Early Diagenetic Processes in the Sediments of the Krka River Estuary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Sample Pretreatment
2.3. Porewater and Overlying Water Analysis
2.4. Sediment Analysis
2.5. The Benthic Diffusive Fluxes
3. Results
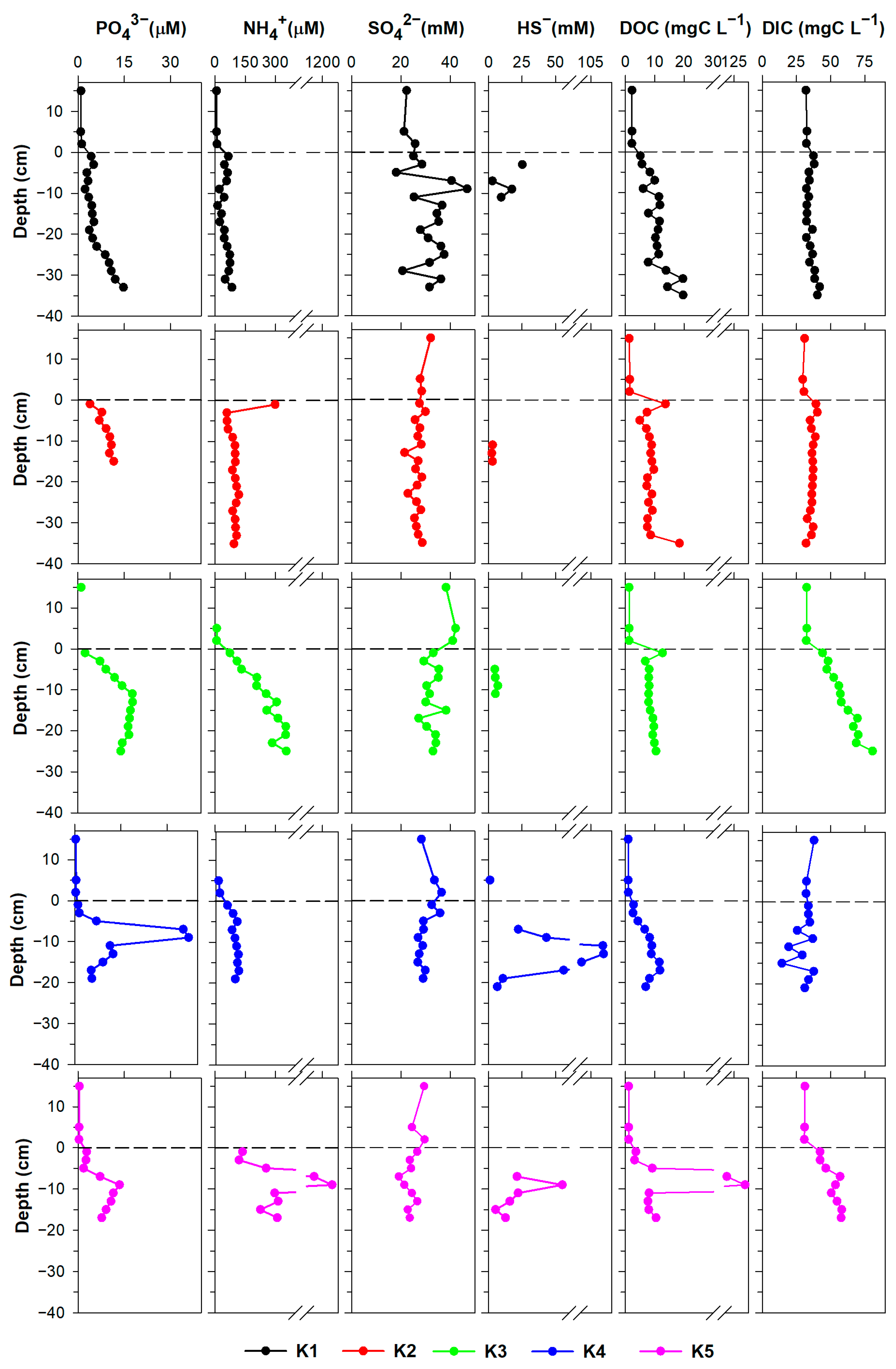
3.1. Pore Water Characterisation
3.1.1. Major Dissolved Species
3.1.2. Trace Metals
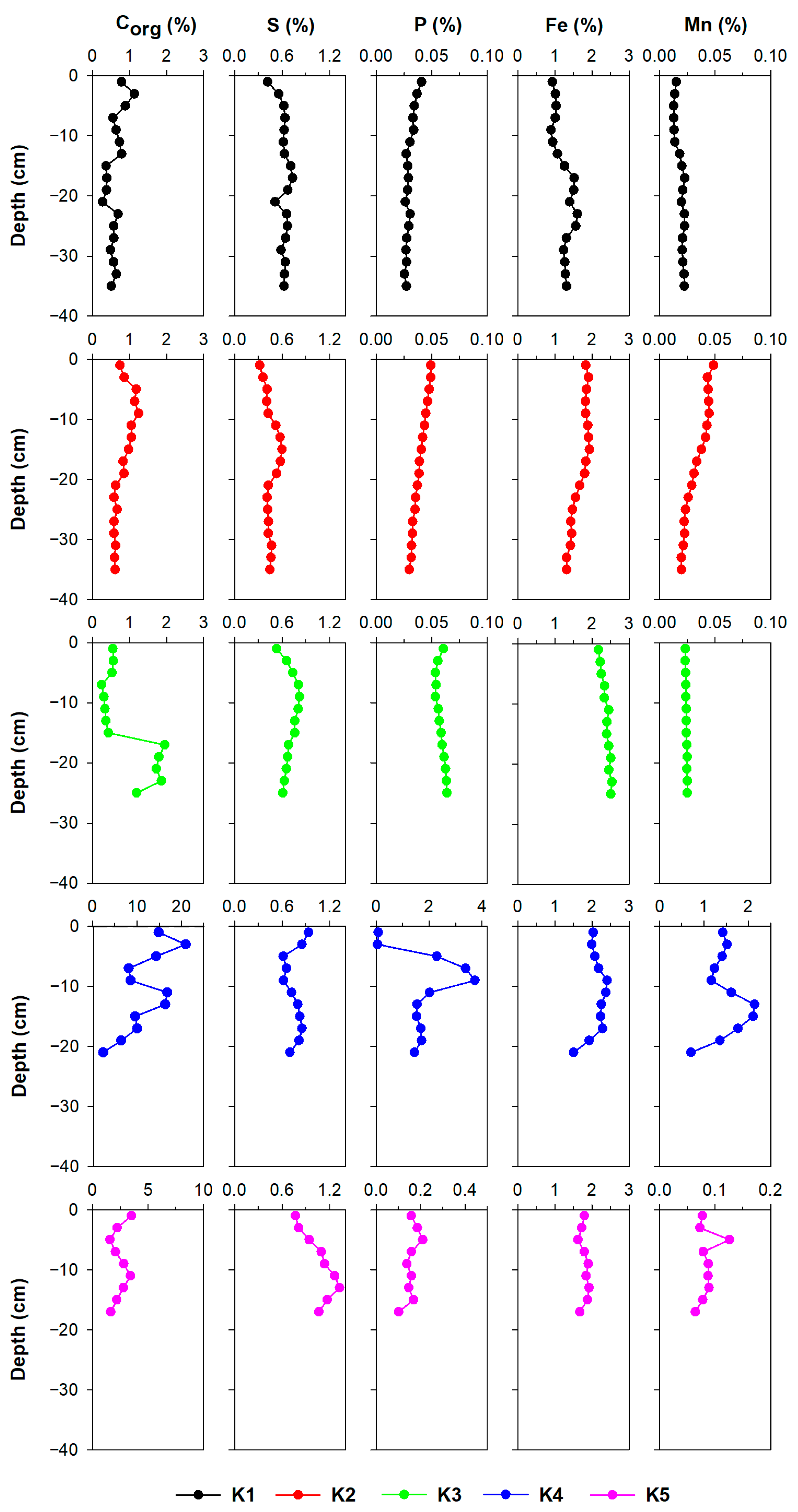
3.2. Sediment Characterisation
3.2.1. Fe, Mn, S, P, and Corg
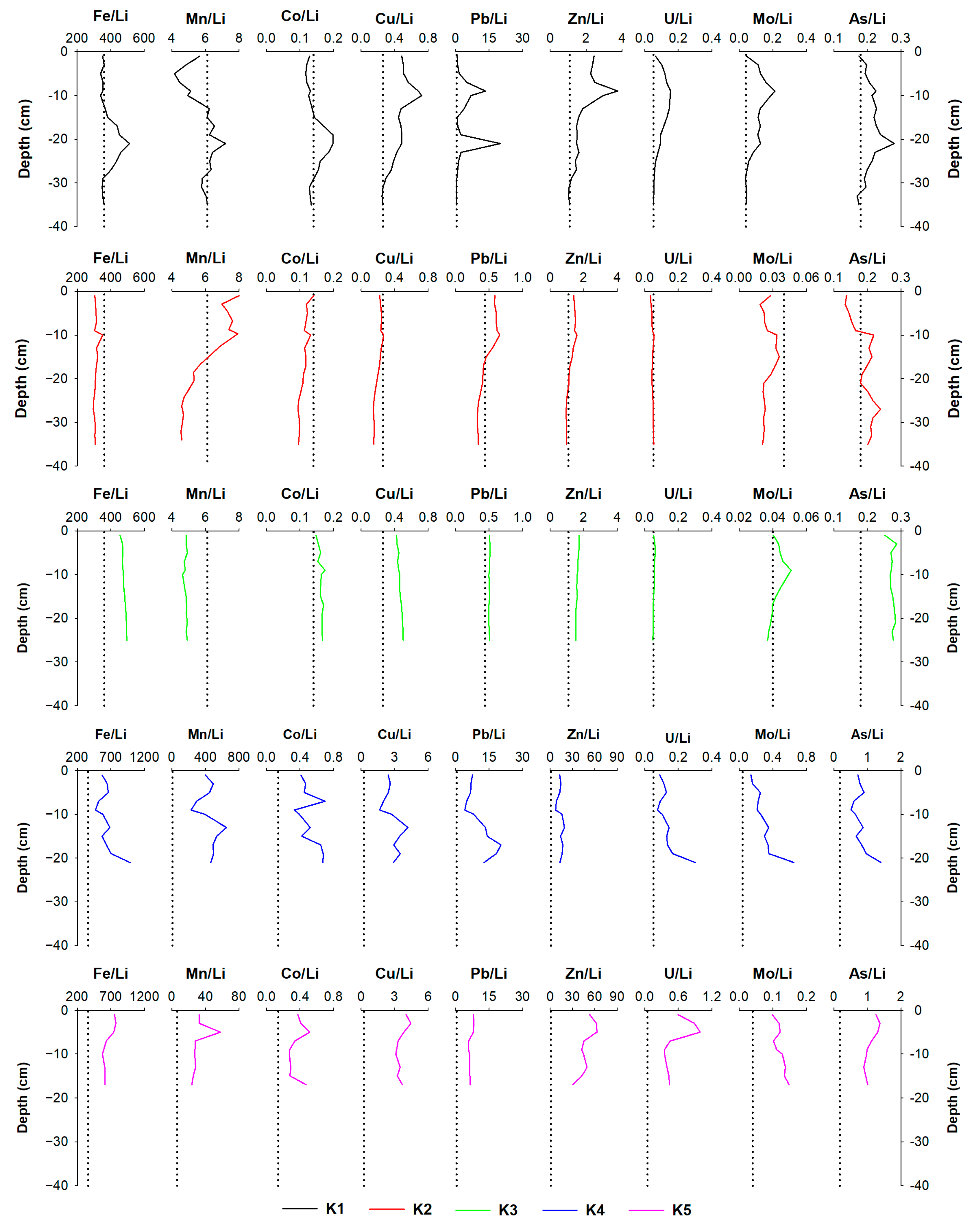
3.2.2. Metals
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of Natural (Diagenetic) Processes and Anthropogenic Input on Metal Distribution in the Solid Phase of the Sediment
4.2. Cycling of Fe and Mn in the Pore Water
4.3. The Post-Depositional Mobility of Metals
4.4. The Benthic Diffusive Fluxes in the KRE
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ridgway, J.; Shimmield, G. Estuaries as Repositories of Historical Contamination and Their Impact on Shelf Seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 903–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohić, E.; Kniewald, G. Heavy Metal Distribution in Recent Sediments of the Krka River Estuary—An Example of Sequential Extraction Analysis. Mar. Chem. 1987, 22, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennish, M.J. Environmental Threats and Environmental Future of Estuaries. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Hu, B.; Yang, S. Distribution, Enrichment and Source of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of the Eastern Beibu Bay, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Yang, L.Y.; Kong, L.H.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.R.; Wang, Y.Q. Spatial Distribution, Source Identification and Pollution Assessment of Metal Content in the Surface Sediments of Nansi Lake, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 140, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.G.; Zeng, G.M.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.Y.; Shen, L.Q.; Hu, L. Effects of Sediment Geochemical Properties on Heavy Metal Bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, J.; Vargas, G.; Sifeddine, A.; Ortlieb, L.; Guiñez, M. Distribution and Enrichment Evaluation of Heavy Metals in Mejillones Bay (23°S), Northern Chile: Geochemical and Statistical Approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulnier, I.; Mucci, A. Trace Metal Remobilization Following the Resuspension of Estuarine Sediments: Saguenay Fjord, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankere-Muller, S.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W.; Finke, N.; Larsen, O.; Stahl, H.; Glud, R.N. Fine Scale Remobilisation of Fe, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu and Cd in Contaminated Marine Sediment. Mar. Chem. 2007, 106, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, E.; Garnier, C.; Mullot, J.U.; Lenoble, V.; Arnaud, M.; Raynaud, M.; Mounier, S. Study of the Spatial and Historical Distribution of Sediment Inorganic Contamination in the Toulon Bay (France). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalnejais, L.H.; Martin, W.R.; Bothner, M.H. The Release of Dissolved Nutrients and Metals from Coastal Sediments Due to Resuspension. