Abstract
The Albufera of Valencia, a Mediterranean coastal lagoon, has been in a turbid state since 1974, with only four episodes of temporary water transparency in spring. Despite its average depth of 1 m and oligohaline waters, excessive turbidity, fish grazing, and toxic compounds have inhibited submerged macrophyte growth. In spring 2018, a significant area of Myriophyllum spicatum emerged and exhibited significant density until its complete disappearance in August 2018. Using Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 imagery, we monitored water quality variables and vegetation density during these months. Our study revealed the first unique occurrence of M. spicatum in more than 40 years. A period of increased transparency from summer 2017 compared to previous years seems to be the cause of this appearance, while high summer temperatures caused its disappearance. While improving water quality may help restore submerged macrophyte meadows, our results suggest that summer maximum temperatures may inhibit recovery. Remote sensing, particularly the NDVI index, proved successful in monitoring aquatic vegetation and understanding species-environment relationships. This methodology can enhance future monitoring efforts for macrophyte colonization and expand knowledge of their occurrence and causes of disappearance in this and other similar areas.
1. Introduction
Plants and algae are important in the ecological functions of aquatic environments. Submerged macrophytes or hydrophytes play a fundamental role in the alternative state model of []. According to this model, there is a turbid phase dominated by phytoplankton and a clear phase dominated by submerged vegetation. This model is based on the fact that nutrient loading increases turbidity due to massive phytoplankton blooms, but the presence of macrophytes reduces turbidity. Although macrophytes disappear above a critical level of turbidity [,], excessive nutrient accumulation in the aquatic environment is detrimental to the growth of submerged macrophytes []. In this sense, hydrophytes have been used in several wetland restoration programs around the world according to Rodrigo [] and references included. This is because the presence of submerged vegetation reduces water turbidity through various mechanisms, such as preventing sediment resuspension [], competing with phytoplankton for access to light and nutrients [,], and inhibiting their proliferation []. In addition, they promote greater water quality by significantly increasing dissolved oxygen through photosynthesis and water transparency [] and absorbing phosphorus from sediments and water through roots [].
In the context of wetlands in general [] and Mediterranean coastal lagoons in particular [], submerged macrophytes are a key component in terms of ecological interactions because they are at the base of trophic chains, providing food for invertebrates, fish, and birds, and being a source of organic carbon for detritivorous bacteria. However, they also participate in non-trophic interactions, serving as substrate for periphyton and shelter for numerous invertebrates and different stages of fish, amphibians, and reptiles [,]. Zooplankton using macrophytes as refuge would be another mechanism against turbidity, due to the grazing control it exerts on phytoplankton []. However, in Mediterranean regions, where high temperatures are reached in the summer, more cover of emergent macrophytes would be necessary to overcome the growth of phytoplankton and filamentous algae []. Since the 1970s, agricultural, industrial, and urban pollution has turned the Albufera of Valencia lagoon (Spain) into a hypertrophic lagoon, losing macrophyte meadows and entering a turbid phase dominated by phytoplankton, especially cyanobacteria []. Currently, according to the Regional Council, the only species found within the boundaries of the Albufera Natural Park is Myriophyllum spicatum (hereinafter referred to as M. spicatum). During the spring of 2018 an important area of M. spicatum in a shallower area of the northern part of the lagoon appeared, which developed a remarkable density of vegetation until emerging to the surface. This event can be described as extraordinary and of great interest to the scientific community, as an extension of macrophytes such as that observed in spring and summer 2018 had not been seen in the lagoon since these plants disappeared in 1972. This demonstrated that if the water quality of the lagoon is properly managed, its environmental recovery would be possible without any intervention other than that of nature itself.
Between 1972 and 2018, several national environmental laws have been enacted concerning the aquatic environment in Spain. In 2001, the first national Water Law was passed [] following the publication of the Water Framework Directive. This law has been modified over the years until 2008 when the Environmental Responsibility Law was passed [].
In this context, environmental monitoring of these conditions is important to assessing the effectiveness of management and restoration strategies in aquatic ecosystems []. Remote sensing has been used in numerous studies [,,,,,,], correlating the reflectance on different spectral bands with phytoplankton and vegetation biomass through spectral indices, taking advantage of the knowledge generated on the optical properties of the different pigments of vegetation and phytoplankton []. A key factor in many studies of terrestrial vegetation is spectral information collected in the red and near infrared (NIR) bands [,]. These bands, along with blue and green, have been combined in different radiometric indices to assess the growth, health, and density of terrestrial [] and aquatic vegetation [,,].
In aquatic vegetation studies, sometimes short wavelength infrared (SWIR) bands are selected [,,] for being sensitive to the presence of floating leaf components []. Taking this into account, NDWI is sensitive to the amount of water contained in the vegetation and is therefore useful for estimating the density of emergent macrophytes, floating and submerged foliage, although it is less sensitive to atmospheric effects []. Moreover, bands and indices more appropriate to terrestrial vegetation have also been adapted [,,,,], such as the well-known NDVI [].
According to Malthus [], aquatic emergent and partially emerged macrophytes have similar optical properties to their terrestrial counterparts, with low reflectance in the blue and red parts of the visible spectrum due to absorption by photosynthetic pigments, and higher reflectance in the red edge area (705 nm) to relatively high reflectance in the near infrared (NIR) (Figure 1), mainly due to a high degree of light scattering. It’s remarkable that NDVI is sensitive to aquatic vegetation, despite some differences between species, up to a depth of 50 cm, beyond which the absorption of water in the NIR makes detection difficult.
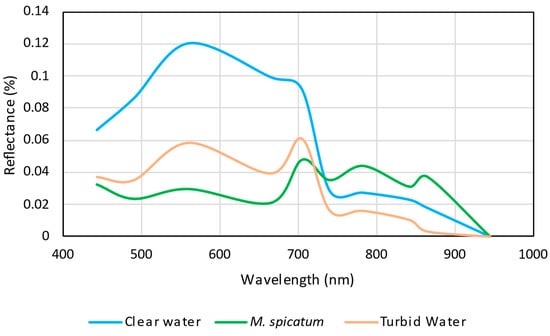
Figure 1.
Spectral characterization of clear water in southern area of the Albufera lagoon, turbid water around the emerging plants and M. spicatum area. Data obtained from the Albufera lagoon using the Sentinel-2 image of 10 July 2018 through SNAP 9.0 software.
Malthus [] also identifies several key challenges in the field of remote sensing of aquatic macrophytes according to the references included in his review. First, there is a need for more systematic studies to understand the spectral signatures and biophysical properties of different macrophyte species and growth habits. This would involve building spectral libraries for different species and substrates. In addition, it is important to understand how factors such as species, phenology, depth, and water quality influence spectral reflectance, as this affects the relationship between macrophyte characteristics and reflectance. Also, the effect of acquisition characteristics, such as the relative position of the sun with respect to the sensor and surface effects, on the retrieval of macrophyte properties should be investigated. Moreover, there is a need to develop standardized methods for assessing morpho-ecological gradients, structural complexity, and functional status of macrophyte-dominated habitats. Finally, efforts should be made to improve the mapping of macrophyte distributions and phenology at regional and global scales, and to gain insight into changes in macrophyte distributions and the resilience of macrophyte communities to external forces and environmental degradation.
