Digging in Deep: Size and Site-Specific Variation in Burrow Morphology and Behaviour of the Mud Shrimp, Trypaea australiensis Dana, 1852
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
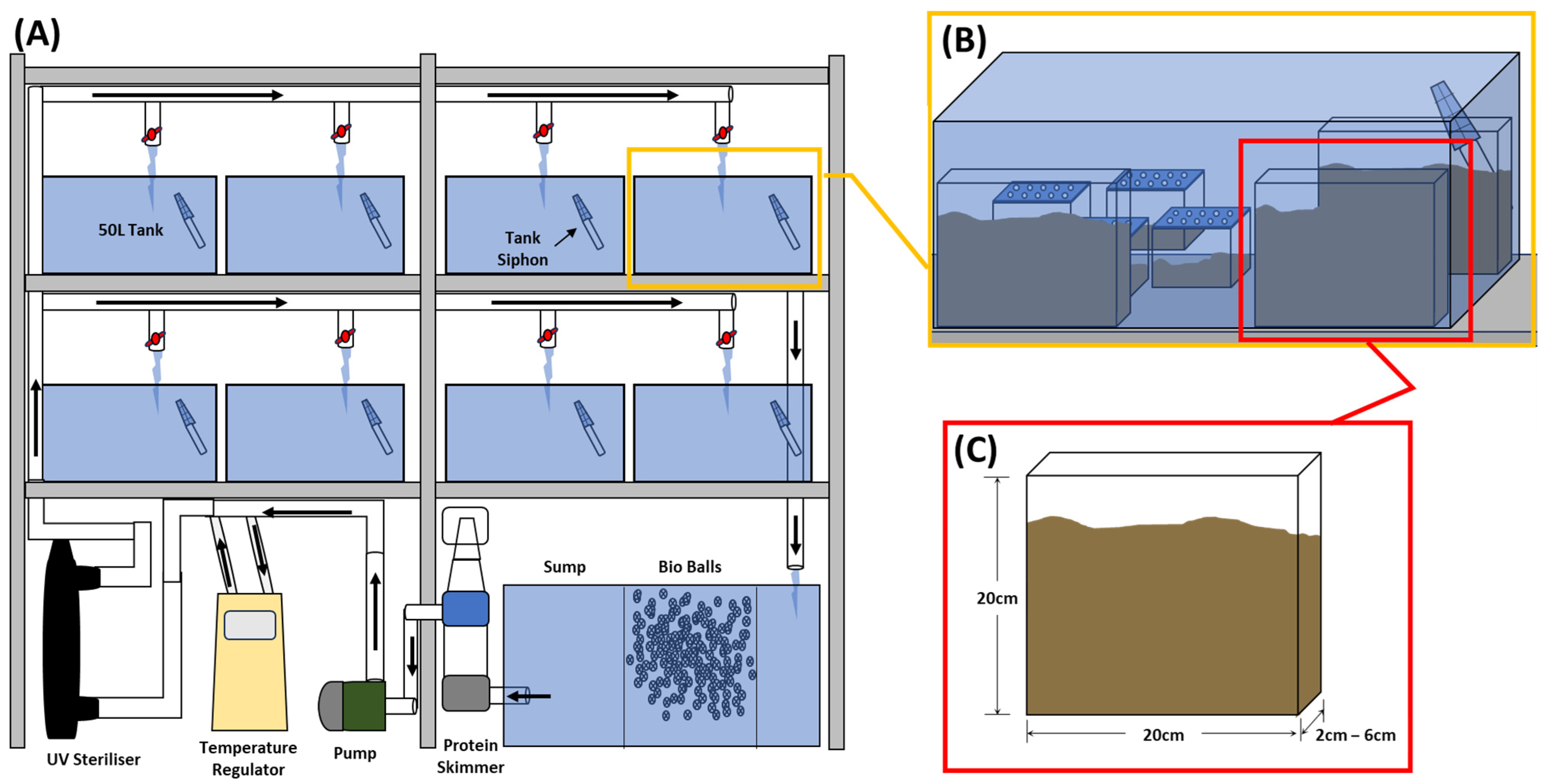
2.2. Burrow Morphology
2.3. Quantifying Burrowing Behaviour
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
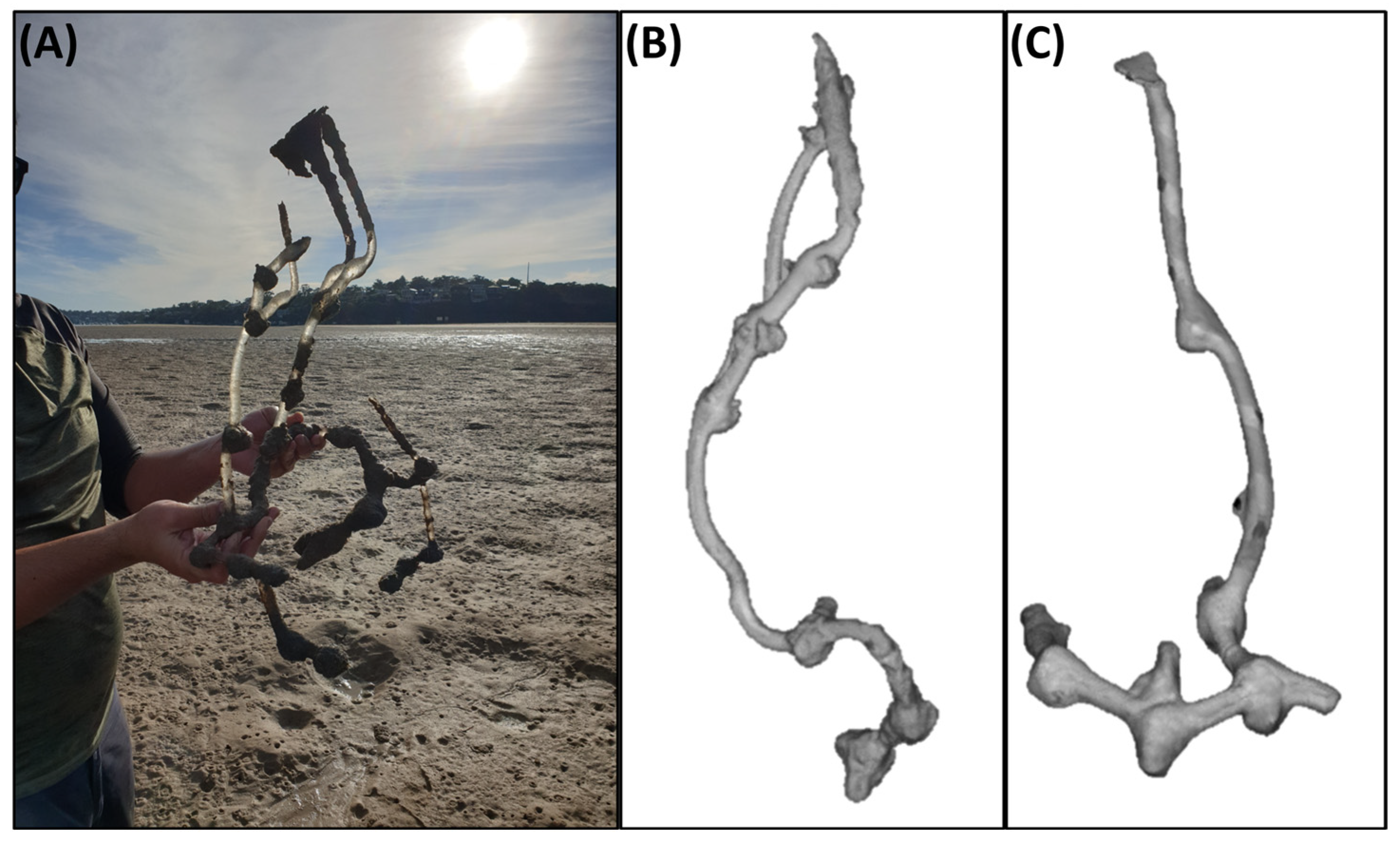
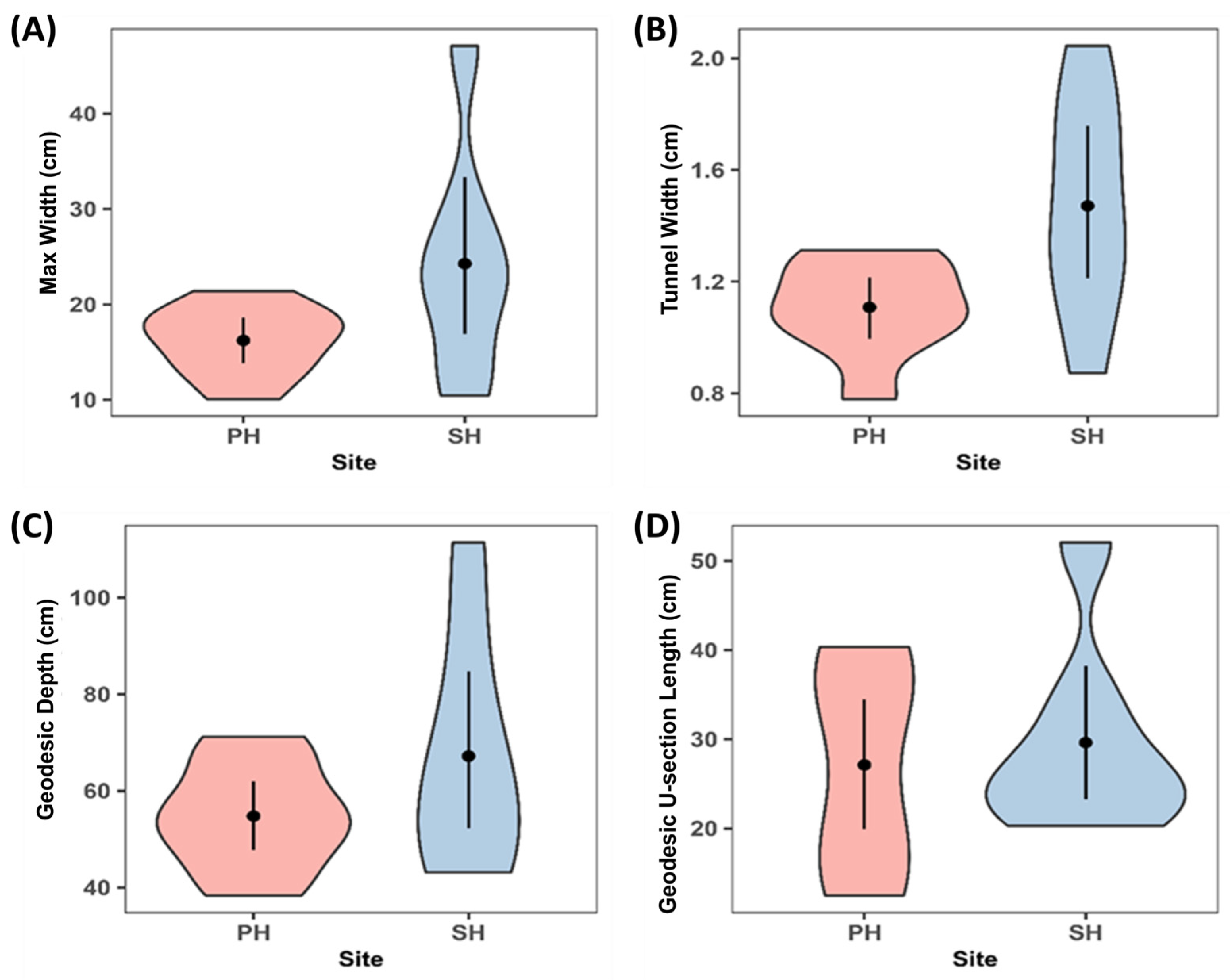
3.1. Burrow Cast Morphology
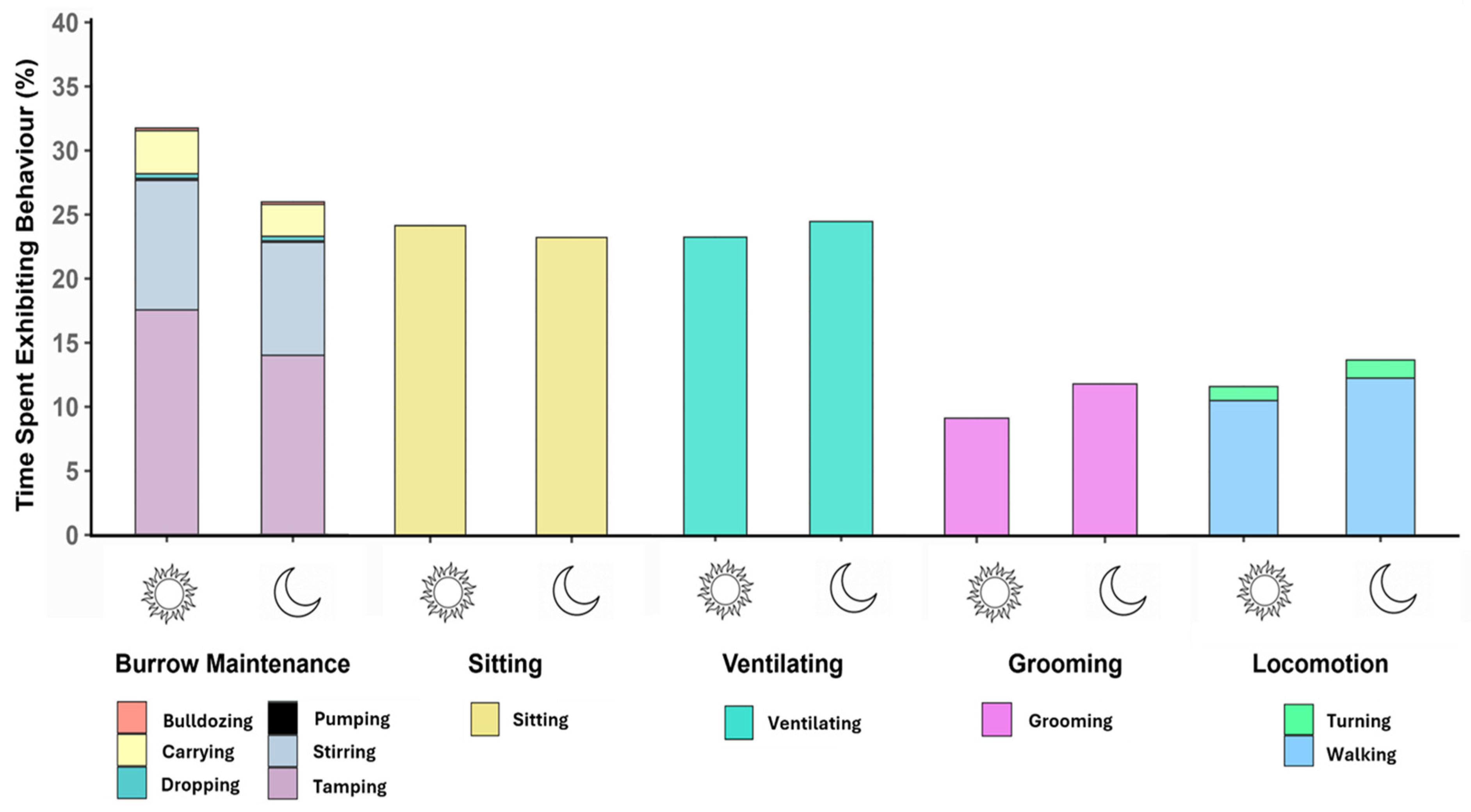
3.2. Burrowing Behaviour
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GLM | Generalised Linear Model. |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance. |
| PH | Port Hacking. |
| SH | Shoalhaven Heads. |
| SIMPER | Similarity Percentages Analysis. |
Appendix A
| Cuvette Tank Dimensions | Resident Shrimp Size |
|---|---|
| 20 cm length × 20 cm height × 2 cm depth | Less than 3 cm |
| 20 cm length × 20 cm height × 4 cm depth | Between 3 cm and 4 cm |
| 20 cm length × 20 cm height × 5 cm depth | Between 4 cm and 5 cm |
| 20 cm length × 20 cm height × 6 cm depth | Greater than 5 cm |
References
- Coelho, V.; Cooper, R.; de Almeida Rodrigues, S. Burrow morphology and behavior of the mud shrimp Upogebia omissa (Decapoda: Thalassinidea: Upogebiidae). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 200, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzer, J.P.; DeLucia, M.B.; Greene, E.; Shumway, C.; Topolski, M.F.; Thomas-Blate, J. The importance of benthic habitats for coastal fisheries. BioScience 2016, 66, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, Y.; Ogura, M.; Takahashi, C.; Kaneko, M.; Imura, A.; Shiino, Y. Burrow morphology of ghost crab Ocypode stimpsoni on Ikarashi beach, Niigata, Japan. Plankton Benthos Res. 2023, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattrijsse, A.; Hampel, H. European intertidal marshes: A review of their habitat functioning and value for aquatic organisms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 324, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwis, R.H.J.; Gamperl, A.K. Adaptations and plastic phenotypic responses of marine animals to the environmental challenges of the high intertidal zone. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; Volume 60, pp. 625–679. [Google Scholar]
- Rife, G.S. Ecosystem services provided by benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in marine coastal zones. In Ecosystem Services & Global Ecology; Hufnagel, L., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Posey, M.H. Predation on a burrowing shrimp: Distribution and community consequences. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1986, 103, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrak, G.; Bird, F.L. Comparative effects of the large bioturbators, Trypaea australiensis and Heloecius cordiformis, on intertidal sediments of Western Port, Victoria, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, S. Effects of macrobenthic burrows on infaunal communities in tropical tidal flats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 134, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, F.L.; Boon, P.I.; Nichols, P.D. Physicochemical and microbial properties of burrows of the deposit-feeding Thalassinidean ghost shrimp Biffarius arenosus (Decapoda: Callianassidae). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.B.; Reiswig, H.M.; Marcotte, B.M. Ecology, functional morphology, behaviour, and feeding in coral- and sponge-boring species of Upogebia (Crustacea: Decapoda: Thalassinidea). Can. J. Zool. 1988, 66, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, K.L.; Long, M.; Bird, F.L. Comparative feeding ecology of two spatially coexisting species of ghost shrimp, Biffarius arenosus and Trypaea Australiensis (Decapoda: Callianassidae). Ophelia 2001, 55, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworschak, P.C.; Koller, H.; Abed-Navandi, D. Burrow