Effectiveness of Different Application Parameters of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for the Treatment of Dysphagia after a Stroke: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
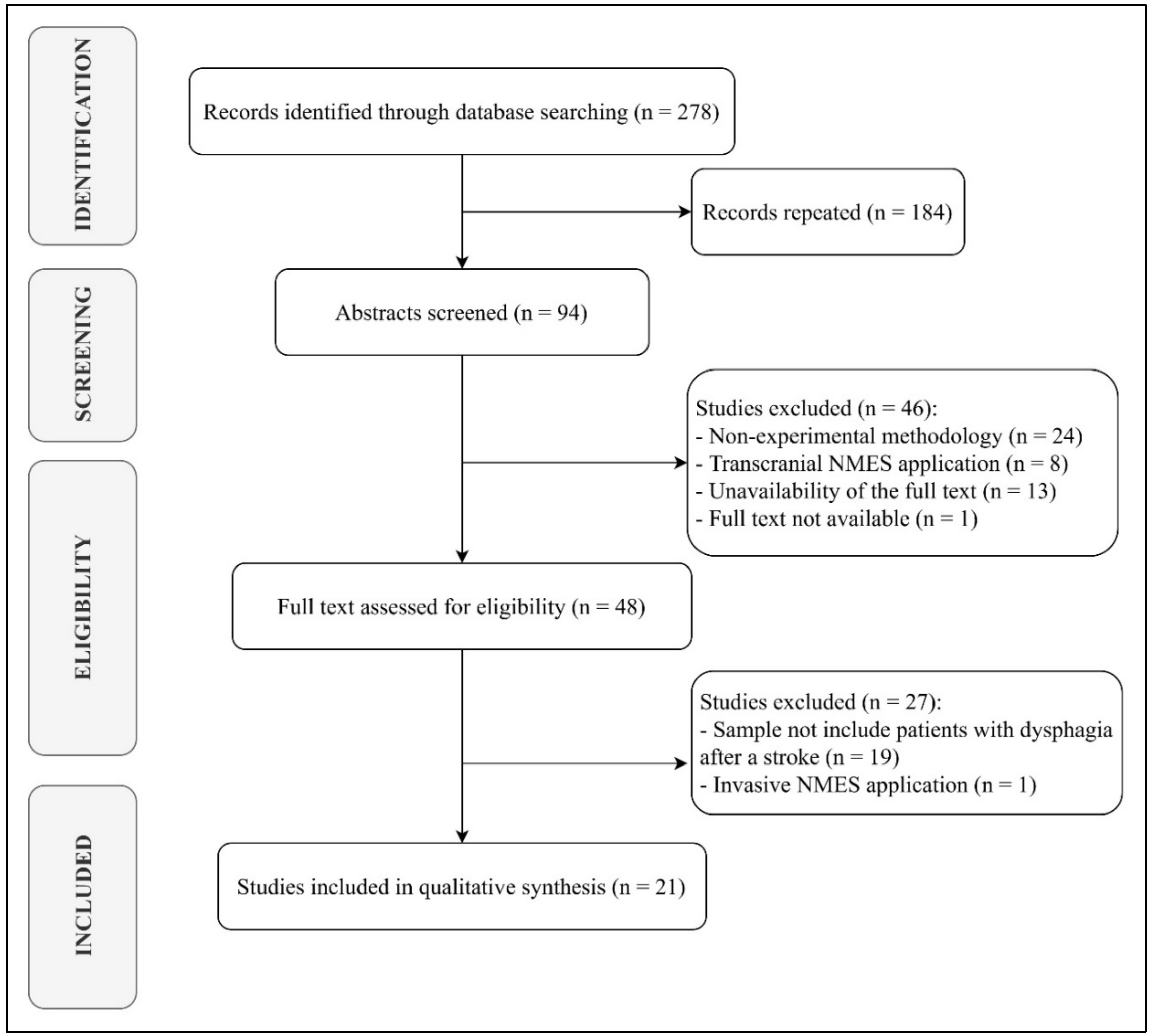
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, D.L.; Roffe, C.; Beavan, J.; Blackett, B.; Fairfield, C.A.; Hamdy, S.; Havard, D.; McFarlane, M.; McLauglin, C.; Randall, M.; et al. Post-stroke Dysphagia: A review and design considerations for future trials. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsetti, P.; Acciai, C.; Palilla, R.; Bosi, M.; Carpinteri, F.; Zingarelli, A.; Pedace, C.; Lenzi, L. Oropharyngeal dysphagia after stroke: Incidence, diagnosis, and clinical predictors in patients admitted to a neurorehabilitation unit. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2009, 18, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dysphagia Section, Oral Care Study Group; Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer (MASCC); International Society of Oral Oncology (ISOO); Raber-Durlacher, J.E.; Brennan, M.T.; Verdonck-de Leeuw, I.M.; Gibson, R.J.; Eilers, J.G.; Waltimo, T.; Bots, C.P.; et al. Swallowing dysfunction in cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, B.A.; Gilbert, J. Dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiation: Assessment, sequelae, and rehabilitation. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 19, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, N.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Han, T.R. Movement of the hyoid bone and the epiglottis during swallowing in patients with dysphagia from different etiologies. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Dziewas, R.; Beck, A.M.; Clave, P.; Hamdy, S.; Heppner, H.J.; Langmore, S.; Herbert, A.; Martino, R.; Pluschinski, P.; et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older persons - from pathophysiology to adequate intervention: A review and summary of an international expert meeting. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martino, R.; Silver, F.; Teasell, R.; Bayley, M.; Nicholson, G.; Streiner, D.L.; Diamant, N.E. The Toronto Bedside Swallowing Screening Test (TOR-BSST) development and validation of a dysphagia screening tool for patients with stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faverio, P.; Aliberti, S.; Bellelli, G.; Suigo, G.; Lonni, S.; Pesci, A.; Restrepo, M.I. The management of community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmerman, A.A.; Speyer, R.; Heijnen, B.J.; Klijn-Zwijnenberg, I.R. Psychometric characteristics of health-related quality-of-life questionnaires in oropharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.P.; Frank, C.; Moltz, C.C.; Vos, P.; Smith, H.J.; Karlsson, U.; Dutta, S.; Midyett, A.; Barloon, J.; Sallah, S. Impact of dysphagia on quality of life after treatment of head-and-neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 61, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, E.H. The mediating and moderating effects of meaning in life on the relationship between depression and quality of life in patients with dysphagia. J. Clin. Nurs. 2019, 28, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, C.; Gemmell, E.; Kenworthy, J.; Speyer, R. A systematic review of the prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, head injury, and pneumonia. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, R.; Dziewas, R. Dysphagia and pharmacotherapy in older adults. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, O.; Cartwright, J.; Whitworth, A.; Cocks, N. Dysphagia therapy post stroke: An exploration of the practices and clinical decision-making of speech-language pathologists in Australia. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2018, 20, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecny, P.; Elfmark, M.; Bastlova, P.; Gaul-Alacova, P. New orofacial physiotherapy of dysphagia after stroke. Int. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 5, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smithard, D.G. Dysphagia management and stroke units. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2016, 4, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suntrup-Krueger, S.; Ringmaier, C.; Muhle, P.; Wollbrink, A.; Kemmling, A.; Hanning, U.; Claus, I.; Warnecke, T.; Teismann, I.; Pantev, C.; et al. Randomized trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for poststroke dysphagia. