Abstract
Persistent localization is a critical requirement for autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) engaged in long-term missions. Conventional dead-reckoning (DR) methods for estimating the position and orientation of AUVs often suffer from drift, necessitating additional information to correct accumulating errors. In this paper, we propose a visual artificial landmarks-based simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) system for AUVs. This system utilizes two types of underwater artificial landmarks that are observed using forward and downward-looking cameras. The information obtained from these detected landmarks, along with incremental DR estimates, is integrated within a framework based on the extended Kalman filter (EKF) SLAM approach, allowing for the recursive estimation of both the robot and the landmark states. We implemented the proposed visual SLAM method using our yShark II AUV and conducted experiments in an engineering basin to validate its effectiveness. A ceiling vision-based reference pose acquisition system was installed, facilitating a comparison between the pose estimation results obtained from DR and those derived from the SLAM method.
1. Introduction
Precise localization of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) in an underwater environment is challenging but essential for the successful accomplishment of various tasks assigned to AUVs. Typical sensor modalities used in AUV localization include the absolute heading reference system (AHRS), the Doppler velocity log (DVL), and depth sensors [1,2]. With these sensors, the AUV can estimate its pose state through the dead reckoning (DR); where vehicle kinematic or dynamic models are typically exploited [3]. However, localization with DR suffers from accumulating errors because it integrates derivative measurements that contain random and systematic noise [4]. In particular, heading estimation by integrating gyroscope measurements is inherently prone to drift errors, which become more severe in nonlinear motions, such as rotations with varying angular velocities. This accumulation of drift can lead to significant deviations between the estimated trajectory and the actual path. To ensure the successful long-term operation of AUVs, it is essential to mitigate this error.
To improve positioning accuracy, additional aids must be integrated with the vehicles. A common approach involves using exterior sensors such as ultrashort baseline (USBL) [5,6] or long baseline (LBL) [7,8] systems. However, the USBL method requires support from the mother ship for the USBL transceiver, and there is an acoustic delay in the position information received. In contrast, the LBL method requires the placement of acoustic beacons on the seafloor, which can limit coverage to fixed areas. Therefore, these approaches are not adequate for the long-term operations of AUVs in deep-sea environments.
AUVs are typically equipped with one or more optical cameras to obtain visual information about underwater environments. By integrating an active lighting system, visual observations can also be employed to determine the pose information of the AUV. In our previous studies [9,10,11], we validated that observing artificial landmarks can improve the accuracy of the AUV localization. However, the assumption that the location of the landmarks should be provided prior to the vehicle deployment limits the generality of the method. The AUV should be capable of creating a map from scratch and identifying the locations of various landmarks, while simultaneously using this information to correct its position. This process is known as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), a well-defined topic extensively studied in robotics [12,13,14] and successfully applied in AUV navigation [15,16,17]. The extended Kalman filter (EKF), unscented Kalman filter (UKF) [18], particle filter [19], and graph optimization [20] are commonly used methods for addressing SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) problems. Among these, the EKF has the advantage of being computationally less demanding, especially when dealing with a finite number of landmarks, as is the case in our study. In this paper, we present an EKF-based SLAM method that incorporates visual measurements from three types of artificial landmarks captured by forward- and downward-looking cameras. We designed our SLAM framework to incorporate the observations from each landmark independently, along with a kinematics-based DR estimate. The highlights of this paper are as follows.
- We proposed a visual navigation system that uses artificial landmarks detected by forward- and downward-looking cameras.
- Visual information was integrated into an EKF-based SLAM framework.
- Experiments conducted with our AUV in an engineering basin demonstrated improved pose estimation compared to dead reckoning methods.
- Ground truth pose data were obtained using a ceiling-mounted vision-based reference system.
This paper expands on the conference paper previously presented [21].
2. Design of Landmarks
We designed three types of artificial landmarks, as shown in Figure 1. The first type is cylindrical landmarks. This one is designed for viewpoint invariant observations, as shown in Figure 2a. When the robot and landmarks are in a similar depth, basic geometric shapes (circle, triangle, etc.) can be seen in any direction from the forward-looking camera. Supervised learning with the random forest was used in the detection of the landmarks. Underwater images of these landmarks under various lighting conditions were used for the training of the ensemble of trees [9]. When the landmarks are detected in the current forward-looking image, conventional template matching with adaptive thresholding is performed to classify the shape of the landmarks, which outputs identification (ID) of the landmark.
