Assessment of Earthworm Viability and Soil Health after Two Years of Raw and Composted De-Inking Paper Sludge Amendment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Origin of the Soil and Waste Materials
2.2. The Experimental Design and Sampling Procedure
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Physical Analysis
2.5. Soil Biological Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
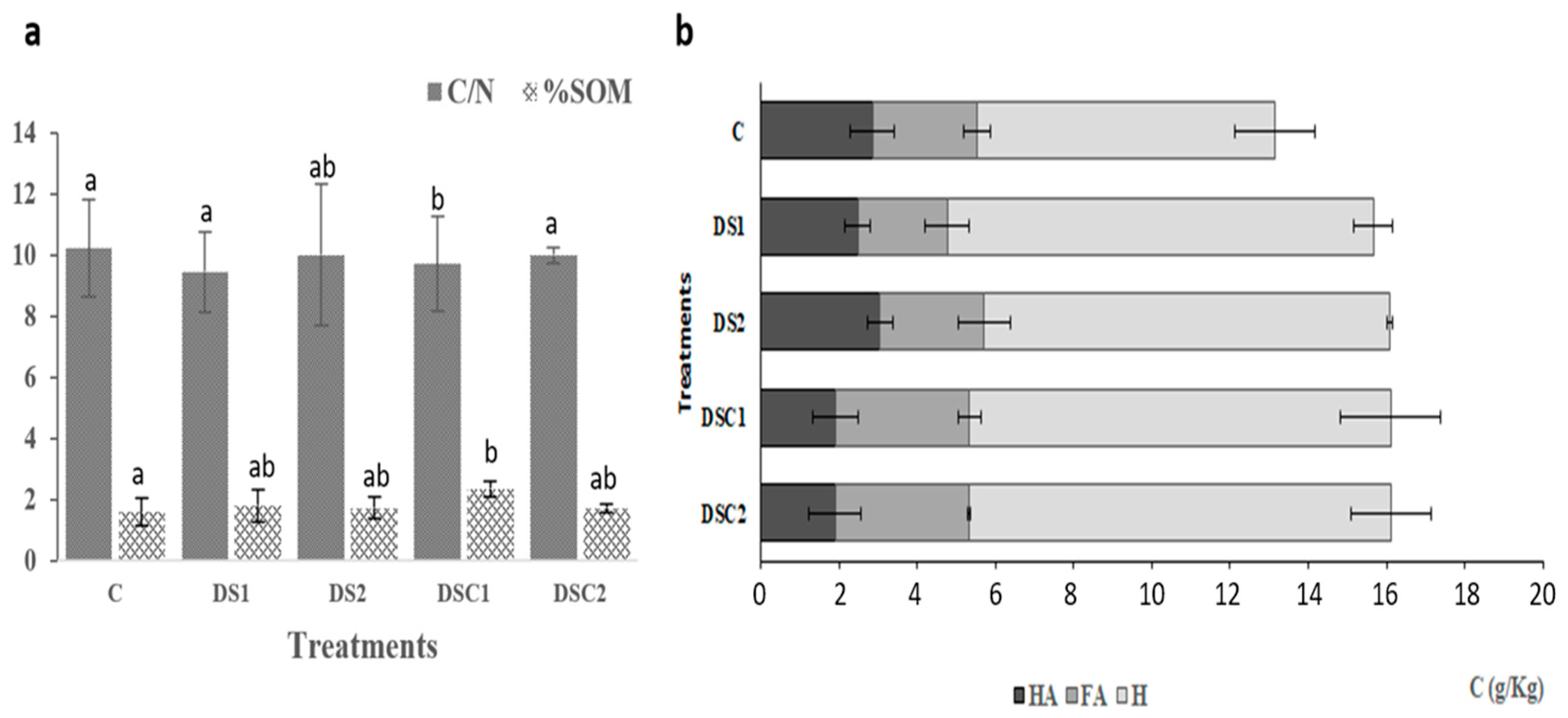
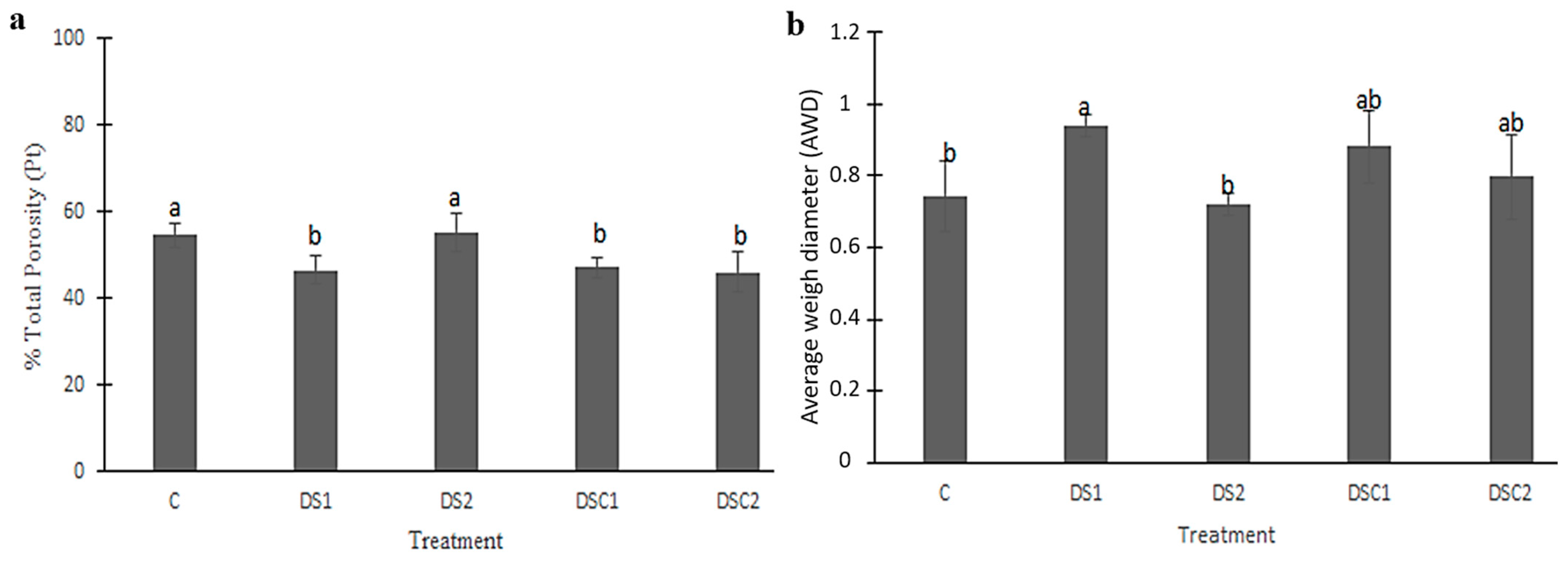
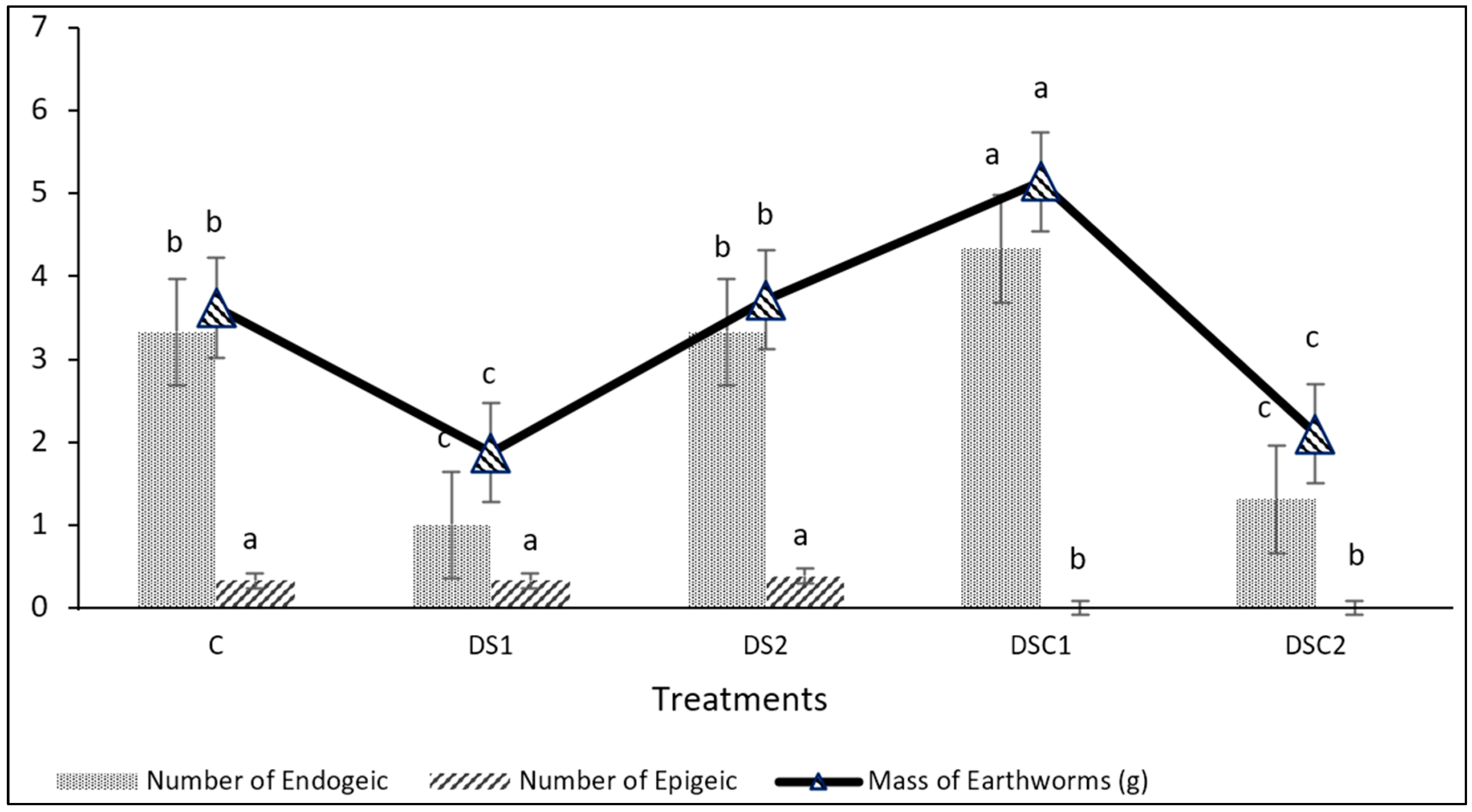
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamarque, P.; Tappeiner, U.; Turner, C.; Steinbacher, M.; Bardgett, R.D.; Szukics, U.; Schermer, M.; Lavorel, S. Stakeholder perceptions of grassland ecosystem services in relation to knowledge on soil fertility and biodiversity. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Bloem, J.; de Vries, F.T.; Kalbitz, K.; Wagg, C. Linking soil biodiversity and agricultural soil management. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2012, 4, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.T.; Rumpel, C.; Thu, T.D.; Henry-Des-Tureaux, T.; Dang, D.K.; Jouquet, P. Use of organic substrates for increasing soil organic matter quality and carbon sequestration of tropical degraded soil: A 3-year mesocosms experiment. Carbon Manag. 2014, 5, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy—A new sustainability paradigm? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, O.; Pulgar, J.A.; Soto, M. Application of organic wastes to soils and legislative intricacies in a circular economy context. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2022, 24, 1871–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayara, T.; Basheer-Salimia, R.; Hawamde, F.; Sánchez, A. Recycling of Organic Wastes through Composting: Process Performance and Compost Application in Agriculture. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, Y.B.; Khalsa, S.D.S.; Ryals, R.; Duncan, R.A.; Brown, P.H.; Hart, S.C. Organic matter amendments improve soil fertility in almond orchards of contrasting soil texture. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2021, 120, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.; Paradelo Núñez, R.; Piñeiro, J.; Barral, M.T. Physicochemical and biochemical properties of an acid soil under potato culture amended with municipal solid waste compost. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, H.; Hechmi, S.; Khelil, M.N.; Zoghlami, I.R.; Benzarti, S.