Soil and Irrigation Water Salinity, and Its Consequences for Agriculture in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
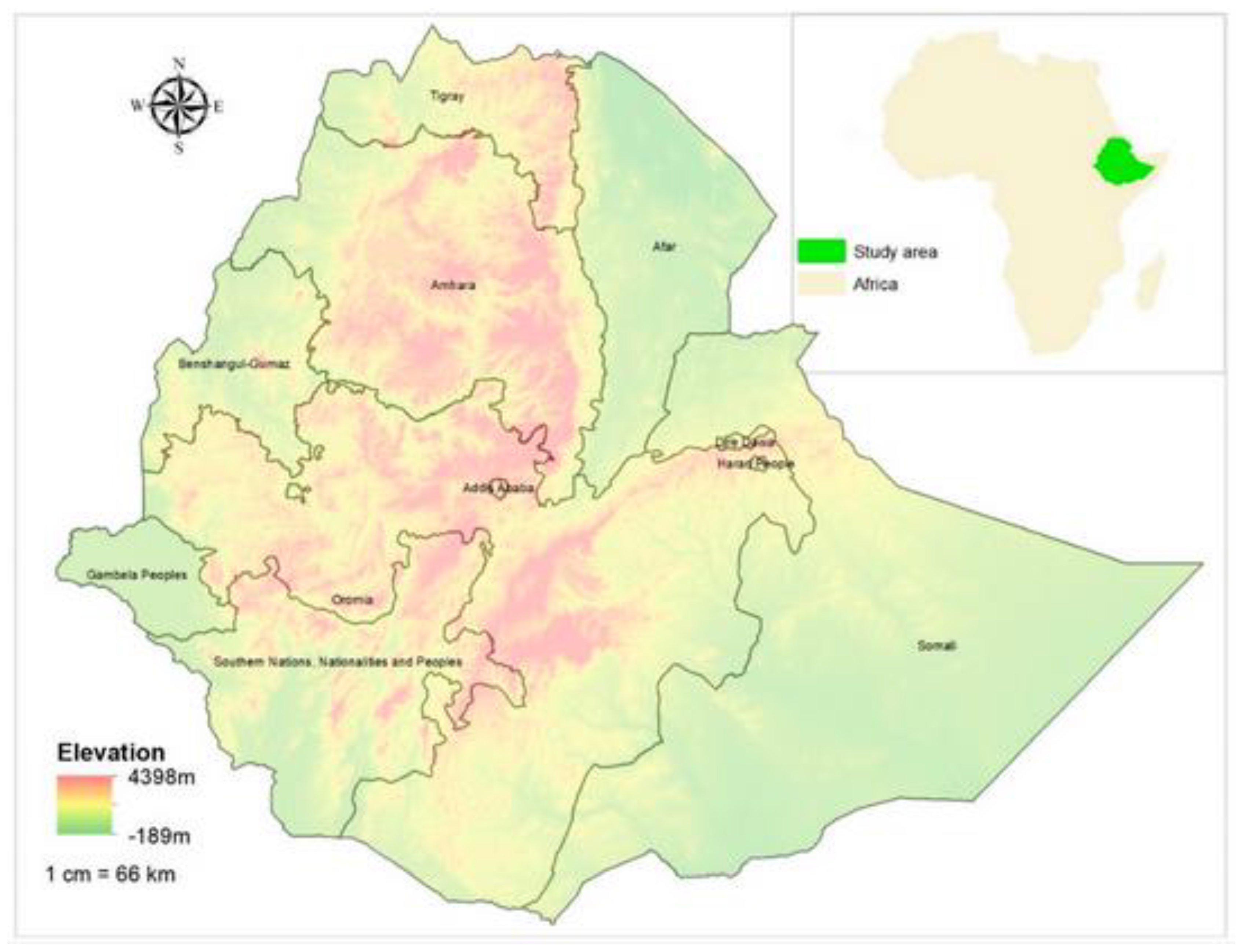
2. Study Area
2.1. Methodological Approach Followed
2.2. Why Salinity Frequently Occurs in Dryland Areas of Ethiopia
3. Severity of Soil Salinity in Agriculturally Potential Areas of Ethiopia
4. Severity of Irrigation Water Salinity in Ethiopia
5. Salinity Effects on Crops at Different Growth Stages
5.1. Effects of Salinity on Vigor, and Relative Water Content of Selected Crops
5.2. Phytotoxicity of Salinity on Shoot, Root, and Seedling Relative Water Content
5.3. Effects of Salinity on Seed Germination and Early Growth Stages
6. Management of Soil Salinity and Its Impacts on Agricultural Production
7. Producers’ Perception and Consequences of Salinity to Rural Socio-Economic Conditions
8. Conclusions from the Reviewed Findings and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ullah, A.; Bano, A.; Khan, N. Climate Change and Salinity Effects on Crops and Chemical Communication Between Plants and Plant Growth-Promoting Microorganisms Under Stress. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 618092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tully, K.; Sullivan, C.; Weil, R.; Sanchez, P. The state of soil degradation in Sub-Saharan Africa: Baselines, trajectories, and solutions. Sustainability 2015, 7, 6523–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sileshi, A. Status of Salinity Affected Soils, Irrigation Water Quality and Land Suitability of Dubti/Tendaho Area, North Eastern Ethiopia. Ph.D. Dissertation, Haramaya University, Haramaya, Ethiopia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- MoA (Ministry of Agriculture). Small-Scale Irrigation Situation Analysis and Capacity Need Assessment; Annual Report; Ministry of Agriculture: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2011.
- Seleshi, B.; Aster, D.; Makonnen, L.; Loiskandl, W.; Mekonnen, A.; Tena, A.; Ministry of Agriculture. Small-Scale Irrigation Situation Analysis and Capacity Need Assessment; Annual Report; Ministry of Agriculture: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007.
- Makombe, G.; Namara, R.; Hagos, F.; Sileshi, B.; Ayana, M.; Bossio, D. A Comparative Analysis of the Technical Efficiency of Rain-Fed and Smallholder Irrigation in Ethiopia; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2011; pp. 37–143. [Google Scholar]
- Belay, M.; Bewket, W. Traditional irrigation and water management practices in highland ethiopia: Case study in dangila woreda. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 62, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhane, H. Salinity Status of Soils of Irrigated Lands, Water Logged Areas and Irrigation Water Quality at Raya Alamata District in Raya Valley, Northern Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Haramaya University, Haramaya, Ethiopia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Debela, A. Characterization salinity-affected of salinity-affected soils and irrigation water at Bule Hora district, West Guji zone. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gebremeskel, G.; Gebremicael, T.; Kifle, M.; Meresa, E.; Gebremedhin, T.; Girmay, A. Salinization pattern and its spatial distribution in the irrigated agriculture of Northern Ethiopia: An integrated approach of quantitative and spatial analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 206, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, C.K.; Sen, S.; Paul, A.K.; Acharya, K. First Report of Alternaria dianthicola Causing Leaf Blight on Withania somnifera from India. