Biotic and Abiotic Factors Affecting Soil C, N, P and Their Stoichiometries under Different Land-Use Types in a Karst Agricultural Watershed, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
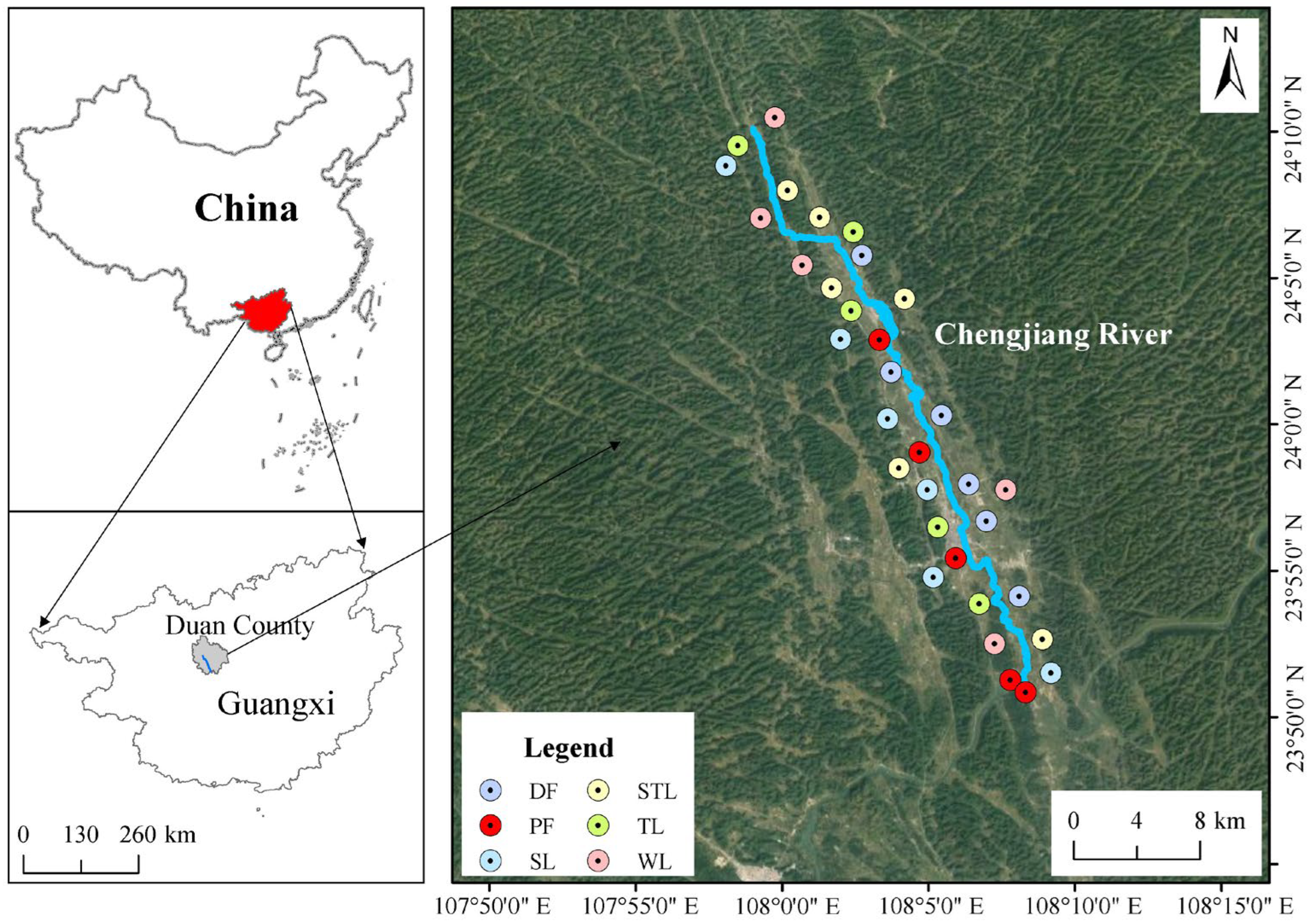
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
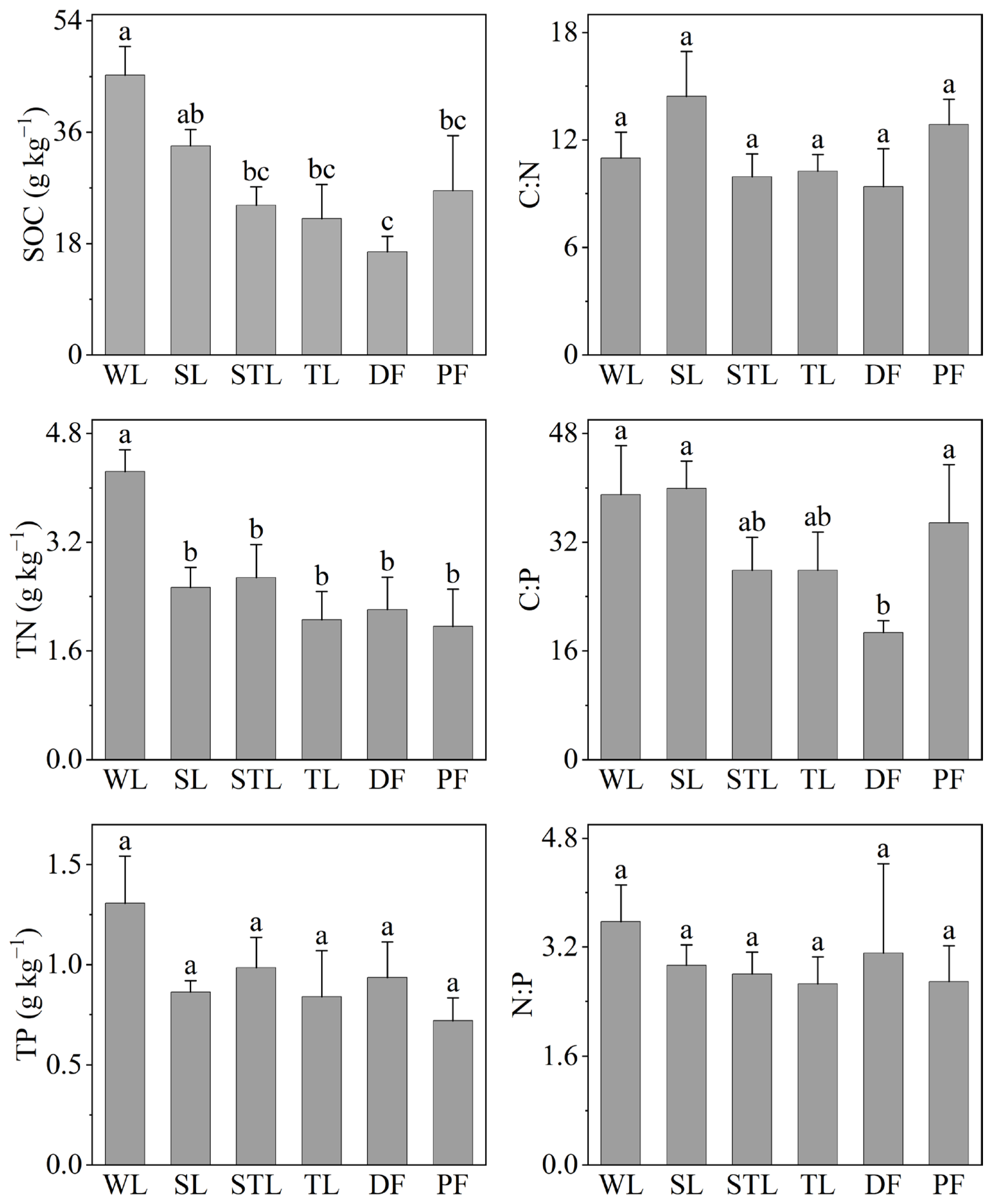
3.1. Soil C, N, and P and Their Stoichiometries
3.2. Environmental Variables
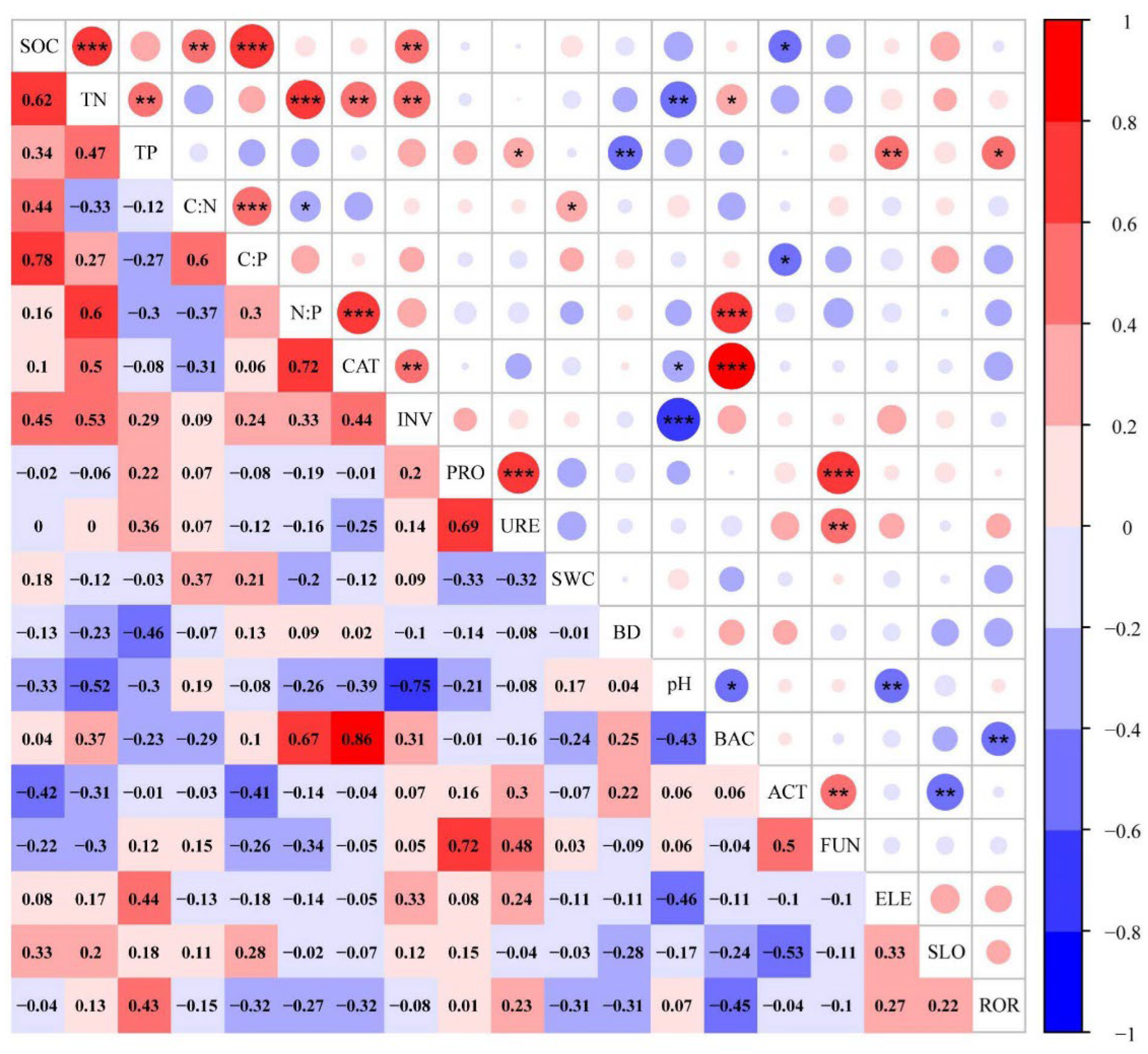
3.3. Correlations between Environmental Variables and Nutrient Traits
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Land-Use Type on Topsoil C, N, and P Content
4.2. Effects of Land Use on Topsoil C, N, and P Stoichiometries
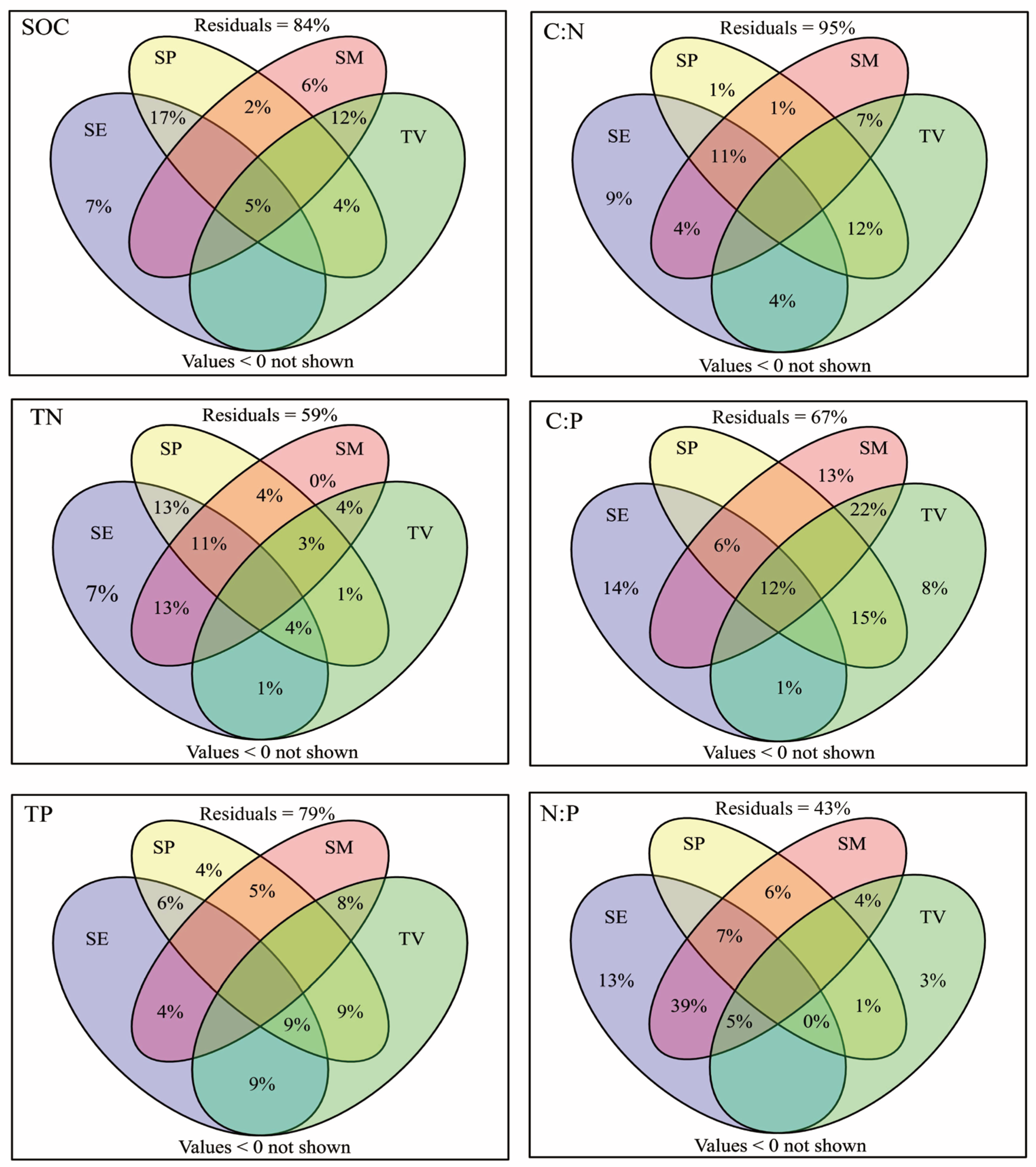
4.3. Factors Affecting soil C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometries
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Stirling, E.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhao, K.K.; Zhou, J.Z.; Singh, B.K.; Tang, C.X.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Xu, J.M. Soil biogeochemical cycle couplings inferred from a function-taxon network. Research 2021, 2021, 7102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Li, M.X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.X.; Dai, G.H.; He, N.P. C:N:P stoichiometry in terrestrial ecosystems in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Feng, J.G.; Ding, Z.J.; Tang, M.; Zhu, B. Changes in soil total, microbial and enzymatic C-N-P contents and stoichiometry with depth and latitude in forest ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S. Soil enzyme kinetics and thermodynamics in response to long-term vegetation succession. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Qu, F.Z.; Bi, X.L.; Xia, J.B.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Yu, J.B. Elemental stoichiometry (C, N, P) of soil in the Yellow River Delta nature reserve: Understanding N and P status of soil in the coastal estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzgall, K.; Vidal, A.; Schubert, D.I.; Höschen, C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Buegger, F.; Pouteau, V.; Chenu, C.; Mueller, C.W. Particulate organic matter as a functional soil component for persistent soil organic carbon. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.Y.; Yang, X.; Shao, M.A.; Wei, X.R.; Li, T.C. Changes in soil C-N-P stoichiometry after 20 years of typical artificial vegetation restoration in semiarid continental climate zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Huang, C.Q. Spatial variability of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus under different land uses in a small watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2009, 150, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havaee, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Keller, T. Impacts of land use on soil organic matter and degree of compactness in calcareous soils of central Iran. