Asthma/Rhinitis (The United Airway) and Allergy: Chicken or Egg; Which Comes First?
Abstract
1. Introduction
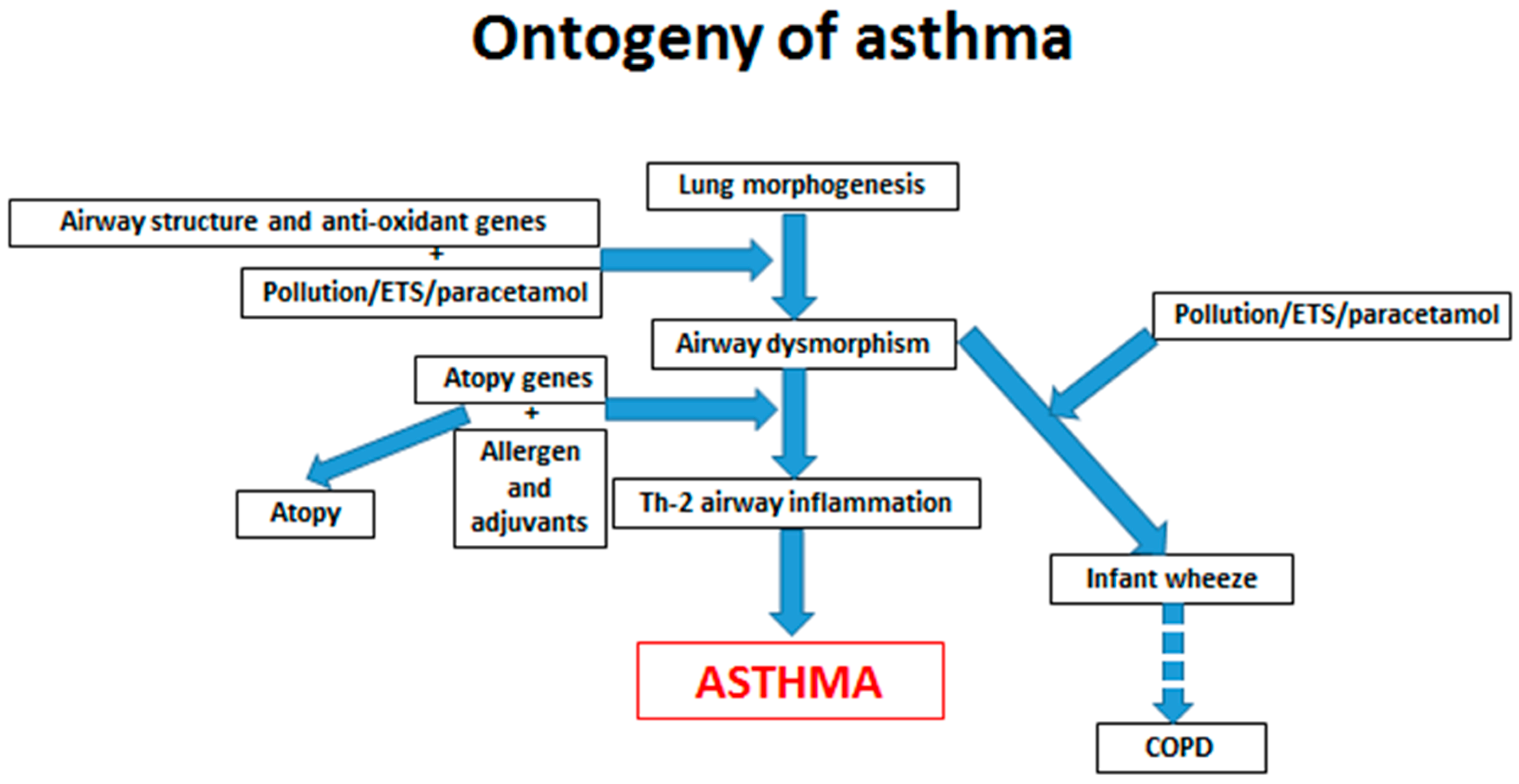
2. Gene/Environment Interactions
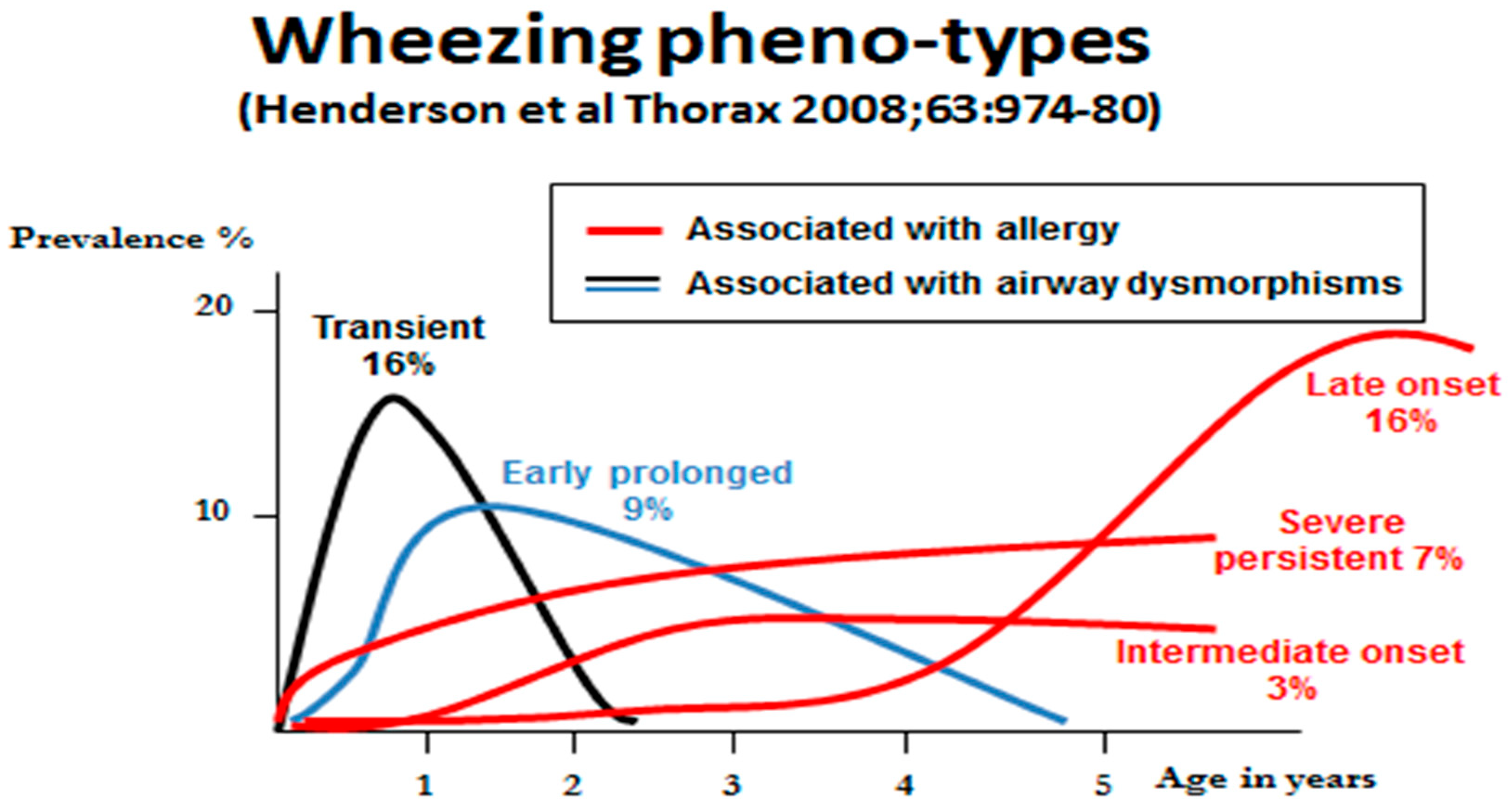
3. Wheeze Phenotypes
4. Early Life Origins of Allergy
5. Prevention and Treatment of Allergy
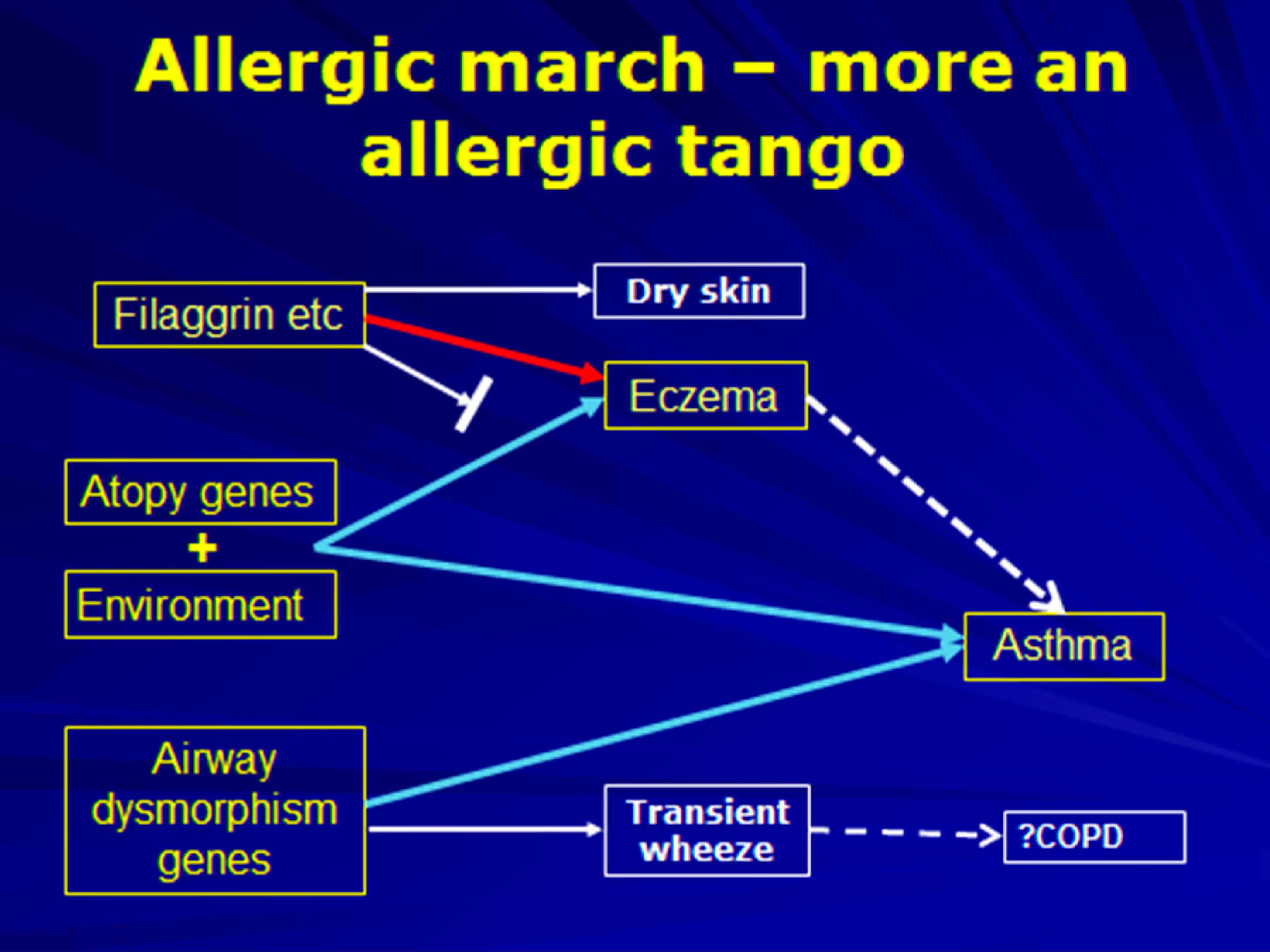
6. The Allergic March
7. Pharmaco-Therapy for United Airway Diseases
8. Allergen Immunotherapy
9. New Approaches to Management of Allergic Airway Diseases
10. A Shared Misunderstanding between Patient and Physician
11. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sunyer, J.; Jarvis, D.; Pekkanen, J.; Chinn, S.; Janson, C.; Leynaert, B.; Luczynska, C.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Burney, P.; Antó, J.M.; et al. Geographic variations in the effect of atopy on asthma in the European Community Respiratory Health Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, J.O.; Boner, A.L. Paediatric Allergy and Asthma. In Allergy, 4th ed.; Holgate, S.T., Church, M.K., Broide, D.H., Martinez, F.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, S.A.; Lockett, G.A.; Holloway, J.W. The genetics of allergic diseases and asthma. In Pediatric Allergy Principles and Practice, 3rd ed.; Leung, Y.M., Sampson, H.A., Geha, R.S., Szefler, S.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eerdewegh, P.; Little, R.D.; Dupuis, J.; Del Mastro, R.G.; Falls, K.; Simon, J.; Torrey, D.; Pandit, S.; McKenny, J.; Braunschweiger, K.; et al. Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma and bronchial hyper-responsiveness. Nature 2002, 418, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, M.F.; Kabesch, M.; Liang, L.; Dixon, A.L.; Strachan, D.; Heath, S.; Depner, M.; von Berg, A.; Bufe, A.; Rietschel, E.; et al. Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature 2007, 448, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, E.R.; Kelly, J.F.C.; Howarth, P.H.; Wilson, D.I.; Holgate, S.T.; Davies, D.E.; Whitsett, J.A.; Haitchicorresponding, H.M. Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for allergic asthma in early life. JCI Insight. 2016, 1, e87632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgerson, D.G.; Ampleford, E.J.; Chiu, G.Y.; Gauderman, W.J.; Gignoux, C.R.; Graves, P.E.; Himes, B.E.; Levin, A.M.; Mathias, R.A.; Hancock, D.B.; et al. Meta-analysis of Genome-wide Association Studies of Asthma In Ethnically Diverse North American Populations. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 887–892. [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt, M.F.; Gut, I.G.; Demenais, F.; Strachan, D.P.; Bouzigon, E.; Heath, S.; von Mutius, E.; Farrall, M.; Lathrop, M.; Cookson, W.O.C.M.; et al. A Large-Scale, Consortium-Based Genome wide Association Study of Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-L.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Hsiue, T.R.; Guo, Y.L. Glutathione S-transferase P1 gene polymorphism and air pollution as interactive risk factors for childhood asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 334, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyers, S.; Weatherall, M.; Jefferies, S.; Beasley, R. Paracetamol in pregnancy and the risk of wheezing in offspring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, R.; Clayton, T.; Crane, J.; von Mutius, E.; Lai, C.K.; Montefort, S.; Stewart, A.; ISAAC Phase Three Study Group. Association between paracetamol use in infancy and childhood, and risk of asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in children aged 6–7 years: Analysis from Phase Three of the ISAAC programme. Lancet 2008, 372, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perzanowski, M.S.; Miller, R.L.; Tang, D.; Ali, D.; Garfinkel, R.S.; Chew, G.L.; Goldstein, I.F.; Perera, F.P.; Barr, R.G. Prenatal acetaminophen exposure and risk of wheeze at age 5 years in an urban low-income cohort. Thorax 2010, 65, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bønnelykke, K.; Sparks, R.; Waage, J.; Milner, J.D. Genetics of allergy and allergic sensitization: Common variants, rare mutations. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 36, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokouchi, Y.; Nukaga, Y.; Shibasaki, M.; Noguchi, E.; Kimura, K.; Ito, S.; Nishihara, M.; Yamakawa-Kobayashi, K.; Takeda, K.; Imoto, N.; et al. Significant evidence for linkage of mite-sensitive childhood asthma to chromosome 5q31-q33 near the interleukin 12 B locus by a genome-wide search in Japanese families. Genomics 2000, 66, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.-J.; Söderhäll, C.; Bustamante, M.; Baïz, N.; Gruzieva, O.; Gehring, U.; Mason, D.; Chatzi, L.; Basterrechea, M.; Llop, S.; et al. DNA methylation in childhood asthma: An epigenome-wide meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munthe-Kaas, M.C.; Willemse, B.W.M.; Koppelman, G.H. Genetics and epigenetics of childhood asthma. Eur. Respir. Monogr. 