In line with these challenges, our study aims to make an innovative contribution by using the radiometric indices of terrestrial vegetation to monitor the pattern of a singular appearance and disappearance of M. spicatum in the Albufera lagoon. Through this approach, our research aims to provide new insights into the relationship between water quality, the temporal dynamics of aquatic species and the factors influencing their density. In particular, by highlighting the effectiveness of the method in overcoming absorption limitations in the NIR due to the subsurface nature of the species, we aim to provide valuable contributions to be able to understand and manage aquatic habitats in coastal lagoons, thus addressing current challenges in the field of remote sensing of aquatic macrophytes.
Following this line of research, and considering the subsurface character (<10 cm depth) of M. spicatum in the waters of the Albufera lagoon (Appendix A, Figure A1), the main objective of our work is to assess the effectiveness of radiometric indices of terrestrial vegetation for monitoring the sporadic appearance and disappearance of this macrophyte in the northern part of the Albufera during 2018 using remote sensing data, with the intention of quantify the area occupied by the plants and to know their annual evolution from the appearance to their disappearance. We will also hypothesize the possible causes and the factors that determine the density of the species in this area, comparing with other case studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Albufera of Valencia Natural Park is a coastal wetland located in the southern part of the city of Valencia (Figure 2). The park consists of the shallow central lagoon, which has a maximum depth of approximately 1.3 m, and the surrounding marshes, which have been modified mainly for rice cultivation. Currently, the lagoon is in a hypertrophic ecological state, mainly due to urban and industrial discharges and nutrient inputs from agricultural activity.
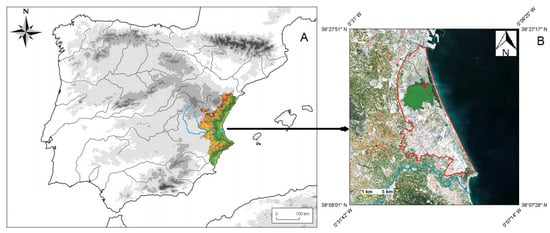
Figure 2.
(A) Study area map, indicating the Iberian Peninsula, (B) geographical coordinates, the border of the Albufera Natural Park with a red line, the Albufera lagoon in green color due to its hypertrophic state, the Jucar River with a blue line, and the study area of the emerging plants with a red circle. Sentinel-2 image in natural false color dated 27 March 2018.
The cultivation cycle begins in spring with the tillage of the land. During the summer, the fields are kept half flooded while the rice crop grows, and it is in September when the rice is harvested. Once the rice is harvested, the fields are flooded to the maximum and emptied again during January to February. Currently, the drained water passes through the central lagoon, to the mechanical gates that connect to the Mediterranean Sea [].
From 2015 and especially in 2016, the presence of different species of aquatic macrophytes, among which we find M. spicatum, began to increase in the Albufera. The most abundant species, during a period spanning from 2015 to the present, was M. spicatum. This species has an important role in aquatic ecosystems because it is an indicator of ecological restoration; however, it has become one of the most invasive species in some parts of North America []. M. spicatum has socioenvironmental importance because its ability to occupy various freshwater habitats makes it valuable for improving and maintaining the ecological balance in aquatic environments.
The largest area of occupation developed in spring 2018, reaching 106,047 m2 in the whole lagoon, concentrated mainly in the northern area []. Other species that appeared in other places are the following: Ceratophyllum demersum, Myriophyllum spicatum, Najas marina, Potamogeton crispus, Potamogeton nodosus, and Potamogeton pectinatus. This exceptional development may be related to a contribution of clean water derived from the Jucar River during the winter, more specifically 9.89 cubic hectometers (hm3).
2.2. Sampling Methods
Field sampling in the lagoon was carried out systematically every month or so to obtain data on its ecological status, trying to coincide with Sentinel-2 imaging. In 2018, one sampling was carried out at the end of March, but it was not possible to observe the beginning of the vegetation from the boat, as it was in a unique area in the northern zone of the lagoon. The observation of the image of 23 May 2018, indicated the presence of a vegetation area that had not been observed before, and then a detailed study of the imagery was carried out since March to investigate the appearance and evolution until that date. From that moment on, more detailed observation efforts were performed on a weekly basis, in which samples of the growing plants were also taken (Appendix A, Figure A1).
The main study area was in the northern area of the Albufera lagoon, which was accessed by boat. In addition to the observation of the presence of the plants, several water quality variables were measured in the area. Water transparency was measured by Secchi disk depth, while water temperature and conductivity were measured using a portable handheld conductivity meter (Hanna Instruments, Smithfield, RI, USA).
Between March and August 2018, a total of nine water samples was collected in the area of interest for subsequent laboratory analysis. Samples were collected around the SAV bed at a distance of 30–50 cm from the plants, consisting of three subsamples at a depth of 10–20 cm (the depth of site sampling was 50–60 cm). Total suspended solids were measured using the filtration method [], having a measured volume of water pass through glass fiber filter with 1 µm pores that was previously desiccated and weighed, then dried at 105 °C, and weighed again; the difference in weight equaled the total suspended solids of the sample.
The nitrate concentration is obtained by calculating the second derivative from the ultraviolet absorbance of the samples measured using a DU600 spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA) at 224 nm [].
Water samples collected in the field were also filtered using 0.47 mm Whatman GF/F glass fiber filters and Chl-a extracted from the filtered samples using a solvent solution prepared with dimethyl sulfoxide and 90% acetone using Shoaf and Lium methodology []. The concentration of the extracted pigment was measured using a spectrophotometer (Beckman DU600, Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA), and the calculation methodology proposed by Jeffrey and Humphrey [] was used for determining [Chl-a]. These values were obtained to validate the measures of fluorometer.
2.3. Remote Sensing Data
Remote sensing was chosen for this study because it provides frequent, large-area data with logistical ease. Its high temporal resolution is critical for more comprehensive monitoring than conventional methods. In addition, simple combinations of different spectral bands allow us to assess vegetation health and cover with significant accuracy, contributing to a more complete understanding of ecological dynamics in our study area.
Sentinel-2 (S2) and Landsat-8 (L8) satellite imagery was used, coinciding with the date of field data collection. S2 satellite images were downloaded atmospherically corrected with Sen2Cor, which was intended to correct the atmospheric effects of Sentinel-2 Level 1C products and obtain Level 2A images []. The source was the European Space Agency (ESA) through its free Open Access Hub platform (currently Copernicus Browser). The Sen2Cor processor was designed for vegetation and terrain, but also provides good results for eutrophic or hypertrophic waters, such as the Albufera of Valencia and its surrounding marshes, according to previous studies carried out in the study site using in situ radiometric data [,]. L8 images were obtained from the USGS (United States Geological Service) server. These images were downloaded at processing level 1 (L1C) with geometric correction and then were atmospherically corrected using ENVI 5.0.3 software (Exelis Visual Information Solutions, Boulder, CO, USA), applying the QUAC (Quick atmospheric correction) procedure [].
