Quality Assessment of Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Ocean Reanalysis Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ocean Reanalysis
2.2. In Situ Analyzed Product
2.3. Mooring Buoy
2.4. Assessment Strategy
3. Results
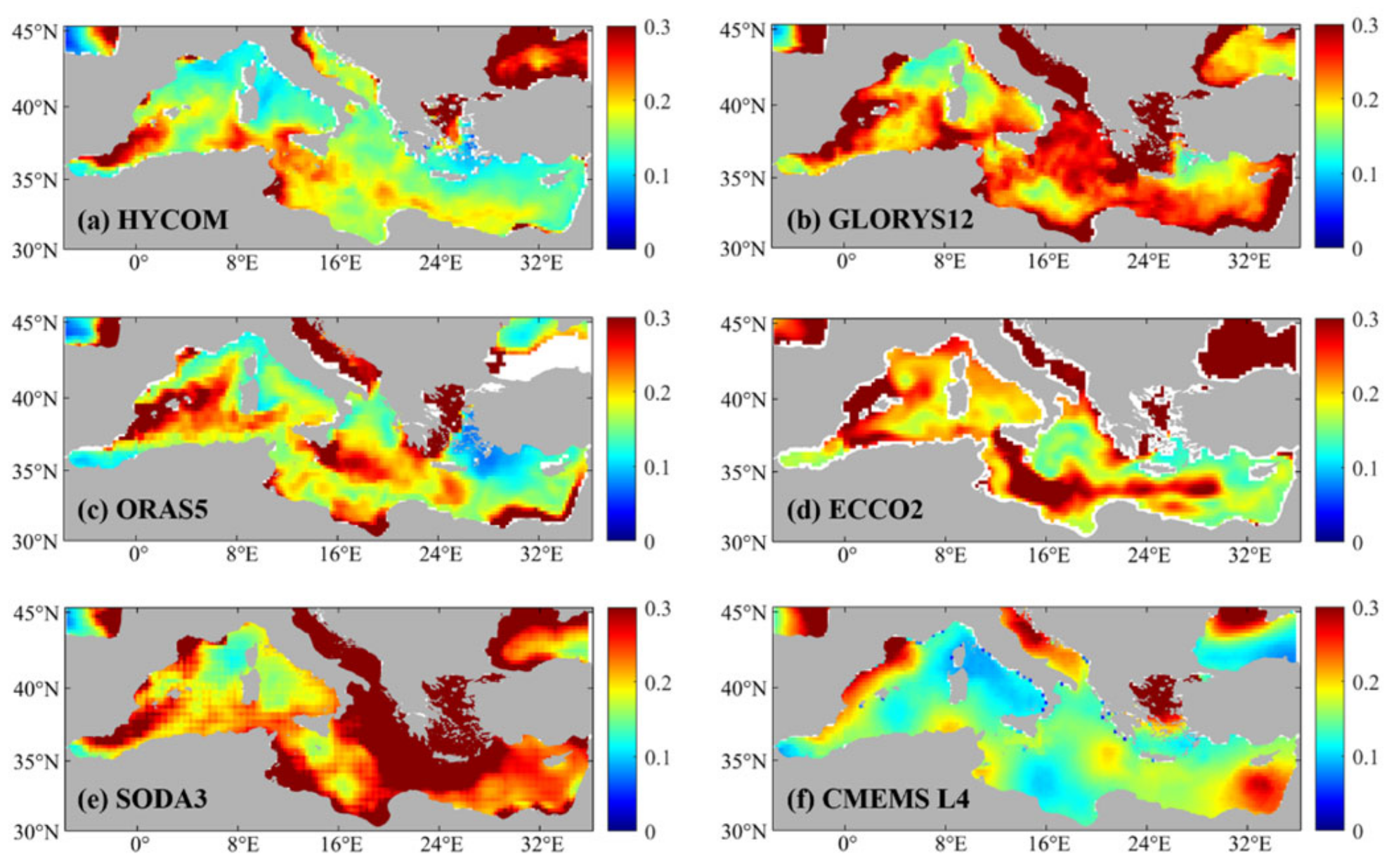
3.1. Regional Assessment in the Mediterranean Sea
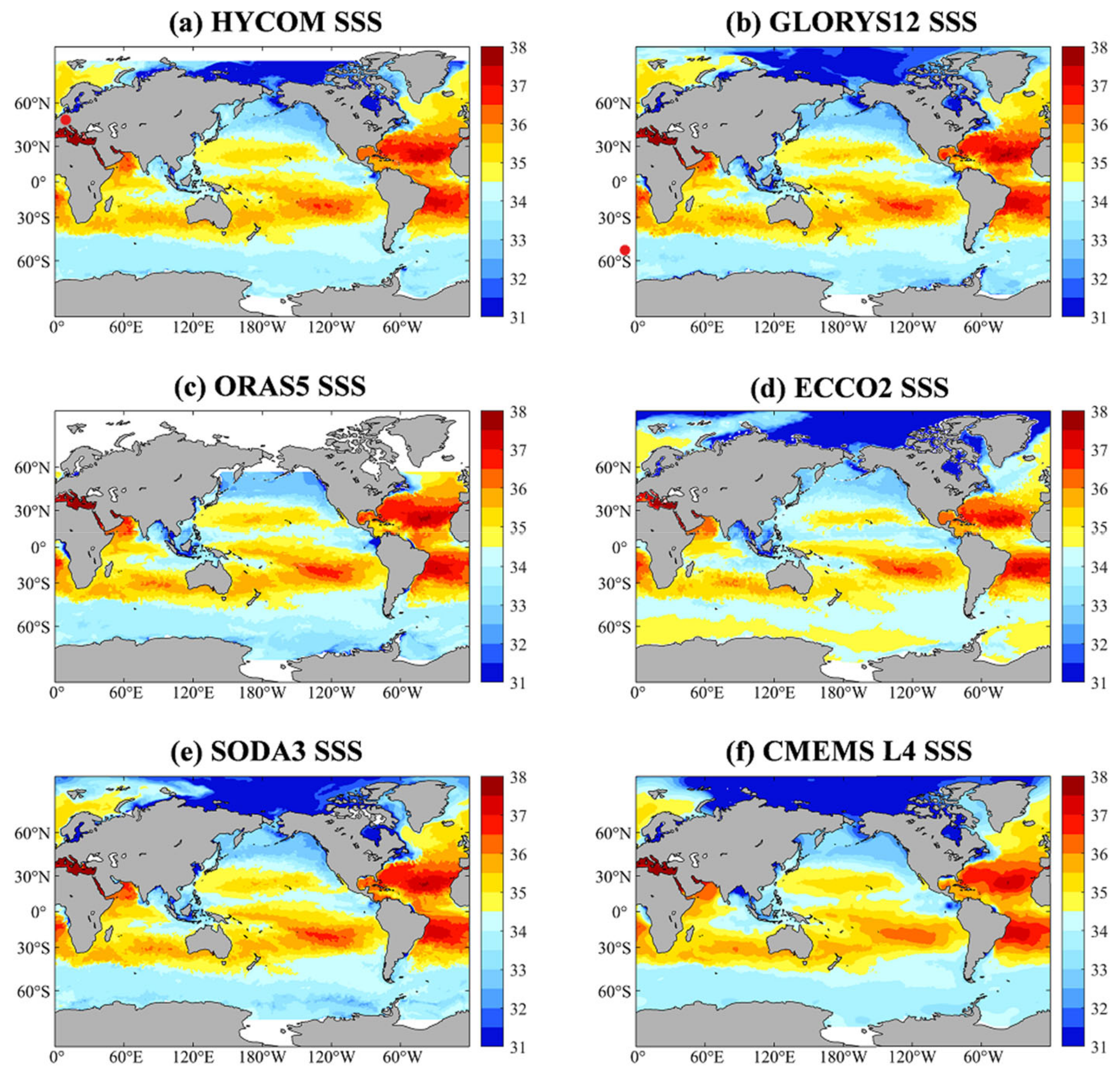
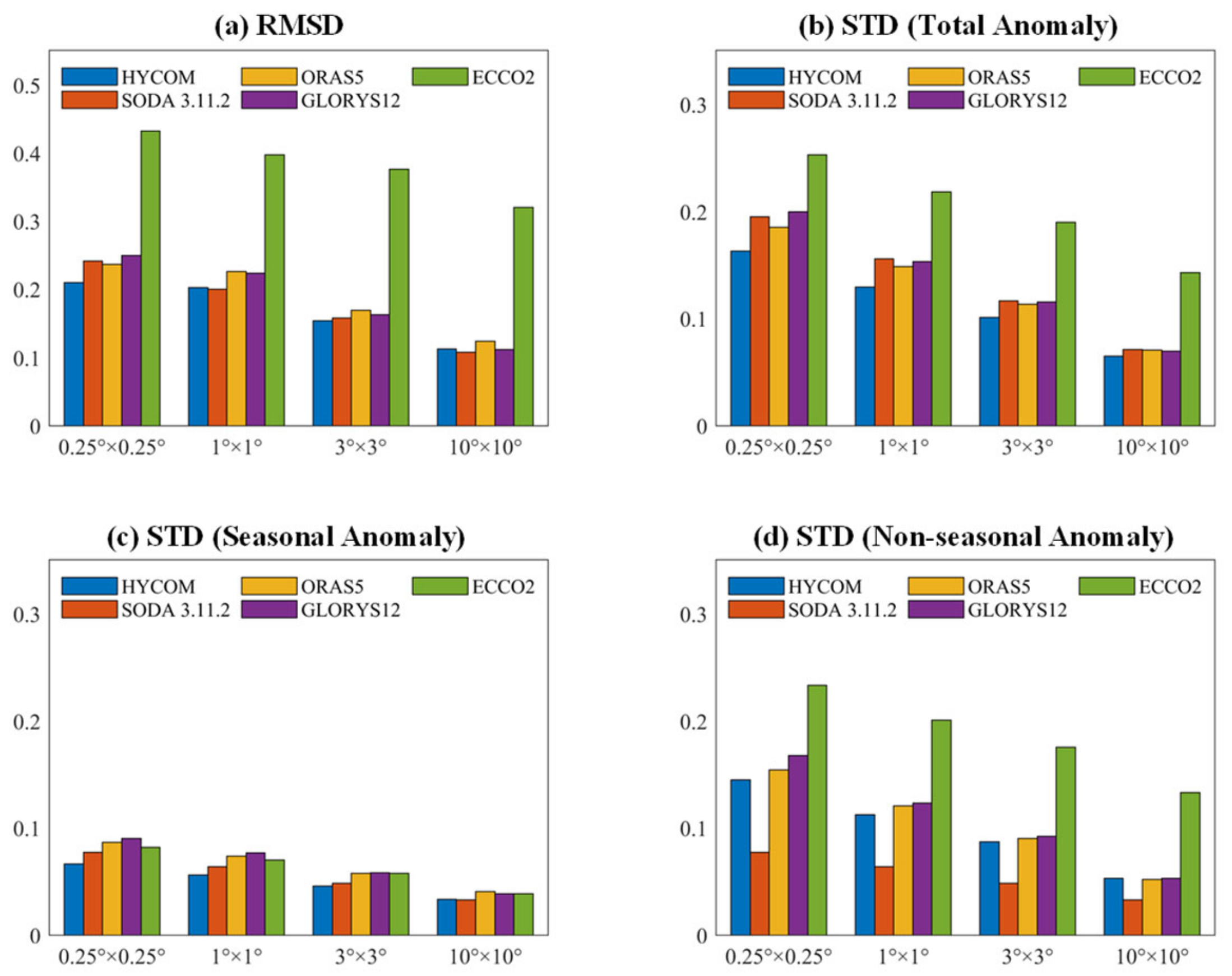
3.2. Global Assessment
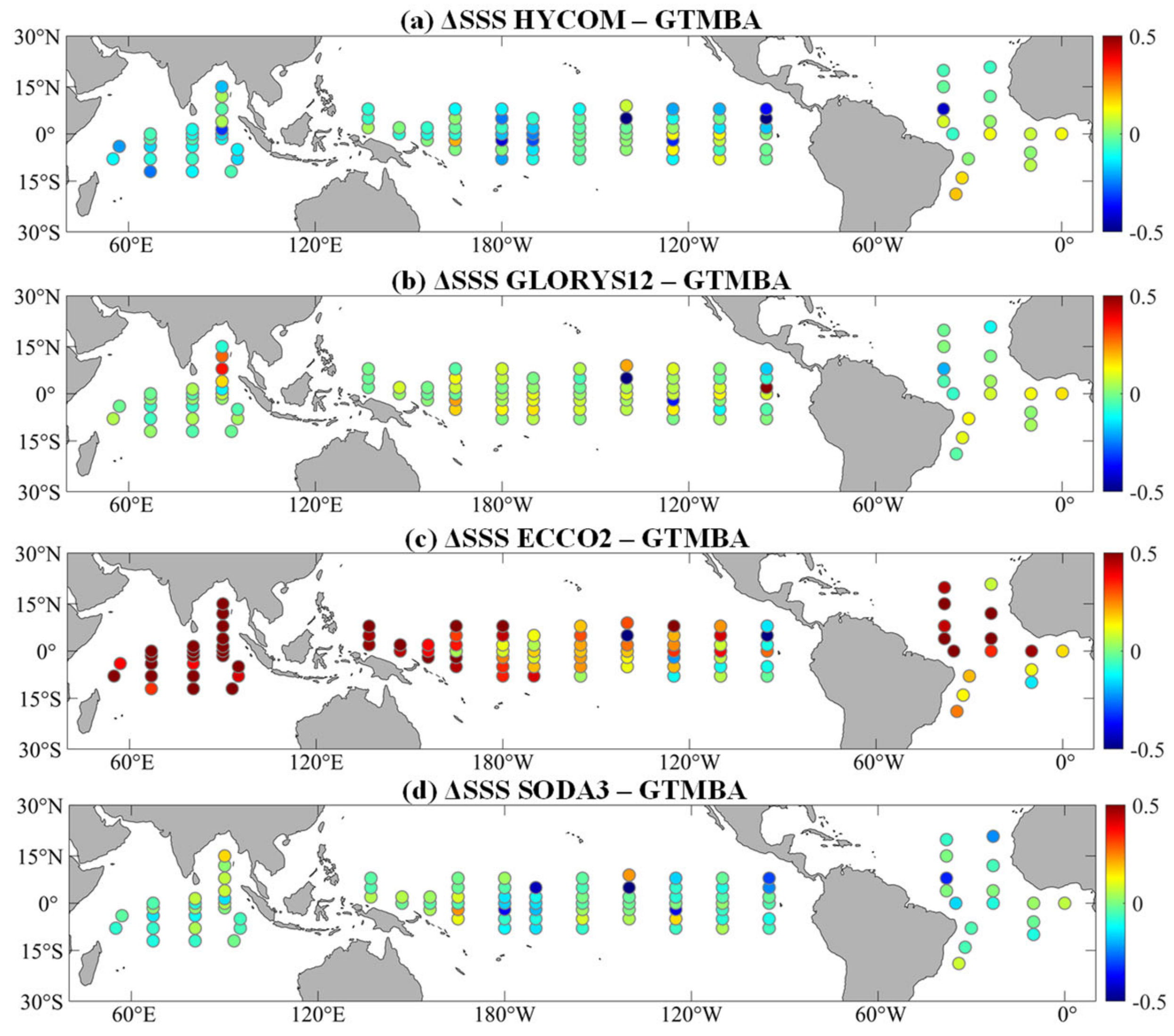
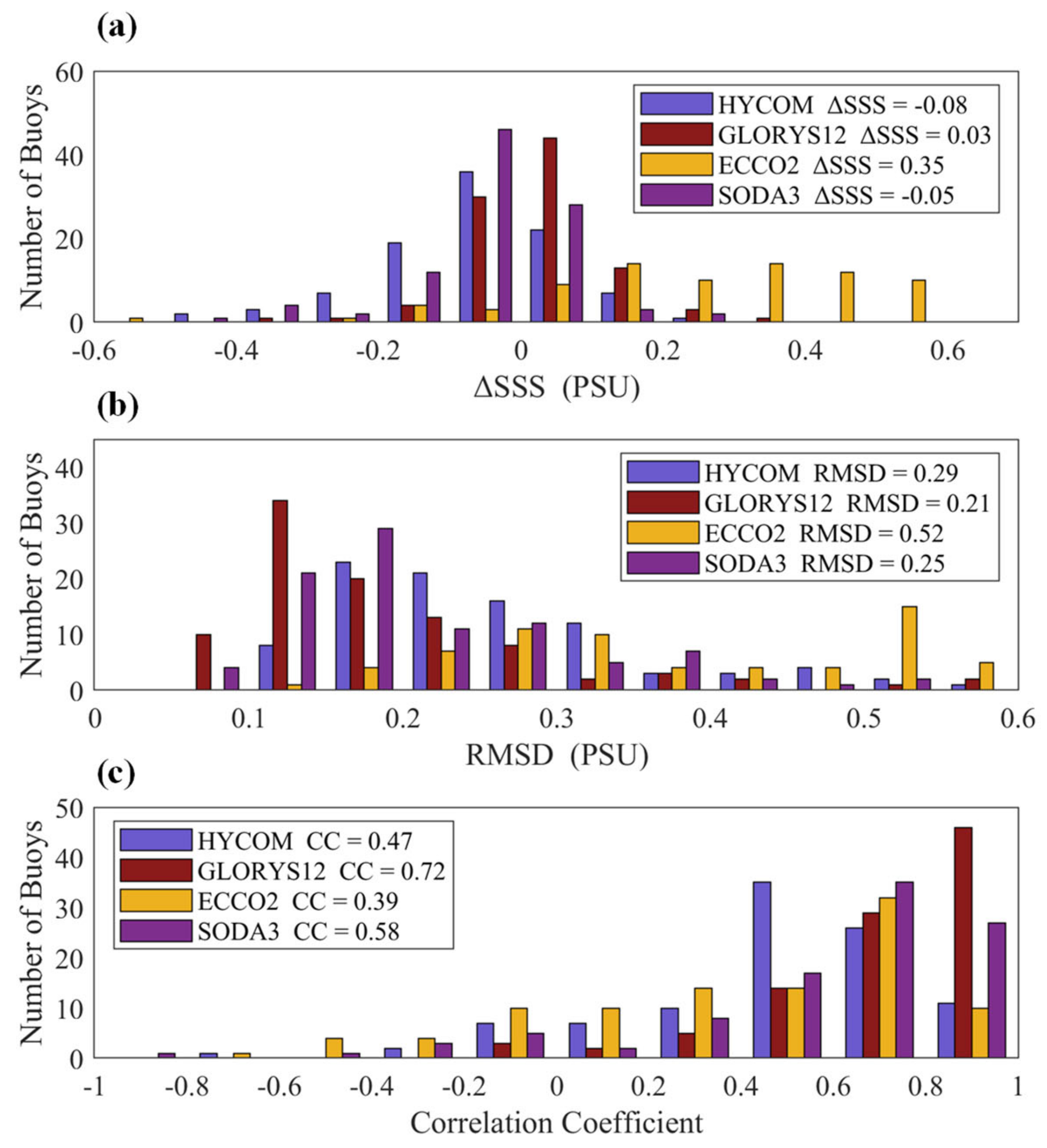
3.3. Comparison with Tropical Moored Buoys
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ponte, R.; Vinogradova, N. An assessment of basic processes controlling mean surface salinity over the global ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7052–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supply, A.; Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.L.; Martin, N.; Hasson, A.; Reverdin, G.; Mallet, C.; Viltard, N. Precipitation estimates from SMOS sea-surface salinity. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Jin, X.; Josey, S.A.; Lee, T.; Kumar, A.; Wen, C.; Xue, Y. The global ocean water cycle in atmospheric reanalysis, satellite, and ocean salinity. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3829–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.L.; Cessi, P.; Marshall, D.P.; Schloesser, F.; Spall, M.A. Recent Contributions of Theory to Our Understanding of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 5376–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, J.; Trenberth, K.E.; Mann, M.E.; Abraham, J.P. Increasing ocean stratification over the past half-century. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gévaudan, M.; Jouanno, J.; Durand, F.; Morvan, G.; Renault, L.; Samson, G. Influence of ocean salinity stratification on the tropical Atlantic Ocean surface. