremoliere, A.; Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: A generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J. Pain 2009, 10, 895–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wylde, V.; Sayers, A.; Lenguerrand, E.; Gooberman-Hill, R.; Pyke, M.; Beswick, A.D.; Dieppe, P.; Blom, A.W. Preoperative widespread pain sensitization and chronic pain after hip and knee replacement: A cohort analysis. Pain 2015, 156, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolke, R.; Magerl, W.; Campbell, K.A.; Schalber, C.; Caspari, S.; Birklein, F.; Treede, R.D. Quantitative sensory testing: A comprehensive protocol for clinical trials. Eur. J. Pain 2006, 10, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapunt, U.; Gantz, S.; Zhuk, A.; Gather, K.; Wang, H.; Schiltenwolf, M. Quantitative sensory testing in physically active individuals and patients who underwent multidisciplinary pain therapy in the longitudinal course. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Papadopoulos, D.V.; Vrioni, G.; Sioutis, S.; Sapkas, G.; Benzakour, A.; Benzakour, T.; Angelini, A.; Ruggieri, P.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; et al. Spinal Infections: An Update. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsook, D.; Youssef, A.M.; Simons, L.; Elman, I.; Eccleston, C. When pain gets stuck: The evolution of pain chronification and treatment resistance. Pain 2018, 159, 2421–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolke, R.; Baron, R.; Maier, C.; Tolle, T.R.; Treede, R.D.; Beyer, A.; Binder, A.; Birbaumer, N.; Birklein, F.; Botefur, I.C.; et al. Quantitative sensory testing in the German Research Network on Neuropathic Pain (DFNS): Standardized protocol and reference values. Pain 2006, 123, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marouf, R.; Piche, M.; Rainville, P. Is temporal summation of pain and spinal nociception altered during normal aging? Pain 2015, 156, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciechanowski, P.; Sullivan, M.; Jensen, M.; Romano, J.; Summers, H. The relationship of attachment style to depression, catastrophizing and health care utilization in patients with chronic pain. Pain 2003, 104, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baastrup, S.; Schultz, R.; Brodsgaard, I.; Moore, R.; Jensen, T.S.; Vase Toft, L.; Bach, F.W.; Rosenberg, R.; Gormsen, L. A comparison of coping strategies in patients with fibromyalgia, chronic neuropathic pain, and pain-free controls. Scand. J. Psychol. 2016, 57, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verra, M. Die Schmerzbewältigung erfassen. Physiopraxis 2007, 5, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinhoven, P.; Ter Kuile, M.; Kole-Snijders, A.M.; Hutten Mansfeld, M.; Den Ouden, D.J.; Vlaeyen, J.W. Catastrophizing and internal pain control as mediators of outcome in the multidisciplinary treatment of chronic low back pain. Eur. J. Pain 2004, 8, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow-Turek, A.L.; Norris, M.P.; Tan, G. Active and passive coping strategies in chronic pain patients. Pain 1996, 64, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstiel, A.K.; Keefe, F.J. The use of coping strategies in chronic low back pain patients: Relationship to patient characteristics and current adjustment. Pain 1983, 17, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, J.; van Breukelen, G.; Sluiter, J.; Frings-Dresen, M.H.; Goossens, M.; Thibault, P.; Boersma, K.; Vlaeyen, J.W. Norming of the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia across pain diagnoses and various countries. Pain 2011, 152, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.C.; Kreddig, N.; Hallner, D.; Hülsebusch, J.; Hasenbring, M.I. Fear of movement/(Re)injury in low back pain: Confirmatory validation of a German version of the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiß, T.; Schaible, H.-G. Strukturen der Nozizeption und der Schmerzverarbeitung. In Angewandte Physiologie: Schmerzen Verstehen und Beeinflussen; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2003; Volume 4, pp. 6–33. [Google Scholar]
- Agostinho, C.M.; Scherens, A.; Richter, H.; Schaub, C.; Rolke, R.; Treede, R.D.; Maier, C. Habituation and short-term repeatability of thermal testing in healthy human subjects and patients with chronic non-neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.; Hystad, T.; Kvale, A.; Baerheim, A. Quantitative sensory testing of patients with long lasting Patellofemoral pain syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2007, 11, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylde, V.; Palmer, S.; Learmonth, I.D.; Dieppe, P. Somatosensory abnormalities in knee OA. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzmán, J.; Esmail, R.; Karjalainen, K.; Malmivaara, A.; Irvin, E.; Bombardier, C. Multidisciplinary rehabilitation for chronic low back pain: Systematic review. BMJ 2001, 322, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nees, T.A.; Riewe, E.; Waschke, D.; Schiltenwolf, M.; Neubauer, E.; Wang, H. Multidisciplinary Pain Management of Chronic Back Pain: Helpful Treatments from the Patients’ Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salathé, C.R.; Melloh, M.; Crawford, R.; Scherrer, S.; Boos, N.; Elfering, A. Treatment Efficacy, Clinical Utility, and Cost-Effectiveness of Multidisciplinary Biopsychosocial Rehabilitation Treatments for Persistent Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 872–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Patients | Female | Male | Pain Duration in Months | Length of Inpatient Stay in Days | Age of Patients in Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 14 | n = 6 | n = 8 | 3.43 (±2.77) | 45.29 (±33.13) | 66 (±16.92) |
| WHO Level 1 | n | WHO Level 2 | n | WHO Level 3 | n | Co-Medication | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metamizol 500 mg | 7 | On demand Tilidin/Naloxon 50 mg/4 mg | 1 | Hydromorphon 2–24 mg or on demand | 2 | Pregabalin 150 mg or 50 mg | 2 |
| Paracetamol 500 mg or 10 mg/mL i.v. | 3 | Oxycodon/Naloxon 40 mg/20 mg | 1 | ||||
| Ibuprofen 600 mg or 40 mg/mL | 2 | On demand Oxycodon 5 mg | 1 | ||||
| ASS 500 mg | 1 | Tapentadol 50 mg | 1 |
| Bacteria Species | n | Antibiotics and Antimycotics | n | Overall Length of Intake in Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staph. api | 4 | Rifampicin | 9 | 63.36 (±27.12) |
| E. coli | 2 | Ciprofloxacin | 8 | |
| Candida albicans | 2 | Cefuroxim | 5 | |
| Staph. aureus | 2 | Amoxicillin + Clavulansäure | 5 | |
| Cutibacterium acnes | 2 | Clindamycin | 4 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1 | Vancomycin | 2 | |
| Strept. gallolyticus | 1 | Fosfomycin | 2 | |
| Strept. intermedius | 1 | Fluconazol + Tazobactam | 1 | |
| None | 5 | And other penicillin, aminoglycoside, macrolides, cephalosporins, cabapenems |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Hemmer, S.; Pepke, W.; Akbar, M.; Schiltenwolf, M.; Dapunt, U. Investigation of Risk Factors for Pain Chronification in Patients Suffering from Infections of the Spine. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124056
Zhao Y, Hemmer S, Pepke W, Akbar M, Schiltenwolf M, Dapunt U. Investigation of Risk Factors for Pain Chronification in Patients Suffering from Infections of the Spine. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124056
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yina, Stefan Hemmer, Wojciech Pepke, Michael Akbar, Marcus Schiltenwolf, and Ulrike Dapunt. 2020. "Investigation of Risk Factors for Pain Chronification in Patients Suffering from Infections of the Spine" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124056
APA StyleZhao, Y., Hemmer, S., Pepke, W., Akbar, M., Schiltenwolf, M., & Dapunt, U. (2020). Investigation of Risk Factors for Pain Chronification in Patients Suffering from Infections of the Spine. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124056







