Relationships between Abyssal Redox Conditions and Rock Magnetic Properties of Surficial Sediments in the Western Pacific
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
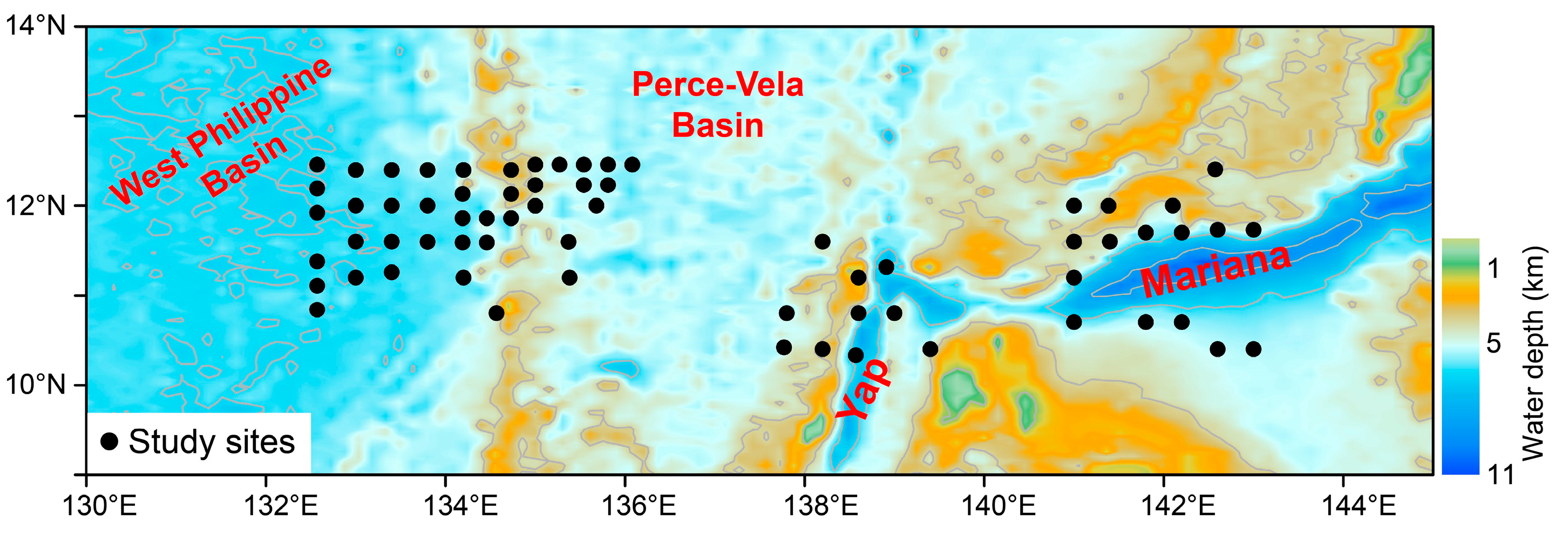
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Magnetic Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Relationships between Magnetic Parameters
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Magnetic Parameters
3.3. Sedimentary Magnetic Mineralogy

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, K.M.; Anderson, R.F.; McManus, J.F.; Winckler, G.; Middleton, J.L.; Langmuir, C.H. Trace element (Mn, Zn, Ni, V) and authigenic uranium (aU) geochemistry reveal sedimentary redox history on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, North Pacific Ocean. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 236, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.C.; Bradbury, H.J.; Hodell, D.A. Changes in North Atlantic deep-water oxygenation across the Middle Pleistocene transition. Science 2022, 377, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, S.L.; Galbraith, E.D.; Martínez-García, A.; Anderson, R.F. Covariation of deep Southern Ocean oxygenation and atmospheric CO2 through the last ice age. Nature 2016, 530, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auderset, A.; Moretti, S.; Taphorn, B.; Ebner, P.-R.; Kast, E.; Wang, X.T.; Schiebel, R.; Sigman, D.M.; Haug, G.H.; Martínez-García, A. Enhanced ocean oxygenation during Cenozoic warm periods. Nature 2022, 609, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, J.; Pagani, M.; Sloan, L.; Thomas, E.; Billups, K. Trends, Rhythms, and Aberrations in Global Climate 65 Ma to Present. Science 2001, 292, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodell, D.A.; Venz, K.A.; Charles, C.D.; Ninnemann, U.S. Pleistocene vertical carbon isotope and carbonate gradients in the South Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2003, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodell, D.A.; Venz-Curtis, K.A. Late Neogene history of deepwater ventilation in the Southern Ocean. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2006, 7, Q09001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackensen, A.; Schmiedl, G. Stable carbon isotopes in paleoceanography: Atmosphere, oceans, and sediments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spero, H.J.; Bijma, J.; Lea, D.W.; Bemis, B.E. Effect of seawater carbonate concentration on foraminiferal carbon and oxygen isotopes. Nature 1997, 390, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Quay, P.D.; Wilbur, D.O. Carbon isotope fractionation during gas-water exchange and dissolution of CO2. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Xu, D.; Jiang, X.; Ma, X.; Ge, Q.; Deng, X.; Wang, H.; Deng, C. Magnetostratigraphy and Authigenic 10Be/9Be Dating of Plio-Pleistocene Abyssal Surficial Sediments on the Southern Slope of Mariana Trench and Sedimentary Processes During the Mid-Pleistocene Transition. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2020JC016250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Medina-Elizalde, M.; Tan, L.; Kemp, D.B.; Li, Y.; Kletetschka, G.; Xie, Q.; Yao, H.; He, H.; Deng, C.; et al. Plio-Pleistocene deep-sea ventilation in the Eastern Pacific and potential linkages with Northern Hemisphere glaciation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaccard, S.L.; Hayes, C.T.; Martínez-García, A.; Hodell, D.A.; Anderson, R.F.; Sigman, D.M.; Haug, G.H. Two Modes of Change in Southern Ocean Productivity Over the Past Million Years. Science 2013, 339, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Shi, X.; Liu, J.; Bi, L. Deepwater redox changes in the southern Okinawa Trough since the last glacial maximum. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 135, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, L.; Deng, X.; He, G. Geochemical and Mineral Properties of Quaternary Deep-Sea Sediments in the Central-Tropical Pacific and Its Response to the Mid-Pleistocene Transition. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Flierdt, T.; Frank, M. Neodymium isotopes in paleoceanography. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 2439–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Ferretti, P.; Greaves, M.; Crowhurst, S.; McCave, I.N.; Hodell, D.; Piotrowski, A.M. Evolution of Ocean Temperature and Ice Volume Through the Mid-Pleistocene Climate Transition. Science 2012, 337, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöppelmeier, F.; Lippold, J.; Blaser, P.; Gutjahr, M.; Frank, M.; Stocker, T.F. Neodymium isotopes as a paleo-water mass tracer: A model-data reassessment. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 279, 107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruiver, P.P.; Passier, H.F. Coercivity analysis of magnetic phases in sapropel S1 related to variations in redox conditions, including an investigation of the S ratio. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2001, 2, 2001GC000181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Bolton, C.T.; Dekkers, M.J.; Hayashida, A.; Heslop, D.; Krijgsman, W.; Kodama, K.; Paterson, G.A.; Roberts, A.P.; Rohling, E.J.; et al. Asian monsoon modulation of nonsteady state diagenesis in hemipelagic marine sediments offshore of Japan. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2016, 17, 4383–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissel, C.; Laj, C.; Jian, Z.; Wang, P.; Wandres, C.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M. Past environmental and circulation changes in the South China Sea: Input from the magnetic properties of deep-sea sediments. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 236, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, J.A.; Dobeneck, T.v.; Reitz, A. Integrated Rock Magnetic and Geochemical Quantification of Redoxomorphic Iron Mineral Diagenesis in Late Quaternary Sediments from the Equatorial Atlantic. In The South Atlantic in the Late Quaternary; Wefer, G., Mulitza, S., Ratmeyer, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 237–260. [Google Scholar]
- Korff, L.; von Dobeneck, T.; Frederichs, T.; Kasten, S.; Kuhn, G.; Gersonde, R.; Diekmann, B. Cyclic magnetite dissolution in Pleistocene sediments of the abyssal northwest Pacific Ocean: Evidence for glacial oxygen depletion and carbon trapping. Paleoceanography 2016, 31, 600–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kars, M.; Musgrave, R.J.; Kodama, K.; Jonas, A.-S.; Bordiga, M.; Ruebsam, W.; Mleneck-Vautravers, M.J.; Bauersachs, T. Impact of climate change on the magnetic mineral assemblage in marine sediments from Izu rear arc, NW Pacific Ocean, over the last 1Myr. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2017, 480, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Yu, Y.; Seo, I.; Hyeong, K.; Lim, D.; Kim, W. Magnetic Properties of Deep-Sea Sediments From the North Pacific: A Proxy of Glacial Deep-Water Ventilation. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2018, 19, 4433–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P. Magnetic mineral diagenesis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 151, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, K.; Williams, W.; Liu, Q.; Yu, Y. Effects of the core-shell structure on the magnetic properties of partially oxidized magnetite grains: Experimental and micromagnetic investigations. