Injury of the Tibial Nutrient Artery Canal during External Fixation for Lower Extremity Fractures: A Computed Tomography Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Imaging Protocol
2.3. Radiologic Assessment
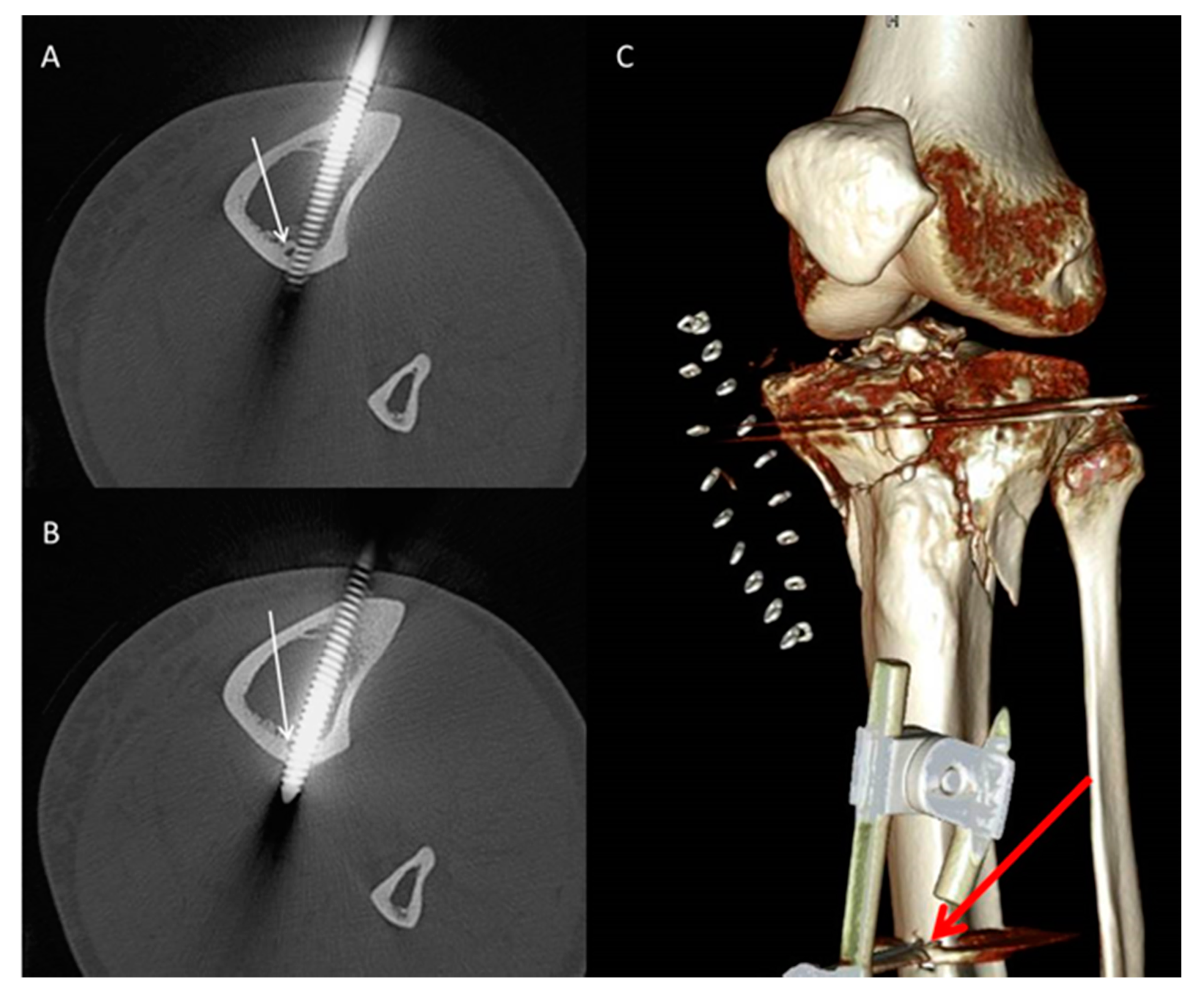
- Pin characteristics (orientation of pin application: anteromedial/tibial crest, anterolateral) and cortical position of the pins (bicortical/monocortical/transcortical) (Figure 2).
