Clinical, Radiological, and Laboratory Features of Spinal Cord Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients and Biomaterials
2.2. NFL and Anti-SSA(Ro)-Antibody Analyses
2.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Protocols
2.4. Standard Protocol Approval, Registration, and Patient Consent
3. Results
3.1. Cohort
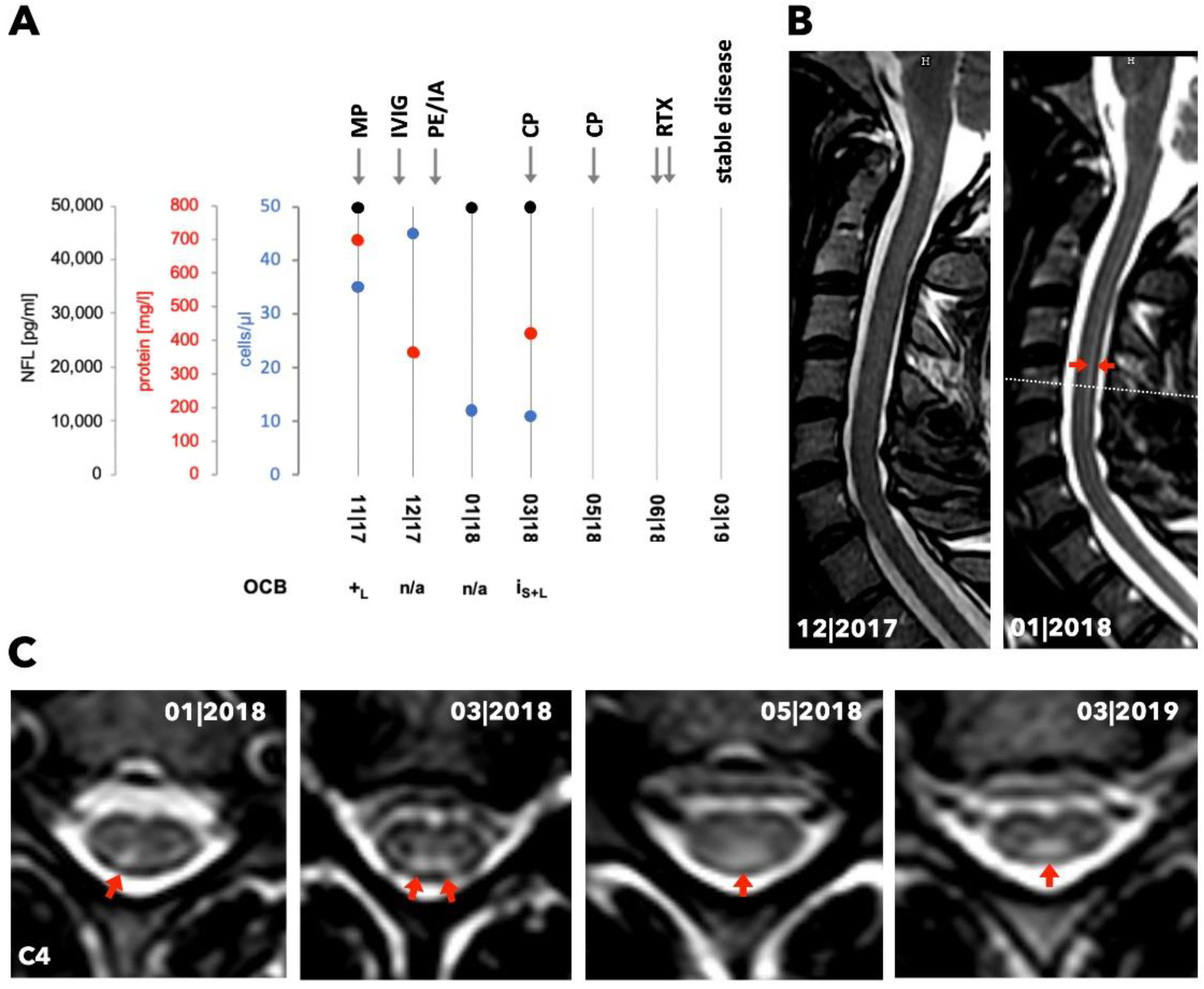
3.2. Case 1
3.3. Case 2
3.4. Case 3
3.5. Case 4
3.6. MRI Pattern
3.7. Antibody Analyses
3.8. NFL Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flores-Chávez, A.; Kostov, B.; Solans, R.; Fraile, G.; Maure, B.; Feijoo-Massó, C.; Rascón, F.-J.; Pérez-Alvarez, R.; Zamora-Pasadas, M.; García-Pérez, A.; et al. Severe, life-threatening phenotype of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Clinical characterisation and outcomes in 1580 patients (GEAS-SS Registry). Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 112), 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Seeliger, T.; Prenzler, N.K.; Gingele, S.; Seeliger, B.; Körner, S.; Thiele, T.; Bönig, L.; Sühs, K.-W.; Witte, T.; Stangel, M.; et al. Neuro-Sjögren: Peripheral Neuropathy with Limb Weakness in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal Alegria, G.; Guellec, D.; Mariette, X.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Dernis, E.; Dubost, J.-J.; Trouvin, A.-P.; Hachulla, E.; Larroche, C.; Le Guern, V.; et al. Epidemiology of neurological manifestations in Sjögren’s syndrome: Data from the French ASSESS Cohort. RMD Open 2016, 2, e000179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, I.; Teixeira, F.; Martins Silva, A.; Vasconcelos, C.; Farinha, F.; Santos, E. Frequent involvement of central nervous system in primary Sjögren syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Solans, R.; Rosas, J.; Camps, M.T.; Gil, A.; Del Pino-Montes, J.; Calvo-Alen, J.; Jiménez-Alonso, J.; Micó, M.-L.; Beltrán, J.; et al. Primary Sjögren syndrome in Spain: Clinical and immunologic expression in 1010 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2008, 87, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Kurien, B.T.; Scofield, R.H. Autoantibodies in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliotis, F.; Mavragani, C.; Moutsopoulos, H. Central nervous system involvement in Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobón, G.J.; Pers, J.-O.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Youinou, P. Neurological Disorders in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Autoimmune Dis. 2012, 2012, 645967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégevand, P.; Chizzolini, C.; Chofflon, M.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Lalive, P.H.; Picard, F. Cerebrospinal fluid anti-SSA autoantibodies in primary Sjogren’s syndrome with central nervous system involvement. Eur. Neurol. 2007, 57, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, L.K.; Krishnan, C.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Rosen, A.; Morris, S.; Mahoney, J.A.; Kerr, D.A.; Wigley, F.M. Recurrent transverse myelitis associates with anti-Ro (SSA) autoantibodies. Neurology 2004, 62, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, S.; Farinazzo, A.; Monaco, S.; Gajofatto, A.; Zanusso, G.; Schanda, K.; Capra, R.; Mancinelli, C.; Bonora, A.; Bombardi, R.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain in NMOSD and Related Disorders: Comparison According to Aquaporin-4 and Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibodies Status. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2017, 3, 2055217317743098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridel, C.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Alvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Andreasson, U.; Axelsson, M.; Bäckström, D.C.; Bartos, A.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein in Neurology: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H.; Lange, P. Quantification of virus-specific antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: Sensitive and specific detection of antibody synthesis in brain. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Consensus and Data-Driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, R.; Bowman, S.J.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Theander, E.; Bootsma, H.; Tzioufas, A.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Dörner, T.; Ravaud, P.; et al. EULAR Sjögren’s syndrome disease activity index (ESSDAI): A user guide. RMD Open 2015, 1, e000022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, R.; Ravaud, P.; Bowman, S.J.; Baron, G.; Tzioufas, A.; Theander, E.; Gottenberg, J.-E.; Bootsma, H.; Mariette, X.; Vitali, C. EULAR Sjogren’s syndrome disease activity index: Development of a consensus systemic disease activity index for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; de Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, D.M.; Mason, D.K. Labial salivary gland biopsy in Sjögren’s disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 1968, 21, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikyan, G.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; D’Suoza, A.; Akhtar, N.; Elzouki, A.N.; Hammoudeh, M. Transverse Myelitis Associated with Anti-Ro (SSA) Autoantibodies: A Record of Two Cases. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2012, 2012, 515768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sá, M.J. Acute transverse myelitis: A practical reappraisal. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 9, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlenberg, J.M. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder as an initial presentation of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 40, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Qiu, W.; Lu, Z.; Dai, Y.; Wu, A.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bao, J.; Hu, X. Acute transverse myelitis in demyelinating diseases among the Chinese. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 2206–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Ruprecht, K.; Kleiter, I.; Borisow, N.; Asgari, N.; Pitarokoili, K.; Pache, F.; Stich, O.; Beume, L.-A.; Hümmert, M.W.; et al. MOG-IgG in NMO and related disorders: A multicenter study of 50 patients. Part 2: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, radiological and laboratory features, treatment responses, and long-term outcome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmand, N.; Wahren-Herlenius, M.; Gunnarsson, I.; Svenungsson, E.; Löfström, B.; Ioannou, Y.; Isenberg, D.A.; Magnusson, C.G. Ro/SSA and La/SSB specific IgA autoantibodies in serum of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1999, 58, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, G.V.; Marques, M.; Balbi, V.; Gormezano, N.W.S.; Kozu, K.; Sakamoto, A.P.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Terreri, M.T.; Magalhães, C.S.; Guariento, A.; et al. Anti-RO/SSA and anti-La/SSB antibodies: Association with mild lupus manifestations in 645 childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevorach, D.; Raz, E.; Steiner, I. Evidence for intrathecal synthesis of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus with neurological involvement. Lupus 1994, 3, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlitzki, M.; Butryn, M.; Kirchner, F.; Färber, J.; Beuing, O.; Minnerup, J.; Meuth, S.G.; Neumann, J. CSF Neurofilament light chain level predicts axonal damage in cerebral vasculitis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1134–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Disanto, G.; Tsagkas, C.; Amann, M.; Naegelin, Y.; Leppert, D.; Gobbi, C.; Granziera, C.; Yaldizli, Ö.; et al. Serum neurofilament as a predictor of disease worsening and brain and spinal cord atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2018, 141, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Perotin, S.; Castillo-Villalba, J.; Cubas-Nuñez, L.; Gasque, R.; Hervas, D.; Gomez-Mateu, J.; Alcala, C.; Perez-Miralles, F.; Gascon, F.; Dominguez, J.A.; et al. Combined Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Chain Protein and Chitinase-3 Like-1 Levels in Defining Disease Course and Prognosis in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Plavina, T.; Barro, C.; Disanto, G.; Sangurdekar, D.; Singh, C.M.; Moor, C.; de Engle, B.; Kieseier, B.C.; Fisher, E.; et al. Neurofilament light levels are associated with long-term outcomes in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2019, 1352458519885613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Michalak, Z.; Isobe, N.; Barro, C.; Leppert, D.; Matsushita, T.; Hayashi, F.; Yamasaki, R.; Kuhle, J.; et al. Serum GFAP and neurofilament light as biomarkers of disease activity and disability in NMOSD. Neurology 2019, 93, e1299–e1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study center | Magdeburg | Münster | Hannover | Hannover |
| Sex | female | female | female | male |
| Age (years) | 39 | 50 | 55 | 52 |
| Disease duration (months) of Sjögren’s syndrome | 0 | 60 | 27 | 1 |
| Leading neurological symptoms | severe sensory ataxia, mild paraparesis | slight sensory ataxia, dysesthesia | dysesthesia, mild sensorimotor tetraparesis | sensorimotor tetraparesis |
| Further organ manifestation | sicca symptoms, alopecia, hearing loss | sicca symptoms, arthralgias | sicca symptoms | sicca symptoms, arthralgias |
| ACR-EULAR-Score (baseline) | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| ESSDAI (baseline) | 15 | 20 | 17 | 17 |
| Histology (lip salivary gland, Chisholm & Mason grade [18]) | 0 | n/a | 4 | 1 |
| MEP (tibialis anterior muscle) | abnormal | unremarkable | not done | unremarkable |
| SEP (tibial nerve) | abnormal | unremarkable | abnormal | abnormal |
| Motor/sensory neurography u/l limb | unremarkable | unremarkable | unremarkable | unremarkable |
| Brain T2 lesions | no | no | yes | yes |
| Extent spinal cord T2 lesion | C3-T5 | C3-C6 | C2-7 | C1-6; T12 |
| Gd+ of spinal cord lesion | no | no | no | yes |
| CSF cell count (n/µl) | 45 | 0 | 3 | 39 |
| CSF OCB | positive | negative | negative | positive |
| CSF TPC (mg/l) | 355 | 380 | 394 | 462 |
| Qalb | 10.9 | 5.0 | 5.01 | 6.99 |
| CSF NFL (pg/ml) | 50,000 | 621 | 3161 | 9984 |
| Serum SSA(Ro)- antibodies total (U/ml) | 58 | 2080 | 0 | 184 |
| CSF SSA(Ro)- antibodies total (U/ml) | 0.75 | 5.3 | 0 | 6.1 |
| ASI SSA(Ro) | 2.2 | 1 | / | 5.1 |
| Treatment history | IV GCS rituximab IV cyclophosphamide PE/IA IV immunoglobulins | oral GCS hydroxychloroquine methotrexate | oral GCS rituximab IV cyclophosphamide | IV + oral GCS rituximab IV cyclophosphamide IA azathioprine |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butryn, M.; Neumann, J.; Rolfes, L.; Bartels, C.; Wattjes, M.P.; Mahmoudi, N.; Seeliger, T.; Konen, F.F.; Thiele, T.; Witte, T.; et al. Clinical, Radiological, and Laboratory Features of Spinal Cord Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051482
Butryn M, Neumann J, Rolfes L, Bartels C, Wattjes MP, Mahmoudi N, Seeliger T, Konen FF, Thiele T, Witte T, et al. Clinical, Radiological, and Laboratory Features of Spinal Cord Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051482
Chicago/Turabian StyleButryn, Michaela, Jens Neumann, Leoni Rolfes, Claudius Bartels, Mike P. Wattjes, Nima Mahmoudi, Tabea Seeliger, Franz F. Konen, Thea Thiele, Torsten Witte, and et al. 2020. "Clinical, Radiological, and Laboratory Features of Spinal Cord Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051482
APA StyleButryn, M., Neumann, J., Rolfes, L., Bartels, C., Wattjes, M. P., Mahmoudi, N., Seeliger, T., Konen, F. F., Thiele, T., Witte, T., Meuth, S. G., Skripuletz, T., & Pawlitzki, M. (2020). Clinical, Radiological, and Laboratory Features of Spinal Cord Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051482







