Neutralizing Antibody Production in Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Patients, in Comparison with Pneumonic COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population and Specimen Collection
2.1.1. Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Patients
2.1.2. Patient Grouping of Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Patients without Pneumonia
2.1.3. Moderate to Severe COVID-19 Patients with Pneumonia
2.1.4. Negative Control Patients
2.2. Serologic Tests for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody
2.2.1. Serum Neutralization Test (MN Assay)
2.2.2. IgM and IgG Antibody Test (FIA Kit)
2.2.3. Total Antibody Test (ELISA Kit)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the COVID-19 Patients
3.2. Antibody Production of Asymptomatic to Pneumonic COVID-19 Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbreak Situation. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Kim, J.Y.; Choe, P.G.; Oh, Y.; Oh, K.J.; Kim, J.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Na, H.K.; Oh, M.-D. The First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Imported into Korea from Wuhan, China: Implication for Infection Prevention and Control Measures. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ko, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-M.; Chung, Y.-S.; Kim, H.M.; Han, M.-G.; Kim, S.Y.; Chin, B.S. Viral Load Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in First Two Patients in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, K.J.; Shin, Y.W.; Lee, J.S.; Chung, S.; Lee, T.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.; Yum, M.S.; et al. Report on the Epidemiological Features of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 2, 2020. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e112. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, K.T.; Ko, J.-H.; Shin, H.; Sung, M.; Kim, J.Y. Drive-Through Screening Center for COVID-19: A Safe and Efficient Screening System against Massive Community Outbreak. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, K.R. Early diagnosis and rapid isolation: Response to COVID-19 outbreak in Korea. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Min, P.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-W. Prevalence and Duration of Acute Loss of Smell or Taste in COVID-19 Patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, H.V.; Singh, A. Asymptomatic transmission during the COVID-19 pandemic and implications for public health strategies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, N.; Simon, P.; Ebner, P.; Eichner, D.; Reynolds, J.; Bendavid, E.; Bhattacharya, J. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibodies Among Adults in Los Angeles County, California, on April 10–11, 2020. JAMA 2020, 323, 2425–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.E.F.; Anderson, D.E.; Wei, W.E.; Pang, J.; Chia, W.N.; Tan, C.W.; Teoh, Y.L.; Rajendram, P.; Toh, M.; Poh, C.; et al. Connecting clusters of COVID-19: An epidemiological and serological investigation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth, J.; Wilde, B.; Dolff, S.; Anastasiou, O.E.; Krawczyk, A.; Jahn, M.; Cordes, S.; Ross, B.; Esser, S.; Lindemann, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody detection in healthcare workers in Germany with direct contact to COVID-19 patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 128, 104437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Sohn, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, Y.; Hyun, J.H.; Baek, Y.