structure, burrowing and feeding behaviour of Corallianassa longiventris and Pestarella tyrrhena (Crustacea: Thalassinidea: Callianassidae). Mar. Biol. 2006, 148, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, L.; Atkinson, R. Functional morphology of burrows and trophic modes of three thalassinidean shrimp species, and a new approach to the classification of thalassinidean burrow morphology. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 128, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, F.L.; Poore, G.C.B. Functional burrow morphology of Biffarius arenosus (Decapoda: Callianassidae) from southern Australia. Mar. Biol. 1999, 134, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candisani, L.C.; Sumida, P.Y.G.; Pires-Vanin, A.M.S. Burrow morphology and mating behaviour of the thalassinidean shrimp Upogebia noronhensis. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2001, 81, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, S.N.; Bird, F.L. Temporal changes in burrow structure of the thalassinidean ghost shrimps Trypaea australiensis and Biffarius arenosus. Nat. Hist. 2008, 42, 2041–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K. Burrow structure of the mud shrimp Upogebia major (Decapoda: Thalassinidea: Upogebiidae). J. Crust. Biol. 2002, 22, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffis, R.; Suchanek, T. A model of burrow architecture and trophic modes in thalassinidean shrimp (Decapoda: Thalassinidea). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 79, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, Y. Studies on the interspecific relationship between gobiid fish and snapping shrimp ll. Life history and pair formation of snapping shrimp alpheus bellulus. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1984, 29, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, K.; Itani, G.; Uchino, T. Burrow morphology and associated animals of the mud shrimp Upogebia yokoyai (Crustacea: Thalassinidea: Upogebiidae). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2010, 90, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, D.; Branch, G. Bioengineering effects of burrowing thalassinidean shrimps on marine soft-bottom ecosystems. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 1st ed.; Gordon, J., Gibson, R.N., Atkinson, R.J.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; Volume 49, pp. 137–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M.; Itani, G. Commensalism of a Bivalve, Peregrinamor Ohshimai, With a Thalassinidean Burrowing Shrimp, Upogebia Major. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1995, 75, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Itani, G. Peregrinamor gastrochaenans (Bivalvia: Mollusca), a New Species Symbiotic with the Thalassinidean Shrimp Upogebia carinicauda (Decapoda: Crustacea). Species Divers. 2000, 5, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, R.; Fukumori, H.; Kano, Y.; Kato, M. Evolutionary gain of red blood cells in a commensal bivalve (Galeommatoidea) as an adaptation to a hypoxic shrimp burrow. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 125, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentich-Scott, P.; Griffiths, C.; Landschoff, J.; Li, R.; Li, J. Bivalves of superfamily Galeommatoidea (Mollusca, Bivalvia) from western South Africa, with observations on commensal relationships and habitats. ZooKeys 2024, 1207, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailstone, T.S.; Stephenson, W. The Biology of Callianassa (Trypaea) Australiensis (Dana 1852) (Crustacea, Thalassinidea); University of Queensland Press: Brisbane, Australia, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Rowden, A.A.; Jones, M.B. A contribution to the biology of the burrowing mud shrimp, Callianassa subterranea (Decapoda: Thalassinidea). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1994, 74, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkenbusch, K.; Rowden, A.A. Latitudinal variation in the reproductive biology of the burrowing ghost shrimp Callianassa filholi (Decapoda: Thalassinidea). Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotherham, D.; West, R. Spatial and temporal patterns of abundance and recruitment of ghost shrimp Trypaea australiensis across hierarchical scales in south-eastern Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 341, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotherham, D.; West, R.J. Patterns in reproductive dynamics of burrowing ghost shrimp Trypaea australiensis from small to intermediate scales. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botter-Carvalho, M.L.; Santos, P.J.P.; Carvalho, P.V.V.C. Population dynamics of Callichirus major (Say, 1818) (Crustacea, Thalassinidea) on a beach in northeastern Brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamhuis, E.J.; Reede-Dekker, T.; van Etten, Y.; de Wiljes, J.J.; Videler, J.J. Behaviour and time allocation of the burrowing shrimp Callianassa subterranea (Decapoda, Thalassinidea). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 204, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotherham, D. Fisheries Biology, Ecology and Recreational Harvesting of Ghost Shrimp (Trypaea australiensis) in South-Eastern Australia. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, R.L.; Wong, M.Y.L. Beneath the surface: Correlates of solitary, paired, and group living in a cryptic burrowing ghost shrimp Trypaea australiensis (Dana, 1852) (Decapoda: Axiidea: Calianassidae). J. Crustac. Biol. 2023, 43, ruad035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, D. Ecosystem engineering by thalassinidean crustaceans: Response variability, contextual dependencies and perspectives on future research. Diversity 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.S. New South Wales estuaries: Their origin and evolution. In Australia, Coastal