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.Q.; Song, J.M.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, H.M.; Li, X.G.; Li, N. Spatial Variation, Fractionation and Sedimentary Records of Mercury in the East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigaud, S.; Radakovitch, O.; Couture, R.M.; Deflandre, B.; Cossa, D.; Garnier, C.; Garnier, J.M. Mobility and Fluxes of Trace Elements and Nutrients at the Sediment-Water Interface of a Lagoon under Contrasting Water Column Oxygenation Conditions. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.H.; Swennen, R.; Cappuyns, V.; Vassilieva, E.; Van Gerven, T.; Van Tran, T. Speciation and Mobility of Selected Trace Metals (As, Cu, Mn, Pb and Zn) in Sediment with Depth in Cam River-Mouth, Haiphong, Vietnam. Aquat. Geochem. 2013, 19, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Organic Matter Diagenesis at the Oxic/Anoxic Interface in Coastal Marine Sediments, with Emphasis on the Role of Burrowing Animals. Hydrobiologia 2000, 426, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.-J.; Sayles, F.L. Oxygen Penetration Depths and Fluxes in Marine Sediments. Mar. Chem. 1996, 52, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnejais, L.H.; Martin, W.R.; Bothner, M.H. Porewater Dynamics of Silver, Lead and Copper in Coastal Sediments and Implications for Benthic Metal Fluxes. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 517, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.H.; Lenoble, V.; Durrieu, G.; Omanović, D.; Mullot, J.U.; Mounier, S.; Garnier, C. Seasonal Variations of Coastal Sedimentary Trace Metals Cycling: Insight on the Effect of Manganese and Iron (Oxy)Hydroxides, Sulphide and Organic Matter. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Song, J.; Liang, X.; Yin, M.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Ren, C.; Zhou, B.; Kang, X.; Yin, X. Dynamics and Diagenesis of Trace Metals in Sediments of the Changjiang Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundby, B. Transient State Diagenesis in Continental Margin Muds. Mar. Chem. 2006, 102, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.W.; Luther, G.W. Chemical Influences on Trace Metal-Sulfide Interactions in Anoxic Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3373–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, Y.; Lam, P.; Boyle, E.A.; Thomson, J. Authigenic Cadmium Enrichments in Suboxic Sediments: Precipitation and Postdepositional Mobility. Sci. Lett. 1995, 132, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charriau, A.; Lesven, L.; Gao, Y.; Leermakers, M.; Baeyens, W.; Ouddane, B.; Billon, G. Trace Metal Behaviour in Riverine Sediments: Role of Organic Matter and Sulfides. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tessier, A. Zero-Valent Sulfur and Metal Speciation in Sediment Porewaters of Freshwater Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7252–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, G.A.; Loch, J.P.G.; Van Der Heijdt, L.M.; Zwolsman, J.J.G. Geochemical Behaviour of Trace Metals in Freshwater Sediments. Trace Met. Environ. 