Once downloaded and atmospherically corrected, S2 and L8 images were processed using Sentinel Applications Platform (SNAP 9.0) software developed by ESA (Brockmann Consult, Hamburg, Germany). The images were resampled to 10 m that allows us to equalize all spectral bands in each image to the same spatial resolution. Through the “Vegetation Radiometric Indices” tool implemented in SNAP 9.0, it is possible to apply different vegetation indices (see Section 2.4 and Section 3.1) and thus determine which one is best suited to the conditions of our study. In order to speed up the processing, the study area should be defined, and a region of interest (ROI) should be drawn as a polygon, so that the program applies the indices only in our study area, as presented in the results section.
2.4. Vegetation Indices
It is possible to estimate plant biomass from spectral data, using regression analysis, with spectral bands or combinations of bands (ratios, indices). A vegetation index is defined as the combination of spectral bands from a satellite to enhance the vegetation cover and attenuate the details of other components such as soil, lighting, etc.
It is important to note that spectral indices commonly used to assess vegetation on land may not be directly applicable or as effective for assessing aquatic plants due to water absorption in the NIR. However, as mentioned above, indices originally designed for terrestrial vegetation also give good or even better results when plants are fully or partially emerged, or at a shallow depth of less than 0.5 m to avoid the effect of water absorption in the NIR, as in the present case []. The indices used in our study to monitor the cover of M. spicatum are described below:
- -
- NDVI (Normalised Difference Vegetation Index) []: this is a vegetation index that uses the difference in reflectance between the near infrared and red parts of the electromagnetic spectrum to quantify vegetation density and health;
- -
- SAVI (Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index) []: This vegetation index is similar to NDVI but considers the reflectivity of the soil. It was developed to correct the influence of soil on vegetation measurements;
- -
- MNDWI (Modified Normalised Difference Water Index) []: This index focuses on the detection of water. It uses the near infrared and green bands to distinguish between water and other types of land cover;
- -
- LAI (Leaf Area Index) []: A key indicator of vegetation structure that represents the total leaf area per unit of ground area. It provides information on the density and distribution of leaves in a vegetation;
- -
- FAPAR (Fraction of Absorbed Photosynthetically Active Radiation): This index measures the proportion of photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by vegetation, which is an indicator of the photosynthetic efficiency of an ecosystem;
- -
- FCOVER (Fraction of Ground Cover): This index quantifies the proportion of the ground covered by vegetation, providing information on the density and cover of vegetation in a given area.
According to our results (see Section 3.1), we chose the NDVI index for this study. Its basis considers that healthy plants absorb most of the visible light (400–700 nm) that they use for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll in plants strongly absorbs light in the blue (430–450 nm) and red (640–680 nm) regions of the spectrum, which makes healthy plants appear green to the naked eye by reflecting green light (500–570 nm). On the other hand, plants reflect a lot in the near-infrared region (700–1300 nm) of the spectrum. The cellular structure of the leaves causes this reflection. When a plant is dehydrated or diseased, this cell structure deteriorates, resulting in lower near-infrared reflection and higher absorption. Therefore, by observing how the reflected light changes in the near infrared compared to red light, we can get an accurate indication of the amount of chlorophyll present, which in turn correlates with the health of the plant. Its Formula (1) is therefore described below:
The adapted versions for the S2 (2) and L8 (3) spectral bands are presented below:
The objective and central wavelengths of the different spectral bands presented above are shown below in Table 1.

Table 1.
Spectral bands for L8 and S2 satellites. Adapted from ESA [] and NASA [].
The values provided by this equation vary between −1 and 1, allowing us to classify the pixels into different categories (Table 2) and, if necessary, to create masks on the processed images.

Table 2.
NDVI values and interpretation of each range. Adapted from Jiang et al. [].
2.5. Data Analysis
Once all the images were processed and the results for the NDVI index were obtained, the positive values corresponding to the previously designated region of interest (ROI) were selected from the satellite images. Values between 0.25–0.7 were considered as vegetation, so we have considered all pixels in this value range to be completely covered by vegetation, and then the area is the sum of these pixels.
For water quality variables, the algorithms of Molner et al. [,] were applied to estimate the Secchi disk depth of vision (ZSD) with an RMSE of only 7 cm [], turbidity and total suspended solids in the S-2 imagery with an RMSE of 13.15 NTU and 26.64 mg/L, respectively [], in the 302.16 ha of the lagoon adjacent to the shore zone where plant growth occurred. In this way, the influence of the annual cycle of these limnological variables on the emergence and disappearance of the plants was analyzed with PAST software version 4.11.
3. Results
3.1. Radiometric Vegetation Indices Analysis
The NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) proved to be the most appropriate indicator and was selected as the most suitable for monitoring M. spicatum in the Albufera lagoon during its exceptional occurrence in spring–summer 2018. Figure 3 shows the results derived from the evaluation of different radiometric vegetation indices, showing that only the NDVI gives plausible results in agreement with field observations.
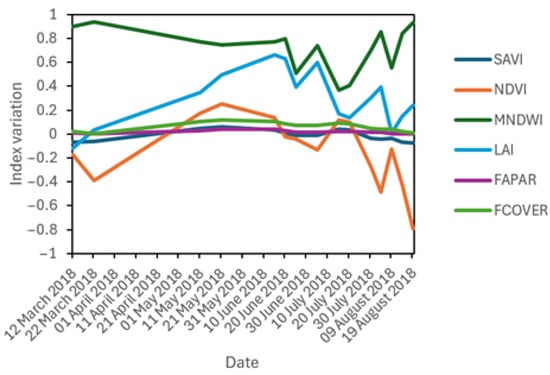
Figure 3.
Average results obtained by the different radiometric vegetation indices for M. spicatum within the region of interest in the northern zone of the Albufera coastal lagoon during the study period (March–August 2018).
Concerning Figure 3, it is important to clarify that it represents the mean index value of all pixels within the region of interest (ROI) established for the plant study on each date. It is important to note that the same pixels were used consistently across all dates, but it should be noted that in some cases, the mean NDVI value may appear negative. This result is attributed to the effect of water pixels at times when the plant emerges or disappears. It should be emphasized that the calculation of the area occupied by M. spicatum only considers pixels designated as vegetation within the ROI, as described in detail in Section 2.4 and Section 2.5 of the study.
3.2. Field and Remote Sensing Data
During 2018, a total of 20 samples were taken in the waters of the Albufera of Valencia and a total of 32 satellite images were processed, of which five were from Landsat-8, nine from Sentinel-2B and eighteen from Sentinel-2A. During this year, the lagoon showed the following results of water quality variables: Water conductivity presented an average value of 2276 µS/cm, with extreme values of 1013 and 3040 µS/cm. The annual average chlorophyll-a values were 94.5 mg/m3, with extreme values of 44.1 and 331.0 mg/m3. Water transparency as measured by the Secchi disk depth was 0.37 m, with extreme values from 0.20 to 0.55 m. These data show that the Albufera lagoon is oligohaline and hypertrophic, as well as shallow, since its average depth is close to 1 m.
