How Biochar Addition Affects Denitrification and the Microbial Electron Transport System (ETSA): A Meta-Analysis Based on a Global Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Date Collection
2.2. Meta-Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Biochar Characteristics on Denitrification
3.1.1. Biochar Physicochemical Properties
3.1.2. Biochar Application Rate
3.1.3. Experiment Duration
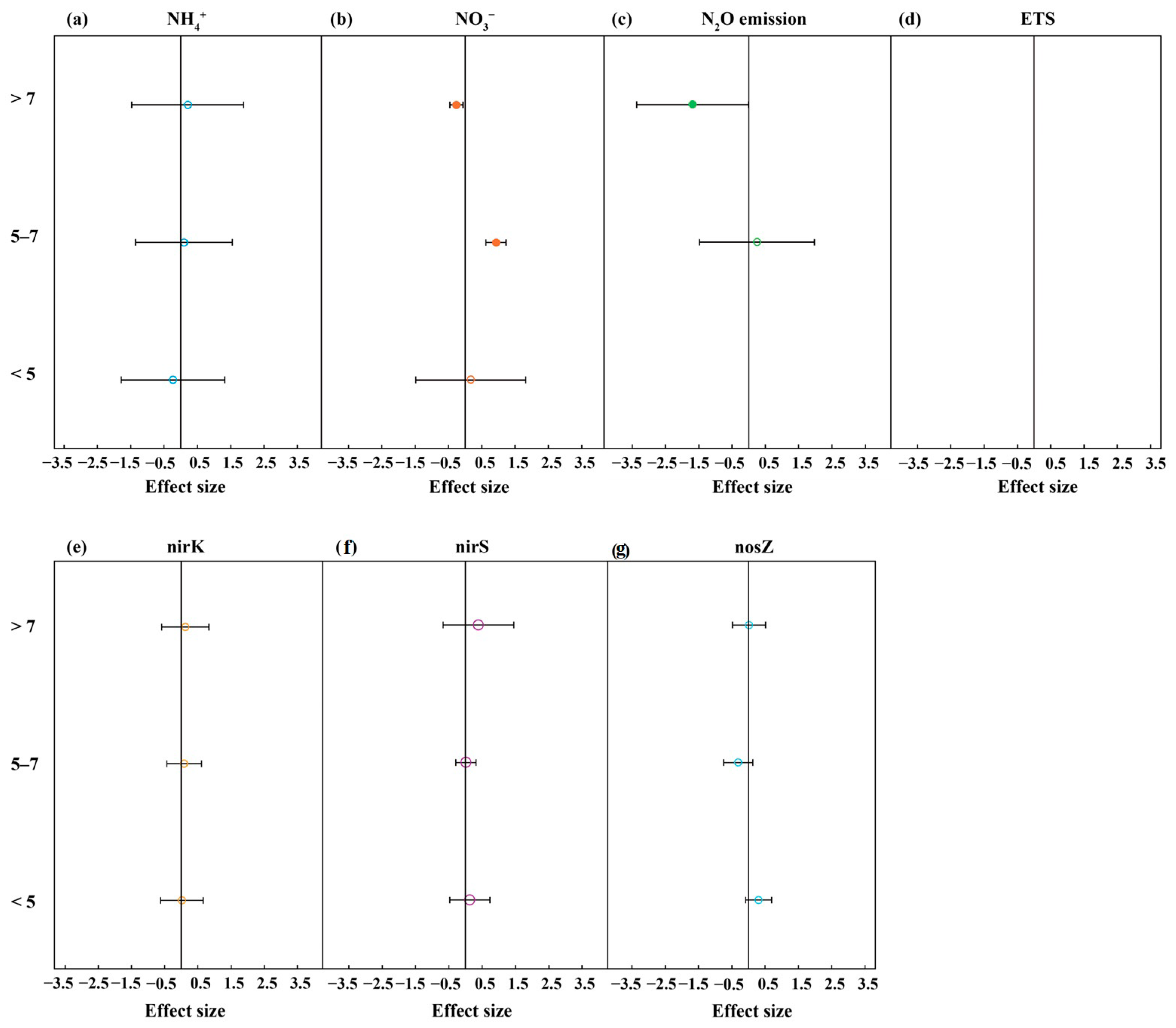
3.2. Effect of Soil Physicochemical Properties Under Biochar Addition on Denitrification
3.3. Effect of Different Ecosystem Types Under Biochar Addition on Denitrification
3.4. Correlation of Soil Properties, Biochar Characteristics, and Denitrification Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Biochar Physicochemical Properties and Experimental Conditions on Denitrification
4.2. Influence of Soil Physicochemical Properties on Denitrification with Biochar
4.3. Impact of Ecosystem Types on Denitrification and Biochar Interactions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, Y.; Ding, W.; Xiang, J. Mechanisms of Nitrous Oxide and Nitric Oxide Production in Soils: A Review. Environ. Sci. 2012, 44, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Hu, H.; Zhu-Barker, X.; Hayden, H.; Wang, J.; Suter, H.; Chen, D.; He, J. Nitrifier-induced denitrification is an important source of soil nitrous oxide and can be inhibited by a nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4851–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, L.; Ren, X. Using 13C isotopes to explore denitrification-dependent anaerobic methane oxidation in a paddy-peatland. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tsui, T.H.; Wah Tong, Y.; Sharon, S.; Shoseyov, O.; Liu, R. Biochar applications in microbial fermentation processes for producing non-methane products: Current status and future prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 386, 129478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Ping, Z.; Mahmood, Q. Influence of various nitrogenous electron acceptors on the anaerobic sulfide oxidation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2931–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-S.; Gong, J.; Huong, C.V.; Oh, D.-S.; Chang, Y.-S. Macroporous alginate substrate-bound growth of Fe0 nanoparticles with high redox activities for nitrate removal from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 298, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Hou, R.; Yang, P.; Qian, S.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Yuan, R.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B. Application of external carbon source in heterotrophic denitrification of domestic sewage: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 153061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Reverchon, F. Review of denitrification in tropical and subtropical soils of terrestrial ecosystems. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Espinosa, C.; Sauvage, S.; Al Bitar, A.; Green, P.A.; Vorosmarty, C.J.; Sanchez-Perez, J.M. Denitrification in wetlands: A review towards a quantification at global scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; McDowell, W.H.; Hou, L. Nitrogen removal rates in a frigid high-altitude river estimated by measuring dissolved N2 and N2O. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol Pereira, E.I.; Léchot, J.; Feola Conz, R.; da Silva Cardoso, A.; Six, J. Biochar Enhances Nitrous Oxide Reduction in Acidic but Not in Near-Neutral pH Soil. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, C.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Rice straw biochar mitigated more N2O emissions from fertilized paddy soil with higher water content than that derived from ex situ biowaste. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhishek, K.; Shrivastava, A.; Vimal, V.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhujbal, S.K.; Biswas, J.K.; Singh, L.; Ghosh, P.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, P.; et al. Biochar application for greenhouse gas mitigation, contaminants immobilization and soil fertility enhancement: A state-of-the-art review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namatsheve, T.; Martinsen, V.; Obia, A.; Mulder, J. Grain yield and nitrogen cycling under conservation agriculture and biochar amendment in agroecosystems of sub-Saharan Africa. A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 376, 109243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Yuan, J.; Yang, X.; Wei, C.; Bi, Y.; Sun, Q.; Meng, J.; Han, X. Biochar application alters soil metabolites and nitrogen cycle-related microorganisms in a soybean continuous cropping system. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, H.; Glaser, B. Effects of biochar compared to organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil quality and plant growth in a greenhouse experiment. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittl, T.F.; Oliveira, D.M.S.; Canisares, L.P.; Sagrilo, E.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Dannenmann, M.; Cerri, C.E.P. High Application Rates of Biochar to Mitigate N2O Emissions From a N-Fertilized Tropical Soil Under Warming Conditions. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 611873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Han, Z.; Zheng, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; et al. Biochar reduced soil nitrous oxide emissions through suppressing fungal denitrification and affecting fungal community assembly in a subtropical tea plantation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Du, S.; Nishimura, O. Rice Rusk-Derived Biochar Suppressed N2O Emission from Acidic Arable Soil by Inhibiting Nitrate Reduction. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouerghi, I.; Rousset, C.; Bizouard, F.; Brefort, H.; Ubertosi, M.; Arkoun, M.; Hénault, C. Hysteretic response of N2O reductase activity to soil pH variations after application of lime to an acidic agricultural soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarnio, S.; Heimonen, K.; Kettunen, R. Biochar addition indirectly affects N2O emissions via soil moisture and plant N uptake. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Q.; Liu, X.; Deng, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Deng, B.; Zhang, L. Biochar derived from spent mushroom substrate reduced N2O emissions with lower water content but increased CH4 emissions under flooded condition from fertilized soils in Camellia oleifera plantations. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hou, D.; Cao, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, B.; Ok, Y.S. Sustainable remediation with an electroactive biochar system: Mechanisms and perspectives. Green. Chem. 2020, 22, 2688–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bolan, N.; Prevoteau, A.; Vithanage, M.; Biswas, J.K.; Ok, Y.S.; Wang, H. Applications of biochar in redox-mediated reactions. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Yuan, H.; He, X.; Hu, H.; Qin, S.; Clough, T.; Wrage-Mönnig, N.; Luo, J.; He, X.; Chen, M.; et al. Identification and verification of key functional groups of biochar influencing soil N2O emission. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupfel, L.; Keiluweit, M.; Kleber, M.; Sander, M. Redox properties of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5601–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevoteau, A.; Ronsse, F.; Cid, I.; Boeckx, P.; Rabaey, K. The electron donating capacity of biochar is dramatically underestimated. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, P.; Faye, M.C.A.S.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of biochar derived from rice husks and its potential in chlorobenzene degradation. Carbon 2018, 130, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Biochar Mitigates N2O Emission of Microbial Denitrification through Modulating Carbon Metabolism and Allocation of Reducing Power. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8068–8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; van Zwieten, L.; Singh, B.P.; Jeffery, S.; Roig, A.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Biochar’s role in mitigating soil nitrous oxide emissions: A review and meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; Maenhout, P.; De Neve, S.; Sleutel, S. Biochar-induced N2O emission reductions after field incorporation in a loam soil. Geoderma 2016, 267, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, M.S. The File-Drawer Problem Revisited: A General Weighted Method for Calculating Fail-Safe Numbers in Meta-Analysis. Evolution 2005, 59, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.; Bardgett, R.D. Influence of single trees on spatial and temporal patterns of belowground properties in native pine forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, T.; Condron, L.; Kammann, C.; Müller, C. A Review of Biochar and Soil Nitrogen Dynamics. Agronomy 2013, 3, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quin, P.; Joseph, S.; Husson, O.; Donne, S.; Mitchell, D.; Munroe, P.; Phelan, D.; Cowie, A.; Van Zwieten, L. Lowering N2O emissions from soils using eucalypt biochar: The importance of redox reactions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Garcà a, M.a.; Roig, A.n.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Cayuela, M.a.L. Biochar increases soil N2O emissions produced by nitrification-mediated pathways. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, J.; Liu, Z.; Lan, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; He, T.; Chen, W. Effects of biochar on N2O emission in denitrification pathway from paddy soil: A drying incubation study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, Z.; Ei-Naggar, A.; Tian, L.