Dietary Glutamine Supplementation Enhances Growth Performance and Jejunum Development in Kele and Large White Hybrid Weaned Piglets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Management
2.2. Experimental Sampling
2.3. Intestinal Morphology Detection
2.4. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
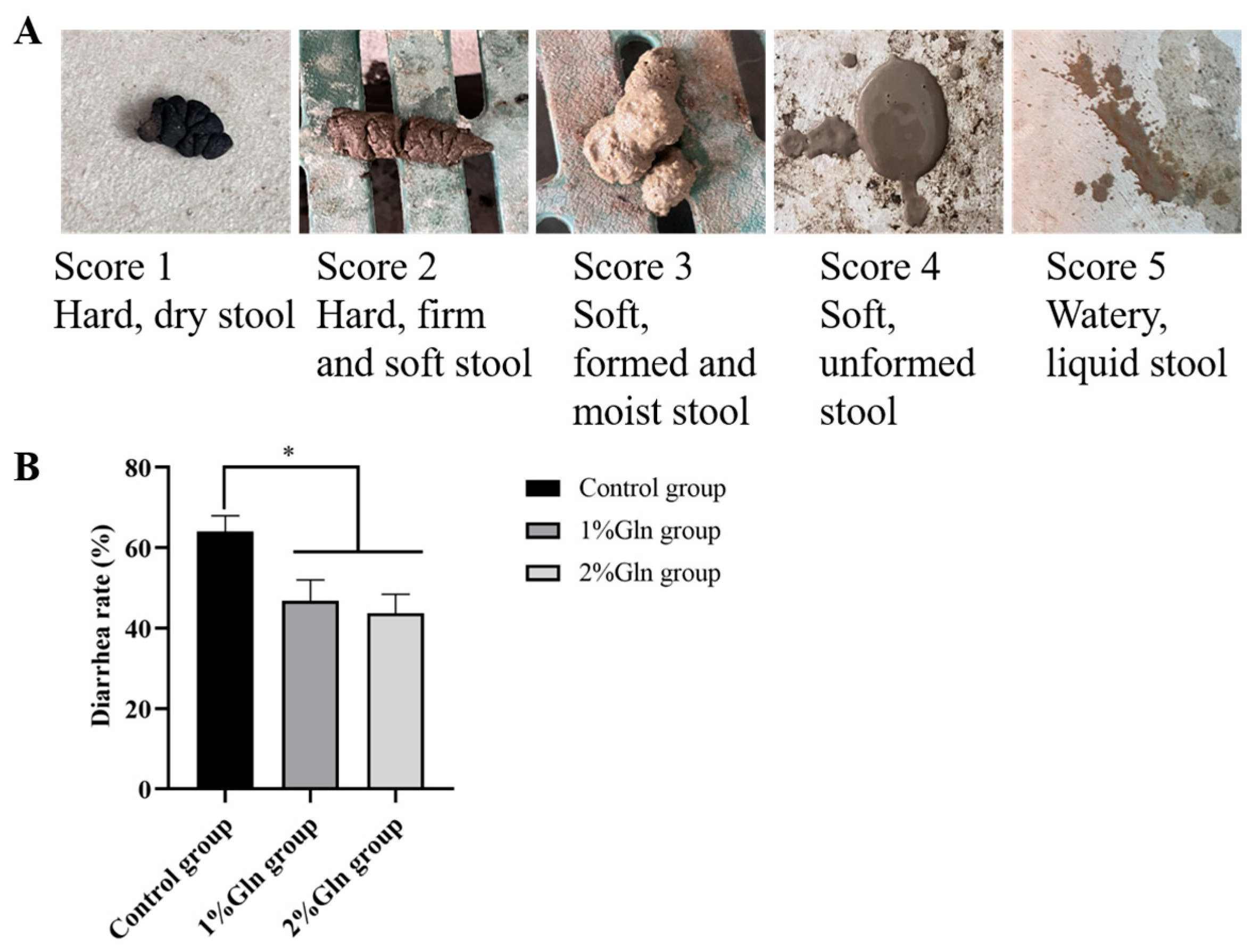
3.2. Diarrhea Rate
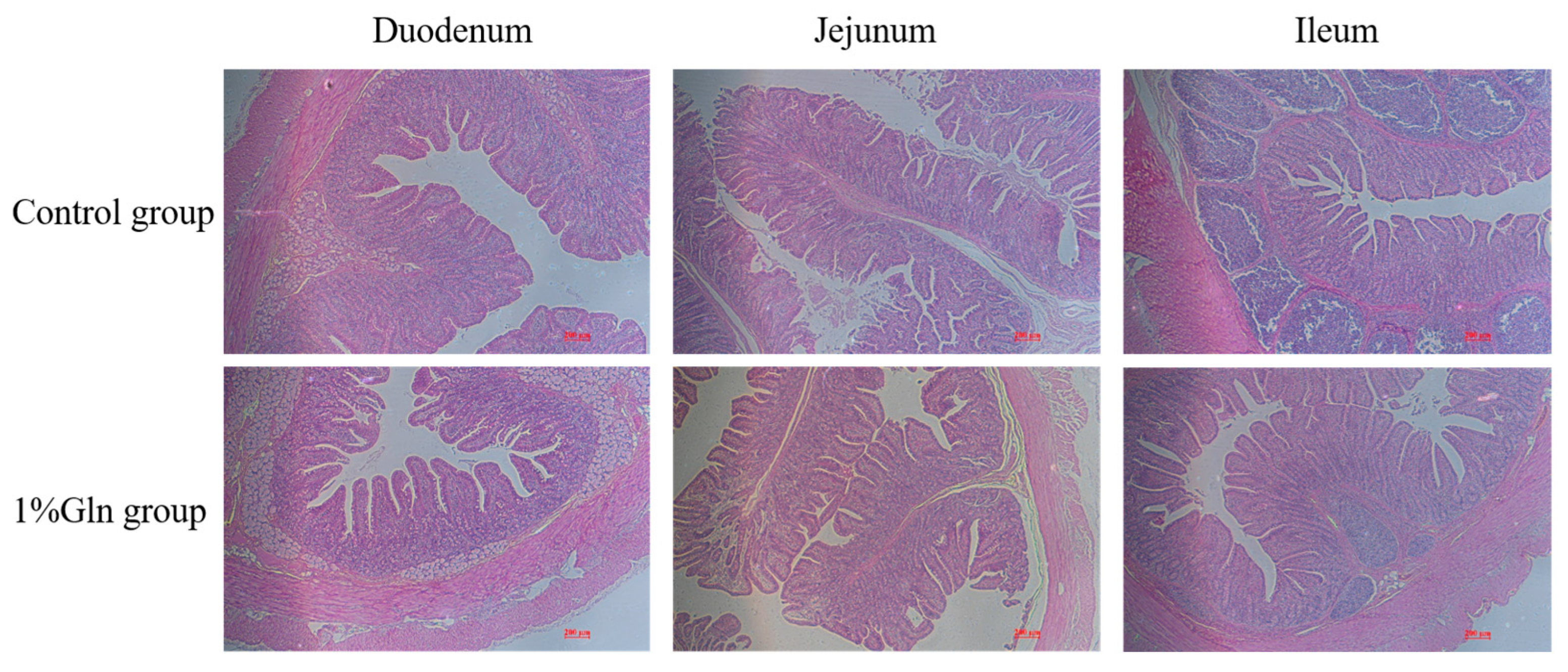
3.3. Small Intestinal Mucosal Morphology
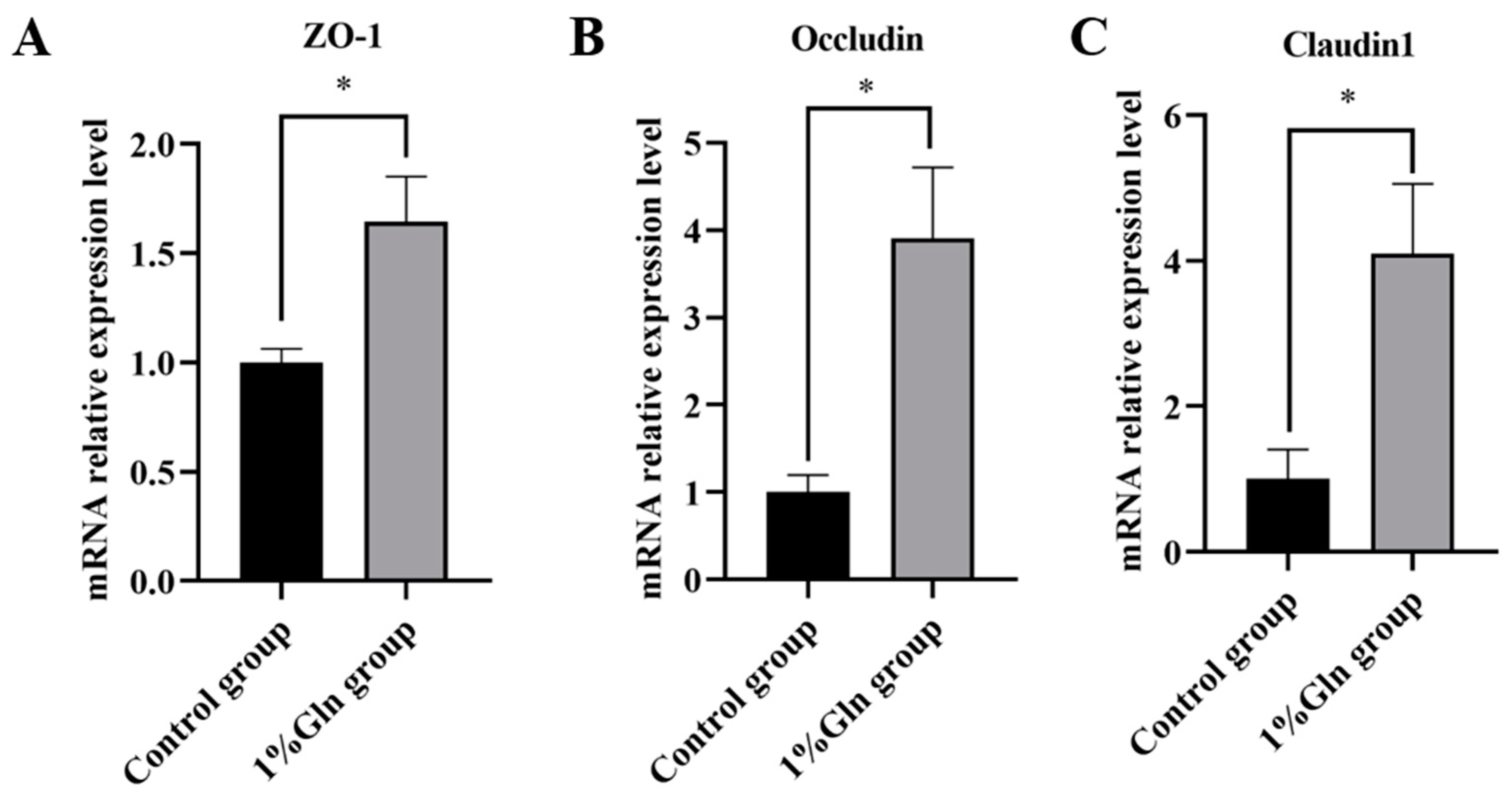
3.4. Tight Junctions
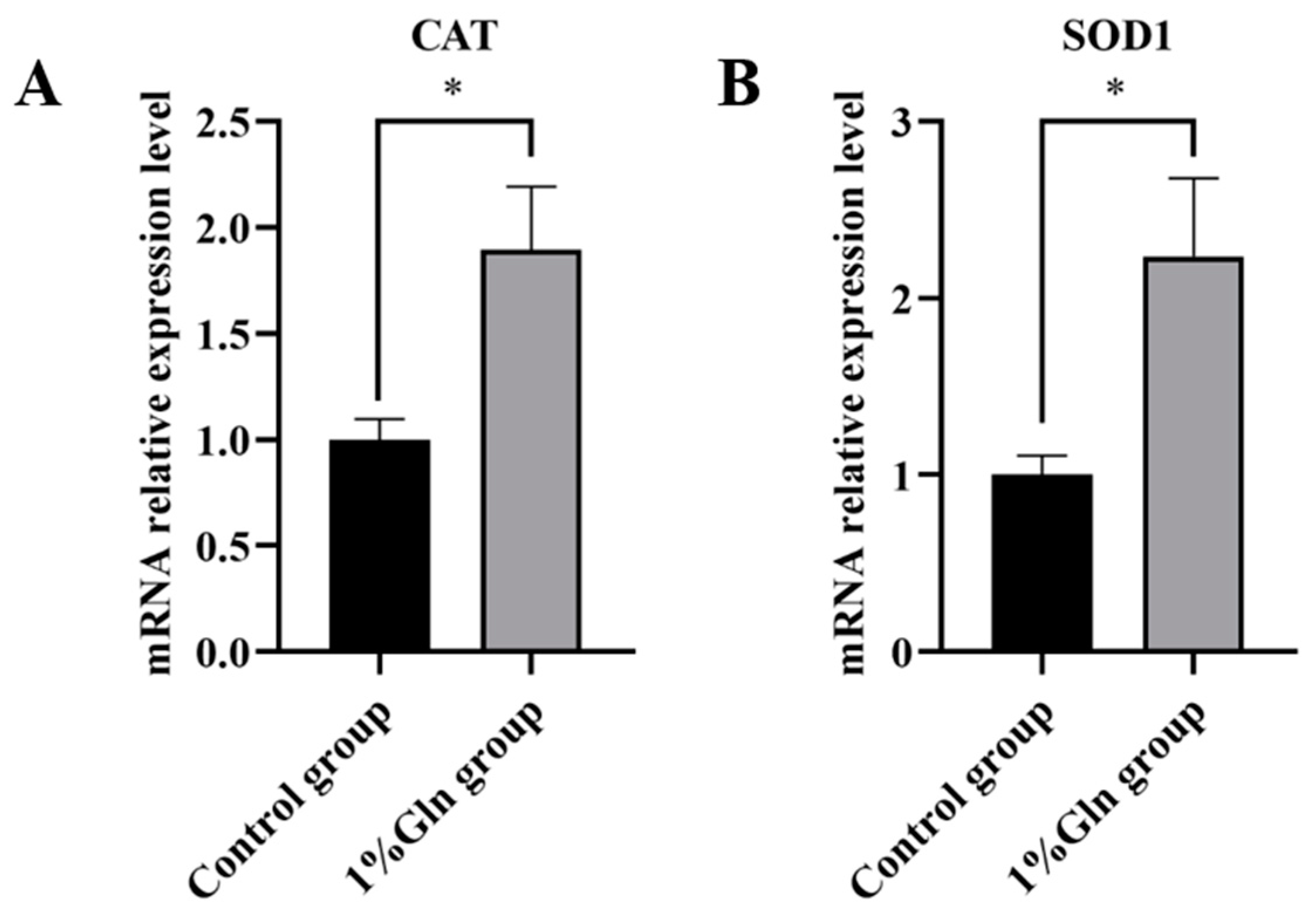
3.5. Antioxidant Ability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ao, Z. Exploring characteristics of placental transcriptome and cord serum metabolome associated with low birth weight in kele pigs. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xiong, K. Intrauterine growth retardation affects intestinal health of suckling piglets via altering intestinal antioxidant capacity, glucose uptake, tight junction, and immune responses. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 2644205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wu, G. Dietary essentiality of “nutritionally non-essential amino acids” for animals and humans. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Yin, Y. Dietary requirements of "nutritionally non-essential amino acids" by animals and humans. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Johnson, G.A.; Knabe, D.A.; Burghardt, R.C.; Spencer, T.E.; Li, X.L.; Wang, J.J. Triennial growth symposium: Important roles for l-glutamine in swine nutrition and production. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shen, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, B.; Guo, S.; Yi, D.; Ding, B.; Wu, T.; et al. Effects of dietary l-glutamine supplementation on the intestinal function and muscle growth of piglets. Life 2024, 14, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, J.S.M.; Vilas-Boas, E.A.; Takahashi, H.K.; Munhoz, A.C.; Araujo, L.C.C.; Carvalho, C.R.; Donato, J., Jr.; Curi, R.; Carpinelli, A.R.; Cruzat, V. Liver lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammation in glutamine-supplemented ob/ob mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 138, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Lai, W.; Yao, L.; Xu, E.