The results for vegetation cover (m2) and the water variables considered interesting for understanding the emergence and disappearance of the plants are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Dates of processed and satellite images (S2A & B: Sentinel-2A & 2B; L8: Landsat-8). Results of M. spicatum area (m2) and other limnological variables for the studied dates during 2018.
Satellite image observation shows that the beginning of the emergence of M. spicatum was on 12 March, reaching its maximum observed extent on 20 June 2018 (Appendix A, Figure A1 and Figure A2), and was last observed on 19 August. This was confirmed in the field, since on 14 August some plants were still observed in a senescence vegetative state (Appendix A, Figure A3), while in the sampling of 24 August no plants were observed on the surface, while some remained completely submerged.
In the area where the plants emerged and during the months that they remained, chlorophyll-a values were between 46.2 (14 August) and 331 mg/m3 (21 May), with an average value of 106.1 mg/m3, while far away, in the central part of the lagoon, these values in the same period were between 68 and 119 mg/m3. Regarding nitrate data, a total of seven samples were recorded, with a minimum concentration of 1.64 mg/L on 5 July, reaching a maximum of 6.66 mg/L on 15 June, and an average of 0.67 mg/L. As for temperature, nine observations are available, with values ranging from a minimum of 16.8 °C (27 March) to a maximum of 30.1 °C (14 August), with an average temperature of 25.9 °C.
With respect to remote sensing data, the Secchi disk depth showed variability with a maximum of 0.54 m on 19 August and a minimum of 0.25 m on 21 May, with an average of 0.39 m. Turbidity, measured in nephelometric turbidity units (NTU), showed a range of values from a minimum of 3.15 NTU (19 August) to a maximum of 36.08 NTU (12 March), with an average of 14.65 NTU. For total suspended solids, a maximum of 137.61 mg/L was recorded on 12 March, a minimum of 12.02 mg/L on 19 August, and an average of 55.87 mg/L.
3.3. Data Analysis
The values of greater transparency are associated with episodes of lower turbidity and total solids concentration in the water. Based on the dates on which transparency and plant cover coincide, a scatter plot (Figure 4) was made to observe the time series during 2018 and evolution between the two variables.
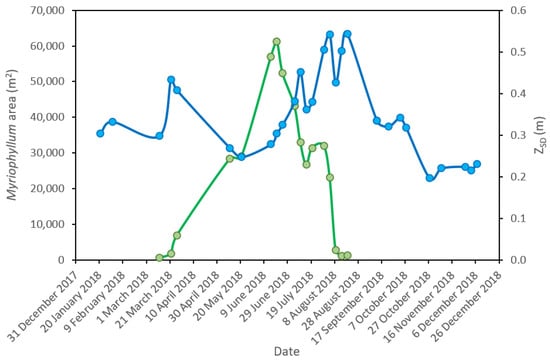
Figure 4.
Temporal evolution of M. spicatum cover (m2) in green and Secchi disk depth (m) in blue in the study area during 2018.
The emergence of plants occurs at the beginning of the meteorological spring, they grow until they reach a maximum at the beginning of the summer and disappear completely at the end. Transparency, on the other hand, represented by the visibility depth of the Secchi disk, follows a bimodal cycle, with values close to or above 30 cm in winter and late summer, while decreasing to values close to 20 cm in spring and autumn. These seasonal patterns are a consequence of algal blooms and retreat, with transparency following a negative relationship with Chlorophyll-a concentration [].
The distribution of the values of surface area covered by M. spicatum follows a normal Gaussian distribution (Figure 5A), the measured values being within the 95% confidence interval, with a p-value < 0.001.
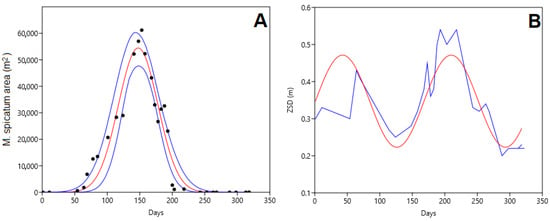
Figure 5.
(A) Temporal evolution of M. spicatum cover (m2); the red line indicates the normal distribution and the blue lines the 95% confidence interval. Day 1 corresponds to 21 January 2018. (B) Secchi disk depth (m) during 2018; the blue line is the observed Secchi disk depth, while the red line is the adjusted statistical sinusoidal distribution.
However, the water transparency values present a bimodal distribution (Figure 5B), fitted to a sine function with a period of 167 days. Regarding this data, it should be noted that the duration of macrophyte presence was also 163 days and that the duration of rice cultivation, from sowing to harvesting, is around 150 days, depending on the variety cultivated. Figure 6 illustrates this evolution at two different moments, one with a low density and the other with a higher density of M. spicatum, which is inside the red polygon in all cases.
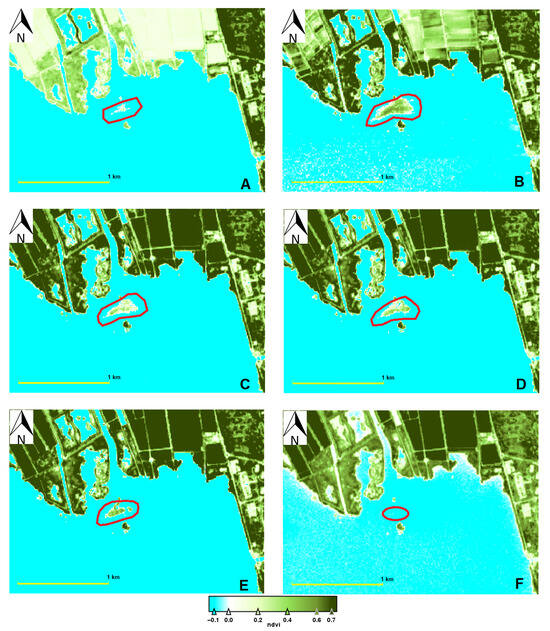
Figure 6.
Comparison of NDVI values in low coverage and high coverage images to disappearance. (A) 27 March 2018. (B) 20 June 2018. (C) 10 July 2018. (D) 30 July 2018. (E) 4 August 2018. (F) 9 August 2018. In each image, a red polygon indicates the emerging plants, and the yellow bar equals 1 km.
The onset of M. spicatum growth seems to coincide with the episode of water clarity that the lagoon undergoes during the month of March (Figure 6A). Despite that, the moment of maximum expansion of the plant cover coincides with the season when the water is most turbid due to the late spring algal bloom (Figure 6B). From this point on, the disappearance of the plants begins, expressed in the graph (Figure 5B) as a decrease in cover (Figure 6C). The clarity of the lagoon begins to recover, but the plants do not recover (Figure 6D,E) and are completely lost by the end of the summer when the transparency reaches its maximum just before the autumn bloom (Figure 6F).