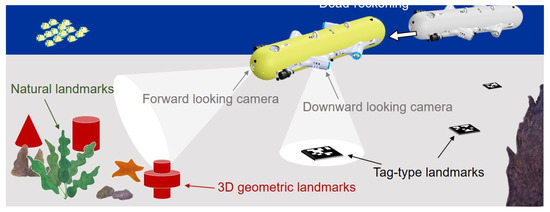
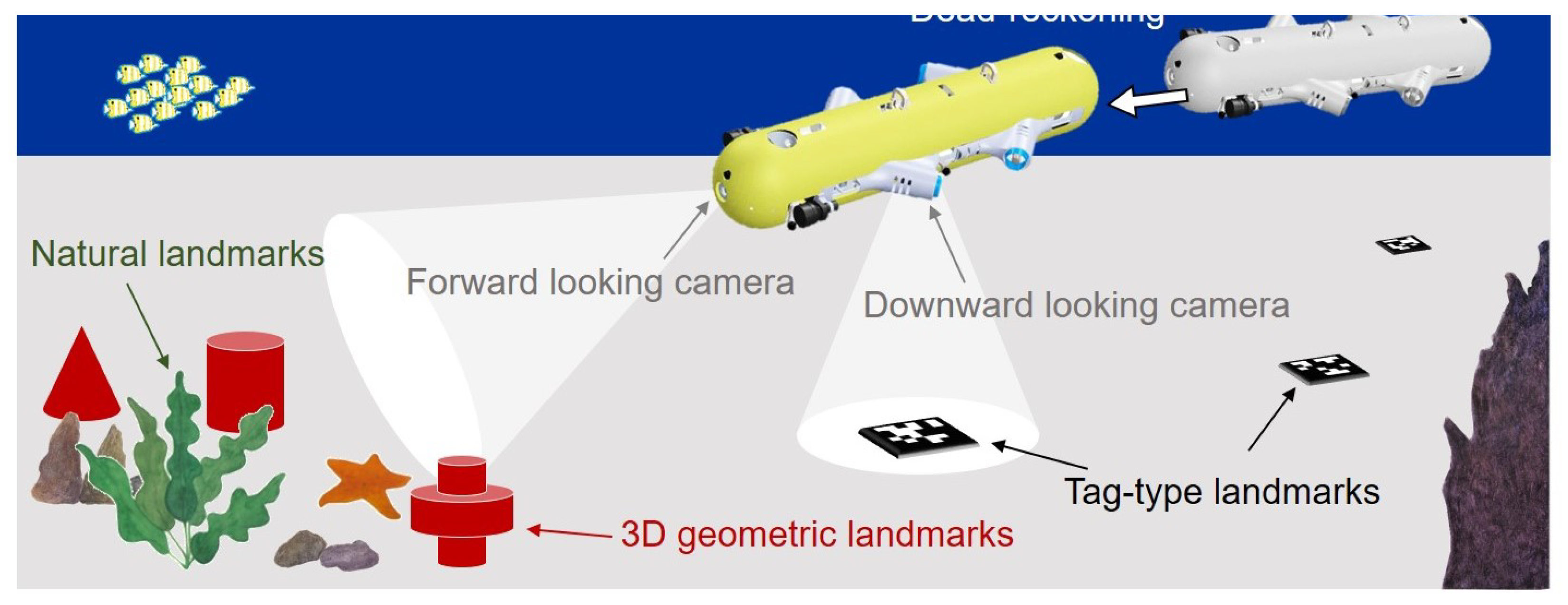
Figure 1.
Underwater navigation scenario.
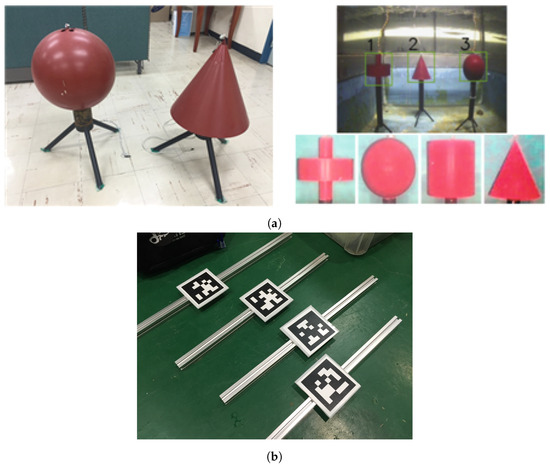
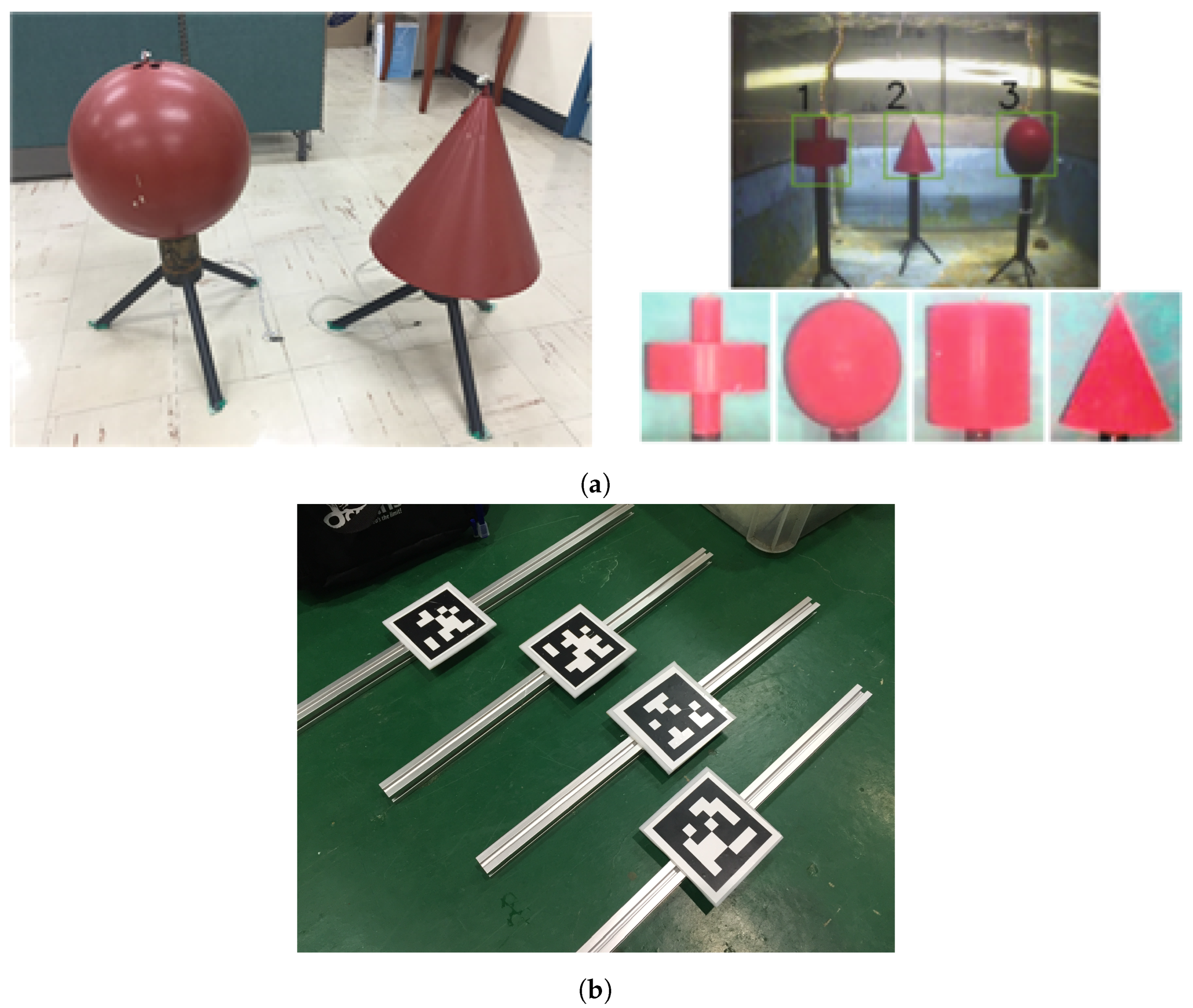
Figure 2.
Artificial landmarks for AUV navigation. (a) Cylindrical landmarks for forward sensing. (b) Fiducial markers for downward sensing.
The second one is tag-type landmarks, as shown in Figure 2b. This one is detected by the down-looking camera. A predefined 2D bar code is printed on these landmarks, allowing a unique ID for each tag. In this paper, AprilTag [22] was used. The advantage of this landmark is that we can obtain a 6 degree-of-freedom (DOF) pose of the camera from a single image. For underwater usage, the tags were coated with water-proof film.
As a third type of landmark, we installed steel panels cluttered with various objects such as rope, plastic pipe, small buoy, etc. In order to detect visual features of these objects, SURF [23] was used in this study. Any other feature extraction algorithms [24,25,26,27,28,29] can be used without the loss of generality.
3. SLAM Framework
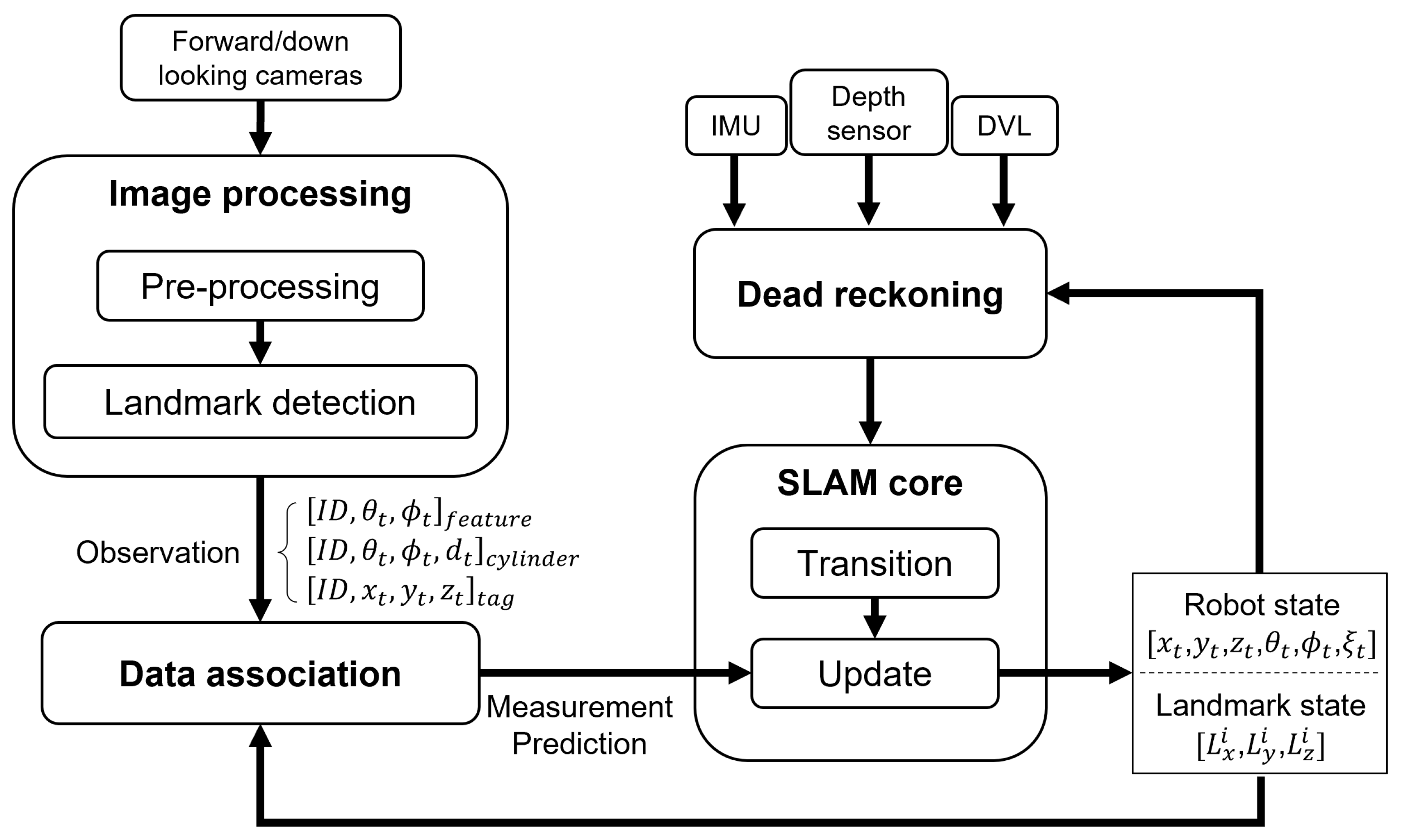