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasant, D.H.; Michou, E.; O’Leary, N.; Vail, A.; Mistry, S.; Hamdy, S. Greater Manchester Stroke Research Network. Pharyngeal Electrical Stimulation in Dysphagia Poststroke: A Prospective, Randomized Single-Blinded Interventional Study. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2016, 30, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayasekeran, V.; Singh, S.; Tyrell, P.; Michou, E.; Jefferson, S.; Mistry, S.; Gamble, E.; Rothwell, J.; Thompson, D.; Hamdy, S. Adjunctive functional pharyngeal electrical stimulation reverses swallowing disability after brain lesions. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suntrup, S.; Marina, T.; Burchard, J.; Suttrup, I.; Muhle, P.; Oelenberg, S.; Hamacher, C.; Minnerup, J.; Warnecke, T.; Dziewas, R. Electrical pharyngeal stimulation for dysphagia treatment in tracheotomized stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziewas, R.; Mistry, S.; Hamdy, S.; Minnerup, J.; van der Tweel, I.; Schäbitz, W.; Bath, P.M. PHAST-TRAC Investigators. Design and implementation of Pharyngeal electrical Stimulation for early de-cannulation in TRACheotomized (PHAST-TRAC) stroke patients with neurogenic dysphagia: A prospective randomized single-blinded interventional study. Int. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, Y.; Sohn, H.J.; Park, J.S.; Gyu, T.; Beom, Y.; Park, M.; Ko, S.H.; Shin, Y.I. Effect of bihemispheric anodal transcranial direct current stimulation for dysphagia in chronic stroke patients: A randomized clinical trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suiter, D.M.; Leder, S.B.; Ruark, J.L. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on submental muscle activity. Dysphagia 2006, 21, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnaby-Mann, G.D.; Crary, M.A. Examining the evidence on neuromuscular electrical stimulation for swallowing: A meta-analysis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.W.; Chang, K.H.; Chen, H.C.; Liang, W.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Lin, Y.N. The effects of surface neuromuscular electrical stimulation on post-stroke dysphagia: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 30, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, H. Effect of the Masako maneuver and neuromuscular electrical stimulation on the improvement of swallowing function in patients with dysphagia caused by stroke. J. Phys. Sci 2016, 28, 2069–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Hwang, N.; Kim, H.; Lee, G.; Jung, Y. Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation combined with effortful swallowing using electromyographic biofeedback on oropharyngeal swallowing function in stroke patients with dysphagia: A pilot study. Medicine 2019, 98, e17702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J. Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on facial muscle strength and oral function in stroke patients with facial palsy. J. Phys. Sci. 2016, 28, 2541–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, D.; Park, J.; Kim, W. Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lip strength and closure function in patients with dysphagia after stroke. J. Phys. Sci. 2017, 29, 1974–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byeon, H. Combined Effects of NMES and Mendelsohn Maneuver on the Swallowing Function and Swallowing–Quality of Life of Patients with Stroke-Induced Sub-Acute Swallowing Disorders. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Park, J.; Nam, K. Effortful swallow with resistive electrical stimulation training improves pharyngeal constriction in patients post-stroke with dysphagia. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mituuti, C.T.; Arone, M.A.S.; Rosa, R.R.; Berretin-Felix, G. Effects of sensory neuromuscular electrical stimulation on swallowing in the elderly affected by stroke. Top. Geriatr. Rehabil. 2018, 34, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahceci, K.; Umay, E.; Gundogdu, I.; Gurcay, E.; Ozturk, E.; Alicura, S. The effect of swallowing rehabilitation on quality of life of the dysphagic patients with cortical ischemic stroke. Iran. J. Neurol. 2017, 16, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Oh, D.; Hwang, N.; Lee, J. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation combined with effortful swallowing on post-stroke oropharyngeal dysphagia: A randomised controlled trial. J. Oral Rehabil. 