Nevertheless, when applying the linear regression method, the results show an apparent correlation between the decrease in M. spicatum cover and the increase in water transparency, which contradicts what would be expected according to common sense and the literature cited. On the other hand, a relatively low coefficient of determination (R2) is observed (0.2248), suggesting a weak relationship or the possible influence of other factors not included in the analysis. This contradictory relationship could indicate the presence of additional variables, insufficient data to establish a clear relationship, or seasonal effects that could influence the dynamics of the aquatic plants in the lagoon.
Moreover, looking at Table 3, we can conclude that the presence of M. spicatum can also be limited in summer due to the high concentration of nitrates from the rice fields, in addition to the sharp increase in temperatures, sometimes reaching or exceeding 30 °C.
A correlation analysis between M. spicatum cover (in square meters) and the corresponding values of nitrate and summer temperature showed different results. In the case of nitrate, a positive correlation is evident, indicating that an increase in nitrate levels is associated with an increase in M. spicatum cover, although in a modest way, since the coefficient of determination (R2) is close to 0.2. Nevertheless, when temperature is considered, a significant decrease in M. spicatum cover is observed with increasing temperature. This response pattern is more pronounced and the R² obtained is slightly higher, reaching about 0.35. All these data suggest a more than likely combination of both physical and chemical water factors affecting the presence and density of M. spicatum, but temperature may have a more pronounced effect on the dynamics of M. spicatum compared to nitrate levels during the summer period.
4. Discussion
The presence of macrophytes in lakes and ponds and their function in these ecosystems is determined by the quality of water in which they develop [,,]. Several factors influence the distribution patterns of aquatic macrophytes. Many studies have concluded that light and water clarity are the factors that most influence the abundance, composition, and distribution of macrophytes [,,]. Thus, high water clarity allows light to reach greater depths and given that the Albufera has an average depth of 120 cm, when these two parameters are in good condition, plant growth is optimal.
In the specific case of the Albufera, the onset of M. spicatum growth seems to coincide with a period of greater water clarity in the lagoon during the month of March. However, the point of maximum expansion of the plant cover coincides with the period of highest water turbidity. After this point, the plants begin to decline and although the clarity of the lagoon begins to recover, the plants do not recover and disappear completely by late summer, just before the fall bloom when transparency is at its peak. The unclear and contradictory relationship observed in our results between transparency and plant cover contrasts with what is reported in the literature and raises the possibility of the existence of unaccounted variables or unidentified seasonal effects that could influence the dynamics of aquatic plants in the lagoon.
In addition, the combination of light and temperature affects plant growth, morphology, photosynthesis, chlorophyll composition and reproduction [,]. While a temperature within the tolerance range allows plants to grow and reproduce, a drop in temperature can be a critical factor for reduced growth []. Turbidity in the water also appears to be a determining factor in the expansion of submerged aquatic plants [,], as it directly affects the transparency of the water and the penetration of light, which is essential for the process of photosynthesis.
The factors related to the presence of sediments, such as their composition (organic or inorganic), reduction of available oxygen, grain size composition, etc., have been defined by several authors [,,] as influencing the distribution and diversity of aquatic macrophytes. Finally, the increased presence of nutrients can cause significant changes in the density, species composition and richness of aquatic vegetation in lakes [,,]. However, it can also promote the growth of phytoplankton populations, which in turn increases water turbidity and ultimately leads to a decrease in light availability and its consequences [,]. In the 1970s, the introduction of nutrients and suspended solids from industrial, urban and, above all, agricultural discharges increased their concentrations, leading to a change in the trophic state of the Albufera lagoon water. As stated in other studies [,,], light seems to be the most important factor for the growth and distribution of M. spicatum in the Albufera de Valencia. When the algal biomass decreases, the water transparency measured with the Secchi disk increases, with the winter and summer seasons being when we can find a higher water transparency (up to 50 cm). According to Wetzel [], the main mechanism for the growth and spread of macrophyte populations is vegetative reproduction. The most favorable period for macrophyte growth and development is between March and June. During the first part of the year, the lagoon water is more transparent, which allows the propagules to germinate and grow. After this, the plant begins to spread, and we can see a greater vegetation cover. During the period before the appearance of M. spicatum, the water transparency is maintained at around 30 cm, which coincides with the time when the rice fields surrounding the lagoon remain dry. In summer, solar radiation increases, which favors the photosynthetic response of the macrophytes, coinciding with the maximum expansion of the plant. During these months, rice is planted, and the fields are flooded for growth. The pesticides used during this planting can have serious effects on the development and growth of macrophytes, according to a report by GVA []. We found that during the period of greatest expansion, water transparency decreased due to increased turbidity, and although according to Lloret et al. [] high nutrient concentrations may allow macrophytes to continue to grow and expand, they cannot reproduce, and hypothetically aquatic plants affected by the lack of light will eventually die. However, it should be noted that according to Carpenter and Adams [], the density of M. spicatum decreases with increasing nitrate concentration, and 75% of the individuals die when temperatures reach 30 °C. This hypothesis seems to be supported by our results, since, according to our results, temperature emerges as the environmental variable with the highest coefficient of determination (R2) and, moreover, with the direction of the expected relationship: at higher temperatures, a significant decrease in the presence of aquatic plants is observed.
Despite several hypotheses suggesting the combined effects of water transparency, nitrate concentration, temperature, turbidity, and suspended solids on the presence and density of submerged macrophytes in general, including M. spicatum in particular, our results indicate that temperature is the environmental variable with the most notable correlation. In our study, correlations with other environmental factors, such as water transparency and nitrate concentration, were significantly lower. Although the data collected in 2018 are not sufficiently numerous to provide strong, concrete evidence or a meaningful statistical basis to fully confirm which factor(s) are responsible for the disappearance of these plants, temperature would indeed emerge as the factor that most significantly contributed to their disappearance during our study period. However, this study could lay the basis for future research. Favorable conditions, such as the underground nature of the plants allow reflectivity similar to that of terrestrial species, which is little affected by water absorption in the NIR. These conditions provide an opportunity to continue this line of research in subsequent years. The successful application of NDVI not only for monitoring M. spicatum, but also for other similar species in different locations, highlights its potential for assessing the dynamics of aquatic ecosystems.
Although it was an extraordinary event and we do not know if it will happen again, for future occurrences of this phenomenon, more extensive and detailed data collection will be required to allow a more robust and statistical assessment of the variables that could influence this process. By expanding the data set and observations, the goal is to establish more precise relationships between specific factors, such as water transparency, suspended solids, or other environmental variables, and the appearance or disappearance of macrophytes in the Albufera lagoon. This approach will provide a deeper and more precise understanding of the dynamics of this ecosystem and the factors that cause these specific changes. As plants were absent for over 40 years, with no comparison to data from earlier years, there is insufficient information to ascertain whether the seasonal measurements accurately represent the optimal conditions for aquatic vegetation growth. In cases where vegetation has been absent for an extended period, a “hysteresis effect” may occur, requiring enhancements beyond historical conditions for vegetation to reestablish.
