Side-Scan Sonar Coupled with Scuba Diving Observation for Enhanced Monitoring of Benthic Artificial Reefs along the Coast of Terengganu, Peninsular Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
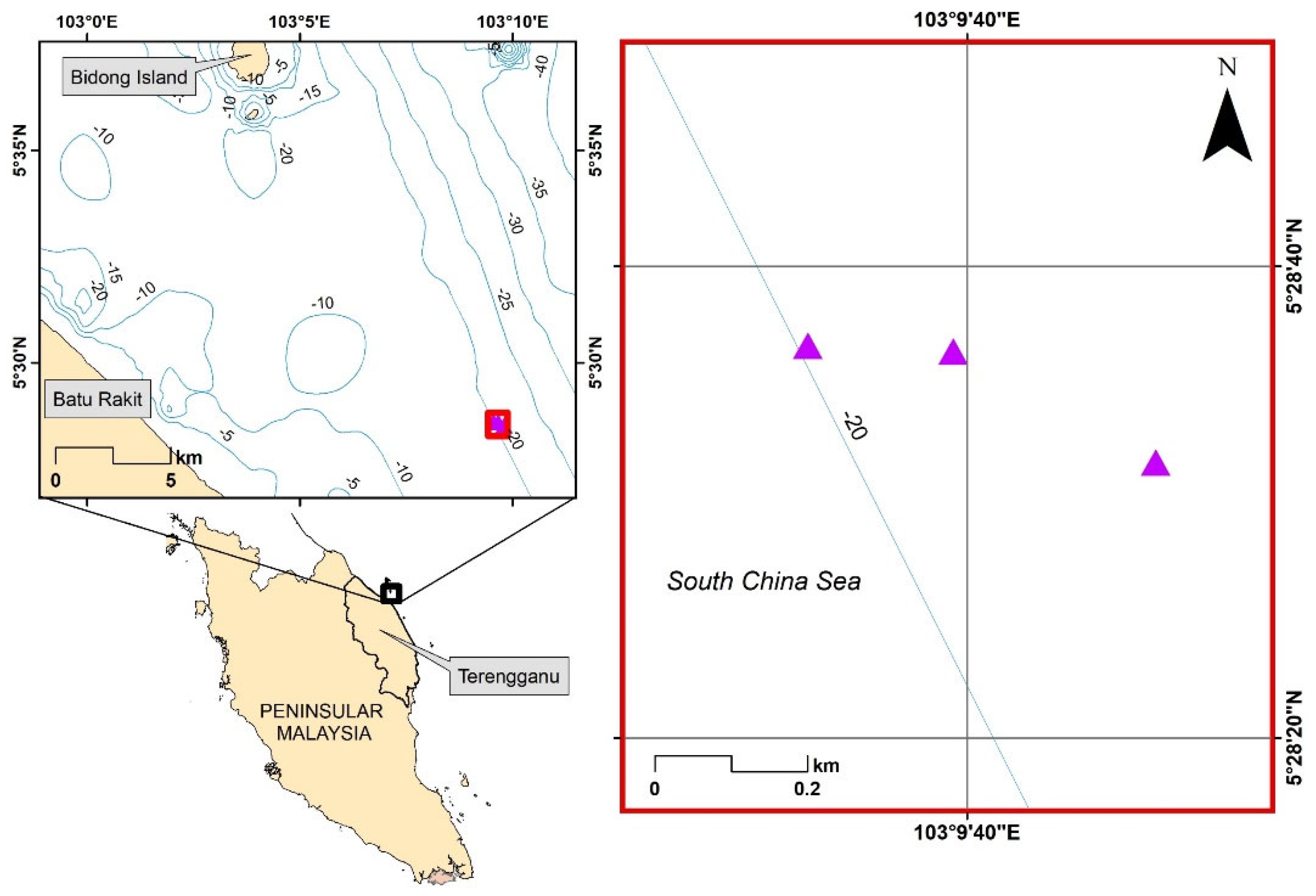
2.1. Study Area
