Effects of Seven-Year-Optimized Irrigation and Nitrogen Management on Dynamics of Soil Organic Nitrogen Fractions, Soil Properties, and Crop Growth in Greenhouse Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis and Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Yield, Dry Biomass, and Water Use Efficiency (WUE) Under Various Irrigation and N Rates
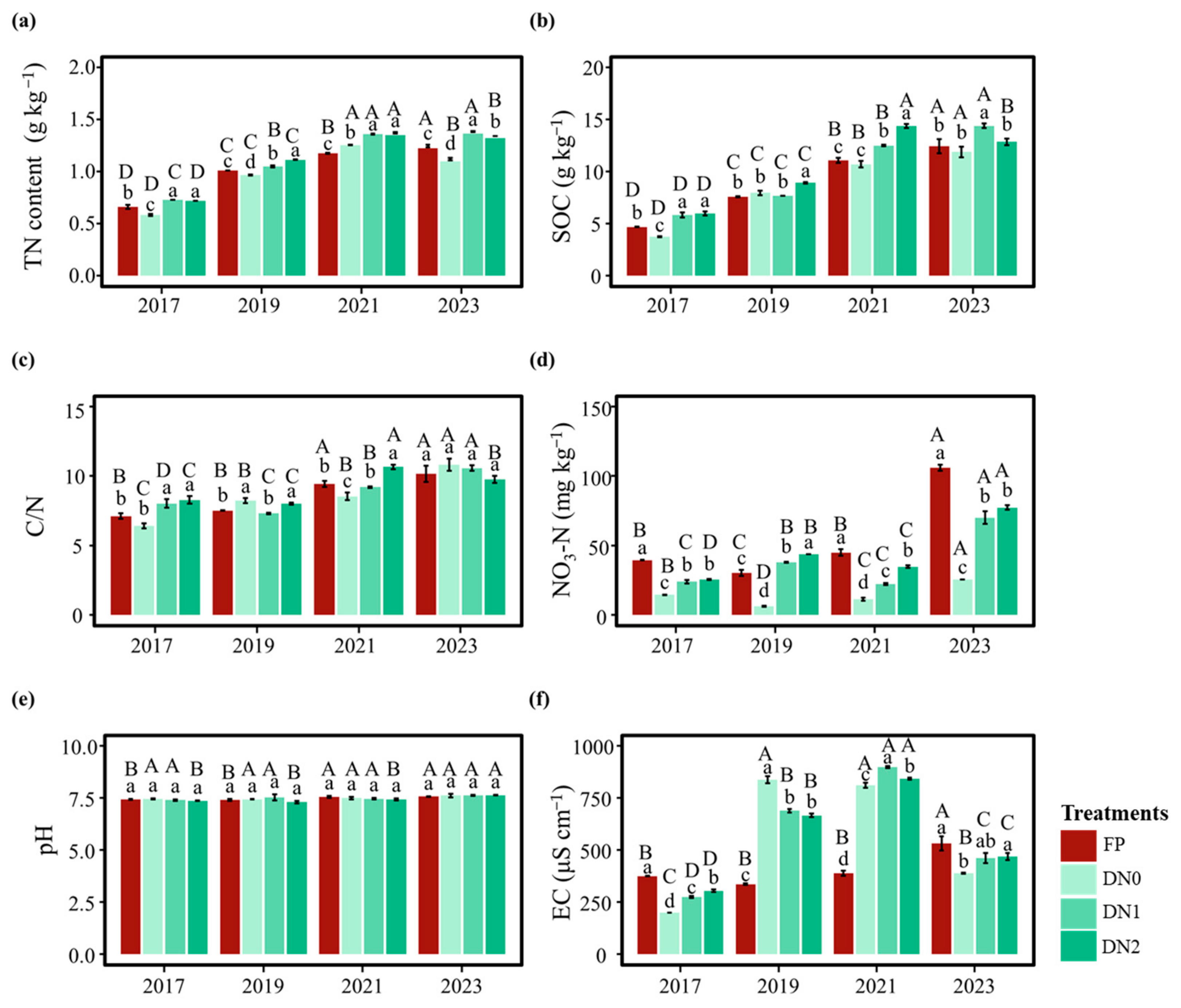
3.2. Soil Properties Under Various Irrigation and N Application Rates
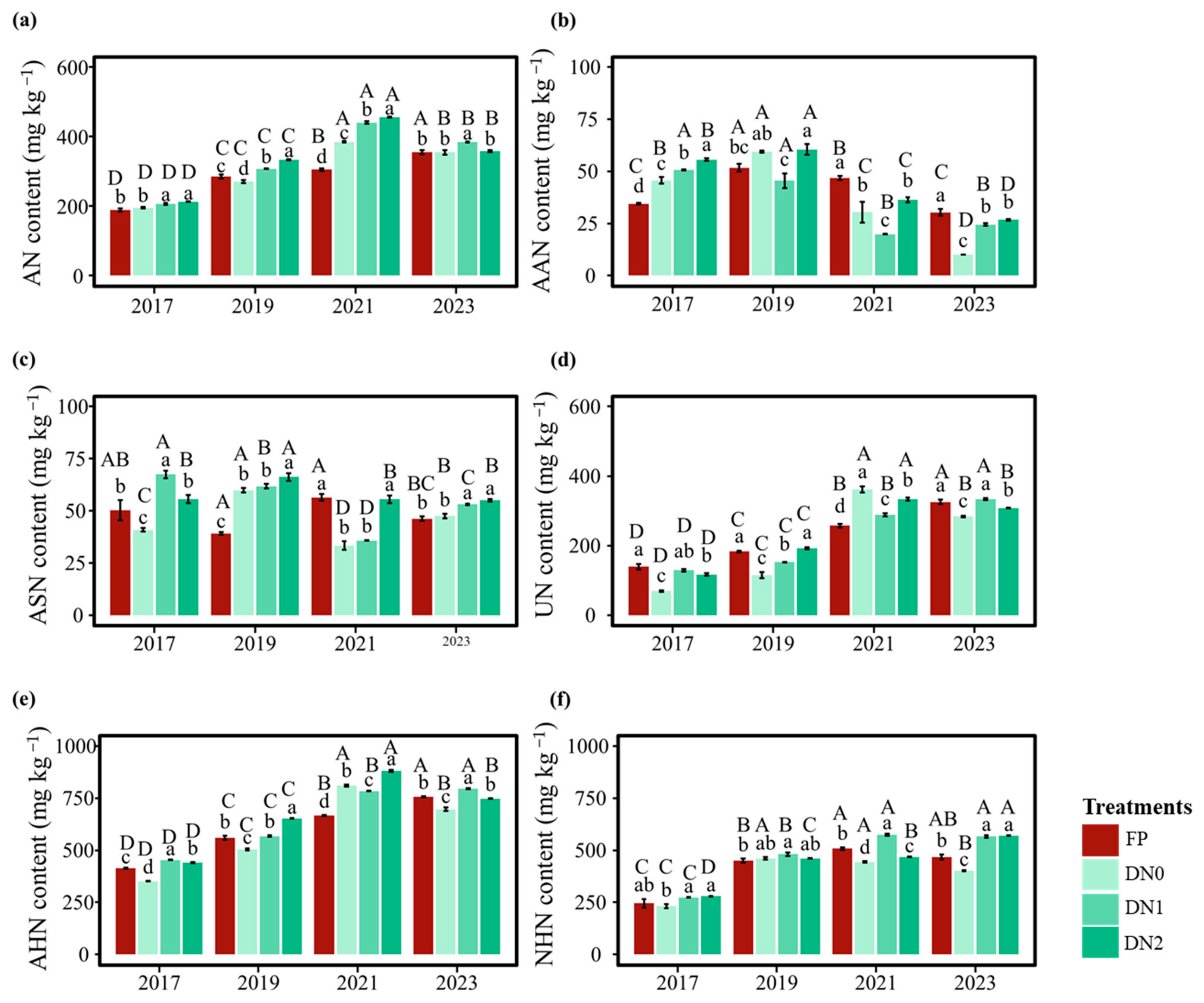
3.3. Soil Organic N Fractions in the Greenhouse Under Different Irrigation and Fertilization Practices
3.3.1. Total N, Acid-Hydrolyzable N, and Non-Hydrolyzable Nitrogen
3.3.2. Soil AHN Fractions
3.4. Drivers of Soil Organic N Fractions
4. Discussion
4.1. Vegetable Yield and Soil Properties Under Different Irrigation Methods and N Application Rates
4.2. Soil Organic N Fractions Under Different Irrigation Methods and N Rates
4.3. Driving Factors Regulating the Content and Distribution of Soil Organic N Components
4.4. Practical Implications
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Z.; Fei, L.; Huang, D.; Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Cai, Y. Coupling effects of irrigation and nitrogen levels on yield, water and nitrogen use efficiency of surge-root irrigated jujube in a semiarid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Interactive effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer on yield, nitrogen uptake, and recovery of two successive Chinese cabbage crops as assessed using 15N isotope. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 215, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Janz, B.; Engedal, T.; Neergaard, A.D. Effect of irrigation regimes and nitrogen rates on water use efficiency and nitrogen uptake in maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; An, J.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, N. Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse soil organic nitrogen fractions and soil-soluble nitrogen pools. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Liu, R.; Min, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhu, P.; Zhu, J. Regulation of soil water threshold on tomato plant growth and fruit quality under alternate partial root-zone drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 238, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Jiao, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, J. Identification of optimal irrigation and fertilizer rates to balance yield, water and fertilizer productivity, and fruit quality in greenhouse tomatoes using TOPSIS. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 311, 111829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Organic Forms of Soil Nitrogen. Nitrogen Agric. Soils. USA Am. Soc. Agron. 1982, 22, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Organic Forms of Nitrogen//BLACK C A. Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy Incorporation: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1148–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, S. Nitrogen Mineralization from Animal Manures and Its Relation to Organic N Fractions. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, W.; Ma, D.; Zhang, B. Long-term nitrogen fertilization-induced enhancements of acid hydrolysable nitrogen are mainly regulated by the most vital microbial taxa of keystone species and enzyme activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wan, S.; Guo, J.; Han, G.; Gutknecht, J.; Schmid, B.; Yu, L.; Liu, W.; Bi, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Precipitation modifies the effects of warming and nitrogen addition on soil microbial communities in northern Chinese grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wei, K.; Condron, L.M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, L. Effects of elevated nitrogen and precipitation on soil organic nitrogen fractions and nitrogen-mineralizing enzymes in semi-arid steppe and abandoned cropland. Plant Soil 2017, 417, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Dong, Q.; Siddique, K.H.M. Biochar incorporation increases winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production with significantly improving soil enzyme activities at jointing stage. CATENA 2022, 211, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shao, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, K.; Shang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, T.; Yang, X. Short-term biochar effect on soil physicochemical and microbiological properties of a degraded alpine grassland. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lan, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Cao, D.; Wang, Q.; Ma, C.; An, X. Response of bacterial communities, enzyme activities and dynamic changes of soil organic nitrogen fractions to six-year different application levels of biochar retention in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 240, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.V.; Joshi, N.L.; Singh, D.V.; Saxena, A. Response of Chili to Water and Nitrogen under Drip and Check-basin Methods of Irrigation. Ann. Arid. Zone 1999, 38, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon, K.S.; Singh, J.P.; Mehla, D.S. Long-term effect of manure and mineral fertilizer application on the distribution of organic nitrogen fractions in soil under a rice–wheat cropping system. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2011, 7, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, R.; Luan, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, S. Temperature Matters More than Fertilization for Straw Decomposition in the Soil of Greenhouse Vegetable Field. Agronomy 2024, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Han, Q.; Leng, P. Phosphatase activities and available nutrients in soil aggregates affected by straw returning to a calcareous soil under the maize–wheat cropping system. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1208323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, S.; Xia, L.; Sun, J.; Zha, Y.; Yang, P. Retrieval of chromium and mercury concentrations in agricultural soils: Using spectral information, environmental covariates, or a fusion of both? Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. Water use and soil nitrate nitrogen changes under supplemental irrigation with nitrogen application rate in wheat field. Field Crops Res. 2015, 183, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhang, G.; Yi, X.; Kang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Chang, N.; Li, H. Improving potential of reactive nitrogen and carbon footprint of intensified greenhouse cucumber-tomato production with optimized drip irrigation with nitrogen reduction strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 424, 138898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Qu, H.; Hou, M.; Zhou, K.; Jiao, X.; Sui, Y. Effects of different irrigation and fertilization practices on nitrogen leaching in facility vegetable production in northeastern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.Y.; Akhtar, K.; Sarwar, G.R.; Ashraf, M.Y. Role of the rooting system in salt tolerance potential of different guar accessions. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, K.J.; Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.M. Drought and crop yield. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Gao, Q.; Lu, W. Response of Organic Nitrogen in Black Soil to Long-term Different Fertilization and Tillage Practices in Northeast China. Soil Water Res. 2016, 11, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, E.; Chen, B. Soil nitrogen and its fractions between long-term conventional and no-tillage systems with straw retention in dryland farming in northern China. Geoderma 2016, 269, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S.; Zhu, Z. Soil organic nitrogen composition and mineralization of paddy soils in a cultivation chrono sequence in China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Duan, P.; Cong, Y.; An, T.; Yu, N.; Zou, H.; Dang, X.; An, J.; Fan, Q.; et al. Evaluation and simulation of nitrogen mineralization of paddy soils in Mollisols area of Northeast China under waterlogged incubation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e171022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braos, L.B.; Carlos, R.S.; Kuhnen, F.; Ferreira, M.E.; Mulvaney, R.L.; Khan, S.A.; Cruz, M.C.P.D. Predicting Soil Nitrogen Availability for Maize Production in Brazil. Nitrogen 2022, 3, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, U.N.; Ball, B.A. Impacts of altered precipitation regimes on soil communities and biogeochemistry in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulten, H.R.; Schnitzer, M. The chemistry of soil organic nitrogen: A review. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1997, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Prieto, S.J.; Jocteur-Monrozier, L.; Hétier, J.M.; Carballas, T. Changes in the soil organic N fractions of a tropical Alfisol fertilized with 15N-urea and cropped to maize or pasture. Plant Soil 1997, 195, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Xie, W. Soil Organic N Forms and N Supply as Affected by Fertilization Under Intensive Rice Cropping System1 1Project supported by the International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFI), France; the Potast & Phosphate Institute (PPI), USA and Canada; and the International Potassium Institute (IPI), Switzerland. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Yawei, Y.; Jianxin, L.; Zhibiao, O. The Characteristics and the Relationships Between Humus Compounds and Organic Nitrogen Compounds in Different Altitude Soil of Zhangjiajie Tobacco Planting Area. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 13, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Wu, X.; Han, F.; Zhang, T. Effects of long-term chemical fertilization and organic amendments on dynamics of soil organic C and total N in paddy soil derived from barren land in subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Different Irrigation Methods on Forms and Profile Distribution of Soil Organic Nitrogen in Protected Field. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 21, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Qi, P.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Yao, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhang, R. Effects of Different Nitrogen Application Rates on Soil Organic Nitrogen Components and Enzyme Activities in Farmland. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, M.; Ramos, F.; Weber, O.; Muller, C. Organic carbon and total nitrogen in the densimetric fractions of organic matter under different soil management. Rev. Caatinga 2016, 29, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Nayak, A.K.; Puree, C.; Tripathi, R.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, A.; Panda, B.B.; et al. Carbon and nitrogen fractions and stocks under 41 years of chemical and organic fertilization in a sub-humid tropical rice soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurisso, T.T.; Norton, J.B.; Mukhwana, E.J.; Norton, U. Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Fractions and Sugar Beet Sucrose Yield in Furrow-Irrigated Agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ussiri DA, N.; Lal, R. Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Fractions under Different Land Uses and Tillage Practices. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; He, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, H.; Hu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Dynamics of fertilizer-derived organic nitrogen fractions in an arable soil during a growing season. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näsholm, T.; Kielland, K.; Ganeteg, U. Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C.; Monaghan, R.; Carran, A. Gross nitrogen mineralisation rates in pastural soils and their relationships with organic nitrogen fractions, microbial biomass and protease activity under glasshouse conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 42, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Eldor, P. The chemical and functional characterization of soil N and its biotic components. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Luo, S.; Xia, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yang, L.; Yue, K.; Fan, Y. Influences of nitrogen fertilization on soil organic nitrogen 587 components in agroecosystems: A meta-analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, F.; Li, G.; Lin, Q.; Jensen, C.R. Soil microbial response, water and nitrogen use by tomato under different irrigation regimes. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Z.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, M. Yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen leaching of sensor-based fertigation-cultured tomato in a shallow groundwater region: Effect of shallow groundwater on tomato irrigation. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wan, L.; Wang, J.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Lin, S. Conventional flooding irrigation and over fertilization drives soil pH decrease not only in the top-but also in subsoil layers in solar greenhouse vegetable production systems. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liao, S.; Zou, G.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Effects of two slow-release nitrogen fertilizers and irrigation on yield, quality, and water- fertilizer productivity of greenhouse tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 186, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, B. Long-term effects of mineral versus organic fertilizers on soil labile nitrogen fractions and soil enzyme activities in agricultural soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2014, 20, 525–533. [Google Scholar]


| Year | Growing Season | Crop | Irrigation (mm) | Organic N (kg N ha−1) | Chemical N (kg N ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furrow | Drip | FP | DN0 | DN1 | DN2 | ||||
| 2017 | WS | cucumber | 330 | 231 | 271 | 379 | 0 | 189.5 | 284.25 |
| AW | tomato | 252 | 176 | 183 | 256 | 0 | 128 | 192 | |
| 2018 | WS | cucumber | 411 | 288 | 279 | 371 | 0 | 185.5 | 278.25 |
| AW | tomato | 271 | 189 | 206 | 233 | 0 | 116.5 | 174.75 | |
| 2019 | WS | cucumber | 365 | 256 | 291 | 359 | 0 | 179.5 | 269.25 |
| AW | celery | 130 | 91 | 71 | 254 | 0 | 127 | 190.5 | |
| 2020 | WS | cucumber | 346 | 242 | 244 | 406 | 0 | 203 | 304.5 |
| AW | tomato | 263 | 184 | 216 | 223 | 0 | 111.5 | 167.25 | |
| 2021 | WS | cucumber | 327 | 228 | 259 | 391 | 0 | 195.5 | 293.25 |
| AW | tomato | 216 | 183 | 186 | 253 | 0 | 126.5 | 189.75 | |
| 2022 | WS | cucumber | 363 | 254 | 234 | 416 | 0 | 208 | 312 |
| AW | tomato | 282 | 198 | 133 | 306 | 0 | 153 | 229.5 | |
| 2023 | WS | tomato | 240 | 168 | 147 | 292 | 0 | 146 | 219 |
| AW | tomato | 211 | 148 | 154 | 285 | 0 | 142.5 | 213.75 | |
| Year | Crop | Index | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP | DN0 | DN1 | DN2 | |||
| 2017 | cucumber | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 12.04 ± 0.12 a | 8.22 ± 0.17 d | 10.7 ± 0.27 b | 9.57 ± 0.4 c |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 179.78 ± 0.54 a | 126.02 ± 0.32 d | 167.01 ± 1.08 b | 157.87 ± 0.71 c | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 54.48 ± 0.16 c | 54.55 ± 0.14 c | 72.3 ± 0.47 a | 68.34 ± 0.31 b | ||
