Lime Application Reduces Methane Emissions Induced by Pig Manure Substitution from a Double-Cropped Rice Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yield
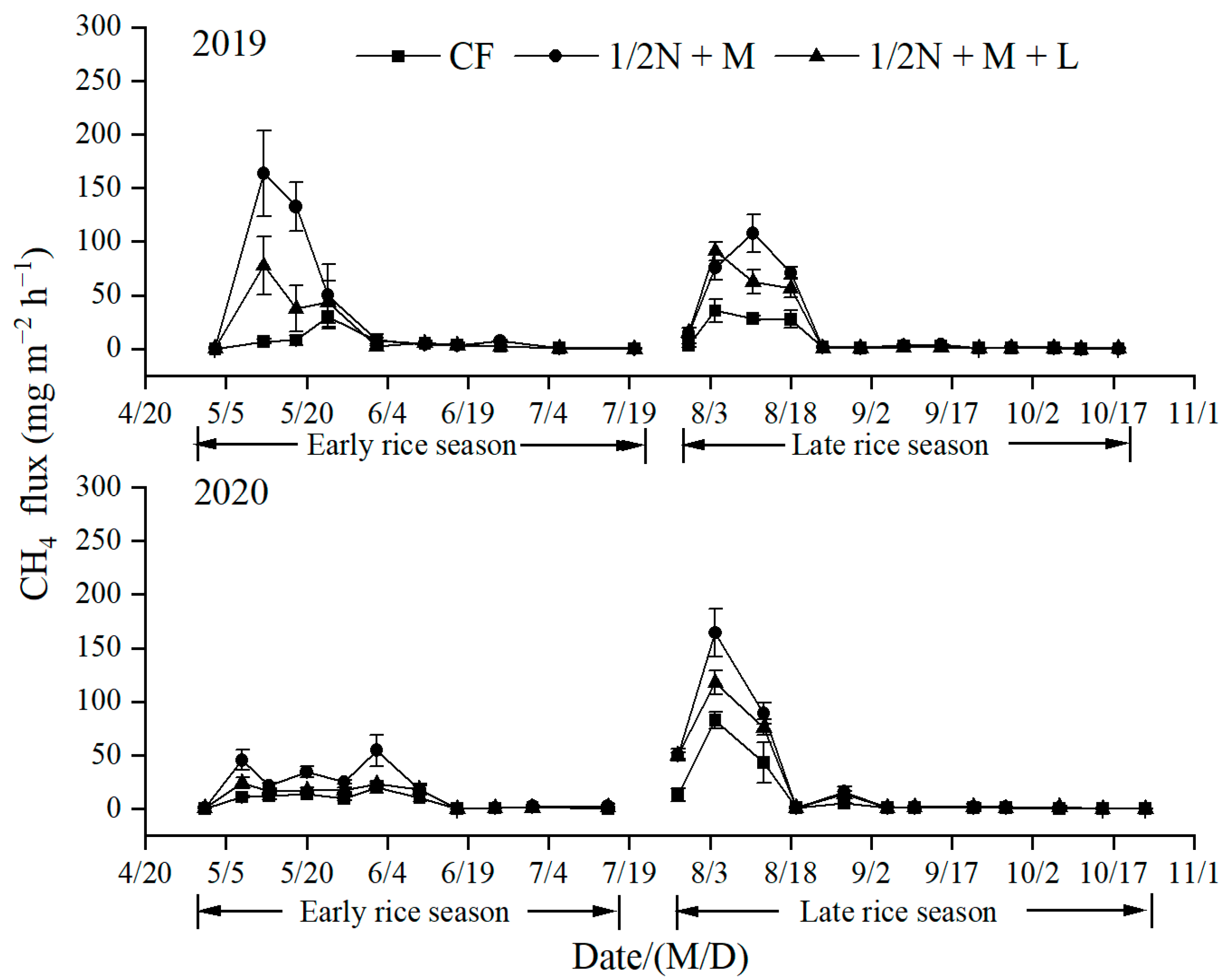
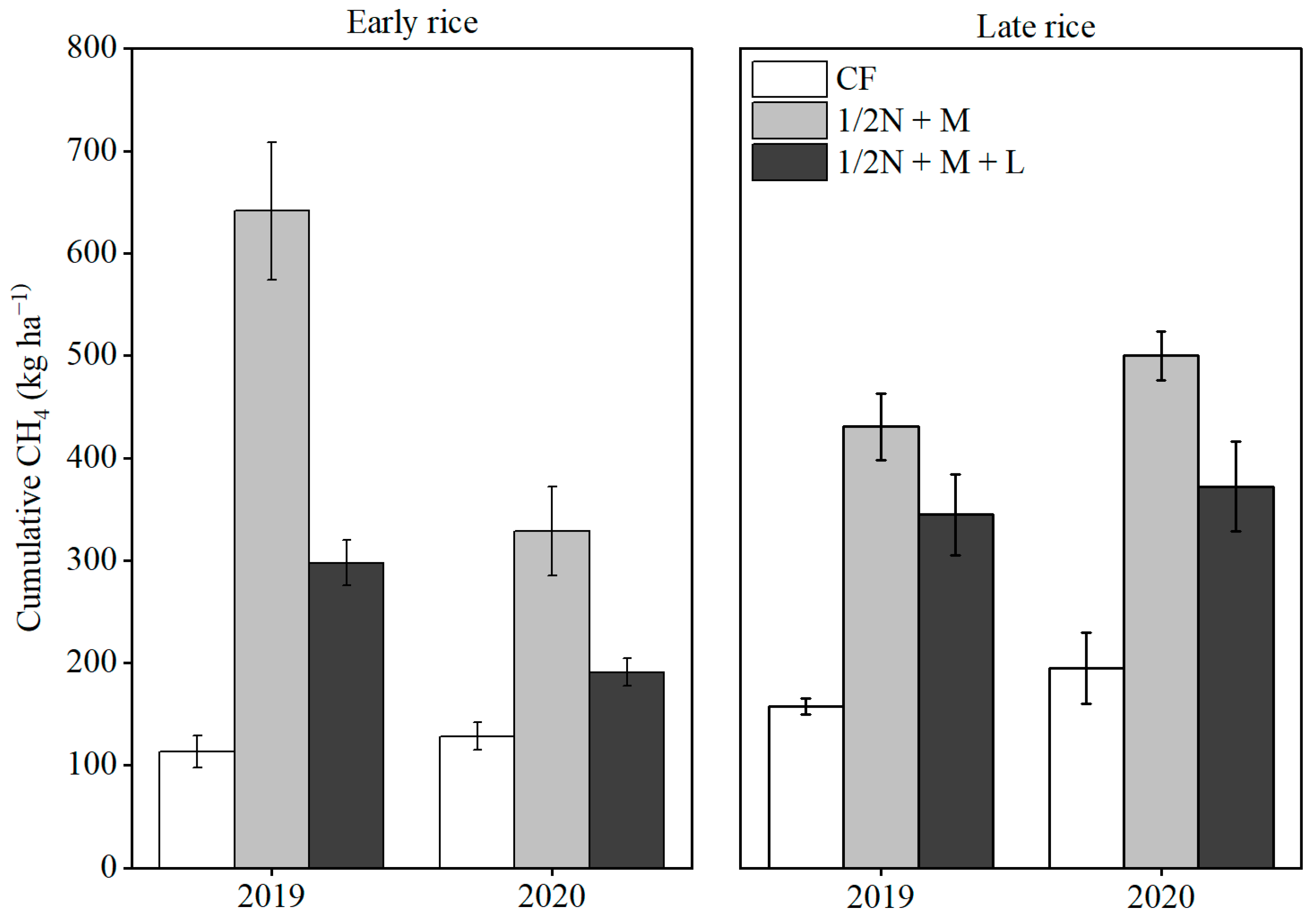
3.2. CH4 Emissions
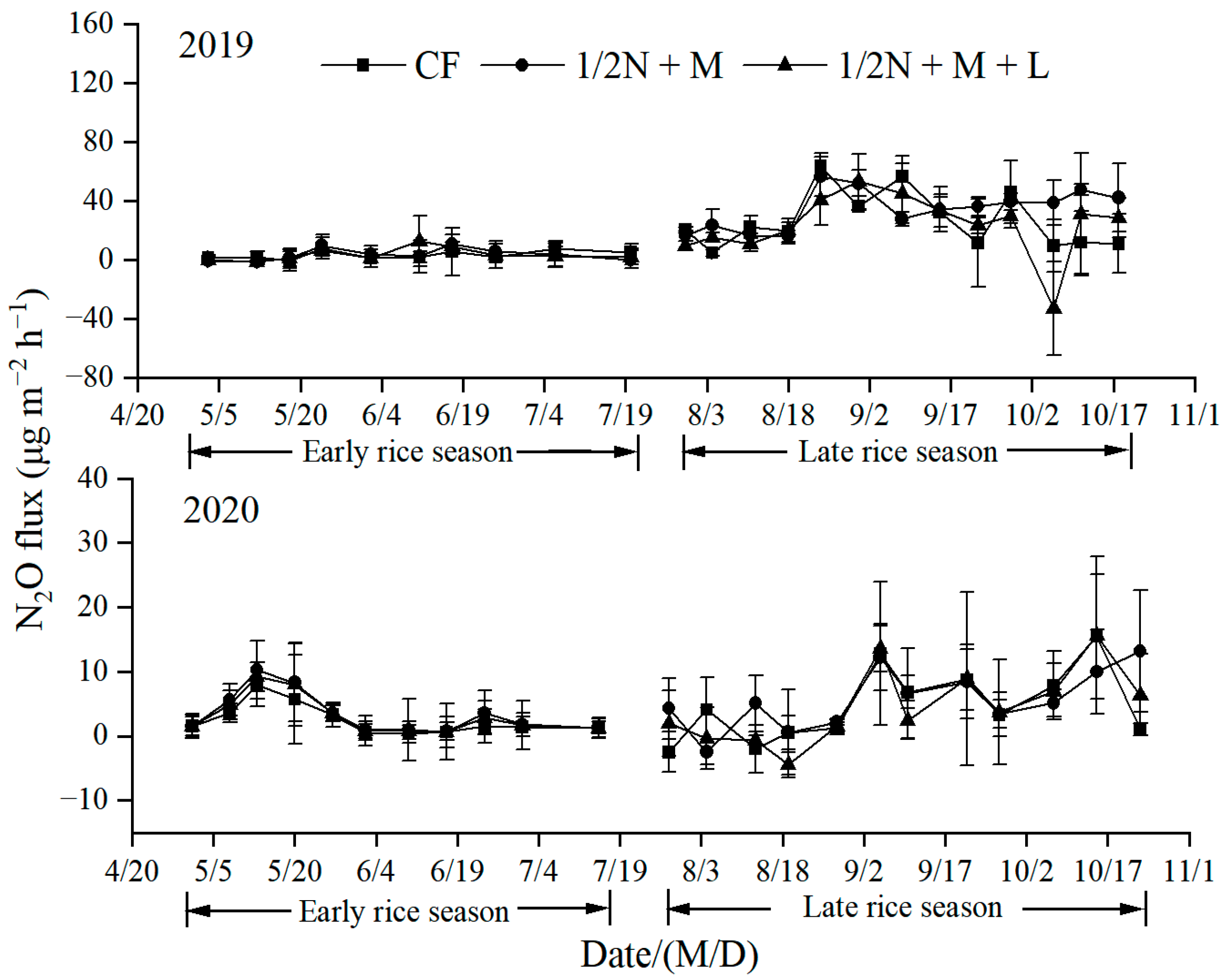
3.3. N2O Emissions
3.4. GWP and GHGI
3.5. Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Rice Yield
4.2. CH4 Emissions
4.3. N2O Emissions
4.4. GWP and GHGI
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MOA. Ministry of Agriculture of China. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Zhu, Q.C.; de Vries, W.; Liu, X.J.; Hao, T.X.; Zeng, M.F.; Shen, J.B.; Zhang, F.S. Enhanced acidification in Chinese croplands as derived from element budgets in the period 1980–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/zh/#data/EMN (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Jin, S.Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, B.; Han, D.M.; Hu, Y.; Ren, C.C.; Zhang, C.Z.; Wei, X.; Wu, Y.; Arthur, P.J.M.; et al. Decoupling livestock and crop production at the household level in China. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.X.; Zhou, P.; Li, Z.P.; Smith, P.; Li, L.Q.; Qiu, D.S.; Zhang, X.H.; Xu, X.B.; Shen, S.Y.; Chen, X.M. Combined inorganic/organic fertilization enhances N efficiency and increases rice productivity through organic carbon accumulation in a rice paddy from the Tai Lake region, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 131, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockeviciene, I.; Repsiene, R.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K.; Karcauskiene, D.; Slepetiene, A.; Lepane, V. Effect of long-term application of organic fertilizers on improving organic matter quality in acid soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Q.; Wang, M.; Li, P.; Shen, L.Y.; Ma, M.Y.; Xu, B.Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Sha, C.Y.; Ye, C.M.; Xiong, L.J.; et al. Effects of Pig Manure and Its Organic Fertilizer Application on Archaea and Methane Emission in Paddy Fields. Land 2022, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. In Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Z.S.; Zhan, Y.; Zheng, X.H.; Zhou, M.H.; Yan, G.X.; Wang, L.; Werner, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Potential benefits of liming to acid soils on climate change mitigation and food security. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2807–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradelo, R.; Virto, I.; Chenu, C. Net effect of liming on soil organic carbon stocks: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 202, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Liang, Z.; Dörsch, P.; Elsgaard, L. Trade-offs in greenhouse gas emissions across a liming-induced gradient of soil pH: Role of microbial structure and functioning. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5084-2021; Standard for Irrigation Water Quality. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- IPCC. The Earth’s Energy Budget, Climate Feedbacks, and Climate Sensitivity. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Q.Y.; Yang, X.X.; Gao, C.M.; Wu, P.P.; Liu, J.J.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Zou, J.W.; Guo, S.W. Net annual global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in Chinese double rice-cropping systems: A 3-year field measurement in long-term fertilizer experiments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 17, 2196–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPCD. China Products Carbon Footprint Factors Database. Available online: https://lca.cityghg.com (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Springer Science & Business Media Press: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, A.; He, L.; Ali, I.; Yuan, P.L.; Khan, A.; Hua, Z.; Wei, S.Q.; Jiang, L.G. Partial substation of organic fertilizer with chemical fertilizer improves soil biochemical attributes, rice yields, and restores bacterial community diversity in a paddy field. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 895230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.A.; Shu, A.P.; Song, W.F.; Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, G.G.; Yuan, F.S.; Zhang, S.X.; et al. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shi, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Hu, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.; He, X.H.; Evgenia, B. Improved nitrogen use efficiency, carbon sequestration and reduced environmental contamination under a gradient of manure application. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.J.; Ros, G.H.; Xu, M.G.; Cai, Z.J.; Sun, N.; Duan, Y.H.; de Vries, W. Long-term impacts of mineral and organic fertilizer inputs on nitrogen use efficiency for different cropping systems and site conditions in Southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 146, 126797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Li, S.T. A review on nitrogen mineralization of organic manure and affecting factors. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2012, 18, 749–757. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.F.; Zhou, J.; Peng, B.; Li, Q.J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Q.M.; Wang, Y.L. Differences of nitrogen uptake and utilization of conventional rice varieties with different growth duration. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2011, 44, 4570–4582. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Fang, Q.C.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.Q.; Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F.S. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Huang, S.; Van Gestel, N.C.; Zeng, Y.J.; Wu, Z.M.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Liming and straw retention interact to increase nitrogen uptake and grain yield in a double rice-cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2018, 216, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.N.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Y.J.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Liming reduces nitrogen uptake from chemical fertilizer but increases that from straw in a double rice cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, F.; Bochu, V.; Findeling, A.; Doelsch, E. Repeated pig manure applications modify nitrate and chloride competition and fluxes in a Nitisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; Bell, S.M.; Liu, J.S.; Sun, Y.N.; Zeng, Y.J.; Zhang, H.C.; Huang, S. Interaction of lime application and straw retention on ammonia emissions from a double-cropped rice field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 344, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Li, S.Q.; Jin, Y.G.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.W.; Zou, J.W. Linking methane emissions to methanogenic and methanotrophic communities under different fertilization strategies in rice paddies. Geoderma 2019, 347, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Lueders, T.; Friedrich, M.W.; Conrad, R. Methanogenic populations involved in the degradation of rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 38, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liao, P.; van Gestel, N.; Sun, Y.N.; Zeng, Y.J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, W.J.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Lime application lowers the global warming potential of a double rice cropping system. Geoderma 2018, 325, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, S.; Chang, S.X.; Zhang, Q.P. Liming effects on soil pH and crop yield depend on lime material type, application method and rate, and crop species: A global meta-analysis. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The effects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Zhu-Barker, X.; Decock, C. Effects of organic fertilizers on the soil microorganisms responsible for N2O emissions: A review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.H.; Li, L.L.; Xie, J.H.; Wang, J.B.; Anwar, S.; Du, C.L.; Zhou, Y.J. Substituting inorganic fertilizers with organic amendment reduced nitrous oxide emissions by affecting nitrifiers’ microbial community. Land 2022, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xie, G.X.; Yang, Z.H.; He, N.; Yang, D.; Liu, M.D. Variation in abundance, diversity, and composition of nirK and nirS containing denitrifying bacterial communities in a red paddy soil as affected by combined organic-chemical fertilization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D. Biogeochemistry of N2O uptake and consumption in submerged soils and rice fields and implications in climate change. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 2653–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Qin, T.; Du, X.Z.; Sheng, F.; Li, C.F. Effects of irrigation regime and rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions and grain yields from paddy fields in central China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.; Palmada, T.; Berben, P.; Saggar, S.; Luo, J.F.; McMillan, A.M.S. Influence of liming-induced pH changes on nitrous oxide emission.; nirS.; nirK and nosZ gene abundance from applied cattle urine in allophanic and fluvial grazed pasture soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hink, L.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I. Archaea produce lower yields of N2O than bacteria during aerobic ammonia oxidation in soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4829–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z.J.; Sun, N.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Chang, S.X.; Xu, M.G.; et al. Contrasting effects of different pH-raising materials on N2O emissions in acidic upland soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakken, L.; Bergaust, L.; Liu, B.; Frostegard, A. Regulation of denitrification at the cellular level: A clue to the understanding of N2O emissions from soils. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Xiong, Z.Q. Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity from the double rice system with integrated soil-crop system management: A three-year field study. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, X.F.; Shen, J.L.; Chen, D.; Zheng, L.; Ge, T.D.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. Reduction in net greenhouse gas emissions through a combination of pig manure and reduced inorganic fertilizer application in a double-rice cropping system: Three-year results. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.L.; Yin, X.H.; Dorich, C.; Olave, R.; Wang, X.H.; Kou, C.L.; Song, X. Net field global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in typical arid cropping systems of China: A 3-year field measurement from long-term fertilizer experiments. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulding, K.W.T. Soil acidification and the importance of liming agricultural soils with particular reference to the United Kingdom. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; He, Y.X.; Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y.J.; Wu, Z.M.; Huang, S. Interactive effects of liming and straw incorporation on yield and nitrogen uptake in a double rice cropping system. Acta Agron. Sin. 2020, 46, 84–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


| CH4 (kg ha−1) | N2O (g ha−1) | GWP (kg CO2 eq ha−1) | Yield (kg ha−1) | GHGI (kg CO2 eq kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment (T) a | |||||
| CF | 149 c | 413 a | 4123 c | 7146 a | 0.60 c |
| 1/2N + M | 475 a | 534 a | 12,973 a | 6742 b | 1.97 a |
| 1/2N + M + L | 301 b | 444 a | 8257 b | 6686 b | 1.25 b |
| Crop (C) b | |||||
| Early rice | 283 b | 330 b | 7740 b | 6753 b | 1.16 b |
| Late rice | 333 a | 598 a | 9162 a | 6963 a | 1.38 a |
| Year (Y) c | |||||
| 2019 | 331 a | 405 b | 9043 a | 7375 a | 1.26 a |
| 2020 | 286 b | 522 a | 7860 b | 6342 b | 1.28 a |
| F-values | |||||
| T × C | 11.2 *** | NS | 11.2 *** | 199 *** | 9.6 *** |
| T × Y | 13.8 *** | NS | 13.8 *** | NS | 9.9 *** |
| C × Y | 60.4 *** | NS | 60.3 *** | NS | 246 *** |
| T × C × Y | 21.2 *** | NS | 21.2 *** | NS | 49.6 *** |
| pH | SOM (g kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment (T) a | ||
| CF | 5.4 b | 19.0 b |
| 1/2N + M | 5.5 b | 20.7 a |
| 1/2N + M + L | 5.9 a | 20.4 a |
| Year (Y) b | ||
| 2019 | 5.7 a | 20.1 a |
| 2020 | 5.6 a | 20.0 a |
| F-values | ||
| T | 22.3 *** | 11.7 *** |
| Y | NS | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Sun, Y. Lime Application Reduces Methane Emissions Induced by Pig Manure Substitution from a Double-Cropped Rice Field. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071063
Liu J, He Y, Chen J, Huang S, Sun Y. Lime Application Reduces Methane Emissions Induced by Pig Manure Substitution from a Double-Cropped Rice Field. Agriculture. 2024; 14(7):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071063
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinsong, Yuxuan He, Jin Chen, Shan Huang, and Yanni Sun. 2024. "Lime Application Reduces Methane Emissions Induced by Pig Manure Substitution from a Double-Cropped Rice Field" Agriculture 14, no. 7: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071063
APA StyleLiu, J., He, Y., Chen, J., Huang, S., & Sun, Y. (2024). Lime Application Reduces Methane Emissions Induced by Pig Manure Substitution from a Double-Cropped Rice Field. Agriculture, 14(7), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071063