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Glutamine regulates gene expression profiles to increase the proliferation of porcine intestinal epithelial cells and the expansion of intestinal stem cells. Animals 2023, 13, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Lu, E.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, E.; Zhu, M.; Chen, X. Glutamine promotes porcine intestinal epithelial cell proliferation through the wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 7155–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Fang, Y.; Lu, E.; Xu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, M. Extracellular glutamine promotes intestinal porcine epithelial cell proliferation via arf1-mTORC1 pathway independently of rag GTPases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 14251–14262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, X.; Xi, P.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Zhu, W. L-glutamine regulates amino acid utilization by intestinal bacteria. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Feng, G.D.; Ao, X.; Li, Y.F.; Qian, H.X.; Liu, J.B.; Bai, G.Y.; He, Z.Z. Effects of l-glutamine on growth performance, antioxidant ability, immunity and expression of genes related to intestinal health in weanling pigs. Livest. Sci. 2016, 189, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Z.; Dou, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Ding, K.; Zhang, C. Glutamine protects cow’s ruminal epithelial cells from acid-induced injury in vitro. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 69, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wen, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, K.; Liang, X.; Xiao, H. Glutamine protects intestinal immunity through microbial metabolites rather than microbiota. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.J.; Wang, L.X.; Yang, H.S.; Hu, A.; Yin, Y.L. Review: The roles and functions of glutamine on intestinal health and performance of weaning pigs. Animal 2019, 13, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Wu, G. Regulatory role for amino acids in mammary gland growth and milk synthesis. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poklukar, K.; Mestre, C.; Skrlep, M.; Candek-Potokar, M.; Ovilo, C.; Fontanesi, L.; Riquet, J.; Bovo, S.; Schiavo, G.; Ribani, A.; et al. A meta-analysis of genmetic and phenotypic diversity of European local pig breeds reveals genomic regions associated with breed differentiation for production traits. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2023, 55, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ran, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J. Detection of genomic structural variations in Guizhou indigenous pigs and the comparison with other breeds. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite Da Silva, A.; Dos Santos, S.G.C.G.; Saraiva, E.P.; Fonsêca, V.D.F.C.; Givisiez, P.E.N.; Pascoal, L.A.F.; Martins, T.D.D.; de Amorim, M.L.C.M. Supplementation of diets with glutamine and glutamic acid attenuated the effects of cold stress on intestinal mucosa and performance of weaned piglets. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2019, 59, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Qi, M.; Li, J.; Tan, B. Glutamine, glutamate, and aspartate differently modulate energy homeostasis of small intestine under normal or low energy status in piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Chen, J.; Yao, K.; Yin, Y.; Long, L.; Fang, R. The effects of dietary supplementation with porous zinc oxide on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, morphology, and permeability in weaned piglets. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2^(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Shan, A.; Han, Y.; Jin, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, C.; et al. Dietary glutamine supplementation enhances expression of ZO-1 and occludin and promotes intestinal development in min piglets. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. A Anim. Sci. 2017, 67, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Fang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, Z. The Alleviating effect of taxifolin on deoxynivalenol-induced damage in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; He, B.; Dai, Z.; Wu, Z. Glutamine enhances tight junction protein expression and modulates corticotropin-releasing factor signaling in the jejunum of weanling piglets1,2. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.M.; Crenshaw, J.D.; Polo, J. The biological stress of early weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, D.; She, R. Effect of weaning on small intestinal structure and function in the piglet. Arch. Tierernähr. 2002, 56, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Lourdes Bastos, M.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Kos Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López Alonso, M.; López Puente, S.; Marcon, F.; et al. Safety and efficacy of l-glutamine produced using corynebacterium glutamicum NITE BP-02524 for all animal species. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6075. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Bai, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Low-protein diet supplemented with 1% l-glutamine improves growth performance, serum biochemistry, redox status, plasma amino acids, and alters fecal microbiota in weaned piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 17, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.T.; Zheng, G.H.; Fang, X.J.; Jiang, J.F. Effects of glutamine on growth performance of weanling piglets. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 51, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Side effects of long-term glutamine supplementation. JPEN. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 37, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Meier, S.A.; Knabe, D.A. Dietary glutamine supplementation prevents jejunal atrophy in weaned pigs. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.B.; Huang, H.J.; Wang, C.H.; Yen, H.T.; Yu, B. The effect of glutamine supplement on small intestinal morphology and xylose absorptive ability of weaned piglets. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 7003–7008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yan, J.; Tan, C.; Deng, B.; Deng, J.; Yin, Y.; Ren, W. Glutamine supplementation improves intestinal cell proliferation and stem cell differentiation in weanling mice. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.D.; Deng, C.X.; Wang, Z.R.; Ye, Y.L.; You, J.M. Dietary alanyl-glutamine improves growth performance of weaned piglets through maintaining intestinal morphology and digestion–absorption function. Animal 2019, 13, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeser, A.J.; Klok, C.V.; Ryan, K.A.; Wooten, J.G.; Little, D.; Cook, V.L.; Blikslager, A.T. Stress signaling pathways activated by weaning mediate intestinal dysfunction in the pig. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G173–G181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagne, L.; Boudry, G.; Favier, C.; Huërou-Luron, I.L.; Lallès, J.; Sève, B. Main intestinal markers associated with the changes in gut architecture and function in piglets after weaning. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, K.; Khan, R.U.; Zhang, C.; Hu, H. Effect of glutamine on the growth performance, oxidative stress, and nrf2/p38 MAPK expression in the livers of heat-stressed broilers. Animals 2023, 13, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moine, L.; Díaz De Barboza, G.; Pérez, A.; Benedetto, M.; Tolosa De Talamoni, N. Glutamine protects intestinal calcium absorption against oxidative stress and apoptosis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 212, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, E.E.; Lynch, R.D. The tight junction: A multifunctional complex. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 286, C1213–C1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ren, W.; Liu, G.; Duan, J.; Yang, G.; Wu, L.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Birth oxidative stress and the development of an antioxidant system in newborn piglets. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genes | Primer (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Claudin1 | F: TGCTGCTTCTCTCTGCCTTCTG R: GCCTTGGTGTTGGGTAAGATGTTG | 83 |
| ZO-1 | F: CGGCGAAGGTAATTCAGTGT R: TCTTCTCGGTTTGGTGGTCT | 111 |
| Occludin | F: CAGCAGCAGTGGTAACTTGG R: CCGTCGTGTAGTCTGTCTCG | 110 |
| CAT | F: TCCAGCCAGTGACCAGATGA R: CCCGGTCAAAGTGAGCCATT | 182 |
| SOD1 | F: AAGGCCGTGTGTGTGCTGAA R: GATCACCTTCAGCCAGTCCTTT | 118 |
| β-Actin | F: TGCGGGACATCAAGGAGAAG R: AGTTGAAGGTAGTTTCGTGG | 216 |
| Items | Control | 1% Gln | 2% Gln | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial BW, kg | 7.43 | 7.50 | 7.35 | 0.10 | 0.600 |
| Final BW, kg | 16.76 b | 18.89 a | 17.72 ab | 0.38 | 0.011 |
| d 0–14 | |||||
