Hot Water Treatment as a Quarantine Measure for Controlling Pratylenchus penetrans Cobb in Syngonium podophyllum Schott and Perilla frutescens Britton
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nematodes
2.2. Efficacy of Hot Water Treatment on P. penetrans in an In Vitro Test
2.3. Effect of Temperature Increase Relative to the Diameters and Filling Ratio of S. podophyllum Roots
2.4. Efficacy of Hot Water Treatment on P. penetrans Infecting S. podophyllum and P. frutescens in an In Vivo Test
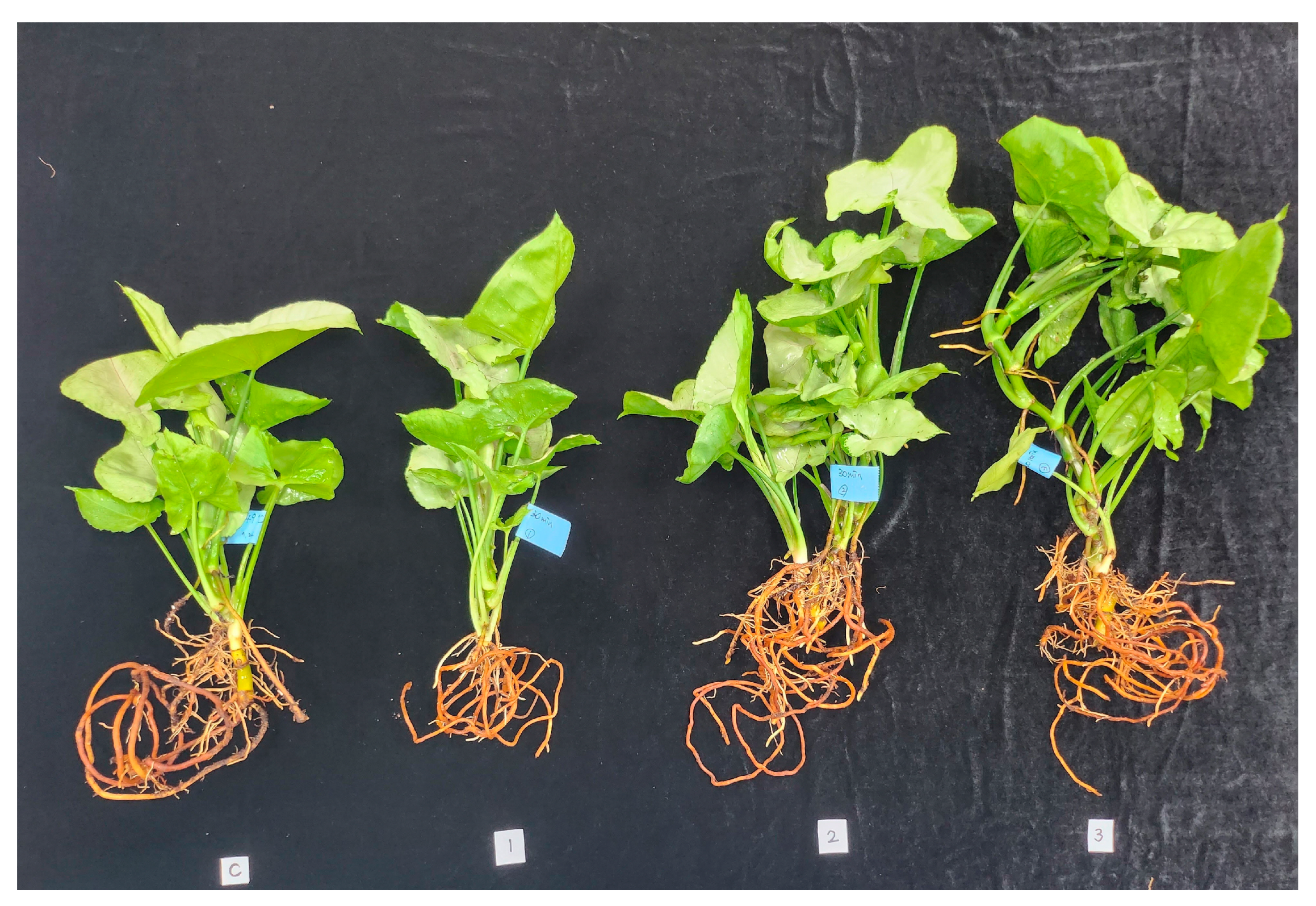
