Gini Coefficient-Based Feature Learning for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Classification with Compact Polarimetric SAR Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We extend the polarimetric decomposition method of specific CP modes to that of GCP mode and extract the GCP decomposition parameters to provide more abundant CP information for CP SAR cross-domain classification.
- (2)
- This study comprehensively explores the potential of multi-mode GCP SAR data in cross-domain classification and realizes the stable description of targets in different domains by GCP features. Furthermore, based on the proposed method, we extract optimal CP feature parameters that contribute to the feature classification effect of both the source and target domains and enhance the alignment effect of feature parameters in domain adaptation methods.
- (3)
- Based on the proposed stable and robust method, four types of unsupervised cross-domain image classification are carried out. This includes cross-domain classification of GCP data from different sensors over the same area, GCP data acquired over different areas, FP + GCP data over different areas, and FP + GCP data over different crop types.
- (4)
- In the land-cover classification of PolSAR, most of the studies only consider the FP information without considering the partial polarimetric information, such as the CP information. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work in which we combine FP and CP features for cross-domain classification and realize high-precision cross-data source, cross-scene, and cross-crop type image classification based on the multi-mode GCP SAR and FP + GCP SAR features, respectively.
2. Study Area and Data Collection
2.1. Study Area
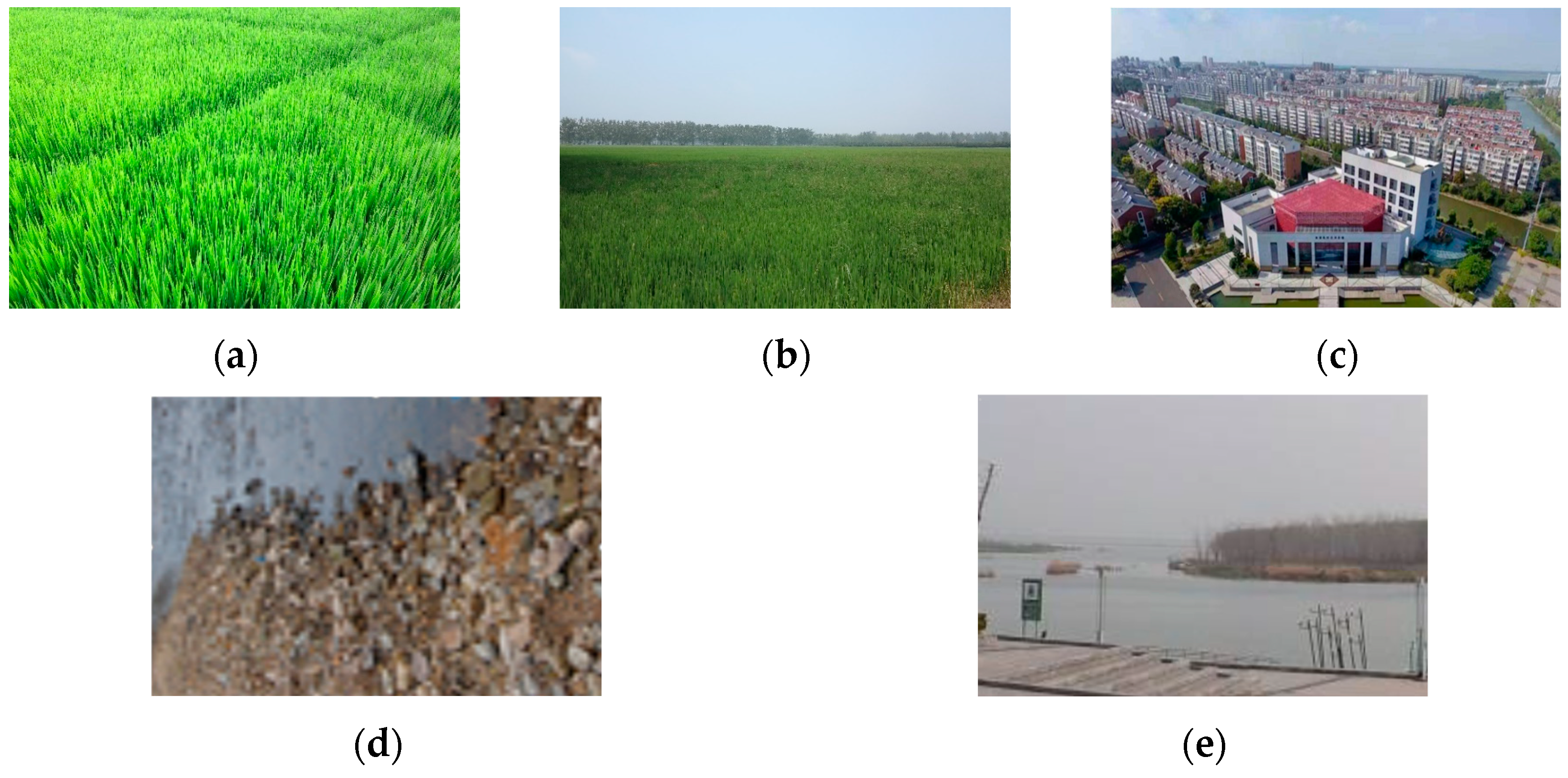
2.2. Data Collection
3. Methodology
3.1. FP/GCP SAR Feature Extraction
3.1.1. GCP SAR Data
3.1.2. GCP Decomposition Parameters
- (1)
- GCP H/α decomposition
- (2)
- GCP m-χ and m-δ decomposition
- (3)
- GCP m-αs decomposition
3.1.3. FP SAR Feature Parameters
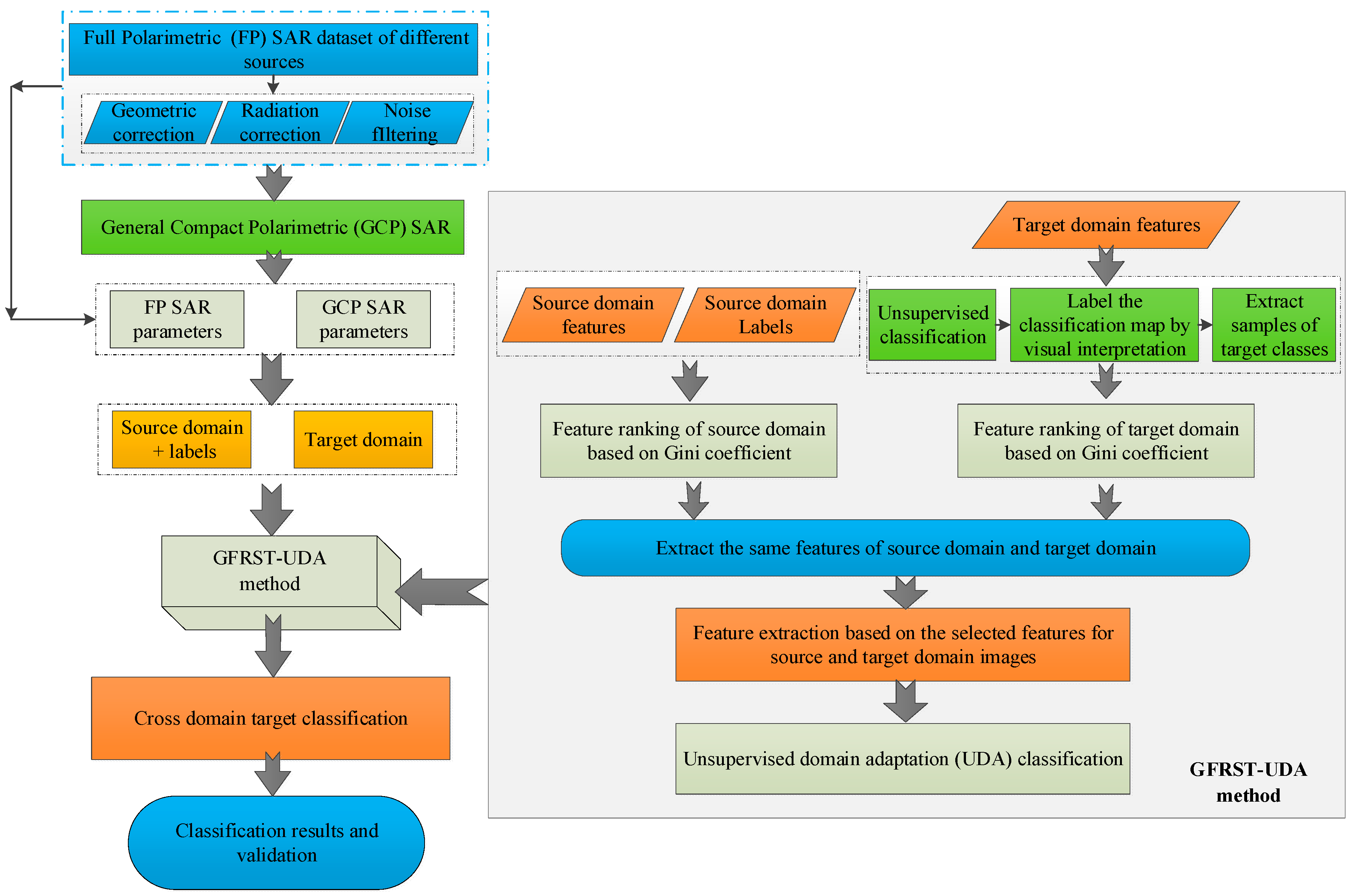
3.2. GFRST-UDA Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Cross-Domain Image Classification Based on the GCP SAR Images
4.1.1. Images from Different Sensors over the Same Area
- (1)
- GFRST feature selection
- (2)
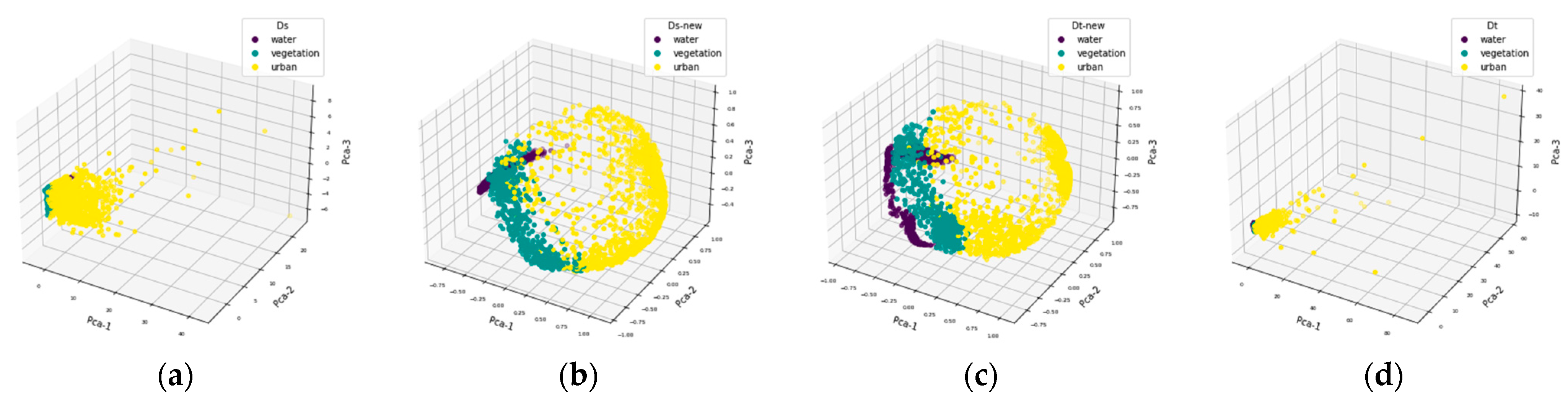
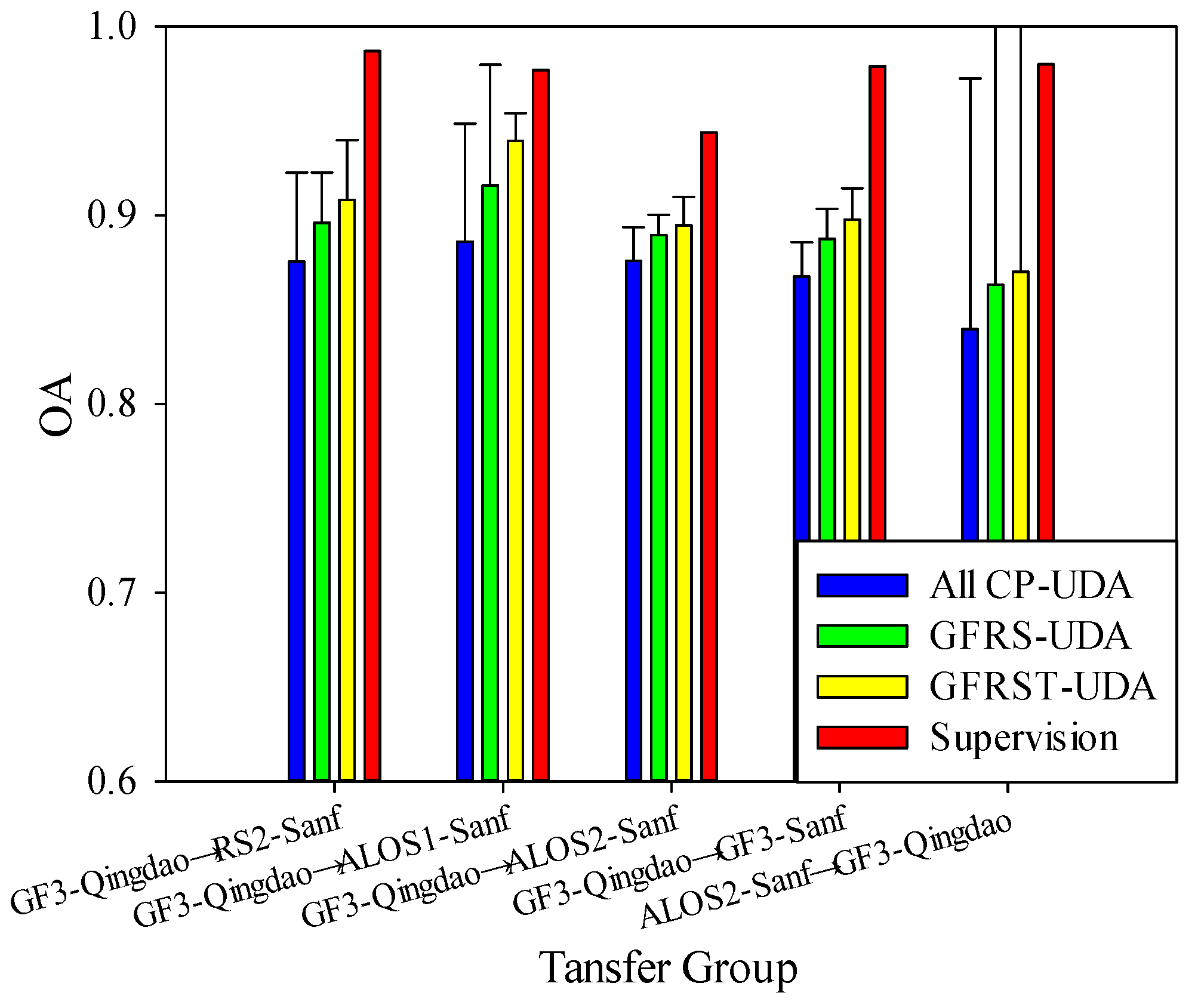
- Evaluation of cross-domain classification results based on the GFRST-UDA method
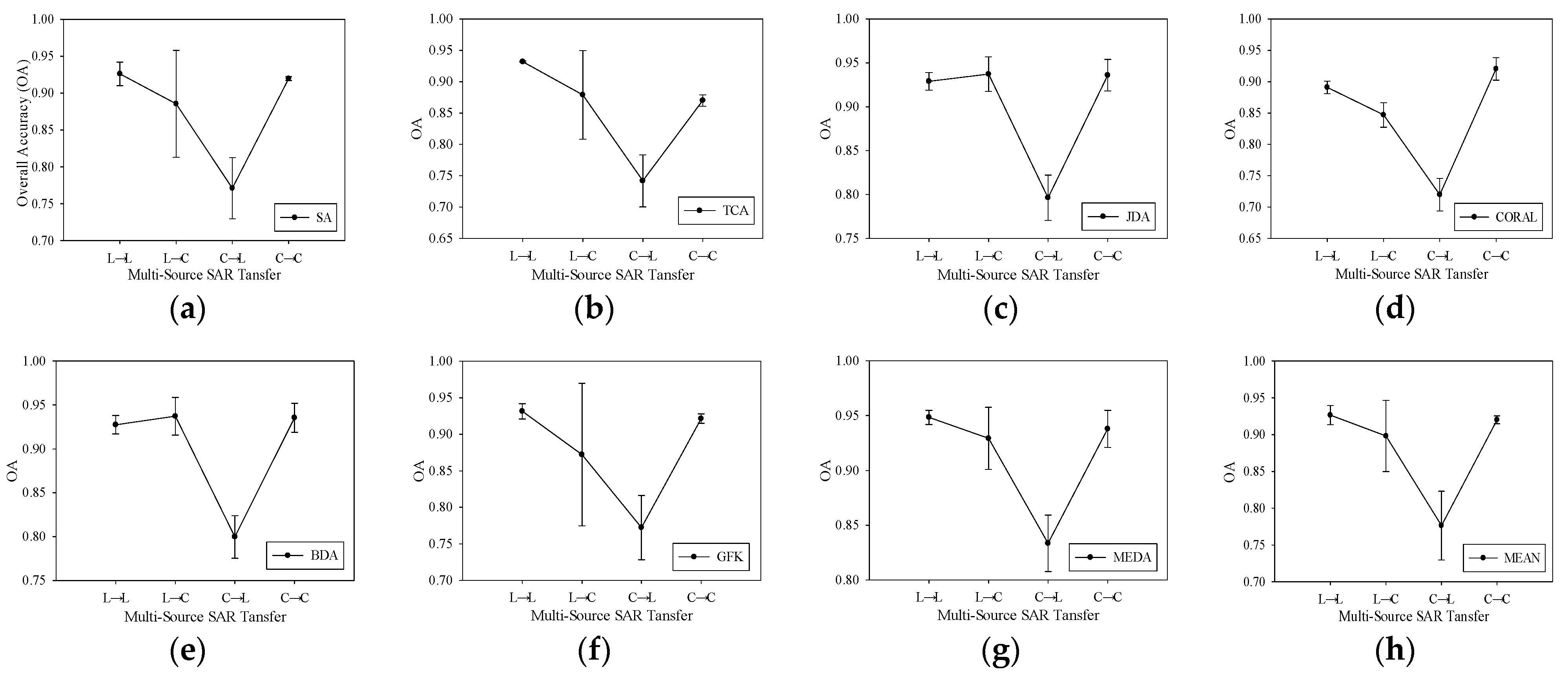
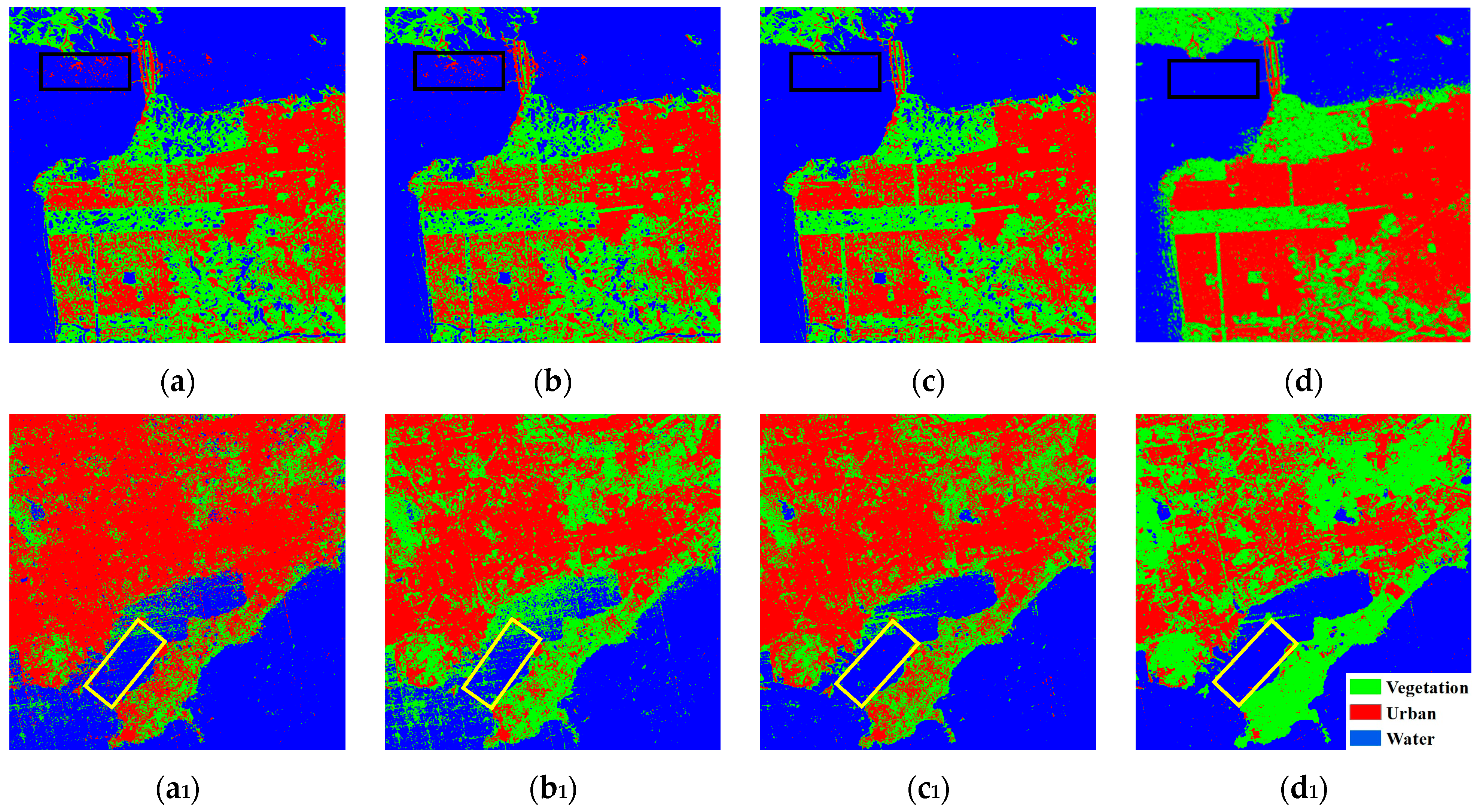