- The anatomic relationship between the TNAC and external fixation pin (topography above/below and at the level of the TNA canal, and distance between the pin and medial tibial plateau and/or the medial malleolus) for different fixation and fracture types.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient-Based Analysis
3.2. Pin-Based Analysis
3.2.1. All Pins
3.2.2. Pins Applied at the Level of the TNAC
3.3. Location of the Tibial Segment at Which the TNA Was Mostly Injured
4. Discussion
4.1. The Significance of the TNAC and the Sequelae of Its Injury
4.2. External Fixation in the Setting of Lower Extremity Fractures and Its Perils
4.3. Safe Application of External Fixation Devices
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, Y.; Hao, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P. Did you notice the tibial nutrient artery when applying external fixation? Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 2089–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhinelander, F.W. Tibial blood supply in relation to fracture healing. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1974, 105, 34–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, A. The clinical significance of the nutrient artery. Orthop. Rev. 1993, 22, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almansour, H.; Armoutsis, E.; Reumann, M.K.; Nikolaou, K.; Springer, F. The Anatomy of the Tibial Nutrient Artery Canal—An Investigation of 106 Patients Using Multi-Detector Computed Tomography. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, G.E., Jr.; Kelly, P.J.; Peterson, L.F.A.; Janes, J.M. Blood supply of the human tibia. JBJS 1960, 42, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, M.R.; Kummer, F.J.; Koval, K.J.; Egol, K.A. Intramedullary nailing of the lower extremity: Biomechanics and biology. JAAOS-J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2007, 15, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, J., Jr.; Prickett, W.; Song, E.; Becker, D.; Ricci, W. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: A human cadaveric study. J. Orthop. Trauma 2002, 16, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueta, J. Blood supply and the rate of healing of tibial fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1974, 105, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Kinose, S.; Kato, K.; Sakai, T.; Ichimura, K. Anatomic characterization of the femoral nutrient artery: Application to fracture and surgery of the femur. Clin. Anat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.; Palumbo, B.; Badman, B.; Brooks, J.; Van Gelderen, J.; Mighell, M. Humeral shaft fractures: A review. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2011, 20, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.F.; Pellico, L.G.; Alias, M.G.; Fernandez-Valencia, R. A study of the nutrient foramina in human long bones. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1987, 9, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paar, O.; Magin, M.; Prescher, A. Disruption of the arteria nutricia tibiae by reamed and unreamed intramedullary nailing. Study of the vascular architecture of the human tibial intramedullary cavity. Z. Fur Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 2000, 138, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejwani, N.; Polonet, D.; Wolinsky, P.R. External fixation of tibial fractures. JAAOS-J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2015, 23, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carroll, E.A.; Andrew Koman, L. External fixation and temporary stabilization of femoral and tibial trauma. J. Surg. Orthop. Adv. 2011, 20, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, E.V.; Lavadia, W.T.; Blebea, J. Vascular impingement by external fixator pins: A case report. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1995, 38, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staeheli, G.R.; Fraser, M.R.; Morgan, S.J. The dangers of damage control orthopedics: A case report of vascular injury after femoral fracture external fixation. Patient Saf. Surg. 2012, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.R.; Bronk, J.T.; Kelly, P.J. Effect of fracture fixation on cortical bone blood flow. J. Orthop. Res. 1990, 8, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; Khan, R.; Davies, R.; Lavender, P. The uptake by the canine tibia of the bone-scanning agent 99mTc-MDP before and after an osteotomy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1978, 60, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triffitt, P.D.; Cieslak, C.A.; Gregg, P.J. A quantitative study of the routes of blood flow to the tibial diaphysis after an osteotomy. J. Orthop. Res. 1993, 11, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolini, E.; Goumenos, S.D.; Giannoudi, M.; Sanguineti, F.; Stella, M.; Giannoudis, P.V. Femoral and tibial blood supply: A trigger for non-union? Injury 2014, 45, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilkanat, E.; Boyan, N.; Ozsahin, E.T.; Soames, R.; Oguz, O. Location, number and clinical significance of nutrient foramina in human long bones. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2007, 189, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snell, R.S. Clinical Anatomy for Medical Students; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Audigé, L.; Griffin, D.; Bhandari, M.; Kellam, J.; Rüedi, T.P. Path analysis of factors for delayed healing and nonunion in 416 operatively treated tibial shaft fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 438, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilat, C.; Leutenegger, A.; Rüedi, T. Osteosynthesis of 245 tibial shaft fractures: Early and late complications. Injury 1994, 25, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funsten, R.V.; Lee, R.W. Healing time in fractures of the shafts of the tibia and femur. JBJS 1945, 27, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Heppenstall, R.B.; Brighton, C.T.; Esterhai, J.J.; Muller, G.A. Prognostic factors in nonunion of the tibia: An evaluation of 185 cases treated with constant direct current. J. Trauma 1984, 24, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, M.; Andrés-Cano, P.; Pascual-López, F. Suppl 1: M9: Periarticular Fractures of the Knee in Polytrauma Patients. Open Orthop. J. 2015, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, M.; Bouillon, B.; Shafizadeh, S.; Paffrath, T.; Lefering, R.; Wafaisade, A. Epidemiology of extremity injuries in multiple trauma patients. Injury 2013, 44, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encinas-Ullán, C.A.; Martínez-Diez, J.M.; Rodríguez-Merchán, E.C. The use of external fixation in the emergency department: Applications, common errors, complications and their treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.A. Complications of external skeletal fixation. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1983, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-K.; Hwang, J.H.; Sahu, D.; Jun, S.H. Complication rate and pitfalls of temporary bridging external fixator in periarticular communited fractures. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2011, 3, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhandari, M.; Guyatt, G.H.; Swiontkowski, M.F.; Tornetta, I.I.I.P.; Hanson, B.; Weaver, B.; Sprague, S.; Schemitsch, E.H. Surgeons’ preferences for the operative treatment of fractures of the tibial shaft: An international survey. JBJS 2001, 83, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzioupis, C.; Giannoudis, P.V. Prevalence of long-bone non-unions. Injury 2007, 38, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershuni, D.H.; Pinsker, R. Bone grafting for nonunion of fractures of the tibia: A critical review. J. Trauma 1982, 22, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, R.; Lyons, T.; Webb, J. Complications of external fixation of open fractures of the tibia. Injury 1987, 18, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, P.; Bøe, A.; Mølster, A.O.; Solheim, E.; Hordvik, M. Open tibial fractures treated with the Ex-fi-re external fixation system. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 326, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, M.R.; Bailey, D.E. Fracture healing in tibia fractures with an associated vascular injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1997, 42, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, G.R.; Kelly, P. Blood flow and mineral deposition in canine tibial fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1975, 57, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, K.; Katzman, S.; Delgado, E.; Contreras, D. Delayed unions and nonunions of open tibial fractures. Correlation with arteriography results. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.A.; Patka, P.; Koomen, A.R.; Rauwerda, J. Vascular injury from external fixation. J. Trauma 1992, 33, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhal, A.; Chadha, M.; Lal, H.; Singh, T.; Tyagi, S. Encounters with pseudoaneurysms in orthopaedic practice. Injury 2001, 32, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vives, M.J.; Abidi, N.A.; Ishikawa, S.N.; Taliwal, R.V.; Sharkey, P.F. Soft tissue injuries with the use of safe corridors for transfixion wire placement during external fixation of distal tibia fractures: An anatomic study. J. Orthop. Trauma 2001, 15, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höntzsch, D. AO Foundation-AO Surgery Reference. Available online: https://surgeryreference.aofoundation.org/orthopedic-trauma/adult-trauma/proximal-tibia/extraarticular-fracture-metaphyseal-simple/bridging-external-fixator-temporary?searchurl=%2fSearchResults#principles-of-joint-bridging-external-fixation (accessed on 12 May 2020).



