Abstract
With the recent developments in widespread internet usage and digital technology, an ultimate worldwide transformation in information and communications technology has occurred. Especially, how people engage in the virtual market for buying and selling goods has changed dramatically, which flourished the playground of electronic commerce (EC). Interestingly, it has become crucial to create an ample opportunity for farmers to utilize a more comprehensive market range for selling their products. However, farmers participating in e-commerce sales platforms may be interrupted by various internal and external factors. Therefore, the study’s primary goal is to evaluate the impacts of various external and internal factors on shaping farmers’ behavior in participating in e-commerce sales platforms. The study utilized a demand observable bivariate Probit model to analyze the village environment and capital endowment effects to craft the findings. The study utilized micro-survey data from 686 households in the leading kiwifruit-producing area as the empirical setup. The findings illustrated that the village environment is the main factor that restricts farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior, among which the infrastructure and policy environments have a significant contribution to farmers’ e-commerce sales intention and behavior. However, the effect of capital endowment on farmers’ e-commerce selling behavior has been found as significant. The village environment significantly affects both large- and small-scale farmers, and the capital endowment has a higher binding effect on small-scale farmers. Therefore, the paper suggests that improving the village environment for e-commerce development and laying the foundation for e-commerce development should be fostered. A differentiated incentive mechanism to improve the capital endowment of farmers should be constructed. A well-structured capital endowment triggering small farmers to capture the benefits of e-commerce sales should be imposed. The government should extend the support of the agricultural demonstration zone to facilitate practical training among the smallholder farmers. The formal and informal risk-sharing and financial institutions should prioritize building infrastructure to support farmers’ short- and long-term investments. Farmers should realize the importance of e-commerce for integrating the agricultural value chain.
1. Introduction
China holds the largest share of the global e-commerce marketplace, accounting for USD 2 trillion yearly turnovers [1]. The modern era of digital technology and widespread internet coverage spreads e-commerce from China’s urban regions to lower-income families-dominated rural regions. However, many of the country’s impoverished areas are experiencing the highest growth in e-commerce [2]. Under China’s existing agricultural economic system, relying solely on the expansion of agricultural marketing to achieve sustainable income growth for farmers has not achieved the desired results [3]. It burdens the escalating transaction costs brought by expansion scale and makes it difficult for farmers to rely on their ability to broaden their marketing channels to sell more products faster with a higher price [4]. Therefore, the e-commerce environment can create a significant economic potential for small entrepreneurs and smallholder agribusiness [5] with the dual-plan implementation of “Internet” + action and “e-commerce.” The use of digital technology is spurring a revolution in farm-to-kitchen approaches [6,7]. E-commerce companies are changing the lives of China’s farmers and urban consumers for a country whose rural sector is dominated by small farms with minimal technology. The integrated e-commerce platforms, such as Taobao, Pinduoduo, and Jingdong, compete to enter the rural market, and they help farmers to effectively solve the problems of asymmetric market information, many intermediary links, and high transaction costs in the marketing process [8]. They also allow agricultural operators to obtain more value-added profits from agricultural products [9,10]. Although e-commerce businesses receive significant exposure, they are not the prime reason for China’s e-commerce development [11].
Over the last decades, various governmental regulations, developmental initiatives, and incentives have served as critical contributions in establishing the digital and physical infrastructures that allow consumers to complete online transactions and transport products at a lower cost [12]. Since 2014, the Chinese government has introduced several regional and local policies for farmers to achieve sustainable development with e-commerce to promote rural e-commerce development [13]. According to the China Rural E-Commerce Development Report (2019–2020), China’s rural network sales exceeded 1.7 trillion yuan in 2019, including 397.5 billion yuan of agricultural products’ network sales. Globally, rural e-commerce has become an essential tool for small farmers to dock efficiently with the big market [14]. However, in rural China, the dominance of small-scale farmers and the highly dynamic market organization system make traditional sales channels mainly capture agricultural products [15]. Although most farmers have been concerned about the higher expected benefits of e-commerce, the actual process of farmers’ willingness and degree of participation in e-commerce varies widely. With the constraint of resource endowment, digital infrastructure, and other factors, e-commerce shows the characteristics of uneven regional development, especially in rural areas [16]. There are more misconceptions about the perception of rural e-commerce, and the degree of farmers’ e-commerce participation is not high [17,18]. Generally, as a potential actor of e-commerce sales, farmers tend to determine the efficiency of rural e-commerce promotion by whether they conduct e-commerce sales or not [19].
Several studies have recognized the importance of rural farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales channels for improving their income, reducing poverty levels, and upholding a better lifestyle (such as Jin et al. [20], Huang et al. [21], and Nadarajan et al. [22]). In academia, farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior and its influencing factors mainly focus on two aspects: First, the analysis of internal factors, such as personal characteristics, family business characteristics, and psychological cognition. Among them, Lin et al. [23] pointed out that farmers with higher resource endowment and e-commerce awareness levels are more likely to adopt e-commerce sales. Zeng et al. [24] found that the richer the farmers’ previous experience in entrepreneurship and training, the more likely they are to adopt e-commerce sales behavior. Cui et al. [25] and Dan and QiHong [26] found that social capital had a significant positive effect on farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior by expanding their access to information. Second, external factors such as infrastructure, logistics status, and information media are analyzed. Leroux et al. [27] analyzed farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior in e-commerce demonstration counties and found that farmers in areas with better computer equipment and network infrastructure were more likely to participate in sales. Fecke et al. [28] found that both mass media channels and organizational channels are essential factors influencing farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior. In addition, many scholars have focused on examining the impact of a specific factor, such as the size of farms, policy support, and network externalities, on farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior (such as Baourakis et al. [29], Banerjee et al. [30], and Beckman et al. [31]).
The above research results provide a valid reference for studying farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior, but many directions can be expanded. First, although previous studies have focused on the influence of a specific capital endowment of farmers and the external environment on farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior, fewer studies have combined the two. Generally, farmers’ behavioral decisions result from internal and external factors, and villages with blood and geopolitical ties in the vast rural areas are the carriers, where farmers live. The decisions of farmers living in villages are often made under the spatial constraints of the village domain with group characteristics. Second, previous studies have analyzed farmers as a whole, ignoring the variability of farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior at different business scales.
Moreover, there might be several motivating factors and barriers which could be crucial for shaping the behavior of farmers for participating in e-commerce sales. This leads to the following research questions that should be evaluated: What exactly prevents farmers from participating in rural e-commerce to sell their agricultural products? Are farmers’ own needs insufficient, or does the external environment constrain them? Are there any differences in the influencing factors among different groups of farmers? Therefore, by exploring the issues mentioned above, this study comprehensively evaluates the key factors affecting farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales. The study provides a theoretical and practical base point for improving farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior and promoting the smooth development of rural e-commerce. The empirical setup comprised 686 farmers from the main kiwifruit production areas of Shaanxi and Sichuan provinces. The study uses a bivariate Probit model to craft the findings from the dual perspectives of village environment and capital endowment, which is the main innovation of the study.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Mechanisms of the Influence of Capital Endowment on Farmers’ Willingness and Behavior to Participate in E-Commerce Sales
Capital is regarded in the classical and neoclassical theories as one of three main production factors, besides land and labor [32], and in a dynamic sector such as agriculture, where the capital should be kept intact [33]. Interestingly, most endowments are designed to keep the principal amount intact while using the investment income for resource investments [34]. Bourdieu [35] links objective capital endowments to subjective behavior. He pointed out that capital has several forms, such as cumulative labor in materialized form and a set of resources and rights that can maximize productivity. The capital endowment has a significant impact on the farmer’s behavior choice and decision-making [36]. The study defines farm household capital endowment as the natural and acquired resources and capabilities possessed by farm households, including economic capital, human capital, social capital, and information capital. Farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales can be regarded as a kind of investment behavior [37], i.e., farmers invest their capital endowment in rural e-commerce sales to gain income from the sale of agricultural products and the resulting premium income in the future adoption of e-commerce sales behavior. Therefore, farmers usually tend to fully consider the status of their capital endowment before deciding whether to participate in e-commerce sales [38]. If their endowment is not sufficient to support the need for the corresponding behavior, farmers will show lower demand and low behavior [39]. Based on this, the study proposes Hypothesis 1 as:
Hypothesis 1.