2.5. Effect of Hot Water Treatment on the Quality of S. podophyllum
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy of Hot Water Treatment on P. penetrans in In Vitro Tests
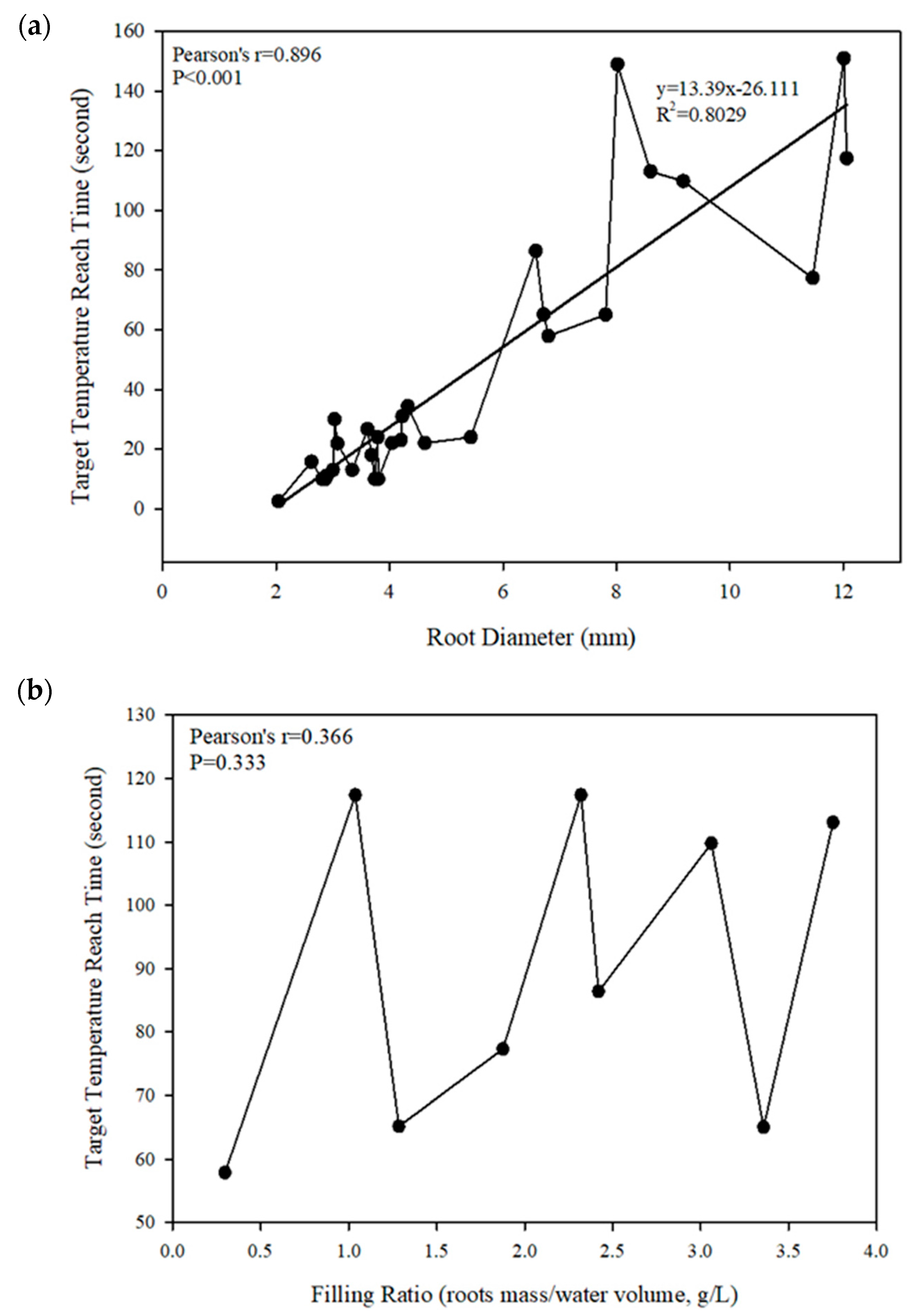
3.2. Effect of Temperature Increase in Relation to Diameter and Filling Ratio of Syngonium Roots
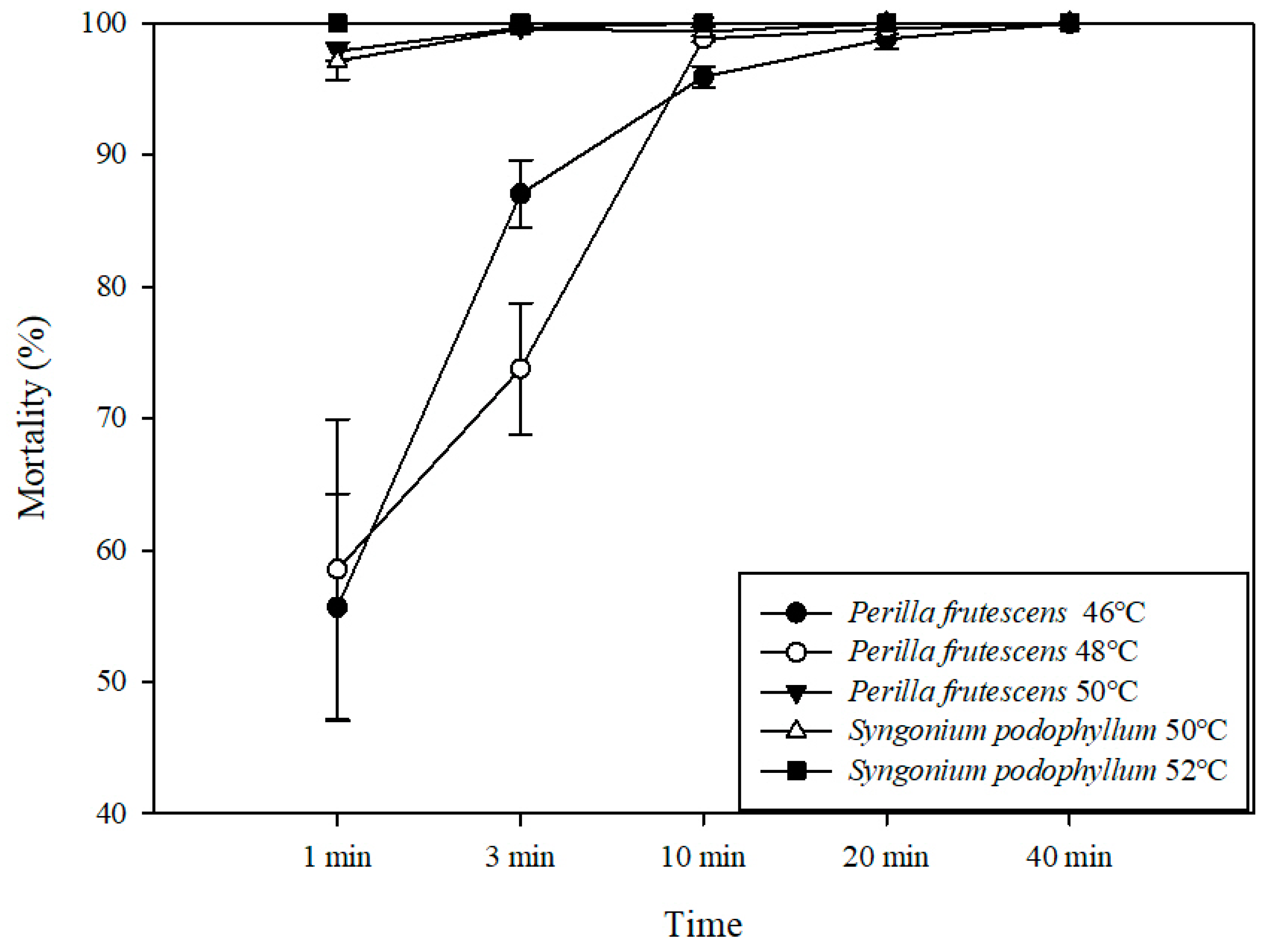
3.3. Efficacy of Hot Water Treatment on P. penetrans Infecting S. podophyllum and P. frutescens
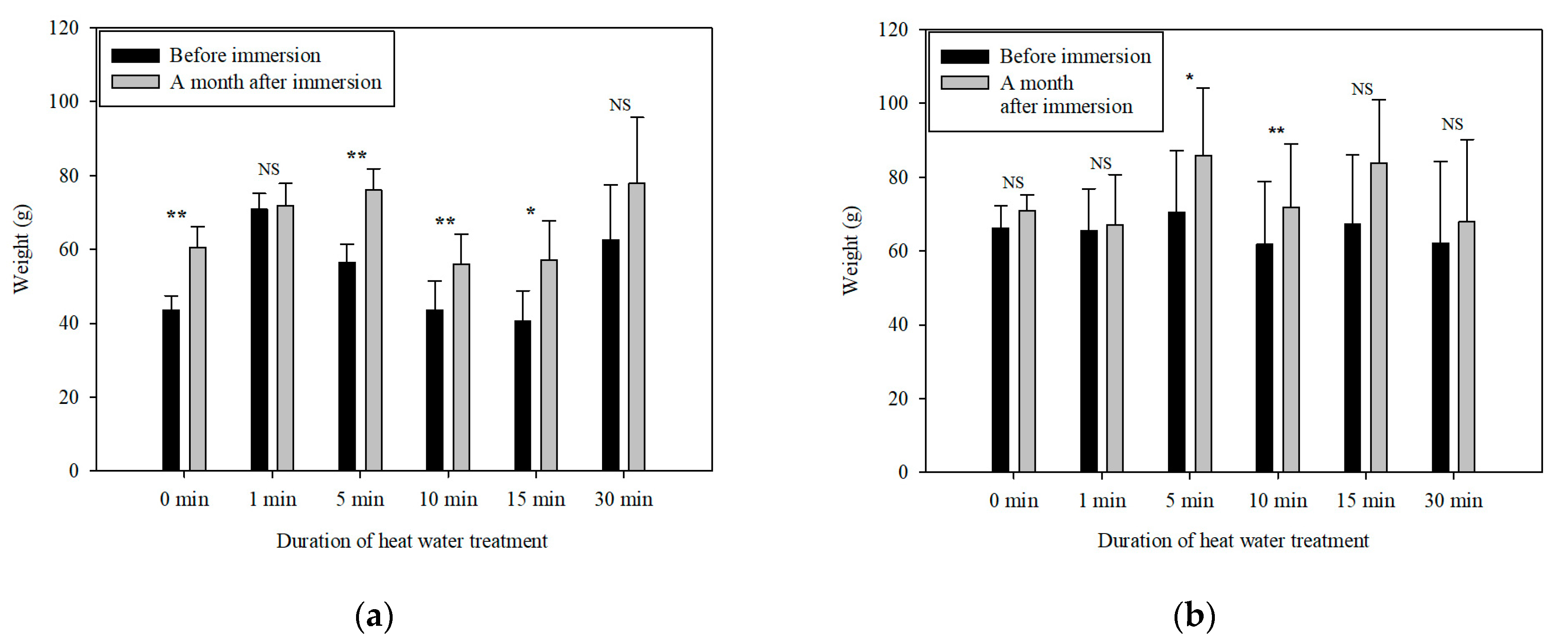
3.4. Effect of Hot Water Treatment on Quality of S. podophyllum
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- APQA. Pest Information System. Available online: http://10.110.128.100 (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Wolverton, B.C.; McDonald, R.C.; Watkins, E. Foliage plants for removing indoor air pollutants from energy-efficient homes. Econ. Bot. 1984, 38, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Le, T.M.L.; Trinh, Q.P. First report of Pratylenchus penetrans (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) associated with artichokes in Vietnam. J. Nematol. 2023, 55, 20230060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-I.; Minagawa, N. Classification of root-lesion nematodes occurring in vinyl-houses planted horticultural crops. RDA J. Agric. Sci. Crop Prot. 1996, 38, 530–538. [Google Scholar]
- EPPO. EPPO Global Database. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/PRATPE/categorization (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Seo, S. The Summer Fallow Season Is the Right Time to Control Root Lesion Nematodes in Perilla Plantations. Available online: https://www.agrinet.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=301761 (accessed on 28 March 2024). (In Korean).