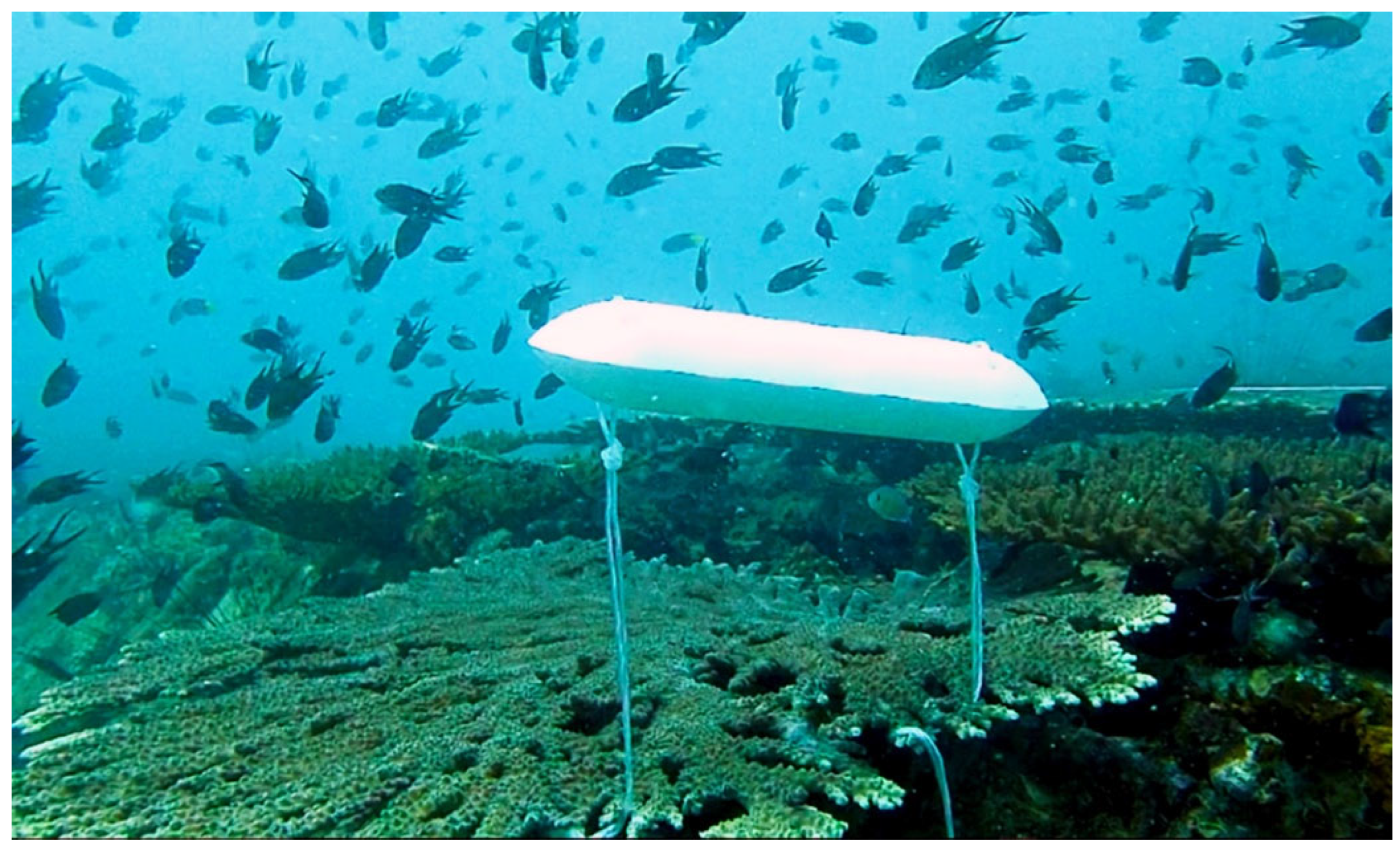
2.2. Bioceramic Korean AR Module
2.3. Side-Scan Sonar Survey
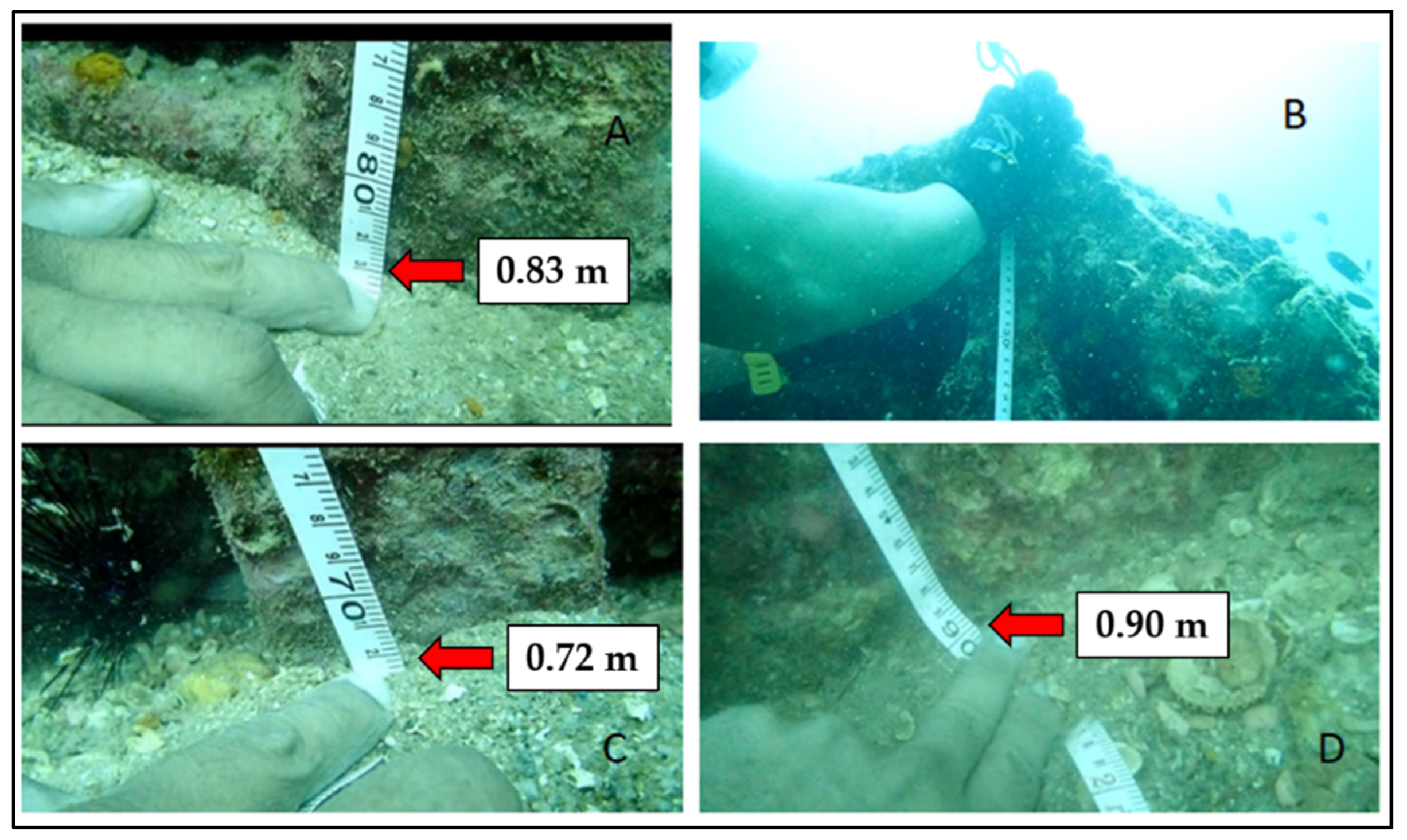
2.4. Ground Truthing
2.5. Fish Assemblage Data
2.5.1. Field Survey
2.5.2. Fish Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Side-Scan Sonar and Ground Truthing
3.2. Fish Diversity in the Deployed BK AR Modules
3.3. Fish Biomass
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- i.
- Fulfilment of the pre-deployment aim(s);
- ii.
- Location and condition of the AR physical structure;
- iii.