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Singh, C.; Boudh, S.; Rai, P.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, J.S. Land use change: A key ecological disturbance declines soil microbial biomass in dry tropical uplands. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.D.; Gao, D.X.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.C.; Deng, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient dynamics along a revegetation chronosequence in the soils of abandoned land and Robinia pseudoacacia plantation on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chai, Y.B.; Xie, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yang, X.; Hao, S.L.; Gai, J.P.; Chen, Y.L. Responses of soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality to three land-use changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Kirschbaum, M.U.F.; Eichler-Löbermann, B.; Gifford, R.M.; Liáng, L.L. The effect of land-use change on soil C, N, P, and their stoichiometries: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 348, 108402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Rashti, M.R.; Brough, D.M.; Burford, M.A.; Liu, W.Z.; Liu, G.H.; Chen, C.R. Stoichiometric control on riparian wetland carbon and nutrient dynamics under different land uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.M.; Xia, Y.H.; Hu, Y.J.; Chen, X.B.; Rui, Y.C.; Gunina, A.; He, X.Y.; Ge, T.D.; Wu, J.S.; Su, Y.R.; et al. Stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil: Effects of agricultural land use and climate at a continental scale. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 209, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hu, J.S.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, J.C.; Dong, Y.Q.; Li, B. Soil C, N, P stocks and stoichiometry as related to land use types and erosion conditions in lateritic red soil region, south China. Catena 2022, 210, 105888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Z.W.; Li, L.H. Soil nutrient contents and stoichiometry as affected by land-use in an agro-pastoral region of northwest China. Catena 2017, 150, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.Y.; Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Ren, C.J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Wang, J.; Doughty, R. Changes