Farmers’ capital endowment significantly affects farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
Human capital is the sum of individual abilities, knowledge level, and basic skills embedded in the worker [40]. Farmers with more abundant human capital have more vital cognitive and understanding abilities, and their ability to adapt to new things is relatively more vital [41,42]. They can grasp and apply emerging e-commerce sales technologies at a faster rate in the face of them, and they can take timely action to reallocate resources to deal with the uncertainties that arise in e-commerce sales, reduce the losses caused by inappropriate use of e-commerce sales by farmers, and thus increase their willingness to participate in e-commerce sales [43]. Based on this, the study proposes Hypothesis 2 as:
Hypothesis 2.
Farmers’ human capital significantly impacts farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
Economic capital is the tangible materials owned by farmers and the capital that can be directly converted into money and turned into property rights, which are essential prerequisites and guarantees for farmers to take risks and make the capital investment in e-commerce sales behavior [44]. Farmers who adopt e-commerce sales behavior need to pay funds to purchase computers, cell phones, and other hardware facilities to maintain customer relationships, as well as other operating costs, and economic capital-rich farmers have higher economic capital support. The higher the ability to resist risk, the easier to participate in e-commerce sales behavior and to meet required capital investment, and the higher the ability to cope with the uncertainty risks faced in the process of participation and more robust responses [45]. Based on this, the study proposes Hypothesis 3 as:
Hypothesis 3.
Farmers’ economic capital significantly impacts farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
Social capital refers to the sum of resources or capabilities mobilized by individual actors through social networks for instrumental and affective purposes [46], and they can aggregate dispersed individuals and influence the collective sense of the action of social members [47]. Social capital formed by relying on geo-networks can help farmers provide sources of information, technical experience, and emotional support, and farmers will reduce the transaction and trial-and-error costs of participating in e-commerce sales through mutual learning and imitation [48]. In addition, frequent communication among farmers in the relationship network can establish a positive interaction of trust, cooperation, and reciprocity [49], improving the speed of disseminating e-commerce sales knowledge and increasing the level of understanding of knowledge [50], thus promoting the adoption of e-commerce sales behavior by farmers. Based on this, the study proposes Hypothesis 4 as:
Hypothesis 4.
Farmers’ social capital significantly affects farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
Information capital refers to the ability of farmers to obtain multi-channel information, high-quality information, and the extensive use of processing information [51,52]. The higher information capital can help farmers quickly obtain rich, accurate, and timely information from diversified channels [53]. This can also assist them in breaking the technical information barriers, enhancing the accumulation of knowledge and experience in e-commerce sales [53], deepening their knowledge of participation in e-commerce sales [54], and thus increase the willingness of farmers to participate in e-commerce sales. Based on this, Hypothesis 5 has been proposed as:
Hypothesis 5.
Farmers’ information capital significantly affects farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
2.2. Mechanisms of Influence of Village Environment on Farmers’ Willingness and Behavior to Participate in E-Commerce Sales
Bourdieu’s practice theory points out that individual practice behavior is influenced by field, habit, and capital, and the village, which relies on blood and geographical relations, constitutes the essential field of farmers’ production life [55,56]. Farmers’ decision-making behavior is deeply embedded in the village’s social structure, with prominent community-type characteristics [57]. The village environment is a combination of natural and social factors in a specific village area, including various factors, such as resource environment, market environment, and economic development level [58]. This is a carrier of external conditions for farmers to adopt new technologies and learn new knowledge, and a basis for obtaining policy support, forming collaborative relationships, and exchange activities [59]. According to the main constraints farmers face in their participation in e-commerce sales behavior, the study divides the village environment related to participation in e-commerce into industrial development and policy support environments. Based on this, the study proposes Hypothesis 6 as:
Hypothesis 6.
There is a significant positive effect of village environmental improvement on farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce.
The infrastructure environment refers to the state of transportation, logistics, and network infrastructure development needed to support e-commerce development in a given village area [60]. The better conditions of a good e-commerce infrastructure environment can provide the fundamental guarantee for farmers to participate in e-commerce sales activities and ensure the standard and smooth implementation of farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales [61]. However, the infrastructure environment, including the smooth network elements, transportation, and logistics supports, helps farmers strengthen their understanding and judgment of market information and subjects [62]. It allows farmers to open network sales channels and obtain e-commerce sales information, which enhances farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales [63]. Based on this, the study proposes Hypothesis 7 as:
Hypothesis 7.
There is a significant positive impact of improved infrastructure environment on farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
Village industrial development environment refers to industries related to e-commerce development in a specific village area. A well-structured industrial development environment is an inherent condition and basis for the development of rural e-commerce, which can not only integrate local advantageous agricultural products and gather regional service resources, but also provide the complementary resources needed for farmers to participate in e-commerce sales, and promote farmers’ exploration of new e-commerce sales models [64]. At the same time, the villages with good industrial development have a complete industrial organization model [65]. Seemingly, the participation of new business entities such as cooperatives and agricultural enterprises in e-commerce sales can form a radiation-driven and demonstration effect on neighboring farmers [66], which enhances the willingness of most farmers in the village to participate in e-commerce sales. Based on this, the study proposes Hypothesis 8 as:
Hypothesis 8.
There is a significant positive impact of the industrial development environment on farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
E-commerce training and information sharing opportunities positively improve farmers’ cognitive level and understanding of e-commerce [67]. This helps them to understand the difficulties and knowledge of e-commerce sales more comprehensively [68] and enhances their confidence and risk resistance to participate in e-commerce sales [68], and improves farmers’ decision response to participate in e-commerce sales. Village policy support can create a good atmosphere for e-commerce development [69]. The policy support environment refers to the in-kind or non-in-kind incentives (including publicity, broadcasting, training, subsidies, etc.) provided by villages to support e-commerce development [70]. Through subsidies and training, favorable signals of e-commerce development will be realized [71], and farmers can make full use of these information resources to interact, cooperate, and then make a decisive response to participate in e-commerce sales [72]. Based on this, Hypothesis 9 has been proposed in the study:
Hypothesis 9.
There is a significant positive effect of improved policy support environment on farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales.
3. Materials and Methods
In the study, we adopted the definition of e-commerce provide by Mueller [73] and simplified it as “the business deals and transactions conducted over the internet”.