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Hassen, A.; Jedidi, N. Repetitive land application of urban sewage sludge: Effect of amendment rates and soil texture on fertility and degradation parameters. CATENA 2019, 172, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghlami, R.I.; Hamdi, H.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Khelil, M.N.; Ben Aissa, N.; Jedidi, N. Changes in light-textured soil parameters following two successive annual amendments with urban sewage sludge. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghlami, R.I.; Hamdi, H.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Hechmi, S.; Khelil, M.N.; Ben Aissa, N.; Moussa, M.; Bousnina, H.; Benzarti, S.; Jedidi, N. Monitoring the variation of soil quality with sewage sludge application rates in absence of rhizosphere effect. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechmi, S.; Hamdi, H.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Zoghlami, R.I.; Khelil, M.N.; Jellali, S.; Benzarti, S.; Jedidi, N. Variation of soil properties with sampling depth in two different light-textured soils after repeated applications of urban sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechmi, S.; Zoghlami, R.I.; Khelil, M.N.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Kallel, A.; Trabelsi, I.; Jedidi, N. Cumulative effect of sewage sludge application on soil adsorption complex and nutrient balance: A field study in semi-arid region (Oued Souhil, Tunisia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysargyris, A.; Xylia, P.; Akinci, G.; Moustakas, K.; Tzortzakis, N. Printed Paper Waste as an Alternative Growing Medium Component to Produce Brassica Seedlings under Nursery Conditions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouani, E.; Benzina, N.K.; Ziadi, N.; Bouslimi, B.; Abida, K.; Tlijani, H.; Koubaa, A. CO2 Emission and Change in the Fertility Parameters of a Calcareous Soil Following Annual Applications of Deinking Paper Sludge (The Case of Tunisia). Agronomy 2020, 10, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaria, G.; Silva, C.P.; Ferreira, C.I.A.; Otero, M.; Calisto, V. Sludge from paper mill effluent treatment as raw material to produce carbon adsorbents: An alternative waste management strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likon, M.; Trebše, P. Recent Advances in Paper Mill Sludge Management. Ind. Waste 2012, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, A.; Barriga, S.; Fidalgo, J.M.; Gascó, G. Adsorbent materials from paper industry waste materials and their use in Cu(II) removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, F.; Scartazza, A.; Scatena, M.; Rosellini, I.; Tassi, E.; Cinelli, F.; Bretzel, F. De-inked paper sludge and mature compost as high-value components of soilless substrate to support tree growth. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, T.; Gebrekidan, H.; Kibret, K.; Woldetsadik, K.; Shimelis, B.; Yadav, H. Comparative effectiveness of different composting methods on the stabilization, maturation and sanitization of municipal organic solid wastes and dried faecal sludge mixtures. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Moral, R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouani, E.; Benzina, N.K.; Ziadi, N.; Bouslimi, B.; Abouda, A.; Koubaa, A. Deinking sludge compost stability and maturity assessment using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2019, 37, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A.; Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of the Degtjareff Method for Determining Soil Organic Matter, and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, J.M.; Ministere de l’Enseignement Superieur, de l’Informatique et de la Recherche Scientifique; Van Ranst, E.; Verloo, M.; Mvondo Ze, A.; Administration Generale de la Cooperation au Developpement. Manuel de Laboratoire de Pedologie: Methodes d’AnaLyses de Sols et de Plantes, Equipement, Gestion de Stocks de Verrerie et de Produits Chimiques. 1992. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=XF2016038771 (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-Total. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods. 2018. Chapter 37. pp. 1085–1121. Available online: https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2136/sssabookser5.3.c37 (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Olsen, S.R. 1916-Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; US Departament of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Fourti, O.; Jedidi, N.; Hassen, A. Humic substances change during the co-composting process of municipal solid wastes and sewage sludge. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 2117–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campitelli, P.; Ceppi, S. Effects of composting technologies on the chemical and physicochemical properties of humic acids. Geoderma 2008, 144, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Le Souder, C. Measurement of aggregate stability for the assessment of soil crustability and