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, G. Mapping ocean observations in a dynamical framework: A 2004–06 ocean atlas. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1201–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.; Toole, J.; Forget, G.; Zika, J.D.; Naveira Garabato, A.C.; Nurser, A.G.; Yu, L. Recent wind-driven variability in Atlantic water mass distribution and meridional overturning circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, G.; Lyman, J.; Boyer, T.; Cheng, L.; Domingues, C.; Gilson, J.; Ishii, M.; Killick, R.; Monselesan, D.; Purkey, S. Global oceans: Ocean heat content. state of the climate in 2017. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc 2018, 99, S72–S77. [Google Scholar]
- Balmaseda, M.A.; Mogensen, K.; Weaver, A.T. Evaluation of the ECMWF ocean reanalysis system ORAS4. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 1132–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.-H.; Choi, B.-J.; Cho, Y.-K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S. Evaluation of a regional ocean reanalysis system for the East Asian Marginal Seas based on the ensemble Kalman filter. Ocean. Sci. J. 2015, 50, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Bertino, L.; Counillon, F.; Lisæter, K.A.; Sakov, P. Quality assessment of the TOPAZ4 reanalysis in the Arctic over the period 1991–2013. Ocean. Sci. 2017, 13, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.; Renfrew, I.; Orr, A.; Webber, B.; Holland, D.; Lazzara, M. Evaluation of four global reanalysis products using in situ observations in the Amundsen Sea Embayment, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6240–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, H.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Mogensen, K.; Tietsche, S. OCEAN5: The ECMWF Ocean Reanalysis System and its Real-Time Analysis Component; European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Breivik, Ø.; Mogensen, K.; Bidlot, J.R.