- RDA. Dignosis and Management of Major Plant-Parasitic Nematodes; National Institute of Agricultural Sciences: Jeonju, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IPPC. Phytosanitary Treatments for Regulated Pests; ISPM 28; FAO/IPPC: Rome, Italy, 2007; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gebremichael, G.N.; Gebrehiwot, A. A Review on Biology and Management of Radopholus similis. Adv. Life Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, P.N.V. Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae): Diagnosis, Biology, Pathogenicity and Management; Hunt, D.J., Ed.; Koninklijke Brill NV: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Koen, H. Thermotherapeutic control of Pratylenchus brachyurus in potato tubers. Phytophylactica 1969, 1, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D.H.; Park, B.R.; Chun, J.Y.; Noh, Y.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, M.G.; Kim, D.; Lee, K.Y. Hot water immersion of Allium hookeri roots for the control of the plant parasitic nematodes Meloidogyne javanica and Pratylenchus coffeae. Entomol. Res. 2017, 47, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.; Koh, K.-B.; Park, Y. Study on hot water immersion treatment for control of Meloidogyne spp. and Pratylenchus spp. in a ginger, Zingiber officinale. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 56, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lear, B. Hot-water treatment of grapevine rootings for eradication of a root-lesion nematode, Pratylenchus vulnus. Plant Dis. Rep. 1966, 50, 858–859. [Google Scholar]
- APQA. Phytosanitary Disinfestation Guidelines. Available online: http://www.qia.go.kr/plant/disinpect/listXdclbzWebAction.do (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Baermann, G. Eine einfache methode zur auffindung von Ancylostomum (Nematoden) larven in erdproben. Geneeskd. Tijdschr. Ned. Indie 1917, 57, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Don-Pedro, K. Mode of action of fixed oils against eggs of Callosobruchus maculatus (F.). Pestic. Sci. 1989, 26, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Cho, Y.; Jeong, B.; Choi, D. Control effect on root-knot nematodes by hot water dipping treatment in kiwifruit. Korean J. Org. Agric. 2011, 19, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Elsen, A.; Goossens, B.; Belpaire, B.; Neyens, A.; Speijer, P.; De Waele, D. Recolonisation by nematodes of hot water treated cooking banana planting material in Uganda. Nematology 2004, 6, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S. Effects of fertilizer and hot-water treatment upon establishment, survival and yield of plantain (Musa spp., AAB, French). Field Crops Res. 2000, 66, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.; Hara, A.; Sipes, B. Hot-water treatments of potted palms to control the burrowing nematode, Radopholus similis. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.M.; Kara, A.; Sipes, B. Efficacy of hot water drenches of Anthurium andraeanum plants against the burrowing nematode Radopholus similis and plant thermotolerance. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2004, 145, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lear, B.; Lider, L. Eradication of root-knot nematodes from grapevine rootings by hot water. Plant Dis. Rep. 1959, 14, 314–317. [Google Scholar]
- McSorley, R.; McMillan, R., Jr.; Parrado, J. Meloidogyne incognita on society garlic and its control. Plant Dis. 1984, 68, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suatmadji, R.W. Control of root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne javanica, in rooted stocks of grapevine, Vitis vinifera, by immersion in nematicide solutions at different temperatures and in hot water. Nematol. Mediterr. 1982, 10, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Brcka, C.; McSorley, R.; Frederick, J.J. Effect of hot water treatments on root-knot nematodes and caladium tubers. In Proceedings of the Florida State Horticultural Society, Florida, FL, USA, 23–25 July 2000; pp. 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Coyne, D.; Wasukira, A.; Dusabe, J.; Rotifa, I.; Dubois, T. Boiling water treatment: A simple, rapid and effective technique for nematode and banana weevil management in banana and plantain (Musa spp.) planting material. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitwood, B.; Haasis, F.; Blanton, F. Hot-water–formalin treatment (at 110–111° F) of field grown and of forced narcissus bulbs infected with the bulb or stem nematode. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1941, 8, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nega, E.; Ulrich, R.; Werner, S.; Jahn, M. Hot water treatment of vegetable seed—An alternative seed treatment method to control seed-borne pathogens in organic farming/ Heißwasserbehandlung von Gemüsesaatgut—Eine alternative Saatgutbehandlungsmethode zur Bekämpfung samenbürtiger Pathogene im ökologischen Landbau. Z. Pflanzenkrankh. Pflanzenschutz J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2003, 110, 220–234. [Google Scholar]
- Cuc, N.T.T.; Son, N.T.; Trung, T.M.; văn Trang, N.; Đang, L.M.; Pilon, M. Hot water treatment prevents Aphelenchoides besseyi damage to Polianthes tuberosa crops in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcinas, A.C. Hot Water Drench Treatments for the Control of Burrowing Nematode, Radopholus Similis. In Tropical Ornamentals; University of Hawaii at Manoa: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Way, J. Phytothermotherapy for nematode control. In Proceedings of the Nematological Society of Southern Africa Newsletter, Nelspruit, South Africa, 9–10 April 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Viaene, N.; Coyne, D.L.; Kerry, B.R. Biological and Cultural Control; Perry, R.N., Ed.; Plant Nematology, CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