Geomorphology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, P.S.; Williams, R.J.; Jones, A.R.; Yassini, I.; Gibbs, P.J.; Coates, B. Structure and function of south-east Australian estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 53, 351–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, R Package, version 2.6-4 ed; CRAN (Comprehensive R Archive Network): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Griffis, R.B.; Chavez, F.L. Effects of sediment type on burrows of Callianassa californiensis Dana and C. gigas Dana. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1988, 117, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingras, M.; Dashtgard, S.; MacEachern, J.; Pemberton, S. Biology of shallow marine ichnology: A modern perspective. Aquat. Biol. 2008, 2, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V.; Gallo, C.; Marin, M.G. Effects of temperature on cellular and biochemical parameters in the crab Carcinus aestuarii (Crustacea, Decapoda). Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiva, F.P.; Urbina, M.A.; Cumillaf, J.P.; Gebauer, P.; Paschke, K. Physiological responses of the ghost shrimp Neotrypaea uncinata (Milne Edwards 1837) (Decapoda: Thalassinidea) to oxygen availability and recovery after severe environmental hypoxia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 189, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, F.P.; Niklitschek, E.J.; Paschke, K.; Gebauer, P.; Urbina, M.A. Tide-related biological rhythm in the oxygen consumption rate of ghost shrimp, Neotrypaea uncinata (Milne Edwards 1837). J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 13, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Stanzel, C.; Finelli, C. The effects of temperature and salinity on ventilation behavior of two species of ghost shrimp (Thalassinidea) from the northern Gulf of Mexico: A laboratory study. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 312, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.A.; Welsh, D.T.; Dunn, R.J.K.; Teasdale, P.R. Influence of Trypaea australiensis population density on benthic metabolism and nitrogen dynamics in sandy estuarine sediment: A mesocosm simulation. J. Sea Res. 2009, 61, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernáez, P.; Villegas-Castro, E.; João, M.C.A.; Duarte, R.C.; Rivadeneira, M.M. Inferring the mating system in the burrowing shrimp Lepidophthalmus bocourti (Decapoda, Axiidea, Callichiridae) from the social structure and sexual dimorphism. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2021, 75, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultgren, K.; Duffy, E.; Rubenstein, D.R. Sociality in Shrimps. In Comparative Social Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 224–252. [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, J.E. Eusociality in a coral-reef shrimp. Nature 1996, 381, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, E. The ecology and evolution of eusociality in sponge dwelling shrimp. In Genes, Behaviour, and Evolution in Social Insects; University of Hokkaido Press: Sapporo, Japan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, E.; Morrison, C.; Macdonald, K. Colony defense and behavioral differentiation in the eusocial shrimp Synalpheus regalis. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2002, 51, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, C.; Brand, A. Oxygen consumption and oxygen-independence in marine crustaceans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1980, 2, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.N.; Atkinson, R.J.A.; Gordon, J.D.M. (Eds.) Aspects of the physiology, biology and ecology of thalassinidean shrimps in relation to their burrow environment. In Oceanography and Marine Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 183–220. [Google Scholar]