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruts, H.; Haileselassie, H.; Desta, Y. Reclamation of Salt-affected Soils in the Drylands of Ethiopia: A Review. Res. Dev. Saline Agric. 2019, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, S.B.; Yilma, A.D.; Loulseged, M.; Loiskandl, W.; Ayana, M.; Alamirew, T. Water Resources and Irrigation De-velopment in Ethiopia; Working Paper 123; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2007; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Kempen, B.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Walsh, M.G.; Shepherd, K.D.; Sila, A.; Macmillan, R.A.; De Jesus, J.M.; Tamene, L. Mapping Soil Properties of Africa at 250 m Resolution: Random Forests Significantly Improve Current Predictions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, G. Management of Salinity Affected Soils. Soil Analysis for Soil Salinity and Fertility Status; VDM Publishing House Ltd.: Riga, Latvia, 2011; p. 84. [Google Scholar]
- Bekele, Y.; Tadesse, N.; Konka, B. Preliminary Study on the Impact of Water Quality and Irrigation Practices on Soil Salinity and Crop Production, Gergera Watershed, Atsbi-Wonberta, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Momona Ethiop. J. Sci. 2012, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, J.; Walker, G.; Stace, P.; Wel, B.V.; Leaney, R. Assessing the Impact of Dryland Salinity on South Australia’s Water Re-Sources: A Sub-Project of the National Land and Water Resources Audit Dryland Salinity Theme Project 1. CSIRO Land and Water Technical Report 9/00. Canberra: Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization 2000. Available online: http://www.clw.csiro.au/publications/technical2000/tr9-00.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Degol, F.; Abrha, K.; Bereket, H.; Gebremedhin, W. Preliminary Soil and Water Characterization of Gergele Swampy Area, Alamata District; Annual research report; Tigray Agricultural Research Institute: Mekelle, Ethiopia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, S.; Belayneh, M.; Ahmed, F. Reclamation and amelioration of saline-sodic soil using gypsum and halophytic grasses: Case of Golina-Addisalem irrigation scheme, Raya Kobo Valley, Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2021, 7, 1859847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steenbergen, F.; Mehari, A.H. Spate irrigation: Good for people, livestock and crops. Leisa 2009, 25, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, S.; Tessema, G. Evaluation of soil and water salinity for irrigation in North-eastern Ethiopia: Case study of Fursa small scale irrigation system in Awash River Basin. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, B.; Wogi, L.; Tamiru, S. Salinity Status of Soils of Irrigated Lands and Irrigation Water Quality at Raya Alamata District, Northern Ethiopia. Int. J. Res. Agric. Sci. 2020, 7, 2348–3997. [Google Scholar]
- Heluf, G. Evaluation of the Potential Use of Langbeinite (K2SO4.2MgSO4) as a Reclaiming Material for Sodic and Saline Sodic Soils. Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 1995; 166p. [Google Scholar]
- Zewdie, E. Selected physical, chemical and mineralogical characteristics of major soils occurring in Character Highlands, Eastern Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Nat. Resour. 2001, 1, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Adhanom, O.G. Salinity and sodicity hazard characterization in major irrigated areas and irrigation water sources, Northern Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2019, 5, 1673110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USSLS (United State Salinity Laboratory Staff). Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils. Agriculture Hand Book 60; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Kitila, K.; Jalde, A.; Workina, M. Evaluation and Characterization of Soil Salinity Status at Small-Scale Irrigation Farms at Bora and Lume Districts of East Showa Zone, Oromia, Ethiopia. Sci. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 4, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiflu, A.; Beyene, S.; Jeff, S. Characterization of problem soils in and around the south-central Ethiopian Rift Valley. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2013, 7, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kefyalew, A.; Kibebew, K. Evaluation of the Effect of Salinity Affected Soil on Selected Hydraulic Properties of Soils in Meki Ogolcha Area in East Showa Zone of Oromia Region, Ethiopia. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2016, 6, 2224–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Mesfin, A. Nature and Management of Ethiopian Soils; Alamaya University of Agriculture: Adama, Ethiopia, 2001; 272p. [Google Scholar]
- Girma, M.M.; Awulachew, S.B. Irrigation Practices in Ethiopia: Characteristics of Selected Irrigation Schemes; IWMI Working Paper 124; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2007; 80p. [Google Scholar]
- Megersa, O.; Willibald, L.; Josef, F. Effect of Lake Basaka Expansion on the Sustainability of Matahara SE in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the 34th WEDC International Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 18–22 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zeleke, T.; Yusuf, K.; Girma, A.; Ademe, A. Re-evaluation of some Fields’ Land Suitability at Kesem Sugar Project. Afr. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 2, 196–200. [Google Scholar]
- Frew, T.; Tena, A.; Fentaw, A. Appraisal and Mapping of Soil Salinity Problem in Amibara Irri-gation Farms, Middle Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2015, 13, 298–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ashenafi, W.; Bedadi, B.; Mohammed, M. Assessment on the Status of Some Micronutrients of Salinity Affected Soils in Amibara Area, Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Acad. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 4, 534–542. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, D.; Selassie, Y.G. Soil physicochemical properties and their significance for sustainable sugarcane production in Kesem Allaideghe plains irrigation project area, Eastern Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 11, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habtamu, A.D.; Kotie, Z.A. The carbon balance at Awash National Park: Emission from deforestation and sequestration through photosynthesis. In Proceedings of the 2nd Annual National Conference on Agriculture and Environ-mental Management for Sustainable Development, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 17–18 June 2016; pp. 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kidane, G.; Abebe, F.; Heluf, G.; Fentaw, A.; Wondimagegne, C.; Hibstu, A.; Asegid, A.; Messele, F.; Mohammed, B. Report of the National Task Force on assessment of salinity affected soils and recommendations on Management Options for Sustainable Utilization. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mulat, A.; Ashenafi, H.; Gezai, A. Characterization and classification of salinity affected soils and irrigation water in Tendaho sugarcane production farm, North-Eastern Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinfe, H. Impact of climate change on the water resources of Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Clim. Res. 1999, 12, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper. 29 Rev.1; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1994; 201p.
- FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization). Water Quality for Agriculture; Irrigation and Drainage Paper 29; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985.
- FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization). Salinity Affected Soils and Their Management; FAO Soils Bulletin 39; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1988.
- Bryan, G.; Donald, A.; Robert, G.; Jason, W.; Dan, M. Managing Irrigation Water Quality for Crop Production in the Pacifc Northwest; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA; University of Idaho: Moscow, ID, USA; Washington State University: Washington, WA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tamire, H. Desertification in Ethiopian highlands, Norwegian Church Regional Senior Consultant on Environment and Natural Resource Management; Report No. 200; RALA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Girma, A. Evaluation of Irrigation Water Quality in Ethiopian Sugar Estates (Research Report); Research and Training Services Division, Ethiopian Sugar Industry Support Centre Sh. Co.: Wonji, Ethiopia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Girma, T.; Endale, B. Saline and saline-sodic soils of the Middle Awash Valley of Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the 3rd Conference of Ethiopian Society of Soil Science, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 28–29 February 1996; pp. 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Waheed, A. Responses of some local/exotic accessions of lentil (Lens culinaris Medic.) to salinity stress. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 1993, 170, 103112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meron, N. Characterization of Salinity Affected Soils in the Central Rift Valley and Assessing Salinity Tolerance of Different Plants: A Case Study at the Southwestern Shore of Lake Ziway. Master’s Thesis, Adiss Ababa University, Adiss Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, C.; Goffeau, A.; Heibloem, M. Irrigation Water Management: Training Manual No. 1–Introduction to Irrigation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985.
- Mordi, P.; Zavareh, M. Effects of salinity on germination and early seedling growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2013, 2, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Katembe, W.J.; Ungar, I.A.; Mitchell, J.P. Effect of salinity on germination and seedling growth of two Atriplex species (Chenopodiaceae). Ann. Bot. 1998, 82, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Lauchli, A. Approaches to increasing the salinity tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtamu, A.A. Impact of salinity on tolerance, vigor, and seedling relative water content of haricot bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 1, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, M.F.; McNeilly, T. Variability for salinity tolerance in Sorghumn bicolor (L.) Moench. Under hydroponic condi-tions. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 1987, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, R.; Ahmad; Zahedi, M.; Ludwiczak, A.; Perez, S.C.; Piernik, A. Effect of salinity on seed germination and seedling development of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) genotypes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Naim, A.M.; Mohammed, K.E.; Ibrahim, E.A.; Suleiman, N.N. Impact of salinity on seed germination and early seedling growth of three sorghum (Sorghum biolor L. Moench) cultivars. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinfemichael, G.A. The Response of Some Haricot Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) Varieties for Salinity Stress during Germination and Seedling Stage. Curr. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 3, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Joachim, H.J.R.M.; Patrick, A.N.; Makoi, J.H.J.R.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Reclamation of sodic soils in northern Tanzania, using locally available organic and inorganic resources. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 1926–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyagi, N.K.; Sharma, D.P. Disposal of drainage water recycling and reuse. In Proceedings of the 8th ICID International Drainage Workshop, New Delhi, India, 31 January–4 February 2000; pp. 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Qamar, I. Productive rehabilitation and use of salt-affected land through afforestation (a review). Sci. Vis. 2004, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hanay, A.; Büyüksönmez, F.; Kiziloglu, F.M.; Canbolat, M.Y. Reclamation of Saline-Sodic Soils with Gypsum and MSW Compost. Compos. Sci. Util. 2004, 12, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Siyal, A.G.; Abro, Z.A. Salt affected soils their identification and reclamation. Pak. J. Appl. Sci. 2002, 2, 537–540. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, R.; Sawhney, A.; Jain, M.; Arif, M.; Rakshit, S. Factors influencing BIM adoption in emerging markets–the case of India. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO). Salt-Affected Soils and Their Management; FAO Soils Bulletin 39; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1988.