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Janssen, P.A. Surface wave effects in the NEMO ocean model: Forced and coupled experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 2973–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, d.P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeais, J.-F.; Ablain, M.; Zawadzki, L.; Zuo, H.; Johannessen, J.A.; Scharffenberg, M.G.; Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Fernandes, M.J.; Andersen, O.B.; Rudenko, S. An improved and homogeneous altimeter sea level record from the ESA Climate Change Initiative. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storto, A.; Oddo, P.; Cipollone, A.; Mirouze, I.; Lemieux-Dudon, B. Extending an oceanographic variational scheme to allow for affordable hybrid and four-dimensional data assimilation. Ocean. Model. 2018, 128, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Murtugudde, R.; Busalacchi, A. On the potential impact of sea surface salinity observations on ENSO predictions. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2002, 107, SRF 8-1–SRF 8-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, D.; Xue, Y. Evaluation of the Global Ocean Data Assimilation System at NCEP: The Pacific Ocean. In Proceedings of the Eighth Symposium on Integrated Observing and Assimilation Systems for Atmosphere, Oceans, and Land Surface, AMS 84th Annual Meeting, Seattle, Washington, 11–15 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Uotila, P.; Goosse, H.; Haines, K.; Chevallier, M.; Barthélemy, A.; Bricaud, C.; Carton, J.; Fučkar, N.; Garric, G.; Iovino, D. An assessment of ten ocean reanalyses in the polar regions. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 1613–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adani, M.; Dobricic, S.; Pinardi, N. Quality assessment of a 1985–2007 Mediterranean Sea reanalysis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 569–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, M.; Beuvier, J.; Somot, S.; Lellouche, J.-M.; Greiner, E.; Jordà, G.; Bouin, M.-N.; Arsouze, T.; Béranger, K.; Sevault, F. Design and validation of MEDRYS, a Mediterranean Sea reanalysis over the period 1992–2013. Ocean. Sci. 2016, 12, 577–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Navarro, J.; Jordá, G.; Amores, A.; Cabos, W.; Somot, S.; Sevault, F.; Macías, D.; Djurdjevic, V.; Sannino, G.; Li, L. Evolution of Mediterranean Sea water properties under climate change scenarios in the Med-CORDEX ensemble. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 2135–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balmaseda, M.; Hernandez, F.; Storto, A.; Palmer, M.; Alves, O.; Shi, L.; Smith, G.C.; Toyoda, T.; Valdivieso, M.; Barnier, B. The ocean reanalyses intercomparison project (ORA-IP). J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2015, 8, s80–s97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Alves, O.; Wedd, R.; Balmaseda, M.; Chang, Y.; Chepurin, G.; Ferry, N.; Fujii, Y.; Gaillard, F.; Good, S. An assessment of upper ocean salinity content from the Ocean Reanalyses Inter-comparison Project (ORA-IP). Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 1009–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnier, B.; Brodeau, L.; Le Sommer, J.; Molines, J.-M.; Penduff, T.; Theetten, S.; Treguier, A.-M.; Madec, G.; Biastoch, A.; Böning, C.W. Eddy-permitting ocean circulation hindcasts of past decades. Clivar Exch. 2007, 42, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Michel, L.; Eric, G.; Romain, B.