Development of a Radially Coupled Wireless Charging System for Torpedo-Shaped Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Coupler Design
2.1. System Overview
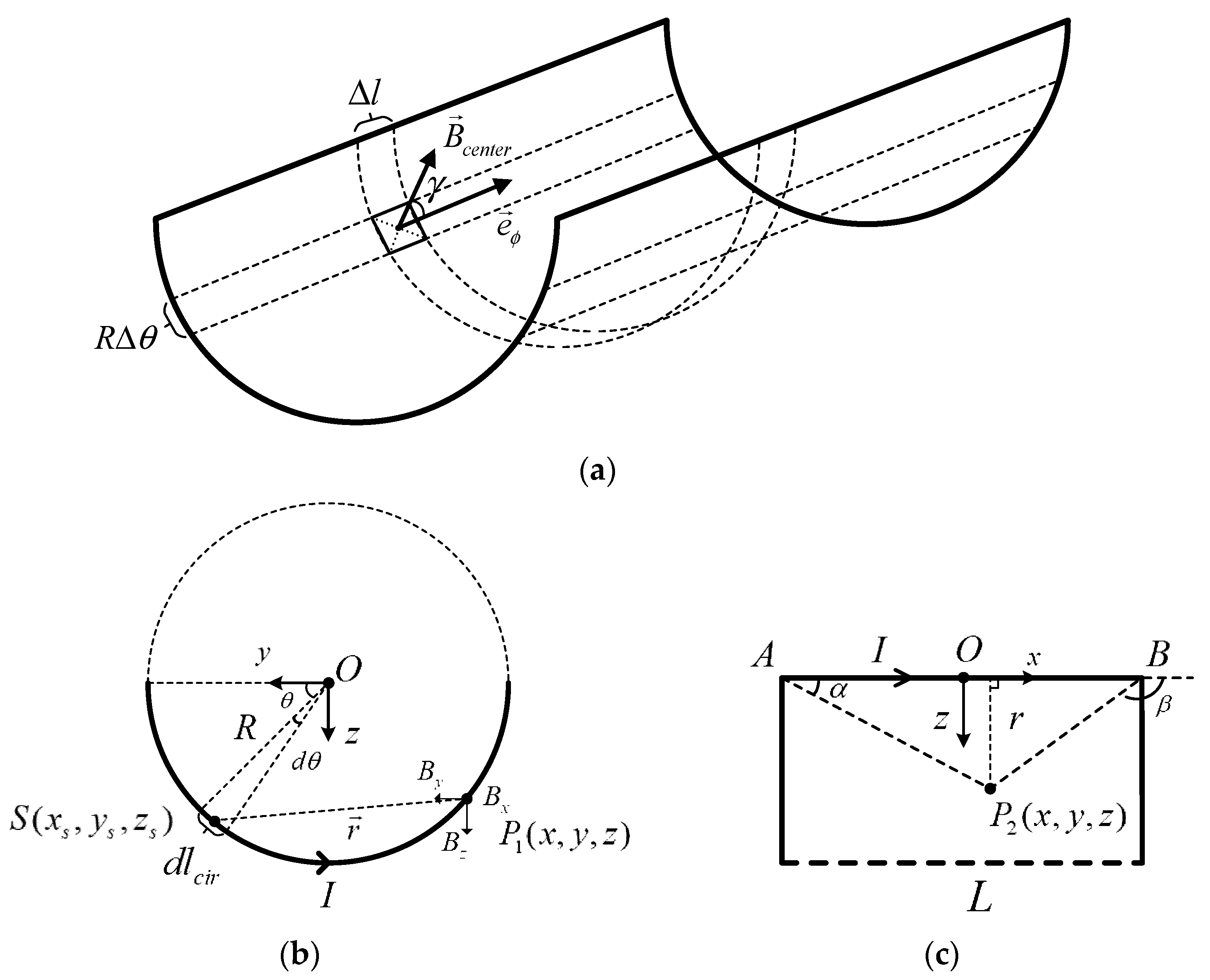
2.2. Modeling of Coils
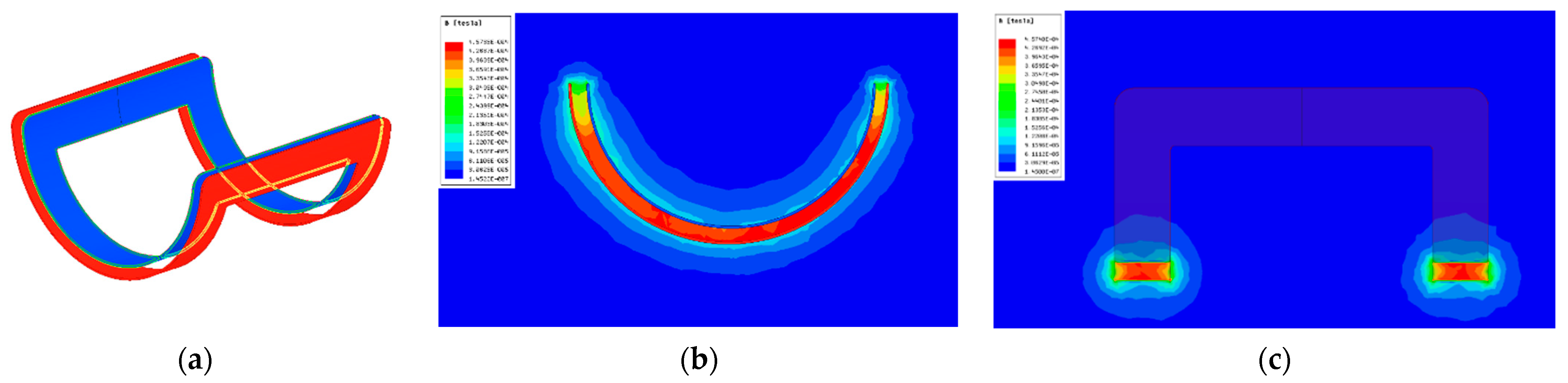
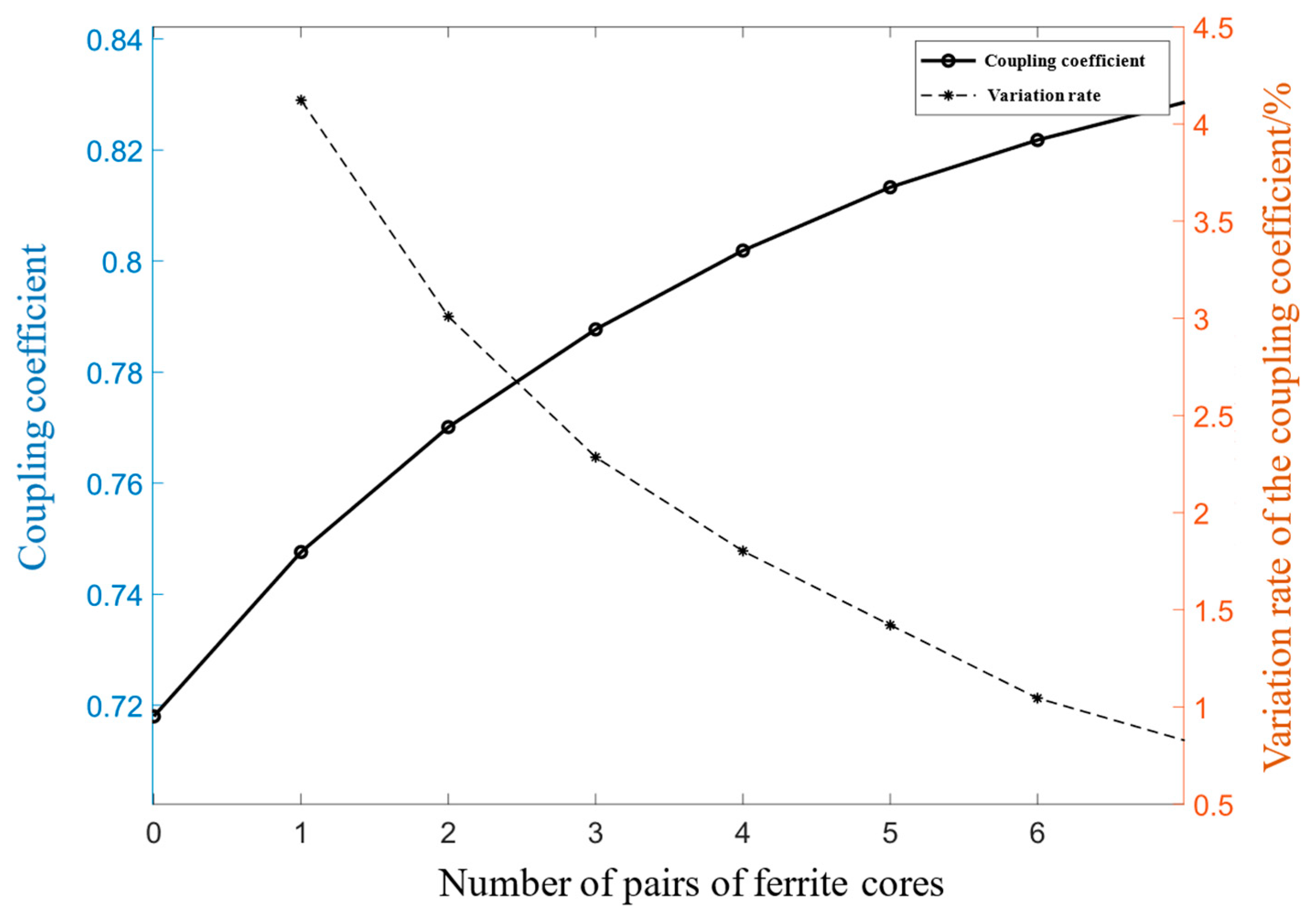
2.3. Optimization of the Coupler
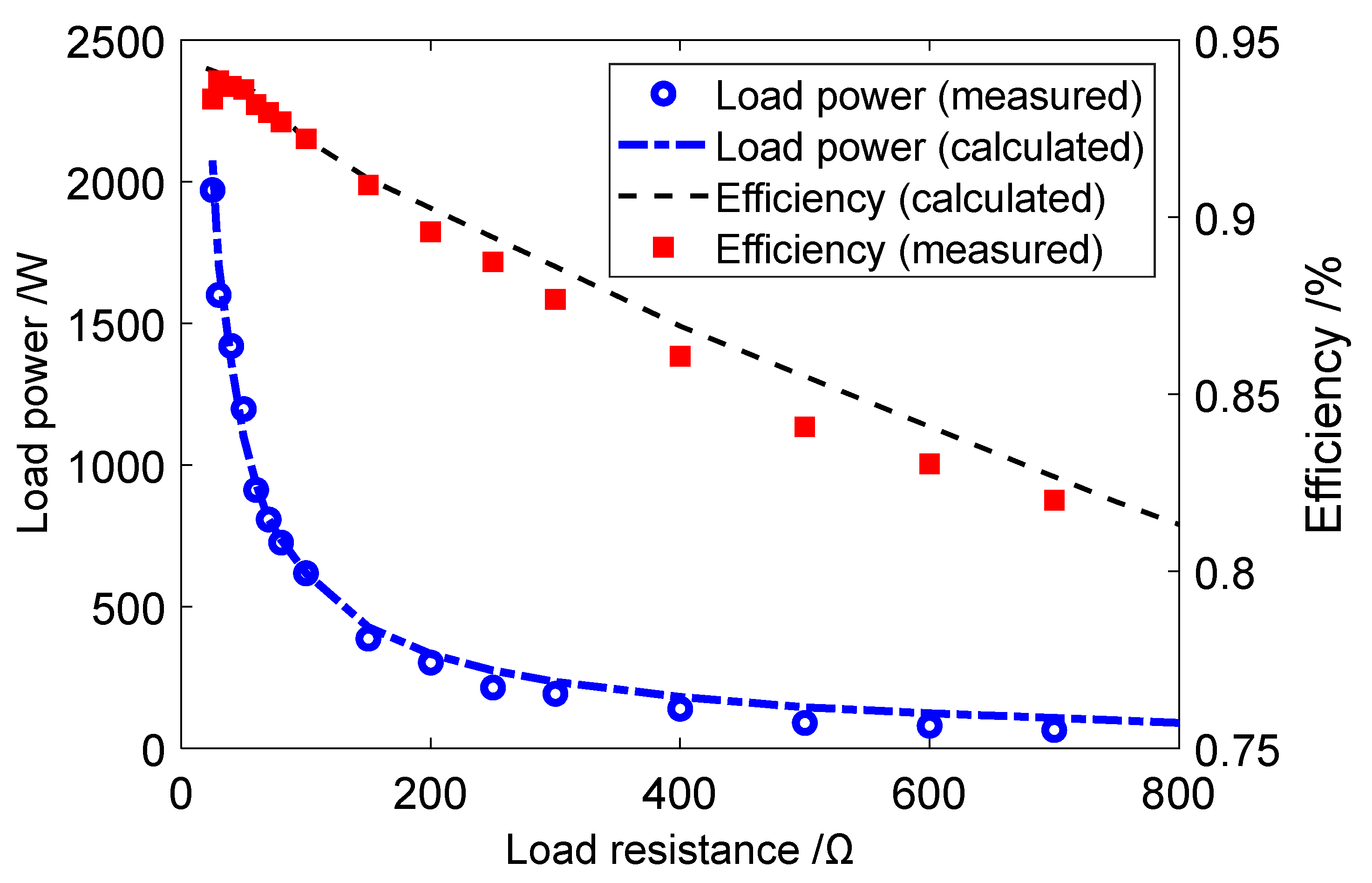
3. AUV WPT System
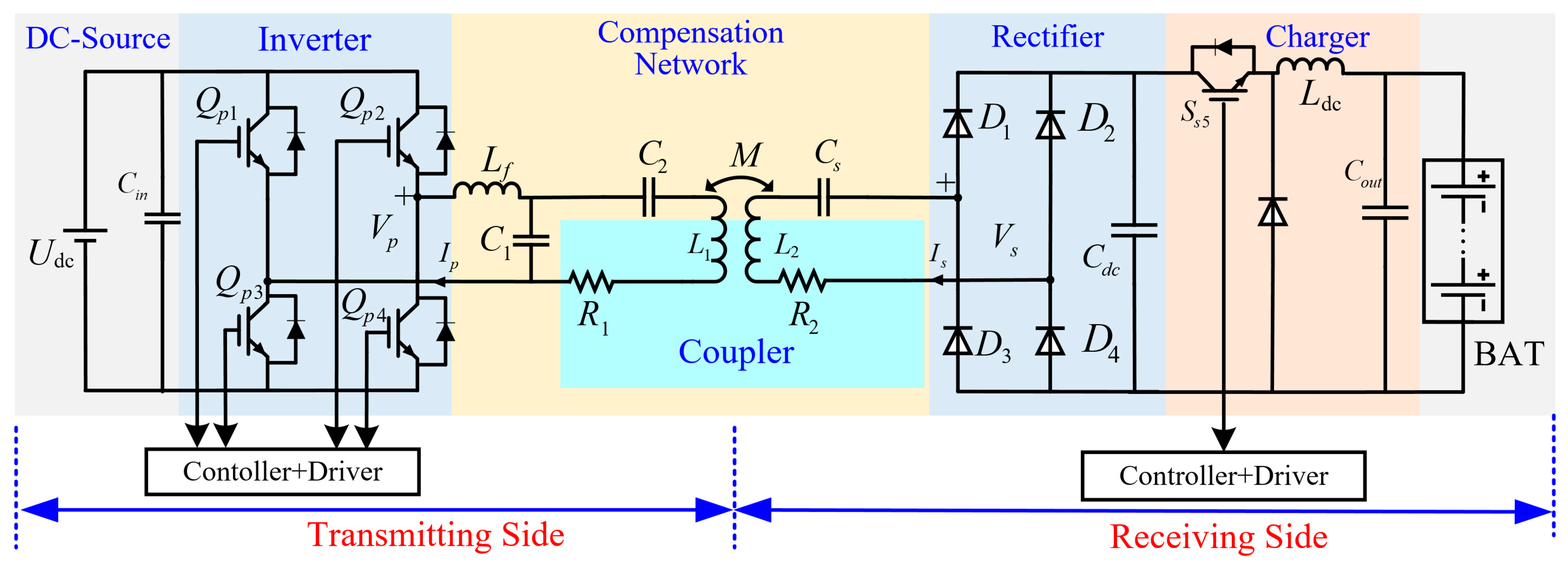
3.1. WPT Circuit
3.2. Topology Design
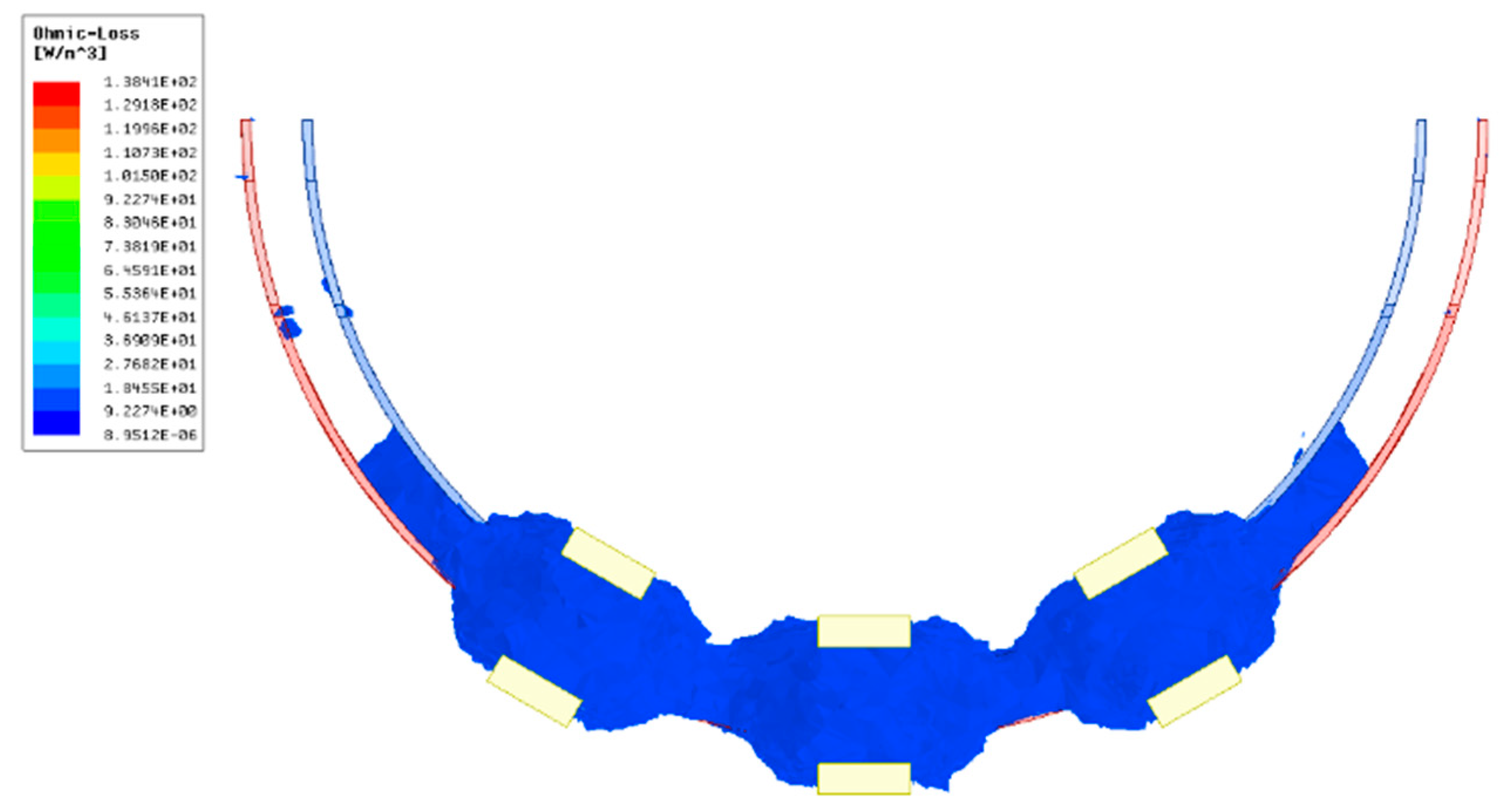
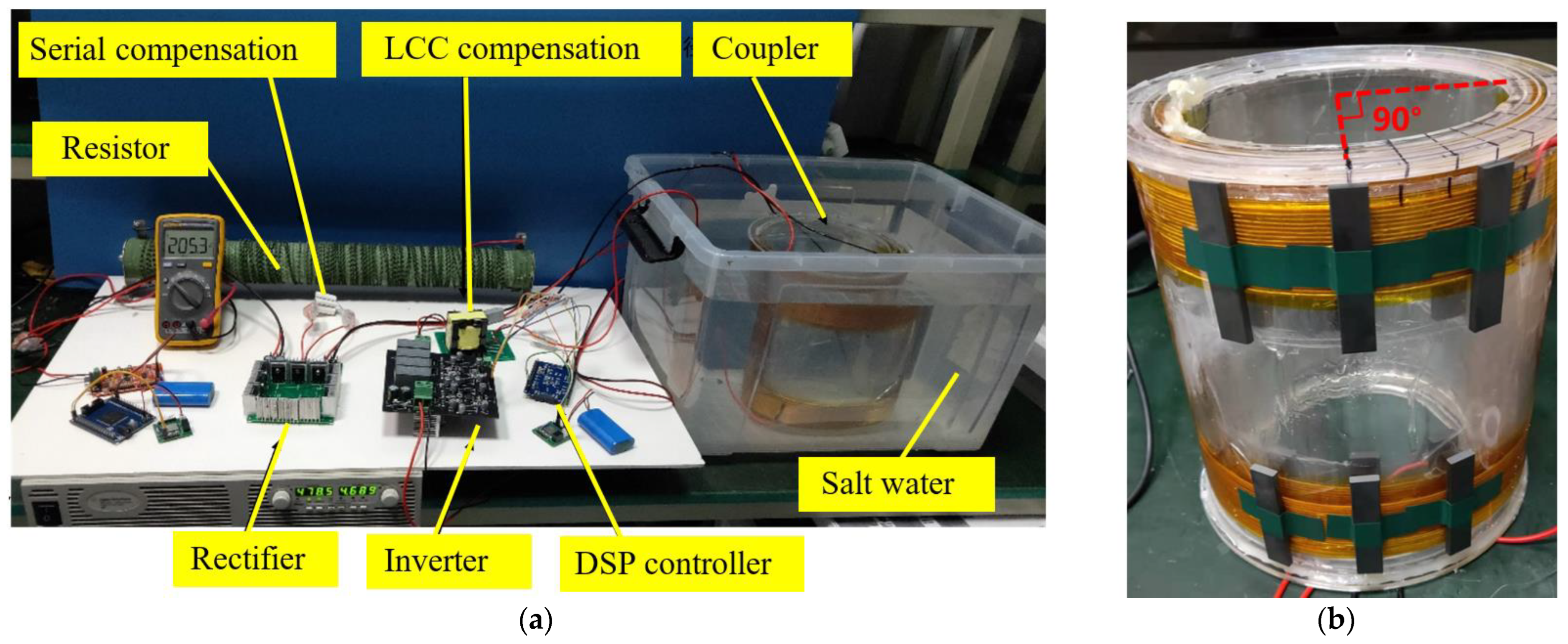
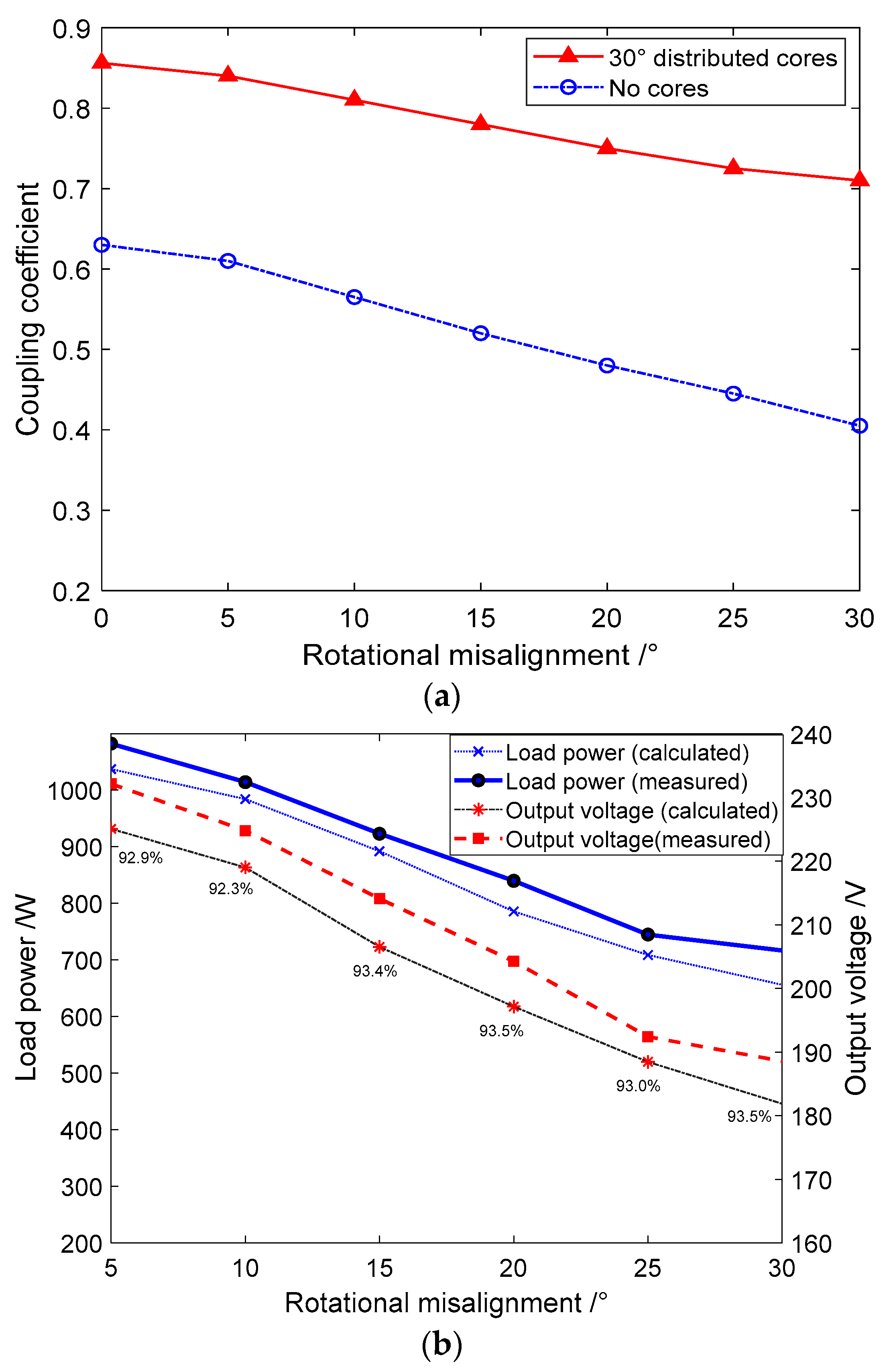
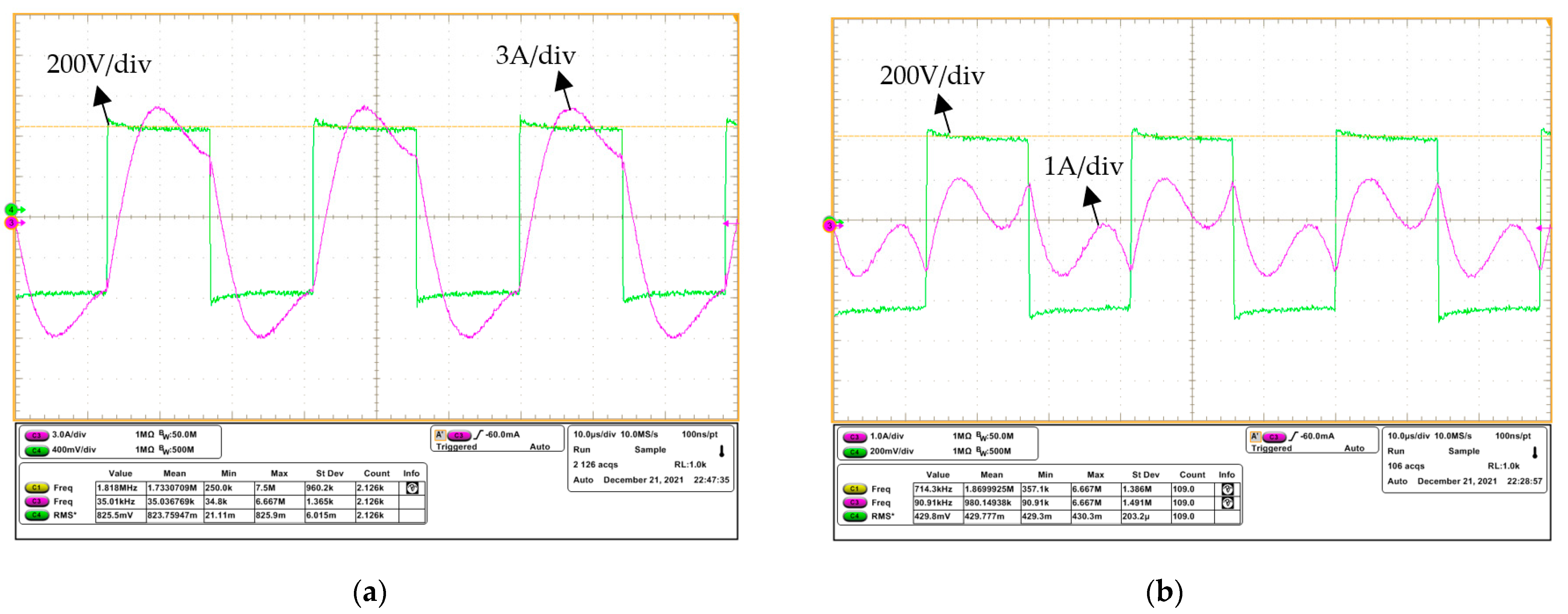
4. Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, M.; Yang, C. Ocean Observation Technologies: A Review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 33, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Cong, Z.; Gong, Y. AUV robust bathymetric simultaneous localization and mapping. Ocean Eng. 2018, 166, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Lin, R.; Yang, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, W. Docking to an underwater suspended charging station: Systematic design and experimental tests. Ocean Eng. 2022, 249, 110766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Maki, T.; Masuda, K.; Matsuda, T.; Sakamaki, T. Autonomous Docking of Hovering Type AUV to Seafloor Charging Station Based on Acoustic and Visual Sensing; IEEE Underwater Technology: Busan, Republic of Korea, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Cui, W. An Overview of Underwater Connectors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, R.P.; Baer, C.; Gabriel, N.; Labosky, J.; Galford, T.C. Non-contact wet mateable connectors for power and data transmission. In Proceedings of the 2013 OCEANS-San Diego, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–27 September 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, C.M.; Alten, M.; Bixler, G.; Fredette, L. Non-Contact Wet Mateable Connector. In Proceedings of the IEEE-OCEANS 2009, Biloxi, MS, USA, 26–29 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, T.; Mai, R.; Mercier, P.; Mi, C.C. Design and Analysis of a Three-Phase Wireless Charging System for Lightweight Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 6622–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Song, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Mao, Z.; Hu, Y. A Rotation-Free Wireless Power Transfer System with Stable