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ku, N.S.; Yeom, J.-S.; et al. Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Two COVID-19 Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- KCDC. Updates on COVID-19 in Republic of Korea, July 9, 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a30402000000&bid=0030 (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- Pollán, M.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Oteo, J.; Hernán, M.A.; Pérez-Olmeda, M.; Sanmartín, J.L.; Fernández-García, A.; Cruz, I.; Fernández de Larrea, N.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Spain (ENE-COVID): A nationwide, population-based seroepidemiological study. Lancet 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percivalle, E.; Cambiè, G.; Cassaniti, I.; Nepita, E.V.; Maserati, R.; Ferrari, A.; Di Martino, R.; Isernia, P.; Mojoli, F.; Bruno, R.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 specific neutralising antibodies in blood donors from the Lodi Red Zone in Lombardy, Italy, as at 06 April 2020. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cheng, S.Z.; Xu, K.W.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Q.T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Xiao, H.; Wang, J.W.; et al. Use of personal protective equipment against coronavirus disease 2019 by healthcare professionals in Wuhan, China: Cross sectional study. BMJ 2020, 369, m2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, M.S.; Kaur, I.P.; Patton, C.D.; Mikhail, N.H.; Vareechon, C.; Granet, K.M. The prevalence of severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) IgG antibodies in intensive care unit (ICU) healthcare personnel (HCP) and its implications-a single-center, prospective, pilot study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.; Leven, E.; Muellers, K.; Stone, K.; Mendu, D.R.; Wajnberg, A. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Among Healthcare Workers at a Tertiary Academic Hospital in New York City. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.B.; Grüter, L.; Boltzmann, M.; Rollnik, J.D. Prevalence of serum IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 among clinic staff. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paderno, A.; Fior, M.; Berretti, G.; Schreiber, A.; Grammatica, A.; Mattavelli, D.; Deganello, A. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Care Workers: Cross-sectional Analysis of an Otolaryngology Unit. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Seok, H.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, Y.E.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.K.; Chung, C.R.; Kang, E.S.; et al. Challenges of convalescent plasma infusion therapy in Middle East respiratory coronavirus infection: A single centre experience. Antivir. Ther. 2018, 23, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisreen, M.A.O.; Marcel, A.M.; Wentao, L.; Chunyan, W.; Corine, H.G.; Victor, M.C.; Mart, M.L.; Reina, S.S.; Erwin de, B.; Felicity, D.C.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2−Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 26, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, T.; Li, J.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients of novel coronavirus disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.A.; Mok, C.