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Chang, S.X.; et al. Contrasting effects of rice husk and its biochar on N2O emissions and nitrogen leaching from Lei bamboo soils under subtropical conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.J.; Wang, X.H.; Li, H.; Yao, H.Y.; Su, J.Q.; Zhu, Y.G. Biochar impacts soil microbial community composition and nitrogen cycling in an acidic soil planted with rape. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9391–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Walkiewicz, A.; Bieganowski, A.; Oenema, O.; Nosalewicz, M.; He, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C. Biochar promotes the reduction of N2O to N2 and concurrently suppresses the production of N2O in calcareous soil. Geoderma 2020, 362, 114091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Ayorinde, B.B.; Ogunbode, T. Combined lime and biochar application enhances cowpea growth and yield in tropical Alfisol. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Q.; Sun, X.; Wei, W.; Hu, C. Biochar is superior to lime in improving acidic soil properties and fruit quality of Satsuma mandarin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yang, X.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Kwon, E.E. Pyrolysis process of agricultural waste using CO2 for waste management, energy recovery, and biochar fabrication. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y. Biochar remediates denitrification process and N2O emission in pesticide chlorothalonil-polluted soil: Role of electron transport chain. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y. High-efficient nitrogen removal and its microbiological mechanism of a novel carbon self-sufficient constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prommer, J.; Wanek, W.; Hofhansl, F.; Trojan, D.; Offre, P.; Urich, T.; Schleper, C.; Sassmann, S.; Kitzler, B.; Soja, G.; et al. Biochar Decelerates Soil Organic Nitrogen Cycling but Stimulates Soil Nitrification in a Temperate Arable Field Trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aamer, M.; Shaaban, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Guoqin, H.; Ying, L.; Hai Ying, T.; Rasul, F.; Qiaoying, M.; Zhuanling, L.; Rasheed, A.; et al. Biochar mitigates the N2O emissions from acidic soil by increasing the nosZ and nirK gene abundance and soil pH. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Easily mineralizable carbon in manure-based biochar added to a soil influences N2O emissions and microbial-N cycling genes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, D.; Saha, D.; Lee, J.; Jagadamma, S.; Adotey, N.; Mengistu, A. Cover crop residue influence on soil N2O and CO2 emissions under wetting-drying intensities: An incubation study. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Q.; Groffman, P.M.; Alewell, C.; Ballantine, K. Soil amendments promote denitrification in restored wetlands. Restor. Ecol. 2017, 26, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Ma, S.; Han, Z.; Yan, X.; Shan, J. Biochar mitigates N2O emissions by promoting complete denitrification in acidic and alkaline paddy soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 74, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, D.; Müller, C.; Zaman, M.; Lindsey, S.; Ding, W. Effect of biochar and nitrapyrin on nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emissions from a sandy loam soil cropped to maize. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaff, M.A.; Classen, A.T.; Castro, H.F.; Schadt, C.W. Labile soil carbon inputs mediate the soil microbial community composition and plant residue decomposition rates. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J. Soil nitrogen transformation and functional microbial abundance in an agricultural soil amended with biochar. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2023, 47, e0220156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Yang, S.-S.; Ding, J.; Wang, G.-Y.; Chen, C.-X.; Xie, G.-J.; Xu, W.; Yuan, F.; Ren, N.-Q. Enhanced nitrogen removal in an electrochemically coupled biochar-amended constructed wetland microcosms: The interactive effects of biochar and electrochemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Luo, Y.; Nie, W.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, T.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y. Biochar boosts nitrate removal in constructed wetlands for secondary effluent treatment: Linking nitrate removal to the metabolic pathway of denitrification and biochar properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 379, 129000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
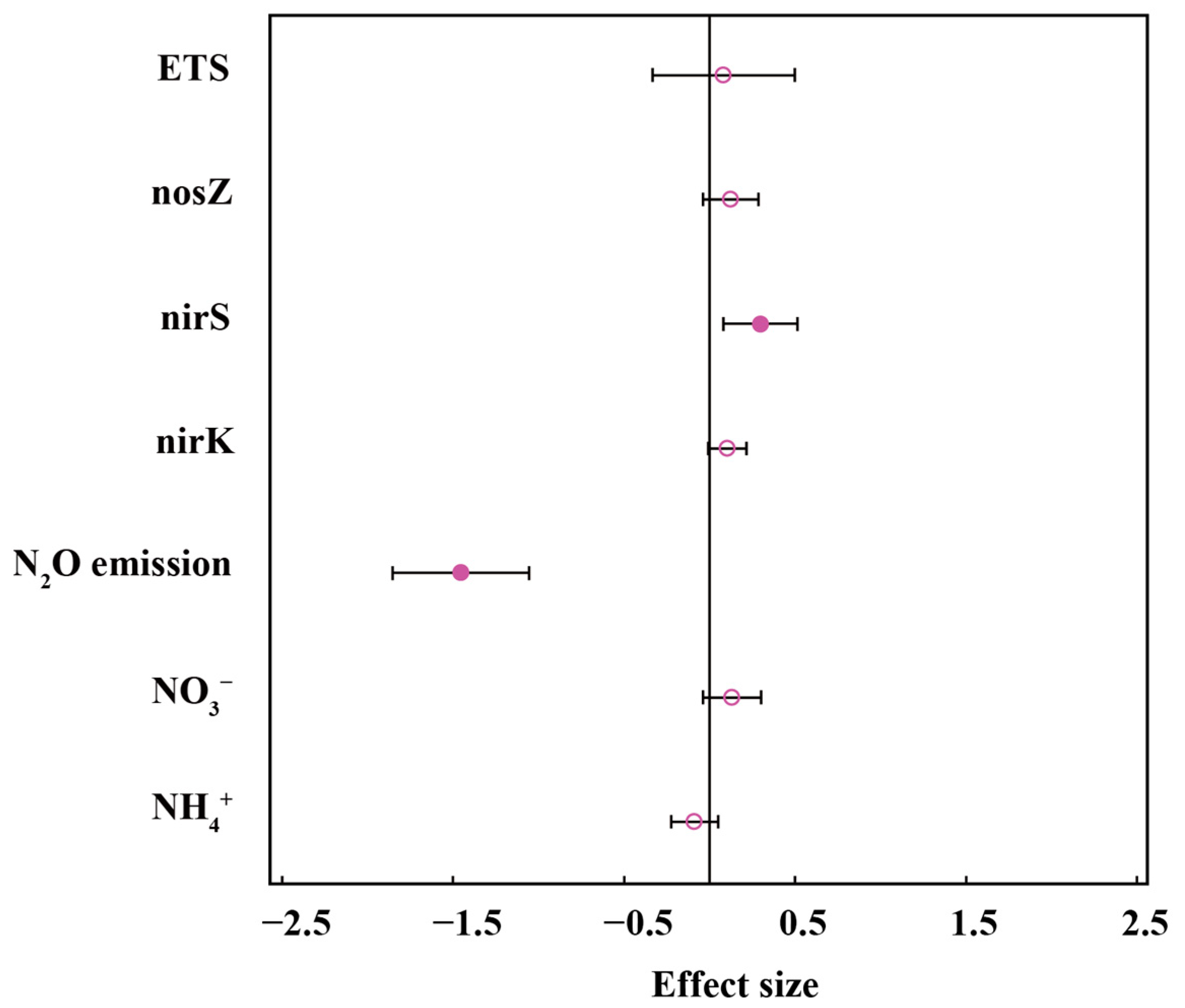




| Variables | Estimate | N | Egger’s Regression | Fail-Safe Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z | p | ||||
| NH4+ | −0.0882 | 132 | −2.3103 | 0.0209 | >5N + 10 |
| NO3− | 0.1325 | 124 | −0.7091 | 0.4782 | >5N + 10 |
| N2O emission | −1.1554 | 34 | 0.8104 | 0.4177 | >5N + 10 |
| nirK | 0.1042 | 28 | 1.5337 | 0.1251 | >5N + 10 |
| nirS | 0.2973 | 31 | −0.1285 | 0.8978 | >5N + 10 |
| nosZ | 0.1239 | 30 | +0.1243 | 0.9010 | >5N + 10 |
| ETS | 0.0830 | 11 | −0.0159 | 0.1251 | >5N + 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Wan, B.; Yang, Q. How Biochar Addition Affects Denitrification and the Microbial Electron Transport System (ETSA): A Meta-Analysis Based on a Global Scale. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122320
Zhang X, Zhou Q, Wang L, Wan B, Yang Q. How Biochar Addition Affects Denitrification and the Microbial Electron Transport System (ETSA): A Meta-Analysis Based on a Global Scale. Agriculture. 2024; 14(12):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122320
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaolei, Qiwen Zhou, Lili Wang, Bo Wan, and Qiannan Yang. 2024. "How Biochar Addition Affects Denitrification and the Microbial Electron Transport System (ETSA): A Meta-Analysis Based on a Global Scale" Agriculture 14, no. 12: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122320
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhou, Q., Wang, L., Wan, B., & Yang, Q. (2024). How Biochar Addition Affects Denitrification and the Microbial Electron Transport System (ETSA): A Meta-Analysis Based on a Global Scale. Agriculture, 14(12), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122320





