Eighteen Months Follow-Up with Patient-Centered Outcomes Assessment of Complete Dentures Manufactured Using a Hybrid Nanocomposite and Additive CAD/CAM Protocol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Structural Characterization of the Hybrid Nanocomposite Obtained Using Additive Manufacturing–DLP Technology
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Methods and Equipment
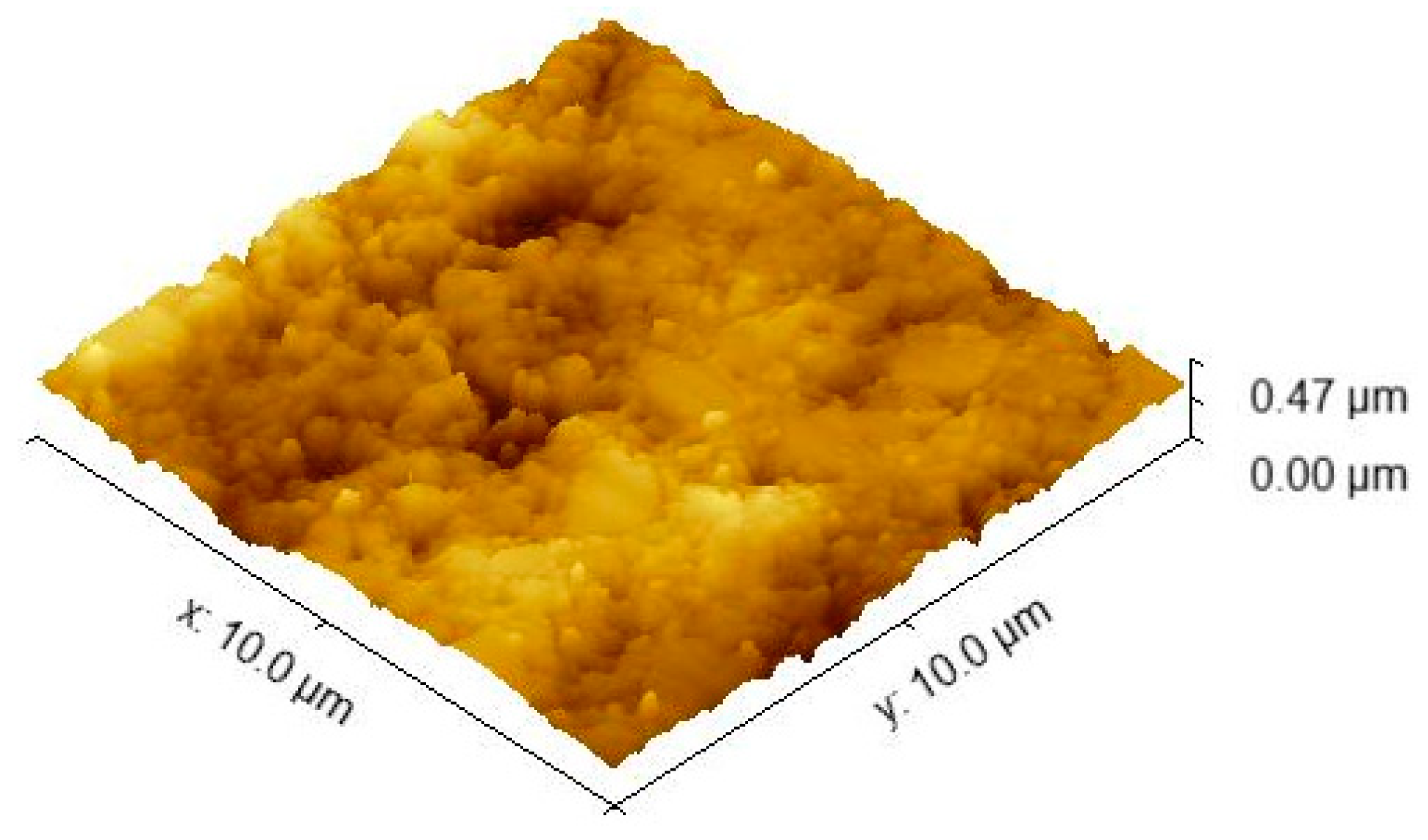
2.1.3. AFM Investigations–Nanoindentation Studies
2.2. Clinical Study Protocol
3. Results
3.1. SEM Investigations
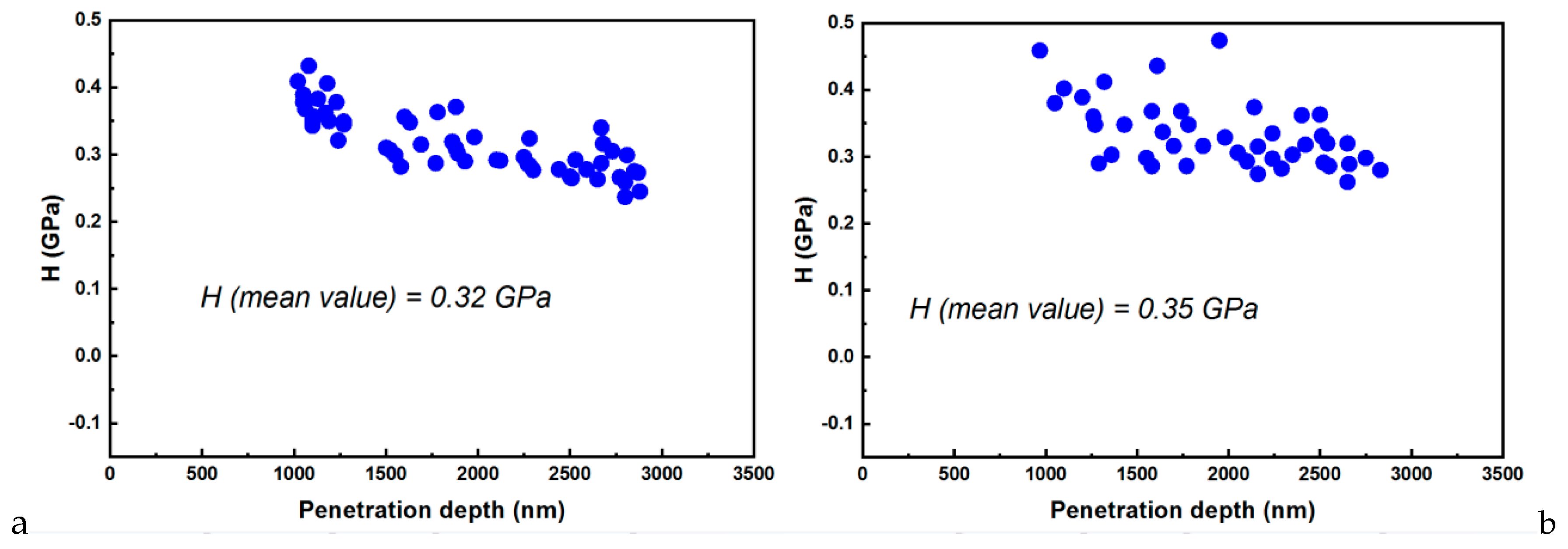
3.2. Nanoindentation–AFM Investigations
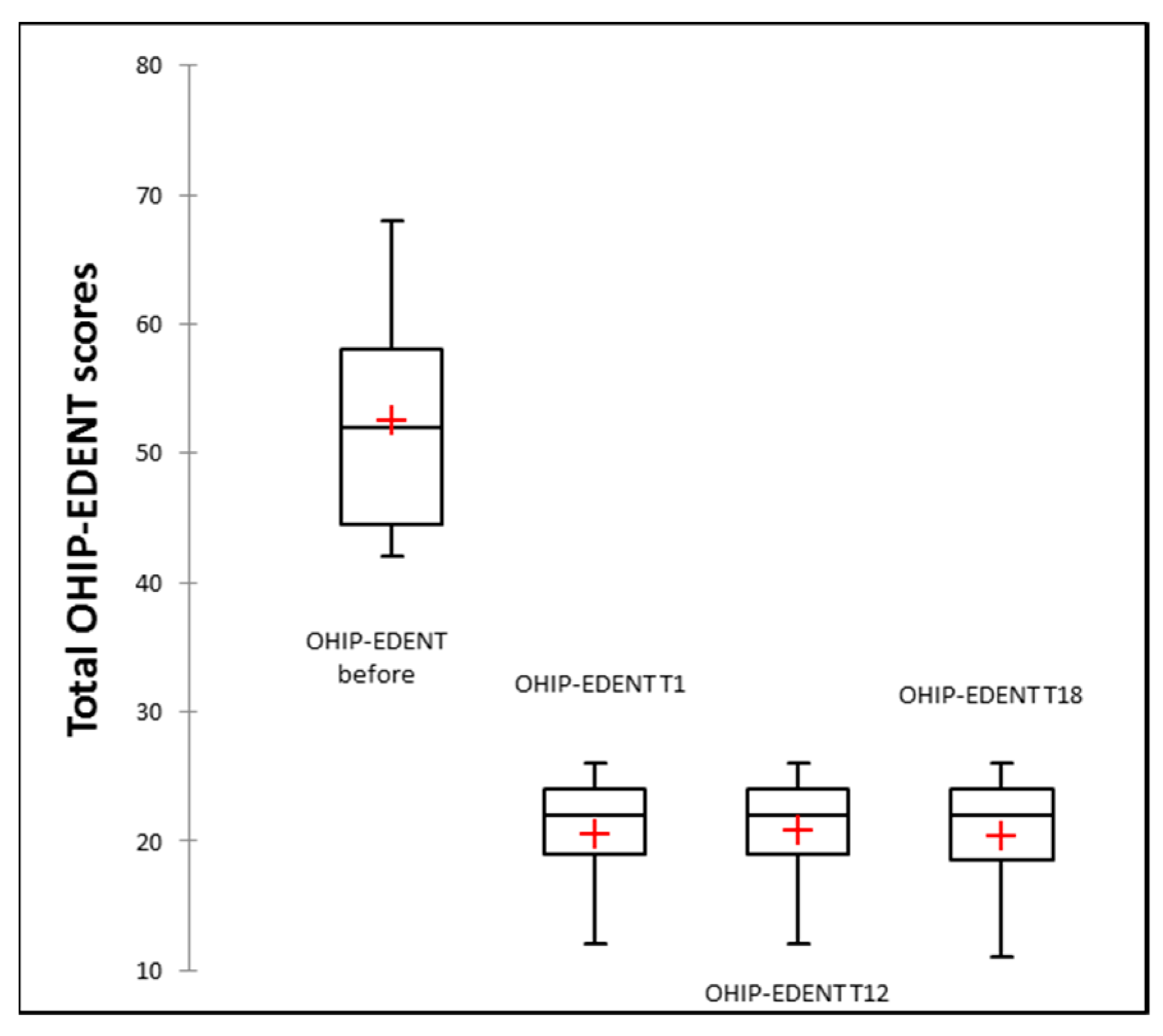
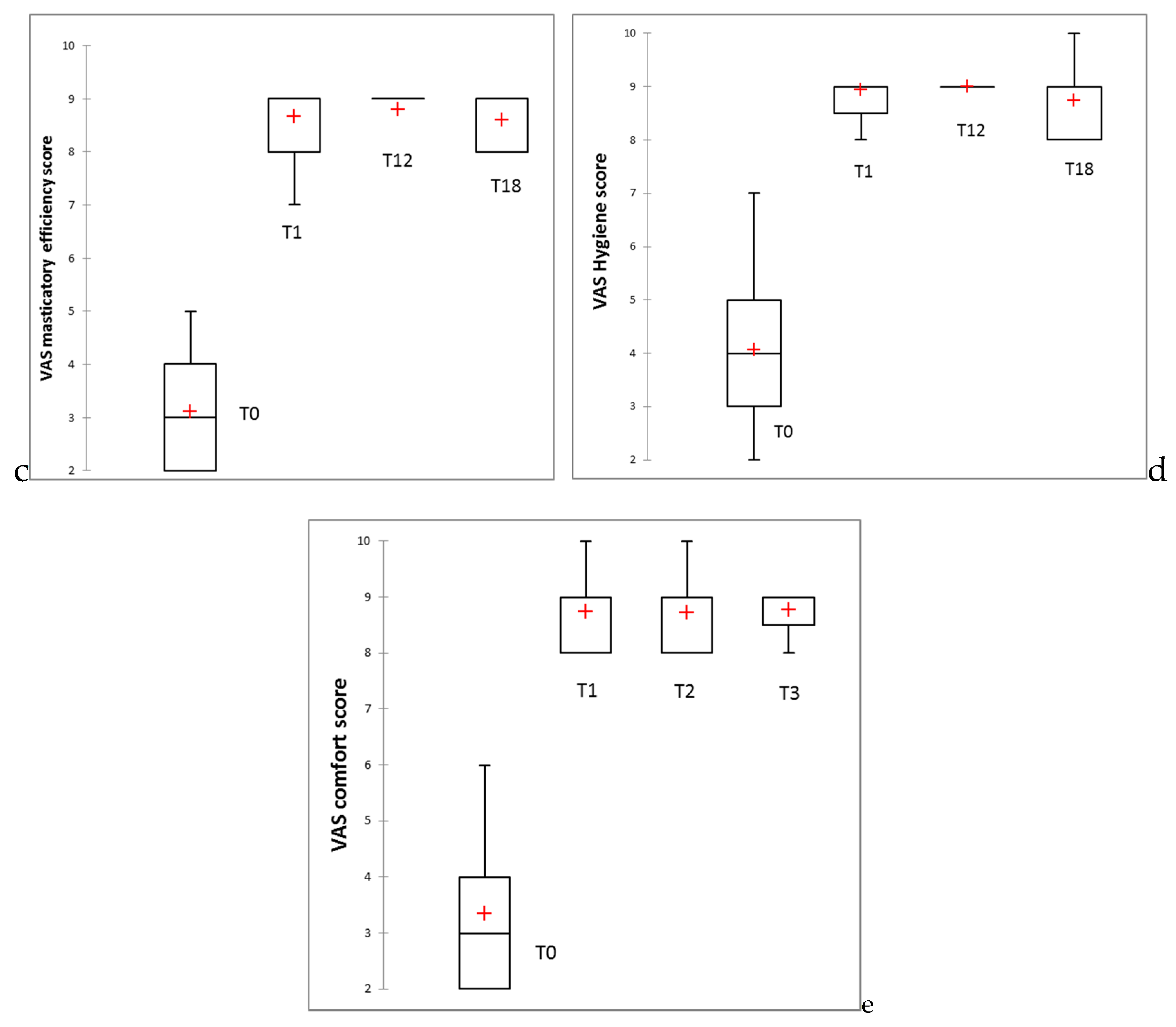
3.3. Clinical Study Results
3.4. Micro-CT Post-Wearing Investigations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The proposed workflow with the nanoTiO2 composite material used is a viable treatment option for patients diagnosed with complete edentulism.
- The results indicate that the OHRQoL was significantly improved, and patients’ satisfaction scores for aesthetic, speech, masticatory efficiency, hygiene, and comfort were significantly higher upon new denture insertion, with these improvements being maintained throughout the entire evaluation period.
- The PMMA nanocomposite with 0.4% TiO2 facilitated the manufacturing of performant 3D-printed complete dentures, which maintained their improved characteristics after permanent usage by patients for 18 months.
