The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Chemosymbiotic Lucinid Bivalve Pillucina pisidium (Dunker, 1860) Occurring in Seagrass Zostera marina Bed in a Lagoon in Jeju Island, Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubilier, N.; Bergin, C.; Lott, C. Symbiotic Diversity in Marine Animals: The Art of Harnessing Chemosynthesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, C.M.; Gardiner, S.L.; Jones, M.L.; Jannasch, H.W.; Waterbury, J.B. Prokaryotic Cells in the Hydrothermal Vent Tube Worm Riftia pachyptila Jones: Possible Chemoautotrophic Symbionts. Science 1981, 213, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duperron, S.; Gaudron, S.M.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Cunha, M.R.; Decker, C.; Olu, K. An Overview of Chemosynthetic Symbioses in Bivalves from the North Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3241–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeo, D.M.; Morrison, C.L.; Sei, M.; Salamone, V.; Demopoulos, A.W.J.; Quattrini, A.M. Genetic Diversity and Connectivity of Chemosynthetic Cold Seep Mussels from the U.S. Atlantic Margin. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2022, 22, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Fields, C.J.; Hui, J.H.L.; Zhang, W.; et al. Adaptation to Deep-Sea Chemosynthetic Environments as Revealed by Mussel Genomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Glover, E. Biology, Evolution and Generic Review of the Chemosymbiotic Bivalve Family Lucinidae; Ray Society: London, UK, 2021; pp. 11–12, 43–52. ISBN 978-0-903874-53-3. [Google Scholar]
- Åström, E.K.L.; Oliver, P.G.; Carroll, M.L. A New Genus and Two New Species of Thyasiridae Associated with Methane Seeps off Svalbard, Arctic Ocean. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, J.J.; Fisher, C.R.; Favuzzi, J.A.; Arp, A.J.; Oros, D.R. The Role of a Zinc-Based, Serum-Borne Sulphide-Binding Component in the Uptake and Transport of Dissolved Sulphide by the Chemoautotrophic Symbiont-Containing Clam Calyptogena elongata. J. Exp. Biol. 1993, 179, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duperron, S.; Fiala-Médioni, A.; Caprais, J.-C.; Olu, K.; Sibuet, M. Evidence for Chemoautotrophic Symbiosis in a Mediterranean Cold Seep Clam (Bivalvia: Lucinidae): Comparative Sequence Analysis of Bacterial 16S rRNA, APS Reductase and RubisCO Genes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, E.A.; Taylor, J.D.; Williams, S.T. Mangrove-Associated Lucinid Bivalves of the Central Indo-West Pacific: Review of the “Austriella” Group with a New Genus and Species (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Lucinidae). Raffles Bull. Zool. Suppl. 