| tomato | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 9.95 ± 0.33 a | 6.65 ± 0.17 c | 8.78 ± 0.27 b | 7.73 ± 0.2 b | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 86.51 ± 1.64 a | 70.32 ± 1.86 c | 79.87 ± 0.34 b | 71.46 ± 0.19 c | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 34.33 ± 0.65 c | 39.95 ± 1.05 b | 45.38 ± 0.2 a | 40.6 ± 0.11 b | ||
| total | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 21.98 ± 0.38 a | 14.87 ± 0.06 d | 19.49 ± 0.53 b | 17.3 ± 0.58 c | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 266.28 ± 1.82 a | 196.34 ± 1.98 d | 246.88 ± 1.29 b | 229.33 ± 0.52 c | ||
| Annual WUE (kg m−3) | 45.75 ± 0.31 d | 48.24 ± 0.49 c | 60.66 ± 0.32 a | 56.35 ± 0.13 b | ||
| 2019 | cucumber | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 10.24 ± 0.4 a | 7.46 ± 0.42 c | 7.58 ± 0.37 c | 8.76 ± 0.14 b |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 113.03 ± 2.37 a | 88.43 ± 2.55 c | 81.46 ± 2.06 c | 95.78 ± 0.28 b | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 30.97 ± 0.65 b | 34.54 ± 1 b | 31.82 ± 0.8 b | 37.41 ± 0.11 a | ||
| celery | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 5.27 ± 0.28 a | 4.1 ± 0.04 b | 5.18 ± 0.14 a | 4.3 ± 0.08 b | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 89.03 ± 0.51 c | 86.43 ± 0.31 d | 106.53 ± 1.78 a | 96.23 ± 1.1 b | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 68.48 ± 0.39 d | 94.97 ± 0.34 c | 117.06 ± 1.96 a | 105.74 ± 1.21 b | ||
| total | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 15.51 ± 0.42 a | 11.56 ± 0.39 c | 12.76 ± 0.24 b | 13.06 ± 0.06 b | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 202.06 ± 1.89 a | 174.86 ± 2.78 b | 187.99 ± 1.89 c | 192.01 ± 1.22 b | ||
| Annual WUE (kg m−3) | 40.82 ± 0.38 d | 50.39 ± 0.8 c | 54.18 ± 0.55 b | 55.33 ± 0.35 a | ||
| 2021 | cucumber | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 12.63 ± 0.28 a | 10.79 ± 0.2 b | 11.66 ± 0.39 a | 10.36 ± 0.31 b |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 168.27 ± 0.25 a | 136.37 ± 2.71 c | 148.06 ± 4.81 b | 146.37 ± 2.71 b | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 51.46 ± 0.08 c | 59.81 ± 1.19 b | 64.94 ± 2.11 a | 64.2 ± 1.19 a | ||
| tomato | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 7.57 ± 0.11 b | 7.75 ± 0.17 b | 7.7 ± 0.06 ab | 8.17 ± 0.15 a | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 85.04 ± 0.64 a | 72.99 ± 1.05 c | 77.54 ± 1.55 b | 77.75 ± 1.85 b | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 32.58 ± 0.25 c | 39.89 ± 0.57 b | 42.37 ± 0.85 a | 42.48 ± 1.01 a | ||
| total | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 20.2 ± 0.37 a | 18.54 ± 0.36 b | 19.37 ± 0.33 a | 18.53 ± 0.42 b | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 253.31 ± 0.4 a | 209.36 ± 2.11 c | 225.6 ± 6.36 b | 224.12 ± 4.54 b | ||
| Annual WUE (kg m−3) | 46.65 ± 0.07 c | 50.94 ± 0.51 b | 54.89 ± 1.55 a | 54.53 ± 1.1 a | ||
| 2023 | tomato | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 14.44 ± 0.54 a | 12.05 ± 0.36 b | 14.14 ± 0.85 a | 12.93 ± 0.31 b |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 133.24 ± 0.63 b | 111.75 ± 2.64 c | 139.5 ± 0.28 a | 139.1 ± 1.72 a | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 55.52 ± 0.26 c | 66.52 ± 1.57 b | 83.04 ± 0.17 a | 82.8 ± 1.02 a | ||