3.1. Data Sources and Sample Characteristics
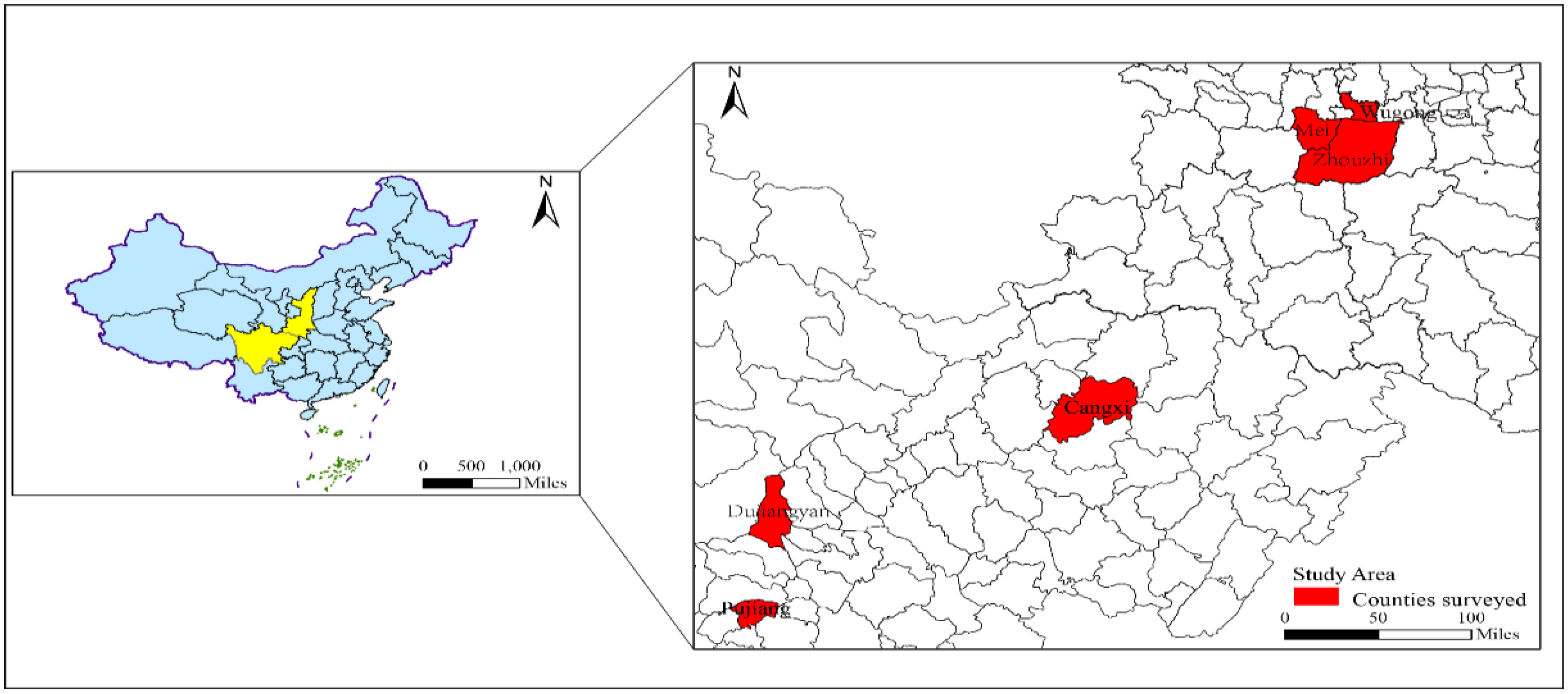
The study’s empirical data were obtained from a household field study conducted by the team of “Kiwifruit Industry Technology System” guided by State Key Laboratory, Northwest A&F University in September–October 2018, in Cangxi, Pujiang, and Dujiangyan counties of Sichuan Province, and Meixian, Zhouzhi, and Wugong counties of Shaanxi Province (see Figure 1). Kiwifruit is an essential target for e-commerce sales as it is a high-value and high-demand agricultural product, and Shaanxi and Sichuan are the two provinces with the largest kiwifruit cultivation areas in China [4]. According to the data of China Intelligence Research Consulting, the kiwifruit planting area in Shaanxi Province was about 1.03 million mu in 2018, and the kiwifruit planting area in Sichuan Province was about 600,000 mu. The development level of kiwifruit e-commerce in Shaanxi and Sichuan Provinces was in the top three in the country [74]. Sichuan Province currently has more than 500 agricultural e-commerce platforms and as many as 100,000 enterprises and businesses related to kiwifruit, generating e-commerce transactions of kiwifruit amounting to 400 billion yuan [75]. E-commerce in Shaanxi Province has covered all villages and towns in the province [76]. The retail sales of rural e-commerce in Shaanxi are nearly 28 billion yuan, and the online retail sales of agricultural products have reached nearly 11 billion yuan.
Figure 1.
Map of the surveyed regions.
In order to ensure the representativeness of the samples, the survey adopted a combination of stratified sampling and typical sampling to select samples, as suggested by Etikan and Bala [77]. First, three counties (cities) were selected randomly from the two provinces, and two–four villages were randomly selected from each county. From the selected villages, we further randomly selected about 15–20 households for the household survey. After eliminating invalid questionnaires and questionnaires (Supplementary Materials) with incorrect logic, a total of 686 valid questionnaires were finally obtained, with a response rate of 97.72%. The distribution of the sample households by district and gender is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Distribution of the sample households by district and gender.
A structured questionnaire and face-to-face interviews were used to obtain information on individual characteristics (e.g., age, gender, education level of the household head), household characteristics (e.g., area of farming land, land quality, kiwi cultivation status, household income, etc.), and socioeconomic status (e.g., social capital, social communication, participation in training). In particular, we investigated specific data on farm households’ participation in e-commerce sales in 2018, including sales income, quantity, and varieties sold.
3.2. Model Selection
Farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior might include a binary discrete choice problem, which is generally estimated using the Probit model [78]. Farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and already participated in e-commerce sales behavior are not independent of each other, and the interaction of the two can form four combinations: (i) neither willingness to participate nor already participated in E-commerce sales behavior, (ii) only willingness to participate, (iii) only already participated in E-commerce sales behavior, and (iv) both willingness to participate and already participated in E-commerce sales behavior. In the following, the four combinations have been modeled:
In Equation (1), , denote the latent variables of farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and participation in e-commerce sales behavior respectively, is the vector of village environment variables, and is the vector of capital endowment variables. all denote the vector of parameters to be estimated. The random perturbation term obeys a two-dimensional joint normal distribution with mean 0 and variance 1. The correlation coefficient, , between the two can be expressed by Equation (2):
The observable variables and are determined by Equations (3) and (4).
Here, is farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales, and is farmers’ participation already in e-commerce sales behavior. Among them, the applicability of the model is tested. If the original hypothesis is rejected, indicating that farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and already participated in e-commerce sales behavior are related, it is necessary to use the bivariate Probit model. If the original hypothesis is accepted, there is no correlation between farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and already participated in e-commerce sales behavior. Therefore, it is unnecessary to use a bivariate Probit model, and two separate Probit models should be selected for analysis.