Figure 3 illustrates the overall framework of the proposed visual SLAM system. We have modules for AUV dead-reckoning, image processing, data association, and the SLAM core. In this work, EKF-SLAM [12] is utilized as the SLAM core. Although we have chosen the EKF, other SLAM methods could also be applied without loss of generality, as the same motion and observation models can be utilized. For instance, when implementing graph optimization-based SLAM, information from the dead-reckoning and image processing blocks can create constraints in the front end, while optimization in the back end can update the entire trajectories.
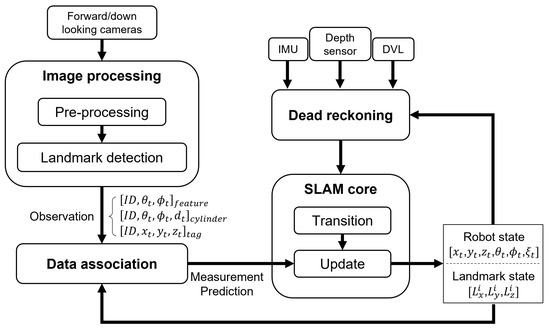
Figure 3.
Visual SLAM framework.
We first define the state variables related to the localization and mapping problems. The robot state {} is defined as SE(3) pose as
where is a quaternion that represents the vehicle’s orientation. The map is then defined as a vector describing the state of each landmarks as follows:
where , , and denote the state of the tag, cylindrical, and feature landmarks, respectively, and , , and denote the total number of the corresponding landmarks registered in a state vector at time step t. We assume that the landmarks are static during the AUV’s operation. The measurement then can be defined as follows:
where , , and denote the measurement for the tag, cylindrical, and feature landmarks, respectively, and denotes the bearing of the detected landmark. d is the distance from the forward camera to the cylindrical landmark, which is calculated as
where f denotes the focal length of the forward looking camera, is the actual cross section area of the observed cylindrical landmark, and is the pixel area of the landmark in the camera image. Finally, the augmented state variable is defined as follows.
3.1. SLAM Formulation
In the EKF SLAM framework, the SLAM procedure consists of two main steps: prediction and measurement update. These steps are executed recursively after the state initialization.
3.1.1. Prediction
In the prediction step, the state of the previous timestep is transformed into the next timestep using the state transition model . We employed the AUV’s kinematics model to describe the transition as follows.
where denotes the control input from the DVL, depth sensor, and AHRS with a noise covariance , denotes the time interval between the current and previous time step, and denotes the heading angle of the AUV. In (10), only the robot state undergoes the state transition and thus is updated. The map states remain unchanged in the prediction step. The error state covariance is also updated in the prediction step as follows.
where is the Jacobian of the state transition model.
