Infinite Weighted p-Norm Sparse Iterative DOA Estimation via Acoustic Vector Sensor Array under Impulsive Noise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
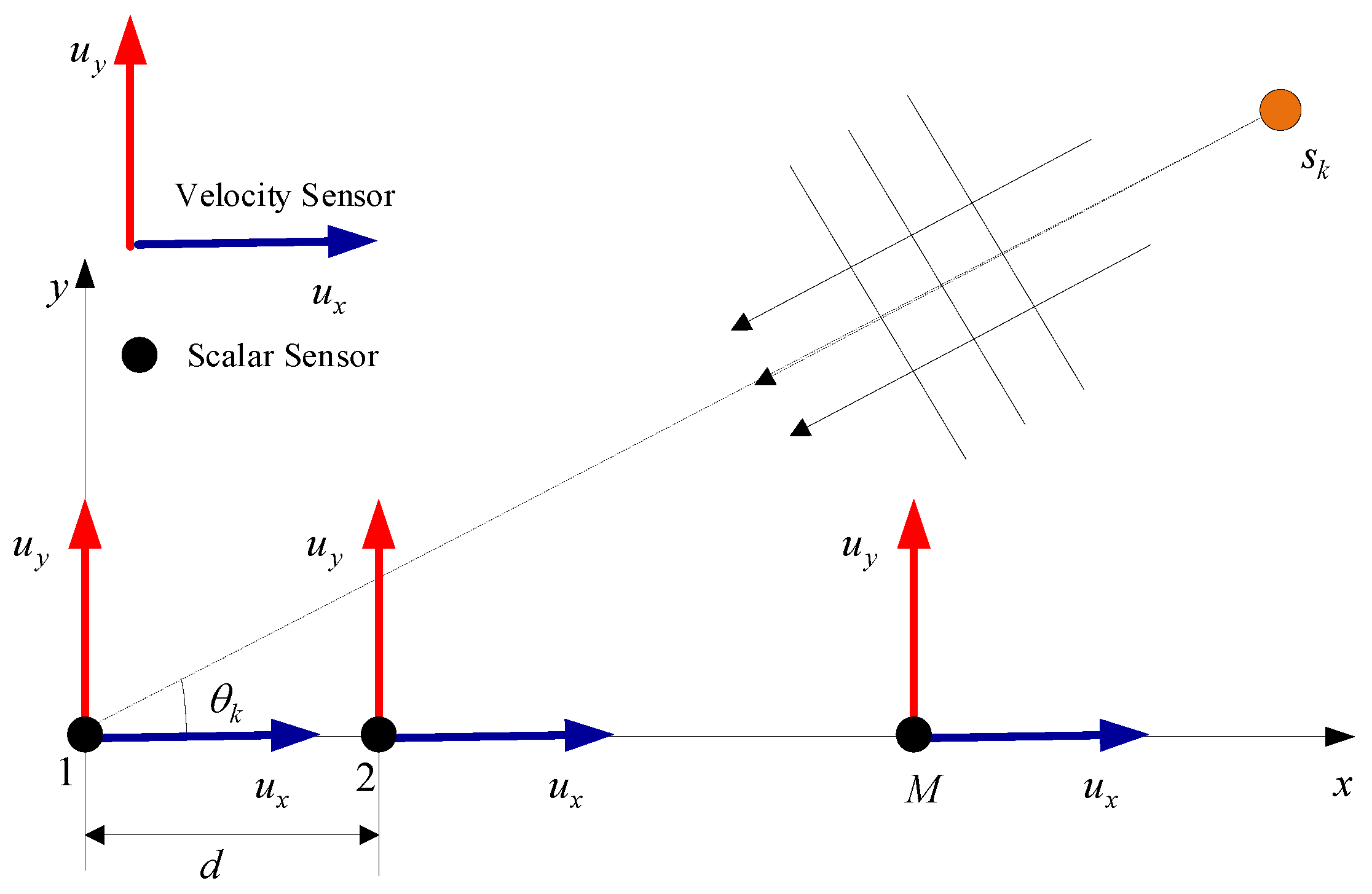
2. Data Model
2.1. Data Model of AVSA
2.2. -Stable Distribution Model
3. The Proposed IWPN-SIA Algorithm
3.1. Weighted Preconditioning with the Infinite Norm
3.2. A Sparse Iterative Algorithm Based on p-Norm
| Algorithm 1: Infinite Weighted p-norm Sparse Iterative Algorithm |
|
4. Simulation Results and Discussions
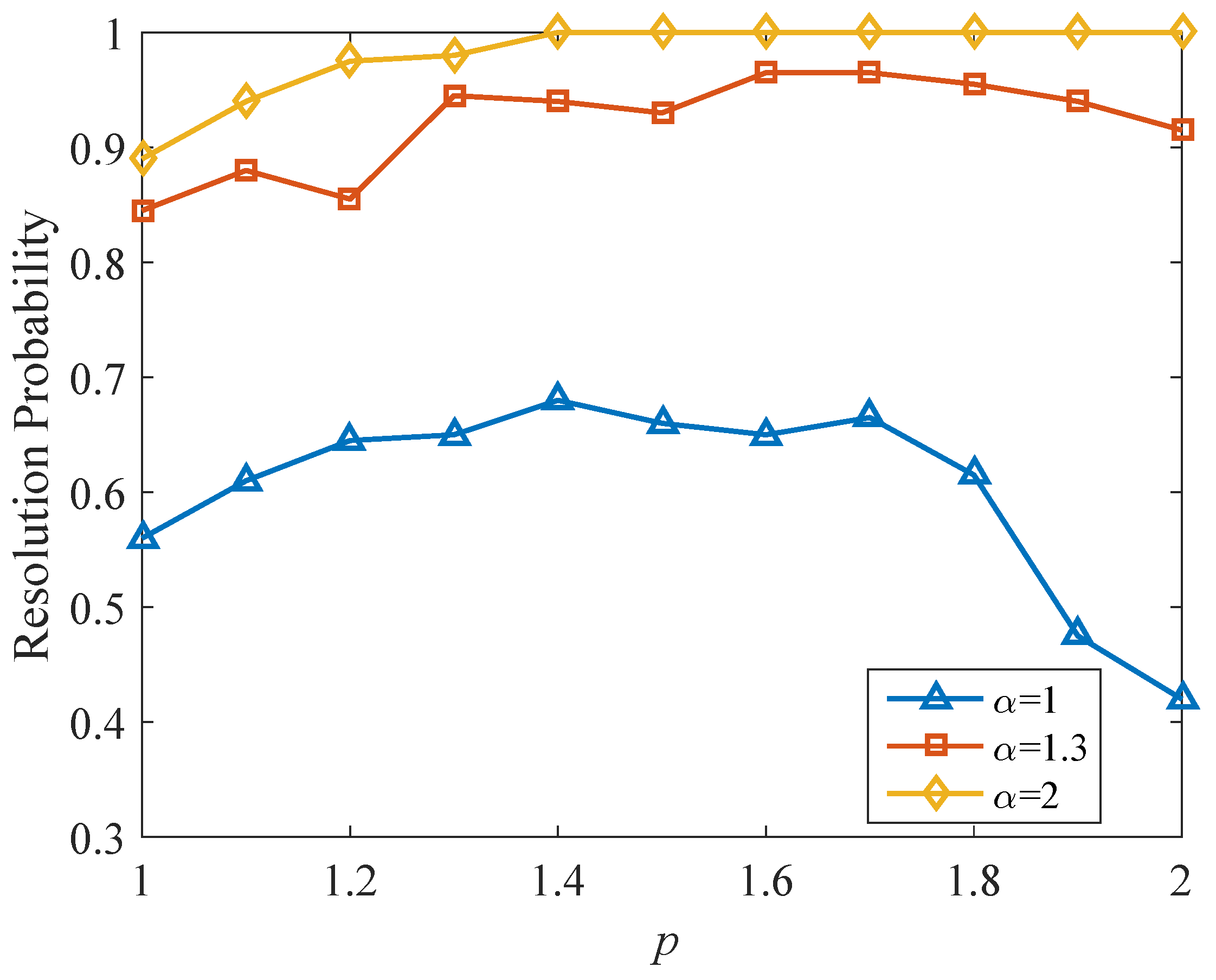
4.1. The Influence of p on Resolution Probability and RMSE
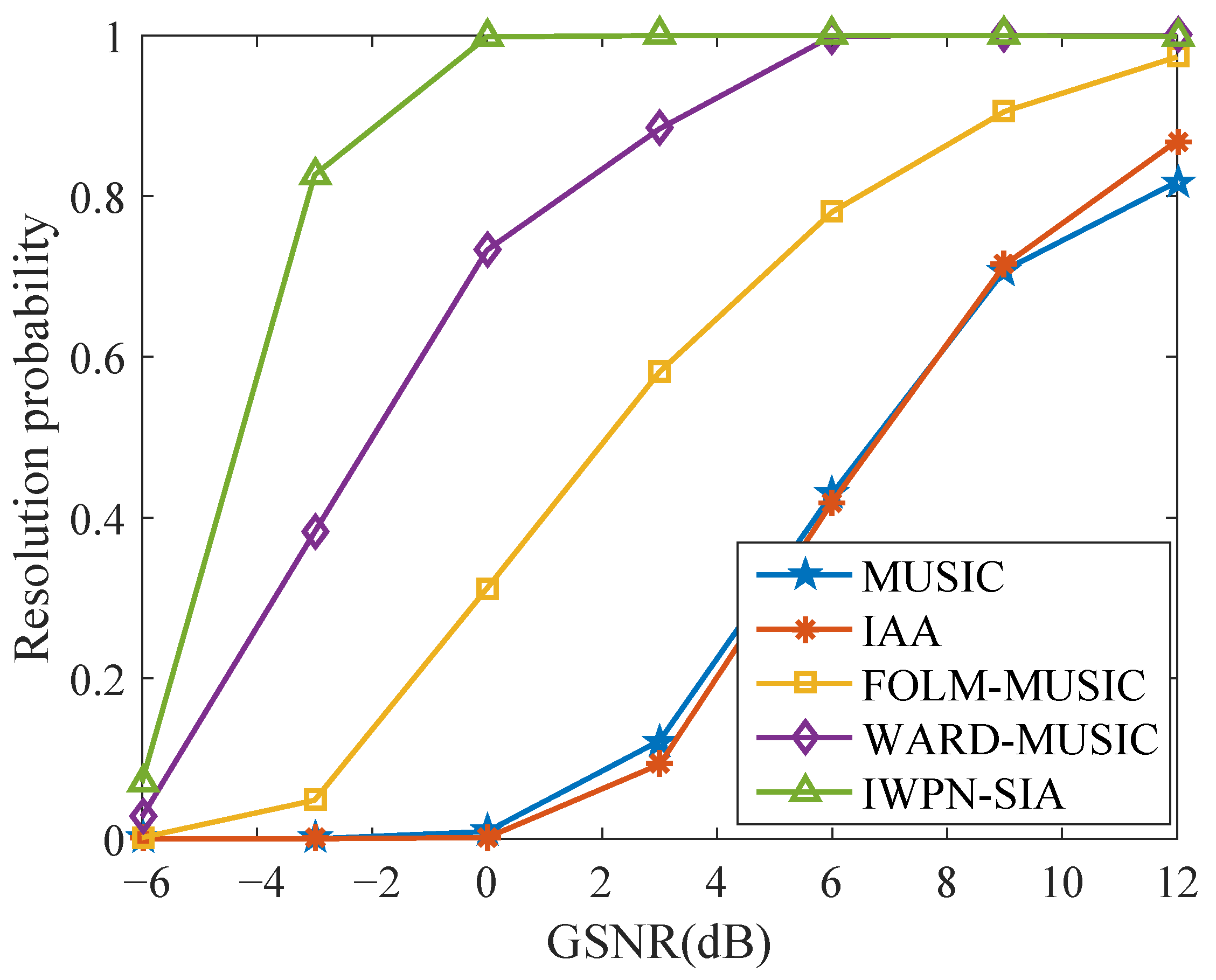
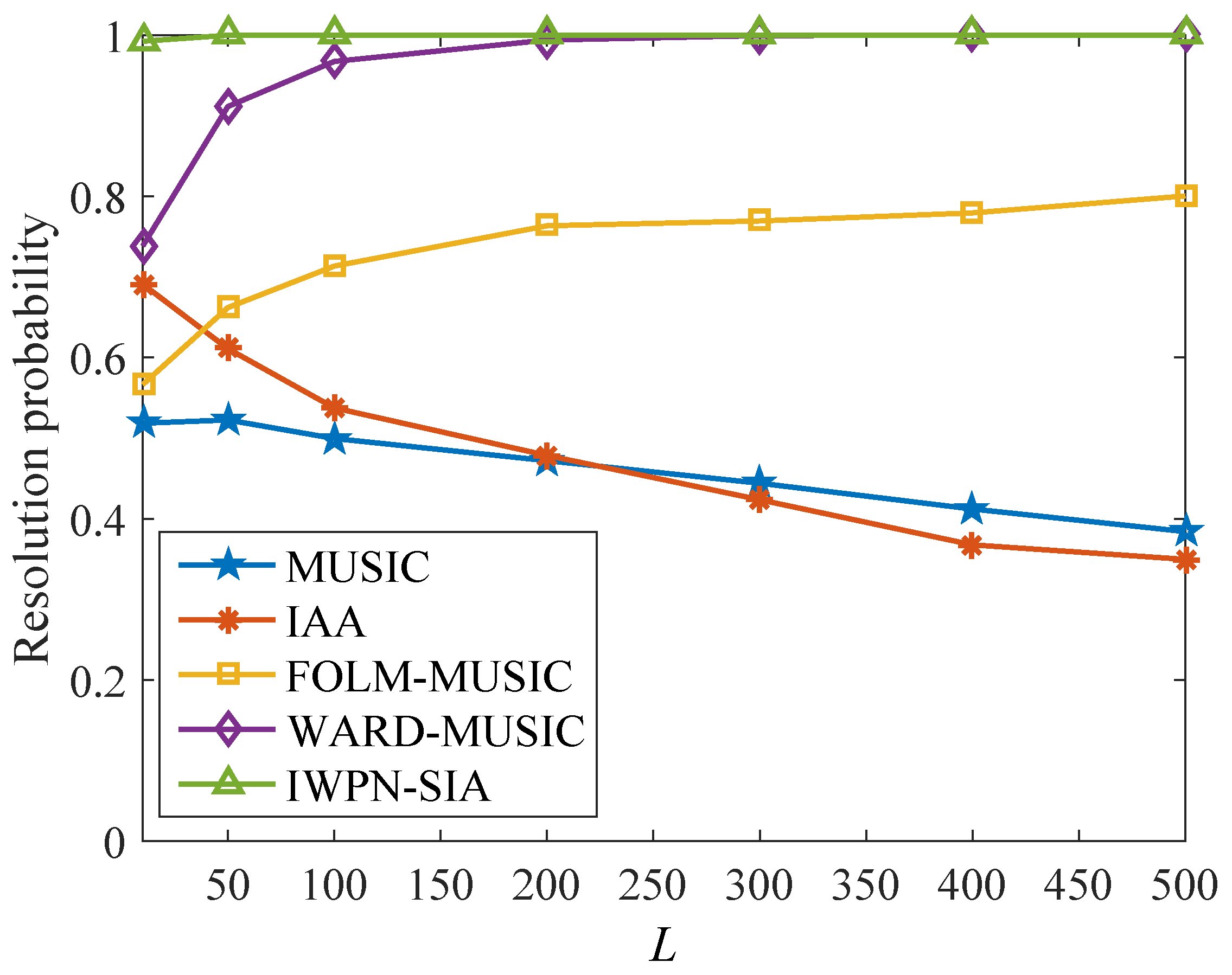
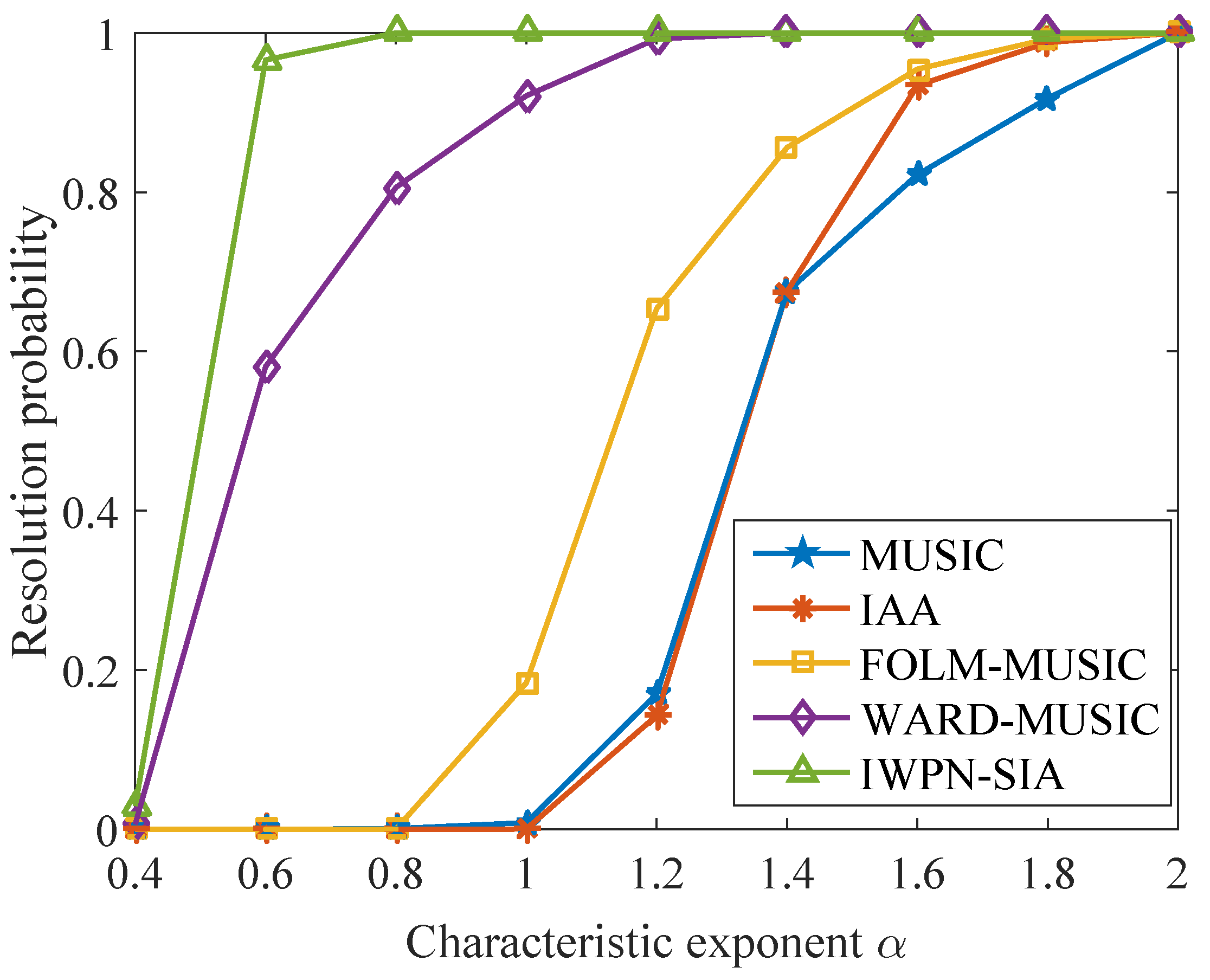
4.2. Comparison of the Resolution Probability
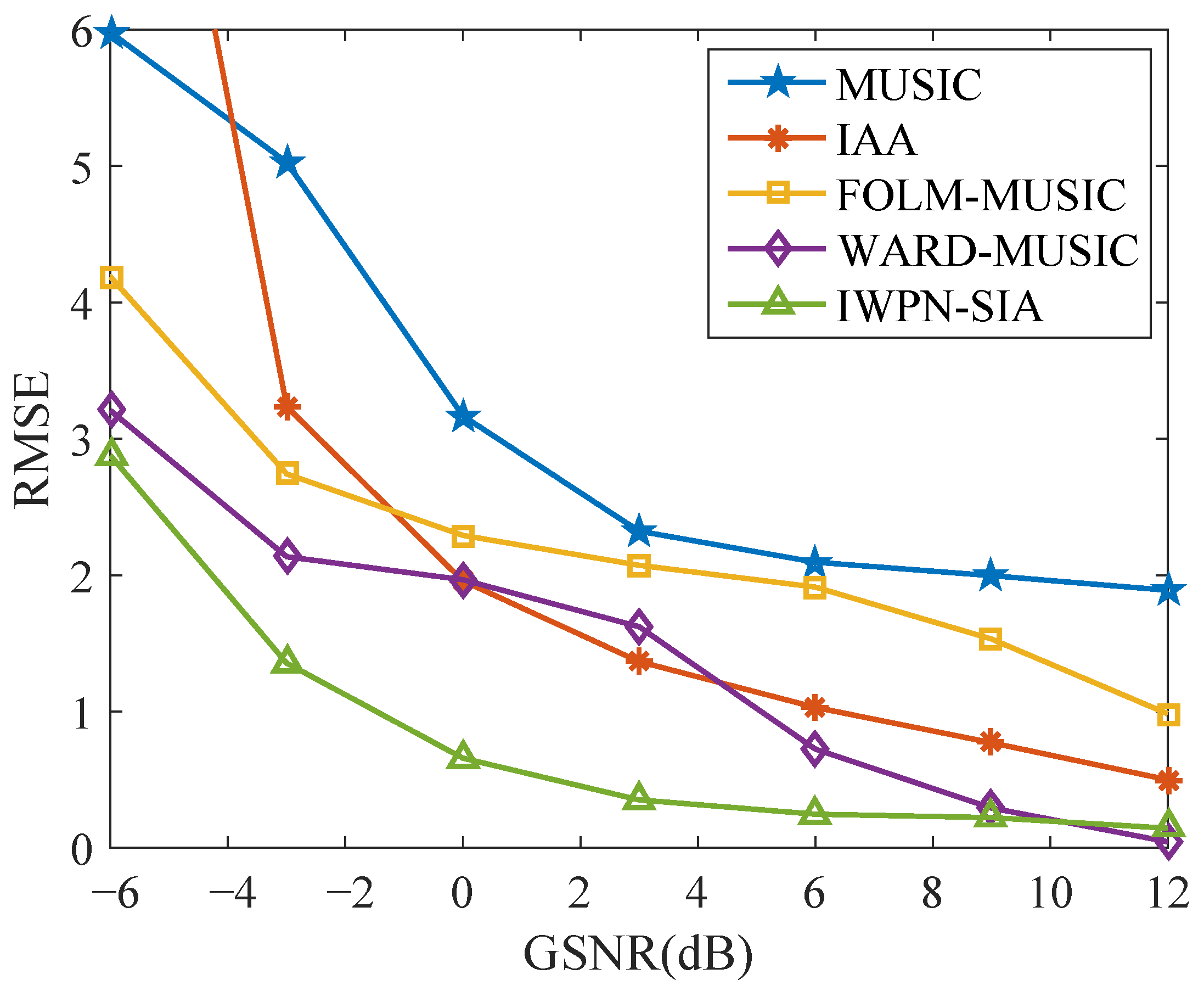
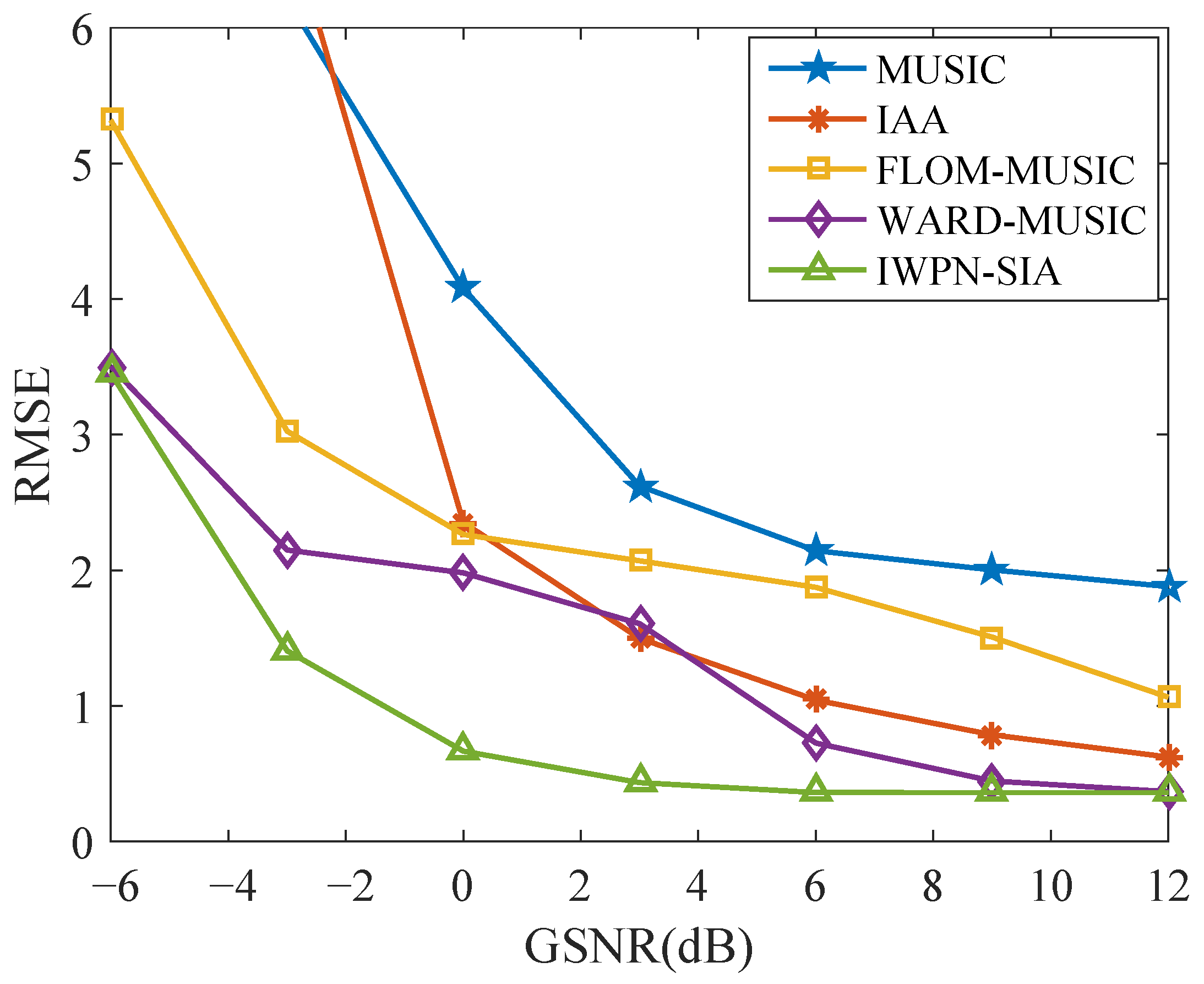
4.3. Comparison of RMSE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, B.M. Ambient noise measurements with vector acoustic hydrophones. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2006, Boston, MA, USA, 18–21 September 2006; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagananda, K.; Anand, G. Underwater target tracking with vector sensor array using acoustic field measurements. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2017-Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, A.; Guldogan, M.B. Joint underwater target detection and tracking with the Bernoulli filter using an acoustic vector sensor. Digit. Signal Process. 