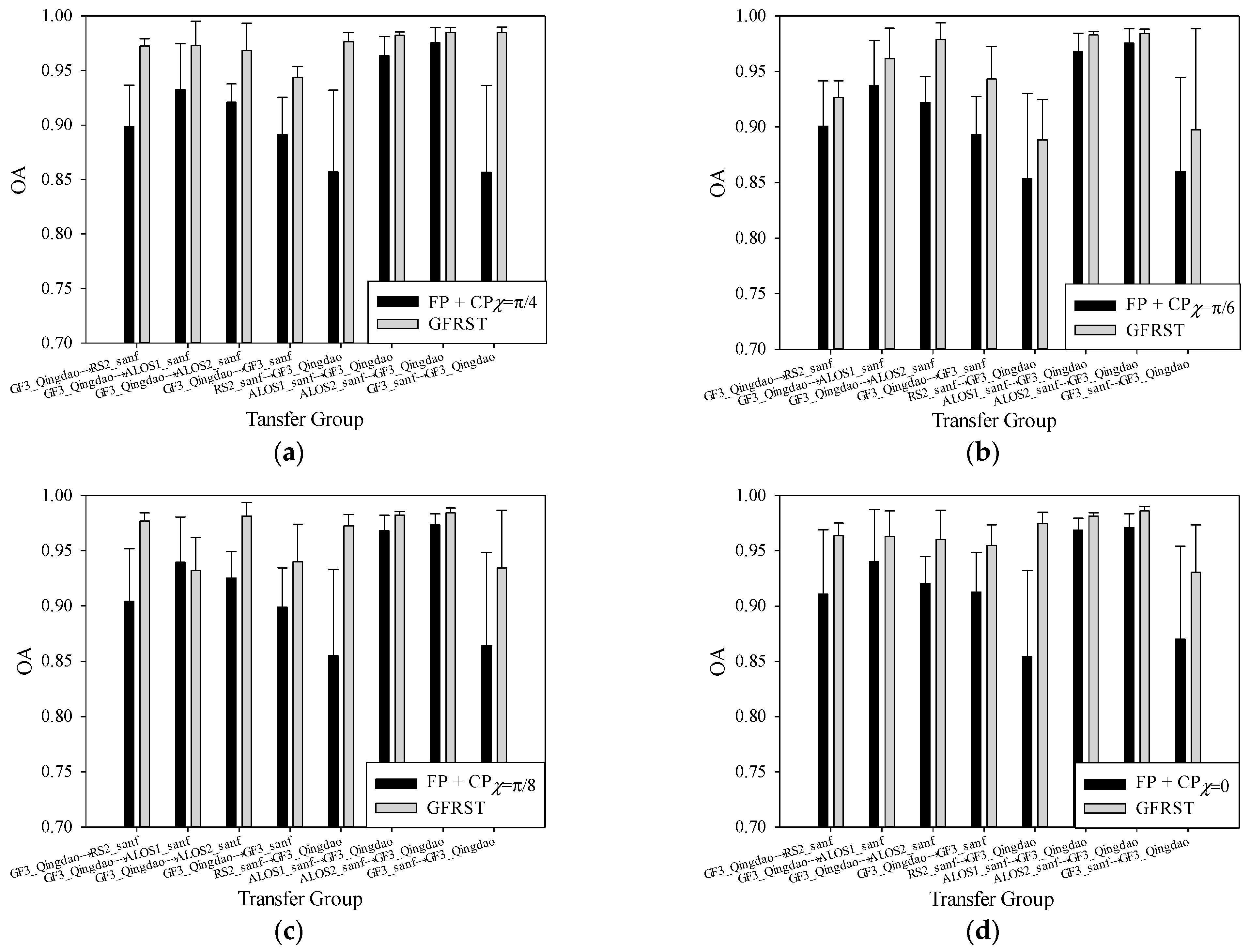
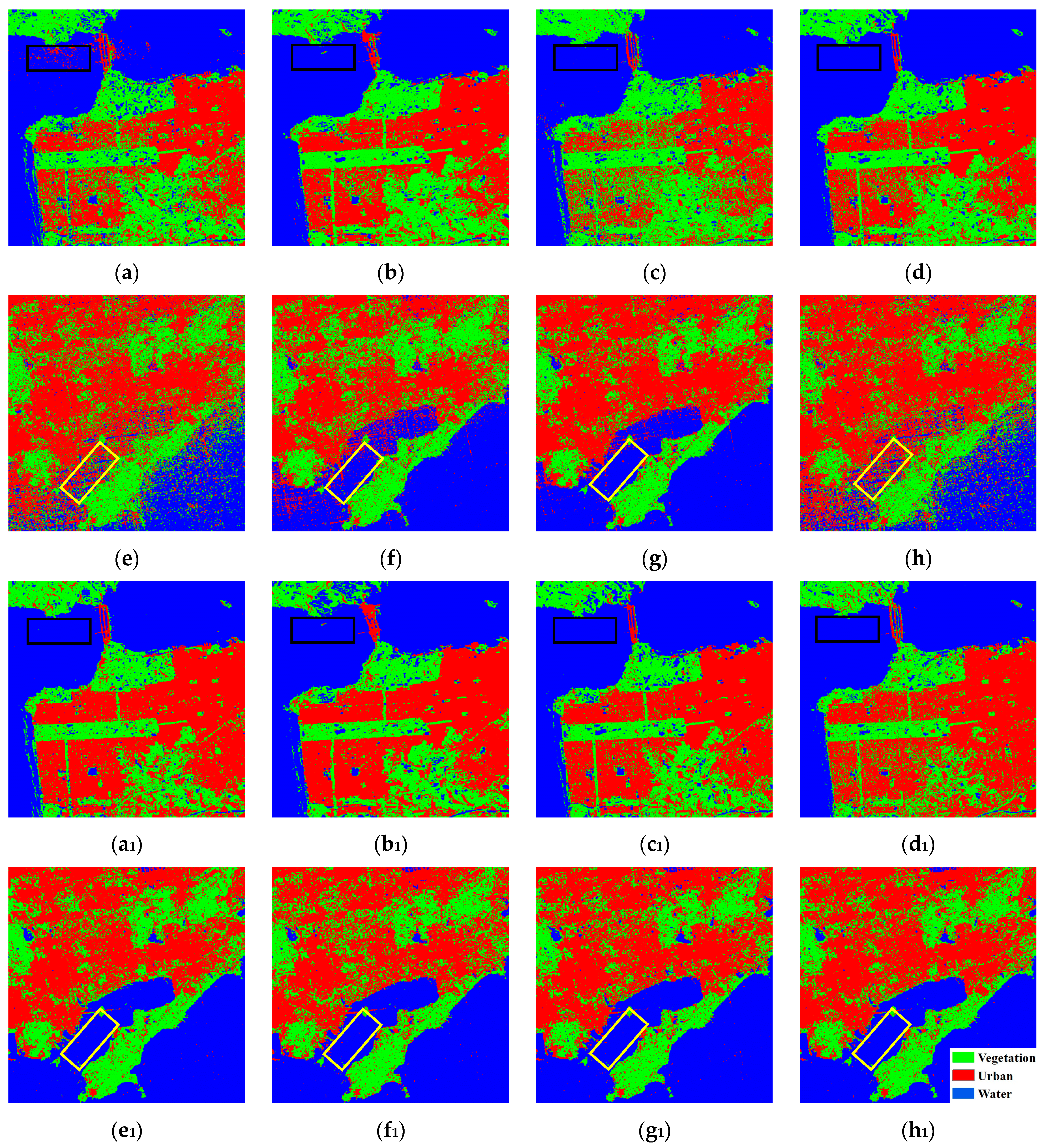
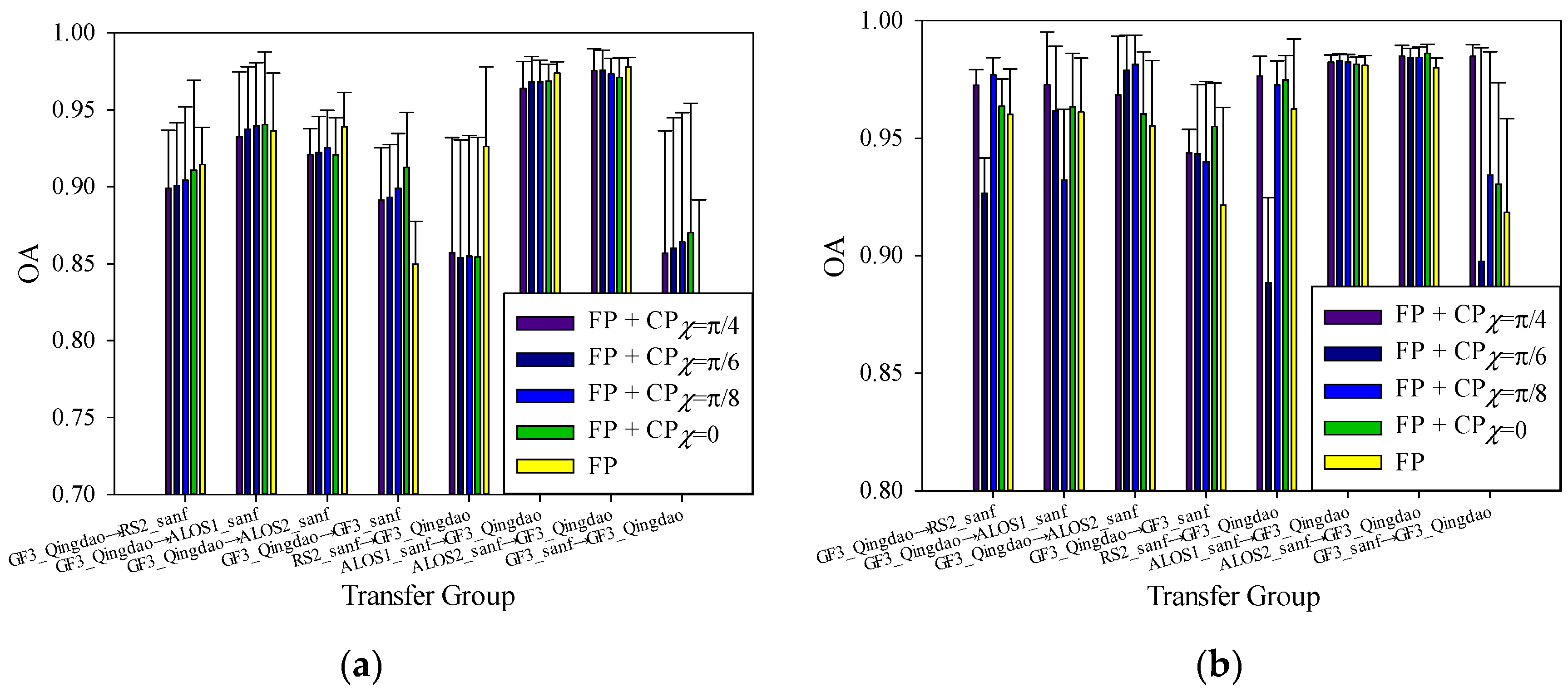
4.1.2. Images Acquired over Different Areas
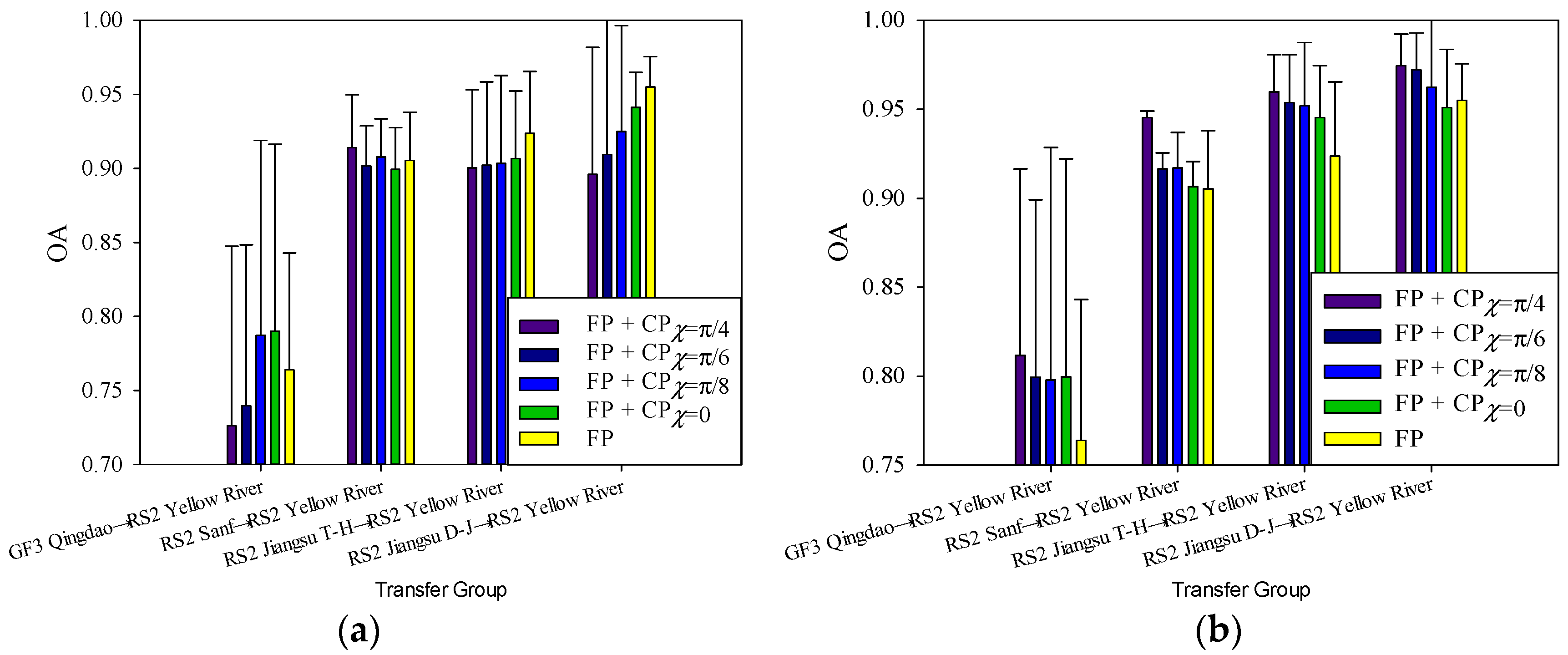
4.2. Cross-Domain Image Classification Based on the FP + GCP SAR Images
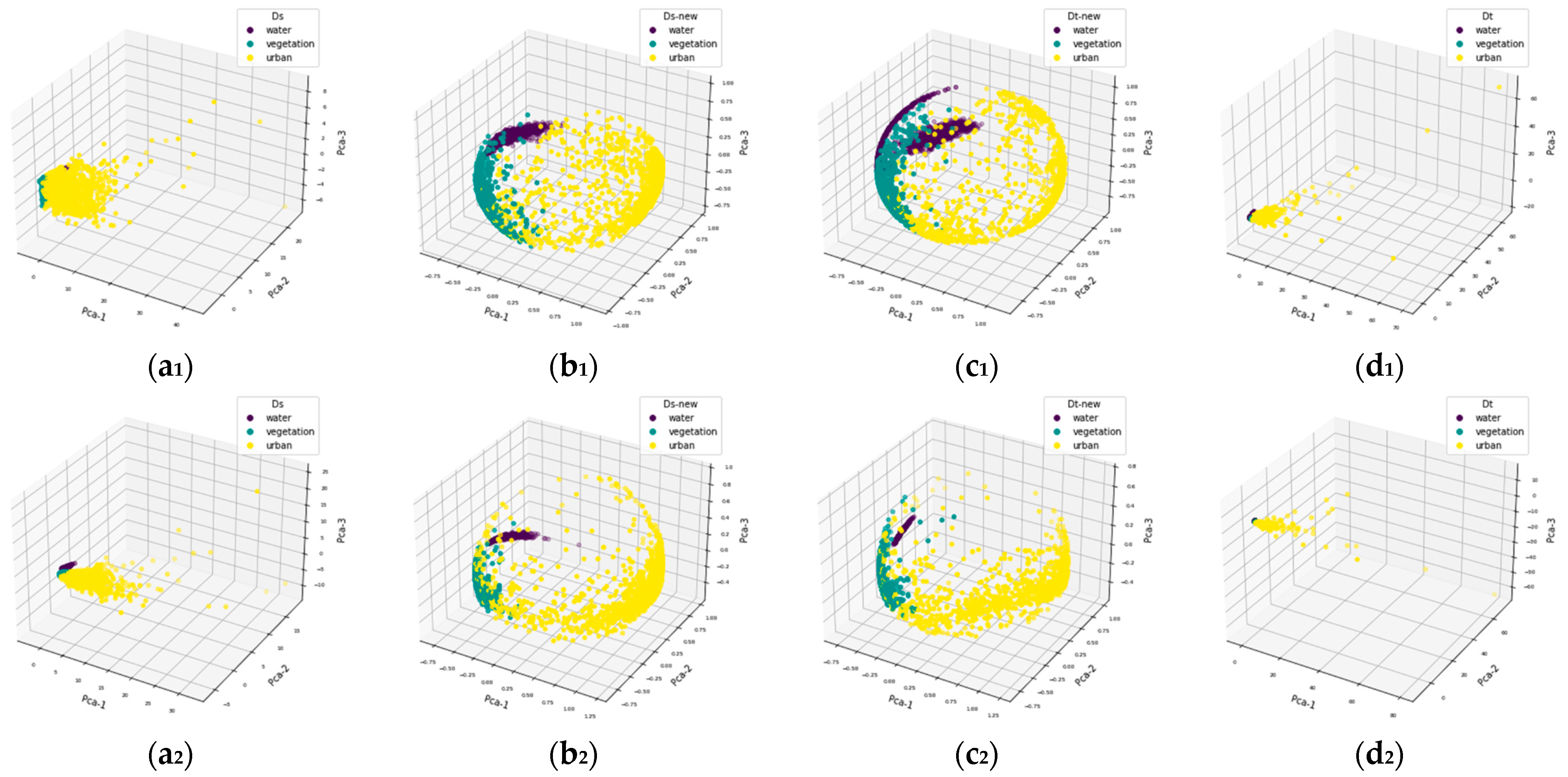
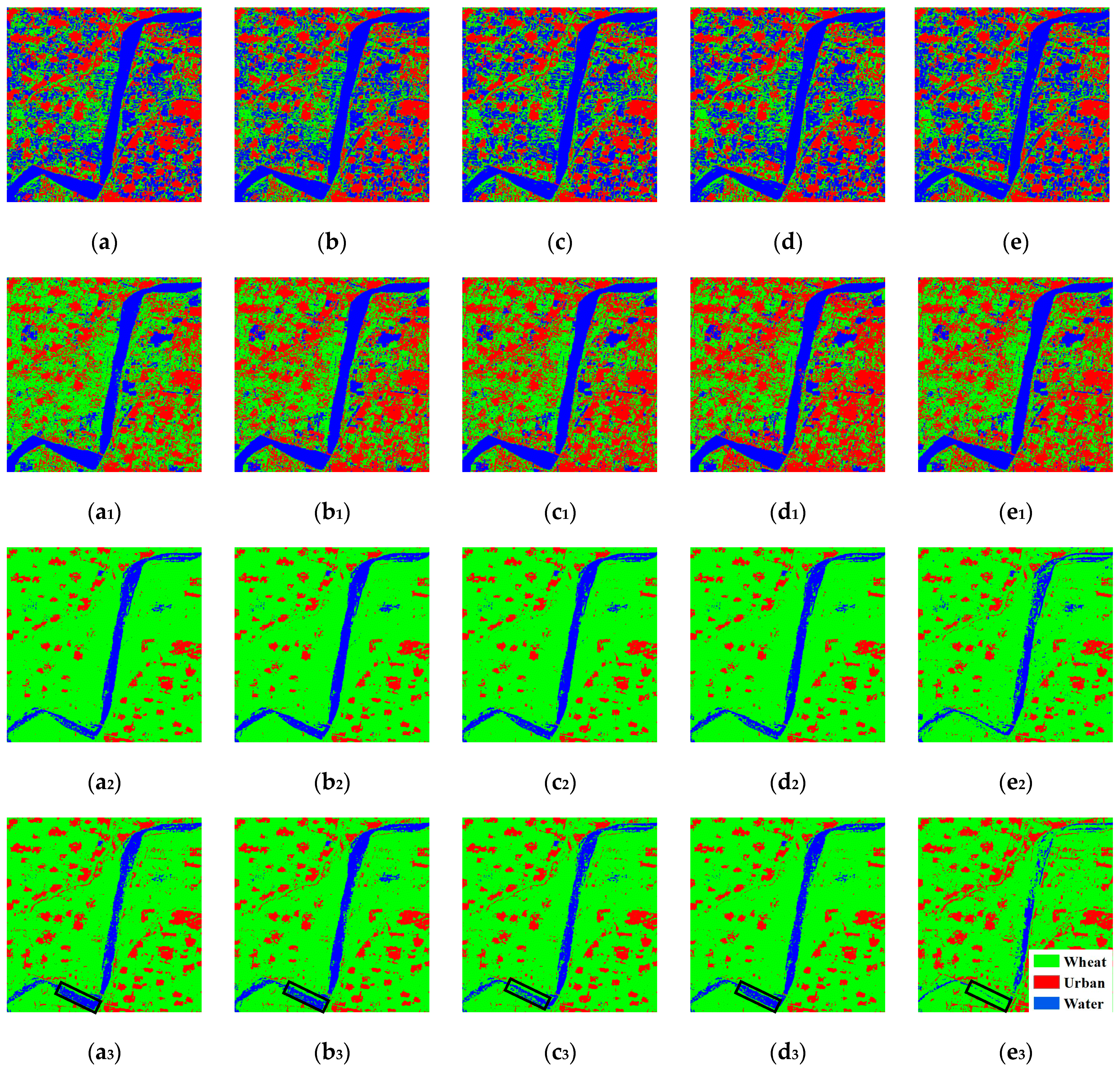
4.2.1. Cross-Scene Image Classification
4.2.2. Cross-Crop Type Image Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Sato, A.; Boerner, W.M.; Sato, R.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering power decomposition with rotation of coherency matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souyris, J.C.; Imbo, P.; Fjortoft, R.; Mingot, S.; Lee, J.S. Compact polarimetry based on symmetry properties of geophysical media: The/spl pi//4 mode. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souyris, J.C.; Mingot, S. Polarimetry based on one transmitting and two receiving polarizations: The π/4 mode. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 629–631. [Google Scholar]
- Stacy, N.; Preiss, M. Compact polarimetric analysis of X-band SAR data. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, EUSAR, Dresden, Germany, 16–18 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Raney, R.K. Dual-polarized SAR and stokes parameters. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K. Hybrid-Polarity SAR Architecture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3397–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, J. Target Decomposition Based on Symmetric Scattering Model for Hybrid Polarization SAR Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Yang, J. Formalism of Compact Polarimetric Descriptors and Extension of the ΔαB/αB Method for General Compact-Pol SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10322–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, L. Oil Spill Discrimination by Using General Compact Polarimetric SAR Features. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K.; Cahil, J.T.S.; Patterson, G.W.; Bussey, D.B.J. The M-Chi decomposition of hybrid dual-polarimetric radar data. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 5093–5096. [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau, F.J.; Brisco, B.; Raney, R.K.; McNairn, H.; Liu, C.; Vachon, P.W.; Shang, J.; DeAbreu, R.; Champagne, C.; Merzouki, A.; et al. Compact polarimetry overview and applications assessment. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, S298–S315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.; Goodenough, D.; Chen, H. Compact decomposition theory. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yin, J.; Li, K.; Yang, J. Fine Classification of Rice Paddy Based on RHSI-DT Method Using Multi-Temporal Compact Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yin, J.; Li, K.; Yang, J.; Shao, Y. Scattering Intensity Analysis and Classification of Two Types of Rice Based on Multi-Temporal and Multi-Mode Simulated Compact Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Xu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, L.; Pu, F. Statistical scattering component-based subspace alignment for unsupervised cross-domain PolSAR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 5449–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Persello, C.; Bruzzone, L. Domain adaptation for the classification of remote sensing data: An overview of recent advances. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Li, B.; Ye, Y. Cross-domain collaborative learning via cluster canonical correlation analysis and random walker for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 3952–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Deng, X.; Ma, X.; Jiang, W. Transfer learning for SAR image classification via deep joint distribution adaptation networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5377–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouw, W.M.; Loog, M. An Introduction to Domain Adaptation and Transfer Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.11806. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Shi, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, G.; Zhang, L. Generating annual high resolution land cover products for 28 metropolises in China based on a deep super-resolution mapping network using Landsat imagery. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 2036–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, P.; Sun, K. A Novel Deep Forest-Based Active Transfer Learning Method for PolSAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep visual domain adaptation: A survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Mura, M.; Prasad, S.; Pacifici, F.; Gamba, P.; Chanussot, J. Challenges and opportunities of multimodality and Data Fusion in Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd European Signal Processing Conference, EUSIPCO, Lisbon, Portugal, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kouw, W.M.; Loog, M. A Review of Domain Adaptation without Target Labels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 766–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamishima, T.; Hamasaki, M.; Akaho, S. TrBagg: A Simple Transfer Learning Method and its Application to Personalization in Collaborative Tagging. In Proceedings of the 2009 Ninth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 6–9 December 2009; pp. 