2016, 43, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, H.; Koh, H.W. Comparison of treatment effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and thermal-tactile stimulation on patients with sub-acute dysphagia caused by stroke. J. Phys. Sci 2016, 28, 1809–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.G.; Jang, K.W. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation for masseter muscle on oral dysfunction after stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 43, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, G.; Yi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, M.; Pan, M.; Tang, C. The Value of Adding Transcutaneous Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (VitalStim) to Traditional Therapy for Poststroke Dysphagia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Top. Geriatr. Rehabil. 2018, 34, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hara, H. Does sensory transcutaneous electrical stimulation prevent pneumonia in the acute stage of stroke? A preliminary study. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2017, 40, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendy, R.M.; Elerian, A.E.; Emara, T.H. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and conventional therapy in post-stroke dysphagic patients: A randomized controlled trial. Biosci. Res. 2019, 16, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Simonelli, M.; Ruoppolo, G.; Iosa, M.; Morone, G.; Fusco, A.; Grasso, M.G.; Gallo, A.; Paolucci, S. A stimulus for eating. The use of neuromuscular transcutaneous electrical stimulation in patients affected by severe dysphagia after subacute stroke: A pilot randomized controlled trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 44, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Han, C.; Gao, J.; Yue, S. The effect of surface neuromuscular electrical stimulation on patients with post-stroke dysphagia. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2018, 31, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproson, L.; Pownall, S.; Enderby, P.; Freeman, J. Combined electrical stimulation and exercise for swallow rehabilitation post-stroke: A pilot randomized control trial. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2018, 53, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.; Yip, J.; Cui, H.; Guan, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Du, H.; Geng, X. Efficacy of neuromuscular electrical stimulation in improving the negative psychological state in patients with cerebral infarction and dysphagia. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillén-Solà, A.; Messagi-Sartor, M.; Bofill-Soler, N.; Duarte, E.; Barrera, M.C.; Marco, E. Respiratory muscle strength training and neuromuscular electrical stimulation in subacute dysphagic stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnaby, G.D.; LaGorio, L.; Silliman, S.; Crary, M. Exercise-based swallowing intervention (McNeill Dysphagia Therapy) with adjunctive NMES to treat dysphagia post-stroke: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J. Oral Rehabil. 2020, 47, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konecny, P.; Elfmark, M. Electrical stimulation of hyoid muscles in post-stroke dysphagia. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2018, 162, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.; Man, W.D.; Gao, W.; Higginson, I.J.; Wilcock, A.; Maddocks, M. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for muscle weakness in adults with advanced disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 10, CD009419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peckham, P.H.; Knutson, J.S. Functional electrical stimulation for neuromuscular applications. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 7, 327–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vromans, M.; Faghri, P.D. Functional electrical stimulation-induced muscular fatigue: Effect of fiber composition and stimulation frequency on rate of fatigue development. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 38, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffiuletti, N.A. Physiological and methodological considerations for the use of neuromuscular electrical stimulation. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhead, L.M.; Sapienza, C.M.; Rosenbek, J.C. Strength-training exercise in dysphagia rehabilitation: Principles, procedures, and directions for future research. Dysphagia 2007, 22, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderthommen, M.; Duchateau, J. Electrical stimulation as a modality to improve performance of the neuromuscular system. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2007, 35, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, D.A. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation. An overview and its application in the treatment of sports injuries. Sports Med. 1992, 13, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, R.L.; Kelly, M.J. Factors influencing quadriceps femoris muscle torque using transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation. Phys. Ther. 1991, 71, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondin, J.; Cozzone, P.J.; Bendahan, D. Is high-frequency neuromuscular electrical stimulation a suitable tool for muscle performance improvement in both healthy humans and athletes? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.; Lee, S.C.; Johnston, T.E.; Binder-Macleod, S.A. The effectiveness of progressively increasing stimulation frequency and intensity to maintain paralyzed muscle force during repetitive activation in persons with spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grill, W.; Mortimer, J.T. The effect of stimulus pulse duration on selectivity of neural stimulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1996, 43, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafoleanu, C.; Enache, R. Preliminary outcomes in transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation use in patients with dysphagia. Rom. J. Rhinol. 2018, 8, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, H.S.; Beom, J.; Oh, B.; Han, T.R. Kinematic effects of hyolaryngeal electrical stimulation therapy on hyoid excursion and laryngeal elevation. Dysphagia 2013, 28, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondin, J.; Guette, M.; Ballay, Y.; Martin, A. Electromyostimulation training effects on neural drive and muscle architecture. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paillard, T. Combined application of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and voluntary muscular contractions. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Oh, J.; Lee, H. Effortful swallowing training combined with electrical stimulation in post-stroke dysphagia: A randomized controlled study. Dysphagia 2012, 27, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.; Lee, H.; Lim, S.; Choi, Y. Neuromuscular electrical and thermal-tactile stimulation for dysphagia caused by stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 41, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, D.S.; Peters, K.; Eroglu, S.T.; Perless-Carroll, M.; Johnson-Greene, D. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation efficacy in acute stroke feeding tube-dependent dysphagia during inpatient rehabilitation. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 92, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, M.; Panepinto, A.; Sabatini, A.M.; Danti, S. Tongue rehabilitation device for dysphagic patients. Sensors 2019, 19, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Database | Search Equation |
|---|---|
| PubMed | (“Electric Stimulation Therapy”[Mesh]) AND “Stroke”[Mesh]) AND “Deglutition Disorders”[Mesh] |
| (“Stroke”[Mesh]) AND “Electric Stimulation Therapy”[Mesh] AND “Dysphagia” | |
| Medline | (MH “Deglutition Disorders”) AND (MH “Stroke”) AND (MH “Electric Stimulation Therapy”) |
| (MH “Stroke”) AND (MH “Electric Stimulation Therapy”) AND “Dysphagia” | |
| Cinahl | (MH “Stroke”) AND (MH “Electric Stimulation”) AND (MH “Deglutition Disorders”) |
| (MH “Stroke”) AND (MH “Electric Stimulation”) AND “Dysphagia” | |
| Web of Science | TOPIC: (‘deglutition disorders’) AND TOPIC: (‘stroke’) AND TOPIC: (‘electrical stimulation therapy’) |
| TOPIC: (‘dysphagia’) AND TOPIC: (‘stroke’) AND TOPIC: (‘electrical stimulation therapy’) | |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (‘deglutition AND disorders’) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (‘stroke’) AND TITLE-ABS- KEY (‘electrical AND stimulation AND therapy’) |
| TITLE-ABS-KEY (‘dysphagia’) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (‘stroke’) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (‘electrical AND stimulation AND therapy’) |
| Authors | Design | Sample Size | Inclussion Criteria | Exclussion Criteria | Jadad Scale | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD * | BD ** | WD *** | Final Score | |||||