2016, 48, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Han, X.; Zhu, Z. Feature extraction of underwater target signal using mel frequency cepstrum coefficients based on acoustic vector sensor. J. Sensors 2016, 2016, 7864213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yin, J.; Yu, G.; Du, P. Experimental demonstration of single carrier underwater acoustic communication using a vector sensor. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 98, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Ma, L.; Hui, J.; Liu, L. Research and implementation of bistatic sonar positioning system based on vector hydrophone. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 9–11 January 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, F.d.A.; Jesus, S.M. Vector sensor beam steering for underwater acoustic communications. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2020, 42, 070002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghukumar, K.; Chang, G.; Spada, F.; Jones, C. A vector sensor-based acoustic characterization system for marine renewable energy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.; Rodríguez, O.; Felisberto, P.; Jesus, S. Seabed geoacoustic characterization with a vector sensor array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeem, S.; Kiran, K.; Malarkodi, A.; Latha, G. Open lake experiment for direction of arrival estimation using acoustic vector sensor array. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 119, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehorai, A.; Paldi, E. Acoustic vector-sensor array processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.; Zoltowski, M.D. Extended-aperture underwater acoustic multisource azimuth/elevation direction-finding using uniformly but sparsely spaced vector hydrophones. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1997, 22, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, D. Modified MUSIC algorithm for estimating DOA of signals. Signal Process. 1996, 48, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ng, B.P. MUSIC-like DOA estimation without estimating the number of sources. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 58, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Cao, B.; Yan, F.; Greco, M.; Gini, F.; Zhang, Y. Real-Valued MUSIC for Efficient Direction of Arrival Estimation with Arbitrary Arrays: Mirror Suppression and Resolution Improvement. Signal Process. 2023, 202, 108766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalem, M.; Barkat, O. DOA estimation of linear dipole array with known mutual coupling based on ESPRIT and MUSIC. Radio Sci. 2022, 57, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malioutov, D.; Cetin, M.; Willsky, A. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 3010–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, M.; Nehorai, A. Acoustic vector-sensor correlations in ambient noise. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, A.; Shi, J. Sparse representation based direction-of-arrival estimation using circular acoustic vector sensor arrays. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 99, 102675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, A.; Zhu, Z. DOA estimation of coherent signals based on the sparse representation for acoustic vector-sensor arrays. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 39, 3553–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardibi, T.; Li, J.; Stoica, P.; Xue, M.; Baggeroer, A. Source localization and sensing: A nonparametric iterative adaptive approach based on weighted least squares. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tan, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, W. Source localization utilizing weighted power iterative compensation via acoustic vector hydrophone array. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tan, W.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H. Direction finding based on iterative adaptive approach utilizing weighted l2-norm penalty for acoustic vector sensor array. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 33, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackard, K.L.; Rappaport, T.S.; Bostian, C.W. Measurements and models of radio frequency impulsive noise for indoor wireless communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 1993, 11, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, P.L.; Hinich, M.; Wilson, G.R. Nonlinear and non-Gaussian ocean noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Dong, C.; Liu, W.; Cai, J. Generalized ℓ2-ℓp minimization based DOA estimation for sources with known waveforms in impulsive noise. Signal Process. 2022, 190, 108313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozick, R.J.; Sadler, B.M. Maximum-likelihood array processing in non-Gaussian noise with Gaussian mixtures. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 3520–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, R.C.; Yu, W. Robust Sparse Recovery in Impulsive Noise via ℓp-ℓ1 Optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 65, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Jiang, F.; Liu, P.; Gong, F.; Zhao, N. 2-D DOA robust estimation of echo signals based on multiple satellites passive radar in the presence of alpha stable distribution noise. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 16032–16042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gu, F.; Liang, C.; Meng, H.; Wu, K.; Zhou, Z. Review on Active Noise Control Technology for α-Stable Distribution Impulsive Noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 41, 956–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Chen, S. A modified adaptive weight-constrained FxLMS algorithm for feedforward active noise control systems. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 164, 107227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakalides, P.; Nikias, C.L. The robust covariation-based MUSIC (ROC-MUSIC) algorithm for bearing estimation in impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.H.; Mendel, J.M. A subspace-based direction finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkacemi, H.; Marcos, S. Robust subspace-based algorithms for joint angle/Doppler estimation in non-Gaussian clutter. Signal Process. 2007, 87, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Z. WARD: A weighted array data scheme for subspace processing in impulsive noise. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing Proceedings, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006; pp. 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, R.; Lin, B.; Sun, F. DOA estimation based on sparse representation of the fractional lower order statistics in impulsive noise. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2016, 5, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Tang, J. Robust DOA estimation via sparse signal reconstruction with impulsive noise. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Su, W. Iterative reweighted DOA estimation for impulsive noise processing based on off-grid variational Bayesian learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 104642–104654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Sun, Y.; Dai, J.; Chang, C. Robust DOA estimation for burst impulsive noise. Digit. Signal Process. 2021, 114, 103059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Lan, X. Robust Sparse Bayesian Learning Scheme for DOA Estimation with Non-Circular Sources. Mathematics 2022, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, H. Robust sparse Bayesian learning based on the Bernoulli-Gaussian model of impulsive noise. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 136, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Joo, Y.H. Multisource DOA Estimation in Impulsive Noise Environments Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2022, 2022, 5325076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Shi, Y.; Shi, Y.; Bai, Z.; He, W.; Lv, X. Off-grid sparse based two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation of acoustic vector sensor array in impulse noise. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2022, 53, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Qiu, T.; Cai, R. DOA estimation for CD sources by complex cyclic correntropy in an impulsive noise environment. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Guo, Y. A bistatic MIMO radar angle estimation method for coherent sources in impulse noise background. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 116, 3567–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, A.; McKeown, J.J. Matrix Computation; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Haagerup, U. Lp-Spaces Associated with an ARBITRARY von Neumann Algebra. Algebres d’Opérateurs et Leurs Applications en Physique Mathématique. 1977, pp. 175–184. Available online: https://dmitripavlov.org/scans/haagerup.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2023).




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Shi, W.; Ali, W. Infinite Weighted p-Norm Sparse Iterative DOA Estimation via Acoustic Vector Sensor Array under Impulsive Noise. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11091798
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang W, Li X, Li H, Shi W, Ali W. Infinite Weighted p-Norm Sparse Iterative DOA Estimation via Acoustic Vector Sensor Array under Impulsive Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(9):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11091798
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhiqiang, Yongqing Zhang, Weidong Wang, Xiangshui Li, Hui Li, Wentao Shi, and Wasiq Ali. 2023. "Infinite Weighted p-Norm Sparse Iterative DOA Estimation via Acoustic Vector Sensor Array under Impulsive Noise" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 9: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11091798
APA StyleLiu, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Li, X., Li, H., Shi, W., & Ali, W. (2023). Infinite Weighted p-Norm Sparse Iterative DOA Estimation via Acoustic Vector Sensor Array under Impulsive Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(9), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11091798