- Evaluating the performance of the AR structures and the habitats they create.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohnsack, J.A.; Sutherland, D.L. Artificial reef research: A review with recommendations for future priorities. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 11–39. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, T.C.; Brian, N.T.; William, J.W. Socioeconomic consequences of fishing displacement from marine protected areas in Hawaii. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 160, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.J.; Vianna, G.M.S.; Meeuwig, J.J.; Meekan, M.; Pannell, D. Estimating the economic benefits and costs of highly-protected marine protected areas. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, A.B.; Shertzer, K.W.; Bacheler, N.M.; Kellison, G.T.; Riley, K.L.; Taylor, J.C. Meta-Analysis Reveals Artifical Reefs Can Be Effective Tools for Fish Community Enhancement but Are Not One-Size-Fits-All. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramm, L.A.; Florisson, J.H.; Watts, S.L.; Becker, A.; Tweedley, J.R. Artificial reefs in the Anthropocene: A review of ge-ographical and historical trends in their design, purpose, and monitoring. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2021, 97, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woohhead, P.M.J.; Jacobson, M.E. Epifauna settlement, the process of community development and succession over two years on an artificial reef in New York Bight. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 364–376. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, L.M. Artificial reefs of Southeast Asia-Do they enhance or degrade the marine environment? Environ. Monit. Assess. 1997, 44, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baine, M. A review of their design, application, management and performance. Ocean Coast. Manag. J. 2001, 44, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S.G.; Bushnell, S.L. Socio-economic aspects of artificial reefs: Considerations for the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2007, 50, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.; Edwards, A.J. An evaluation of artificial reef structures as tools for marine habitat rehabilitation in the Maldives. Aquat. Conserv.: Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 1999, 9, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, R.E. Beyond fisheries enhancement: Artificial reefs and ecotourism. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Claudet, J.; Pelletier, D. Marine protected areas and artificial reefs: A review of the interactions between management and scientific studies. Aquatic 2004, 17, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.H. Construction of artificial reefs in Malaysia (In Malay). Ber. Nelayan 1981, 27, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Saharudin, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Lokman, M.H.; Wan Salihin, W.A. Historical Development and Management of Malaysian Artificial Reefs (Ars). Environ. Sci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukarno, W.; Raja Mohammad Noordin, R.O.; Che Omar, M.H. Assement of artificial reefs in Terengganu (In Malay). In Proceedings of the Fisheries Research Seminar 1991, Gelugur Pulau Pinang, Malaysia; 1991; pp. 418–428. [Google Scholar]
- Latun, A.R.B. Artificial Reefs in Malaysia: The Malaysian Experience in Resource Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 1st Regional Workshop on Enhancing Coastal Resources: Artificial Reefs, Stationary Fishing Gear Design and Construction and Marine Protected Areas, Bangkok, Thailand, 30 September–3 October 2003; pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, A.J.; Cato, I.; Desprez, M.; Fader, G.; Schuttenhelm, R.T.E.; Side, J. An overview of seabed-mapping technologies in the context of marine habitat Classification. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.T.; Holliday, D.V.; Kloser, R.; Reid, D.G.; Simard, Y. Acoustic seabed classification: Current practice and future directions. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arney, R.; Froehlich, C.; Kline, R. Recruitment Patterns of Juvenile Fish at an Artificial Reef Area in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Coast. Fish. Dyn. Manag. Ecosyst. Sci. 2017, 9, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortone, S.A.; Brandini, P.P.; Fabi, S.; Otake, S. Artificial Reefs in Fishery Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; 350. [Google Scholar]
