Application and Development of Natural Plant Metabolite Oleanolic Acid in the Nano Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sources of Oleanolic Acid
3. Pharmacological Effects of Oleanolic Acid
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of OA
3.1.1. Inhibition of the Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
3.1.2. Increase Antioxidant Production
3.1.3. Inhibition of Activation of Mitochondria-Associated Inflammatory Vesicles
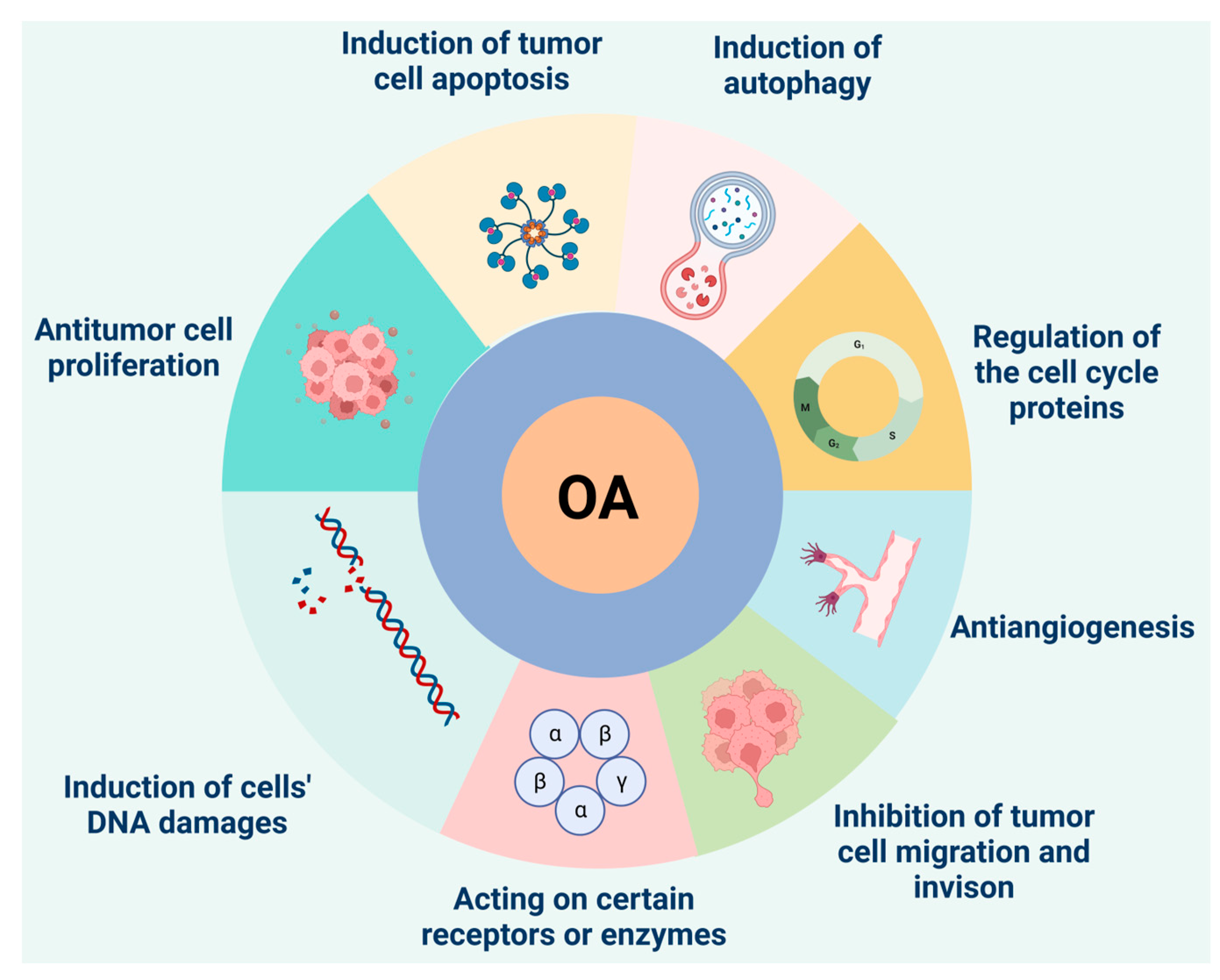
3.2. Antitumor Effect of Oleanolic Acid
3.2.1. Inhibition of Tumor Cell Proliferation
3.2.2. Induction of Apoptosis in Tumor Cells
3.2.3. Induction of Autophagy
3.2.4. Regulation of Cell Cycle Regulatory Proteins
3.3. Other Pharmacological Effects
4. Development and Utilization of Oleanolic Acid
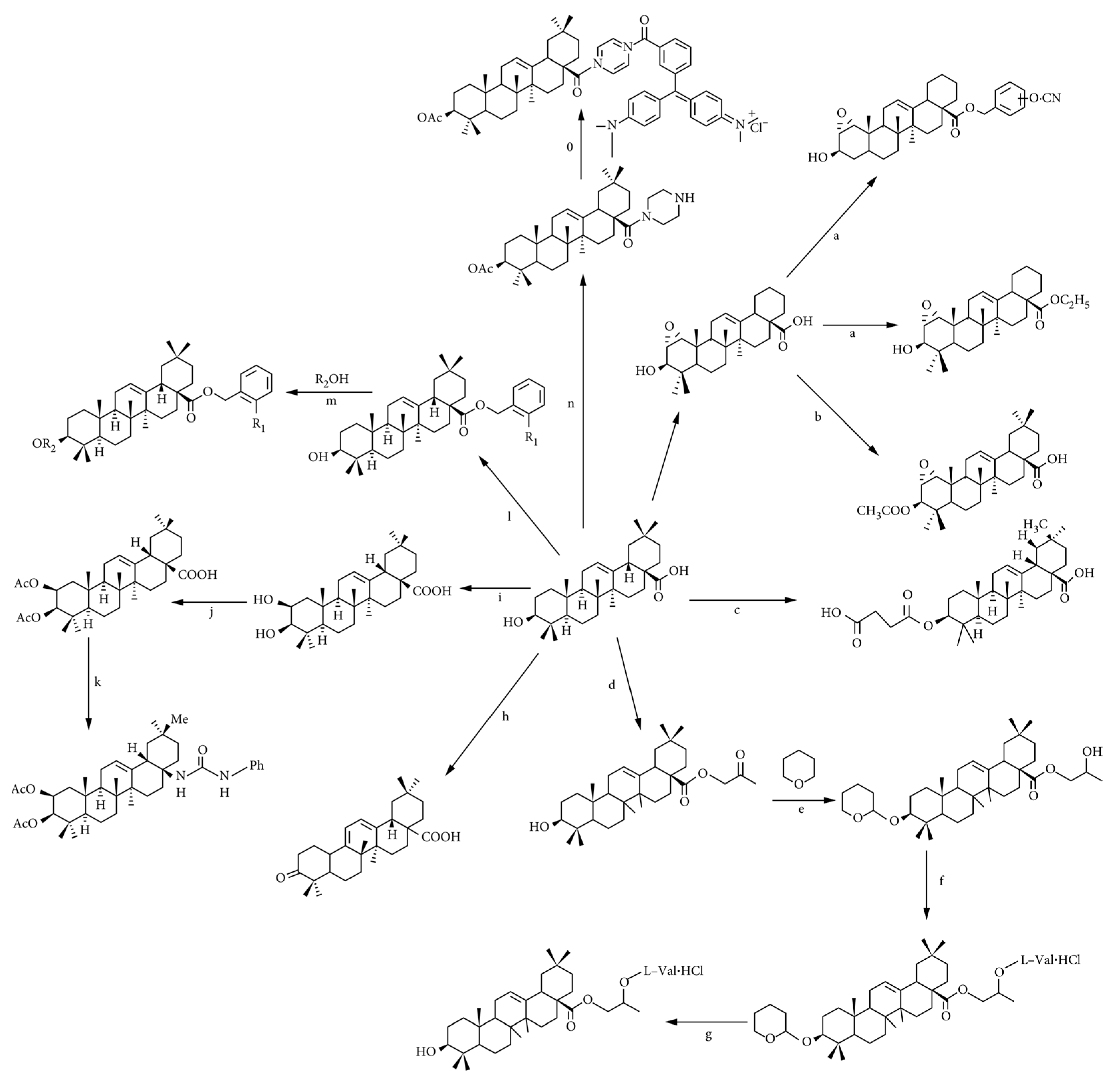
4.1. Structural Modification of Oleanolic Acid
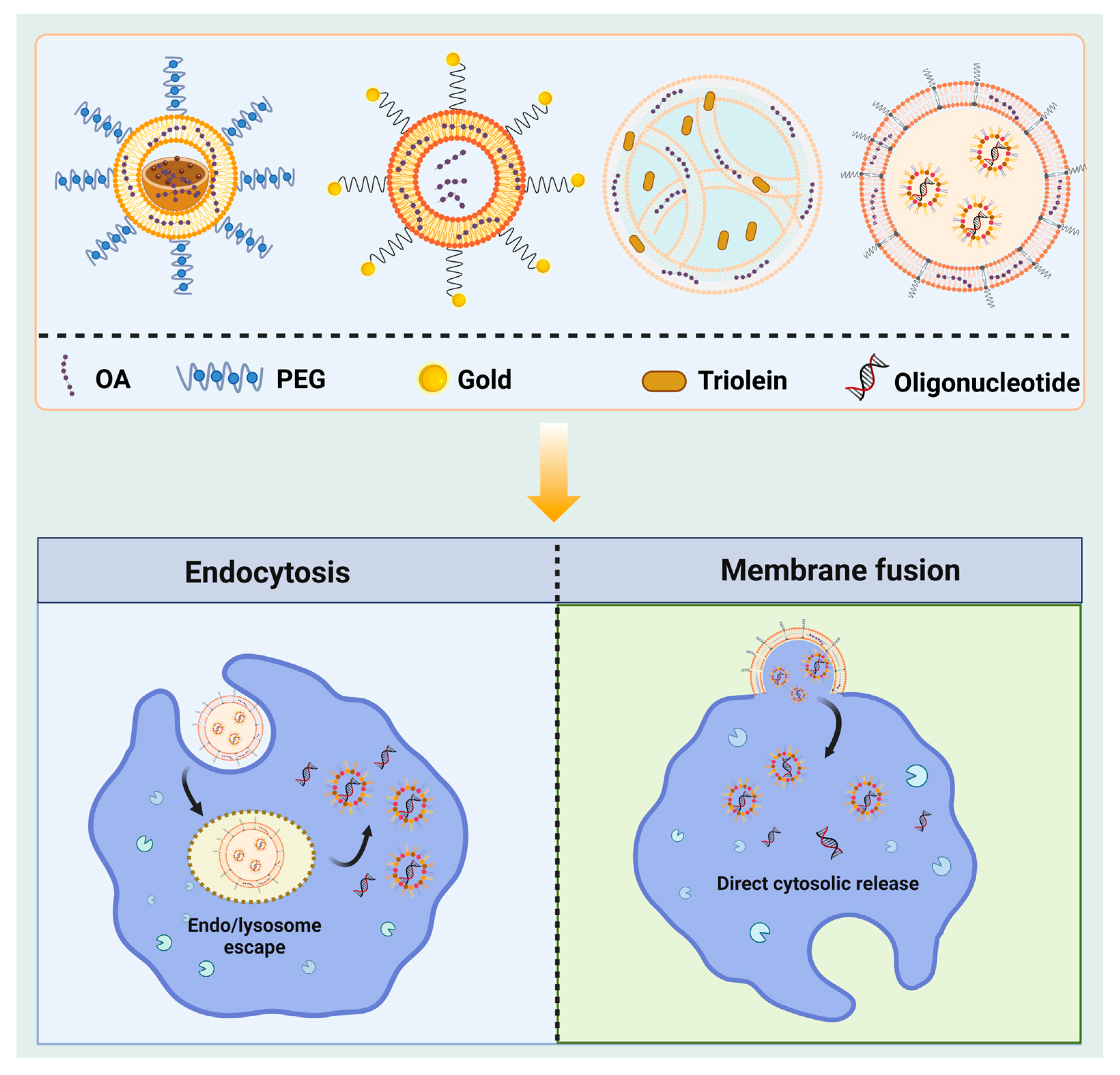
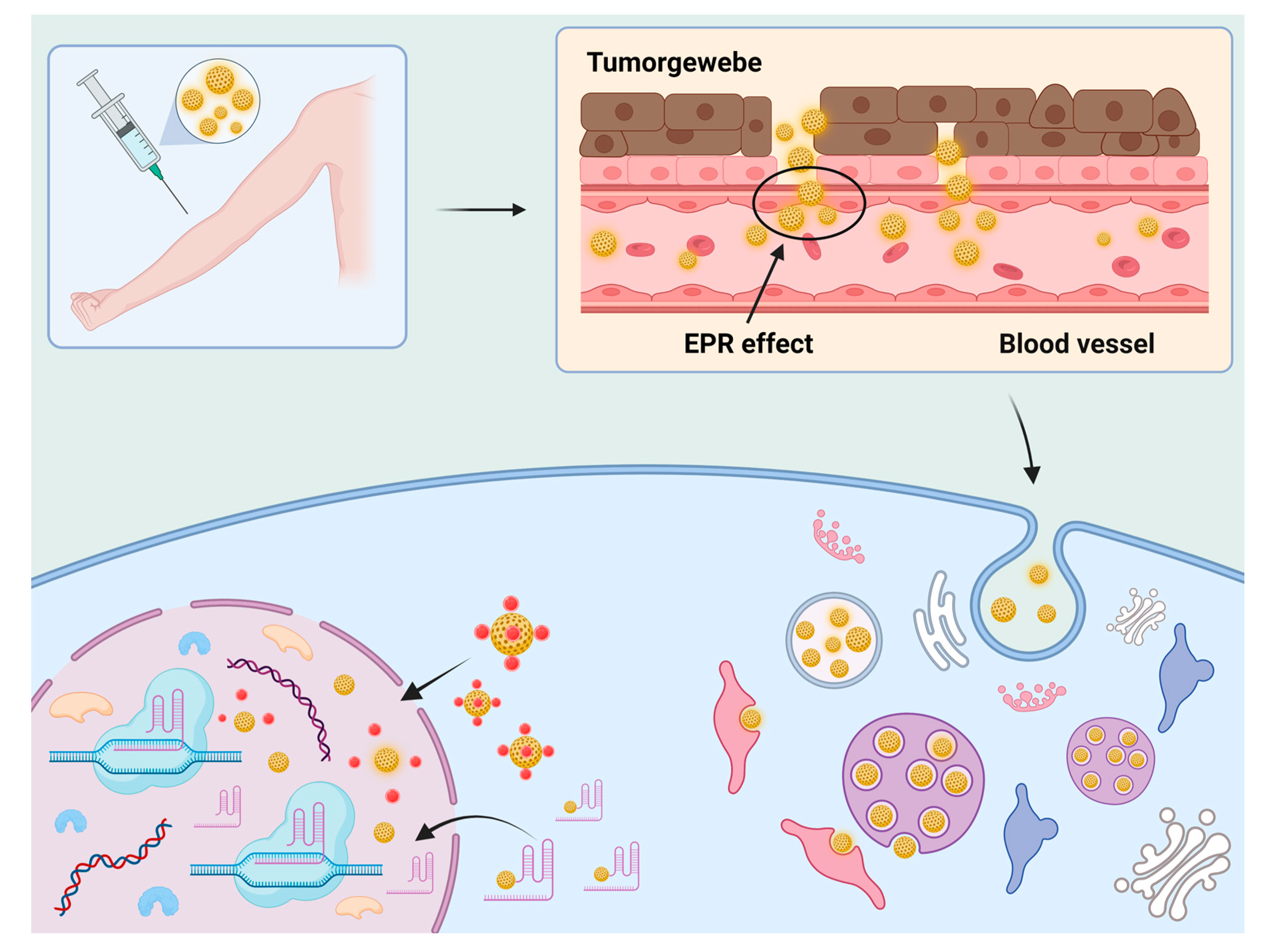
4.2. Nanoscale Preparation
4.2.1. Nanoliposomes
4.2.2. Nanoparticles
4.2.3. Other Nanoscale Preparation Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laszczyk, M.N. Pentacyclic triterpenes of the lupane, oleanane and ursane group as tools in cancer therapy. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, X. Identification of a novel multifunctional oxidosqualene cyclase from Zea mays sheds light on the biosynthetic pathway of three pentacyclic triterpenoids. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2022, 7, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Tuli, H.S.; Sharma, A.K. Ursolic acid (UA): A metabolite with promising therapeutic potential. Life Sci. 2016, 146, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proshkina, E.; Plyusnin, S.; Babak, T.; Lashmanova, E.; Maganova, F.; Koval, L.; Platonova, E.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Moskalev, A. Terpenoids as Potential Geroprotectors. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.C.; Li, S.Y.; Tang, J.X.; Liu, D.; Feng, X.Y.; Rao, K.R.; Zhao, X.D.; Li, H.M.; Li, R.T. Triterpenoids, steroids and other constituents from Euphorbia kansui and their anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. Phytochemistry 2022, 204, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kumar, P.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Bishayee, A.; Kumar, S. Pentacyclic triterpenes: New tools to fight metabolic syndrome. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2018, 50, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Rebolledo, G.A.; Siordia-Reyes, A.G.; Meckes-Fischer, M.; Jiménez-Arellanes, A. Hepatoprotective properties of oleanolic and ursolic acids in antitubercular drug-induced liver damage. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A. Prophylactic and therapeutic roles of oleanolic acid and its derivatives in several diseases. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 1767–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Yoon, Y.; Choi, K.H. Antimicrobial action of oleanolic acid on Listeria monocytogenes, Enterococcus faecium, and Enterococcus faecalis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Han, B.; Luo, K.; Ren, Z.; Cai, L.; Sun, L. NOX2-ROS-HIF-1α signaling is critical for the inhibitory effect of oleanolic acid on rectal cancer cell proliferation. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprean, C.; Mioc, M.; Csányi, E.; Ambrus, R.; Bojin, F.; Tatu, C.; Cristea, M.; Ivan, A.; Danciu, C.; Dehelean, C.; et al. Improvement of ursolic and oleanolic acids’ antitumor activity by complexation with hydrophilic cyclodextrins. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, B.; Lakshma Nayak, V.; Ramakrishna, S.; Venkata Mallavadhani, U. Synthesis of ring-C modified oleanolic acid derivatives and their cytotoxic evaluation. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 68, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouaïb, K.; Hichri, F.; Nguir, A.; Daami-Remadi, M.; Elie, N.; Touboul, D.; Ben Jannet, H.; Hamza, M.A. Semi-synthesis of new antimicrobial esters from the natural oleanolic and maslinic acids. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, R.; Cordova, C.; San Román, J.A.; Gutierrez, B.; Cachofeiro, V.; Nieto, M.L. Oleanolic acid modulates the immune-inflammatory response in mice with experimental autoimmune myocarditis and protects from cardiac injury. Therapeutic implications for the human disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 72, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.M.; Ramos-Romero, S.; Perona, J.S. Oleanolic Acid: Extraction, Characterization and Biological Activity. Nutrients 2022, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, W.; Cheng, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, X. Nanomedicine-Cum-Carrier by Co-Assembly of Natural Small Products for Synergistic Enhanced Antitumor with Tissues Protective Actions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 42537–42550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milan, A.; Mioc, A.; Prodea, A.; Mioc, M.; Buzatu, R.; Ghiulai, R.; Racoviceanu, R.; Caruntu, F.; Şoica, C. The Optimized Delivery of Triterpenes by Liposomal Nanoformulations: Overcoming the Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, K.; Morales, J.; Rodríguez, L.; Günther, G. Potential use of nanocarriers with pentacyclic triterpenes in cancer treatments. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 3139–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporn, M.B.; Liby, K.T.; Yore, M.M.; Fu, L.; Lopchuk, J.M.; Gribble, G.W. New synthetic triterpenoids: Potent agents for prevention and treatment of tissue injury caused by inflammatory and oxidative stress. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaza, V.; Oyedeji, O.O.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Antiviral Activities of Oleanolic Acid and Its Analogues. Molecules 2018, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Si, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D. Recent progress in the antiviral activity and mechanism study of pentacyclic triterpenoids and their derivatives. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 951–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Lv, S.; Hu, Y.; Tao, J. Herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) as an alternative source of oleanolic and ursolic acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J. Variation of oleanolic and ursolic acid in the flesh of persimmon fruit among different cultivars. Molecules 2010, 15, 6580–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, S.; Trojan, H.; Kopp, T.; Laszczyk, M.N.; Scheffler, A. Pentacyclic triterpene distribution in various plants—Rich sources for a new group of multi-potent plant extracts. Molecules 2009, 14, 2016–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoja, E.; Ndukwe, I.G. Isolation of oleanolic acid from chloroform extract ofBorreria stachydea[(DC) Hutch. and Dalziel]. J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour. 2013, 3, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Odun-Ayo, F.; Chetty, K.; Reddy, L. Determination of the ursolic and oleanolic acids content with the antioxidant capacity in apple peel extract of various cultivars. Braz. J. Biol. = Rev. Brasleira De Biol. 2022, 82, e258442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyło, A.; Nowicka, P.; Turkiewicz, I.P.; Tkacz, K.; Hernandez, F. Comparison of bioactive compounds and health promoting properties of fruits and leaves of apple, pear and quince. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-P.; Liao, D.-D.; Zhang, X.-H. Ultrasonic assisted extraction of ursolic acid from apple pomace: A novel and facile technique. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terigar, B.G.; Balasubramanian, S.; Boldor, D.; Xu, Z.; Lima, M.; Sabliov, C.M. Continuous microwave-assisted isoflavone extraction system: Design and performance evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Duan, Z.; Fan, L.; Li, J. Supercritical CO₂ Fluid Extraction of Elaeagnus mollis Diels Seed Oil and Its Antioxidant Ability. Molecules 2019, 24, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilkickyte, G.; Raudone, L. Optimization, Validation and Application of HPLC-PDA Methods for Quantification of Triterpenoids in Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. Molecules 2021, 26, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumoska, K.; Vovk, I. Analysis of triterpenoids and phytosterols in vegetables by thin-layer chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1381, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, S.; Pandey, M.M.; Kumar Singh Rawat, A. Medicinal plants of the genus Betula--traditional uses and a phytochemical-pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 159, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, K.; Sun, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Determination of oleanolic acid, ursolic acid and amygdalin in the flower of Eriobotrya japonica Lindl. by HPLC. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2007, 21, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.; Theoduloz, C.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Razmilic, I.; Yáñez, T.; Rodríguez, J.A. Gastroprotective and ulcer-healing activity of oleanolic acid derivatives: In vitro-in vivo relationships. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Zhi-yan, Z.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Feng-ju, N.; Zhang, X.; Han, C. The advances in research on the pharmacological effects of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 281873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.Q.; Yu, Y.Y.; Xu, X.R.; Deng, G.F.; Guo, Y.J.; Li, H.B. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, R.M.; Pandey, D.K. Optimizing conditions for oleanolic acid extraction from Lantana camara roots using response surface methodology. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 27, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrisor, G.; Motelica, L.; Craciun, L.N.; Oprea, O.C.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A. Melissa officinalis: Composition, Pharmacological Effects and Derived Release Systems-A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.M.; Alvarado, H.L.; Abrego, G.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Garduño-Ramirez, M.L.; García, M.L.; Calpena, A.C.; Souto, E.B. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Oleanolic/Ursolic Acids-Loaded in PLGA Nanoparticles in Different Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xing, Y. Oleanolic acid inhibits cell survival and proliferation of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 7599–7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, N.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Y. Extraction optimization of oleanolic and ursolic acids from pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) flowers. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, J.A.; Lago, J.H.; Laurenti, M.D.; Yamamoto, E.S.; Passero, L.F. Antimicrobial activity of oleanolic and ursolic acids: An update. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2015, 2015, 620472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Cognigni, A.; de Faria, E.L.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Zirbs, R.; Freire, M.G.; Bica, K. Valorization of olive tree leaves: Extraction of oleanolic acid using aqueous solutions of surface-active ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, R. Studies of selected plant raw materials as alternative sources of triterpenes of oleanolic and ursolic acid types. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuka, D.; Nowak, A.; Zakłos-Szyda, M.; Kochan, E.; Szymańska, G.; Motyl, I.; Blasiak, J. American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium L.) as a Source of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Pro-Health Properties. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Houghton, P.J.; Soumyanath, A. alpha-Amylase inhibitory activity of some Malaysian plants used to treat diabetes; with particular reference to Phyllanthus amarus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Jiao, W.H.; Han, B.N.; Liu, Z.X.; Qiu, F.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Anti-inflammatory secondary metabolites from the leaves of Rosa laevigata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, S.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Fang, X.; et al. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid: Novel hepatitis C virus antivirals that inhibit NS5B activity. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleńsk, M.; Czapińska, E.; Woźniak, M.; Ceremuga, I.; Włodarczyk, M.; Terlecki, G.; Ziółkowski, P.; Seweryn, E. Triterpenoid Acids as Important Antiproliferative Constituents of European Elderberry Fruits. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razboršek, M.I.; Vončina, D.B.; Doleček, V.; Vončina, E. Determination of Oleanolic, Betulinic and Ursolic Acid in Lamiaceae and Mass Spectral Fragmentation of Their Trimethylsilylated Derivatives. Chromatographia 2008, 67, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajac, R.; Stojanovic, D.; Petrović, J.; Milanov, D.; Vasić, R.; Stojanov, I.M.; Lako, B. Antibacterial activity of the essential oil of Mountain Savory (Satureja montana) against Arcanobacterium pyogenes. Planta Med. 2011, 77, PN5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, K.; Li, M.M.; Pan, Z.H.; Peng, L.Y.; Zhao, Q.S. Triterpenoids and diterpenoids from Viburnum chingii. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niampoka, C.; Suttisri, R.; Bavovada, R.; Takayama, H.; Aimi, N. Potentially cytotoxic triterpenoids from the root bark of Siphonodon celastrineus Griff. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2005, 28, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, R. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils and extracts of rosinweed (Silphium trifoliatum and Silphium integrifolium) plants used by the American Indians. Flavour Fragr. J. 2008, 23, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, K.; Shiota, S.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kuroda, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Antimicrobial activity of oleanolic acid from Salvia officinalis and related compounds on vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Esmaeilizadeh, M. Pharmacological properties of Salvia officinalis and its components. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Ueno, H.; Inagaki, M. Glutaminase inhibitory activities of pentacyclic triterpenes isolated from Thymus vulgaris L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rali, S.; Oyedeji, O.O.; Aremu, O.O.; Oyedeji, A.O.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N. Semisynthesis of Derivatives of Oleanolic Acid from Syzygium aromaticum and Their Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8401843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, S.; Winkler, K.; Pfüller, U.; Scheffler, A. Solubility studies of oleanolic acid and betulinic acid in aqueous solutions and plant extracts of Viscum album L. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shao, J.; Zhao, C.; Shen, J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M.; Fan, J. Chemical constituents from Viburnum fordiae Hance and their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2018, 41, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunoki, K.; Sasaki, G.; Tokuji, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Naito, A.; Aida, K.; Ohnishi, M. Effect of dietary wine pomace extract and oleanolic acid on plasma lipids in rats fed high-fat diet and its DNA microarray analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 12052–12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamede, M.; Mabuza, L.; Ngubane, P.; Khathi, A. Plant-Derived Oleanolic Acid (OA) Ameliorates Risk Factors of Cardiovascular Diseases in a Diet-Induced Pre-Diabetic Rat Model: Effects on Selected Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Molecules 2019, 24, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.; Yao, N.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Xia, C. Upregulation of UGT1A1 expression by ursolic acid and oleanolic acid via the inhibition of the PKC/NF-κB signaling pathway. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2021, 92, 153726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Luan, M.; Zhao, F.; Meng, Q. Advances on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Oleanolic Acid and Derivatives. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2020–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Yan, W.; Xu, K.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Ran, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, L. Oleanolic Acid Decreases IL-1β-Induced Activation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes via the SIRT3-NF-κB Axis in Osteoarthritis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 7517219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Tao, M.; Dai, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q. Inhibition of NF-κB is required for oleanolic acid to downregulate PD-L1 by promoting DNA demethylation in gastric cancer cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zeng, H.; Xu, M.; Huang, C.; Tao, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Xia, J.; Li, C.; et al. Oleanolic Acid Improves Obesity-Related Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Regulating Macrophages Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 697483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Hu, Q.; Wang, B.; Cui, W.; Wu, F.; Ding, Y. Oleanolic acid alleviates diabetic rat carotid artery injury through the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8413–8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, A.; Choi, J.W. Oleanolic Acid Provides Neuroprotection against Ischemic Stroke through the Inhibition of Microglial Activation and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; He, G. PI3K and ERK/Nrf2 pathways are involved in oleanolic acid-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Bai, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, P.; Liao, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Hai, C. Inhibitory effect of oleanolic acid on hepatocellular carcinoma via ERK-p53-mediated cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Jo, H.J.; Lee, K.J.; Choi, J.W.; An, J.H. Oleanolic acid induces p53-dependent apoptosis via the ERK/JNK/AKT pathway in cancer cell lines in prostatic cancer xenografts in mice. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26370–26386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Chen, W.; Yin, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, N.; Chen, W. Oleanolic acid induces apoptosis of MKN28 cells via AKT and JNK signaling pathways. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, Y.C. Oleanolic acid suppresses ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation and Th2-mediated allergic asthma by modulating the transcription factors T-bet, GATA-3, RORγt and Foxp3 in asthmatic mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 18, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phull, A.R.; Eo, S.H.; Kim, S.J. Oleanolic acid (OA) regulates inflammation and cellular dedifferentiation of chondrocytes via MAPK signaling pathways. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-Le-Grand Fr.) 2017, 63, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, L.J.; Fan, Y.S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q. Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis on the Action Mechanism of Oleanolic Acid to Alleviate Osteoporosis. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 28410–28420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, M.; Li, D. Oleanolic acid suppresses the proliferation of lung carcinoma cells by miR-122/Cyclin G1/MEF2D axis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 400, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F.; Wang, J.T.; Zhang, L.X.; Xing, S.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, K.; Deng, S.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Tang, L.; Wu, H.S. Oleanolic acid derivative DKS26 exerts antidiabetic and hepatoprotective effects in diabetic mice and promotes glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion and expression in intestinal cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2912–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, T.; Lv, L.; Jia, L.; Ruan, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, L. Oleanolic acid targets the regulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and activates autophagy in chondrocytes to improve osteoarthritis in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 94, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Xie, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, L.; Wang, N. Oleanolic acid ameliorates high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction via PPARδ activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lin, J.; Sun, G.; Wei, L.; Shen, A.; Zhang, M.; Peng, J. Oleanolic acid inhibits colorectal cancer angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro via suppression of STAT3 and Hedgehog pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5276–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Sun, L.; Pei, Y.; Wang, D. Oleanolic Acid Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Angiogenesis by Blocking the VEGFR2 Signaling Pathway. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.T.; Ma, X.D.; Tang, Z.Y. Anticancer activity of oleanolic acid and its derivatives: Recent advances in evidence, target profiling and mechanisms of action. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Dong, Y.; Li, N.; Niu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chu, P.; Tang, Z. An oleanolic acid derivative, K73-03, inhibits pancreatic cancer cells proliferation in vitro and in vivo via blocking EGFR/Akt pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.M.; Guinda, A.; Delgado, T.; Rada, M.; Cayuela, J.A. Biochemical basis of the antidiabetic activity of oleanolic acid and related pentacyclic triterpenes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Liby, K.T.; Stephenson, K.K.; Holtzclaw, W.D.; Gao, X.; Suh, N.; Williams, C.; Risingsong, R.; Honda, T.; Gribble, G.W.; et al. Extremely potent triterpenoid inducers of the phase 2 response: Correlations of protection against oxidant and inflammatory stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4584–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liao, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Qin, X.; Hai, C. Oleanolic acid improves hepatic insulin resistance via antioxidant, hypolipidemic and anti-inflammatory effects. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 376, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Aparicio, Á.; Correa-Rodríguez, M.; Castellano, J.M.; Schmidt-RioValle, J.; Perona, J.S.; González-Jiménez, E. Potential Molecular Targets of Oleanolic Acid in Insulin Resistance and Underlying Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yang, E.J.; Ku, S.K.; Song, K.S.; Bae, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of oleanolic acid on LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation 2013, 36, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Xue, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Bi, C.; Shan, A. Oleanolic acid enhances tight junctions and ameliorates inflammation in Salmonella typhimurium-induced diarrhea in mice via the TLR4/NF-κB and MAPK pathway. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehangir, A.; Shahzad, M.; Shahid, K.; Waheed, A.; Ayub, F. Zinc and iron complexes of oleanolic acid, (OA) attenuate allergic airway inflammation in rats. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.H.; Yang, Q.; Harada, M.; Li, G.Q.; Yamahara, J.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Li, Y. Pomegranate flower extract diminishes cardiac fibrosis in Zucker diabetic fatty rats: Modulation of cardiac endothelin-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 46, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, K.; Nakane, T.; Masuda, K.; Ishii, H. Ursolic acid and oleanolic acid, members of pentacyclic triterpenoid acids, suppress TNF-α-induced E-selectin expression by cultured umbilical vein endothelial cells. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2010, 17, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Mir, R.; Godavari, G.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Ahmad, B.; Mothana, R.A.; Ullah, R.; Almarfadi, O.M.; Jachak, S.M.; Masoodi, M.H. Design, Synthesis, Molecular Modelling, and Biological Evaluation of Oleanolic Acid-Arylidene Derivatives as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeziri, F.Z.; Belarbi, M.; Murtaza, B.; Hichami, A.; Benammar, C.; Khan, N.A. Oleanolic acid improves diet-induced obesity by modulating fat preference and inflammation in mice. Biochimie 2018, 152, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.M.; Garcia-Rodriguez, S.; Espinosa, J.M.; Millan-Linares, M.C.; Rada, M.; Perona, J.S. Oleanolic Acid Exerts a Neuroprotective Effect Against Microglial Cell Activation by Modulating Cytokine Release and Antioxidant Defense Systems. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, B.; Gallardo, I.; Ruiz, L.; Alvarez, Y.; Cachofeiro, V.; Margolles, A.; Hernandez, M.; Nieto, M.L. Oleanolic acid ameliorates intestinal alterations associated with EAE. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, X.L.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.L.; Bai, H.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.L.; Hai, C.X. Antioxidant activities of oleanolic acid in vitro: Possible role of Nrf2 and MAP kinases. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2010, 184, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, G.; Xie, Y.; Yin, H.Y.; Li, X.J.; Yang, Y.D. Compositional characterization of Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim and their antioxidant activities and induction of apoptosis in Bel-7402 cell. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Fu, H.; Hai, C. Oleanolic acid co-administration alleviates ethanol-induced hepatic injury via Nrf-2 and ethanol-metabolizing modulating in rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 221, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskender, H.; Dokumacioglu, E.; Terim Kapakin, K.A.; Yenice, G.; Mohtare, B.; Bolat, I.; Hayirli, A. Effects of oleanolic acid on inflammation and metabolism in diabetic rats. Biotech. Histochem. Off. Publ. Biol. Stain Comm. 2022, 97, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricker, M.; Tolkovsky, A.M.; Borutaite, V.; Coleman, M.; Brown, G.C. Neuronal Cell Death. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 813–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hou, D.; He, J.; Zeng, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, R.; Huang, H.; et al. Oxidative-Damaged Mitochondria Activate GABARAPL1-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasomes in an Autophagic-Exosome Manner after Acute Myocardial Ischemia. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7958542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, G.; Holley, C.L.; Schroder, K. Parkinson’s disease: Connecting mitochondria to inflammasomes. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Dai, X.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Oleanolic acid and its synthetic derivatives for the prevention and therapy of cancer: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Cancer Lett. 2014, 346, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potočnjak, I.; Šimić, L.; Vukelić, I.; Batičić, L.; Domitrović, R. Oleanolic acid induces HCT116 colon cancer cell death through the p38/FOXO3a/Sirt6 pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 363, 110010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, L.; Ma, L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, N.; Liu, G.; Lin, X. Oleanolic acid inhibits proliferation and invasiveness of Kras-transformed cells via autophagy. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Kudo, R.; Tsurushima, K.; Ohnishi, K.; Ikeda, T.; Takeya, M. Oleanolic acid inhibits macrophage differentiation into the M2 phenotype and glioblastoma cell proliferation by suppressing the activation of STAT3. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birts, C.N.; Banerjee, A.; Darley, M.; Dunlop, C.R.; Nelson, S.; Nijjar, S.K.; Parker, R.; West, J.; Tavassoli, A.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J.J.; et al. p53 is regulated by aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells by the CtBP family of NADH-dependent transcriptional regulators. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaau9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wei, L.; Shen, A.; Chu, J.; Lin, J.; Peng, J. Oleanolic acid modulates multiple intracellular targets to inhibit colorectal cancer growth. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wu, T.; Lu, X. Oleanolic acid reduces aerobic glycolysis-associated proliferation by inhibiting yes-associated protein in gastric cancer cells. Gene 2019, 712, 143956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, R.Y.; Qian, K.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lee, K.H. Plant-derived triterpenoids and analogues as antitumor and anti-HIV agents. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1321–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamai, H.; Sawada, N.; Yoshida, T.; Seike, J.; Takizawa, H.; Kenzaki, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Kondo, K.; Bando, Y.; Ohnishi, Y.; et al. Triterpenes augment the inhibitory effects of anticancer drugs on growth of human esophageal carcinoma cells in vitro and suppress experimental metastasis in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, M.E.; Planas, J.M.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Daniel, H.; Wenzel, U. Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing effects of maslinic and oleanolic acids, two pentacyclic triterpenes from olives, on HT-29 colon cancer cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuttan, G.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; Manu, K.A.; Kuttan, R. Inhibition of tumor progression by naturally occurring terpenoids. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, M.H.; Kao, T.C.; Yen, G.C. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid induce apoptosis in HuH7 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through a mitochondrial-dependent pathway and downregulation of XIAP. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6110–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhao, R.; Pan, S.T.; Zhe, H.; He, Z.X.; Duan, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Qiu, J.X.; et al. Bardoxolone methyl induces apoptosis and autophagy and inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness in esophageal squamous cancer cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 993–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Chaki, R.; Mandal, V.; Mandal, S.C. COX-2 as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol. Rep. PR 2010, 62, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiram, N.B.; Indranie, C.; Malisetty, S.V.; Jagan, P.; Steele, V.E.; Rao, C.V. Chemoprevention of colon carcinogenesis by oleanolic acid and its analog in male F344 rats and modulation of COX-2 and apoptosis in human colon HT-29 cancer cells. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Song, Q.; Hu, D.; Zhuang, X.; Yu, S.; Teng, D. Oleanolic acid induced autophagic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and ROS-dependent pathway. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Korean Physiol. Soc. Korean Soc. Pharmacol. 2016, 20, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xing, Y. AMPK activation-dependent autophagy compromises oleanolic acid-induced cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67942–67954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Yakisich, J.S. Natural products targeting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as anticancer agents. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, J.Z.; Liao, N.; Yu, W.H.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.L.; Hai, C.X. Protective effect of oleanolic acid against beta cell dysfunction and mitochondrial apoptosis: Crucial role of ERK-NRF2 signaling pathway. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2013, 27, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lúcio, K.A.; Rocha Gda, G.; Monção-Ribeiro, L.C.; Fernandes, J.; Takiya, C.M.; Gattass, C.R. Oleanolic acid initiates apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines and reduces metastasis of a B16F10 melanoma model in vivo. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bo, F.; Li, L. Development and Evaluation of Oleanolic Acid Dosage Forms and Its Derivatives. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1308749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Lu, Y.F.; Pi, J. New insights into generalized hepatoprotective effects of oleanolic acid: Key roles of metallothionein and Nrf2 induction. Biochem. Pharm. 2008, 76, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.; Gu, T.; Pang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X. Natural Products Targeting Liver X Receptors or Farnesoid X Receptor. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 772435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisman, S.A.; Aleksunes, L.M.; Klaassen, C.D. Oleanolic acid activates Nrf2 and protects from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity via Nrf2-dependent and Nrf2-independent processes. Biochem. Pharm. 2009, 77, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajemiroye, J.O.; Polepally, P.R.; Chaurasiya, N.D.; Tekwani, B.L.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Costa, E.A. Oleanolic acid acrylate elicits antidepressant-like effect mediated by 5-HT1A receptor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 49, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid: Research perspectives. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.T.; Li, J.; Liu, B.B.; Luo, L.; Liu, Q.; Geng, D. BDNF-ERK-CREB signalling mediates the role of miR-132 in the regulation of the effects of oleanolic acid in male mice. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. JPN 2014, 39, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.T.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Geng, D.; Zhou, Y.F.; Ke, X.Q.; Chen, H.; Weng, L.J. Antidepressant-like effect of oleanolic acid in mice exposed to the repeated forced swimming test. J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.Q.; Wang, S.S.; Zhu, J.X.; Mu, R.H.; Li, C.F.; Geng, D.; Liu, Q.; Yi, L.T. Oleanolic acid decreases SGK1 in the hippocampus in corticosterone-induced mice. Steroids 2019, 149, 108419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.P.; Shi, L.Y.; Li, J.P.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, W.; Tang, S.Y.; Jia, L.J.; Zhang, J.; Gan, G.X. Oleanolic acid inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via ER alpha/miR-503/RANK signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.Y.; Jin, B.R.; Kim, H.J.; An, H.J. Oleanolic Acid Ameliorates Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating PCNA-Dependent Cell Cycle Progression In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Shen, Q.; Feng, Z.H.; Wu, J.; Li, J.X. An oleanolic acid derivative reduces denervation-induced muscle atrophy via activation of CNTF-mediated JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 861, 172612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Meng, L.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Shao, L.; Chen, K.; Zhou, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, F. Design, synthesis of oleanolic acid-saccharide conjugates using click chemistry methodology and study of their anti-influenza activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, R. Oleanolic acid and related triterpenoids from olives on vascular function: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somova, L.O.; Nadar, A.; Rammanan, P.; Shode, F.O. Cardiovascular, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of oleanolic and ursolic acids in experimental hypertension. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2003, 10, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Wu, P.; Lu, Y.J.; Hou, N.; Chen, W.H.; Wong, W.L. New Applications of Oleanolic Acid and its Derivatives as Cardioprotective Agents: A Review of their Therapeutic Perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3740–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camer, D.; Yu, Y.; Szabo, A.; Huang, X.F. The molecular mechanisms underpinning the therapeutic properties of oleanolic acid, its isomer and derivatives for type 2 diabetes and associated complications. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Han, Z. Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of oleanolic acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Phytother. Res. PTR 2009, 23, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buus, N.H.; Hansson, N.C.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, R.; Stankevicius, E.; Andersen, M.R.; Simonsen, U. Antiatherogenic effects of oleanolic acid in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboh, M.; Govender, L.; Siwela, M.; Mkhwanazi, B.N. Anti-Diabetic Potential of Plant-Based Pentacyclic Triterpene Derivatives: Progress Made to Improve Efficacy and Bioavailability. Molecules 2021, 26, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NA, J.C.F.; Pirson, L.; Edelberg, H.; Miranda, L.M.; Loira-Pastoriza, C.; Preat, V.; Larondelle, Y.; André, C.M. Pentacyclic Triterpene Bioavailability: An Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollier, J.; Goossens, A. Oleanolic acid. Phytochemistry 2012, 77, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A.; Ahmed, S.; Brankov, N.; Perloff, M. Triterpenoids as potential agents for the chemoprevention and therapy of breast cancer. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Fazio, G.C.; Matsuda, S.P. On the origins of triterpenoid skeletal diversity. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 261–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Oyedeji, O.O.; Oyedeji, A.O.; Ndebia, E.J. Anti-inflammatory and membrane-stabilizing properties of two semisynthetic derivatives of oleanolic acid. Inflammation 2015, 38, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Holmes, S.S.; Baker, G.A.; Challa, S.; Bose, H.S.; Song, Z. Ionic derivatives of betulinic acid as novel HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ren, C.; Du, K.; Zhu, H.; Ai, Y.; Kang, F.; Luo, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; et al. Olean-28,13b-olide 2 plays a role in cisplatin-mediated apoptosis and reverses cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer through multiple signaling pathways. Biochem. Pharm. 2019, 170, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Song, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Peng, J.; Han, G.; et al. Anticancer effect of SZC017, a novel derivative of oleanolic acid, on human gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.G.; Su, C.H.; Yang, L.D.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.F. Synthesis of oleanolic acid dimers linked at C-28 and evaluation of anti-tumor activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Niu, R.; Gao, K.; Yang, B.; Liao, X.; Zhang, J. Solid inclusion complexes of oleanolic acid with amino-appended β-cyclodextrins (ACDs): Preparation, characterization, water solubility and anticancer activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, V.K.; Singh, M.P. Cancer Nanotechnology: A New Revolution for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ukidve, A.; Kim, J.; Mitragotri, S. Targeting Strategies for Tissue-Specific Drug Delivery. Cell 2020, 181, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriadis, G. Engineering liposomes for drug delivery: Progress and problems. Trends Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, N.; Udayakumar, T.S.; D’Souza, W.D.; Simone, C.B.; Raghavan, S.R.; Polf, J.; Mahmood, J. Liposomes: Clinical Applications and Potential for Image-Guided Drug Delivery. Molecules 2018, 23, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Bian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Xing, S.; Li, L.; Gao, D. Combined Near Infrared Photothermal Therapy and Chemotherapy Using Gold Nanoshells Coated Liposomes to Enhance Antitumor Effect. Small 2016, 12, 4103–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Tang, S.; Tong, Q. Oleanolic acid liposomes with polyethylene glycol modification: Promising antitumor drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3517–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Ma, T.; Tian, Y.; Li, H. Nanocrystallized Oleanolic Acid Better Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Intracranial Glioma via Caspase-3 Pathway. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Afzal, A.; Yang, T.; Gai, Y.; Raza, S.M.; Khan, M.W.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Xiang, G. Development of Dual Drug Loaded Nanosized Liposomal Formulation by A Reengineered Ethanolic Injection Method and Its Pre-Clinical Pharmacokinetic Studies. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Afzal, A.; Raza, S.M.; Bashir, S.; Madni, A.; Khan, M.W.; Ma, X.; Xiang, G. Liposomal co-delivered oleanolic acid attenuates doxorubicin-induced multi-organ toxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47136–47153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Pi, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhong, Z. Optimized formulation of multivesicular liposomes loaded with oleanolic acid enhanced anticancer effect in vitro. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurj, A.; Braicu, C.; Pop, L.A.; Tomuleasa, C.; Gherman, C.D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The new era of nanotechnology, an alternative to change cancer treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2871–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Yang, X. Self-assembled small molecule natural product gel for drug delivery: A breakthrough in new application of small molecule natural products. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Xu, H.; Bao, X.; Zhang, C.; Guan, X.; Liu, H.; Lv, L.; Deng, S.; Gao, D.; Wang, C.; et al. Oleanolic acid-loaded PLGA-TPGS nanoparticles combined with heparin sodium-loaded PLGA-TPGS nanoparticles for enhancing chemotherapy to liver cancer. Life Sci. 2016, 165, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Liu, H.; Lv, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Z. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro/vivo studies of oleanolic acid-loaded lactoferrin nanoparticles. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Li, G.; Zhu, S.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Lei, J. Amphiphilic carboxylated cellulose-g-poly(l-lactide) copolymer nanoparticles for oleanolic acid delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pengbo, Z.; Yunyun, M.; He, J.; Lei, J. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on poly(ethylene glycol)–oleanolic acid conjugates for co-delivery of anticancer drugs. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29591–29598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cai, L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Cancer Cell Membrane-Decorated Zeolitic-Imidazolate Frameworks Codelivering Cisplatin and Oleanolic Acid Induce Apoptosis and Reversed Multidrug Resistance on Bladder Carcinoma Cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhong, Q.; Zhong, R.; Huang, H.; Xia, Z.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Jia, X. Preparation and antitumor evaluation of self-assembling oleanolic acid-loaded Pluronic P105/d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate mixed micelles for non-small-cell lung cancer treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6337–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, H.L.; Abrego, G.; Souto, E.B.; Garduño-Ramirez, M.L.; Clares, B.; García, M.L.; Calpena, A.C. Nanoemulsions for dermal controlled release of oleanolic and ursolic acids: In vitro, ex vivo and in vivo characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 130, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Das, S.; Ng, K.Y.; Heng, P.W. Formulation, biological and pharmacokinetic studies of sucrose ester-stabilized nanosuspensions of oleanolic Acid. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 2020–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plant Species | Family | Plant Part | Biological Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betula alba | Betulaceae | Bark | Anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-viral, antitumor | [25,34] |