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Lv, H.; Ko, R.L.; Wu, N.C.; Yuan, M.; Leung, W.S.; Chan, J.M.; Chik, T.S.; et al. Serological assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), March 2020. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, J.H.; Müller, M.A.; Seok, H.; Park, G.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, Y.E.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, J.M.; et al. Serologic responses of 42 MERS-coronavirus-infected patients according to the disease severity. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 89, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-W.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, J.-Y. A Brief Telephone Severity Scoring System and Therapeutic Living Centers Solved Acute Hospital-Bed Shortage during the COVID-19 Outbreak in Daegu, Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kwon, M.; Moon, J.D.; Hwang, M.W.; Lee, J.M.; Park, K.H.; Yun, S.J.; Bae, H.J.; Choi, A.; Lee, H.; et al. Development of a Rapid Automated Fluorescent Lateral Flow Immunoassay to Detect Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg), Antibody to HBsAg, and Antibody to Hepatitis C. Ann. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryan, A.; Pepper, G.; Wener, M.H.; Fink, S.L.; Morishima, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Jerome, K.R.; Mathias, P.C.; Greninger, A.L. Performance Characteristics of the Abbott Architect SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assay and Seroprevalence in Boise, Idaho. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimeglio, C.; Loubes, J.M.; Deporte, B.; Dubois, M.; Latour, J.; Mansuy, J.M.; Izopet, J. The SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence is the key factor for deconfinement in France. J. Infect. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oran, D.P.; Topol, E.J. Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, F.; Li, D.; Yang, M.; Xing, L.; et al. Treatment of 5 Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 With Convalescent Plasma. JAMA 2020, 323, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechotta, V.; Chai, K.L.; Valk, S.J.; Doree, C.; Monsef, I.; Wood, E.M.; Lamikanra, A.; Kimber, C.; McQuilten, Z.; So-Osman, C.; et al. Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: A living systematic review. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 7, Cd013600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.-H.; Joo, E.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Huh, K.; Cho, S.Y.; Kang, C.-I.; Chung, D.R.; Kang, E.-S.; Peck, K.R. Clinical Application of Rapid Diagnostic Test Kit for SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies into the Field of Patient Care. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sang, L.; Ye, F.; Ruan, S.; Zhong, B.; Song, T.; Alshukairi, A.N.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Kinetics of viral load and antibody response in relation to COVID-19 severity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Asymptomatic/ Anosmia Group n = 15 | Mild Symptomatic Group n = 49 | Pneumonia Group n = 18 * | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 25.2 ± 8.0 | 30.9 ± 9.0 | 65.7 ± 13.2 | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 8 (53.3%) | 20 (40.8%) | 3 (50%) | 0.665 |
| Underlying disease | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (100%) † | <0.001 |