- Tessier, E.; Chabanet, P.; Pothin, K.; Soria, M.; Lasserre, G. Visual censuses of tropical fish aggregations on artificial reefs: Slate versus video recording techniques. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 315, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, C.Y.M.; Kline, R.J. Using fish population metrics to compare the effects of artificial reef density. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.; Cintra-Buenrostro, C.E.; Kline, R.; Shively, D.; Shipley-Lozano, B. Artificial Reef Fish Survey Methods: Counts vs. Log-Categories Yield Different Diversity Estimates. In Proceedings of the 68th Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute Meeting, Panama, Panama, 9–13 November 2015; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, M.B.; Glasby, T.M.; Boys, C.A.; Folpp, H.; Suthers, I.; Gregson, M. Response of fish communities to the deployment of estuarine artificial reefs for fisheries enhancement. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2013, 21, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajemian, M.J.; Wetz, J.J.; Shipley-Lozano, B.; Shively, J.D.; Stunz, G.W. An analysis of artificial reef fish community structure along the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico shelf: Potential impacts of ‘‘Rigs-to-Reefs’’ programs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, M.; Bava, S.; Canese, S.; Angiolillo, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bavestrello, G. Fishing impact on deep Mediterranean rocky habitats as revealed by ROV investigation. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 171, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen-Miin, T. Side-Scan Sonar Techniques for The Characterization of Physical Properties of Artificial Benthic Habitats. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2011, 59, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wen-Miin, T. The Application of Side-Scan Sonar System in Monitoring Benthic Artificial Reefs. In Proceedings of the 1998 International Symposium on Underwater Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 17 April 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Collier, J.S.; Brown, C.J. Correlation of sidescan backscatter with grain size distribution of surficial seabed sediments. Mar. Geol. 2005, 214, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, H.G.; Yoklavich, M.M.; Starr, R.M.; O’Connell, V.M.; Wakefield, W.W.; Sullivan, D.E.; Cailliet, G.M. A classification scheme for deep seafloor habitats. Oceanol. Acta 1999, 22, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, R.S.; Zabloudil, K.; Norall, T.; Deysher, L. Effects of El Nino events on natural kelp beds and artificial reefs in southern California. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, S330–S337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degraer, S.; Moerkerke, G.; Rabaut, M.; Van Hoey, G.; Du Four, I.; Vincx, M.; Van Lancker, V. Very-high resolution side-scan sonar mapping of biogenic reefs of the tube-worm Lanice conchilega. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3323–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaut, M.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. Do Lanice conchilega (sandmason) aggregations classify as reefs? Quantifying habitat modifying effects. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2008, 63, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, M.C.; Appeldoorn, R.S.; Rivera, J.A. The effects of minimum map unit in coral reefs maps generated from high resolution side scan sonar mosaics. Coral Reefs 2008, 27, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, M.A.; Kline, R.J. Validating sidescan sonar as a fish survey tool over artificial reefs. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 33, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, K.J.; Buchanan, M.V.; Moss, D. Utilizing side scan sonar as an artificial reef management tool. In Proceedings of the Oceans ’02 MTS/IEEE, Biloxi, MI, USA, 29–31 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.R.; Nelson, C.H. Side-scan sonar assessment of gray whale feeding in the Bering Sea. Science 1984, 225, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kros, P.; Bernhard, M.; Werner, F.; Hukriede, W. Otter trawl tracks in Kiel Bay (Western Baltic) mapped by side-scan sonar. Meeresforschung 1990, 32, 344–353. [Google Scholar]