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2014, 15, 2021–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Worm, H.-U.; Banerjee, S.K. Fourier analysis of digital hysteresis data: Rock magnetic applications. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1990, 65, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslop, D. Numerical strategies for magnetic mineral unmixing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 256–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslop, D.; Roberts, A.P. Unmixing Magnetic Hysteresis Loops. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. Magnetic properties of some synthetic sub-micron magnetites. Geophys. J. 1988, 94, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q. Anhysteretic remanent magnetization (ARM) and its application to geoscience. Prog. Geophys. 2012, 27, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.E.; Heller, F. Environmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; p. 322. [Google Scholar]
- van Haren, H.; Berndt, C.; Klaucke, I. Ocean mixing in deep-sea trenches: New insights from the Challenger Deep, Mariana Trench. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2017, 129, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Xin, Y. Mineral composition and geochemical characteristics of sinking particles in the Challenger Deep, Mariana Trench: Implications for provenance and sedimentary environment. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 196, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Hu, B.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, X.; Shu, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, F.; Ding, X.; Liu, G.; et al. Magnetostratigraphy of Abyssal Deposits in the Central Philippine Sea and Regional Sedimentary Dynamics During the Quaternary. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatology 2022, 37, e2021PA004365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Wang, H.; Deng, X.; Yuan, H.; Xu, D.; Yao, H. Geochronology and Geochemical Properties of Mid-Pleistocene Sediments on the Caiwei Guyot in the Northwest Pacific Imply a Surface-to-Deep Linkage. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T. Environmental magnetism of Pleistocene sediments in the North Pacific and Ontong-Java Plateau: Temporal variations of detrital and biogenic components. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2009, 10, Q07Z04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T. Paleoposition of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the eastern Pacific inferred from glacial-interglacial changes in terrigenous and biogenic magnetic mineral fractions. Geology 2012, 40, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.; Fuller, M.; Schmidt, V.A. Hysteresis properties of titanomagnetites: Grain-size and compositional dependence. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1977, 13, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxbauer, D.P.; Feinberg, J.M.; Fox, D.L. MAX UnMix: A web application for unmixing magnetic coercivity distributions. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 95, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.J. Theory and application of the Day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc) 1. Theoretical curves and tests using titanomagnetite data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, EPM 4-1-EPM 4-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.J. Theory and application of the Day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc) 2. Application to data for rocks, sediments, and soils. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, EPM 5-1-EPM 5-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Heslop, D.; Zhao, X.; Pike, C.R. Understanding fine magnetic particle systems through use of first-order reversal curve diagrams. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 557–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Pike, C.R.; Verosub, K.L. First-order reversal curve diagrams: A new tool for characterizing the magnetic properties of natural samples. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 28461–28475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yi, L.; Paterson, G.A.; Qin, H.; Wang, H.; Yao, H.; Ren, J.; Ge, J.; Xu, H.; Deng, C.; et al. Magnetostratigraphic evidence for deep-sea erosion on the Pacific Plate, south of Mariana Trench, since the middle Pleistocene: Potential constraints for Antarctic bottom water circulation. Int. Geol. Rev. 2016, 58, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Roberts, A.P.; Pan, H.; Xiao, T.; Pan, Y. Classification of a Complexly Mixed Magnetic Mineral Assemblage in Pacific Ocean Surface Sediment by Electron Microscopy and Supervised Magnetic Unmixing. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 609058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Yao, H.; Deng, X. Magnetic minerals in Mid-Pleistocene sediments on the Caiwei Guyot, Northwest Pacific and their response to the Mid-Brunhes climate event. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Tauxe, L.; Heslop, D.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z. A Critical Appraisal of the “Day” Diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 2618–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ö.; Dunlop, D.J. Hallmarks of maghemitization in low-temperature remanence cycling of partially oxidized magnetite nanoparticles. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B02101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Ren, J.-b.; He, G.; Chen, W.; Yi, L. Pleistocene magnetostratigraphy of four cores in the West Philippian Basin and regional sedimentary shift during the Mid-Pleistocene Transition. Geol. J. 2021, 56, 2919–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sites | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Water Depth (m) | Sites | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Water Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A14 | 137.77 | 10.42 | 4690 | E04 | 133.80 | 12.00 | 5720 |
| A15 | 138.20 | 10.40 | 4200 | E07 | 135.00 | 12.00 | 4620 |
| A16 | 138.57 | 10.33 | 5990 | E09 | 135.68 | 12.00 | 4750 |
| A18 | 139.40 | 10.40 | 3890 | E22 | 141.00 | 12.00 | 4070 |
| J01A | 142.28 | 10.35 | 4430 | E23 | 141.38 | 12.00 | 2630 |
| A27 | 142.60 | 10.40 | 4920 | E25 | 142.10 | 12.00 | 4120 |
| B06 | 134.57 | 10.80 | 4025 | F02 | 133.00 | 12.40 | 5540 |
| B14 | 137.80 | 10.80 | 4230 | F03 | 133.40 | 12.40 | 5850 |
| B16 | 138.60 | 10.80 | 5340 | F04 | 133.80 | 12.40 | 5220 |
| B17 | 139.00 | 10.80 | 3540 | F05 | 134.20 | 12.40 | 5180 |
| B22 | 141.00 | 10.70 | 5605 | F26 | 142.57 | 12.41 | 3560 |
| B24 | 141.80 | 10.70 | 4800 | G01 | 132.57 | 12.46 | 5830 |
| B25 | 142.20 | 10.70 | 5090 | G09 | 134.73 | 12.40 | 3390 |
| C02 | 133.00 | 11.20 | 5720 | G10 | 135.00 | 12.46 | 4040 |
| C03 | 133.40 | 11.26 | 5710 | G11 | 135.27 | 12.46 | 4610 |
| C05 | 134.20 | 11.20 | 5330 | G12 | 135.54 | 12.46 | 4880 |
| C08 | 135.38 | 11.20 | 4200 | G13 | 135.81 | 12.46 | 5041 |
| C16 | 138.60 | 11.20 | 3120 | G14 | 136.08 | 12.46 | 5063 |
| C17 | 138.91 | 11.32 | 5670 | G15 | 132.57 | 12.19 | 6060 |
| C22 | 141.00 | 11.20 | 4780 | G21 | 134.19 | 12.13 | 5020 |
| D02 | 133.00 | 11.60 | 5950 | G23 | 134.73 | 12.13 | 3430 |