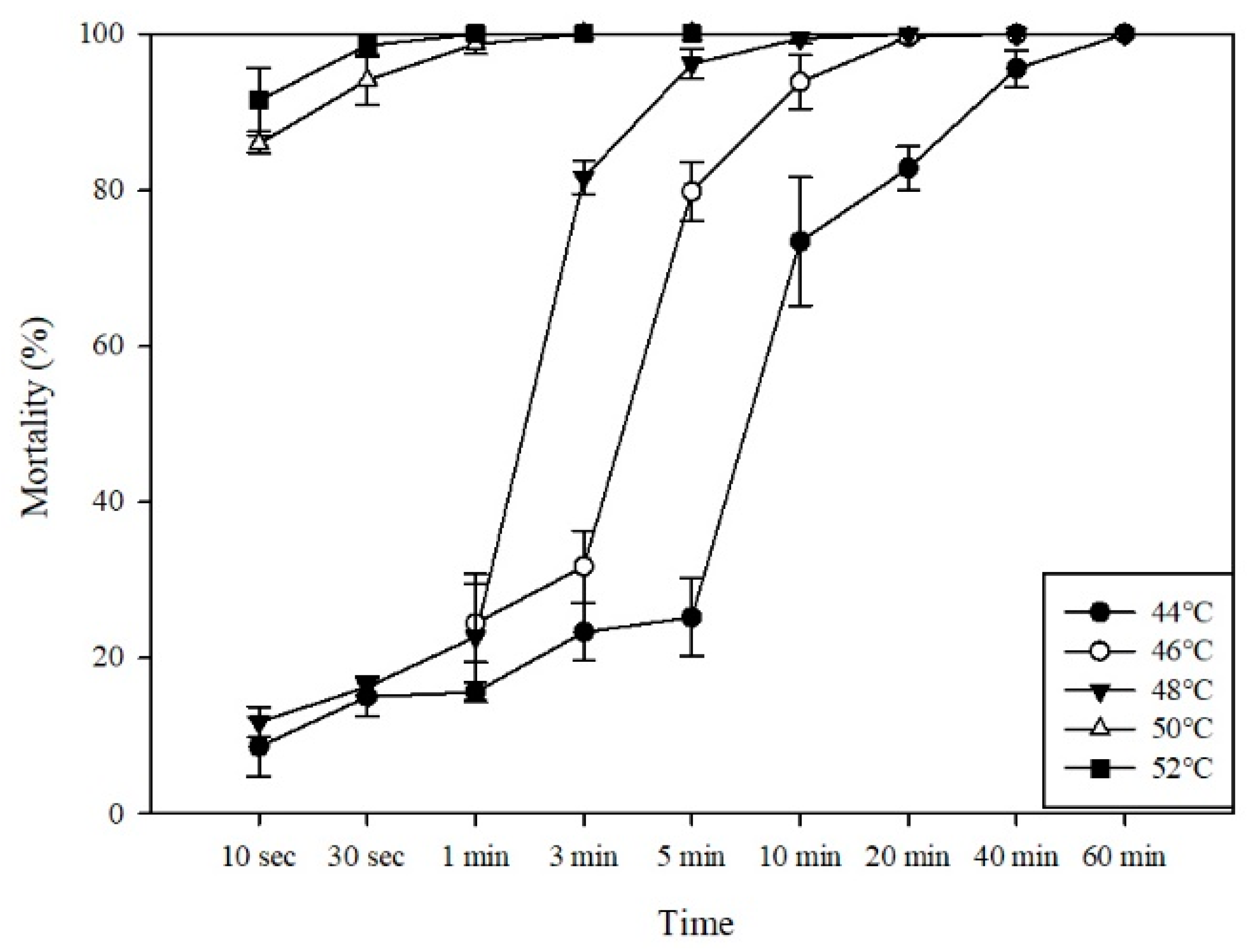

| Temp. (°C) | No. of P. penetrans | LT50% a (95% CI, min) | LT99% a (95% CI, min) | Slope ± SE b | df c | X2 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44 | 1008 | 3.31 (2.41–4.48) | 119.13 (69.22–245.43) | 1.49 ± 0.12 | 19 | 166.07 |
| 46 | 1399 | 2.68 (2.09–3.36) | 27.03 (17.20–54.80) | 2.32 ± 0.27 | 19 | 76.51 |
| 48 | 1649 | 1.08 (0.91–1.29) | 14.70 (10.48–22.59) | 2.05 ± 0.13 | 25 | 239.72 |
| 50 | 799 | 0.03 (0.01–0.06) | 1.40 (0.90–3.16) | 1.43 ± 0.24 | 13 | 34.66 |
| 52 | 386 | 0.04 (0.01–0.08) | 0.48 (0.31–5.48) | 2.09 ± 0.79 | 13 | 6.95 |
| Plant | Temp. (°C) | LT50% a (95% CI, min) | LT99% a (95% CI, min) | Slope ± SE b | df c | X2 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. frustescens | 46 | 0.77 (0.50–1.05) | 18.42 (11.82–36.50) | 1.69 ± 0.18 | 13 | 84.92 |
| 48 | 0.90 (0.49–1.30) | 18.59 (10.34–55.91) | 1.77 ± 0.27 | 13 | 42.56 | |
| 50 | 0.03 (0.01–0.08) | 1.68 (1.32–2.19) | 1.32 ± 0.24 | 10 | 31.00 | |
| S. podophyllum | 50 | 0.01 (0.01–0.04) | 2.67(1.69–4.95) | 0.91 ± 0.21 | 13 | 18.04 |
| 52 | <1.00 | <1.00 | - | - | - |
| Temp. (°C) | Treatment Time | F | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 1 min | 5 min | 10 min | 15 min | 30 min | |||
| 49 °C | 38.6 ± 6.9 | 18.7 ± 6.4 | 35.3 ± 4.0 | 31.0 ± 6.6 | 41.7 ± 4.1 | 25.7 ± 7.3 | 2.896 | 0.053 |
| 51 °C | 9.6 ± 8.3 | 3.3 ± 2.3 | 24.2 ± 5.76 | 20.1 ± 7.2 | 33.0 ± 15.2 | 17.5 ± 12.6 | 1.180 | 0.367 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, G.-E.; Heo, M.-S.; Park, M.-G. Hot Water Treatment as a Quarantine Measure for Controlling Pratylenchus penetrans Cobb in Syngonium podophyllum Schott and Perilla frutescens Britton. Agriculture 2024, 14, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040582
Lim G-E, Heo M-S, Park M-G. Hot Water Treatment as a Quarantine Measure for Controlling Pratylenchus penetrans Cobb in Syngonium podophyllum Schott and Perilla frutescens Britton. Agriculture. 2024; 14(4):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040582
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Ga-Eul, Moon-Sun Heo, and Min-Goo Park. 2024. "Hot Water Treatment as a Quarantine Measure for Controlling Pratylenchus penetrans Cobb in Syngonium podophyllum Schott and Perilla frutescens Britton" Agriculture 14, no. 4: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040582
APA StyleLim, G.-E., Heo, M.-S., & Park, M.-G. (2024). Hot Water Treatment as a Quarantine Measure for Controlling Pratylenchus penetrans Cobb in Syngonium podophyllum Schott and Perilla frutescens Britton. Agriculture, 14(4), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040582