Nevertheless, visual observations and literature support the hypothesis of the combined influence of water transparency (caused by the presence of suspended solids and affecting light availability), nitrates and changing temperatures as the most reasonable option, although in our study only temperature provided a more significant result. It is worth noting that, in this context, the NDVI index has proven to be a valuable tool in monitoring this appearance, contributing significantly to the understanding, and tracking of the observed changes in the dynamics of the aquatic ecosystem. Jiang et al. [] suggest that the NDVI index is a suitable measure for inferring the vegetation fraction, provided that the assumption of linearity of the spectral mixture is met. However, Jiang et al. [] note that this index does not consider differential transmissions at red and near-infrared wavelengths or the non-linear spectral mixing of soil and vegetation components. In contrast, Villa et al. [] used various indices that focused on macrophytes and concluded that the multi-temporal WAVI index, which is specific to aquatic vegetation, performed the best. However, they emphasized that the use of different indices is very helpful in mapping macrophyte communities in different systems using satellite data directly.
Remote sensing can be a valuable tool in ecological studies, providing early detection of significant ecological events. It enables the creation of detailed maps that show the heterogeneity of water bodies and the behavior of certain species, such as plants, helping us to understand their dynamics and relationship with environmental conditions. The combination of remote sensing data with geographic information systems (GIS) enables a more comprehensive view of the relationship between the presence of floating vegetation and spatial factors, facilitating management decisions. Also, remote sensing is a tool that can be used to estimate biophysical measurements and is very useful for monitoring macrophyte communities. One of its main advantages is the temporal acquisition of images, which allows the calculation of time series through which seasonal patterns can be analyzed [,]. But it is important to consider the effect of acquisition characteristics, such as the relative position of the sun with respect to the sensor and surface effects, on the retrieval of macrophyte properties. Moreover, there is a need to develop standardized methods for assessing morpho-ecological gradients, structural complexity, and functional status of macrophyte-dominated habitats, according to Villa et al. [].
The monitoring of water bodies is important for understanding the role of macrophytes in biogeochemical cycles, and for assessing their health and response to environmental changes. It can also be useful for assessing the effectiveness of management and restoration efforts in aquatic ecosystems. Remote sensing applied to the study of terrestrial vegetation growth, health, and dynamics can be of great use in environmental monitoring, biodiversity conservation, agriculture, forestry, urban green infrastructure, and other related fields []. The use of satellite data to map macrophyte communities in various systems is a significant advancement in macrophyte mapping beyond the local scale. This method supports in situ monitoring and enables the observation of spatial and temporal dynamics in freshwater ecosystems []. Wetlands are intricate ecosystems that exhibit rapid vegetative responses, allowing for quick changes to occur []. The use of remote sensing is a valuable tool for managing and preventing changes in such dynamic systems.
5. Conclusions
This study of the Albufera of Valencia in 2018 found the singular appearance of M. spicatum coinciding with an increase in water transparency compared to previous years. However, high summer temperatures seem to be the most important environmental factor associated with their disappearance. Improving water quality in the Albufera could help restore the submerged macrophyte meadows that existed before the 1970s, when pollution altered the waters; however, given our results, summer maximum temperatures could hinder this recovery. Previous research has shown that water clarity and suspended solids have a significant effect on the abundance, composition, and distribution of aquatic macrophytes. Factors such as turbidity, the presence of sediment, nutrient composition, and light availability also influence macrophyte density and distribution. Nevertheless, more comprehensive data collection is needed to establish stronger relationships between these factors and the emergence or disappearance of macrophytes in the Albufera lagoon. The use of remote sensing, particularly the NDVI index, has been valuable in monitoring changes in the aquatic ecosystem and understanding species–environment relationships. Remote sensing combined with geographic information systems (GIS) provides a comprehensive view of environmental management and monitoring of macrophyte communities. The methodology used in this study will serve so that on future occasions when a new colonization by macrophytes may occur, this study can be followed, and the knowledge of the causes of the appearance and disappearance of the plants can be expanded.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.S. and S.R.; methodology, J.M.S., L.V.-H. and S.R.; software, J.V.M. and R.P.-G.; formal analysis, J.M.S. and J.V.M.; investigation, J.M.S., J.V.M., R.P.-G., B.A., L.V.-H. and S.R.; data curation, J.M.S., J.V.M., R.P.-G., B.A., L.V.-H. and S.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.V.M., R.P.-G. and B.A.; writing—review and editing, J.M.S., J.V.M., R.P.-G., B.A., L.V.-H. and S.R.; supervision, J.M.S.; project administration, S.R.; funding acquisition, S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by Generalitat Valenciana (Spanish Regional Government), Anthropocene Prometheus Project, grant number PROMETEO/2018/155.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Satellite images are available through the ESA Copernicus Browser and the USGS website; the data presented may be used for scientific purposes in accordance with the provisions of the Berne Convention.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
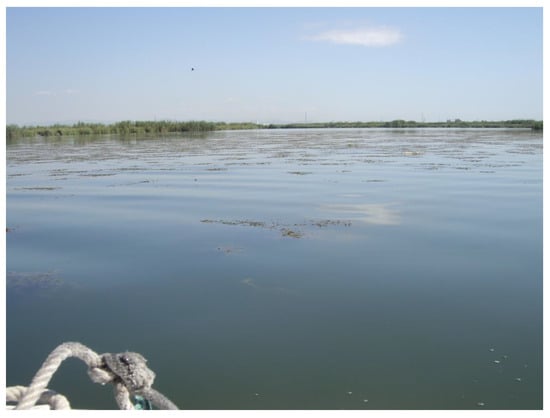

Figure A1.
General view of the area of the emerging macrophytes on 14 June 2018 (picture by J.M.S.).
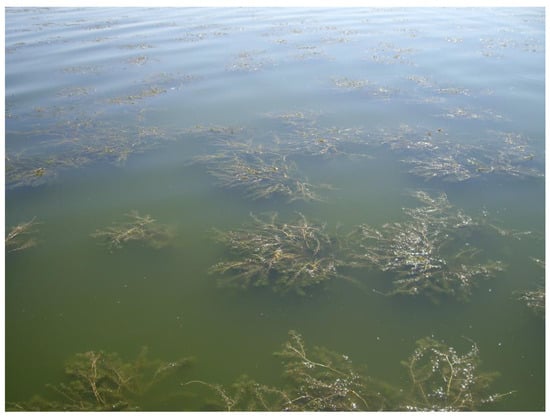

Figure A2.
Detail of the macrophytes on 14 June 2018 (picture by J.M.S.).