2012, 56, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lodge, C.J.; Brabak, L.; Lowe, A.J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Olsson, D.; Forsberg, B. Grandmaternal smoking increases asthma risk in grandchildren: A nationwide Swedish cohort. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeranki, S.P.; Gebretsadik, T.; Mitchel, E.F.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Hartert, T.V.; Cooper, W.O.; Dupont, W.D.; Dorris, S.L.; Hartman, T.J.; Carroll, K.N. Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation during Pregnancy and Early Childhood Asthma. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazani, S.; Wechsler, M.E.; Israel, E. The role of pharmacogenetics in improving the management of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.; Granell, R.; Heron, J.; Sherriff, A.; Simpson, A.; Woodcock, A.; Strachan, D.P.; Shaheen, S.O.; Sterne, J.A. Associations of wheezing phenotypes in the first 6 years of life with atopy, lung function and airway responsiveness in mid-childhood. Thorax 2008, 63, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisgaard, H.; Loland, L.; Holst, K.K.; Pipper, C.B. Prenatal determinants of neonatal lung function in high-risk newborns. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.O. The early life origins of asthma and related allergic disorders. Arch. Dis. Child 2004, 89, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.O. Developmental origins of asthma and related allergic disorders. In Developmental Origins of Health and Disease; Gluckman, P., Hanson, M., Eds.; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 349–369. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.A.; Warner, J.A.; Warner, J.O. Fetal swallowing of IgE. Lancet 1998, 351, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.A.; Vance, G.H.S.; Power, L.L.; Pender, S.L.F.; MacDonald, T.T.; Warner, J.O. Costimulatory molecules in the developing human gastrointestinal tract: A pathway for fetal allergen priming. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenmalm, M.C.; Björksten, B. Cord blood levels of immune-globulin-G subclass antibodies to food and inhalant allergens in relation to maternal atopy and the development of atopic disease during the first 8 years of life. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, G.H.S.; Grimshaw, K.E.C.; Briggs, R.; Lewis, S.A.; Mullee, M.A.; Thornton, C.A.; Warner, J.O. Serum ovalbumin-specific immunoglobulinG responses during pregnancy reflect maternal intake of dietary egg and relate to the development of allergy in early infancy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glovsky, M.M.; Ghekiere, L.; Rejzek, E. Effect of maternal immunotherapy on immediate skin test reactivity, specific Rye-1 IgG & IgE antibody and total IgE of the children. Ann. Allergy 1991, 67, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mitselou, N.; Hallberg, J.; Stephansson, O.; Almqvist, C.; Melén, E.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Cesarean delivery, preterm birth, and risk of food allergy: Nationwide Swedish cohort study of more than 1 million children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1510–1514.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.G.; Pollak, J.; Glass, T.A.; Poulsen, M.N.; Bailey-Davis, L.; Mowery, J.; Schwartz, B.S. Early-life antibiotic use and subsequent diagnosis of food allergy and allergic diseases. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Elsen, L.W.J.; Garssen, J.; Burcelin, R.; Verhasselt, V. Shaping the Gut Microbiota by Breastfeeding: The Gateway to Allergy Prevention? Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harm Wopereis, H.; Kathleen Sim, K.; Alexander Shaw, A.; Warner, J.O.; Knol, J.; Kroll, J.S. Intestinal microbiota in infants at high risk for allergy: Effects of prebiotics and role in eczema developmentin high risk newborns. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.; Naspitz, C.; Warner, J.O. Early immunological influences in prevention of allergy and allergic disease. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2004, 84, 102–127. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, J.O.; Turner, P.J. Allergy; The Science of Paediatrics; Lissauer, T., Carroll, W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 297–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gøtzsche, P.C.; Johansen, H.K. House dust mite control measures for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, CD001187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroni, D.G.; Boner, A.L.; Vallone, G.; Antolini, I.; Warner, J.O. Effective allergen avoidance at high altitude reduces allergen induced bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, R.J.; Pedroletti, C.; Wickman, M.; Bjermer, L.; Valovirta, E.; Dahl, R.; von Berg, A.; Zetterström, O.; Warner, J.O.; for the 4A Study Group. Nocturnal temperature controlled laminar airflow for treating atopic asthma: A randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2012, 67, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.O. Use of temperature-controlled laminar airflow in the management of atopic asthma: Clinical evidence and experience. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2017, 11, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Thoracic Society/Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. British Guideline on the Management of Asthma; British Thoracic Society: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brożek, J.L.; Bousquet, J.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Bonini, S.; Canonica, G.W.; Casale, T.B.; van Wijk, R.G.; Ohta, K.; Zuberbier, T.; Schünemann, H.J.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, W.H.I. Filaggrin failure—From ichthyosis vulgaris to atopic eczema and beyond. Brit. J. Derm. 2016, 175, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.E.; Warner, J.O. The Atopic Dance. Curr. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 30, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Moscato, G. Occupational allergic airway disease. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2017, 5, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, M.K.; Illi, S.; Ege, M.J.; Lau, S.; Keil, T.; Wahn, U.; von Mutius, E.; Multicentre Allergy Study (MAS) Group. Allergic rhinitis as a predictor for wheezing onset in school-aged children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, P.W.; Stricker, W.E.; Chu, C.-P.; Naessens, J.M.; Naessens, J.M.; Reese, M.E.; Reed, C.E.; Marcoux, J.P. Efficacy of Beclomethasone Nasal Solution, Flunisolide, and Cromolyn in Relieving Symptoms of Ragweed Allergy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1987, 62, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, M.J.; Puy, R.M.; Weiner, J.M. Injection allergen immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, CD001186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, S.R.; Walker, S.M.; Varga, E.-M.; Jacobson, M.R.; O’Brien, F.; Noble, W.; Till, S.J.; Hamid, Q.A.; Nouri-Aria, K.T. Long-Term Clinical Efficacy of Grass-Pollen Immunotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, P.A.; Borer-Reinhold, M.; Heijnen, I.A.; Gnehm, H.P. Twelve-year follow-up after discontinuation of preseasonal grasspollen immunotherapy in childhood. Allergy 2006, 61, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, L.; Niggemann, B.; Dreborg, S.; Ferdousi, H.A.; Reese, M.E.; Reed, C.E.; Marcoux, J.P. Specific immunotherapy has long-term preventive effect of seasonaland perennial asthma: 10-year follow-up on the PAT study. Allergy 2007, 62, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaar, O.; Lou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Klimek, L.; Zhang, L. Recent developments and highlights in allergen immunotherapy. Allergy 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incorvaia, C.; Mauro, M.; Makri, E.; Leo, G.; Ridolo, E. Two decades with omalizumab: What we still have to learn. Biol. Targets Ther. 2018, 12, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.O. Omalizumab for childhood asthma. Expert Rev. Resp. Med. 2010, 4, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Benralizumab for Treating for Treating Severe Eosinophilic Asthma Eosinophilic; Technology Appraisal Guidance; National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: London, UK, 2019; Available online: nice.org.uk/guidance/ta565 (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Abrams, E.M.; Becker, A.B.; Szefler, S.J. Current State and Future of Biologic Therapies in the Treatment of Asthma in Children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2018, 31, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, C.; Griffin, R.; Rothenberg, T.; Tallett, A.; Hopwood, B.; Sizmur, S.; O’Keeffe, C.; Warner, J.O. New patient-reported experience measure for children with allergic disease: Development, validation and results from integrated care. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.O.; Spitters, S. Integrating Care for Children with Allergic Diseases: UK experience. Curr. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 30, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Warner, J.O. Asthma/Rhinitis (The United Airway) and Allergy: Chicken or Egg; Which Comes First? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051483
Warner JO. Asthma/Rhinitis (The United Airway) and Allergy: Chicken or Egg; Which Comes First? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051483
Chicago/Turabian StyleWarner, John O. 2020. "Asthma/Rhinitis (The United Airway) and Allergy: Chicken or Egg; Which Comes First?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051483
APA StyleWarner, J. O. (2020). Asthma/Rhinitis (The United Airway) and Allergy: Chicken or Egg; Which Comes First? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051483