2000, 4, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilinski, H.; Kwokal, Ž.; Plavšić, M.; Wrischer, M.; Branica, M. Mercury Distribution in the Water Column of the Stratified Krka River Estuary (Croatia): Importance of Natural Organic Matter and of Strong Winds. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, Y.; Garnier, C.; Lenoble, V.; Mounier, S.; Cukrov, N.; Omanović, D.; Pižeta, I. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Copper-Dissolved Organic Matter Complexation in Water Column of the Stratified Krka River Estuary (Croatia). Mar. Chem. 2009, 114, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempéré, R.; Cauwet, G. Occurrence of Organic Colloids in the Stratified Estuary of the Krka River (Croatia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viličić, D.; Legović, T.; Žutić, V. Vertical Distribution of Phytoplankton in a Stratified Estuary. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 51, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šupraha, L.; Bosak, S.; Ljubešić, Z.; Mihanović, H.; Olujić, G.; Mikac, I.; Viličić, D. Cryptophyte Bloom in a Mediterranean Estuary: High Abundance of Plagioselmis Cf. Prolonga in the Krka River Estuary (Eastern Adriatic Sea). Sci. Mar. 2014, 78, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djogić, R.; Pižeta, I.; Branica, M. Electrochemical Determination of Dissolved Uranium in Krka River Estuary. Wat. Res. 2001, 35, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Ming Guan, D.; Martin, J.-M. Trace Metal Behaviour in a Highly Stratified Mediterranean Estuary: The Krka (Yugoslavia). Mar. Chem. 1991, 32, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindrić, A.M.; Garnier, C.; Oursel, B.; Pižeta, I.; Omanović, D. Evidencing the Natural and Anthropogenic Processes Controlling Trace Metals Dynamic in a Highly Stratified Estuary: The Krka River Estuary (Adriatic, Croatia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 94, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legović, T. Exchange of Water in a Stratified Estuary with an Application to Krka (Adriatic Sea). Mar. Chem. 1991, 32, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legović, T.; Petricioli, D.; Žutić, V. Hypoxia in a Pristine Stratified Estuary (Krka, Adriatic Sea). Mar. Chem. 1991, 32, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legović, T.; Žutić, V.; Gržetić, Z.; Cauwet, G.; Precali, R.; Viličić, D. Eutrophication in the Krka Estuary. Mar. Chem. 1994, 46, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gržetić, Z.; Precali, R.; Degobbis, D.; Škrivanić, A. Nutrient Enrichment and Phytoplankton Response in an Adriatic Karstic Estuary. Mar. Chem. 1991, 32, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohić, E.; Juračić, M. Heavy Metals in Sediments—Problems Concerning Determination of the Anthropogenic Influence. Study in the Krka River Estuary, Eastern Adriatic Coast, Yugoslavia. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1989, 13, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juračić, M.; Prohić, E. Mineralogy, Sources of Particles, and Sedimentation in the Krka River Estuary (Croatia). Geološki Vjesnik 1991, 44, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Martinčić, D.; Kwokal, Ž.; Branica, M. Distribution of Zinc, Lead, Cadmium and Copper between Different Size Fractions of Sediments II. The Krka River Estuary and the Kornati Islands (Central Adriatic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 95, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, O.; Andrić, I.; Roje-Bonacci, T. Hydrological Analysis of Skradinski Buk Tufa Waterfall (Krka River, Dinaric Karst, Croatia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrov, N.; Barišić, D.; Juračić, M. Calculated Sedimentation Rate in the Krka River Estuary Using Vertical Distribution of 137Cs. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Medit. 2007, 38, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Mikac, N.; Kwokal, Z.; May, K.; Branica, M. Mercury Distribution in the Krka River Estuary (Eastern Adriatic Coast). Mar. Chem. 1989, 28, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinčič, D.; Kwokal, Ž.; Stoeppler, M.; Branica, M. Trace Metals in Sediments from the Adriatic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 1989, 84, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwokal, Z.; Franiković-Bilinski, S.; Bilinski, H.; Branica, M. A Comparison of Anthropogenic Mercury Pollution in Kastela Bay (Croatia) with Pristine Estuaries in Ore (Sweden) and Krka (Croatia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, D.; Ujević, I.; Zvonarić, T.; Barić, A. Distribution of Selected Trace Metals in Coastal Surface Sediments from the Middle and South Adriatic. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2004, 13, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Cukrov, N.; Cindrić, A.-M.; Omanović, D.; Cukrov, N. Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk Assessment, and Source Identification of Metals in Sediments of the Krka River Estuary (Croatia). Sustainability 2024, 16, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreščanin, V.; Barišić, D.; Mikelić, L.; Lovrenčić, I.; Rubčić, M.; Rožmarić-Mačefat, M.; Lulić, S. Environmental Contamination Assessment of the Surroundings of the Ex-Šibenik’s Ferro-Manganese Smelter, Croatia. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2004, 39, 2493–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrov, N.; Doumandji, N.; Garnier, C.; Tucaković, I.; Dang, D.H.; Omanović, D.; Cukrov, N. Anthropogenic Mercury Contamination in Sediments of Krka River Estuary (Croatia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7628–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, E.; Simonucci, C.; Viollier, E.; Sarazin, G.; Prévot, F.; Jézéquel, D. Benthic Response to Shellfish Farming in Thau Lagoon: Pore Water Signature. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 72, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oursel, B.; Garnier, C.; Durrieu, G.; Mounier, S.; Omanović, D.; Lucas, Y. Dynamics and Fates of Trace Metals Chronically Input in a Mediterranean Coastal Zone Impacted by a Large Urban Area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 69, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A Single-Solution Method for the Determination of Soluble Phosphate in Sea Water. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1958, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A Modified Single Solution Method for the Determination of Phosphate in Natural Waters. Anal Chim Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storms, M.A.; Natland, J.H. (Eds.) Ocean Drilling Program, 132 Initial Reports; Ocean Drilling Program: College Station, TX, USA, 1991; Volume 132. [Google Scholar]