| Bahceci et al. (2017) | ECS | 72 | Diagnosis of DP in the first 30 days after the stroke. Age between 50 and 75 years. | Diagnosis of cancer, dementia, psychiatric disorder, brain stem disease and/or bleeding (subcortical or bilateral). History of stroke, head and/or neck surgery, impaired swallowing. Smokers | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Byeon (2016) | ES | 47 | Diagnosis of DP for more than six months. | Severe cognitive or communicative disorder, depression or nasogastric tube | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Byeon (2020) | ECS | 43 | Over 60 years old. Alteration of swallowing after stroke for more than six months of evolution. Korean Mini-Mental State score at least of 20 points. | Receive some treatment for swallowing earlier. | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Byeon & Koh (2016) | ES | 53 | Diagnosis of moderate or severe DF for more than six months. | Diagnosis of any mental illness, depression or nasogastric tube | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Carnaby et al. (2019) | RCCT | 53 | Stroke for more than two years. Mann Test score less than 18 points. | Previous diagnosis of swallowing disorder. History of head and/or neck surgery | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| Choi (2016) | ES | 9 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke for less than three months. Mini-Mental State Examination score at least of 24 points. | Pacemaker wearer. Severe communication difficulty (dementia and/or aphasia). Epilepsy. Unstable medical condition. Skin disorders in the head and/or neck. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Guillén-Sòla et al. (2017) | RCCT | 50 | Diagnosis of DP after ischemic stroke. Penetration Aspiration Scale score at least of 3 points. | Diagnosis of previous neurological pathology. Cognitive impairment. | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Hamada et al. (2016) | RCCT | 53 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke. | Not described | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hendy et al. (2019) | RCCT | 30 | Diagnosis of DP between 1–3 months of evolution. Age between 45–85 years. Conserved cognitive skills | Pacemakers, orthoses and/or metal implants wearer. Pregnancy. Diagnosis of compulsive disorder and/or cancer. | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Kim et al. (2017) | ES | 19 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke. Cognitive and the swallowing function preserved | Diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage and/or carotid stenosis. Inability to tolerate NMES. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Konecny & Elfmark (2018) | RCCT | 108 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke. Cooperative patient. Negative water test result. | Not described | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Lee et al. (2019) | ES | 40 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke. | Diagnosis of previous oral dysfunction and/or stroke. Presence of abnormalities of the oral cavity. Reduced mental capacity and/or severe impairment of cognitive function. Unstable medical condition with inability to swallow. | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Li et al. (2018) | RCCT | 135 | Diagnosis of DP. Stroke for more than three months. Age between 50-80 years. Communication skills, movement of the hyoid bone and constriction of the pharynx preserved. Stable health condition. | Diagnosis of progressive stroke, cancer and/or other neurological disorders (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s). Radiotherapy treatment. History of head and/or neck surgery. Inability to swallow and/or nasogastric tube. | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Meng et al. (2018) | RCCT | 30 | Diagnosis of DP. Stroke for more than six months. Age between 50-80 years. | Pacemaker wearer. Diagnosis of severe pulmonary or cardiac pathology, dementia, aphasia. Non-collaborating patient. Presence of severe aspiration and/or inability to swallow. | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Mituuti et al. (2018) | ES | 10 | Diagnosis of DP. Stroke for more than six months. Over 60 years. Regular neurological monitoring. Speech therapy treatment lasting more than six months. Stable oral health condition. Token Test-Short Form score complete. | Diagnosis of cancer. Dental rehabilitation during the