- Astall, C.M.; Taylor, A.C.; Atkinson, R.J.A. Behavioural and physiological implications of a burrow-dwelling lifestyle for two species of upogebiid mud-shrimp (Crustacea: Thalassinidea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, N.; Webster, I.; Ford, P. Non-destructive measurement of the time evolution of burrowing shrimp mound topography. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

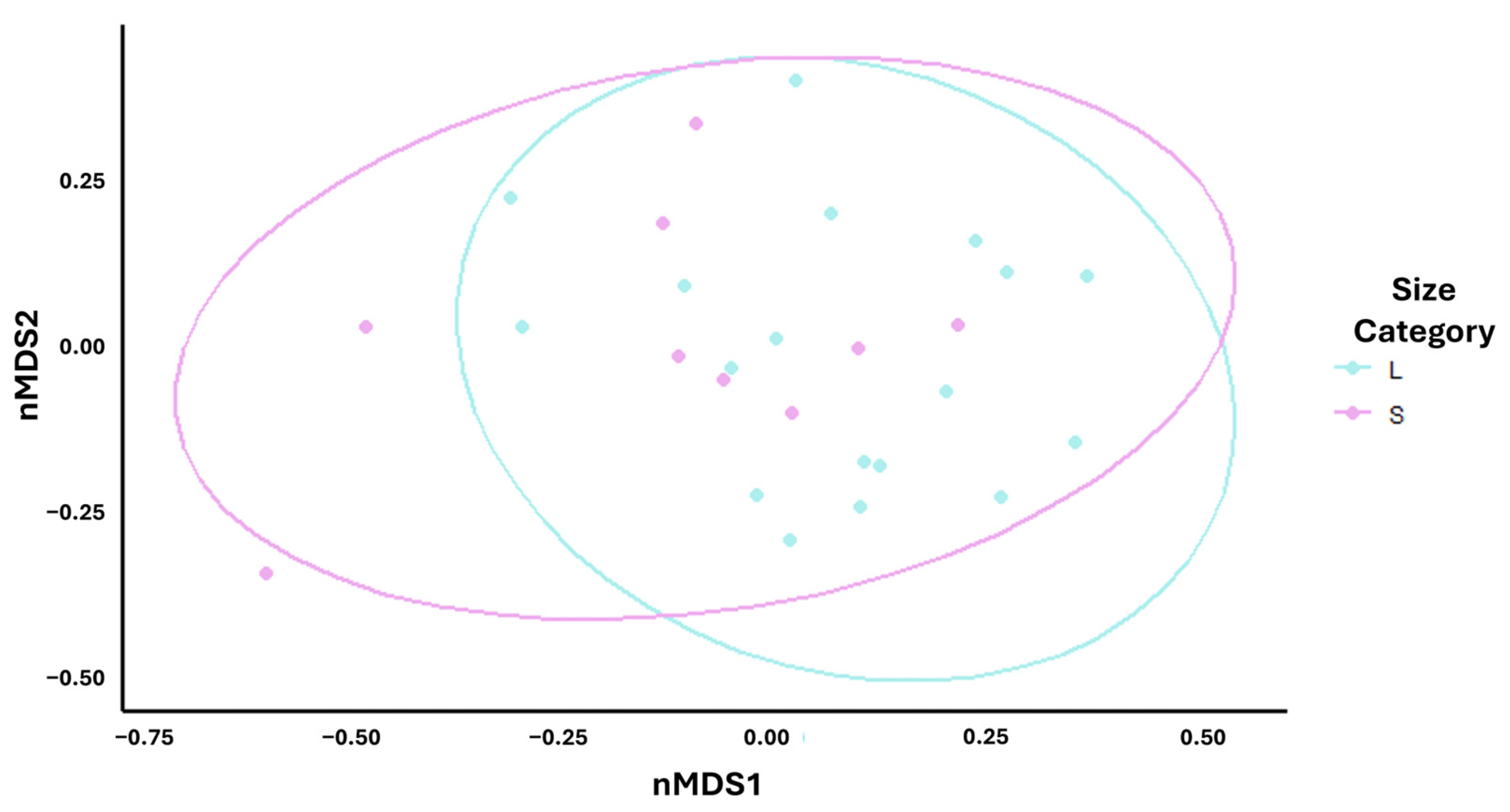
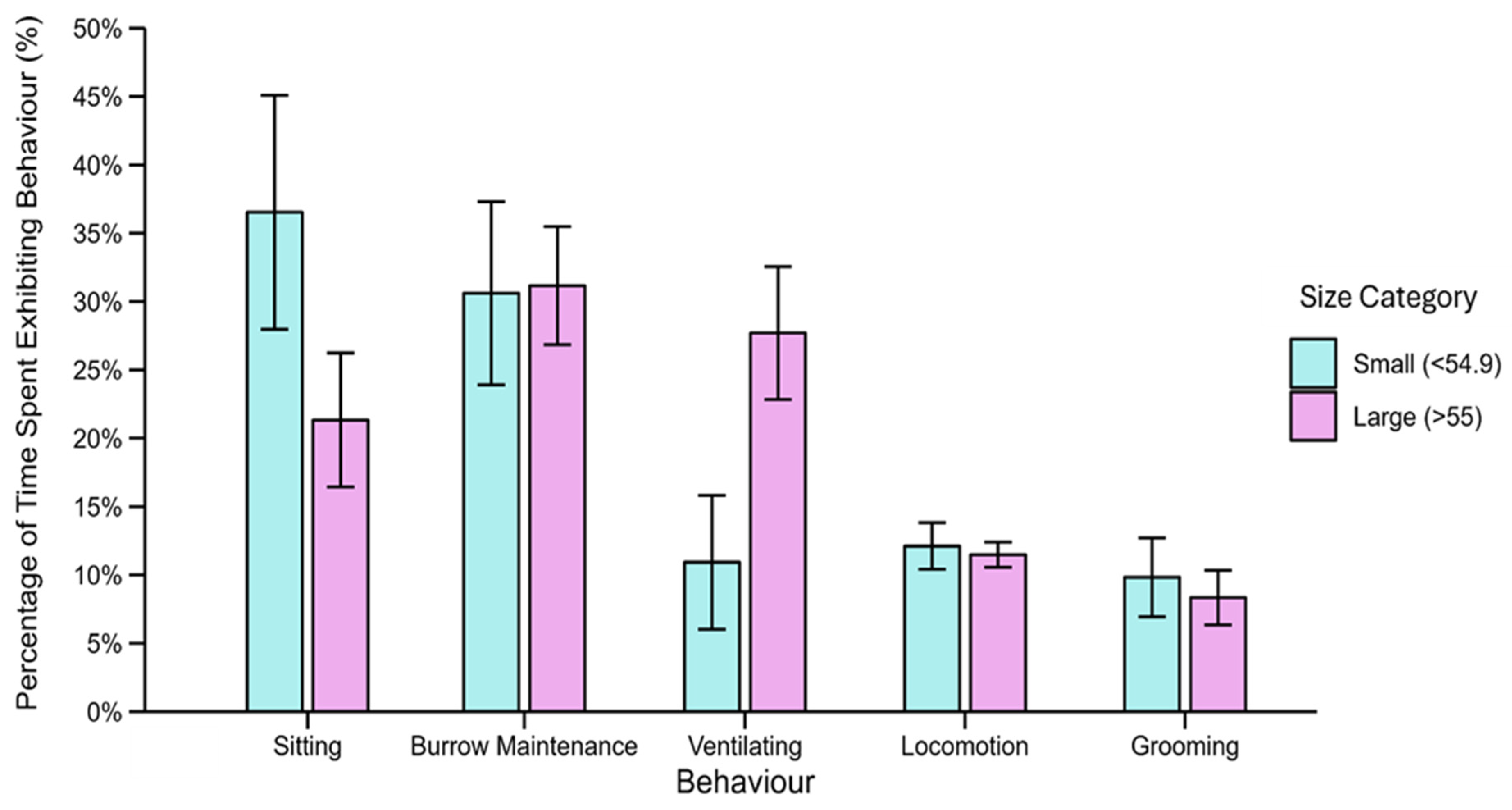
| Average | SD | Ratio | Ava | Avb | Cumsum | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ventilating | 0.073 | 0.051 | 1.44 | 2.85 | 4.87 | 0.29 | 0.05 |
| Sitting | 0.064 | 0.049 | 1.29 | 5.82 | 4.28 | 0.55 | 0.17 |
| Burrow Maintenance | 0.055 | 0.044 | 1.26 | 5.16 | 5.43 | 0.77 | 0.21 |
| Grooming | 0.040 | 0.028 | 1.41 | 3.04 | 2.68 | 0.93 | 0.67 |
| Locomotion | 0.018 | 0.015 | 0.23 | 3.54 | 3.49 | 1.00 | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirby, R.L.; Wong, M.Y.L. Digging in Deep: Size and Site-Specific Variation in Burrow Morphology and Behaviour of the Mud Shrimp, Trypaea australiensis Dana, 1852. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030432
Kirby RL, Wong MYL. Digging in Deep: Size and Site-Specific Variation in Burrow Morphology and Behaviour of the Mud Shrimp, Trypaea australiensis Dana, 1852. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030432
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirby, Renae L., and Marian Y. L. Wong. 2025. "Digging in Deep: Size and Site-Specific Variation in Burrow Morphology and Behaviour of the Mud Shrimp, Trypaea australiensis Dana, 1852" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 3: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030432
APA StyleKirby, R. L., & Wong, M. Y. L. (2025). Digging in Deep: Size and Site-Specific Variation in Burrow Morphology and Behaviour of the Mud Shrimp, Trypaea australiensis Dana, 1852. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(3), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030432