- Ullman, W.J.; Sandstrom, M.W. Dissolved Nutrient Fluxes from the Nearshore Sediments of Bowling Green Bay, Central Great Barrier Reef Lagoon (Australia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1987, 24, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan-Hui, L.; Gregory, S. Diffusion of Ions in Sea Water and in Deep-Sea Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1974, 38, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, F.; Hensen, C.; Noffke, A.; Rohde, A.; Liebetrau, V.; Wallmann, K. Early Diagenesis of Redox-Sensitive Trace Metals in the Peru Upwelling Area—Response to ENSO-Related Oxygen Fluctuations in the Water Column. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 7257–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed Sediment-Associated Trace Metals in an Urban Stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billon, G.; Ouddane, B.; Laureyns, J.; Boughriet, A. Chemistry of Metal Sulfides in Anoxic Sediments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Diaz, M.A.; Tessier, A.; Carignan, R. Geochemistry of Trace Metals Associated with Reduced Sulfur in Freshwater Sediments. Appl. Geochem. 1998, 13, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusius, J.; Calvert, S.; Pedersen, T.; Sage, D. EPSL Rhenium and Molybdenum Enrichments in Sediments as Indicators of Oxic, Suboxic and Sulfidic Conditions of Deposition. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 145, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helz, G.R.; Miller, C.V.; Charnock, J.M.; Mosselmans, J.F.W.; Pattrick, R.A.D.; Garner, C.D.; Vaughan, D.J. Mechanism of Molybdenum Removal from the Sea and Its Concentration in Black Shales: EXAFS Evidence. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 3631–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, B.E.; Helz, G.R. Molybdenum(VI) Speciation in Sulfidic Waters: Stability and Lability of Thiomolybdates. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morford, J.L.; Emerson, S. The Geochemistry of Redox Sensitive Trace Metals in Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 1735–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Anderson, R.F.; Van Geen, A.; Fleisher, M.Q. Remobilization of Authigenic Uranium in Marine Sediments by Bioturbation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdige, D.J. The Biogeochemistry of Manganese and Iron Reduction in Marine Sediments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1993, 35, 249–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingri, J.; Pekka, L.; Dauvalter, V.; Rodushkin, I.; Peinerud, E. Manganese Redox Cycling in Lake Imandra Manganese Redox Cycling in Lake Imandra: Impact on Nitrogen and the Trace Metal Sediment Record Manganese Redox Cycling in Lake Imandra. Biogeosci. Discuss 2011, 8, 273–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorny, J.; Billon, G.; Noiriel, C.; Dumoulin, D.; Lesven, L.; Madé, B. Chromium Behavior in Aquatic Environments: A Review. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellwig, O.; Schnetger, B.; Meyer, D.; Pollehne, F.; Häusler, K.; Arz, H.W. Impact of the Major Baltic Inflow in 2014 on Manganese Cycling in the Gotland Deep (Baltic Sea). Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitte, J.; Akob, D.M.; Kaufmann, C.; Finster, K.; Banerjee, D.; Burkhardt, E.M.; Kostka, J.E.; Scheinost, A.C.; Büchel, G.; Küsel, K. Microbial Links between Sulfate Reduction and Metal Retention in Uranium- and Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriil, A.M.; Angelidis, M.O. Metal Diagenesis in a Shallow Semi-Enclosed Marine System in the Aegean Sea, Greece. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 70, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Echeandia, J.; Prego, R.; Cobelo-García, A.; Millward, G.E. Porewater Geochemistry in a Galician Ria (NW Iberian Peninsula): Implications for Benthic Fluxes of Dissolved Trace Elements (Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, V, Zn). Mar. Chem. 2009, 117, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajith, A.; Rao, V.P.; Chakraborty, P. Distribution, Provenance and Early Diagenesis of Major and Trace Metals in Sediment Cores from the Mandovi Estuary, Western India. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokinen, S.A.; Jilbert, T.; Tiihonen-Filppula, R.; Koho, K. Terrestrial Organic Matter Input Drives Sedimentary Trace Metal Sequestration in a Human-Impacted Boreal Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, B.B.; Kasten, S. Sulfur Cycling and Methane Oxidation. In Marine Geochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 271–309. ISBN 3540321438. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, W.X. Trace Metal Behavior in Sediments of Jiulong River Estuary and Implication for Benthic Exchange Fluxes. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lesven, L.; Gillan, D.; Sabbe, K.; Billon, G.; De Galan, S.; Elskens, M.; Baeyens, W.; Leermakers, M. Geochemical Behavior of Trace Elements in Sub-Tidal Marine Sediments of the Belgian Coast. Mar. Chem. 2009, 117, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W.; Dillard, J.G. The Oxidation of Cobalt(II) Adsorbed on Manganese Dioxide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, J.; Audry, S. Control of Early Diagenesis Processes on Trace Metal (Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and U) and Metalloid (As, Sb) Behaviors in Mining- and Smelting-Impacted Lacustrine Environments of the Bolivian Altiplano. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Mikac, N.; Vdović, N.; Ivanić, M.; Furdek, M.; Škapin, S.D. Geochemistry of Recent Aragonite-Rich Sediments in Mediterranean Karstic Marine Lakes: Trace Elements as Pollution and Palaeoredox Proxies and Indicators of Authigenic Mineral Formation. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.H.; Tessier, E.; Lenoble, V.; Durrieu, G.; Omanović, D.; Mullot, J.U.; Pfeifer, H.R.; Mounier, S.; Garnier, C. Key Parameters Controlling Arsenic Dynamics in Coastal Sediments: An Analytical and Modeling Approach. Mar. Chem. 2014, 161, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audry, S.; Blanc, G.; Schäfer, J.; Chaillou, G.; Robert, S. Early Diagenesis of Trace Metals (Cd, Cu, Co, Ni, U, Mo, and V) in the Freshwater Reaches of a Macrotidal Estuary. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2264–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M. Early Diagenesis in Differing Depositional Environments: The Response of Transition Metals in Pore Water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Lenstra, W.; Jong, D.; Meysman, F.J.R.; Sapart, C.J.; Van Der Veen, C.; Röckmann, T.; Gonzalez, S.; Slomp, C.P. Rapid Sediment Accumulation Results in High Methane Effluxes from Coastal Sediments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, A.; Richard, L.-F.; Lucotte, M.; Guignard, C. The Differential Geochemical Behavior of Arsenic and Phosphorus in the Water Column and Sediments of the Saguenay Fjord Estuary, Canada. Aquat. Geochem. 2000, 6, 293–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourino-Cabana, B.; Lesven, L.; Billon, G.; Denis, L.; Ouddane, B.; Boughriet, A. Benthic Exchange of Sedimentary Metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni and Zn) in the Dele River (Northern France). Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Mikutta, C.; Kretzschmar, R. Bisulfide Reaction with Natural Organic Matter Enhances Arsenite Sorption: Insights from X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11788–11797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaillou, G.; Anschutz, P.; Lavaux, G.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G. The Distribution of Mo, U, and Cd in Relation to Major Redox Species in Muddy Sediments of the Bay of Biscay. Mar. Chem. 2002, 80, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.H.; Evans, R.D.; Wang, W.; Omanović, D.; El Houssainy, A.; Lenoble, V.; Mullot, J.U.; Mounier, S.; Garnier, C. Uranium Isotope Geochemistry in Modern Coastal Sediments: Insights from Toulon Bay, France. Chem. Geol. 2018, 481, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.F.; Lehuray, A.P.; Fleisher, M.Q.; Murray, J.W. Uranium Deposition in Saanich Inlet Sediments, Vancouver Island. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranich, E.; Croce, S.; Crosera, M.; Pavoni, E.; Faganeli, J.; Adami, G.; Covelli, S. Mobility of Metal(Loid)s at the Sediment-Water Interface in Two Tourist Port Areas of the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26887–26902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrov, N. Metal Dynamics in the Sediments of the Krka River Estuary. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sakellari, A.; Plavšić, M.; Karavoltsos, S.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M. Assessment of Copper, Cadmium and Zinc Remobilization in Mediterranean Marine Coastal Sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 91, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Duarte, I.; Flegal, A.R. Porewater Gradients and Diffusive Benthic Fluxes of Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Cd in San Francisco Bay. Croat. Chem. Acta 1997, 70, 389–417. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.R.; Millward, G.E.; Nimmo, M.; Fones, G. Fluxes of Cu, Pb and Mn to the North-Eastern Irish Sea: The Importance of Sedimental and Atmospheric Inputs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 36, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| EF | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | K2 | K3 | K4 | K5 | |||||||||||