- Blackinton, J.G.; Hussong, D.M.; Kosalos, J.G. First results from a combination side-scan sonar and seafloor mapping system (SeaMARC II). In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 2–5 May 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Rusby, S. A long-range side-scan sonar for use in the deep sea (Gloria project). Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 2015, 47, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, R.D.; McCann, A.M.; Yoerger, D.; Whitcomb, L.; Mindell, D.; Oleson, J.; Giangrande, C. The discovery of ancient history in the deep sea using advanced deep submergence technology. Deep Sea Res. Part I: Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2000, 47, 1591–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Adams, J.; Mindell, D.; Foley, B. Imaging underwater for archaeology. J. Field Archaeol. 2000, 27, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, P.; Le Pichon, X.; Lallemant, S.; Foucher, J.P.; Westbrook, G.; Hobart, M. Mud volcano field seaward of the Barbados Accretionary Complex: A deep-towed side scan sonar survey. J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth 1990, 95, 8917–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.P.; Helferty, M. The geological interpretation of side-scan sonar. Rev. Geophys. 1990, 28, 357–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A.; Hall, A.J. The characteristics of breaking waves, bubble clouds, and near-surface currents observed using side-scan sonar. Cont. Shelf Res. 1983, 1, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Forsythe, W.; Breen, C.; Dean, M.; Lawrence, M.; Liscoe, S. Comparison of the maritime Sites and Monuments Record with side-scan sonar and diver surveys: A case study from Rathlin Island, Ireland. Geoarchaeology: Int. J. 2002, 17, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, T.S.; Tyler-Jedlund, A.J.; Keenan, S.F.; Weather, E.J. Benthis habitats, as derived from classification of side-scan sonar mapping data, are important determinants of reef-fish assemblage structure in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2020, 12, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, B.; Dauvin, J.; Naxon, M.; Rusig, A.; Mussio, I.; Orvain, F.; Boutouil, M.; Claquin, P. Marine artificial reefs, a meta-analysis of their design, objectives and effectiveness. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ali, A.; Arsad, S.; Kameel, F.; Latif, R. Detecting and Mapping of Artificial Reefs Using Side Scan Sonar & Sub Bottom Profiler; Institute of Oceanography and Environment & Department of Fisheries: Terengganu, Malaysia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, P.H.; Wijeratne, S.; Akhir, M.F.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Roseli, N.H.; Mohamad Ali, F.S. Interconnection between the Southern South China Sea and the Java Sea through the Karimata Strait. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, P.H.; Akhir, M.F.; Tangang, F.T. Thermal frontal zone along the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 110, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, A. Side-scan sonar as a tool for seafloor imagery: Examples from the Mediterranean Continental Margin. In Sonar Systems; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Y.P. Physical characteristics and engineering at reef sites. In Artificial Reef Evaluation; Seaman, W., Ed.; with Application to Natural Marine Habitats; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 51–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, A.P.K.; Ahmad, A.; Nor Azman, Z.; Mohd Saki, N. Field Guide to Fishes and Crustaceans of the Southeast Asian Region. Malaysia; Jabatan Perikanan Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Allen, G.; Steene, R.; Humann, P.; Deloach, N. Reef Fish Identification—Tropical Pacific; New World Publications: Delhi, India, 2003; p. 502. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loya, Y. Plotless and transect methods. In Coral Reefs: Research Methods; Stoddart, D.R., Johannes, R.E., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1978; pp. 197–217. [Google Scholar]
