The Combined Effect of Two Alternaria Mycotoxins (Alternariol and Alternariol Monomethyl Ether) on Porcine Epithelial Intestinal Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
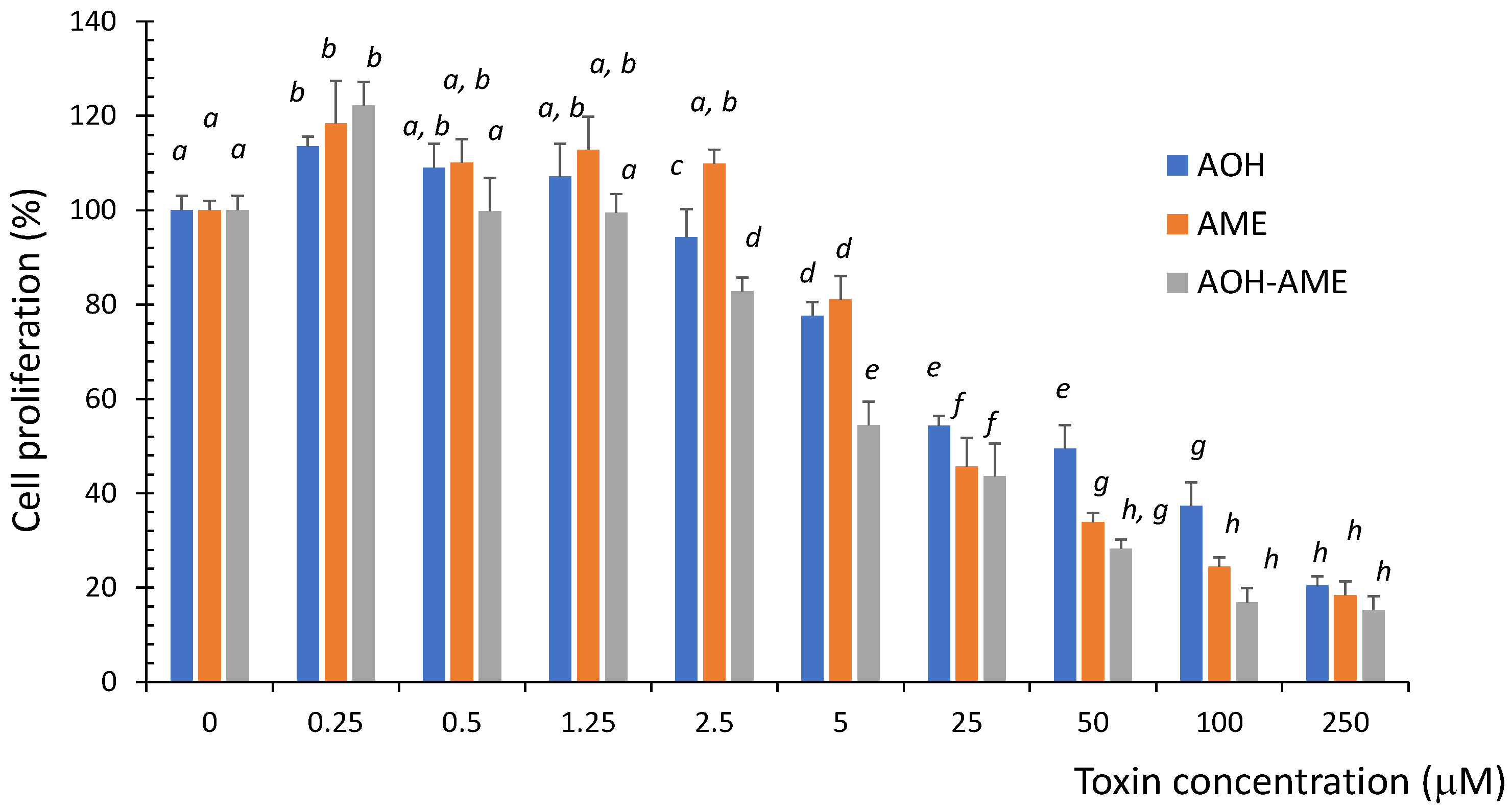
3.1. Effects of AOH, AME, and a Combination of the Two on IPEC-1 Cell Viability
3.2. Types of Interactions between Mycotoxins Related to IPEC-1 Cell Viability
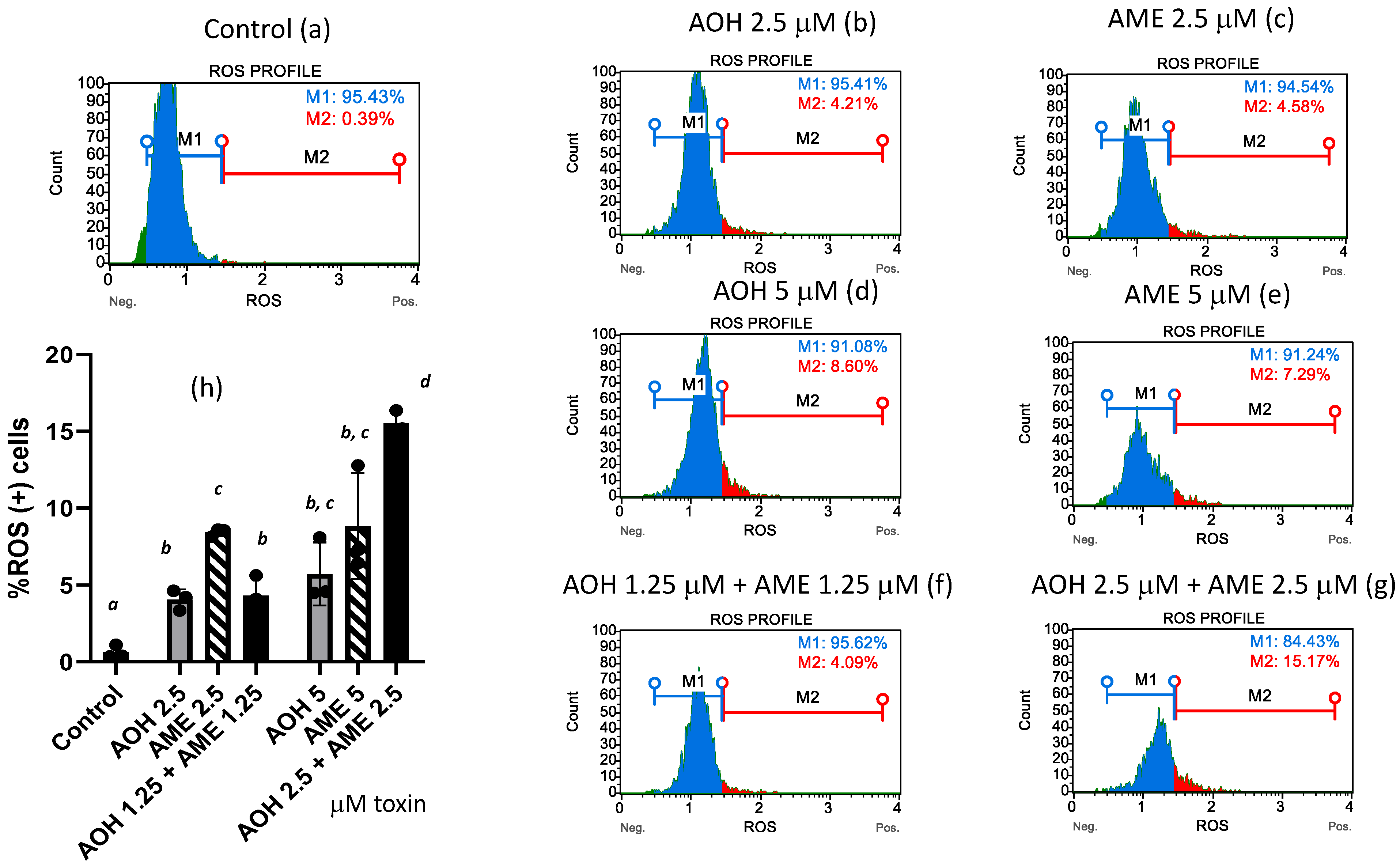
3.3. Effects of AOH, AME, and Combinations Thereof on Reactive Oxygen Species
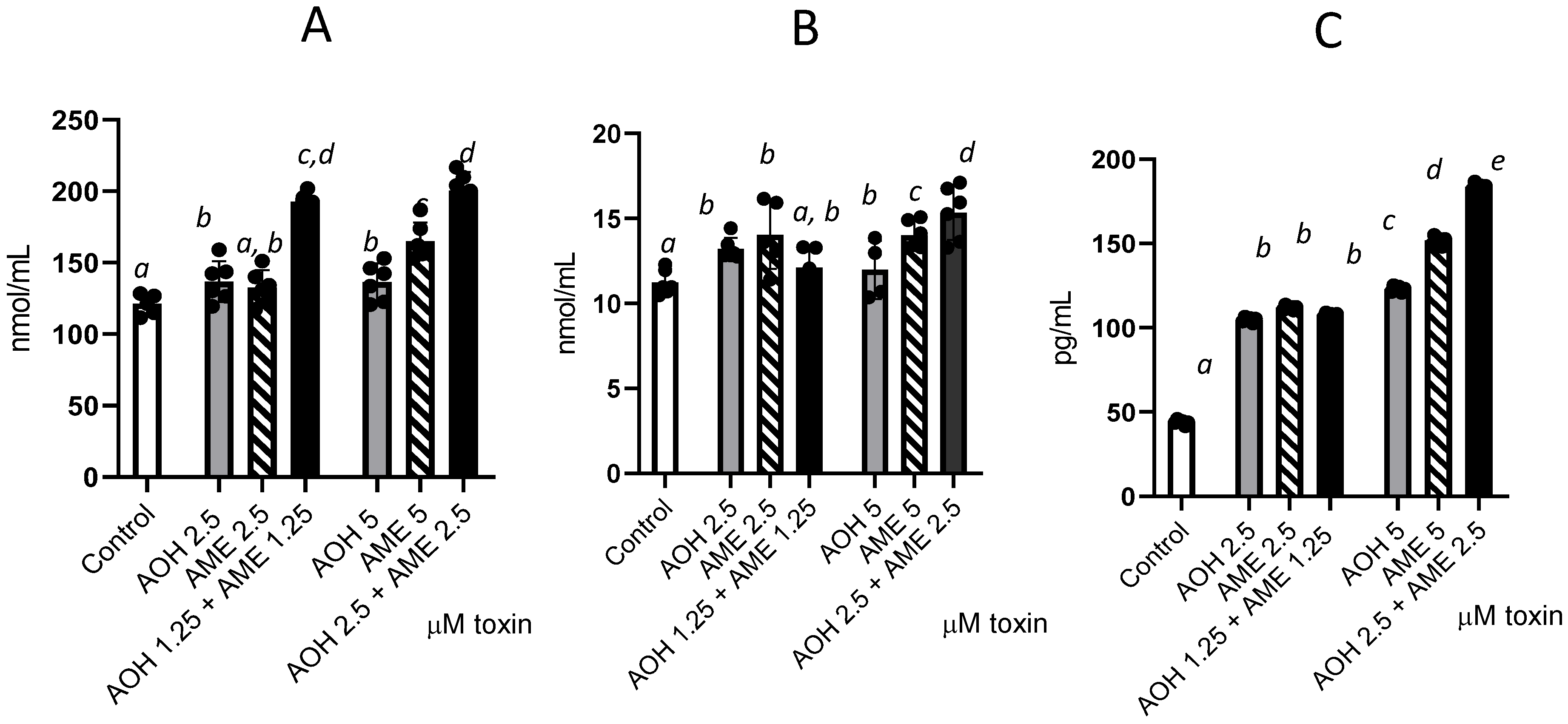
3.4. Effects of AOH, AME, and Their Combinations on Protein, Lipid, and DNA Oxidation
3.5. Effects of AOH, AME, and a Combination of the Two on Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in IPEC-1 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miranda-Apodaca, J.; Artetxe, U.; Aguado, I.; Martin-Souto, L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Lacuesta, M.; Becerril, J.M.; Estonba, A.; Ortiz-Barredo, A.; Hernández, A.; et al. Stress response to climate change and postharvest handling in two differently pigmented lettuce genotypes: Impact on alternaria alternata invasion and mycotoxin production. Plants 2023, 12, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, R. Alternaria allergy and immunotherapy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagda, A.; Meena, M. Alternaria mycotoxins in food and feed: Occurrence, biosynthesis, toxicity, analytical methods, control and detoxification strategies. Food Control 2024, 158, 110211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hollander, D.; Holvoet, C.; Demeyere, K.; De Zutter, N.; Audenaert, K.; Meyer, E.; Croubels, S. Cytotoxic effects of alternariol, alternariol monomethyl-ether, and tenuazonic acid and their relevant combined mixtures on human enterocytes and hepatocytes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 849243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, E.; Schwab, C.; Sulyok, M.; Naehrer, K.; Krska, R.; Schatzmayr, G. Multi-mycotoxin screening reveals the occurrence of 139 different secondary metabolites in feed and feed ingredients. Toxins 2013, 5, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Shao, B.; Yang, D.; Li, F.; Zhu, J. Natural occurrence of alternaria toxins in wheat-based products and their dietary exposure in china. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvača, N.; Avantaggiato, G.; Merkuri, J.; Vuković, G.; Bursić, V.; Cara, M. Occurrence and determination of alternaria mycotoxins alternariol, alternariol monomethyl ether, and tentoxin in wheat grains by quechers method. Toxins 2022, 14, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of alternaria toxins in feed and food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudo, F.; Hong, C.; Varga, E.; Del Favero, G.; Marko, D. Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of the alternaria mycotoxin alternariol in combination with the process contaminant acrylamide. Toxins 2023, 15, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, C.; Ellmer, D.; Mikula, H.; Pahlke, G.; Warth, B.; Gehrke, H.; Zimmermann, K.; Heiss, E.; Fröhlich, J.; Marko, D. Impact of phase i metabolism on uptake, oxidative stress and genotoxicity of the emerging mycotoxin alternariol and its monomethyl ether in esophageal cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Kozieł, M.J.; Urbanek, K.A.; Habrowska-Górczyńska, D.E.; Domińska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Estrogen receptor β participates in alternariol-induced oxidative stress in normal prostate epithelial cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvača, N.; Tanasković, S.; Bursić, V.; Petrović, A.; Merkuri, J.; Shtylla Kika, T.; Marinković, D.; Vuković, G.; Cara, M. Optical characterization of Alternaria spp. Contaminated wheat grain and its influence in early broilers nutrition on oxidative stress. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speijers, G.J.; Speijers, M.H. Combined toxic effects of mycotoxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensassi, F.; Gallerne, C.; Sharaf el dein, O.; Hajlaoui, M.R.; Bacha, H.; Lemaire, C. Combined effects of alternariols mixture on human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Blanco, C.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Role of quercetin on caco-2 cells against cytotoxic effects of alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 89, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Jia, B.; Wu, A. Cytotoxicities of co-occurring alternariol, alternariol monomethyl ether and tenuazonic acid on human gastric epithelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 171, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holanda, D.M.; Kim, S.W. Mycotoxin occurrence, toxicity, and detoxifying agents in pig production with an emphasis on deoxynivalenol. Toxins 2021, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, B.; Rainer, V.; Sulyok, M.; Haltrich, D.; Schatzmayr, G.; Mayer, E. Twenty-eight