3.3. Variable Selection and Descriptive Statistics
3.3.1. Explanatory Variables
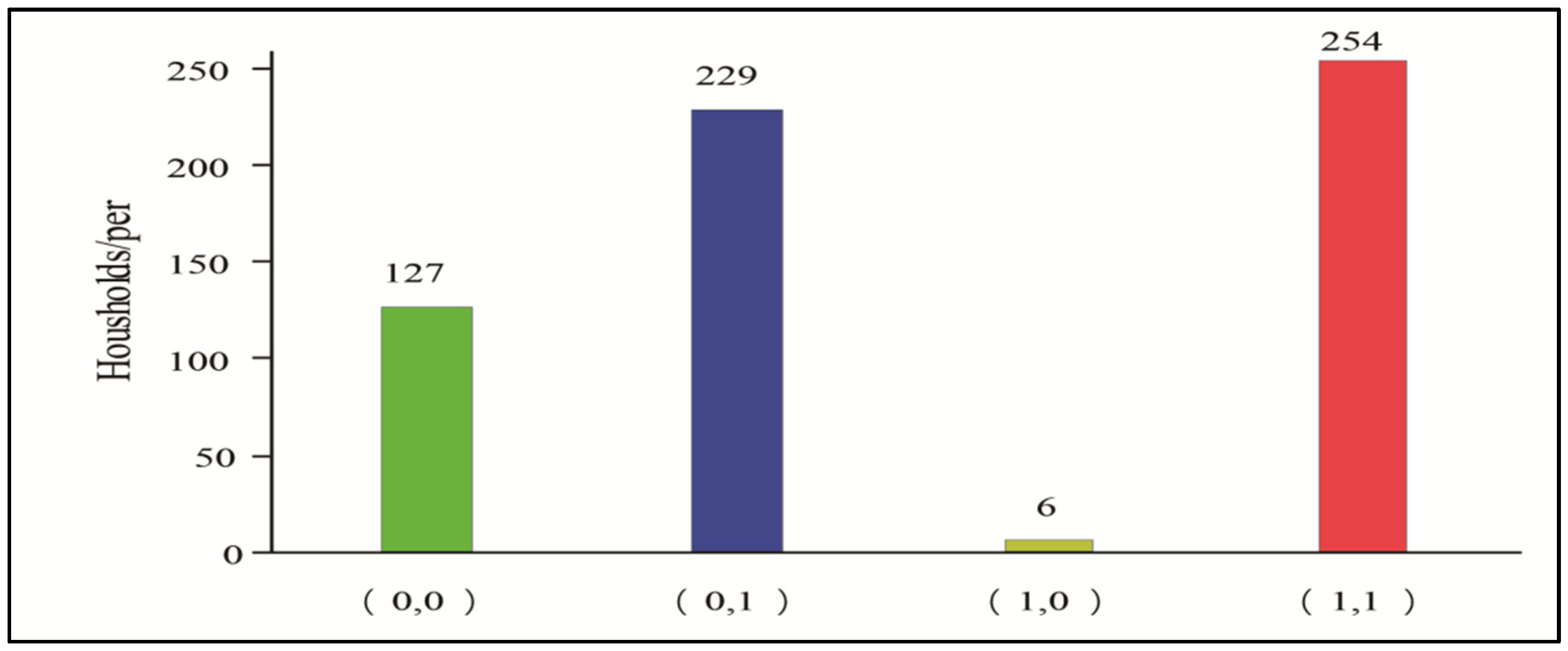
The explanatory variables in this paper are farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and already participated in e-commerce sales behavior. The question that reflects the willingness to participate in e-commerce sales is, “Does your household have the willingness to sell kiwifruit through rural e-commerce?” If a farmer answered “yes”, the value of 1 was assigned, and if not, the value of 0 was assigned. The question that reflects the e-commerce participation is, “Has your household sold kiwifruit through e-commerce channels before?” If the farmer answered “yes”, the household was assigned a value of 1 if the household had already participated in e-commerce sales, and 0 if not. At this point, in practical terms, farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce and participation in e-commerce sales behavior can be expressed as four categories: (0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), and (1, 1). While Figure 2 shows that 127 farmers in the sample area have neither willingness to nor have already participated in e-commerce sales (A), 229 farmers have no willingness to participate in e-commerce sales but have already participated in e-commerce sales behavior (B). Moreover, 6 farmers are willing to participate in e-commerce sales but have not participated in e-commerce sales behavior (C), and 254 have both willingness and participation in e-commerce sales behavior (D). The specific variable definitions and descriptive statistics are shown in Table 2.
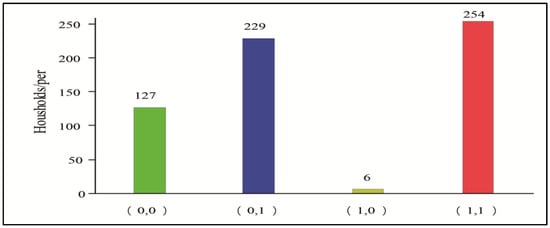
Figure 2.
Distribution of farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and already participated in e-commerce sales behavior.

Table 2.
Variable selection and descriptive statistics.
3.3.2. Indicators
The capital endowment includes four aspects: human capital, economic capital, social capital, and information capital. Seemingly, human capital is reflected by three indicators: the number of household laborers, the frequency of household agricultural training, and household education level. Previous experience has found that human capital has a significant effect on the decision-making behavior of farm households. For example, Wang et al. [79] found that well-educated farmers were more likely to use the internet. Better education improved farmers’ ability to judge the usefulness of the internet and enabled them to access information related to agricultural production activities through the internet. The current study expects these variables to have a similar effect on the likelihood of willingness and behavior to engage in e-commerce sales.
Three indicators reflect economic capital: the scale of the farming operation, household income level, and household income structure, and social capital is also reflected by three indicators: the number of friends and relatives, the proportion of human expenditure, and supply chain organization exchange. Lin et al. [80] found that social capital, as a resource embedded in social networks, can promote the social status of individuals, thus creating an information advantage to promote farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior. In contrast, Davern [81] found that social capital is only for the rich and does not significantly affect the average farmer. Therefore, the study expects social capital to positively impact farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales. However, in the study, information capital is reflected by one indicator: the share of communication expenses.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Regression Results
Table 3 reports the estimated results of village environment and capital endowment on e-commerce sales behavior. The results of the bivariate Probit model show a p-value of 0.000 for the Wald test, indicating an association between e-commerce sales behavior and demand. Therefore, sample selection and the bivariate Probit model estimates are valid [82]. Table 3 also reports the estimation results of the Probit model, which are generally consistent with those of the bivariate Probit, which corroborates the robustness of the bivariate Probit model [83].

Table 3.
The results of the impact of village environment and capital endowment on Farmers’ e-commerce sales demand and behavior.
4.1.1. Estimation Results of the Village Environment
From the village infrastructure environment, traffic convenience has no significant impact on e-commerce sales willingness but has a significant positive impact on participated in e-commerce sales behavior, passing the test at a 5% significance level. It indicates that the more convenient traffic positively impacts the farmers who have already participated in e-commerce sales. Logistics convenience and network penetration significantly impact both e-commerce sales willingness and behavior, and both pass the test at a 5% significance level. Therefore, we can assume that the more convenient logistics and higher network penetration rate influence both the farmers’ willingness and participating behavior of e-commerce sales. This could have occurred as a sound infrastructure environment in the village is the basis for farmers’ e-commerce sales. A sound infrastructure environment allows farmers to break through the geographical limitation of sales. It also could have boosted the learning, the catch-up, and the proximity effect in the village. The village’s learning, catch-up, and proximity effect promote farmers to fully grasp the sales market and provide a more excellent chance to join the e-commerce sales. The outcomes are also supported by the findings of Zhang et al. [76] and Zhang [64]. Therefore, Hypothesis 2 was supported.
In terms of the village industrial development environment, market specialization has a significant positive effect on e-commerce sales intention at a 10% significance level but does not significantly affect e-commerce sales behavior. The market organization does not show a significant effect on e-commerce sales intention and behavior. Therefore, it could be said that the village industrial development environment has a negligible effect on e-commerce sales behavior. The possible reasons for this result are that farmers with a sound industrial development environment in the village area have already built cooperative relationships with traditional sales channels, and farmers can obtain higher profits without selling through e-commerce. In addition, new business organizations in the village area are essential channels for farmers to sell, providing necessary guarantees for farmers’ sales income [60]. Therefore, Hypothesis 3 has not been supported.