of soil microbial and enzyme activities are linked to soil C, N and P stoichiometry in afforested ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 427, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.C. The main factors controlling spatial variability of soil organic carbon in a small karst watershed, Guizhou Province, China. Geoderma 2020, 357, 113938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.F.; Xie, M.D.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, W.R.; Hu, J.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ji, W.J.; Li, S.; Hong, Y.S.; Yang, M.H.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in farmland soils in southern China: Spatial pattern and related dominates. Catena 2022, 217, 106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.M.; Yang, R.; Tang, Y.X.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Z.H.; Shi, Z.H.; Hu, P.L.; Wu, H.Q.; Wang, K.L. Lithologic control of soil C:N:P stoichiometry across a climatic gradient in southwest China. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.H.; Peng, X.D.; Wang, P.J.; Li, C.L.; Shao, H.B. Surface erosion and underground leakage of yellow soil on slopes in karst regions of southwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.J.; Yue, Y.M.; Wang, K.; Fensholt, R.; Tong, X.W.; Brandt, M. Ecological restoration enhances ecosystem health in the karst regions of southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.W.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.M.; Horion, S.; Wang, K.L.; De Keersmaecker, W.; Tian, F.; Schurgers, G.; Xiao, X.M.; Luo, Y.Q.; et al. Increased vegetation growth and carbon stock in China karst via ecological engineering. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Chen, H.S.; Yue, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Qi, X.K.; Fu, Z.Y. Karst landscapes of China: Patterns, ecosystem processes and services. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2743–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.W.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.M.; Ciais, P.; Jepsen, M.R.; Penuelas, J.; Wigneron, J.P.; Xiao, X.M.; Song, X.P.; Horion, S.; et al. Forest management in southern China generates short term extensive carbon sequestration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, H.S.; Fu, Z.Y.; Wang, K.L. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil properties along an elevation gradient in the karst region of southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 320, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Hu, B.Q. Soil quality characteristics during the ecological restoration process of karst rocky desertification ecosystem: A case study of Chengjiang Watershed in Du’an County, Guangxi. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2009, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Su, G.S. Effects of land use patterns on microorganism and enzyme activity in karst small watershed soil: A case study at Chengjiang small watershed in Du’an County, Guangxi. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 28, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Su, G.S.; Wang, S.J.; Hu, B.Q.; Yang, X.Q. The impact of different land use patterns on soil physical properties and microbes in a small Karst watershed: A case study of Chengjiang Small Watershed in Du’an County, Guangxi. Earth Environ. 2013, 41, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cooperative Research Group on Chinese Soil Taxonomy. Chinese Soil Taxonomy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L. A fast and accurate circle detection algorithm based on random sampling. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 123, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shao, M.A.; Li, T.C.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gan, M.; Chen, M.Y.; Bai, X. Distribution of soil nutrients under typical artificial vegetation in the desert–loess transition zone. Catena 2021, 200, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.J.; Han, X.R.; Wang, X.P.; Wang, L.Q.; Liang, T. Long-term ecological effects of two artificial forests on soil properties and quality in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.J.; Zhao, F.Z.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.H.; Han, X.H.; Tong, X.G.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Linkages of C: N: P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Solanki, A.C.; Gurjar, N.S.; Sharma, S.; Wang, Z.; Kumar, A.; Solanki, M.K.; Divvela, P.K.; Yadav, K.; Kashyap, B.K. Decoding seasonal changes: Soil parameters and microbial communities in tropical dry deciduous forests. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1258934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Li, H.X.; Wu, J.Q. Effects of water stress on nutrients and enzyme activity in rhizosphere soils of greenhouse grape. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1376849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangir, R.; Maurya, B.R.; Yadav, M.; Goswami, S.P.; Yadav, S.L. Impact of potassium inoculants and biotite on soil microbial population and enzymatic activity under maize (Zea mays L.) cultivation in Gangetic Plains. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, W.R. Psych: Procedures for Personality and Psychological Research; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.B.; Chen, T.; Pu, J.; Yang, F.Q.; Shukla, M.K.; Chang, Q.R. Response of soil physical, chemical and microbial biomass properties to land use changes in fixed desertified land. Catena 2018, 160, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovo, O.; Aburto, F.; Albornoz, M.F.; Southard, R. Soil type modulates the response of C, N, P stocks and stoichiometry after native forest substitution by exotic plantations. Catena 2021, 197, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Fu, L.J.; Lu, X.Y.; Yan, Y. Characteristics of soil nutrients and their ecological stoichiometry in different land use types in the Nianchu River Basin. Land 2022, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Chen, H.S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.L. Soil nutrients and stoichiometric ratios as affected by land use and lithology at county scale in a karst area, southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Xu, C.H.; Luo, W. Improvements in soil quality with vegetation succession in subtropical China karst. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.B.; Liang, W.; Miao, C.Y. Hydrogeomorphic Ecosystem Responses to Natural and Anthropogenic Changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Tang, M.; Ding, Z.J.; Jiang, L.; Li, P.; Ma, S.H.; Tian, D.; Xu, L.C.; Zhu, J.X.; et al. Nitrogen deposition has minor effect on soil extracellular enzyme activities in six Chinese forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.M.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, K.L. Increased associated effects of topography and litter and soil nutrients on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass along vegetation successions in karst ecosystem, southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16979–16990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, M.H.; Mao, Q.G.; Xiao, K.C.; Wang, K.L.; Li, D.J. Cropland conversion changes the status of microbial resource limitation in degraded karst soil. Geoderma 2019, 352, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.S.; Ye, Y.Y.; Xiao, D.; Chen, W.R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.L. Effects of tillage on soil N availability, aggregate size, and microbial biomass in a subtropical karst region. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 192, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.S.; Li, Z.W.; Xie, H.X.; Ouyang, K.; Yuan, H.; Duan, L.X. Land use change impacts on red slate soil aggregates and associated organic carbon in diverse soil layers in subtropical China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spohn, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Phosphorus mineralization can be driven by microbial need for carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 61, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Li, T.Y.; He, B.H.; Feng, M.D.; Liang, K. Effects of vegetation succession on topsoil C, N, and P contents and stoichiometry following agricultural abandonment in a representative karst trough valley. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 192, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, C.; Zhong, C.; Li, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Responses of soil nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry to different human land uses in a subtropical tidal wetland. Geoderma 2014, 232, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S.; Sun, C.L. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen storage as affected by land use in a small watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 54, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E. Prospects for using soil microorganisms to improve the acquisition of phosphorus by plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2001, 28, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Deng, H.J.; Du, K.; Rafay, L.; Zhang, G.S.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.Z.; Lin, H.; Yu, W.; et al. Combined effects of climate, restoration measures and slope position in change in soil chemical properties and nutrient loss across lands affected by the Wenchuan Earthquake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Yang, L.; Wen, D.N.; Liu, L.J.; Ni, K.; Cao, J.H.; Zhu, T.B.; Mueller, C. Soil calcium constrains nitrogen mineralization and nitrification rates in subtropical karst regions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 186, 109176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.N.; Feng, S.; Wang, S.K.; Zhang, B.L.; Ning, Z.Y.; Wang, R.X.; Chen, X.P.; Yu, L.L.; Zhao, H.S.; Lan, D.M.; et al. Patterns and driving mechanism of soil organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry across northern China’s desert-grassland transition zone. Catena 2023, 220, 106695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.S.; Liu, S.L.; Shen, J.L.; Huang, D.Y.; Su, Y.R.; Wei, W.X.; Syers, J.K. Is the C:N:P stoichiometry in soil and soil microbial biomass related to the landscape and land use in southern subtropical China? Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 2012, 26, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Slessarev, E.; Marschmann, G.L.; Nicolas, A.; Blazewicz, S.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Firestone, M.K.; Foley, M.M.; Hestrin, R.; Hungate, B.A.; et al. Life and death in the soil microbiome: How ecological processes influence biogeochemistry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, J.; Guan, P. Soil degradation regulates the effects of litter decomposition on soil microbial nutrient limitation: Evidence from soil enzymatic activity and stoichiometry. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1090954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.L.; Jia, P.; Feng, S.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Zheng, J.; Ou, S.N.; Wu, Z.H.; Liao, B.; Shu, W.S.; Liang, J.L.; et al. Remarkable effects of microbial factors on soil phosphorus bioavailability: A country-scale study. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 4459–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.W.; Wu, Z.S.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.C.; Li, T.; He, Y.H.; Li, B.B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yu, B. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms regulate the release and transformation of phosphorus in biochar-based slow-release fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.F.; Li, J.; Qu, L.R.; Wang, X.; Sang, C.P.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.Z.; Wanek, W.; Moorhead, D.L.; Bai, E.D.; et al. Phosphorus limitation reduces microbial nitrogen use efficiency by increasing extracellular enzyme investments. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Land Use | SOC | TN | TP | C/N | C/P | N/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WL | 22.8 | 16.98 | 40.48 | 29.43 | 41.21 | 33.8 |
| SL | 19.07 | 28.29 | 16.13 | 42.55 | 24.62 | 24.78 |
| STL | 30.04 | 44 | 37.69 | 31.42 | 42.57 | 28.18 |
| TL | 55.83 | 45.06 | 62.21 | 20.23 | 45.05 | 33.41 |
| DF | 36.7 | 52.97 | 46.79 | 55.11 | 23.51 | 39.12 |
| PF | 74.93 | 62.41 | 35.34 | 24.64 | 54.81 | 44.06 |
| Enzyme Variables | Soil Variables | Microbial Variables | Topographic Variables | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | CAT (mL∙g−1∙min−1) | INV (mL∙g−1∙min−1) | PRO (mL∙g−1∙24h−1) | URE (mL∙g−1∙24h−1) | SWC (% vol.) | BD (g∙cm−3) | pH | BAC (cfu∙g−1) | ACT (cfu∙g−1) | FUN (cfu∙g−1) | ELE (m) | SLO (°) | ROR (%) |