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, J.; Hoffman, J.; Rodner, E.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation with Instance Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 668–675. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.A.; da Silva Torres, R. Semi-supervised transfer subspace for domain adaptation. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 75, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Pasolli, E.; Emery, W. Using active learning to adapt remote sensing image classifiers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2232–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matasci, G.; Volpi, M.; Kanevski, M.; Bruzzone, L.; Tuia, D. Semi-supervised transfer component analysis for domain adaptation in remote sensing image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3550–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.J.; Tsang, I.W.; Kwok, J.T.; Yang, Q. Domain Adaptation via Transfer Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Xu, D.; Tsang, I.W. Domain Adaptation from Multiple Sources: A Domain-Dependent Regularization Approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, E.; Bazi, Y.; Melgani, F.; Alhichri, H.; Alajlan, N.; Zuair, M. Domain Adaptation Network for Cross-Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4441–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Ogunbona, P. Joint Geometrical and Statistical Alignment for Visual Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5150–5158. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Yang, J.; Li, P.; Sun, W.; Liu, W. A Novel Relational-Based Transductive Transfer Learning Method for PolSAR Images via Time-Series Clustering. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Q. Adversarial deep domain adaptation for multi-band SAR images classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78571–78583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, L.; He, Q.; Kuang, G. Pixel-Level and Feature-Level Domain Adaptation for Heterogeneous SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Qiu, X.; Yu, W.; Xu, F. Simulation-assisted SAR target classification based on unsupervised domain adaptation and model interpretability analysis. J. Radars 2022, 