2008, 18, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.J.; Davis, B.G.; Gill, D.E.; Walton, J.; Nachman, E.; Engel, A.S.; Anderson, L.C.; Campbell, B.J. Taxonomic and Functional Heterogeneity of the Gill Microbiome in a Symbiotic Coastal Mangrove Lucinid Species. ISME J. 2019, 13, 902–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heide, T.; Govers, L.L.; de Fouw, J.; Olff, H.; van der Geest, M.; van Katwijk, M.M.; Piersma, T.; van de Koppel, J.; Silliman, B.R.; Smolders, A.J.P.; et al. A Three-Stage Symbiosis Forms the Foundation of Seagrass Ecosystems. Science 2012, 336, 1432–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, E.A.; Taylor, J.D. Lucinidae of the Philippines: Highest Known Diversity and Ubiquity of Chemosymbiotic Bivalves from Intertidal to Bathyal Depths (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Trop. Deep-Sea Benthos 2016, 29, 65–234. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.D.; Glover, E.A. Lucinidae (Bivalvia)–the Most Diverse Group of Chemosymbiotic Molluscs. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 148, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkiel, L.; Mouëza, M. Gill Ultrastructure and Symbiotic Bacteria in Codakia Orbicularis (Bivalvia, Lucinidae). Zoomorphology 1995, 115, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkiel, L.; Gros, O.; Mouëza, M. Gill Structure in Lucina Pectinata (Bivalvia: Lucinidae) with Reference to Hemoglobin in Bivalves with Symbiotic Sulphur-Oxidizing Bacteria. Mar. Biol. 1996, 125, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herry, A.; Diouris, M.; Le Pennec, M. Chemoautotrophic Symbionts and Translocation of Fixed Carbon from Bacteria to Host Tissues in the Littoral Bivalve Loripes lucinalis (Lucinidae). Mar. Biol. 1989, 101, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.D.; Glover, E.A. Functional Anatomy, Chemosymbiosis and Evolution of the Lucinidae. In The Evolutionary Biology of the Bivalvia; Harper, E.M., Taylor, J.D., Crame, J.A., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2000; Volume 177, ISBN 978-1-86239-076-8. [Google Scholar]
- König, S.; Gros, O.; Heiden, S.E.; Hinzke, T.; Thuermer, A.; Poehlein, A.; Meyer, S.; Vatin, M.; Tocny, J.; Ponnudurai, R. Nitrogen Fixation in a Chemoautotrophic Lucinid Symbiosis. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.M.; Kemper, A.; Gruber-Vodicka, H.; Cardini, U.; Van Der Geest, M.; Kleiner, M.; Bulgheresi, S.; Mußmann, M.; Herbold, C.; Seah, B.K. Chemosynthetic Symbionts of Marine Invertebrate Animals Are Capable of Nitrogen Fixation. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, E.; Taylor, J. Systematic Revision of Australian and Indo-Pacific Lucinidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia): Pillucina, Wallucina and Descriptions of Two New Genera and Four New Species. Rec. Aust. Mus. 2001, 53, 263–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, I.A.; Yushin, V.V. Procaryotic Symbionts in Gill Cells of the Bivalve Mollusc Pillucina Pisidium. Biol. Morya 1991, 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.D.; Glover, E.A.; Williams, S.T. Diversification of Chemosymbiotic Bivalves: Origins and Relationships of Deeper Water Lucinidae. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 111, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uede, T.; Yamauchi, M.; Takahashi, Y. Distribution and Habitat Environment of Pillucina pisidium (Bivalvia, Licinidae) in Zostera Japonica Beds in the Intertidal Zone at Uchinoura, Tanabe Bay, Wakayama, Japan. Jpn. J. Benthol. 2013, 68, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.K.; Lee, J.S.; Koh, D.B.; Je, J.G. Mollusks in Korea; Min Molluscan Research Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2004; p. 566. [Google Scholar]
- Zhukova, N.V.; Kharlamenko, V.I.; Svetashev, V.I.; Rodionov, I.A. Fatty Acids as Markers of Bacterial Symbionts of Marine Bivalve Molluscs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 162, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlamenko, V.I.; Kiyashko, S.I.; Imbs, A.B.; Vyshkvartzev, D.I. Identification of Food Sources of Invertebrates from the Seagrass Zostera Marina Community Using Carbon and Sulfur Stable Isotope Ratio and Fatty Acid Analyses. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 220, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Noseworthy, R.G.; Park, S.; Hong, H.-K.; Lee, B.-G.; Choi, K.-S. Report on the Molluscan Fauna in Tongbatarl Lagoon on the East Coast of Jeju, Korea. Korean J. Malacol. 2014, 30, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutaenko, K.A.; Je, J.-G.; Shin, S.-H. Bivalve Mollusks in Yeongil Bay, Korea. 2. Faunal Analysis. Korean J. Malacol. 2006, 22, 63–86. [Google Scholar]
- Noseworthy, R.G.; Lim, N.-R.; Choi, K.-S. A Catalogue of the Mollusks of Jeju Island, South Korea. Korean J. Malacol. 2007, 23, 65–104. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.D.; Glover, E.A.; Smith, L.; Dyal, P.; Williams, S.T. Molecular Phylogeny and Classification of the Chemosymbiotic Bivalve Family Lucinidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 163, 15–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.R.; Nunnari, J. Mitochondrial Form and Function. Nature 2014, 505, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L. Insect Mitochondrial Genomics: Implications for Evolution and Phylogeny. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Choi, H.; Kim, H.; Kang, J.; Jeong, H.G.; Eyun, S.; Kang, J.-H. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome, Ecological Distribution, and Morphological Features of the Marine Gastropod Mollusc Lophocochlias parvissimus (Gastropoda, Tornidae). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yang, P.; Jiang, F.; Chapuis, M.; Shali, Y.; Sword, G.A.; Kang, L. Mitochondrial Genomes Reveal the Global Phylogeography and Dispersal Routes of the Migratory Locust. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 4344–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osvatic, J.T.; Wilkins, L.G.E.; Leibrecht, L.; Leray, M.; Zauner, S.; Polzin, J.; Camacho, Y.; Gros, O.; van Gils, J.A.; Eisen, J.A.; et al. Global Biogeography of Chemosynthetic Symbionts Reveals Both Localized and Globally Distributed Symbiont Groups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104378118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, S. MitoZ: A Toolkit for Animal Mitochondrial Genome Assembly, Annotation and Visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. metaSPAdes: A New Versatile Metagenomic Assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Jeon, D.; Park, Y.; Woo, H.; Eyun, S. Dietary Exposure of the Water Flea Daphnia Galeata to Microcystin-LR. Anim. Cells Syst. 2024, 28, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.-S.; Jeong, D.M.; Doh, H.; Kang, H.A.; Jung, H.; Eyun, S. A Practical Comparison of the Next-Generation Sequencing Platform and Assemblers Using Yeast Genome. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202201744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Ventura, T.; Chung, J.S.; Kim, W.-J.; Nam, B.-H.; Kong, H.J.; Kim, Y.-O.; Jeon, M.-S.; Eyun, S. Twelve Quick Steps for Genome Assembly and Annotation in the Classroom. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de Novo Metazoan Mitochondrial Genome Annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, İ.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An Information Aesthetic for Comparative Genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New Methods for Selecting Partitioned Models of Evolution for Molecular and Morphological Phylogenetic Analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum Likelihood-Based Phylogenetic Analyses with Thousands of Taxa and Mixed Models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A Fast, Scalable and User-Friendly Tool for Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4453–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference under Mixed Models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunker, W.B.R.H. Mollusca Japonica Descripta et Tabulis Tribus Iconum; Schweizerbart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1861; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.A.; Yonge, M. On the Basic Form and Adaptations to Habitat in the Lucinacea (Eulamellibranchia). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 241, 421–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distel, D.L.; Felbeck, H. Endosymbiosis in the Lucinid Clams Lucinoma aequizonata, Lucinoma annulata and Lucina floridana: A Reexamination of the Functional Morphology of the Gills as Bacteria-Bearing Organs. Mar. Biol. 1987, 96, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.A.; Fernandez, C.; Pergent, G. The Ecological Importance of an Invertebrate Chemoautotrophic Symbiosis to Phanerogam Seagrass Beds. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 71, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Kim, J.G.; Kwon, O.