- Muxika, I.; Borja, A.; Bonne, W. The suitability of the marine biotic index (AMBI) to new impact sources along European coasts. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 5, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Velasco, A.; Fernández-Rivera-Melo, F.J.; Melo-Merino, S.M. Occurrence of Holacanthus clarionensis (Pomacanthidae), Stegastes leucorus, and Stegastes acapulcoensis (Pomacentridae) at Magdalena Bay, B.C.S., Mexico. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2016, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.R.; Souza, A.T.; Ilarri, M.I. Habitat use and behavioral ecology of the juveniles of two sympatric damselfishes (Actinopterygii: Pomacentridae) in the south-western Atlantic Ocean. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 1599–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, P.F. Apparent effect of prior experience on a habitat preference exhibited by the reef fish, Dascyllus aruanus (Pisces: Pomacentridae). Anim. Behav. 1971, 19, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afiq-Firdaus, M.A.; Lim, C.S.; Din, M.S.C.; Kadir, S.T.S.A.; Ramasamy, A.M.A.; Ab Manaf, N.; Bachok, Z. Coral Reef Fish Community at Pulau Bidong, Terengganu, South China Sea. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2021, 16, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindo, J.P.V.; Bucol, L.A.; Bucol, A.A.; Wagey, B.T. Abundance and Diversity of Fishes in Bayawan river, Negros Oriental, Philipines. J. Ilm. Sains 2019, 19, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Ilias, Z.; Ismail, M.; Goeden, G.B.; Yap, C.K.; Al-Mutairi, K.A.; Al-Shami, S.A. Coral health assessment in Malaysia: A case study of Pulau Anak Datai, Langkawi. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 45860–45871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, J.M.; Olson, E.; Patenaude, G. Re-exploring the application of artificial reefs for community-based fishery management in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the American Fisheries Society Symposium, Alexandria, Virginia, 17–19 July 2018; Volume 86, pp. 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, G.M.N.; Noh, K.M.; Sidique, S.F.; Noh, A.F.M. Economic impact of artificial reefs: A case study of small-scale fishers in Terengganu, Peninsular Malaysia. Fish. Res. 2014, 151, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, G.M.N.; Noh, K.M.; Sidique, S.F.; Noh, A.F.M.; Ali, A. Economic impacts of artificial reefs on small-scale fishers in Peninsular Malaysia. Hum. Ecol. 2014, 42, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, A.D.; Gunathilaka, M.D.E.K. Rapid Assessment Survey Using Side Scan Sonar: International Obligations and Role of Hydrography in Ensuring Safety of Navigation–Case Study of the Aftermath of MV X-Press Pearl Incident. J. Geospat. Surv. 2022, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, E.; Metaxas, A.; Scheibling, R.E. A systematic review of artificial reefs as platforms for coral reef research and conservation. PLoS ONE 2020, 17, e0261964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Index Number | Description | Percentage Range (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Literally non-existent, main structures non-visible. Mostly destroyed linkages. | 0–20 |
| 2 | Bad condition, main structures mostly destroyed. Mostly broken linkages. | 20–40 |
| 3 | Good condition, main structures intact with damages. Mostly intact linkages. | 40–60 |
| 4 | Fairly good condition, structures intact with some signs of damage. Some broken linkages. | 60–80 |
| 5 | Extremely good condition, structures mostly intact, no sign of degradation. Strong linkages. | 80–100 |
| Cluster | Sonar Image | Average Module Height (m) | Distribution Area (m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2022 | |||
| 1 |  Total AR module = 24 Total AR module = 24 |  Total AR module = 24 Total AR module = 24 | 1.7–1.8 | 6000 |
| 2 |  Total AR module = 32 Total AR module = 32 |  Total AR module = 32 Total AR module = 32 | 1.7–1.8 | 1200 |
| 3 |  Total AR module = 52 Total AR module = 52 |  Total AR module = 52 Total AR module = 52 | 1.7–1.8 | 4800 |
| Family | Genus | Species | IUCN Status | Habitat Preference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apogonidae | Ostorhinchus | Ostorhinchus endekataenia | NE | RA |
| Taeniamia | Taeniamia fucata | LC | RA | |
| Caesionidae | Caesio | Caesio cuning | LC | RA |
| Pterocaesio | Pterocaesio chrysozona | LC | RA, NonM | |
| Carangidae | Carangoides | Carangoides chrysophrys | LC | RA |
| Chaetodontidae | Chaetodon | Chaetodon octofasciatus | LC | RA |