-B.; Gilles, G.; Angélique, M.; Marie, D.; Clement, B.; Mathieu, H.; Olivier, L.G.; Charly, R. The Copernicus global 1/12 oceanic and sea ice GLORYS12 reanalysis. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 698876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monitoring, G.; Center, F. GLORYS12 V1—Global Ocean Physical Reanalysis Product; EU Copernicus Marine Service Information: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Carton, J.A.; Chepurin, G.A.; Chen, L. SODA3: A new ocean climate reanalysis. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 6967–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackett, D.R.; McDougall, T.J.; Feistel, R.; Wright, D.G.; Griffies, S.M. Algorithms for density, potential temperature, conservative temperature, and the freezing temperature of seawater. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 1709–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Tietsche, S.; Mogensen, K.; Mayer, M. The ECMWF operational ensemble reanalysis–analysis system for ocean and sea ice: A description of the system and assessment. Ocean. Sci. 2019, 15, 779–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McPhaden, M.J. The Tropical Atmosphere Ocean Array Is Completed. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servain, J.; Busalacchi, A.J.; McPhaden, M.J.; Moura, A.D.; Reverdin, G.; Vianna, M.; Zebiak, S.E. A pilot research moored array in the tropical Atlantic (PIRATA). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcphaden, M.J.; Meyers, G.; Ando, K.; Masumoto, Y.; Murty, V.; Ravichandran, M.; Syamsudin, F.; Vialard, J.; Yu, L.; Yu, W. RAMA: The research moored array for African–Asian–Australian monsoon analysis and prediction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Minato, S. COARE Seacat data: Calibrations and quality control procedures COARE Seacat data: Calibrations and quality control procedures, 1999. J. Oceanogr. 