-N.; Park, J.J.C.; Lee, K.-W.; Choi, Y.-U. On the Species Identification of Korean Geoduck Clam (Panopea Sp. 1) Based on the Morphological and Molecular Evidence. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, G.D.; Audino, J.A.; Grula, C.; Porath-Krause, A.; Pairett, A.N.; Alejandrino, A.; Lacey, L.; Masters, F.; Duncan, P.F.; Strong, E.E.; et al. Molecular Phylogeny of the Pectinoidea (Bivalvia) Indicates Propeamussiidae to Be a Non-Monophyletic Family with One Clade Sister to the Scallops (Pectinidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 137, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

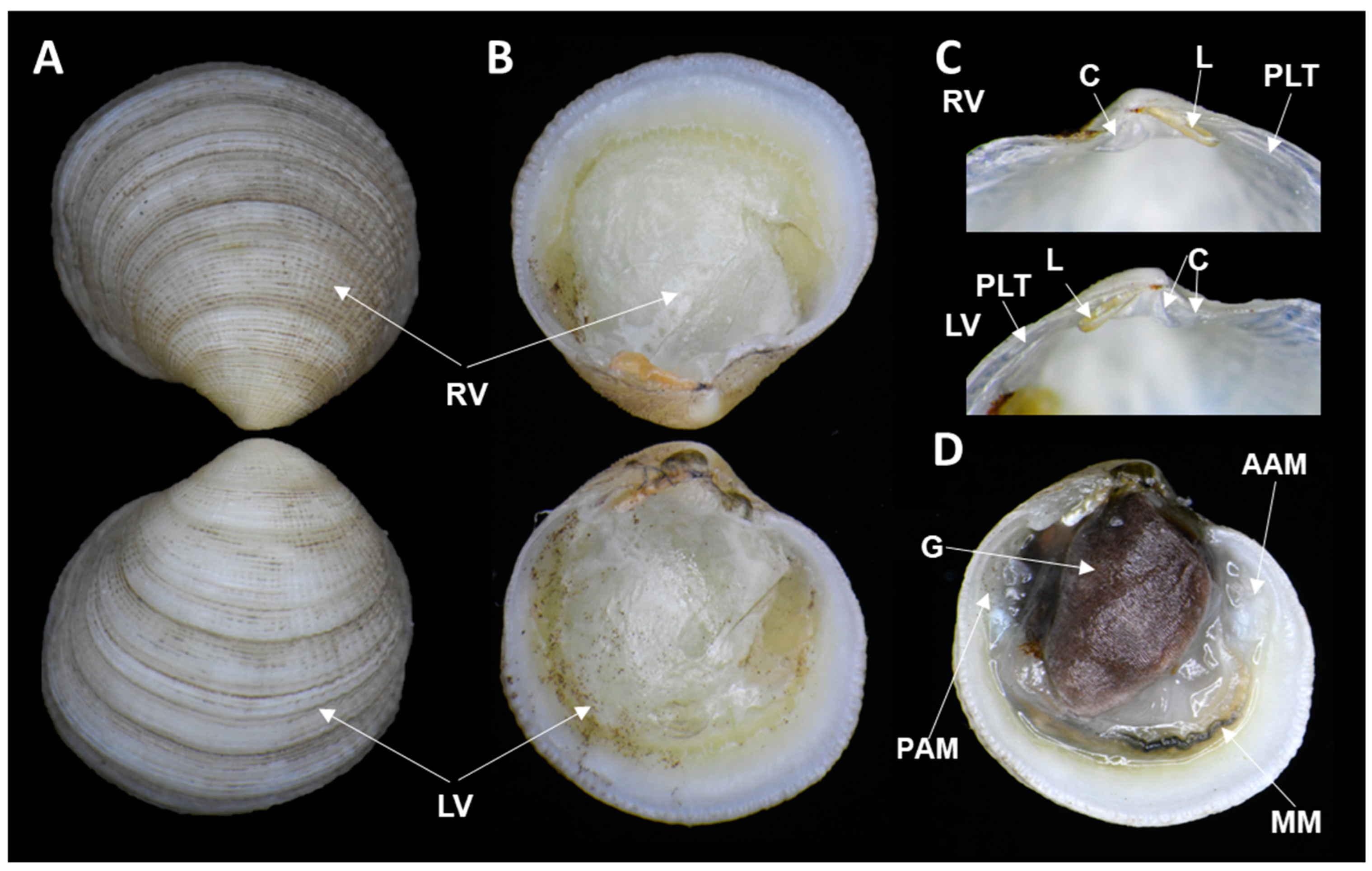

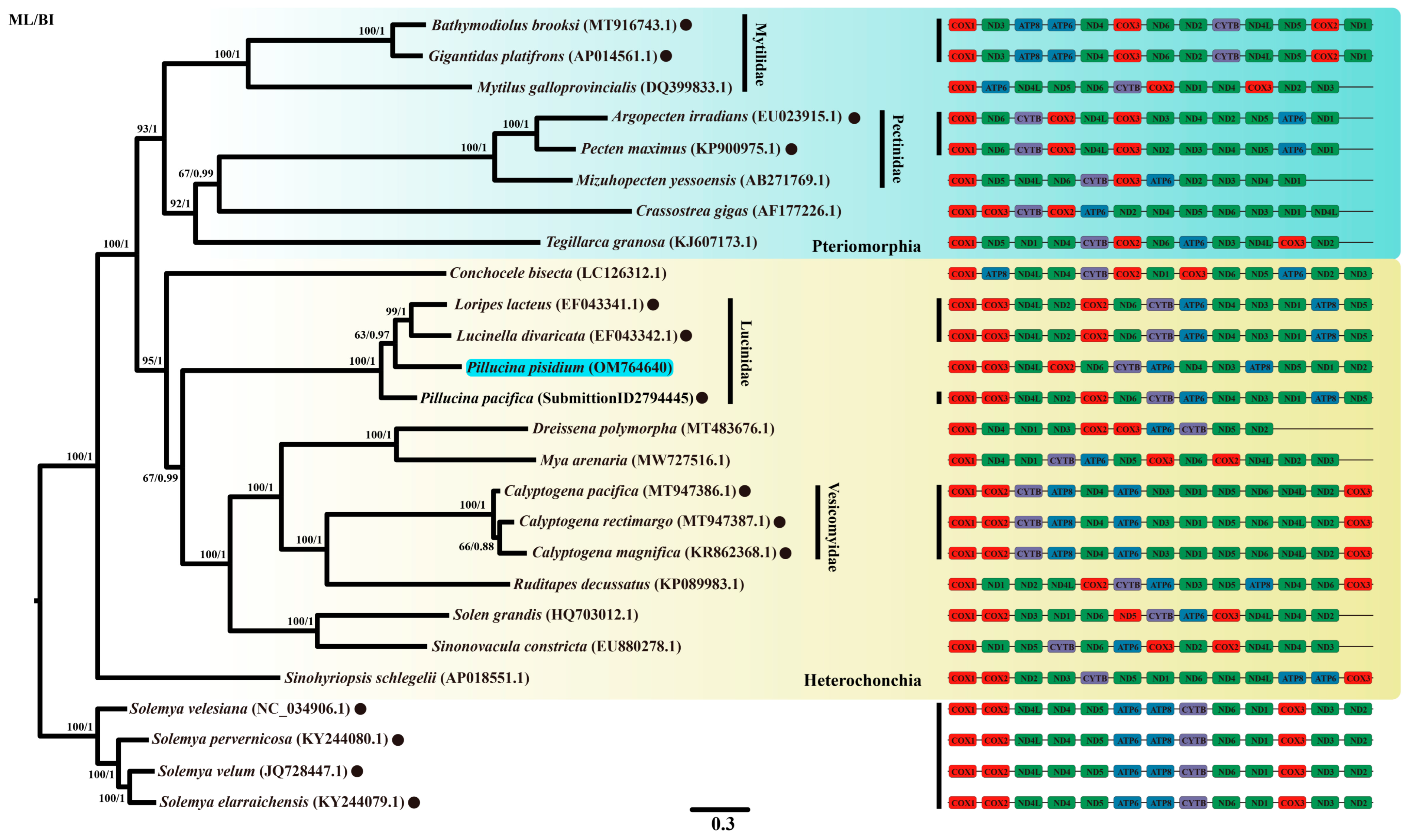
| Subclass | Infraclass | Order | Family | Species Name | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autobranchia | Heteroconchia | Adapedonta | Pharidae | Sinohyriopsis schlegelii | AP018551.1 |
| Sinonovacula constricta | EU880278.1 | ||||
| Solenidae | Solen grandis | HQ703012.1 | |||
| Lucinida | Lucinidae | Loripes lacteus | EF043341.1 | ||
| Lucinella divaricata | EF043342.1 | ||||
| Pillucina pacifica | BK067723 | ||||
| Pillucina pisidium | NC_071184.1 | ||||
| Thyasiridae | Conchocele bisecta | LC126312.1 | |||
| Myida | Dreissenidae | Dreissena polymorpha | MT483676.1 | ||
| Myidae | Mya arenaria | MW727516.1 | |||
| Venerida | Veneridae | Ruditapes decussatus | KP089983.1 | ||
| Vesicomyidae | Calyptogena magnifica | KR862368.1 | |||
| Calyptogena pacifica | MT947386.1 | ||||
| Calyptogena rectimargo | MT947387.1 | ||||
| Pteriomorphia | Arcida | Arcidae | Tegillarca granosa | KJ607173.1 | |
| Mytilida | Mytilidae | Bathymodiolus brooksi | MT916743.1 | ||
| Gigantidas platifrons | AP014561.1 | ||||
| Mytilus galloprovincialis | DQ399833.1 | ||||
| Ostreida | Ostreidae | Crassostrea gigas | AF177226.1 | ||
| Pectinida | Pectinidae | Argopecten irradians | EU023915.1 | ||
| Mizuhopecten yessoensis | AB271769.1 | ||||
| Pecten maximus | KP900975.1 | ||||
| Protobranchia | - | Solemyida | Solemyidae | Solemya elarraichensis | KY244079.1 |
| Solemya pervernicosa | KY244080.1 | ||||
| Solemya velesiana | NC_034906.1 | ||||
| Solemya velum | JQ728447.1 |
| Gene | Position | Length (bp) | Initiation Codon | Stop Codon | Intergenic Nucleotide (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COX1) | 1–1536 | 1536 | ATG | TAA | 2112 |
| tRNA-Phe (trnF) | 2973–3039 | 67 | 1436 | ||
| tRNA-Lys (trnK) | 3109–3173 | 65 | 69 | ||
| tRNA-His (trnH) | 3185–3244 | 60 | 14 | ||
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit III (COX3) | 3257–4054 | 798 | ATG | TAG | 12 |
| tRNA-Met (trnM) | 4105–4173 | 69 | 50 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4L (ND4L) | 4239–4517 | 279 | ATG | TAA | 65 |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II (COX2) | 5243–6118 | 876 | ATA | TAA | 725 |