| Chelmon | Chelmon rostratus | LC | RA, NonM | |
| Haemulidae | Plectorhinchus | Plectorhinchus picus | NE | RA, NonM |
| Holocentridae | Sargocentron | Sargocentron rubrum | LC | RA |
| Labridae | Halichoeres | Halichoeres melanurus | LC | RA |
| Labroides | Labroides dimidiatus | LC | RA, NonM | |
| Thalassoma | Thalassoma lunare | LC | RA | |
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus | Lutjanus johnii | LC | RA, OD |
| Lutjanus lutjanus | LC | RA | ||
| Lutjanus vitta | LC | RA | ||
| Nemipteridae | Scolopsis | Scolopsis affinis | LC | RA |
| Scolopsis taenioptera | LC | DE | ||
| Scolopsis vosmeri | LC | RA | ||
| Pempheridae | Pempheris | Pempheris oualensis | NE | RA |
| Pomacanthidae | Pomacanthus | Pomacanthus annularis | LC | RA, NonM |
| Acanthochromis | Acanthochromis polycanthus | LC | RA, NonM | |
| Chromis | Chromis alpha | LC | RA, NonM | |
| Dascyllus | Dascyllus flavicaudus | NE | RA, NonM | |
| Dascyllus reticulatus | NE | RA, NonM | ||
| Neopomacentrus | Neopomacentrus cyanomos | NE | RA, NonM | |
| Pomacentrus | Pomacentrus philippinus | NE | RA, NonM | |
| Serranidae | Cephalopholis | Cephalopholis boenak | LC | RA, NonM |
| Cephalopholis formosa | LC | RA, NonM | ||
| Diploprion | Diploprion bifasciatum | LC | RA | |
| Plectropomus | Plectropomus maculatus | LC | RA | |
| Siganidae | Siganus | Siganus guttatus | LC | RA |
| Siganus javus | LC | RA, OD | ||
| Tetraodontidae | Arothron | Arothron mappa | LC | RA |
| Arothron stellatus | LC | RA |
| Species | CR1 | CR2 | CR3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taeniamia fucata | 33.17 | 11.44747 | 8.680262 |
| Caesio cuning | 11.40059 | ||
| Pterocaesio chrysozona | 1.37 | 0.00095 | 21.08494 |
| Carangoides chrysophrys | 11.15717 | ||
| Chelmon rostratus | 0.002675 | ||
| Plectorhinchus picus | 0.07367 | ||
| Sargocentron rubrum | 21.65403 | ||
| Halichoeres melanurus | 0.000315 | ||
| Labroides dimidiatus | 0.03 | 0.000791 | |
| Thalassoma lunare | 0.03 | 0.013188 | |
| Lutjanus johnii | 28.93954 | 0.327519 | |
| Lutjanus lutjanus | 1.05 | 27.44845 | 0.001552 |
| Lutjanus vitta | 9.06 | 2398.265 | 0.022659 |
| Scolopsis vosmeri | 0.001594 | 0.006376 | |
| Pempheris oualensis | 0.01 | 1.109167 | |
| Dascyllus reticulatus | 0.554377 | ||
| Neopomacentrus cyanomos | 372.34 | 1.034356 | 557.5101 |
| Pomacentrus philippinus | 0.09 | 0.004936 | 0.241878 |
| Cephalopholis boenak | 0.01 | 0.001766 | |
| Cephalopholis formosa | 0.03 | 0.007726 | |
| Diploprion bifasciatum | 0.01 | 0.012502 | 0.003126 |
| Plectropomus maculatus | 0.01073 | ||
| Siganus guttatus | 0.810502 | ||
| Siganus javus | 0.531251 | ||
| Arothron stellatus | 0.17606 | 0.17606 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, A.; Abdullah, M.R.; Safuan, C.D.M.; Afiq-Firdaus, A.M.; Bachok, Z.; Akhir, M.F.M.; Latif, R.; Muhamad, A.; Seng, T.H.; Roslee, A.; et al. Side-Scan Sonar Coupled with Scuba Diving Observation for Enhanced Monitoring of Benthic Artificial Reefs along the Coast of Terengganu, Peninsular Malaysia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091309
Ali A, Abdullah MR, Safuan CDM, Afiq-Firdaus AM, Bachok Z, Akhir MFM, Latif R, Muhamad A, Seng TH, Roslee A, et al. Side-Scan Sonar Coupled with Scuba Diving Observation for Enhanced Monitoring of Benthic Artificial Reefs along the Coast of Terengganu, Peninsular Malaysia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(9):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091309
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Azizi, Muhammad Ruzi Abdullah, Che Din Mohd Safuan, Aminudin Muhammad Afiq-Firdaus, Zainudin Bachok, Mohd Fadzil Mohd Akhir, Roslan Latif, Azri Muhamad, Tan Hock Seng, Adina Roslee, and et al. 2022. "Side-Scan Sonar Coupled with Scuba Diving Observation for Enhanced Monitoring of Benthic Artificial Reefs along the Coast of Terengganu, Peninsular Malaysia" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 9: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091309
APA StyleAli, A., Abdullah, M. R., Safuan, C. D. M., Afiq-Firdaus, A. M., Bachok, Z., Akhir, M. F. M., Latif, R., Muhamad, A., Seng, T. H., Roslee, A., & Ismail, K. (2022). Side-Scan Sonar Coupled with Scuba Diving Observation for Enhanced Monitoring of Benthic Artificial Reefs along the Coast of Terengganu, Peninsular Malaysia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(9), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091309