From the village policy support environment, e-commerce training has a significant positive effect on e-commerce sales willingness and behavior, and both pass the test at a 1% significance level; that is, e-commerce training promotes farmers’ e-commerce sales. We have found a non-significant effect of subsidies on e-commerce sales intentions but a significant positive effect on e-commerce sales behavior, which passed the test at the 5% significance level. As e-commerce subsidies can compensate for the uncertainty of income brought about by farmers’ adoption of e-commerce sales [70], farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior is strengthened under the financial subsidy incentive [79], which could be the primary reason for the outcomes. Therefore, Hypothesis 4 was verified.
In summary, the village environment significantly impacts e-commerce sales intentions and e-commerce sales behavior, with differences in the specific influencing factors. Specifically, the village infrastructure, industrial development, and policy support environment significantly positively affect e-commerce sales intentions. The village infrastructure environment and village policy support environment have significant positive effects on e-commerce sales behavior. It can be seen that the village environment has a significant positive impact on farmers’ willingness and behavior of e-commerce sales. Hypothesis 1 was verified based upon the above discussion.
4.1.2. Estimation Results of Capital Endowment
From the human capital point of view, the number of the family labor force has no significant effect on the willingness and behavior of e-commerce sales. The frequency of family agricultural training significantly affects the willingness and behavior of e-commerce sales and passes the test at a 1% significance level. Receiving agricultural training improves the e-commerce sales behavior of farmers, probably because farmers who often participate in agricultural training have a relatively broad vision, and it is easy to change their original sales methods [67]. The family’s level of education has a significant positive effect on the willingness of e-commerce sales and passes the test at the 1% significance level, but has no significant effect on e-commerce sales behavior. The level of education improves the willingness of farmers to sell e-commerce, probably because the higher the level of education of the family labor force, the broader its exposure and the ability to accept the innovation brought by the sales model [31]. Therefore, Hypothesis 7 was supported.
In terms of economic capital, the scale of the farming operation, household income level, and household income structure all have insignificant effects on e-commerce sales intentions. However, all have significant effects on already participated in e-commerce sales behavior, indicating that economic capital is not an essential factor limiting e-commerce sales intentions [40]. The possible reason is that the consumability of agricultural products limits farmers with large farming scales, and the scale of e-commerce sales can hardly meet the demand of production, so farmers tend to rely on traditional sales channels [53]. Seemingly, household income level significantly affects e-commerce sales behavior at the 1% significance level. The possible reason is that farmers with high household income levels are risk-averse and have extra funds to invest in e-commerce sales [16]. At the same time, household income structure has a significant positive effect on e-commerce sales behavior. It passes the 1% significance level test, possibly because farmers relying on the kiwifruit industry are faced with a potentially profitable decision to sell through e-commerce, and do tend to sell through e-commerce. Therefore, Hypothesis 8 was supported.
In terms of social capital, the number of friends and relatives had a non-significant effect on the willingness and behavior of e-commerce sales. The possible reason is that farmers with a high proportion of favor spending have higher social capital channels and can obtain higher returns without selling through e-commerce, so they do not show statistical significance. The main reason is that the information diffusion function of supply chain organizations allows farmers to develop their vision and grasp business opportunities [80]. However, the information diffusion function of supply chain organizations allows farmers to expand their horizons and grasp business opportunities. Therefore, Hypothesis 9 was supported.
In terms of information capital, the effect of the communication expenditure ratio on e-commerce sales intention is not significant. However, it has a significant positive effect on e-commerce sales behavior. It passes the test at the 5% significance level, indicating that information capital is not an essential factor affecting e-commerce sales intention but has a vital role in promoting e-commerce sales behavior [84]. The possible reason is that the accumulation of rural information capital is mainly established in neighborhood communication and commitment. Although the share of communication expenditure is an essential indicator of information capital, informal communication among farmers plays a more important role [53]. Therefore, Hypothesis 5 was supported.
In summary, the capital endowment significantly affects e-commerce sales willingness and e-commerce sales behavior, with significant differences in the specific refined indicators. Specifically, human capital significantly affects e-commerce selling intention, but economic capital, social capital, and information capital do not significantly affect e-commerce selling intention [37]. It can be seen that capital endowment is not a significant factor influencing farmers’ willingness to sell by e-commerce, but it is an essential factor limiting farmers’ e-commerce selling behavior. Therefore, Hypothesis 6 was verified.
4.2. Variation Analysis of Farms of Different Sizes
To further analyze the effects of village environment and capital endowment on the willingness and behavior of e-commerce sales under farmer differentiation, farmers were divided into small-scale farmers and large-scale farmers according to the size of their farming operations. According to demographic statistics, 78.59% of small-scale farmers in the research area have e-commerce sales willingness, and only 32.38% of small-scale farmers have already participated in e-commerce sales behavior. On the other hand, 83.17% of large-scale farmers have e-commerce sales willingness, and only 44.88% of large-scale farmers have already participated in e-commerce sales behavior. It can be seen that large-scale farmers have significantly higher e-commerce sales willingness and behavior than small-scale farmers. To further explore the differences in the effects of village environment and capital endowment on e-commerce sales intentions and e-commerce sales behaviors of farms of different sizes, the estimates were conducted separately for large-scale farmers and small-scale farmers. The estimated results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The results of the impact of village environment and capital endowment on the e-commerce sales demand and behavior of different scale farmers.
4.2.1. Estimation Results of the Village Environment
The factors that affect the willingness of small-scale farmers and large-scale farmers to sell by e-commerce and e-commerce sales behavior are quite different from the village environment. The village infrastructure environment only influences the willingness of small-scale farmers to sell by e-commerce. While the willingness of large-scale farmers to sell by e-commerce is influenced by the village market environment and the village policy support environment, there are no common influencing factors for both. The e-commerce selling behavior of small-scale farmers and large-scale farmers is influenced by the village infrastructure environment and the village policy support environment, but there are differences in the specific indicators and the degree of influence. From both common factors, network penetration has a significant favorable influence on the e-commerce sales behavior of large-scale farmers and small-scale farmers, passing the test at 1% and 10% significance levels. From the size of the influence coefficient, the influence coefficient of small-scale (0.010) is greater than that of large-scale farmers (0.008), so it can be considered that the enhancement of network penetration has a more substantial effect on small-scale farmers. Village domain e-commerce training has a significant positive impact on the e-commerce sales behavior of both large-scale and small-scale farmers, and the coefficient of small-scale farmers is relatively more prominent. Therefore, it can be presumed that the enhancement effect of village-based e-commerce training on small-scale farmers is significant.
4.2.2. Estimation Results of Capital Endowment
In terms of capital endowment, there are significant differences in the factors that affect the willingness of small-scale farmers and large-scale farmers to sell by e-commerce and their e-commerce selling behavior. In terms of influencing the willingness of different scale farmers to sell by e-commerce, both small-scale and large-scale farmers’ e-commerce sales intentions are only affected by human capital, consistent with the overall regression results. However, there are some differences in the specific impact indicators and the degree of impact, i.e., the number of household laborers only affects the e-commerce sales intentions of small-scale farmers. In terms of e-commerce sales behavior, small-scale farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior is significantly influenced by human capital, economic capital, social capital, and information capital, while large-scale farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior is only significantly influenced by economic capital and information capital. Economic capital and social capital are no longer factors that constrain large-scale farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior, i.e., small-scale farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior is more likely to be constrained by the capital endowment. In summary, village environment and capital endowment significantly affect both large-scale and small-scale farmers’ willingness to sell and e-commerce selling behavior, but the factors constraining different-scale farmers’ willingness to sell and e-commerce selling behavior vary.