| tRNA-Ser (trnS2) | 6145–6209 | 65 | 26 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6 (NAD6) | 6210–6704 | 495 | ATT | TAG | 0 |
| Cytochrome b (COB) | 6709–7851 | 1143 | ATG | TAA | 4 |
| ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 (ATP6) | 7870–8574 | 705 | ATT | TAA | 18 |
| tRNA-Leu (trnL1) | 8594–8660 | 67 | 19 | ||
| tRNA-Glu (trnE) | 8916–8980 | 65 | 255 | ||
| 12S ribosomal RNA (rrnS) | 8994–9808 | 815 | 13 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 (NAD4) | 9854–11,194 | 1341 | ATT | TAA | 45 |
| tRNA-Asn (trnN) | 11,230–11,301 | 72 | 35 | ||
| tRNA-Asp (trnD) | 11,343–11,411 | 69 | 41 | ||
| tRNA-Pro (trnP) | 11,426–11,493 | 68 | 14 | ||
| tRNA-Trp (trnW) | 11,509–11,582 | 74 | 15 | ||
| tRNA-Gly (trnG) | 11,589–11,656 | 68 | 6 | ||
| tRNA-Arg (trnR) | 11,667–11,735 | 69 | 10 | ||
| tRNA-Thr (trnT) | 11,738–11,802 | 65 | 202 | ||
| tRNA-Val (trnV) | 11,819–11,885 | 67 | 16 | ||
| tRNA-Leu (trnL2) | 11,903–11,971 | 69 | 17 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 (NAD3) | 11,972–12,319 | 348 | ATT | TAG | 0 |
| tRNA-Ile (trnI) | 12,369–12,435 | 67 | 49 | ||
| 16S ribosomal RNA | 12,435–13,596 | 1162 | −1 | ||
| tRNA-Tyr (trnY) | 13,597–13,676 | 80 | 0 | ||
| RNA-Ala (trnA) | 13,820–13,883 | 64 | 143 | ||
| tRNA-Gln (trnQ) | 13,887–13,952 | 66 | 3 | ||
| ATP synthase F0 subunit 8 (ATP8) | 13,975–14,088 | 114 | ATT | TAA | 22 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 (NAD5) | 14,161–15,891 | 1731 | ATA | TAA | 72 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (NAD1) | 16,389–17,342 | 954 | ATG | TAA | 497 |
| tRNA-Cys (trnC) | 17,402–17,464 | 63 | 59 | ||
| tRNA-Ser (trnS1) | 17,830–17,897 | 68 | 366 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 (NAD 2) | 17,949–18,947 | 999 | ATA | TAA | 51 |
| Gene | Position | Length (bp) | Initiation Codon | Stop Codon | Intergenic Nucleotide (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COX1) | 1–1557 | 1557 | TTG | TAA | 4 |
| tRNA-Thr (trnT) | 1610–1679 | 70 | 52 | ||
| tRNA-Pro (trnP) | 1681–1747 | 67 | 1 | ||
| tRNA-Phe (trnF) | 1770–1836 | 67 | 22 | ||
| tRNA-Lys (trnK) | 1851–1914 | 64 | 14 | ||
| tRNA-His (trnH) | 1921–1985 | 65 | 6 | ||
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit III (COX3) | 1996–2793 | 798 | ATG | TAA | 10 |
| tRNA-Met (trnM) | 2814–2883 | 70 | 20 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4L (ND4L) | 2947–3234 | 288 | ATG | TAA | 63 |
| tRNA-Ser (trnS1) | 3248–3316 | 69 | 13 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 (NAD2) | 3369–4370 | 1002 | ATT | TAG | 52 |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II (COX2) | 4377–5312 | 936 | TTG | TAG | 6 |
| tRNA-Val (trnV) | 5331–5395 | 65 | 18 | ||
| tRNA-Ser (trnS2) | 5410–5472 | 63 | 14 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6 (NAD6) | 5480–5972 | 493 | ATT | TAA | 7 |
| Cytochrome b (COB) | 5973–7106 | 1134 | ATG | TAG | 0 |
| ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 (ATP6) | 7136–7781 | 646 | ATA | TAA | 29 |
| tRNA-Glu (trnE) | 8780–8845 | 66 | 998 | ||
| tRNA-Trp (trnW) | 8889–8954 | 66 | 43 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 (NAD4) | 8973–10,331 | 1359 | ATT | TAA | 18 |
| tRNA-Tyr (trnY) | 10,521–10,584 | 64 | 189 | ||
| tRNA-Leu (trnL1) | 10,595–10,661 | 67 | 10 | ||
| 12S ribosomal RNA (rrnS) | 10,682–11,511 | 830 | 20 | ||
| tRNA-Arg (trnR) | 11,578–11,648 | 71 | 66 | ||
| tRNA-Leu (trnL2) | 11,766–11,833 | 68 | 117 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 (NAD3) | 11,833–12,180 | 348 | ATA | TAG | -1 |
| tRNA-Ile (trnI) | 12,191–12,258 | 68 | 10 | ||
| 16S ribosomal RNA (rrnL) | 12,289–13,455 | 1167 | 30 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (NAD1) | 13,483–14,442 | 960 | ATA | TAA | 27 |
| tRNA-Asn (trnN) | 14,449–14,513 | 65 | 6 | ||
| tRNA-Gly (trnG) | 14,517–14,583 | 67 | 3 | ||
| tRNA-Gln (trnQ) | 14,616–14,694 | 79 | 32 | ||
| ATP synthase F0 subunit 8 (ATP8) | 14,702–14,815 | 114 | ATT | TAG | 7 |
| tRNA-Ala (trnA) | 14,862–14,928 | 67 | 46 | ||
| tRNA-Cys (trnC) | 14,961–15,023 | 63 | 32 | ||
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 (NAD5) | 15,025–16,740 | 1716 | TTG | TAG | 1 |
| tRNA-Asp (trnD) | 16,748–16,814 | 67 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.-S.; Song, C.-u.; Choi, H.; Yang, S.H.; Kwon, K.K.; Eyun, S.-i.; Choi, K.-S. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Chemosymbiotic Lucinid Bivalve Pillucina pisidium (Dunker, 1860) Occurring in Seagrass Zostera marina Bed in a Lagoon in Jeju Island, Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050847
Shin J-S, Song C-u, Choi H, Yang SH, Kwon KK, Eyun S-i, Choi K-S. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Chemosymbiotic Lucinid Bivalve Pillucina pisidium (Dunker, 1860) Occurring in Seagrass Zostera marina Bed in a Lagoon in Jeju Island, Korea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(5):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050847
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jong-Seop, Chi-une Song, Hyeongwoo Choi, Sung Hyun Yang, Kae Kyoung Kwon, Seong-il Eyun, and Kwang-Sik Choi. 2024. "The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Chemosymbiotic Lucinid Bivalve Pillucina pisidium (Dunker, 1860) Occurring in Seagrass Zostera marina Bed in a Lagoon in Jeju Island, Korea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 5: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050847
APA StyleShin, J.-S., Song, C.-u., Choi, H., Yang, S. H., Kwon, K. K., Eyun, S.-i., & Choi, K.-S. (2024). The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Chemosymbiotic Lucinid Bivalve Pillucina pisidium (Dunker, 1860) Occurring in Seagrass Zostera marina Bed in a Lagoon in Jeju Island, Korea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(5), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050847