fungal secondary metabolites detected in pig feed samples: Their occurrence, relevance and cytotoxic effects in vitro. Toxins 2019, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Bulgaru, V.C.; Pertea, A.; Grosu, I.A.; Pistol, G.C.; Taranu, I. Alternariol monomethyl-ether induces toxicity via cell death and oxidative stress in swine intestinal epithelial cells. Toxins 2024, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Bulgaru, C.V.; Taranu, I. Cytotoxic and inflammatory effects of individual and combined exposure of hepg2 cells to zearalenone and its metabolites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babič, J.; Tavčar-Kalcher, G.; Celar, F.A.; Kos, K.; Knific, T.; Jakovac-Strajn, B. Occurrence of alternaria and other toxins in cereal grains intended for animal feeding collected in slovenia: A three-year study. Toxins 2021, 13, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yoshizawa, T. Alternaria mycotoxins in weathered wheat from china. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2920–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.J.; Macáková, P.; Juan-García, A.; Font, G. Cytotoxic effects of mycotoxin combinations in mammalian kidney cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiltunen, M.; Söderhäll, K. Alternatiol-o-methyltransferase fromalternaria alternata: Partial purification and relation to polyketide synthesis. Exp. Mycol. 1992, 16, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.; Zeidan, R.; Abu-Dieyeh, M. The characteristics, occurrence, and toxicological effects of alternariol: A mycotoxin. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 1659–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudo, F.; Varga, E.; Aichinger, G.; Galaverna, G.; Marko, D.; Dall’Asta, C.; Dellafiora, L. Co-occurrence and combinatory effects of alternaria mycotoxins and other xenobiotics of food origin: Current scenario and future perspectives. Toxins 2019, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Bulgaru, C.V.; Anghel, C.A.; Pistol, G.C.; Dore, M.I.; Palade, M.L.; Taranu, I. Grape seed waste counteracts aflatoxin b1 toxicity in piglet mesenteric lymph nodes. Toxins 2020, 12, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Hogan, S.P. Intestinal barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 3–20; quiz 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.-P.