intervention period. NMES contraindications (pain and/or intolerance to stimulation). | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Oh et al. (2017) | ES | 8 | Diagnosis of DP. Stroke in the last six months. Difficulty closing the lips and to communicate | Not described | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Park et al. (2016) | ES | 50 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke for more than six months. Ability to swallow against resistance. Cooperator. Mini-Mental State Examination score at least of 24 points. | Diagnosis of psychiatric and/or communication disorder, dementia, aphasia and/or epilepsy. Unstable medical condition. Skin disorders in the head or neck. | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Park et al. (2019) | ES | 10 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke. Cough after Water Swallowing Test (3 oz). Initiative to swallow without stimulation of less than six months of evolution. | Pacemaker wearer. Cognitive impairment and/or communication difficulties (dementia and/or aphasia). Unstable medical condition. Skin disorders in the head and/or neck. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Simonelli et al. (2018) | RCCT | 31 | Diagnosis of severe-deep DP between three weeks and three months of evolution after stroke (the first one for the patient). Age between 18–85 years. Stable health condition. | Pacemaker wearer. Cognitive impairment. Diagnosis of epilepsy, depression, cancer and/or neurodegenerative disease. Unstable cardio-pulmonary state. History of head or neck surgery. Previous swallowing treatment. | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Sproson et al. (2018) | RCCT | 30 | DP with reduced pharyngeal elevation. Stroke for more than one month. Stable clinical status. | Pacemaker wearer. Diagnosis of serious heart conditions or other neurological pathologies. | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Zeng et al. (2018) | RCCT | 112 | Diagnosis of DP after stroke (the first one for the patient). Cooperative patient. | Pacemaker, metal implants and/or orthosis wearer. Critical medical condition. Presence of cognitive impairment. Diagnosis of aphasia, cancer, skin disease, peripheral nerve and/or heart disease, epilepsy. Inability to communicate. | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Authors | Intervention | Time of Intervention | Number of Sessions (Frequency) | Electrode Position | F | IT | I | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental Group | Control Group | ||||||||
| Bahceci et al. (2017) | NMES + CT | CT: oral hygiene and dietary modifications, swallowing maneuvers, cranio-cervical postural correction, oral strengthening exercises for lips, tongue and jaw, thermal stimulation with cold, and cognitive, respiratory- and sensory-motor rehabilitation therapies. | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Not described | Not described | Not described | Not described | |
| Byeon (2016) | Group 1: NMES. Group 2: Masako maneuver | --- | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Mylohyoid and thyroid muscles | 80 Hz | 300 ms | Not described | |
| Byeon (2020) | Group 1: NMESGroup 2: NMES + Medelsohn maneuver | Medelsohn maneuver | Not described | 16 (not described) | Hyoid and cricoid bones | 80 Hz | 300–700 μs | 6.5 mA (increase to painful threshold) | |
| Byeon and Koh (2016) | Group 1: NMESGroup 2: CT (stimulation of the anterior faucial pillar) | --- | 3 weeks | 15 (5 days/week) | Mylohyoid and thyroid muscles | 80 Hz | 300 ms | 2.5–20 mA | |
| Carnaby et al. (2019) | NMES + CT | Placebo NMES + CT (swallowing behavior intervention and McNeill therapy) | 3 weeks | 15 (5 days/week) | Hyoid and cricoid bones | Not described | Not described | Motor threshold | |
| Choi (2016) | NMES | --- | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Paretic facial area | 80 Hz | 700 μs | Motor threshold | |
| Guillén- Sòla et al. (2017) | Group 1: NMES + RMT+ CT Group 2: RMT + CT | CT: educational intervention, oral exercises and compensatory techniques | 3 weeks | 15 (5 days/week) | Suprahyoid muscles | 80 Hz | Not described | Motor threshold | |
| Hamada et al. (2016) | NMES + CT | CT (not described) | Not described | Not described | Mylohyoid muscle and hyoid bone | 80 Hz | 700 ms | Sensitive threshold | |