11, 168–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.; Luo, Y. Transferable SAR image classification crossing different satellites under open set condition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Si, L.; Qiang, W.; Miao, W.; Zheng, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. A Polarimetric Scattering Characteristics-Guided Adversarial Learning Approach for Unsupervised PolSAR Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Liu, L.; Sun, N.; Jin, X. A CA_Based Weighted Clustering Adversarial Network for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, Y.B.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, S.X.; Xing, M.D.; He, W. Applying H/α decomposition to compact polarimetric SAR. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2012, 6, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, C.; Wu, F.; Zhang, B. Investigation of the capability of H-α decomposition of compact polarimetric SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, J. Symmetric scattering model based feature extraction from general compact polarimetric sar imagery. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 1703–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Moon, W.M.; Yang, J. Novel model-based method for identification of scattering mechanisms in polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ishido, M.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, X.S.; Sato, M. Uniform polarimetric matrix rotation theory and its applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 4756–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, B.; Habrard, A.; Sebban, M.; Tuytelaars, T. Subspace Alignment For Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Wang, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J.; Yu, P. Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2200–2207. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Feng, J.; Saenko, K. Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Hao, S.; Feng, W.; Shen, Z. Balanced Distribution Adaptation for Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–21 November 2017; pp. 1129–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, B.; Shi, Y.; Sha, F.; Grauman, K. Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2066–2073. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Huang, M.; Yu, P.S. Visual Domain Adaptation with Manifold Embedded Distribution Alignment. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 402–410. [Google Scholar]
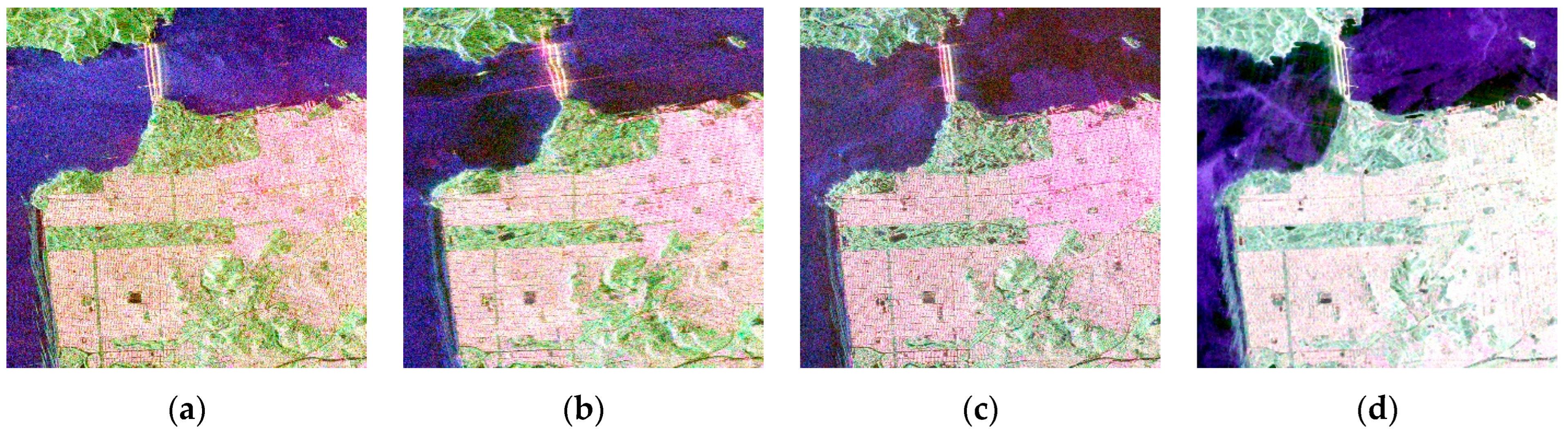