- Gupta, R.K.; Abrol, I.P. Salt-Affected Soils: Their Reclamation and Management for Crop Production. Adv. Soil Sci. 1990, 223–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C. Salinity and Sodicity Management: Soil and Water Management Module 2; Montana State University: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pearl, R.L.; Hopkins, C.H.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Wadden, T.A. Group cognitive-behavioral treatment for internalized weight stigma: A pilot study. Eat Weight Disord. 2018, 23, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, M.G.; Läuchli, A. Global Impact of Salinity and Agricultural Ecosystems. In Salinity: Environmental Plants-Molecules; Lauchli, A., Luttge, U., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Abegaz, F. An overview of salt-affected soils and their management status in Ethiopia [Paper presentation]. In A Paper Presented in the 3rd International Workshop on Water Management Project; Haramaya University: Haramaya, Ethiopia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Daba, A.W.; Qureshi, A.S.; Nisaren, B.N. Evaluation of Some Rhodes Grass (Chloris gayana) Genotypes for Their Salt Tolerance, Biomass Yield and Nutrient Composition. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.S.; Ertebo, T.; Mehansiwala, M. Prospects of alternative copping systems for salt-affected soils in Ethiopia. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2018, 9, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G.; Rehman, M.Z.; Saifullah; Sabir, M. Reclamation and salt leaching efficiency for tile drained saline-sodic soil using marginal quality water for irrigating rice and wheat crops. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaygan, M.; Mulligan, D.; Baumgartl, T. The potential of three halophytes (Tecticornia pergranulata, Sclerolaena longicuspis, and Frankenia serpyllifolia) for the rehabilitation of brine-affected soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2002–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, A. Restoration of mined lands—using natural processes. Ecol. Eng. 1997, 8, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaygan, M.; Reading, L.P.; Arnold, S.; Baumgartl, T. Modeling the effect of soil physical amendments on reclamation and revegetation success of a saline-sodic soil in a semi-arid environment. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2018, 32, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardane, N.; Chan, K. The management of soil physical properties limiting crop production in Australian sodic soils: Areview. Soil Res. 1994, 32, 13–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Senadhira, D. Salinity tolerance of progenies between Korean cultivars and IRR’s new plant type lines in rice. Korena J. Crop. Sci. 1998, 43, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, I.R.; Shaikh, P.R.; Shaikh, R.A.; Shaikh, A.A. phytotoxic effects of Heavy metals (Cr, Cd, Mn and Zn) on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seed Germination and Seedlings growth in Black Cotton Soil of Nanded, India. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2013, 3, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
| Water Parameter | Units | Degree of Restriction [43] | Values for Fursa River | Severity Status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Slight to Moderate | Severe | ||||
| Electrical conductivity (EC) | dS/m | <0.7 | 0.7–3 | >3.00 | 1.31 | Slight to moderate |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) | mg/L | <450 | 450–2000 | >2000 | 838.40 | Slight to moderate |
| Sodium (Na+) | meq/L | 70.00 | Severe | |||
| SAR | meql-1/2 | <3 | 3–9 | >9.00 | 10.00 | Severe |
| Adjusted SAR | 20.40 | |||||
| Calcium (Ca2+) | meq/L | 0 to 800: normal range | 88.80 | Normal | ||
| Magnesium (Mg2+) | meq/L | 0–120: normal range | 8.51 | Normal | ||
| Potassium (K+) | - | - | 30.00 | Normal | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tessema, N.; Yadeta, D.; Kebede, A.; Ayele, G.T. Soil and Irrigation Water Salinity, and Its Consequences for Agriculture in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010109
Tessema N, Yadeta D, Kebede A, Ayele GT. Soil and Irrigation Water Salinity, and Its Consequences for Agriculture in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review. Agriculture. 2023; 13(1):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010109
Chicago/Turabian StyleTessema, Negash, Dame Yadeta, Asfaw Kebede, and Gebiaw T. Ayele. 2023. "Soil and Irrigation Water Salinity, and Its Consequences for Agriculture in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review" Agriculture 13, no. 1: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010109
APA StyleTessema, N., Yadeta, D., Kebede, A., & Ayele, G. T. (2023). Soil and Irrigation Water Salinity, and Its Consequences for Agriculture in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review. Agriculture, 13(1), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13010109