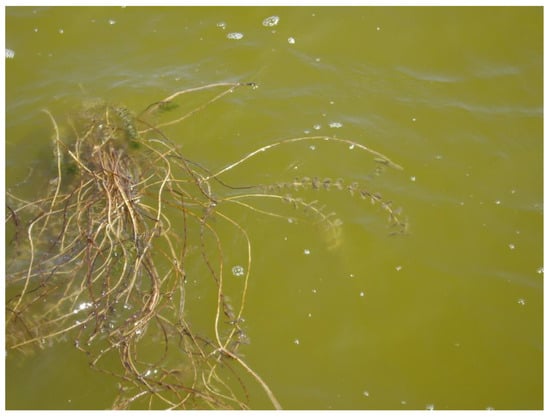

Figure A3.
Detail of the senescent macrophytes on 14 August 2018 (pictures by J.M.S.).
References
- Scheffer, M.; Hosper, S.H.; Meijer, M.-L.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative equlibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; van Nes, E.H. Shallow lakes theory revisited: Various alternative regimes driven by climate, nutrients, depth and lake size. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Ni, L.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M. Effects of moderate ammonium enrichment on three submersed macrophytes under contrasting light availability. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, M.A. Wetland Restoration with Hydrophytes: A Review. Plants 2021, 10, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, W.F.; Barko, J.W.; Butler, M.G. Shear stress and sediment resuspension in relation to submersed macrophyte biomass. Hydrobiologia 2004, 515, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Moss, B. Impact of submerged macrophytes on phytoplankton in shallow freshwater lakes. In The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Han, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Bi, F.; Feng, D. Reproduction capacity of Potamogeton crispus fragments and its role in water purification and algae inhibition in eutrophic lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 580, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, D.; Liu, C. Response of sediment and water microbial communities to submerged vegetations restoration in a shallow eutrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhou, Q.H.; Zeng, L.; He, F.; Wu, Z.B. Synergistic removal effect of P in sediment of all fractions by combining the modified bentonite granules and submerged macrophyte. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RejmánkováJ, E. The role of macrophytes in wetland ecosystems. Ecol. Field Biol. 2011, 34, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fur, I.; De Wit, R.; Plus, M.; Oheix, J.; Simier, M.; Ouisse, V. Submerged benthic macrophytes in Mediterranean lagoons: Distribution patterns in relation to water chemistry and depth. Hydrobiologia 2018, 808, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, R.M.; Moss, B. Prevention of growth of potentially dense phytoplankton populations by zooplankton grazing, in the presence of zooplanktivorous fish, in a shallow wetland ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, J. An example of relationships between macrophytes, macroinvertebrates and their food resources in a shallow euthrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 1996, 339, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.F. Primary production in a shallow eutrophic lake dominated alternately by phytoplankton and by submerged macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 1989, 33, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, S.; García-Murcia, A.; Villena, M.J.; Sánchez, V.; Ballester, A. Tendencias del fitoplancton en el lago de la Albufera de Valencia e implicaciones para su ecología, gestión y recuperación. Limnetica 2008, 27, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official State Gazette (BOE). Royal Legislative Decree 1/2001, of 20 July 2001, approving the revised text of the Water Law. BOE 2001, 176, 26791–26817. [Google Scholar]
- Official State Gazette (BOE). Royal Decree 2090/2008, of 22 December 2008, approving the Regulations for the partial development of Law 26/2007, of 23 October 2007, on Environmental Responsibility. BOE 2008, 308, 51626–51646. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Su, B. Significant remote sensing vegetation indices: A review of developments and application. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 1353691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samboni, N.E.; Carvajal, Y.; Escobar, J. Revisión de parámetros fisicoquímicos como indicadores de calidad y contaminación del agua. Ing. E Investig. 2007, 27, 172–181. Available online: https://repositorio.unal.edu.co/handle/unal/28869 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Paredes-Arquiola, J.; Andreu-Álvarez, J.; Martín-Monerris, M.; Solera, A. Water quantity and quality models applied to the Jucar River Basin, Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 2759–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.W. A current review of empirical procedures of remote sensing in inland and near-coastal transitional waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6855–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestir, E.L.; Brando, V.E.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Matta, E.; Villa, P.; Dekker, A.G. Measuring freshwater aquatic ecosystems: The need for a hyperspectral global mapping satellite mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Shiqiang, Z.; Jianping, W. Detecting, extracting and monitoring surface water from space using optical sensors: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompêo, M.; Moschini-Carlos, V.; Bitencourt, M.D.; Sòria-Perpinyà, X.; Vicente, E.; Delegido, J. Water quality assessment using Sentinel-2 imagery with estimates of chlorophyll-a, Sechhi disk depth and cyanobacteria cell number: The Cantareira system reservoirs (São Paulo, Brazil). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34990–35011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.S.; Skidmore, A.K. Spectral discrimination of vegetation types in a coastal wetland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, W.J.; McIlwee, A.; Lawler, I.; Aragones, L.; Woolnough, A.P.; Berding, N. Ecological Applications of near Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy—A Tool for Rapid, Cost-Effective Prediction of the Composition of Plant and Animal Tissues and Aspects of Animal Performance. Oecologia 1998, 116, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malthus, T.J. Bio-optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Aquatic Macrophytes. In Bio-Optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 263–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Longhi, D.; Pinardi, M.; Bartoli, M.; Vascellari, M. Imaging spectrometry of productive inland waters. Application to the lakes of Mantua. Ital. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 41, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q.; Zimmerman, M.J.; Flint, S.; Waldron, M.C. Differentiating aquatic plant communities in a eutrophic river using hyperspectral and multispectral remote sensing. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1658–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, P.; Laini, A.; Bresciani, M.; Bolpagni, R. A Remote Sensing Approach to Monitor the Conservation Status of Lacustrine Phragmites Australis Beds. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 21, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, P.; Bresciani, M.; Bolpagni, R.; Pinardi, M.; Giardino, C. A rule-based approach for mapping macrophyte communities using multi-temporal aquatic vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; Liu, H.Q.; Batchily, K.; van Leeuwen, W. A comparison of vegetation indices over a global set of TM images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, P.; Mousivand, A.; Bresciani, M. Aquatic vegetation indices assessment through radiative transfer modeling and linear mixture simulation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espel, D.; Courty, S.; Auda, Y.; Sheeren, D.; Elger, A. Submerged macrophyte assessment in rivers: An automatic mapping method using Pleiades imagery. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.M.; Vera-Herrera, L.; Calvo, S.; Romo, S.; Vicente, E.; Sahuquillo, M.; Sòria-Perpinyà, X. Residence time analysis in the Albufera of Valencia, a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon, Spain. Hydrology 2021, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Liu, G. The effect of temperature, water level and burial depth on seed germination of Myriophyllum spicatum and Potamogeton malaianus. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 92, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directorate General for the Natural Environment and Environmental Assessment. Distribution and Conservation Status of Aquatic Macrophytes in Albufera de Valencia Lake (Report); Generalitat Valenciana: Valencia, Spain, 2017; (In Spanish). Available online: https://parquesnaturales.gva.es/documents/80302883/165126079/Distribucion+y+estado+de+conservacion+de+macrofitos+acuaticos+en+el+lago+de+l_Albufera+de+Valencia.pdf/040fb483-35d4-428d-8609-8126e6c6cbba?t=1514550696577 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Bridgewater, L.L., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Rice, E.W., American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-87553-287-5. [Google Scholar]