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Artopoulos, A.; Juszczyk, A.S.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Clark, R.K.F.; Radford, D.R. Three-dimensional processing deformation of three denture base materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 110, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totu, E.E.; Cristache, C.M. Could the old poly(methylmethacrylate) face arrising challanges of new advanced technologies for dental prosthesis manufacturing? Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHelal, A.; AlRumaih, H.S.; Kattadiyil, M.T.; Baba, N.Z.; Goodacre, C.J. Comparison of retention between maxillary milled and conventional denture bases: A clinical study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, M.; Gjengedal, H.; Cattani-Lorente, M.; Moussa, M.; Durual, S.; Schimmel, M.; Müller, F. CAD/CAM milled complete removable dental prostheses: An in vitro evaluation of biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and surface roughness. Dent. Mater. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Totu, E.E.; Nechifor, A.C.; Nechifor, G.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Cristache, C.M. Poly(methyl methacrylate) with TiO2 nanoparticles inclusion for stereolitographic complete denture manufacturing − the fututre in dental care for elderly edentulous patients? J. Dent. 2017, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.Y.; Park, M.S.; Lee, J.W.; Yun, J.S. A study on the rheological and mechanical properties of photo-curable ceramic/polymer composites with different silane coupling agents for SLA 3D printing technology. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Valk, D.C.; van der Ven, C.F.T.; Blaser, M.C.; Grolman, J.M.; Wu, P.J.; Fenton, O.S.; Lee, L.H.; Tibbitt, M.W.; Andresen, J.L.; Wen, J.R.; et al. Engineering a 3d-bioprinted model of human heart valve disease using nanoindentation-based biomechanics. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alla, R.K.; Sajjan, S.; Alluri, V.R.; Ginjupalli, K.; Upadhya, N. Influence of Fiber Reinforcement on the Properties of Denture Base Resins. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cierech, M.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Kolenda, A.; Krawczyk-Balska, A.; Prochwicz, E.; Woźniak, B.; Łojkowski, W.; Mierzwińska-Nastalska, E. Zinc oxide nanoparticles cytotoxicity and release from newly formed PMMA–ZNO nanocomposites designed for denture bases. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Totu, E.E.; Cristache, C.M.; Isildak, I.; Yildirim, R.; Burlibasa, M.; Nigde, M.; Burlibasa, L. Preliminary Studies on Citotoxicity and Genotoxicity Assessment of the PMMA-TiO2 Nanocompozites for Stereolithographic Complete Dentures Manufacturing. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totu, E.E.; Cristache, C.M.; Isildak, S.; Tavukcuoglu, O.; Pantazi, A.; Enachescu, M.; Buga, R.; Burlibasa, M.; Totu, T. Structural Investigations on Poly (methyl methacrylate) Various Composites Used for Stereolithographyc Complete Dentures. Mater. Plast. 2018, 55, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totu, E.E.; Cristache, C.M.; Voicila, E.; Oprea, O.; Agir, I.; Tavukcuoglu, O.; Didilescu, A.C. On physical and chemical characteristics of Poly(methylmethacrylate) nanocomposites for dental applications. I. Mater. Plast. 2017, 54, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristache, C.M.; Totu, E.E.; Grosu, A.R.; Ene, O.; Beuran, I.A.; Burlibasa, M. Nanocomposite for rapid prototyped complete denture eighteen months follow-up on clinical performance. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, G.D.; Spencer, A.J. Development and evaluation of the Oral Health Impact Profile. Community Dent. Health 1994, 11, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allen, F.; Locker, D. A modified short version of the oral health impact profile for assessing health-related quality of life in edentulous adults. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 15, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Additive3d.com. Available online: https://additive3d.com/3d-printer-comparison/ (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Ghorbal, A.; Grisotto, F.; Charlier, J.; Palacin, S.; Goyer, C.; Demaille, C.; Brahim, A. Nano-Electrochemistry and Nano-Electrografting with an Original Combined AFM-SECM. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khulbe, K.C.; Feng, C.Y.; Matsuura, T. Synthetic Atomic Force Microscopy. In Polymeric Membranes: Characterization by Atomic Force Microscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-73993-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y. Atomic and subnanometer resolution in ambient conditions by atomic force microscopy. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2009, 64, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, M.Z.; Schwarz, U.D. Noncontact atomic force microscopy III. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J. Am. Coll. Dent. 2014. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGarry, T.J.; Nimmo, A.; Skiba, J.F.; Ahlstrom, R.H.; Smith, C.R.; Koumjian, J.H.; Guichet, G.N. Classification system for the completely dentate patient. J. Prosthodont. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlers, M.O. Simulation of occlusion in Restorative Dentistry. The Artex System; Denta Concept: Hamburg, Germany; ISBN 3933465079.