2005, 61, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Yan, H.; Chen, J. Comparison of Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Salinity Products from SMOS, Aquarius, and SMAP. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Fore, A.; Yueh, S.; Lee, T.; Hayashi, A.; Sanchez-Franks, A.; Martinez, J.; King, B.; Baranowski, D. Validating SMAP SSS with in situ measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.; Lagerloef, G.; Kao, H.Y.; McPhaden, M.J.; Willis, J.; Gierach, M.M. The influence of salinity on tropical Atlantic instability waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 8375–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Yu, J.-Y. ENSO indices from sea surface salinity observed by Aquarius and Argo. J. Oceanogr. 2014, 70, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grunseich, G.; Subrahmanyam, B.; Wang, B. The Madden-Julian oscillation detected in Aquarius salinity observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5461–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y. Satellite and Argo observed surface salinity variations in the tropical Indian Ocean and their association with the Indian Ocean dipole mode. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sammartino, M.; Aronica, S.; Santoleri, R.; Buongiorno Nardelli, B. Retrieving Mediterranean Sea Surface Salinity Distribution and Interannual Trends from Multi-Sensor Satellite and In Situ Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnichenko, O.; Amores, A.; Maximenko, N.; Hacker, P.; Potemra, J. Signature of mesoscale eddies in satellite sea surface salinity data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Sea-surface salinity fronts and associated salinity-minimum zones in the tropical ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 4205–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Dataset | Model | Forcing | Grid Resolution | Assimilation Method | Assimilated Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HYCOM GOFS 3.0 | HYCOM 2.2 | NCEP CFSR | 1/12° | 3D MVOI | Satellite SST Altimeter SLA Ship and buoy T/S profiles In situ ocean currents |