| WL | 0.17 ± 0.07 a | 1.18 ± 0.04 a | 0.36 ± 0.14 a | 0.4 ± 0.25 a | 25.77 ± 1.1 a | 1.35 ± 0.03 a | 6.21 ± 0.25 a | 0.17 ± 0.07 a | 0.44 ± 0.17 b | 0.36 ± 0.14 a | 235.6 ± 5.04 a | 38 ± 8.36 a | 41 ± 19.1 a |
| SL | 0.05 ±0 a | 0.87 ± 0.1 ab | 0.55 ± 0.15 a | 0.83 ± 0.25 a | 21.57 ± 2.54 ab | 1.44 ± 0.05 a | 7.24 ± 0.32 a | 0.05 ± 0 a | 0.73 ± 0.06 ab | 0.5 ± 0.12 a | 210.17 ± 20.09 a | 33.83 ± 3.81 ab | 49.5 ± 13.66 a |
| STL | 0.09 ± 0.05 a | 0.64 ± 0.1 b | 0.39 ± 0.09 a | 0.52 ± 0.24 a | 18.85 ± 1.05 b | 1.38 ± 0.05 a | 7.42 ± 0.36 a | 0.09 ± 0.05 a | 0.64 ± 0.1 ab | 0.39 ± 0.09 a | 247.17 ± 46.08 a | 33 ± 6.65 ab | 44.33 ± 6.69 a |
| TL | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.89 ± 0.19 ab | 0.49 ± 0.06 a | 0.6 ± 0.2 a | 19.37 ± 1.65 b | 1.5 ± 0.02 a | 6.65 ± 0.44 a | 0.08 ± 0.05 a | 1 ± 0.19 a | 0.49 ± 0.06 a | 237.4 ± 25.9 a | 26.4 ± 8.3 ab | 31.2 ± 10.29 a |
| DF | 0.12 ± 0.09 a | 0.81 ± 0.1 b | 0.52 ± 0.08 a | 0.94 ± 0.16 a | 17.36 ± 1.03 b | 1.39 ± 0.06 a | 7.15 ± 0.32 a | 0.14 ± 0.09 a | 1.08 ± 0.14 a | 0.62 ± 0.08 a | 201.33 ± 18.78 a | 7 ± 7 bc | 44.5 ± 11.36 a |
| PF | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.68 ± 0.02 b | 0.44 ± 0.01 a | 0.68 ± 0.22 a | 27.34 ± 3.63 a | 1.49 ± 0.05 a | 7.63 ± 0.27 a | 0.14 ± 0.05 a | 1.01 ± 0.16 a | 0.64 ± 0.2 a | 171.6 ± 12.06 a | 0 ± 0 c | 0 ± 0 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, C.; Zhong, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Z. Biotic and Abiotic Factors Affecting Soil C, N, P and Their Stoichiometries under Different Land-Use Types in a Karst Agricultural Watershed, China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071083
Hu G, Huang X, Chen S, Hu C, Zhong C, Xu C, Zhang Z. Biotic and Abiotic Factors Affecting Soil C, N, P and Their Stoichiometries under Different Land-Use Types in a Karst Agricultural Watershed, China. Agriculture. 2024; 14(7):1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071083
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Gang, Xiaoxing Huang, Siyu Chen, Cong Hu, Chaofang Zhong, Chaohao Xu, and Zhonghua Zhang. 2024. "Biotic and Abiotic Factors Affecting Soil C, N, P and Their Stoichiometries under Different Land-Use Types in a Karst Agricultural Watershed, China" Agriculture 14, no. 7: 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071083
APA StyleHu, G., Huang, X., Chen, S., Hu, C., Zhong, C., Xu, C., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Biotic and Abiotic Factors Affecting Soil C, N, P and Their Stoichiometries under Different Land-Use Types in a Karst Agricultural Watershed, China. Agriculture, 14(7), 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071083