| D03 | 133.40 | 11.60 | 5630 | G24 | 135.00 | 12.23 | 3680 |
| D04 | 133.80 | 11.60 | 5230 | G26 | 135.54 | 12.23 | 4770 |
| D08 | 135.37 | 11.60 | 4260 | G27 | 135.81 | 12.23 | 5100 |
| D15 | 138.20 | 11.60 | 4180 | G28 | 132.57 | 11.92 | 5970 |
| D22 | 141.00 | 11.60 | 3310 | G34 | 134.19 | 11.86 | 5510 |
| D23 | 141.40 | 11.60 | 4100 | G35 | 134.46 | 11.86 | 3330 |
| D24 | 141.80 | 11.70 | 5370 | G36 | 134.73 | 11.86 | 4940 |
| D25 | 142.20 | 11.70 | 5590 | G46 | 134.19 | 11.59 | 5580 |
| D26 | 142.60 | 11.73 | 5020 | G47 | 134.46 | 11.59 | 4750 |
| D27 | 143.00 | 11.73 | 3960 | G51 | 132.57 | 11.38 | 5770 |
| E02 | 133.00 | 12.00 | 5880 | G57 | 132.57 | 11.11 | 5820 |
| E03 | 133.40 | 12.00 | 5640 | G60 | 132.57 | 10.84 | 5790 |
| Units | Min | Max | Mean | Standard Deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χLF | m3/kg | 1.4 × 10−7 | 7.8 × 10−6 | 1.9 × 10−6 | 1.4 × 10−6 | 1.5 | 3.6 |
| χHF | m3/kg | 1.2 × 10−7 | 7.5 × 10−6 | 1.8 × 10−6 | 1.4 × 10−6 | 1.5 | 3.4 |
| χfd | % | 1.1 | 33.1 | 8.2 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 4.0 |
| χARM | m3/kg | 3.8 × 10−7 | 6.7 × 10−5 | 1.2 × 10−5 | 1.1 × 10−5 | 2.8 | 10.8 |
| SIRM | Am2/kg | 2.8 × 10−4 | 9.6 × 10−3 | 2.8 × 10−3 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
| IRM–0.1T | Am2/kg | 1.6 × 10−4 | 4.7 × 10−3 | 1.8 × 10−3 | 1.3 × 10−3 | 0.7 | −0.6 |
| IRM–0.3T | Am2/kg | 2.7 × 10−4 | 9.4 × 10−3 | 2.7 × 10−3 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 1.0 | 1.1 |
| χLF | χfd | χARM | SIRM | χARM/χ | SIRM/χ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χLF | 1 | |||||
| χfd | −0.48 | 1 | ||||
| χARM | 0.64 | −0.38 | 1 | |||
| SIRM | 0.88 | −0.51 | 0.87 | 1 | ||
| χARM/χ | −0.32 | 0.32 | 0.34 | −0.04 1 | 1 | |
| χARM/SIRM | −0.22 1 | 0.24 1 | 0.36 | −0.04 1 | 0.91 | 1 |
| SIRM/χ | −0.38 | 0.25 | 0.14 1 | 0.57 | 0.69 | 0.39 |
| Units | Min | Max | Mean | Standard Deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bc | mT | 4.5 | 17.1 | 13.5 | 2.7 | −1.4 | 1.9 |
| Bcr | mT | 32.0 | 55.5 | 43.6 | 4.2 | −0.6 | 1.2 |
| Mrs/Ms | - | 0.055 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.05 | −1.3 | 1.3 |
| Cont1 | % | 49.2 | 57.7 | 52.8 | 2.1 | 0.6 | −0.2 |
| Coe1 | mT | 9.9 | 17.7 | 13.1 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| Cont2 | % | 42.3 | 50.8 | 47.2 | 2.1 | −0.6 | −0.2 |
| Coe2 | mT | 44.0 | 68.9 | 54.7 | 5.3 | 0.6 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Xu, D.; Qin, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Yi, L. Relationships between Abyssal Redox Conditions and Rock Magnetic Properties of Surficial Sediments in the Western Pacific. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061132
Chen Y, Xu D, Qin H, Liu G, Li Y, Chen W, Yi L. Relationships between Abyssal Redox Conditions and Rock Magnetic Properties of Surficial Sediments in the Western Pacific. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(6):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061132
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yanping, Dong Xu, Huafeng Qin, Geng Liu, Yibing Li, Weiwei Chen, and Liang Yi. 2023. "Relationships between Abyssal Redox Conditions and Rock Magnetic Properties of Surficial Sediments in the Western Pacific" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 6: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061132
APA StyleChen, Y., Xu, D., Qin, H., Liu, G., Li, Y., Chen, W., & Yi, L. (2023). Relationships between Abyssal Redox Conditions and Rock Magnetic Properties of Surficial Sediments in the Western Pacific. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(6), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061132