| GLORYS12 | NEMO 3.1 | ERA-Interim | 1/12° | 3D-Var Reduced-order Kalman Filter | Altimeter SLA AVHRR SST CORA T/S profiles |
| SODA3 | MOM5 | DFS5.2 | 1/4° | Linear Deterministic Sequential Filter | WOD09 T/S profiles Satellite SST ICOADS SST |
| ECCO2 | MITgcm | NCEP/NCAR | 1/4° | Least Squares Fit | GHRSST-PP SST WOCE T/S profiles TAO, Argo, XBT T/S profiles |
| ORAS5 | NEMO 3.4 | ERA-Interim | ∼1/4° | 3D-Var FGAT (NEMOVAR) | EN4 T/S profiles corrected by XBT/MBT data HadISST2 + OSTIA SST |
| Statistical Parameter | Algorithm | |
|---|---|---|
| SSS Mean | (1) | |
| ΔSSS | (2) | |
| STD | (3) | |
| RMSD | (4) | |
| CC 1 | (5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; You, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, P.; Ren, K. Quality Assessment of Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Ocean Reanalysis Products. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010054
Wang H, You Z, Guo H, Zhang W, Xu P, Ren K. Quality Assessment of Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Ocean Reanalysis Products. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haodi, Ziqi You, Hailong Guo, Wen Zhang, Peng Xu, and Kaijun Ren. 2023. "Quality Assessment of Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Ocean Reanalysis Products" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010054
APA StyleWang, H., You, Z., Guo, H., Zhang, W., Xu, P., & Ren, K. (2023). Quality Assessment of Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Ocean Reanalysis Products. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010054