erodibility. Etude Gest. Sols 1995, 2, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Annabi, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Le Villio-Poitrenaud, M.; Houot, S. Improvement of soil aggregate stability by repeated applications of organic amendments to a cultivated silty loam soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Amoozegar, A.; Heitman, J. Measuring dynamic changes of soil porosity during compaction. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 193, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouché, M.B. The establishment of earthworm communities. Earthworm Ecol. 1983, 38, 431–448. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Lou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fang, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, M.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Response of soil organic matter fractions and composition of microbial community to long-term organic and mineral fertilization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purakayastha, T.J.; Rudrappa, L.; Singh, D.; Swarup, A.; Bhadraray, S. Long-term impact of fertilizers on soil organic carbon pools and sequestration rates in maize–wheat–cowpea cropping system. Geoderma 2008, 144, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Han, X.Z. Changes of soil properties and carbon fractions after long-term application of organic amendments in Mollisols. CATENA 2016, 143, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Bejger, R.; Debaene, G.; Smreczak, B. Characterization of Soil Organic Matter Individual Fractions (Fulvic Acids, Humic Acids, and Humins) by Spectroscopic and Electrochemical Techniques in Agricultural Soils. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, M.; Sinha, N.K.; Hati, K.M.; Painuli, D.K.; Chaudhary, R.S. Stability of Soil Aggregates under Different Vegetation Covers in a Vertisol of Central India. J. Agric. Phys. 2012, 12, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lipiec, J.; Turski, M.; Hajnos, M.; Świeboda, R. Pore structure, stability and water repellency of earthworm casts and natural aggregates in loess soil. Geoderma 2015, 243–244, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mer, G.; Bottinelli, N.; Dignac, M.F.; Capowiez, Y.; Jouquet, P.; Mazurier, A.; Baudin, F.; Caner, L.; Rumpel, C. Exploring the control of earthworm cast macro- and micro-scale features on soil organic carbon mineralization across species and ecological categories. Geoderma 2022, 427, 