5. Discussion
The study focused on the relationship between internal capital endowment of farm households and external village environmental support on farm households’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and sales behavior. The proportion of actual participation in e-commerce sales behavior is low, and there are significant differences in willingness to participate and participation behavior, which is parallel with the findings of Lin et al. [23]. The regression results show that capital endowment and village environment positively impact farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales. These findings can help to prove the important role of capital endowment and the external environment in farmers’ decision-making behavior. Our findings are consistent with many scholars’ studies [85,86,87,88] and are also in line with theoretical and logical expectations. However, due to the complexity of farmers’ capital endowment, we used four variables, economic capital, social capital, information capital, and human capital, to measure capital endowment. According to the regression results of different capital endowments on farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and sales behavior, only human capital significantly affects farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales. In contrast, the effects of economic capital, social capital, and information capital are not significant. However, there are differences between this research and the conclusions of some scholars, especially the research conclusions of Liu et al. [1]. They pointed out that the apple farmers’ social capital has a positive impact on selling their products through e-commerce. At the same time, the study explored the differences in the behavior and willingness of farmers to participate in e-commerce from the perspective of willingness and behavior correlation. The effects of economic capital, social capital, and information capital in capital endowment on farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales were not significant. The impacts of the village industrial development environment on farmers’ participation in e-commerce sales behavior were also not significant. The research results are consistent with the research of most of the scholars within similar directions [89,90]. Due to the differences in farmers’ household capital endowment and external environment, different farmers will make behavioral decisions based on different household income goals, which eventually leads to significant inconsistencies between farmers’ behavioral decisions and willingness [91]. This also provides new ideas to promote the transformation of farmers who are willing to participate in e-commerce sales, but not in e-commerce sales behavior. In addition, the differences in the farming scales of farmers may further affect the differences in farmers’ willingness and behavior to participate in e-commerce sales. The proportion of large-scale farmers’ willingness to participate in e-commerce sales and sales behavior is higher than that of small-scale farmers. The factors affecting the willingness and behavior of large- and small-scale farmers to participate in e-commerce are significantly different, which is as the same as in the research of Xie et al. [92] and Lu et al. [93], and differences in behavior and willingness decision-making among farmers of different scales were also found.
6. Conclusions
Using data from field research conducted by the project team in Shaanxi and Sichuan Provinces in 2018, this study used a bivariate Probit model to estimate the effects of village environment and capital endowment on e-commerce sales behavior. It examined the effects of village environment and capital endowment on e-commerce sales intentions and e-commerce sales behavior of farmers of different sizes based on a farmer differentiation perspective. The empirical results showed that the village environment is an essential factor affecting e-commerce sales and e-commerce sales behavior. Village infrastructure environment, village industrial development environment, and village policy support environment all had significant positive effects on e-commerce sales willingness, and village infrastructure environment and village policy support environment had significant positive effects on e-commerce sales behavior. However, the village industrial development environment did not have significant effects on e-commerce sales behavior.
Interestingly, the capital endowment was not an essential factor affecting farmers’ willingness to sell e-commerce, but it limits farmers’ e-commerce selling behavior. The capital endowment was found to significantly affect both e-commerce selling willingness and e-commerce selling behavior, and human capital significantly affects e-commerce selling willingness. However, economic capital, social capital, and information capital were not found to significantly affect willingness to participate in e-commerce selling, but they all had a significant effect on e-commerce selling behavior. The village environment and capital endowment significantly affected large-scale and small-scale farmers’ willingness to sell and e-commerce selling behavior. However, the factors constraining farmers’ willingness to sell and e-commerce selling behavior of different sizes vary.
Based on the above findings, the study proposes the following policy recommendations: First, we should pay attention to the internalization function of the village environment on the impact of farmers’ e-commerce sales, and strengthen and improve the village environment construction. Investment in transportation, communication, and other infrastructure and additional logistics sites should be increased. Key focuses should be on improving external conditions that restrict the sale of agricultural products and promoting the transformation from farmers’ use of the traditional sales model to the use of the e-commerce sales model. The promotion of market specialization along with the “one village, one product” should focus on the leading role of cooperatives and other social organizations. Governments should provide full support to farmers to guide the role of e-commerce sales and actively promote e-commerce training. They should also impose new policies to reduce the cost of access to information for farmers, farmers’ e-commerce sales inputs, uncertainty and risk of farmers’ sales, and improve the e-commerce subsidy mechanism.
Second, farmers’ capital endowment heterogeneity should be recognized, and a differentiated incentive mechanism needs to be established to improve farmers’ e-commerce sales behavior. Governments should improve human capital quality by strengthening agricultural technology and professional farmer training. The vital role of social networks should also be fully endorsed. A well-structured information dissemination platform should be implemented to foster social interaction and experience sharing. The mechanism of farmers’ information access channels should be broadened to reduce farmers’ information collection costs.
Third, the promotion of large-scale operation should be strengthened and small-scale farmers should be encouraged to expand the scale of land operation to obtain scale benefits. More policy support should be provided to large-scale farmers, human capital investment of farmers with large planting scales should be strengthened, and the transformation of marketing mode of large-scale farmers should be promoted. Under the current system, attention should also be paid to the cultivation of small-scale farmers’ e-commerce sales potential and the reduction of capital endowment constraints.