- Oancea, L.; Stegaroiu, R.; Cristache, C.M. The influence of temporomandibular joint movement parameters on dental morphology. Ann. Anat. 2018, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, M.T.; Reissmann, D.R.; Feuerstahler, L.; Waller, N.; Baba, K.; Larsson, P.; Čelebić, A.; Szabo, G.; Rener-Sitar, K. Exploratory factor analysis of the oral health impact profile. J. Oral Rehabil. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omura, Y.; Kanazawa, M.; Sato, D.; Kasugai, S.; Minakuchi, S. Comparison of patient-reported outcomes between immediately and conventionally loaded mandibular two-implant overdentures: A preliminary study. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, M.T.; Feuerstahler, L.; Waller, N.; Baba, K.; Larsson, P.; Čelebić, A.; Kende, D.; Rener-Sitar, K.; Reissmann, D.R. Confirmatory factor analysis of the oral health impact profile. J. Oral Rehabil. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bhushan, B. A review of nanoindentation continuous stiffness measurement technique and its applications. Mater. Charact. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Ania, F.; Flores, A. Nanoindentation in polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 67, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attar, H.; Ehtemam-Haghighi, S.; Kent, D.; Okulov, I.V.; Wendrock, H.; Bӧnisch, M.; Volegov, A.S.; Calin, M.; Eckert, J.; Dargusch, M.S. Nanoindentation and wear properties of Ti and Ti-TiB composite materials produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Paufler, P. Micro- and nanoindentation techniques for mechanical characterisation of materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Hassler, U.; Fernandes, H.; Genest, M.; Robitaille, F.; Joncas, S.; Holub, W.; Sheng, Y.; Maldague, X. An experimental and analytical study of micro-laser line thermography on micro-sized flaws in stitched carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazari, A.; Sadr, A.; Saghiri, M.A.; Campillo-Funollet, M.; Hamba, H.; Shimada, Y.; Tagami, J.; Sumi, Y. Non-destructive characterization of voids in six flowable composites using swept-source optical coherence tomography. Dent. Mater. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totu, E.E.; Cristache, C.M.; Vlasceanu, G.; Josceanu, A.M.; Nechifor, A.C. On physical and chemical characteristics of poly(methylmethacrylate) nanocomposites for dental applications.II. Mater. Plast. 2019, 56, 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Márton, K.; Hermann, P.; Dankó, K.; Fejérdy, P.; Madléna, M.; Nagy, G. Evaluation of oral manifestations and masticatory force in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olshan, A.M.; Ross, N.M.; Mankodi, S.; Melita, S. A modified Kapur scale for evaluating denture retention and stability: Methodology study. Am. J. Dent. 1992, 5, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kapur, K.K. A clinical evaluation of denture adhesives. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1967, 18, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, B.J.; Goodacre, C.J.; Baba, N.Z.; Kattadiyil, M.T. Comparison of denture base adaptation between CAD-CAM and conventional fabrication techniques. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Park, E.J.; Yoon, H.I. Assessment of the trueness and tissue surface adaptation of CAD-CAM maxillary denture bases manufactured using digital light processing. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 121, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, S.T.; Fernández, M.R.; de Moura, C.M.; Meireles, S.S. Color stability of a nanofill composite: Effect of different immersion media. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2009, 17, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristache, C.M.; Oancea, L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Burlibasa, M.; Totu, E.E. Color changes and stainability of complete dentures manufactured using pmma-TiO2 nanocomposite and 3D printing technology—One year evaluation. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leles, C.R.; Ferreira, N.P.; Vieira, A.H.; Campos, A.C.V.; Silva, E.T. Factors influencing edentulous patients’ preferences for prosthodontic treatment. J. Oral Rehabil. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.; de Paula, J.; de Morais, M.; Ferreira, R.; Gomes, V. Impact of Treatment with Conventional Complete Dentures on (Oral) Health-Related Quality of Life: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, O.; Sutow, E.J. Posterior palatal seal adaptation: Influence of processing technique, palate shape and immersion. J. Oral Rehabil. 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| E-Dent 100 | PMMA with 0.4% nanoTiO2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Ra | 40.3 nm | 59.1 nm |
| RMS | 52.4 nm | 77.8 nm |
| E-Dent 100 | PMMA with 0.4% nanoTiO2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Ra | 21.3 nm | 25.9 nm |
| RMS | 28.5 nm | 34.6 nm |
| Ra (nm) | RMS (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEFORE | AFTER | BEFORE | AFTER | |
| E-Dent 100 | 98.7 | 105.9 | 125.7 | 131.7 |
| PMMA with 0.4% nanoTiO2 | 88.3 | 96.3 | 107.5 | 119.7 |
| Patients According to Restored Arches | Mean (Standard Deviation) of Total OHIP-EDENT Scores | p (T0 and T18) | p (T1 and T18) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T12 | T18 | |||
| Maxilla (n = 21) | 52.62 (8.70) | 20.62 (4.51) | 20.81 (4.37) | 20.33 (4.27) | p ≤ 0.00 | 0.75 |
| Mandible (n = 4) | 56.50 (6.66) | 21.25 (2.99) | 21.25 (2.99) | 22.25 (3.10) | 0.02 | 0.76 |
| Both arches (n = 10) | 50.90 (7.67) | 20.10 (5.22) | 20.40 (4.84) | 19.90 (5.32) | p ≤ 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Overall (n = 35) | 52.57 (8.16) | 20.54 (4.48) | 20.74 (4.27) | 20.43 (4.42) | p ≤ 0.00 | 0.89 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cristache, C.M.; Totu, E.E.; Iorgulescu, G.; Pantazi, A.; Dorobantu, D.; Nechifor, A.C.; Isildak, I.; Burlibasa, M.; Nechifor, G.; Enachescu, M. Eighteen Months Follow-Up with Patient-Centered Outcomes Assessment of Complete Dentures Manufactured Using a Hybrid Nanocomposite and Additive CAD/CAM Protocol. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020324
Cristache CM, Totu EE, Iorgulescu G, Pantazi A, Dorobantu D, Nechifor AC, Isildak I, Burlibasa M, Nechifor G, Enachescu M. Eighteen Months Follow-Up with Patient-Centered Outcomes Assessment of Complete Dentures Manufactured Using a Hybrid Nanocomposite and Additive CAD/CAM Protocol. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(2):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020324
Chicago/Turabian StyleCristache, Corina Marilena, Eugenia Eftimie Totu, Gabriela Iorgulescu, Aida Pantazi, Dorel Dorobantu, Aurelia Cristina Nechifor, Ibrahim Isildak, Mihai Burlibasa, Gheorghe Nechifor, and Marius Enachescu. 2020. "Eighteen Months Follow-Up with Patient-Centered Outcomes Assessment of Complete Dentures Manufactured Using a Hybrid Nanocomposite and Additive CAD/CAM Protocol" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 2: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020324
APA StyleCristache, C. M., Totu, E. E., Iorgulescu, G., Pantazi, A., Dorobantu, D., Nechifor, A. C., Isildak, I., Burlibasa, M., Nechifor, G., & Enachescu, M. (2020). Eighteen Months Follow-Up with Patient-Centered Outcomes Assessment of Complete Dentures Manufactured Using a Hybrid Nanocomposite and Additive CAD/CAM Protocol. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(2), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020324