| Fracture Type | Total No. of Patients | Complete Injury | Partial Injury | No Injury | p * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients | % | No. of Patients | % | No. of Patients | % | |||
| Distal femur | 19 | 4 | 14.8% | 1 | 7.7% | 14 | 21.5% | 0.12 |
| Proximal tibia | 26 | 11 | 40.7% | 3 | 23.1% | 12 | 18.5% | |
| Tibial shaft | 32 | 4 | 14.8% | 7 | 53.8% | 21 | 32.3% | |
| Distal tibia | 28 | 8 | 29.6% | 2 | 15.4% | 18 | 27.7% | |
| Total | 105 | 27 | 25.7% | 13 | 12.3% | 65 | 30.3% | |
| External Fixator Type | Total No. of Patients | Complete Injury | Partial Injury | No Injury | p * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients | % | No. of Patients | % | No. of Patients | % | |||
| Unimodular non-bridging | 18 | 1 | 3.7% | 4 | 30.8% | 13 | 20% | 0.16 |
| Knee bridging | 53 | 17 | 63% | 5 | 38.5% | 31 | 47.7% | |
| Ankle bridging | 34 | 9 | 33.3% | 4 | 30.8% | 21 | 32.3% | |
| Total | 105 | 27 | 25.7% | 13 | 12.3% | 65 | 30.3% | |
| External Fixator Type | Total No. of Pins | At the Level of the TNA | Below/Above the TNA | p * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Pins | % | No. of Pins | % | |||
| Unimodular non-bridging | 56 | 13 | 23.2% | 43 | 76.8% | 0.01 |
| Knee-bridging | 92 | 43 | 46.7% | 49 | 53.3% | |
| Ankle bridging | 66 | 29 | 43.9% | 37 | 56.1% | |
| Total | 214 | 85 | 39.7% | 129 | 60.3% | |
| Fracture Type | Total No. of Pins | Complete Injury | Partial Injury | No Injury | p * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Pins | % | No. of Pins | % | No. of Pins | % | |||
| Distal femur | 16 | 4 | 25% | 1 | 6% | 11 | 69% | 0.069 |
| Proximal tibia | 22 | 11 | 50% | 3 | 14% | 8 | 36% | |
| Tibial shaft | 23 | 4 | 17% | 8 | 35% | 11 | 48% | |
| Distal tibia | 24 | 9 | 38% | 2 | 8% | 13 | 54% | |
| Total | 85 | 28 | 33% | 14 | 16% | 43 | 51% | |
| External Fixator Type | Total No. of Pins | Complete Injury | Partial Injury | No Injury | p * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Pins | % | No. of Pins | % | No. of Pins | % | |||
| Unimodular non-bridging | 13 | 2 | 15% | 4 | 31% | 7 | 54% | 0.39 |
| Knee-bridging | 43 | 17 | 39% | 5 | 12% | 21 | 49% | |
| Ankle bridging | 29 | 9 | 31% | 5 | 17% | 15 | 52% | |
| Total | 85 | 28 | 33% | 14 | 16% | 43 | 51% | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almansour, H.; Jacoby, J.; Baumgartner, H.; Reumann, M.K.; Nikolaou, K.; Springer, F. Injury of the Tibial Nutrient Artery Canal during External Fixation for Lower Extremity Fractures: A Computed Tomography Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072235
Almansour H, Jacoby J, Baumgartner H, Reumann MK, Nikolaou K, Springer F. Injury of the Tibial Nutrient Artery Canal during External Fixation for Lower Extremity Fractures: A Computed Tomography Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072235
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmansour, Haidara, Johann Jacoby, Heiko Baumgartner, Marie K. Reumann, Konstantin Nikolaou, and Fabian Springer. 2020. "Injury of the Tibial Nutrient Artery Canal during External Fixation for Lower Extremity Fractures: A Computed Tomography Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072235
APA StyleAlmansour, H., Jacoby, J., Baumgartner, H., Reumann, M. K., Nikolaou, K., & Springer, F. (2020). Injury of the Tibial Nutrient Artery Canal during External Fixation for Lower Extremity Fractures: A Computed Tomography Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072235