| tomato | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 7.49 ± 0.5 b | 5.33 ± 0.41 c | 7 ± 0.29 ab | 6.22 ± 0.26 bc | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 63.09 ± 0.88 a | 46.14 ± 0.23 c | 58.49 ± 1.42 b | 56.14 ± 0.98 b | ||
| WUE (kg m−3) | 29.9 ± 0.42 c | 31.18 ± 0.15 b | 39.52 ± 0.96 a | 37.93 ± 0.66 a | ||
| total | Dry biomass (t ha−1) | 21.93 ± 1.03 a | 17.38 ± 0.76 b | 21.14 ± 0.58 a | 19.15 ± 0.47 b | |
| Yield (t ha−1) | 196.34 ± 1.49 a | 157.89 ± 2.55 b | 197.99 ± 1.56 a | 195.25 ± 2.65 a | ||
| Annual WUE (kg m−3) | 43.53 ± 0.33 c | 49.97 ± 0.81 b | 62.66 ± 0.49 a | 61.79 ± 0.84 a | ||
| n = 48 | TN | SOC | C/N | NO3−-N | pH | EC | TP | AP | TK | AK | TDW | TY | Annual WUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | 0.95 ** | 0.91 ** | 0.71 ** | 0.27 | 0.30 * | 0.69 ** | 0.81 ** | 0.78 ** | −0.02 | 0.59 ** | 0.19 | −0.28 | 0.22 |
| ASN | −0.16 | −0.12 | −0.01 | 0.13 | −0.18 | −0.07 | −0.06 | 0.04 | 0.06 | −0.07 | −0.28 | 0.05 | 0.44 * |
| AAN | −0.5 ** | −0.6 ** | −0.6 ** | −0.29 * | −0.55 ** | −0.12 | −0.62 ** | −0.37 ** | 0.23 | −0.52 ** | −0.6 ** | 0.15 | −0.12 |
| UN | 0.89 ** | 0.92 ** | 0.79 ** | 0.47 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.78 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.15 | 0.5 ** | 0.54 ** | −0.12 | 0.14 |
| NHN | 0.93 ** | 0.82 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.58 ** | 0.71 ** | 0.88 ** | −0.12 | 0.56 ** | 0.06 | −0.32 | 0.22 |
| AHN | 0.96 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.78 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.36 * | 0.6 ** | 0.82 ** | 0.75 ** | 0.06 | 0.55 ** | 0.34 * | −0.20 | 0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Pan, L.; Jia, T.; Hou, S.; Jia, Z. Effects of Seven-Year-Optimized Irrigation and Nitrogen Management on Dynamics of Soil Organic Nitrogen Fractions, Soil Properties, and Crop Growth in Greenhouse Production. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122319
Shi J, Jiang L, Wang L, Wang C, Li R, Pan L, Jia T, Hou S, Jia Z. Effects of Seven-Year-Optimized Irrigation and Nitrogen Management on Dynamics of Soil Organic Nitrogen Fractions, Soil Properties, and Crop Growth in Greenhouse Production. Agriculture. 2024; 14(12):2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122319
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jianshuo, Longgang Jiang, Liying Wang, Chengzhang Wang, Ruonan Li, Lijia Pan, Tianyuan Jia, Shenglin Hou, and Zhou Jia. 2024. "Effects of Seven-Year-Optimized Irrigation and Nitrogen Management on Dynamics of Soil Organic Nitrogen Fractions, Soil Properties, and Crop Growth in Greenhouse Production" Agriculture 14, no. 12: 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122319
APA StyleShi, J., Jiang, L., Wang, L., Wang, C., Li, R., Pan, L., Jia, T., Hou, S., & Jia, Z. (2024). Effects of Seven-Year-Optimized Irrigation and Nitrogen Management on Dynamics of Soil Organic Nitrogen Fractions, Soil Properties, and Crop Growth in Greenhouse Production. Agriculture, 14(12), 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122319