| Symptom, duration | ||||
| Anomia and/or dysgeusia | 9 (60.0%), 14.0 (5.5–21.0) | 16 (32.7%), 18.5 (8.3–29.3) | 0 (0%), NA | 0.025 |
| Rhinorrhea and/or nasal stuffiness | 0 (0%), NA | 17 (34.7%), 21.0 (10.5–50.5) | 0 (0%), NA | 0.008 |
| Sore throat | 0 (0%), NA | 18 (36.7%), 6.0 (3.0–18.5) | 1 (16.7%), 5.0 (NA–NA) | 0.017 |
| Cough | 0 (0%), NA | 25 (51.0%), 11.0 (4.5–30.0) | 4 (66.7%), 10.5 (4.0–17.8) | 0.001 |
| Sputum | 0 (0%), NA | 17 (34.7%), 10.0 (7.0–28.0) | 1 (16.7%), 14.0 (NA–NA) | 0.023 |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | 0 (0%), NA | 10 (20.4%), 4.0 (2.8–7.0) | 3 (50.0%), 7.0 (5–NA) | 0.024 |
| Headache | 0 (0%), NA | 9 (18.4%), 3.0 (1.0–5.0) | 3 (50.0%), 17 (5–NA) | 0.021 |
| Fever, chill, and/or myalgia | 0 (0%), NA | 19 (38.8%), 3.0 (1.0–5.0) | 6 (100%), 15.0 (7.3–20.8) | <0.001 |
| Lowest Ct value | 33.6 (32.4–35.7) | 32.2 (30.8–34.1) | 26.4 (19.3–31.1) | 0.003 |
| Duration of shedding | ||||
| from symptom onset | 34.0 (29.5–41.5) ‡ | 40.0 (33.5–45.0) | 29.0 (23.0–38.8) | |
| from diagnosis | 32.0 (26.0–34.0) | 32.0 (29.0–43.5) | 23.0 (18.3–37.8) | 0.181 |
| Sampling time, days | ||||
| from symptom onset | 39.0 (34.5–46.5) ‡ | 43.0 (37.0–49.5) | 24.0 (19.8–38.3) | |
| from diagnosis | 36.0 (30.0–38.0) | 36.0 (31.5–47.5) | 19.5 (16.8–35.5) | 0.001 |
| Asymptomatic/ Anosmia Group n = 15 | Mild Symptomatic Group n = 49 | Pneumonia Group n = 18 * | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutralizing Antibody | ||||
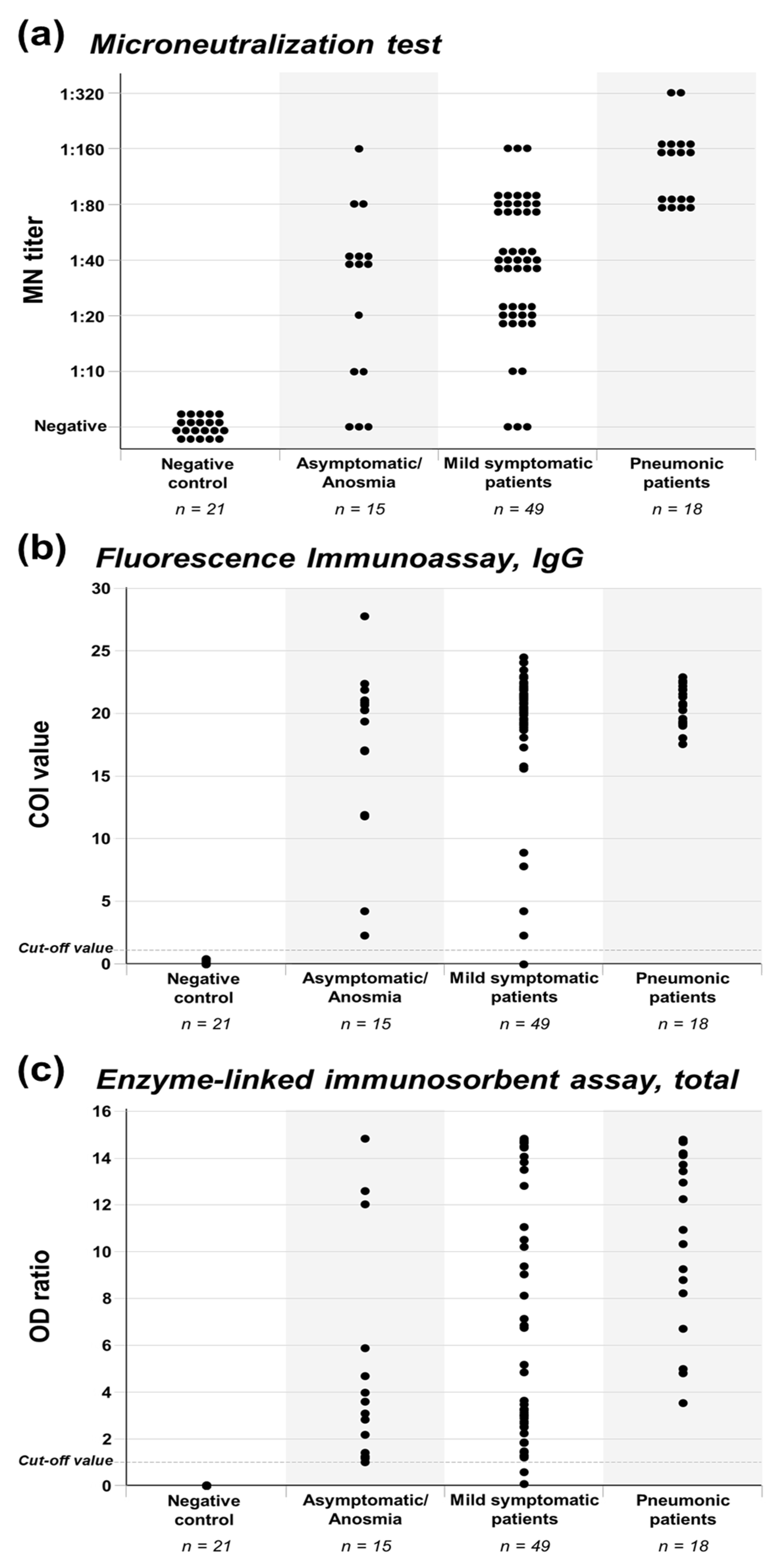
| Positive, titer ≥1:10 | 12 (80.0%) | 46 (93.9%) | 18 (100%) | 0.079 |
| High MN titer, ≥1:80 | 3 (20.0%) | 18 (36.7%) | 18 (100%) | <0.001 |
| FIA, IgG | ||||
| Positive, COI ≥1.1 | 15 (100%) | 48 (98.0%) | 18 (100%) | 0.711 |
| High COI value, ≥15.0 | 11 (73.3%) | 44 (89.8%) | 18 (100%) | 0.049 |
| ELISA, Total | ||||
| Positive, OD ≥ 1.0 | 15 (100%) | 47 (95.9%) | 18 (100%) | 0.501 |
| High OD ratio, ≥ 3.0 | 8 (53.3%) | 32 (65.3%) | 18 (100%) | 0.006 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ko, J.-H.; Joo, E.-J.; Park, S.-J.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, W.D.; Jee, J.; Kim, C.J.; Jeong, C.; Kim, Y.-J.; Shon, H.J.; et al. Neutralizing Antibody Production in Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Patients, in Comparison with Pneumonic COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072268
Ko J-H, Joo E-J, Park S-J, Baek JY, Kim WD, Jee J, Kim CJ, Jeong C, Kim Y-J, Shon HJ, et al. Neutralizing Antibody Production in Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Patients, in Comparison with Pneumonic COVID-19 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072268
Chicago/Turabian StyleKo, Jae-Hoon, Eun-Jeong Joo, Su-Jin Park, Jin Yang Baek, Won Duk Kim, Jaehwan Jee, Chul Joong Kim, Chul Jeong, Yae-Jean Kim, Hye Jin Shon, and et al. 2020. "Neutralizing Antibody Production in Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Patients, in Comparison with Pneumonic COVID-19 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072268
APA StyleKo, J.-H., Joo, E.-J., Park, S.-J., Baek, J. Y., Kim, W. D., Jee, J., Kim, C. J., Jeong, C., Kim, Y.-J., Shon, H. J., Kang, E.-S., Choi, Y. K., & Peck, K. R. (2020). Neutralizing Antibody Production in Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Patients, in Comparison with Pneumonic COVID-19 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072268