| Hendy et al. (2019) | NMES + CT | Placebo NMES + CT (thermal stimulation, exercises for strengthening and increasing the motion of the tongue, swallowing exercises, the Medelsohn maneuver, cranial-cervical postural correction and diet modifications) | 3 weeks | 9 (3 days/week) | Area below the chin and on both sides of the pharynx | 80 Hz | 300 μs | 25 mA (or maximum tolerable without pain) | |
| Kim et al. (2017) | NMES + CT (swallowing muscle strength training) | --- | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Suprahyoid area and sternohyoid muscle | 80 Hz | 700 μs | 5 – 8.5 mA | |
| Konecny & Elfmark (2018) | NMES + CT | CT: postural correction, respiratory rehabilitation, exercises for the tongue, lips and facial muscles, thermal stimulation and swallowing training | 1 week | 5 (5 days/week) | Suprahyoid muscles | 60 Hz | Not described | Motor threshold | |
| Lee et al. (2019) | NMES + CT (oral stimulation with oral and lingual exercises to train strength and endurance) | --- | 10 days | 20 (2 sessions/day) | Group 1: Masseter and suprahyoid muscles. Group 2: Suprahyoid muscles. | 80 Hz | 300 ms | 7 mA | |
| Li et al. (2018) | Group 1: NMES Group 2: NMES + CT | CT: changes in dietary habits and postural correction | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Between thyroid and cricroid cartilages and between digastric muscles and hyoid bone | Not described | Not described | 7 mA | |
| Meng et al. (2018) | NMES + CT | CT: dietary modifications, craniocervical postural correction, swallowing skills training, Shaker and Medelsohn maneuvers, esophageal balloon dilation and respiratory exercises. | 2 weeks | 10 (5 days/week) | Group 1: suprahyoid muscles and cranial and distal to the thyroid cartilage. Group 2: genohyoid and mylohyoid muscles | 80 Hz | --- | 25 mA or motor threshold | |
| Mituuti et al. (2018) | NMES | --- | 4 weeks | 12 (3 days/week) | Mylohyoid and thyroid muscles | 80 Hz | 700 μs | Sensitive threshold | |
| Oh et al. (2017) | NMES | --- | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Oral orbicular muscle | 80 Hz | 700 μs | Motor threshold | |
| Park et al. (2016) | NMES | --- | 6 weeks | 30 (5 days/week) | Sternohyoid muscles | 80 Hz | 700 μs | Group 1: sensitive threshold. Group 2: motor threshold | |
| Park et al. (2019) | NMES | --- | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Below the chin and thyroid cartilage | 80 Hz | 700 μs | 25 mA or motor threshold | |
| Simonelli et al. (2018) | NMES + CT | CT: lingual, oral, facial and pharyngeal exercises, laryngeal elevation exercises, Medelsohn and Masako maneuvers, Shaker exercises and thermal stimulation | 8 weeks | 40 (5 days/week) | Thyroid muscles | 80 Hz | 300 μs | 7.8–12.5 mA | |
| Sproson et al. (2018) | NMES + CT | CT: dietary modifications and three swallowing strengthening exercises. | 4 weeks | 20 (5 days/week) | Sternohyoid muscles | 30 Hz | --- | Minimum motor threshold | |
| Zeng et al. (2018) | NMES + CT + PT | PT (platelet inhibitors, hypolipimics, antihypertensives, euglycemics and facilitators of microcirculation) + CT (massage on cheeks, tongue, retropharyngeal wall, pharyngeal-palatal area and lips with cotton soaked in ice) | 24 days | 24 (1 per day) | Hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage | --- | 800 ms | 28 mA | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diéguez-Pérez, I.; Leirós-Rodríguez, R. Effectiveness of Different Application Parameters of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for the Treatment of Dysphagia after a Stroke: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082618
Diéguez-Pérez I, Leirós-Rodríguez R. Effectiveness of Different Application Parameters of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for the Treatment of Dysphagia after a Stroke: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(8):2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082618
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiéguez-Pérez, Isabel, and Raquel Leirós-Rodríguez. 2020. "Effectiveness of Different Application Parameters of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for the Treatment of Dysphagia after a Stroke: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 8: 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082618
APA StyleDiéguez-Pérez, I., & Leirós-Rodríguez, R. (2020). Effectiveness of Different Application Parameters of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for the Treatment of Dysphagia after a Stroke: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(8), 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082618