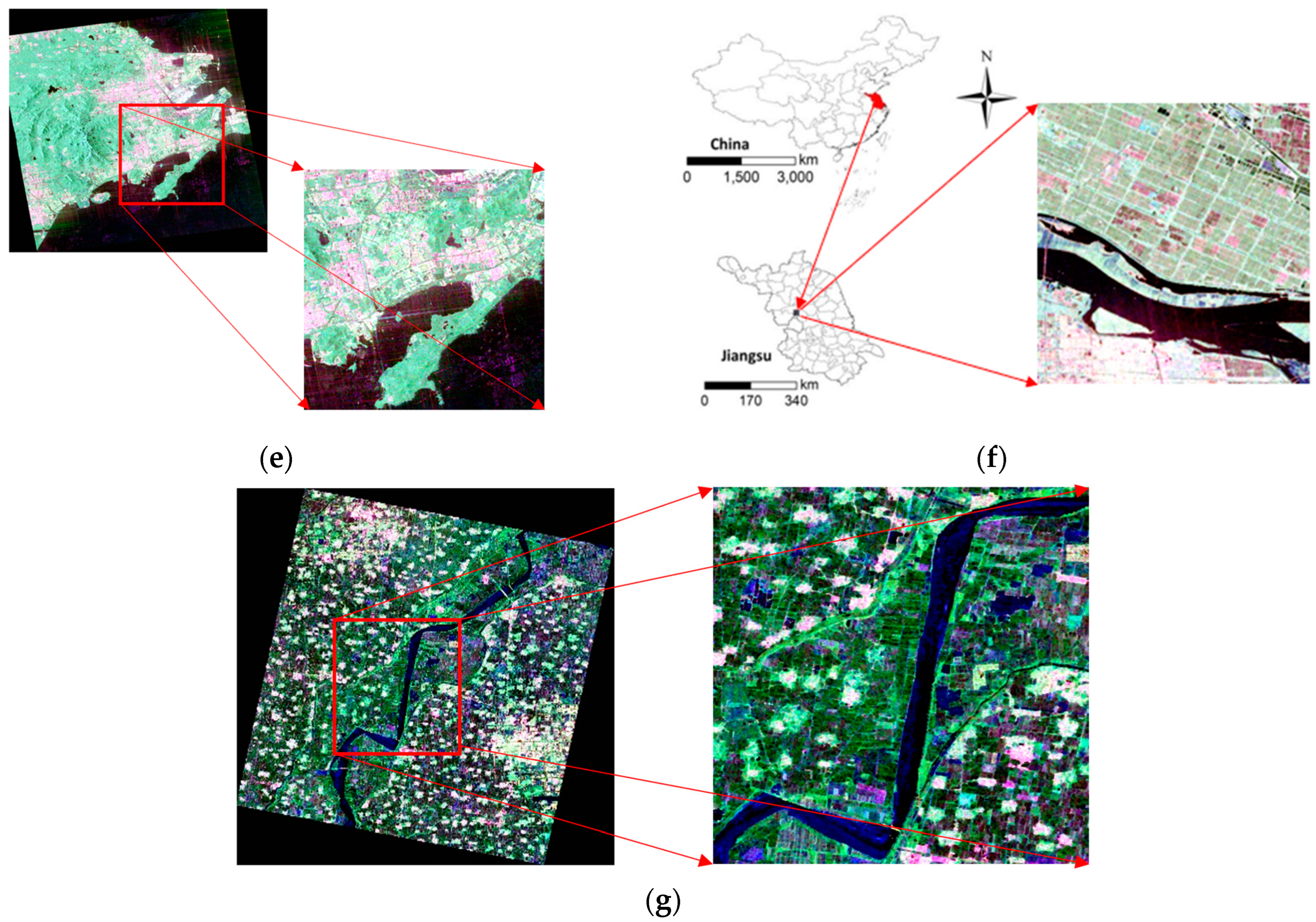








| Data Acquisition (D/M/Y) | SAR Frequency Band | Pixel Spacing (A × R, m) | Center Incidence Angle (°) | Study Area | Satellite Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 April 2008 | C band | 4.73 × 4.82 | 28.92 | San Francisco, CA, USA | RADARSAT-2 |
| 11 November 2009 | L band | 9.37 × 3.54 | 23.87 | San Francisco, CA, USA | ALOS-1 PALSAR-1 |
| 24 March 2015 | L band | 2.86 × 3.21 | 33.88 | San Francisco, CA, USA | ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 |
| 27 March 2018 | C band | 2.25 × 5.79 | 31.35 | San Francisco, CA, USA | GF-3 |
| 20 September 2017 | C band | 4.50 × 5.00 | 48.75 | Qingdao, China | GF-3 |
| 16 September 2015 | C band | 5.20 × 7.60 | 39.95 | Jiangsu, China | RADARSAT-2 |
| 31 March 2023 | C band | 4.73 × 4.74 | 26.70 | Yellow River, China | RADARSAT-2 |
| Parameter Extraction Method | Feature Component | Feature Number |
|---|---|---|
| Stokes matrix | g0, g1, g2, g3 | 4 |
| Backscattering intensity | σCV, σCR, σCH, σCL [14] | 4 |
| m-δ decomposition | Ps_m-δ, Pd_m-δ, Pv_m-δ | 3 |
| m-χ decomposition | Ps_m-χ, Pd_m-χ, Pv_m-χ | 3 |
| m-αs decomposition | Ps_m-αs, Pd_m-αs, Pv_m-αs | 3 |
| H/α decomposition | H, α, A | 3 |
| ΔαBCP/αBCP decomposition | ΔαBCP, αBCP [8] | 2 |
| Total | - | 22 |
| Parameter Extraction Method | Feature Component | Feature Number |
|---|---|---|
| H/α decomposition | H_Full, α_Full, A_Full | 3 |
| Freeman decomposition | Ps_F, Pd_F, Pv_F | 3 |
| ΔαB/αB decomposition [46] | αB, ΔαB, Φ | 3 |
| Yamaguchi decomposition [47] | Ps_Y, Pd_Y, Pv_Y, Ph_Y | 4 |
| Pauli decomposition | Pauli_1, Pauli_2, Pauli_3 | 3 |
| Polarization characteristics of the rotating domain [48] | Re[T12(θnull)], Im[T12(θnull)], Re[T23(θnull)] | 3 |
| Polarimetric coherency matrix | T11, T22, T33 | 3 |
| Total | - | 22 |
| Experimental Transfer Group 1 | Experimental Transfer Group 2 | Experimental Transfer Group 3 | Experimental Transfer Group 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source Domain→Target Domain | Source Domain→Target Domain | Source Domain→Target Domain | Source Domain→Target Domain | ||||
| a | ALOS1-Sanf→RS2-Sanf | a | GF3-Qingdao→RS2-Sanf | a | GF3-Qingdao→RS2-Sanf | a | GF3-Qingdao→RS-2 Yellow River |
| b | ALOS2-Sanf→RS2-Sanf | b | GF3-Qingdao→ALOS1-Sanf | b | GF3-Qingdao→ALOS1-Sanf | b | RS2-Qingdao→RS-2 Yellow River |
| c | GF3-Sanf→RS2-Sanf | c | GF3-Qingdao→ALOS2-Sanf | c | GF3-Qingdao→ALOS2-Sanf | c | Jiangsu T-H→RS-2 Yellow River |
| d | RS2-Sanf→ALOS1-Sanf | d | GF3-Qingdao→GF3-Sanf | d | GF3-Qingdao→GF3-Sanf | d | Jiangsu D-J→RS-2 Yellow River |