116151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatoo, A.M.; Ali, M.N.; Zaheen, Z.; Baba, Z.A.; Ali, S.; Rasool, S.; Sheikh, T.A.; Sillanpää, M.; Gupta, P.K.; Hamid, B.; et al. Assessment of pesticide toxicity on earthworms using multiple biomarkers: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2573–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Singh, S.; Pandey, R.S. Assessment of acute toxicity and biochemical responses to chlorpyrifos, cypermethrin and their combination exposed earthworm, Eudrilus eugeniae. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rato Nunes, J.; Cabral, F.; López-Piñeiro, A. Short-term effects on soil properties and wheat production from secondary paper sludge application on two Mediterranean agricultural soils. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4935–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberato, J.J.; Gagnon, B.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Pan, W.L. Pulp and paper mill by-products as soil amendments and plant nutrient sources. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 86, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlile, W.R.; Cattivello, C.; Zaccheo, P. Organic Growing Media: Constituents and Properties. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, M.E.; Alesso, C.A.; Cosentino, D.; Imhoff, S. Aggregation agents and structural stability in soils with different texture and organic carbon contents. Sci. Agric. 2015, 72, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Soil carbon content drives the biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in the black soil zone of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yan, X.; Gunina, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xiong, Z. Effects of six-year biochar amendment on soil aggregation, crop growth, and nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies in a rice-wheat rotation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Soil | Raw De-Inking Paper Sludge | Composted De-Inking Paper Sludge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay (%) | 38.7 ± 1.47 | - | - |
| Sand (%) | 38.6 ± 0.85 | - | - |
| Loam (%) | 13.5 ± 0.94 | - | - |
| pH (1:2.5) | 7.85 ± 0.36 | 7.45 ± 0.55 | 7.72 ± 0.43 |
| EC (mS.cm−1) | 1.08 ± 0.15 | 1.72 ± 0.52 | 5.03 ± 0.32 |
| OM (%) | 2.82 ± 0.2 | 43.5 ± 1.43 | 25 ± 3.26 |
| TC (%) | 1.63 ± 0.23 | 21.7 ± 1.53 | 12.5 ± 0.80 |
| TN (%) | 0.31 ± 0.05 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 1.26 ± 1.17 |
| C/N | 5.25 ± 0.12 | 94.5 ± 5.14 | 9.92 ± 1.04 |