Output Power and Efficiency for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 4005–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lin, M.; Li, D. Improving Steady and Starting Characteristics of Wireless Charging for an AUV Docking System. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 45, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Li, D.; Yang, C. Design of an ICPT system for battery charging applied to underwater docking systems. Ocean Eng. 2017, 145, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yang, S. Development of a Fit-to-Surface and Lightweight Magnetic Coupler for Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Wireless Charging Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 9927–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, C. Visual navigation and docking for a planar type AUV docking and charging system. Ocean Eng. 2021, 224, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y. Design and analysis of an omnidirectional and positioning tolerant AUV charging platform. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeneti, C.R.; Truscott, T.; Beal, D.; Pantic, Z. Review of Wireless Charging Systems for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 46, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhao, C.; Hu, Q.; Wu, M.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Y. An Underwater Inductive Power Transfer System with a Compact Receiver and Reduced Eddy Current Loss. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallan, J.; Villa, J.; Llombart, A.; Sanz, J.F. Optimal Design of ICPT Systems Applied to Electric Vehicle Battery Charge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Jang, I.G. Layout Optimization of the Receiver Coils for Multitransmitter Wireless Power Transfer Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Song, B.; Mi, C. Underwater wireless power transfer system with a curly coil structure for AUVs. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Equipment | Brand (Parameters) |
|---|---|
| Power source | Keysight N8762 (600 V/8.5 A) |
| Controller | DSP-TMS320F28335 |
| MOSFET QP1~QP4 | G1M080120B |
| Diode D1~D4 | MUR30120PT-BP |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Coil inductance and its AC resistance | 183.13 μH, 0.17 Ω |
| Coil inductance and its AC resistance | 180.02 μH, 0.17 Ω |
| Compensation capacitance | 117.8 nF |
| Compensation capacitance | 121.4 nF |
| Compensation inductance | 175.5 μH |