Three issues should be evaluated by future researchers, which limit our study. First, the scope of the study, as this study was conducted mainly in six central kiwifruit-producing counties in Shaanxi and Sichuan Provinces of China, and the results that may be obtained are difficult to apply in a broader context. Future research should extend the scope of the study to more farmers of different agricultural species and agro-industrial zones, thus enhancing the general applicability of the findings. Second, the study mainly used cross-sectional data, reflecting a point-in-time problem and making it difficult to dynamically observe changes in farmers’ behavior over time. The potential future research should focus on collecting panel data for better understanding of the dynamics of changes in farmers’ behavior. Finally, the questionnaire used in this study was mainly self-reported by farmers, and self-reported e-commerce participation behaviors were usually overestimated because respondents had different comprehension of the questionnaire during the research process. Therefore, future studies should consider counseling farmers on the questionnaire before the research to reduce potential bias due to self-reported behaviors.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture11090868/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and A.S.; methodology, A.S. and X.L.; software, X.L. and A.S.; validation, X.X. and W.H.M.; formal analysis, X.L. and A.S.; investigation, X.L. and A.S.; resources, X.L., X.X. and W.H.M.; data curation, X.L. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L., A.S. and X.X.; writing—review and editing, X.L., X.X. and A.S.; visualization, W.H.M.; supervision, X.X.; project administration, A.S.; funding acquisition, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71933005), Shaanxi Soft Science Joint Project (No. 2018KRLZ04), and National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFC0501707).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study as the study does not collect any personal data of the respondents, and respondents were clearly informed that they could opt-out at any time if they wanted to.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be provided upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, M.; Min, S.; Ma, W.; Liu, T. The Adoption and Impact of E-Commerce in Rural China: Application of an Endogenous Switching Regression Model. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 83, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Ma, B.; Zhang, C. Poverty Alleviation through E-Commerce: Village Involvement and Demonstration Policies in Rural China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, K. Characteristics and Mechanism of Agricultural Transformation in Typical Rural Areas of Eastern China: A Case Study of Yucheng City, Shandong Province. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Sarkar, A.; Qian, L. Evaluating the Impacts of Smallholder Farmer’s Participation in Modern Agricultural Value Chain Tactics for Facilitating Poverty Alleviation—A Case Study of Kiwifruit Industry in Shaanxi, China. Agriculture 2021, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B. Feasibility Study on Building a Mobile E-Commerce Platform for Fresh Agricultural Products in China under the Background of Internet Plus. Ekoloji 2019, 28, 647–658. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Jia, F.; Wan, L.; Guo, H. E-Commerce in Agri-Food Sector: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2017, 20, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, T.L.; Phimister, E.; Roberts, D. From Farm to Kitchen: How Gender Affects Production Diversity and the Dietary Intake of Farm Households in Ethiopia. J. Agric. Econ. 2021, 72, 268–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wei, S.; Wang, D. Factors Influencing Organisational Efficiency in a Smart-Logistics Ecological Chain under e-Commerce Platform Leadership. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2021, 24, 364–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Peng, Y.; Kong, R.; Chen, Q. Impact of E-Commerce Adoption on Farmers’ Participation in the Digital Financial Market: Evidence from Rural China. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 1434–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.A.E. E-Commerce and Entrepreneurship in Agricultural Markets. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2001, 83, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y. E-Urbanism: E-Commerce, Migration, and the Transformation of Taobao Villages in Urban China. Cities 2019, 91, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, J.; Martins, J.; Gonçalves, R.; Branco, F.; Cota, M.P. Analysis, Specification and Design of an e-Commerce Platform That Supports Live Product Customization. In Proceedings of the CIMPS 2016: Trends and Applications in Software Engineering, Aguascalientes, Mexico, 12–14 October 2016; Mejia, J., Muñoz, M., Rocha, Á., San Feliu, T., Peña, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, UK, 2017; pp. 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hongfei, Y. National Report on E-Commerce Development in China. Incl. Sustain. Ind. Dev. Work. Pap. Ser. WP17 2017, 1, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, A.A.; Okhovvat, M.R.; Okhovvat, M. A New Applicable Model of Iran Rural E-Commerce Development. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 3, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Pan, S.L.; Cui, L. Developing Community Capability for E-Commerce Development in Rural China: A Resource Orchestration Perspective. Inf. Syst. J. 2019, 29, 953–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zeng, Y.; Ye, Z.; Guo, H. E-commerce Development and Urban-rural Income Gap: Evidence from Zhejiang Province, China. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2021, 100, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, K. E-Commerce Development in Rural and Remote Areas of BRICS Countries. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changyu, L.I.U.; Jiale, L.I.; Jing, L.I.U. Rural E-Commerce and New Model of Rural Development in China: A Comparative Study of" Taobao Village" in Jiangsu Province. Asian Agric. Res. 2015, 7, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M. What Drives Farmers’ Willingness to Adopt e-Commerce in Rural China? The Role of Internet Use. Agribusiness 2020, 36, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can Rural E-Commerce Service Centers Improve Farmers’ Subject Well-Being? A New Practice of ‘Internet plus Rural Public Services’ from China. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Jin, H.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cheung, S.; Liu, C. The Effects of an Innovative E-Commerce Poverty Alleviation Platform on Chinese Rural Laborer Skills Development and Family Well-Being. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 116, 105189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajan, S.V.; Ismail, R.; Lytour, L. E-Commerce Application Model for the Development of Rural Agriculture Sector and Empowerment of Farmers in Cambodia. Bus. Entrep. J. 2013, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Li, R.; Hou, S.; Li, W. Influencing Factors and Empowering Mechanism of Participation in E-Commerce: An Empirical Analysis on Poor Households from Inner Mongolia, China. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Guo, H.; Yao, Y.; Huang, L. The Formation of Agricultural E-Commerce Clusters: A Case from China. Growth Chang. 2019, 50, 1356–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Pan, S.L.; Newell, S.; Cui, L. Strategy, Resource Orchestration and E-Commerce Enabled Social Innovation in Rural China. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2017, 26, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhou, Q. Development Model of Agricultural E-Commerce in the Context of Social Commerce. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2014, 6, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, N.; Wortman, M.S.; Mathias, E.D. Dominant Factors Impacting the Development of Business-to-Business (B2B) e-Commerce in Agriculture. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2001, 4, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecke, W.; Danne, M.; Musshoff, O. E-Commerce in Agriculture—The Case of Crop Protection Product Purchases in a Discrete Choice Experiment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 151, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baourakis, G.; Kourgiantakis, M.; Migdalas, A. The Impact of E-commerce on Agro-food Marketing: The Case of Agricultural Cooperatives, Firms and Consumers in Crete. Br. Food J. 2002, 104, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Mishra, M.; Debnath, N.C.; Choudhury, P. Implementing E-Commerce Model for Agricultural Produce: A Research Roadmap. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN) 2019, 7, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, J.; Ivanic, M.; Jelliffe, J. Market Impacts of Farm to Fork: Reducing Agricultural Input Usage. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosochatecká, E.; Tomšík, K.; Žídková, D. Selected Problemes of Capital Endowment of Czech Agriculture. Agric. Econ. 2008, 54, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lan, Y.; Wang, X. Impact of Livelihood Capital Endowment on Poverty Alleviation of Households under Rural Land Consolidation. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Han, P. Resource Endowment, Rural Governance, and the “New Agriculture” in China. Mod. China 2021, 47, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdieu, P. The Forms of Capital. In The Sociology of Economic Life; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-429-49433-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Sarkar, A.; Zhang, F. How Capital Endowment and Ecological Cognition Affect Environment-Friendly Technology Adoption: A Case of Apple Farmers of Shandong Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Koondhar, M.A.; Ji, L.; Kong, R. The Nexus between Formal Credit and E-Commerce Utilization of Entrepreneurial Farmers in Rural China: A Mediation Analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 900–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Mu, H. Research on the Development of E-Commerce Model of Agricultural Products. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 100, 02040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.D. Rethinking Land Endowment and Inequality in Rural Africa: The Importance of Soil Fertility. World Dev. 2016, 87, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingen, J.; Serrano, A.; Howard, J. Linking Farmers to Markets: Different Approaches to Human Capital Development. Food Policy 2003, 28, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimhi, A. Differential Human Capital Investments and the Choice of Successor in Family Farms. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1995, 77, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang Dao, M. Factor Endowment, Human Capital, and Inequality in Developing Countries. J. Econ. Stud. 2013, 40, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, C.B.; Sherlund, S.M.; Adesina, A.A. Macroeconomic Shocks, Human Capital and Productive Efficiency: Evidence from West African Rice Farmers. J. Afr. Econ. 2006, 15, 343–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Senthilkumar, K.; Lubbers, M.T.M.H.; de Ridder, N.; Bindraban, P.S.; Thiyagarajan, T.M.; Giller, K.E. Policies to Support Economic and Environmental Goals at Farm and Regional Scales: Outcomes for Rice Farmers in Southern India Depend on Their Resource Endowment. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, H.; Jin, S.; Ma, W.; Zeng, Y. Do Farmers Gain Internet Dividends from E-Commerce Adoption? Evidence from China. Food Policy 2021, 2021, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Policy Support, Social Capital, and Farmers’ Adaptation to Drought in China. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 24, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Singh, P.; Maity, A.; Shubha, K.; Burman, R.R. Enhancing Livelihood Security of Dairy Farmers through Farmers’ Producer Company: A Diagnostic Study of Bundelkhand Region. Range Manag. Agrofor. 2020, 41, 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, J.S.; Smith, M.B. Social Capital and Farming at the Rural–Urban Interface: The Importance of Nonfarmer and Farmer Relations. Agric. Syst. 2003, 76, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warschauer, M. Social Capital and Access. UAIS 2003, 2, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E.; Ahn, T.-K. The Meaning of Social Capital and Its Link to Collective Action. Handb. Soc. Cap. Troika Sociol. Political Sci. Econ. 2009, 3, 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Aleke, B.; Ojiako, U.; Wainwright, D.W. ICT Adoption in Developing Countries: Perspectives from Small-scale Agribusinesses. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2011, 24, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.; Teng, J.T. E-Commerce and the Information Market. Commun. ACM 2001, 44, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Lu, Q. The Influence of Information Communication Technology on Farmers’ Sales Channels in Environmentally Affected Areas of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 42513–42529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, P.N.; Soni, R.G. E-Commerce Usage and Perception of E-Commerce Issues among Small Firms: Results and Implications from an Empirical Study. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2007, 45, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenfell, M.J. Pierre Bourdieu: Key Concepts; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 1-317-54738-1. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, J.; Schirato, T.; Danaher, G. Understanding Bourdieu; Sage: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 1-4462-1043-X. [Google Scholar]
- Bartkowski, B.; Bartke, S. Leverage Points for Governing Agricultural Soils: A Review of Empirical Studies of European Farmers’ Decision-Making. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, N.; Nordin, S.M.; Rahman, I.; Noor, A. The Effects of Knowledge Transfer on Farmers Decision Making toward Sustainable Agriculture Practices: In View of Green Fertilizer Technology. World J. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 15, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Azim, J.A.; Asif, A.A.; Qian, L.; Peau, A.K. Structural Equation Modeling for Indicators of Sustainable Agriculture: Prospective of a Developing Country’s Agriculture. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Niu, C. E-Commerce Participation and Household Income Growth in Taobao Villages. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper No. 8811; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3369986 (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Zapata, S.D.; Isengildina-Massa, O.; Carpio, C.E.; Lamie, R.D. Does E-Commerce Help Farmers’ Markets? Measuring the Impact of MarketMaker. J. Food Distrib. Res. 2016, 47, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Ren, T.; Wang, M. Technology and Infrastructure Considerations for E-Commerce in Chinese Agriculture. Agric. Sci. China 2007, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saban Kumar, K.C.; Timalsina, A.K. Challenges for Adopting E-Commerce in Agriculture in Nepalese Context—A Case Study of Kathmandu Valley. Proceedings of the IOE Graduate Conference. 2016, pp. 305–312. Available online: http://conference.ioe.edu.np/publications/ioegc2016/ (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Zhang, Y. Application of Improved BP Neural Network Based on E-Commerce Supply Chain Network Data in the Forecast of Aquatic Product Export Volume. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 57, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zhongwei, H. Analysis of Agricultural Products E-Commerce Models Based on Supply Chain Management. Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on E-Business and E-Government (ICEE), Shanghai, China, 6–8 May 2011; pp. 1–3. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Analysis-of-agricultural-products-E-commerce-models-Lin-Zhongwei/688f4b1a5729ed352130e8ba1c9bc62278bf06bc (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Wen, W. A Knowledge-Based Intelligent Electronic Commerce System for Selling Agricultural Products. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2007, 57, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darch, H.; Lucas, T. Training as an E-commerce Enabler. J. Workplace Learn. 2002, 14, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanonpaiboon, J.; Pearson, A.M. E-Commerce Adoption: Perceptions of Managers/Owners of Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Thailand. J. Internet Commer. 2006, 5, 53–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhi, X. Does Network Governance Based on Banks’ e-Commerce Platform Facilitate Supply Chain Financing? China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2019, 11, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.; Kraemer, K.L.; Dedrick, J. Environment and Policy Factors Shaping Global E-Commerce Diffusion: A Cross-Country Comparison. Inf. Soc. 2003, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y. Study on the Influence of Agricultural Eco-Environment on the Competitiveness of Agricultural Products E-Commerce Brands in Jilin Province. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 252, 052056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelassi, T.; Leenen, S. An E-Commerce Sales Model for Manufacturing Companies:: A Conceptual Framework and a European Example. Eur. Manag. J. 2003, 21, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.A. Emergent E-Commerce in Agriculture, 14th ed.; Citeseer: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Sarkar, A.; Qian, L. Does Organizational Participation Affect Farmers’ Behavior in Adopting the Joint Mechanism of Pest and Disease Control? A Study of Meixian County, Shaanxi Province. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, R.; Chen, J.; Yi, Z. Analysis on Development Efficiency of Rural E-Commerce Based on DEA in Sichuan Province. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 253, 01061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, W.; Chen, X. The Pricing Strategy for Fuji Apple in Shaanxi of Chain under the E-Commerce Environment. Kybernetes 2018, 47, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etikan, I.; Bala, K. Sampling and Sampling Methods. Biom. Biostat. Int. J. 2017, 5, 00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGurk, E.; Hynes, S.; Thorne, F. Participation in Agri-Environmental Schemes: A Contingent Valuation Study of Farmers in Ireland. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Ma, W.; Tang, J. Risk Preference, Trust, and Willingness-to-Accept Subsidies for pro-Environmental Production: An Investigation of Hog Farmers in China. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2020, 22, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W. Social Capital and Individual Charitable Behaviours in China. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 2021, 16, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davern, M. Social Networks and Prestige Attainment. Am. J. Econ. Sociol. 1999, 58, 843–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.J. Partial Observability in Bivariate Probit Models. J. Econom. 1980, 12, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfardini, C.; Radice, R. Testing Exogeneity in the Bivariate Probit Model: A Monte Carlo Study. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2008, 70, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, R.; Dulle, F.; Lamtane, H. Challenges Associated with the Use of Information and Communication Technologies in Information Sharing by Fish Farmers in the Southern Highlands of Tanzania. J. Inf. Commun. Ethics Soc. 2019, 18, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuepper, D.; Sauer, J. Explaining the Performance of Contract Farming in Ghana: The Role of Self-Efficacy and Social Capital. Food Policy 2016, 62, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugravu-Soilita, N.; Kafrouni, R.; Bouard, S.; Apithy, L. Do Cultural Capital and Social Capital Matter for Economic Performance? An Empirical Investigation of Tribal Agriculture in New Caledonia. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 182, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiiza, B.; Pederson, G. ICT-Based Market Information and Adoption of Agricultural Seed Technologies: Insights from Uganda. Telecommun. Policy 2012, 36, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, F.; Jin, J.; He, R.; Wan, X.; Ning, J. Influence of Livelihood Capital on Adaptation Strategies: Evidence from Rural Households in Wushen Banner, China. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Halder, P.; Zhang, X.; Qu, M. Analyzing the Deviation between Farmers’ Land Transfer Intention and Behavior in China’s Impoverished Mountainous Area: A Logistic-ISM Model Approach. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; von Steiger, R.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F.; Gloeckler, G.M.; Desai, M.; Pogorelov, N.V. Determination of Plasma, Pickup Ion, and Suprathermal Particle Spectrum in the Solar Wind Frame of Reference. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wens, M.L.K.; Mwangi, M.N.; van Loon, A.F.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Complexities of Drought Adaptive Behaviour: Linking Theory to Data on Smallholder Farmer Adaptation Decisions. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 63, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, G.; Song, Y.; Yang, F. How Do Different Rural-Land-Consolidation Modes Shape Farmers’ Ecological Production Behaviors? Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, P.; Hu, H.; Xie, H.; Yu, Z.; Chen, S. Effect of the Grain-Growing Purpose and Farm Size on the Ability of Stable Land Property Rights to Encourage Farmers to Apply Organic Fertilizers. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).