| K (ppm) | 1060 ± 92.12 | 433.3 ± 18.08 | 1300 ± 64.62 |
| P (ppm) | 34.1 ± 1.42 | 17.6 ± 1.27 | 251.8 ± 20.09 |
| Na+ (ppm) | 526.7 ± 31.35 | - | - |
| pH (1:2.5) | EC (mS.cm−1) | TC (%) | TN (%) | P (ppm) | K (ppm) | Na (ppm) | Total CaCO3 (%) | Actif CaCO3 (%) | E4/E6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 8.27 a ± 0.35 | 0.36 c ± 0.06 | 0.92 a ± 0.26 | 0.09 a ± 0.025 | 105.9 a ± 6.34 | 401.3 a ± 148.3 | 561.3 a ± 65.9 | 20.4 a ± 1.36 | 17 b ± 1.8 | 3.84 ab ± 0.27 |
| DS1 | 8.31 a ± 0.35 | 0.23 ab ± 0.03 | 1.04 ab ± 0.3 | 0.11 ab ± 0.03 | 141.7 a ± 12.1 | 260.7 a ± 108.9 | 497 a ± 1 | 20.4 a ± 0.72 | 16.8 b ± 2.08 | 4.12 ab ± 0.45 |
| DS2 | 8.34 a ± 0.3 | 0.28 b ± 0.08 | 1 ab ± 0.21 | 0.1 b ± 0.02 | 156.1 a ± 38.3 | 404.7 a ± 202.1 | 554.7 a ± 82.4 | 20.7 a ± 1.41 | 17.5 b ± 1.5 | 3.54 a ± 0.3 |
| DSC1 | 8.71 a ± 0.24 | 0.17 a ± 0.02 | 1.36 b ± 0.14 | 0.14 ab ± 0.015 | 136.5 a ± 31.1 | 194.7 a ± 85.4 | 910 c ± 46 | 21 a ± 0.77 | 9 a ± 1.32 | 6.37 b ± 1.69 |
| DSC2 | 8.4 a ± 0.15 | 0.21 ab ± 0.02 | 1 ab ± 0.08 | 0.1 b ± 0.01 | 129.4 a ± 27 | 163.3 a ± 78.3 | 778 b ± 40 | 22.4 a ± 1.17 | 20.5 b ± 0.87 | 6.08 ab ± 2.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zoghlami, R.I.; Toukabri, W.; Boudabbous, K.; Hechmi, S.; Barbouchi, M.; Oueriemmi, H.; Moussa, M.; Bahri, H. Assessment of Earthworm Viability and Soil Health after Two Years of Raw and Composted De-Inking Paper Sludge Amendment. Agriculture 2023, 13, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030547
Zoghlami RI, Toukabri W, Boudabbous K, Hechmi S, Barbouchi M, Oueriemmi H, Moussa M, Bahri H. Assessment of Earthworm Viability and Soil Health after Two Years of Raw and Composted De-Inking Paper Sludge Amendment. Agriculture. 2023; 13(3):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030547
Chicago/Turabian StyleZoghlami, Rahma Inès, Wael Toukabri, Khaoula Boudabbous, Sarra Hechmi, Meriem Barbouchi, Houda Oueriemmi, Mohammed Moussa, and Haithem Bahri. 2023. "Assessment of Earthworm Viability and Soil Health after Two Years of Raw and Composted De-Inking Paper Sludge Amendment" Agriculture 13, no. 3: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030547
APA StyleZoghlami, R. I., Toukabri, W., Boudabbous, K., Hechmi, S., Barbouchi, M., Oueriemmi, H., Moussa, M., & Bahri, H. (2023). Assessment of Earthworm Viability and Soil Health after Two Years of Raw and Composted De-Inking Paper Sludge Amendment. Agriculture, 13(3), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030547