3.1.2. Measurement Update
In the measurement update step, both the robot state and the map states are updated according to the measurement model . As explained in the (5)–(7), the measurement is represented in a sensor-fixed frame. The predicted measurement can be modeled as follows.
Update of the vehicle and map states are performed by the Kalman gain calculated from the Jacobian of the observation models (14)–(16) as follows.
where , , and denote the Jacobian matrix corresponding to the each landmark state. The Kalman update is performed as follows:
where denotes the sensor noise covariance, denotes the innovation covariance, and denotes the Kalman gain.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
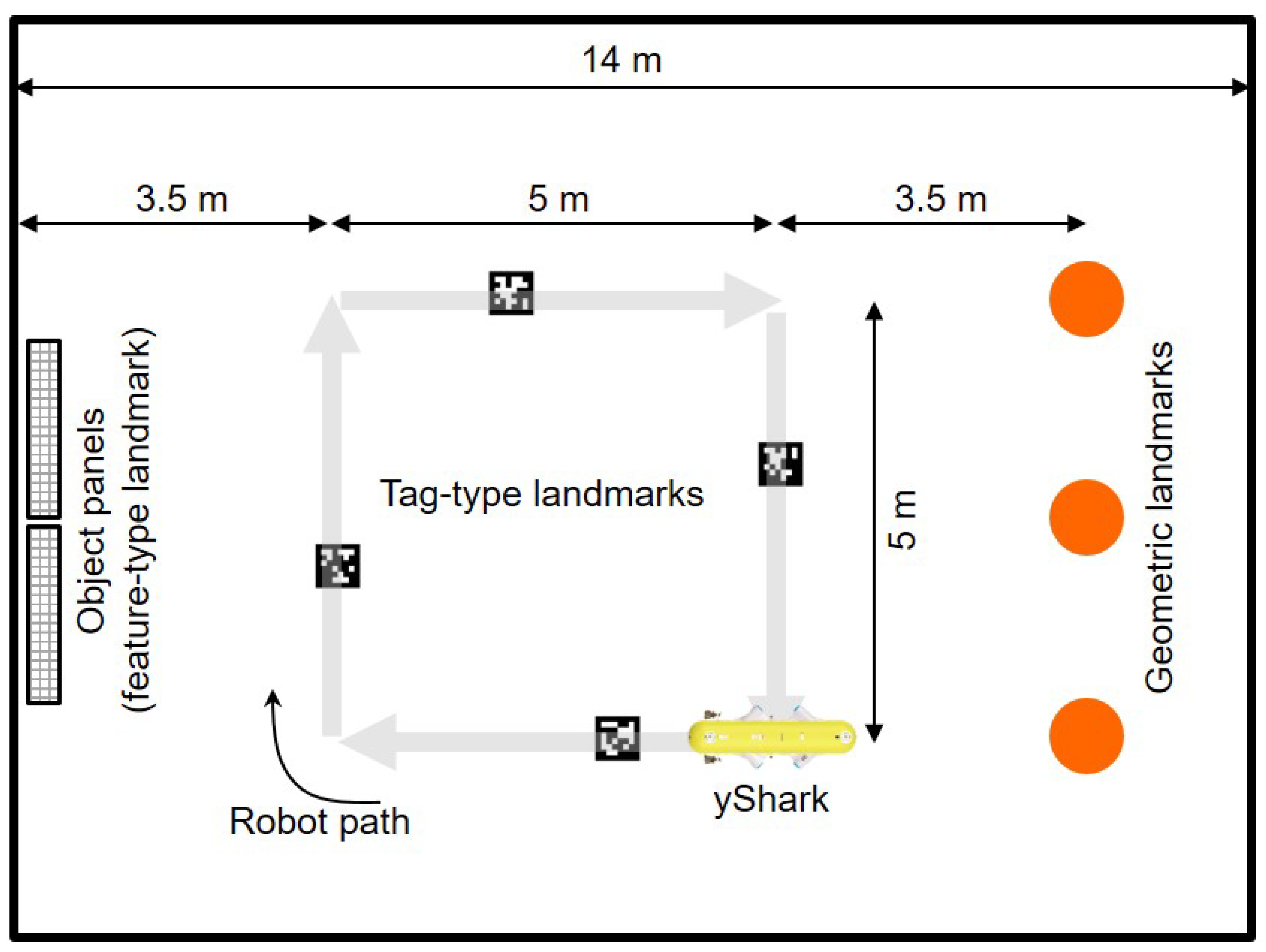
Experiments were conducted in a basin environment to validate the proposed SLAM method. Figure 4 illustrates the setup of the landmarks and path plans for the robot during the tests. We installed 4 tag-type landmarks and 3 cylindrical landmarks within the basin. Additionally, we placed two panels with various objects attached to serve as visual features. The yShark II, an AUV developed by the Korea Research Institute of Ships and Ocean Engineering (KRISO), was utilized in this experiment. The robot moved along the square (5 m by 5 m) path 4 times. Tag-type landmarks were observed from a down-looking camera (PointGrey Grasshopper3), and object panels and cylinder-type landmarks were observed from a forward-looking camera with the same model. Navigation sensors including the AHRS (Microstrain 3DM-GX3-25), DVL (LinkQuest NavQuest600 Micro), and depth sensor (Paroscientific Digiquartz) were used in the calculation of the DR estimation and SLAM prediction. All software for data acquisition, landmark detection, DR, SLAM, and vehicle control was developed in-house in C++.