| Compensation capacitance | 114.2 nF |
| Operating frequency f | 35 kHz |
| Coupler Type | Coaxial Spiral Coils [10] | Fit-to-Surface Coils [12] | Three-Phase Coils [8] | Curly Coils [19] | This Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum efficiency (DC-DC) | 90.0% (in seawater) | 95.1% (in air) | 92.4% (in air) | 95.0% (in air) | 94% (in salt water) |
| Power | 680 W | 1 kW | 1 kW | 1 kW | 2.2 kW |
| Weight of coupler | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Electromagnetic interference | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
| Rotation Tolerance | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Easy to fabricate | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.; Lin, R.; Li, D.; Duan, R. Development of a Radially Coupled Wireless Charging System for Torpedo-Shaped Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061180
Lin M, Lin R, Li D, Duan R. Development of a Radially Coupled Wireless Charging System for Torpedo-Shaped Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(6):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Mingwei, Ri Lin, Dejun Li, and Runtian Duan. 2023. "Development of a Radially Coupled Wireless Charging System for Torpedo-Shaped Autonomous Underwater Vehicles" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 6: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061180
APA StyleLin, M., Lin, R., Li, D., & Duan, R. (2023). Development of a Radially Coupled Wireless Charging System for Torpedo-Shaped Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(6), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061180