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | |
| U | 1.00 | 2.99 | 1.86 | 0.649 | 1.10 | 0.904 | 0.934 | 1.21 | 1.06 | 1.46 | 5.84 | 2.62 | 6.81 | 19.2 | 10.6 |
| Fe | 0.942 | 1.42 | 1.07 | 0.819 | 0.975 | 0.861 | 1.26 | 1.38 | 1.33 | 1.31 | 2.73 | 1.77 | 1.59 | 2.15 | 1.82 |
| Mn | 0.679 | 1.18 | 0.947 | 0.742 | 1.31 | 0.977 | 0.758 | 0.806 | 0.790 | 37.2 | 106 | 72.6 | 3.87 | 9.44 | 5.13 |
| Co | 0.876 | 1.48 | 1.09 | 0.702 | 1.06 | 0.829 | 1.10 | 1.31 | 1.21 | 2.47 | 5.23 | 3.87 | 2.03 | 3.85 | 2.68 |
| Cu | 0.972 | 2.81 | 1.74 | 0.564 | 1.05 | 0.777 | 1.64 | 1.95 | 1.81 | 6.42 | 16.3 | 10.9 | 12.1 | 17.3 | 14.0 |
| Zn | 0.941 | 3.44 | 1.67 | 0.878 | 1.47 | 1.12 | 1.40 | 1.58 | 1.48 | 6.79 | 17.5 | 12.6 | 27.7 | 57.6 | 44.0 |
| Pb | 0.953 | 45.5 | 7.92 | 0.737 | 1.49 | 1.04 | 1.13 | 1.17 | 1.15 | 9.35 | 46.2 | 24.2 | 13.2 | 18.4 | 15.4 |
| As | 0.969 | 1.60 | 1.20 | 0.765 | 1.36 | 1.09 | 1.44 | 1.64 | 1.57 | 2.90 | 8.01 | 4.61 | 5.09 | 7.84 | 6.26 |
| Mo | 0.930 | 5.26 | 2.47 | 0.461 | 0.883 | 0.625 | 0.913 | 1.26 | 1.05 | 3.44 | 16.1 | 7.30 | 2.43 | 3.67 | 3.03 |
| Element | Flux (nmol cm−2 y−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | K2 | K3 | K4 | K5 | |
| Fe | −129 | −912 | −747 | −274 | −160 |
| Mn | −1206 | −3741 | −613 | −3178 | −2996 |
| Co | −0.080 | −1.37 | 0.054 | −0.310 | −0.709 |
| Cu | −0.112 | 0.295 | −7.86 | 0.051 | −0.061 |
| Zn | 38.9 | −16.1 | 1.27 | 0.219 | −7.95 |
| Pb | −0.008 | −0.136 | −0.025 | −0.238 | −0.186 |
| Mo | 0.619 | −8.16 | −3.50 | −13.2 | −3.20 |
| U | 0.188 | −0.058 | 0.215 | 0.024 | 0.015 |
| As | −4.24 | −7.17 | −5.49 | −2.10 | −8.71 |
| Benthic Flux | Riverine Flux | |
|---|---|---|
| (kg y−1) | (kg y−1) | |
| Fe | 5220 | 2210 |
| Mn | 27,100 | 7080 |
| Co | 6.00 | 26.9 |
| Cu | 20.5 | 344 |
| Pb | 5.16 | 14.4 |
| Mo | 111 | 905 |
| As | 87.3 | 254 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cukrov, N.; Cukrov, N.; Omanović, D. Early Diagenetic Processes in the Sediments of the Krka River Estuary. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030466
Cukrov N, Cukrov N, Omanović D. Early Diagenetic Processes in the Sediments of the Krka River Estuary. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(3):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030466
Chicago/Turabian StyleCukrov, Nuša, Neven Cukrov, and Dario Omanović. 2024. "Early Diagenetic Processes in the Sediments of the Krka River Estuary" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 3: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030466
APA StyleCukrov, N., Cukrov, N., & Omanović, D. (2024). Early Diagenetic Processes in the Sediments of the Krka River Estuary. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(3), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030466