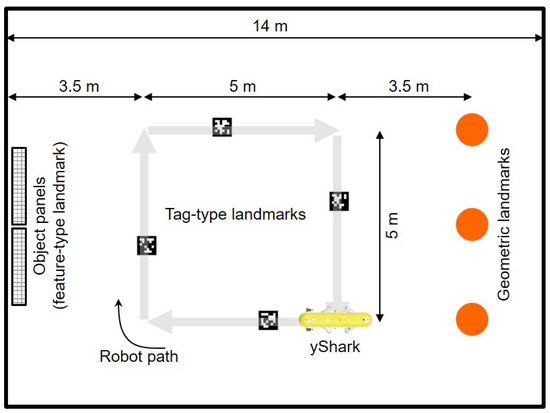
Figure 4.
Landmark setup and robot path plans.
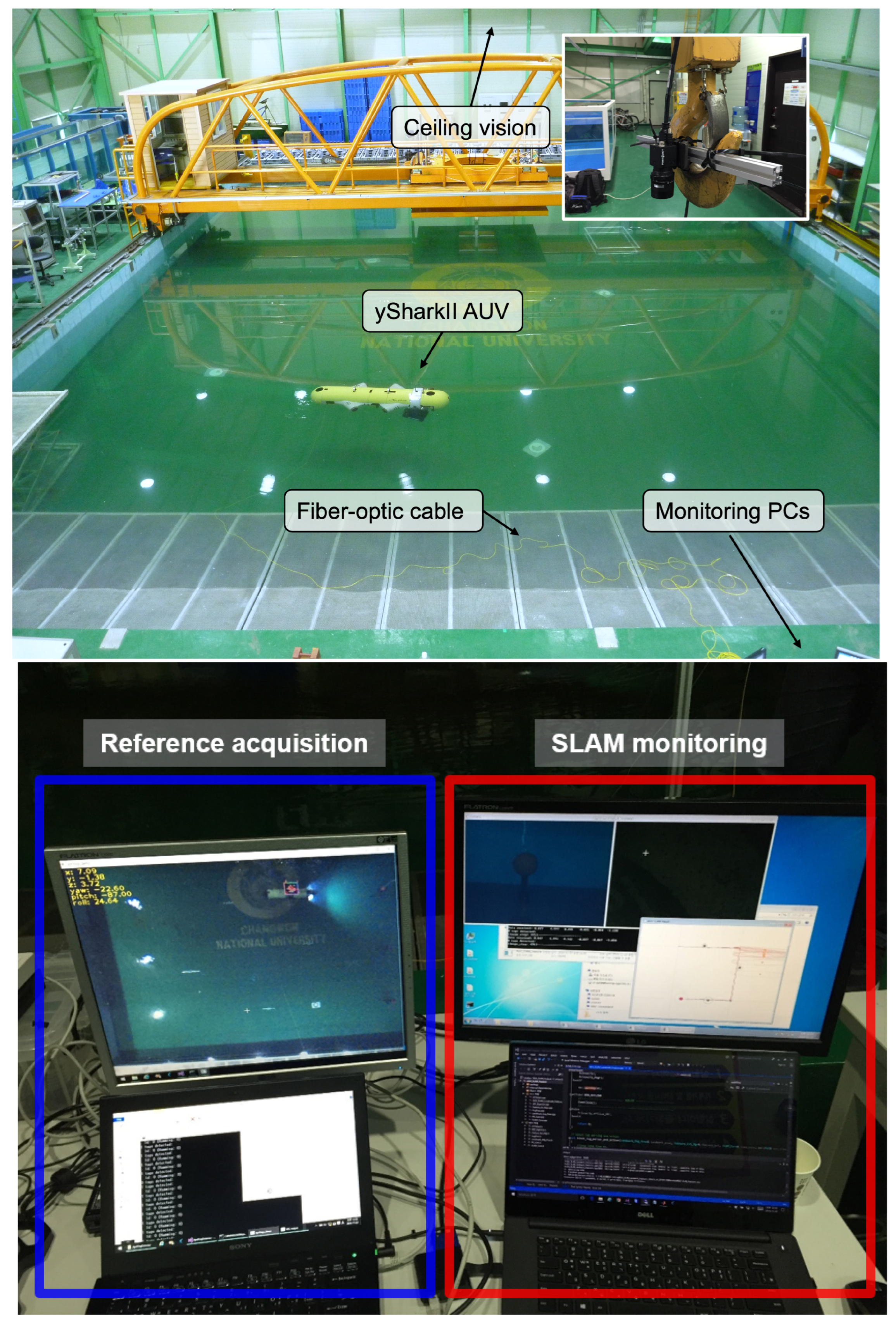
Figure 5 illustrates our testing setup, located in an engineering basin at Changwon National University.