- Crumpton, W.G.; Isenhart, T.M.; Mitchell, P.D. Nitrate and Organic N Analyses with Second-Derivative Spectroscopy. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaf, W.T.; Lium, B.W. Improved extraction of chlorophyll a and b from algae using dimethyl sulfoxide. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1976, 21, 926–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.T.; Humphrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Pflug, B.; Main-Knorn, M.; Bieniarz, J.; Mueller-Wilm, U.; Cadau, E.; Gascon, F. Sentinel-2 Sen2Cor: L2A processor for users. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Soria, X.; Delegido, J.; Urrego, E.P.; Pereira-Sandoval, M.; Vicente, E.; Ruíz-Verdú, A.; Moreno, J. Validación de algoritmos para la estimación de la clorofila-a con Sentinel-2 en la Albufera de València. In Proceedings of the XVII Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección, Murcia, Spain, 3–7 October 2017; pp. 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Ruescas, A.B.; Pereira-Sandoval, M.; Tenjo, C.; Rúiz-Verdú, A.; Steinmetz, F.; De Keukelaere, L. Sentinel-2 Atmospheric Correction Inter-comparison over two lakes in Spain and Peru-Bolivia. In Proceedings of the Colour and Light in the Ocean from Earth Observation (CLEO) Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 6–8 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, L.S. Quick atmospheric correction code: Algorithm description and recent upgrades. Opt. Eng. 2012, 51, 111719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Black, T.A. Defining leaf-area index for non-flat leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Spacial Agency (ESA). Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services; Fletcher, K., Ed.; ESA Communications: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Landsat 8 Bands. Available online: https://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/satellites/landsat-8/landsat-8-bands/ (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Huete, A.R.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, J.; Yan, G.J.; Zhang, X.Y. Analysis of NDVI and scaled difference vegetation index retrievals of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molner, J.V.; Soria, J.M.; Pérez-González, R.; Sòria-Perpinyà, X. Measurement of Turbidity and Total Suspended Matter in the Albufera of Valencia Lagoon (Spain) Using Sentinel-2 Images. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molner, J.V.; Soria, J.M.; Pérez-González, R.; Sòria-Perpinyà, X. Estimating Water Transparency Using Sentinel-2 Images in a Shallow Hypertrophic Lagoon (The Albufera of Valencia, Spain). Water 2023, 15, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, D.M. Herbivory on freshwater macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 1991, 41, 195–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology. In Lake and River Ecosystems; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; p. 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann, T. The Structuring Role of Lake Conditions for Aquatic Macrophytes. Ph.D. Thesis, Estonian University of Life Sciences, Tartu, Estonia, 2012; p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Bini, L.M.; Thomaz, S.M.; Murphy, K.J.; Camargo, A.F.M. Aquatic macrophyte distribution in relation to water and sediment conditions in the Itaipu Reservoir, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 1999, 415, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougheed, V.L.; Crosbie, B.; Chow-Fraser, P. Primary determinants of macrophyte community structure in 62 marshes across the Great Lakes basin: Latitude, land use, and water quality effects. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 5, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, A.K. Freshwater biological resources of Kashmir Himalaya. In Natural Resources of Western Himalaya; Pandit, A.K., Ed.; Valley Book House: Srinagar, India, 2002; pp. 123–174. [Google Scholar]
- Sastroutomo, S.S. Environmental control of turion formation in curly pondweed, Potamogeton crispus L. Physiol. Plant. 1980, 49, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, D.; Freile-Pelegrin, Y. Seasonal variation in photosynthesis and biochemical composition of Caulerpa spp. Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) from the Gulf of Mexico. Phycologia 2005, 44, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barko, J.W.; Smart, R.N. Sediment related mechanism of growth limitation in submerged macrophytes. Ecology 1986, 67, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, V.; Tristal, C.L.; Handoo, J.K. Distribution and production of macrophytes in some aquatic bodies of Kashmir. In Glimpses of Ecology; Singh, J.S., Gopal, B., Eds.; Prakash Publishers: Jaipur, India, 1978; pp. 313–334. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, A.K. Biodiversity of wetlands in Kashmir Himalaya. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 78, 29–51. [Google Scholar]
- Drew, M.C.; Lynch, J.M. Soil anaerobiosis, microorganisms, and root function. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1980, 18, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barko, J.W.; Gunnison, D.; Carpenter, S.R. Sediment interactions with aquatic macrophytes in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 1991, 595, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedeltje, G.; Smolders, A.J.P.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; Groenendael, J.M.V. Constructed shallow zonesalong navigation canals: Vegetation establishment and change in relation to environmental characteristics. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2001, 11, 453–0471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, H.; Huttunen, P. Aquatic macrophytes and ecological gradients in 57 small lakes in southern Finland. Aquat. Bot. 1995, 51, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahuhta, J. Patterns of Aquatic Macrophytes in the Boreal Region: Implications for Spatial Scale Issues and Ecological Assessment. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dennison, W.C. Effects of light on seagrass photosynthesis, growth and depth distribution. Aquat. Bot. 1987, 27, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Ghetti, P.F. Temporal and spatial changes of macroalgae and phytoplankton in a Mediterranean coastal area: The Venice lagoon as a case study. Mar. Environ. Res. 2003, 56, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.A.; Wetzel, R.L. Seasonal variations in eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) responses to nutrient enrichment and reduced light availability in experimental ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 244, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharova, N.; Sfriso, A.; Voinov, A.; Pavoni, B. A simulation model for the annual fluctuation of Zostera marina biomass in the Venice lagoon. Aquat. Bot. 2001, 70, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, D.; Sheng, Y. Relative influence of various water quality parameters on light attenuation in Indian River Lagoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalitat Valenciana (GVA). Evolución de los Macrófitos Acuáticos en el Lago de l’Albufera de Valencia y Relación con Variables Ambientales, Período 2015–2020; Informe técnico 04/2021; Generalitat Valenciana: Valencia, Spain, 2021.
- Lloret, J.; Marin, A.; Marin-Guirao, L.; Velasco, J. Changes in macrophytes distribution in a hypersaline coastal lagoon associated with the development of intensively irrigated agriculture. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2005, 48, 828–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Adams, M.S. Effects of nutrients and temperature on decomposition of Myriophyllum spicatum L. in a hard-water eutrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1979, 24, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.S.F. Imagens EOS-MODIS E Landsat 5 TM No Estudo Da Dinâmica Das Comunidades De Macrófitas Na Várzea Amazônica. Master’s Thesis, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, São José dos Campos, São Paulo, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R.; Narumalani, S.; Weatherbee, O.; Mackey, J.H.E. Measurement of seasonal and yearly cattail and waterlily changes using multidate SPOT panchromatic data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1993, 59, 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, S.J.; Jakeman, A.; Croke, B. Can NDVI response indicate the effective flood extent in macrophyte dominated floodplain wetlands? Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).