| Crataegus pinnatifida | Rosaceae | Leaves | Anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-viral, antitumor | [25] |
| Eriobotrya japonica | Rosaceae | Flowers | Not mentioned | [35] |
| Fabiana imbricata | Solanaceae | Leaves and flowers | Antiviral, antitumor, antihyperlipidemic | [36] |
| Ligustrum lucidum Ait | Oleaceae | Fruits, leaves | Anti-hepatitis, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antiprotozoal, antimutagenic, anticancer | [37,38,39] |
| Gentiana lutea | Gentianaceae | Rhizome | Antimicrobial | [14] |
| Lavandula angustifolia | Lamiaceae | Herbs | Anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial | [25] |
| Lantana camara | Verbenaceae | Leaves and flowers | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antiprotozoal | [39] |
| Melissa officinalis | Lamiaceae | Herbs | Antiviral, hepatoprotective | [25,40,41] |
| Nerium oleander | Apocynaceae | Leaves | Not mentioned | [25] |
| Olea europaea L. | Oleaceae | Fruits, bark, leaves | Anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-diabetic | [25,42,43,44,45] |
| Origanum majorana | Lamiaceae | Herbs | Not mentioned | [25] |
| Panax quinquefolium | Araliaceae | Roots | Anticancer, anti-diabetes, neuroprotection, anti-Aging | [46,47] |
| Phyllanthus amarus | Phyllanthaceae | Leaves, aerials | Anti-diabetes | [48] |
| Punica granatum L. | Lythraceae | Fruit | Antioxidant activity | [13] |
| Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Lamiaceae | Leaves, flowers, stems, branches | Anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, gastroprotective, antiulcer | [43] |
| Rosa laevigata | Rosaceae | Leaves | Anti-inflammatory | [49] |
| Syzygium aromaticum | Myrtaceae | Leaves, flower buds | Antinociceptive, Anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, antioxidant | [36,50] |
| Sambucus nigra | Adoxaceae | Leaves, bark | Anticancer | [25,51] |
| Satureja montana | Lamiaceae | Herbs | Anticancer, anti-bacterial | [25,52,53] |
| Siphonodon celastrineus | Celastraceae | Root bark, stems | Anti-inflammatory | [54,55] |
| Silphium trifoliatum | Asteraceae | Leaves | Anti-bacterial | [46,56] |
| Salvia officinalis | Lamiaceae | Herbs | Anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidative | [25,57,58] |
| Thymus vulgaris | Lamiaceae | Herbs | Glutaminase inhibitor | [25,59] |
| Viscum album | Santalaceae | Leaves, stems | Antitumor, analgesic, anti-inflammatory | [39,60,61] |
| Viburnum chingii | Adoxaceae | Leaves | Antimicrobial | [54,62] |
| Signaling Pathway | Biological Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway | Anti-inflammatory, antitumor | [65,66,67,68] |
| Nod-like receptor pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) signaling pathway | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotection | [69,70,71] |
| Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway | Liver protection, antitumor | [72,73] |
| Protein kinase B/Akt signaling pathway | Antitumor, liver protection | [72,74,75] |
| Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) signaling pathway | Antitumor | [1,75] |
| Orphan receptor γ t signaling pathway | Anti-inflammatory, anti-asthma | [76] |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathway | Anti-inflammatory | [77,78] |
| MiR-122/cyclin G1/myocyte enhancer factor 2D (miR-122/CCNG1/MEF2D) signaling pathway | Antitumor | [79] |
| Cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate/protein kinase A (cAMP/PKA) signaling pathway | Lowers blood sugar and blood lipids, protects pancreatic islets | [80] |
| Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/AKT/mTOR) signaling pathway | Anti-osteoarthritis | [81] |
| Endothelial nitric oxide synthase/Akt/nitric oxide (eNOS/Akt/NO) signaling pathway | Ameliorates high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction | [82] |
| Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway | Inhibits colorectal cancer | [83] |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)/ERK/JNK signaling pathway | Anticancer | [84] |
| Hippo-Yes-associated protein (Hippo-Yap) signaling pathway | Anti-stomach cancer | [85] |
| Epidermal growth factor (EGFR)/AKT signaling pathway | Anti-pancreatic cancer | [86] |
| Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2) signaling pathway | Liver protection, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, maintenance of redox and protein homeostasis | [87,88,89] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Lu, Q.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z. Application and Development of Natural Plant Metabolite Oleanolic Acid in the Nano Era. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122142
Wang K, Lu Q, Cao X, Wang Y, Wu Y, Chen Z, Yang Z. Application and Development of Natural Plant Metabolite Oleanolic Acid in the Nano Era. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122142
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kun, Qinyue Lu, Xiang Cao, Yuhao Wang, Yanni Wu, Zhi Chen, and Zhangping Yang. 2022. "Application and Development of Natural Plant Metabolite Oleanolic Acid in the Nano Era" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122142
APA StyleWang, K., Lu, Q., Cao, X., Wang, Y., Wu, Y., Chen, Z., & Yang, Z. (2022). Application and Development of Natural Plant Metabolite Oleanolic Acid in the Nano Era. Agriculture, 12(12), 2142. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122142