| e | ALOS2-Sanf→ALOS1-Sanf | e | ALOS2-Sanf→GF3-Qingdao | e | RS2-Sanf→GF3-Qingdao | - | |
| f | GF3-Sanf→ALOS1-Sanf | - | f | ALOS1-Sanf→GF3-Qingdao | - | ||
| g | RS2-Sanf→ALOS2-Sanf | - | g | ALOS2-Sanf→GF3-Qingdao | - | ||
| h | ALOS1-Sanf→ALOS2-Sanf | - | h | GF3-Sanf→GF3-Qingdao | - | ||
| i | GF3-Sanf→ALOS2-Sanf | - | - | - | |||
| j | RS2-Sanf→GF3-Sanf | - | - | - | |||
| k | ALOS1-Sanf→GF3-Sanf | - | - | - | |||
| l | ALOS2-Sanf→GF3-Sanf | - | - | - | |||
| RS2→ALOS1 | RS2→ALOS2 | RS2→GF3 | ALOS1→ALOS2 | ALOS1→GF3 | ALOS2→GF3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature Number | 13 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 11 | 11 |
| Optimal parameters | Pd_m-δ, g1, σCL, Pd_m-χ, Pd_m-αs, g0, αBCP, σCR, α, σCH, Pv_m-αs, Pv_m-δ, Pv_m-χ | Pd_m-δ, g1, σCL, Pd_m-χ, Pd_m-αs, g0, σCR, σCH, Pv_m-αs, Pv_m-δ, Pv_m-χ | g1, σCL, Pd_m-αs, g0, αBCP, σCR, α, σCH, Pv_m-αs, Pv_m-δ, Pv_m-χ, H, A | Ps_m-αs, Pd_m-αs, Pd_m-χ, Pd_m-δ, g1, σCV, σCL, σCR, g0, Pv_m-δ, σCH, Pv_m-χ, Pv_m-αs | αBCP, α, Pd_m-αs, g1, σCL, σCR, g0, Pv_m-δ, σCH, Pv_m-χ, Pv_m-αs | Ps_m-δ, g1, Ps_m-χ, Pd_m-αs, Pv_m-αs. Pv_m-δ σCR. Pv_m-χ, σCL, g0, σCH |
| ALOS1→RS2 | ALOS2→RS2 | GF3→RS2 | RS2→ALOS1 | ALOS2→ALOS1 | GF3→ALOS1 | RS2→ALOS2 | ALOS1→ALOS2 | GF3→ALOS2 | RS2→GF3 | ALOS1→GF3 | ALOS2→GF3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFRST-SA | 0.938 | 0.961 | 0.935 | 0.832 | 0.958 | 0.821 | 0.895 | 0.948 | 0.726 | 0.945 | 0.914 | 0.804 |
| GFRST-TCA | 0.936 | 0.968 | 0.935 | 0.842 | 0.940 | 0.882 | 0.879 | 0.905 | 0.863 | 0.945 | 0.931 | 0.779 |
| GFRST-JDA | 0.943 | 0.963 | 0.949 | 0.847 | 0.947 | 0.835 | 0.953 | 0.951 | 0.926 | 0.940 | 0.917 | 0.940 |
| GFRST-CORAL | 0.922 | 0.956 | 0.934 | 0.793 | 0.957 | 0.807 | 0.797 | 0.959 | 0.795 | 0.950 | 0.921 | 0.782 |
| GFRST-BDA | 0.943 | 0.965 | 0.949 | 0.847 | 0.947 | 0.836 | 0.839 | 0.951 | 0.926 | 0.940 | 0.917 | 0.940 |
| GFRST-GFK | 0.940 | 0.956 | 0.940 | 0.831 | 0.959 | 0.822 | 0.894 | 0.949 | 0.728 | 0.942 | 0.914 | 0.803 |
| GFRST-MEDA | 0.944 | 0.968 | 0.970 | 0.841 | 0.946 | 0.930 | 0.967 | 0.942 | 0.960 | 0.937 | 0.921 | 0.939 |
| Supervised classification | 0.987 | 0.977 | 0.944 | 0.979 | ||||||||
| GF3-Qingdao→RS2-Sanf | GF3-Qingdao→ALOS1-Sanf | GF3-Qingdao→ALOS2-Sanf | GF3-Qingdao→GF3-Sanf | ALOS2-Sanf→GF3-Qingdao | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFRST-SA | 0.913 | 0.957 | 0.884 | 0.899 | 0.908 |
| GFRST-TCA | 0.881 | 0.942 | 0.872 | 0.851 | 0.920 |
| GFRST-JDA | 0.937 | 0.920 | 0.914 | 0.898 | 0.935 |
