Hearing with One Ear: Consequences and Treatments for Profound Unilateral Hearing Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
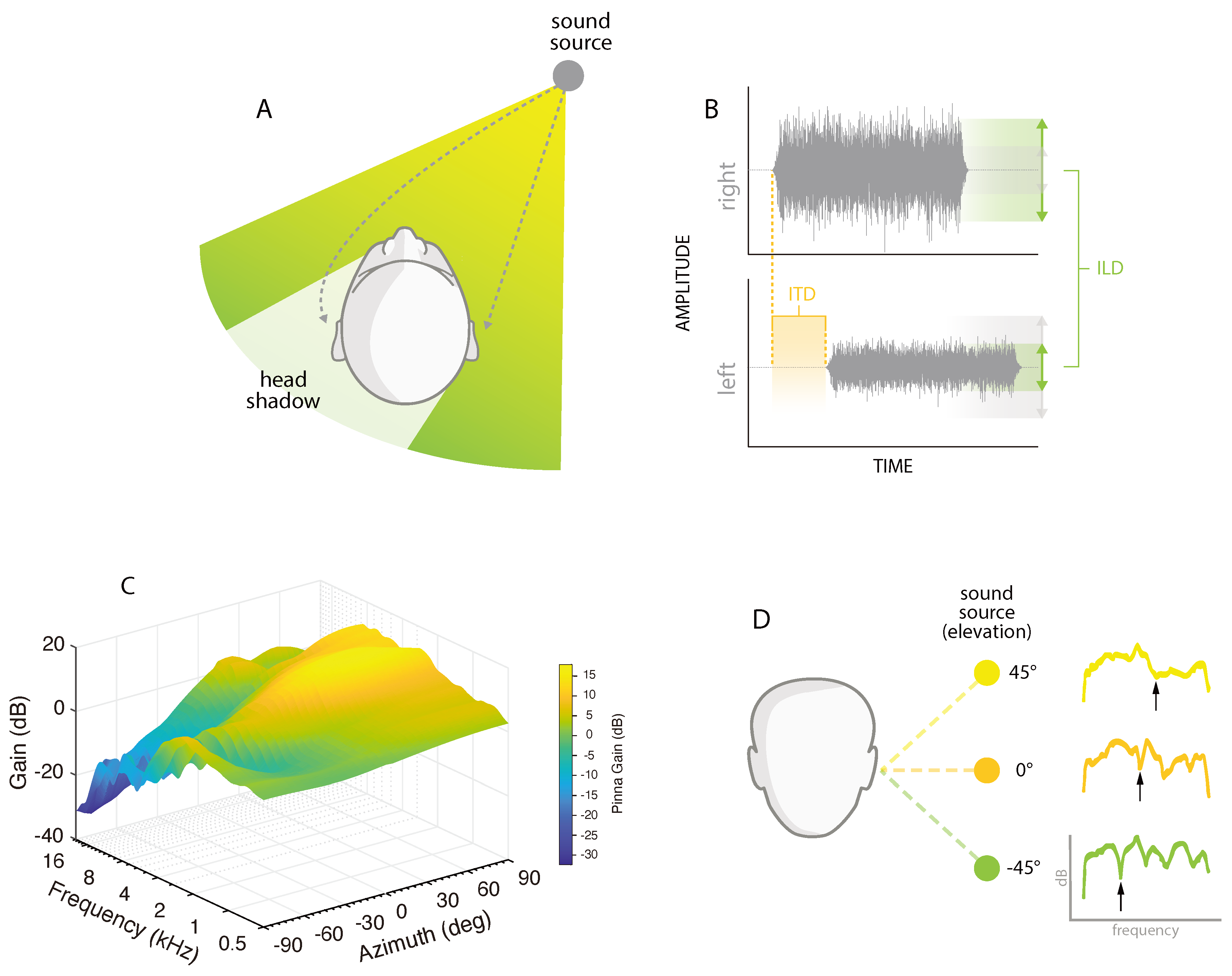
2. Spatial Hearing
3. Unilateral Profound Deafness
4. Treatment
4.1. Rerouting Solutions
4.2. Cochlear Implantation
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreetta, M.D.; Adams, S.G.; Dykstra, A.D.; Jog, M. Evaluation of Speech Amplification Devices in Parkinson’s Disease. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2016, 25, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Estimates on Hearing Loss; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/pbd/deafness/estimates/en/ (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Dalton, D.S.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Klein, B.E.K.; Klein, A.P.; Wiley, T.L.; Nondahl, D.M. The impact of hearing loss on quality of life in older adults. Gerontology 2003, 43, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mick, P.; Kawachi, I.; Lin, F.R. The Association between Hearing Loss and Social Isolation in Older Adults. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2014, 150, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.R. Hearing Loss and Cognition Among Older Adults in the United States. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2011, 66, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, F.R.; Niparko, J.K.; Ferrucci, L. Hearing Loss Prevalence in the United States. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1851–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdahl, B.; Idstad, M.; Skirbekk, V. Hearing loss, family status and mortality—Findings from the HUNT study, Norway. Soc. Sci. Med. 2019, 220, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wie, O.B.; Pripp, A.H.; Tvete, O. Unilateral deafness in adults: Effects on communication and social interaction. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 772–781. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, P.E.; Feldman, J.J.; Dunbar, J.L.; McConkey-Robbins, A.; Niparko, J.K.; Rittenhouse, R.K.; Skinner, M.W. The societal costs of severe to profound hearing loss in the united states. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2000, 16, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, E.; Deutscher, A.; Mosges, R. A present investigation of the epidemiology in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngorhinootologie 2009, 88, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teranishi, M.-A.; Katayama, N.; Uchida, Y.; Tominaga, M.; Nakashima, T. Thirty-year trends in sudden deafness from four nationwide epidemiological surveys in Japan. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2007, 127, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, H.; Okamoto, M.; Ohhashi, K.; Iwasaki, S.; Ogawa, K. Quality of Life Reported by Patients With Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlHanbali, S.; Dawes, P.; Lloyd, S.; Munro, K.J. Self-Reported Listening-Related Effort and Fatigue in Hearing-Impaired Adults. Ear Hear. 2017, 38, e39–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearing, C.O.; Balkany, T.A.; Gates, G.A.; Goldenberg, R.A.; Meyerhoff, W.L.; House, J.W.; Surg, O.H.N. Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of hearing preservation in acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma). American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation, INC. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 179–180. [Google Scholar]
- Baguley, D.M.; Bird, J.; Humphriss, R.; Prevost, A.T. The evidence base for the application of contralateral bone anchored hearing aids in acquired unilateral sensorineural hearing loss in adults. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2006, 31, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.A.; Yeung, P.; Daudia, A.; Gatehouse, S.; O’Donoghue, G.M. Spatial Hearing Disability After Acoustic Neuroma Removal. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatehouse, S.; Noble, W. The Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ). Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bess, F.H.; Davis, H.; Camarata, S.; Hornsby, B.W.Y. Listening-Related Fatigue in Children With Unilateral Hearing Loss. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2020, 51, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.; Schmid, K.; O’Leary, S.; Spalding, J.; Heinrichs-Graham, E.; High, R. Effects of Noise on Speech Recognition and Listening Effort in Children With Normal Hearing and Children With Mild Bilateral or Unilateral Hearing Loss. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2016, 59, 1218–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, F.L. The dominant role of low-frequency interaural time differences in sound localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlebrooks, J.C.; Green, D.M. Sound localization by human listeners. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1991, 42, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauert, J. Spatial Hearing: The Psychophysics of Human Sound Localization; The MIT Press: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tillman, T.W.; Carhart, R.; Nicholls, S. Release from Multiple Maskers in Elderly Persons. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1973, 16, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carhart, R. Monaural and Binaural Discrimination against Competing Sentences. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1965, 37, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, M.L.; Litovsky, R.Y.; Culling, J. The benefit of binaural hearing in a cocktail party: Effect of location and type of interferer. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giolas, T.G.; Wark, D.J. Communication Problems Associated with Unilateral Hearing Loss. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1967, 32, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harford, E.; Barry, J. A Rehabilitative Approach to the Problem of Unilateral Hearing Impairment: The Contralateral Routing of Signals (CROS). J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1965, 30, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, E.C. Some Experiments on the Recognition of Speech, with One and with Two Ears. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1953, 25, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregman, A.S. Auditory Scene Analysis: The Perceptual Organization of Sound; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bronkhorst, A.W. The effect of head-induced interaural time and level differences on speech intelligibility in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agterberg, M.J.; Hol, M.K.S.; Van Wanrooij, M.; Van Opstal, J.; Snik, A.F.M. Single-sided deafness and directional hearing: Contribution of spectral cues and high-frequency hearing loss in the hearing ear. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumpik, D.P.; King, A.J. A review of the effects of unilateral hearing loss on spatial hearing. Hear. Res. 2018, 372, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapp, H.A.; Morgenstein, K.E.; Kuzbyt, B. Speech Perception Outcomes in Transcutaneous Versus Percutaneous Bone Conduction Stimulation in Individuals With Single-sided Deafness. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapp, H.A.; Morgenstein, K.E.; Telischi, F.F.; Angeli, S. Transcranial Attenuation in Patients with Single-Sided Deafness. Audiol. Neurotol. 2016, 21, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snapp, H.A.; Holt, F.D.; Liu, X.; Rajguru, S.M. Comparison of Speech-in-Noise and Localization Benefits in Unilateral Hearing Loss Subjects Using Contralateral Routing of Signal Hearing Aids or Bone-Anchored Implants. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agterberg, M.J.H.; Snik, A.F.; Van De Goor, R.; Hol, M.K.; Van Opstal, J. Sound-localization performance of patients with single-sided deafness is not improved when listening with a bone-conduction device. Hear. Res. 2018, 372, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wanrooij, M.; Van Opstal, J. Contribution of Head Shadow and Pinna Cues to Chronic Monaural Sound Localization. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4163–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofman, P.M.; Van Opstal, J. Spectro-temporal factors in two-dimensional human sound localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 2634–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpik, D.P.; Kacelnik, O.; King, A.J. Adaptive reweighting of auditory localization cues in response to chronic unilateral earplugging in humans. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4883–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noble, W.; Gatehouse, S. Interaural asymmetry of hearing loss, Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) disabilities, and handicap. Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.S. On the psychophysical law. Psychol. Rev. 1957, 64, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, E. Dependence of binaural loudness summation on interaural level differences, spectral distribution, and temporal distribution. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 89, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, H.; Munson, W.A. Loundess, its definition, measurement and calculation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1933, 5, 82–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.C.J.; Gibbs, A.; Onions, G.; Glasberg, B.R. Measurement and modeling of binaural loudness summation for hearing-impaired listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, S.D.; Halpin, C.F.; Antonelli, P.J.; Babu, S.; Carey, J.P.; Gantz, B.; Goebel, J.A.; Hammerschlag, P.E.; Harris, J.P.; Isaacson, B.; et al. Oral vs Intratympanic Corticosteroid Therapy for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. JAMA 2011, 305, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byl, F.M. Sudden hearing loss: Eight years’ experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope 1984, 94, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, S.D.; Geller, L.N. Comparing treatments for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 2012, 1, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedley, A.J.; Kitterick, P.T. Contralateral routing of signals disrupts monaural level and spectral cues to sound localisation on the horizontal plane. Hear. Res. 2017, 353, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapp, H.A. Nonsurgical Management of Single-Sided Deafness: Contralateral Routing of Signal. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2019, 80, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapp, H.A.; Hoffer, M.E.; Liu, X.; Rajguru, S.M. Effectiveness in Rehabilitation of Current Wireless CROS Technology in Experienced Bone-Anchored Implant Users. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazen, J.J.; Spitzer, J.B.; Ghossaini, S.N.; Fayad, J.N.; Niparko, J.K.; Cox, K.; Brackmann, D.E.; Soli, S.D. Transcranial Contralateral Cochlear Stimulation in Unilateral Deafness. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2003, 129, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, M.K.S.; Kunst, S.J.W.; Snik, A.F.M.; Bosman, A.J.; Mylanus, E.A.M.; Cremers, C.W.R.J. Bone-Anchored Hearing Aids in Patients with Acquired and Congenital Unilateral Inner Ear Deafness (Baha CROS): Clinical Evaluation of 56 Cases. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitterick, P.T.; Smith, S.N.; Lucas, L. Hearing Instruments for Unilateral Severe-to-Profound Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Adults. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeire, K.; Van De Heyning, P. Binaural Hearing after Cochlear Implantation in Subjects with Unilateral Sensorineural Deafness and Tinnitus. Audiol. Neurotol. 2008, 14, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firszt, J.B.; Holden, L.K.; Reeder, R.; Waltzman, S.; Arndt, S. Auditory abilities after cochlear implantation in adults with unilateral deafness: A pilot study. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sladen, D.P.; Frisch, C.D.; Carlson, M.L.; Driscoll, C.L.W.; Torres, J.H.; Zeitler, D.M. Cochlear implantation for single-sided deafness: A multicenter study. Laryngoscope 2016, 127, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litovsky, R.Y.; Moua, K.; Godar, S.; Kan, A.; Misurelli, S.M.; Lee, D.J. Restoration of spatial hearing in adult cochlear implant users with single-sided deafness. Hear. Res. 2019, 372, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Távora-Vieira, D.; De Ceulaer, G.; Govaerts, P.J.; Rajan, G.P. Cochlear Implantation Improves Localization Ability in Patients With Unilateral Deafness. Ear Hear. 2015, 36, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.; Aschendorff, A.; Laszig, R.; Beck, R.; Schild, C.; Kroeger, S.; Ihorst, G.; Wesarg, T. Comparison of Pseudobinaural Hearing to Real Binaural Hearing Rehabilitation After Cochlear Implantation in Patients With Unilateral Deafness and Tinnitus. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finke, M.; Strauß-Schier, A.; Kludt, E.; Büchner, A.; Illg, A. Speech intelligibility and subjective benefit in single-sided deaf adults after cochlear implantation. Hear. Res. 2017, 348, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, E.; Dillon, M.T.; Rooth, M.A.; King, E.R.; Deres, E.J.; Buchman, C.A.; Pillsbury, H.C.; Brown, K.D. Effects of Cochlear Implantation on Binaural Hearing in Adults With Unilateral Hearing Loss. Trends Hear. 2018, 22, 2331216518771173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeitler, D.M.; Dorman, M.F.; Natale, S.J.; Loiselle, L.; Yost, W.A.; Gifford, R. Sound Source Localization and Speech Understanding in Complex Listening Environments by Single-sided Deaf Listeners After Cochlear Implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorman, M.F.; Zeitler, D.; Cook, S.J.; Loiselle, L.; Yost, W.A.; Wanna, G.B.; Gifford, R. Interaural level difference cues determine sound source localization by single-sided deaf patients fit with a cochlear implant. Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, J.G.W.; Goupell, M.J.; Schuchman, G.I.; Rivera, A.L.; Brungart, D.S. Having Two Ears Facilitates the Perceptual Separation of Concurrent Talkers for Bilateral and Single-Sided Deaf Cochlear Implantees. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, J.G.W.; Schuchman, G.I.; Rivera, A.L. Head Shadow and Binaural Squelch for Unilaterally Deaf Cochlear Implantees. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, e195–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoesel, R.J.M. Sensitivity to binaural timing in bilateral cochlear implant users. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 2192–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francart, T.; Wiebe, K.; Wesarg, T. Interaural Time Difference Perception with a Cochlear Implant and a Normal Ear. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2018, 19, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, M.A.; Moore, B.C.J. Tolerable Hearing Aid Delays. I. Estimation of Limits Imposed by the Auditory Path Alone Using Simulated Hearing Losses. Ear Hear. 1999, 20, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirn, S.; Arndt, S.; Aschendorff, A.; Wesarg, T. Interaural stimulation timing in single sided deaf cochlear implant users. Hear. Res. 2015, 328, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, L.; Smith, S.N. Improving Health-Related Quality of Life in Single-Sided Deafness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, J.G.W.; Stakhovskaya, O.A.; Jensen, K.K.; Goupell, M.J. Acoustic Hearing Can Interfere With Single-Sided Deafness Cochlear-Implant Speech Perception. Ear Hear. 2019, 22, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.M.; Julyan, P.J.; Hastings, D.L.; Ramsden, R.T. Auditory cortical activation and speech perception in cochlear implant users. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 122, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, P.; Pyman, B.C.; Clark, G.M.; Dowell, R.C.; Gordon, M.; Brown, A.M.; Hollow, R.D. Factors Predicting Postoperative Sentence Scores in Postlinguistically Deaf Adult Cochlear Implant Patients. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1992, 101, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltzman, S.B.; Fisher, S.G.; Niparko, J.K.; Cohen, N.L. Predictors of postoperative performance with cochlear implants. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Suppl. 1995, 165, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahne, T.; Seiwerth, I.; Götze, G.; Heider, C.; Radetzki, F.; Herzog, M.; Plontke, S.K. Functional results after Bonebridge implantation in adults and children with conductive and mixed hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2014, 272, 3263–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, A. Auditory critical periods: A review from system’s perspective. Neuroscience 2013, 247, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Wieringen, A.; Boudewyns, A.; Sangen, A.; Wouters, J.; Desloovere, C. Unilateral congenital hearing loss in children: Challenges and potentials. Hear. Res. 2019, 372, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavora-Vieira, D.; Rajan, G.P. Cochlear implantation in children with congenital and noncongenital unilateral deafness: A case series. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Prosse, S.; Laszig, R.; Wesarg, T.; Aschendorff, A.; Hassepass, F. Cochlear Implantation in Children with Single-Sided Deafness: Does Aetiology and Duration of Deafness Matter? Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.A.; Henkin, Y.; Kral, A. Asymmetric Hearing During Development: The Aural Preference Syndrome and Treatment Options. Pediatrics 2015, 136, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, K.; Kral, A. Animal and human studies on developmental monaural hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2019, 380, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Neumann, K.; Dazert, S.; Voelter, C. Cochlear Implantation in Children With Congenital Single-Sided Deafness. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Snapp, H.A.; Ausili, S.A. Hearing with One Ear: Consequences and Treatments for Profound Unilateral Hearing Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041010
Snapp HA, Ausili SA. Hearing with One Ear: Consequences and Treatments for Profound Unilateral Hearing Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(4):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSnapp, Hillary A., and Sebastian A. Ausili. 2020. "Hearing with One Ear: Consequences and Treatments for Profound Unilateral Hearing Loss" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 4: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041010
APA StyleSnapp, H. A., & Ausili, S. A. (2020). Hearing with One Ear: Consequences and Treatments for Profound Unilateral Hearing Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(4), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041010