| ADG, g | 276 b | 369 a | 335 a | 17.9 | 0.015 |
| ADFI, g | 445 b | 508 a | 522 a | 16.6 | 0.022 |
| G:F | 0.619 | 0.726 | 0.643 | 0.03 | 0.059 |
| d 15–28 | |||||
| ADG, g | 391 | 445 | 406 | 19.3 | 0.181 |
| ADFI, g | 784 | 775 | 796 | 24.7 | 0.835 |
| G:F | 0.499 b | 0.574 a | 0.508 b | 0.02 | 0.036 |
| d 0–28 | |||||
| ADG, g | 333 b | 407 a | 370 ab | 13.0. | 0.010 |
| ADFI, g | 615 | 642 | 659 | 17.0 | 0.232 |
| G:F | 0.543 b | 0.634 a | 0.562 b | 0.02 | 0.017 |
| Items | Control | 1% Gln | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duodenum | |||
| VH, μM | 403.15 ± 12.81 | 453.20 ± 7.86 | 0.029 |
| CD, μM | 350.47 ± 8.95 | 337.24 ± 3.81 | 0.245 |
| VH/CD | 1.16 ± 0.02 | 1.35 ± 0.03 | 0.004 |
| Jejunum | |||
| VH, μM | 261.50 ± 6.02 | 356.31 ± 14.69 | 0.004 |
| CD, μM | 243.25 ± 16.50 | 233.73 ± 2.78 | 0.600 |
| VH/CD | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 1.54 ± 0.07 | 0.014 |
| Ileum | |||
| VH, μM | 339.19 ± 8.52 | 336.55 ± 6.58 | 0.818 |
| CF, μM | 246.97 ± 9.12 | 243.83 ± 1.27 | 0.750 |
| VH/CD | 1.38 ± 0.08 | 1.39 ± 0.02 | 0.916 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, L.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M. Dietary Glutamine Supplementation Enhances Growth Performance and Jejunum Development in Kele and Large White Hybrid Weaned Piglets. Agriculture 2025, 15, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090924
Tan L, Cheng Y, Liu G, Zhang Y, Zhu M. Dietary Glutamine Supplementation Enhances Growth Performance and Jejunum Development in Kele and Large White Hybrid Weaned Piglets. Agriculture. 2025; 15(9):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090924
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Longjuan, Yujie Cheng, Guowei Liu, Yiyu Zhang, and Min Zhu. 2025. "Dietary Glutamine Supplementation Enhances Growth Performance and Jejunum Development in Kele and Large White Hybrid Weaned Piglets" Agriculture 15, no. 9: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090924
APA StyleTan, L., Cheng, Y., Liu, G., Zhang, Y., & Zhu, M. (2025). Dietary Glutamine Supplementation Enhances Growth Performance and Jejunum Development in Kele and Large White Hybrid Weaned Piglets. Agriculture, 15(9), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090924