| GFRST-CORAL | 0.839 | 0.948 | 0.896 | 0.891 | 0.524 |
| GFRST-BDA | 0.930 | 0.934 | 0.900 | 0.901 | 0.913 |
| GFRST-GFK | 0.878 | 0.922 | 0.879 | 0.889 | 0.867 |
| GFRST-MEDA | 0.901 | 0.915 | 0.869 | 0.874 | 0.914 |
| Supervised classification | 0.987 | 0.977 | 0.944 | 0.979 | 0.980 |
| GF3 Qingdao→RS2 Sanf | GF3 Qingdao→ALOS1-Sanf | GF3 Qingdao→ALOS2 Sanf | GF3 Qingdao→GF3-Sanf | RS2 Sanf→GF3 Qingdao | ALOS1 Sanf→GF3 Qingdao | ALOS2 Sanf→GF3 Qingdao | GF3 Sanf→GF3 Qingdao | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | 0.886 | 0.948 | 0.912 | 0.874 | 0.784 | 0.958 | 0.976 | 0.795 |
| GFRST-SA | 0.972 | 0.970 | 0.962 | 0.942 | 0.970 | 0.980 | 0.980 | 0.982 |
| CORAL | 0.831 | 0.852 | 0.897 | 0.844 | 0.794 | 0.937 | 0.949 | 0.802 |
| GFRST-CORAL | 0.967 | 0.937 | 0.937 | 0.942 | 0.979 | 0.980 | 0.981 | 0.984 |
| JDA | 0.933 | 0.960 | 0.932 | 0.928 | 0.885 | 0.983 | 0.980 | 0.908 |
| GFRST-JDA | 0.967 | 0.987 | 0.985 | 0.941 | 0.979 | 0.986 | 0.985 | 0.979 |
| GFK | 0.900 | 0.930 | 0.910 | 0.868 | 0.798 | 0.953 | 0.979 | 0.768 |
| GFRST-GFK | 0.971 | 0.958 | 0.943 | 0.952 | 0.966 | 0.979 | 0.982 | 0.983 |
| BDA | 0.931 | 0.936 | 0.939 | 0.922 | 0.958 | 0.976 | 0.978 | 0.970 |
| GFRST-BDA | 0.973 | 0.990 | 0.987 | 0.928 | 0.975 | 0.983 | 0.990 | 0.988 |
| MEDA | 0.912 | 0.969 | 0.935 | 0.912 | 0.923 | 0.976 | 0.991 | 0.897 |
| GFRST-MEDA | 0.985 | 0.995 | 0.997 | 0.957 | 0.990 | 0.986 | 0.991 | 0.993 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Yin, J.; Li, K.; Yang, J. Gini Coefficient-Based Feature Learning for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Classification with Compact Polarimetric SAR Data. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091511
Guo X, Yin J, Li K, Yang J. Gini Coefficient-Based Feature Learning for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Classification with Compact Polarimetric SAR Data. Agriculture. 2024; 14(9):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091511
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xianyu, Junjun Yin, Kun Li, and Jian Yang. 2024. "Gini Coefficient-Based Feature Learning for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Classification with Compact Polarimetric SAR Data" Agriculture 14, no. 9: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091511
APA StyleGuo, X., Yin, J., Li, K., & Yang, J. (2024). Gini Coefficient-Based Feature Learning for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Classification with Compact Polarimetric SAR Data. Agriculture, 14(9), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091511