-P.; Mohd-Redzwan, S. Mycotoxin: Its impact on gut health and microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrivá, L.; Oueslati, S.; Font, G.; Manyes, L. Alternaria mycotoxins in food and feed: An overview. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 1569748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, C.; Cenk, E.; Marko, D. The alternaria mycotoxin alternariol triggers the immune response of il-1β-stimulated, differentiated caco-2 cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Martorell, M.; González-Contreras, C.; Villagran, M.; Mardones, L.; Tynybekov, B.; Docea, A.O.; Abdull Razis, A.F.; Modu, B.; Calina, D.; et al. An updated overview of anticancer effects of alternariol and its derivatives: Underlying molecular mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1099380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhaug, A.; Vines, L.L.; Ivanova, L.; Spilsberg, B.; Holme, J.A.; Pestka, J.; Collins, A.; Eriksen, G.S. Mechanisms involved in alternariol-induced cell cycle arrest. Mutat. Res./Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2012, 738–739, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessel-Pras, S.; Kieshauer, J.; Roenn, G.; Luckert, C.; Braeuning, A.; Lampen, A. In vitro characterization of hepatic toxicity of alternaria toxins. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Blanco, C.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Oxidative stress of alternariol in caco-2 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejdovszky, K.; Sack, M.; Jarolim, K.; Aichinger, G.; Somoza, M.M.; Marko, D. In vitro combinatory effects of the alternaria mycotoxins alternariol and altertoxin ii and potentially involved mirnas. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 267, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Blanco, C.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Oxidative DNA damage and disturbance of antioxidant capacity by alternariol in caco-2 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 235, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, C.; Fehr, M.; Schwarz, C.; Baechler, S.; Domnanich, K.; Böttler, U.; Pahlke, G.; Marko, D. Modulation of the cellular redox status by the alternaria toxins alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 216, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ros) revisited: Outlining their role in biological macromolecules (DNA, lipids and proteins) and induced pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, M.; Pahlke, G.; Fritz, J.; Christensen, M.O.; Boege, F.; Altemöller, M.; Podlech, J.; Marko, D. Alternariol acts as a topoisomerase poison, preferentially affecting the iiα isoform. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination of reactive oxygen species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nossol, C.; Barta-Böszörményi, A.; Kahlert, S.; Zuschratter, W.; Faber-Zuschratter, H.; Reinhardt, N.; Ponsuksili, S.; Wimmers, K.; Diesing, A.K.; Rothkötter, H.J. Comparing Two Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cell Lines (IPECs): Morphological Differentiation, Function and Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| Cell Viability | CI Value * | Toxin Concentration (μM) | DRI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOH | AME | AOH | AME | ||
| fa = 0.25 (IL25) | 0.51 | 170.1 | 96.3 | 5.3 | 3.03 |
| fa = 0.5 (IL50) | 0.33 | 43.2 | 38.5 | 6.36 | 5.67 |
| fa = 0.75 (IL75) | 0.22 | 10.9 | 15.4 | 7.55 | 10.6 |
| fa = 0.9 (IL90) | 0.16 | 2.7 | 6.1 | 8.96 | 19.8 |
| Drug/Combo | Dm | m | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| AOH | 43.2 | −0.80 | −0.973 |
| AME | 38.5 | −1.19 | −0.923 |
| AOH + AME | 13.59 | −0.71 | −0.957 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marin, D.E.; Grosu, I.A.; Pistol, G.C.; Bulgaru, C.V.; Pertea, A.M.; Taranu, I. The Combined Effect of Two Alternaria Mycotoxins (Alternariol and Alternariol Monomethyl Ether) on Porcine Epithelial Intestinal Cells. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091478
Marin DE, Grosu IA, Pistol GC, Bulgaru CV, Pertea AM, Taranu I. The Combined Effect of Two Alternaria Mycotoxins (Alternariol and Alternariol Monomethyl Ether) on Porcine Epithelial Intestinal Cells. Agriculture. 2024; 14(9):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091478
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarin, Daniela Eliza, Iulian Alexandru Grosu, Gina Cecilia Pistol, Cristina Valeria Bulgaru, Ana Maria Pertea, and Ionelia Taranu. 2024. "The Combined Effect of Two Alternaria Mycotoxins (Alternariol and Alternariol Monomethyl Ether) on Porcine Epithelial Intestinal Cells" Agriculture 14, no. 9: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091478
APA StyleMarin, D. E., Grosu, I. A., Pistol, G. C., Bulgaru, C. V., Pertea, A. M., & Taranu, I. (2024). The Combined Effect of Two Alternaria Mycotoxins (Alternariol and Alternariol Monomethyl Ether) on Porcine Epithelial Intestinal Cells. Agriculture, 14(9), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091478