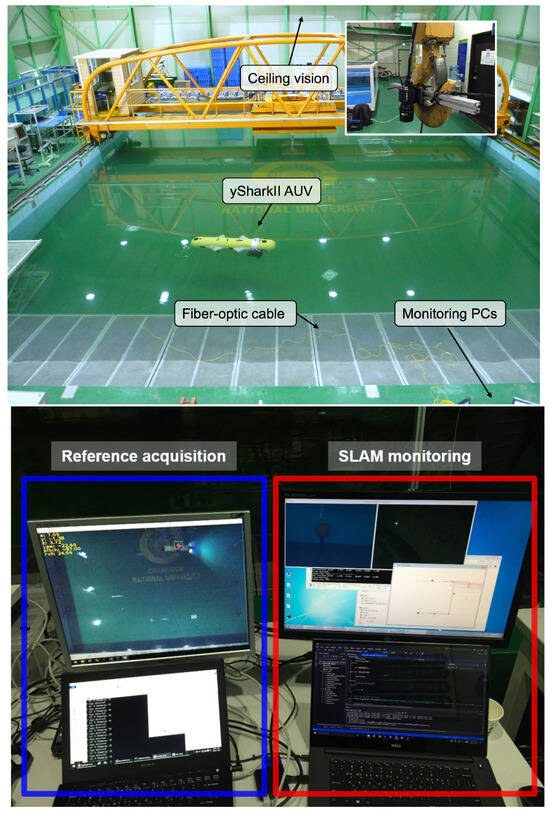
Figure 5.
Testing setup. Top: Engineering basin located at Changwon National University with the yShark II AUV. Bottom: ground control station featuring a reference acquisition system and remote access to the AUV’s internal computer.
We implemented a ceiling-mounted vision-based reference acquisition system (VRS) equipped with a wide field of view ( mm) camera and attached one large AprilTag on the AUV’s back. In the ground station, remote connections to the AUV’s internal PC and the VRS were set through the fiber-optic communication and power-over-ethernet, respectively. The DR and SLAM algorithms were run online and all the sensor data were also saved for the offline evaluations. In the offline evaluation, To generate extreme navigation scenarios, we added synthetic random noises to the DVL and AHRS measurements during the 3rd and 4th loops. Gaussian noise with standard deviation = [0.5 m, 10°] were periodically (once per 100 visual measurements) added to the translation and rotation states of the vehicle, respectively. Total 5 offline datasets were generated in this way.
4.2. Results
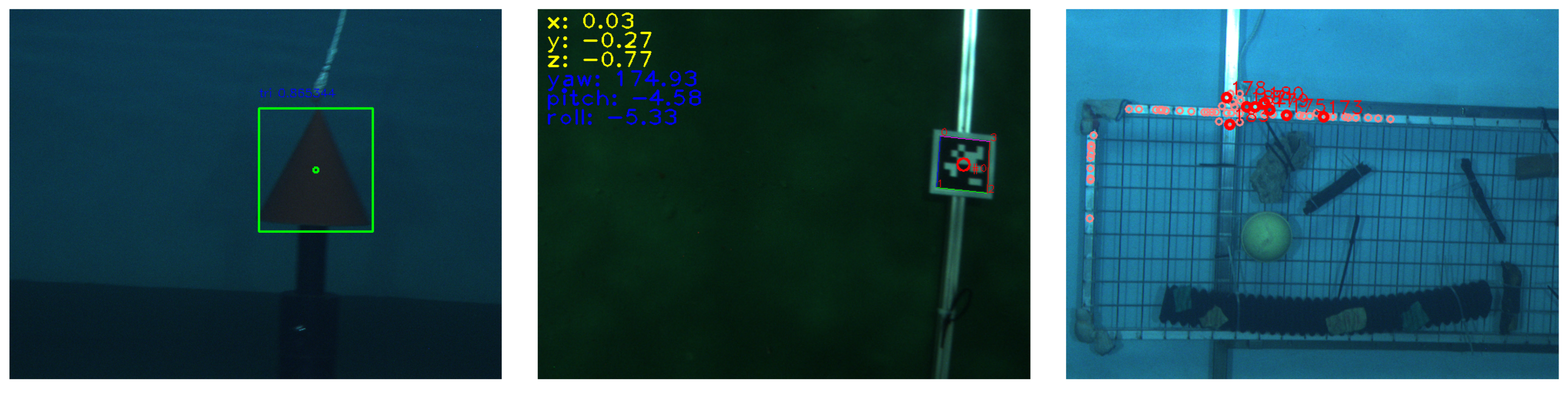
Examples of the landmark detection results are shown in Figure 6. For cylindrical landmarks, the detected bounding box and its center position are used to construct the measurement vector; in (8) is calculated as the area of the bounding box; the bearing in (6) is calculated with the center position. All three types of cylindrical landmarks were successfully detected in our test. Related to the tag landmarks, only 3 to 5 subsequent frames contained the tag images when the AUV moved over the landmark; however, this was sufficient for the update and convergence of the vehicle and map states. Lastly, feature-based landmarks showed that the extracted visual features were dominant around the frame structures, rather than the small objects. This is due to the reflection of the steel frame by the AUV’s lighting system.

Figure 6.
Underwater artificial landmarks and their detection results. From left to right: cylindrical landmarks, tag-type landmarks, and feature-based landmarks.
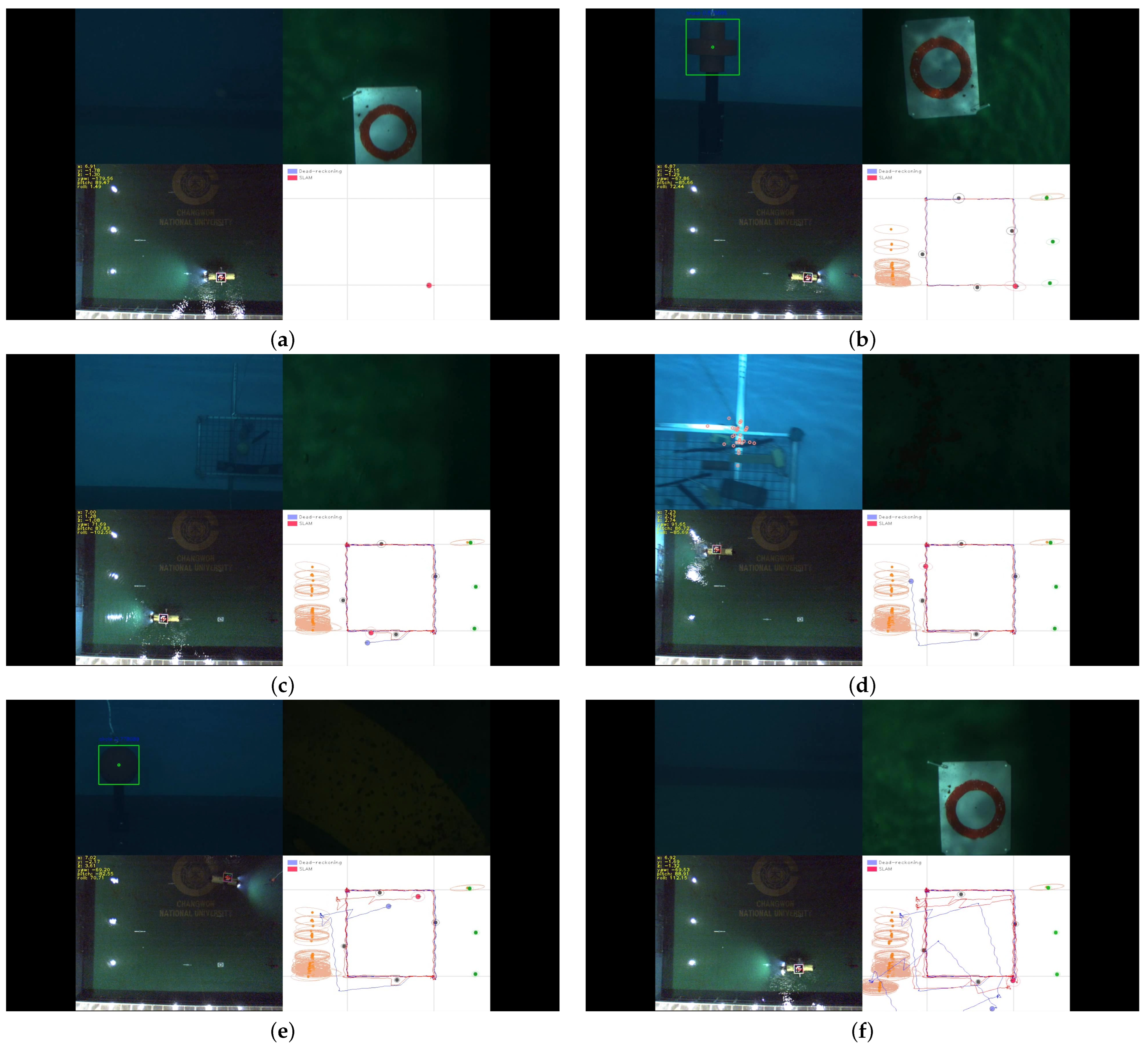
Localization results from one of the noisy datasets are shown in Figure 7. During the first two loops, the SLAM registered every new landmark detected from the forward and down-looking cameras. Because the error covariance increases during the prediction step (11), the covariance ellipse of the first detected landmark (tag-type) had the smallest value; and this contributed to the significant update whenever a large loop-closure occurred. The covariance for the cylindrical landmarks had an elliptical shape at first (Figure 7b), but converged to the circular shape after a few observations (Figure 7c), as the depth estimation described in (8) are available for this type of landmarks. In contrast, the covariance ellipse for the feature landmarks always had a narrow shape as the bearing information was only available. As the DR also has a good short-term performance, its trajectory is similar to the SLAM results until the second loop (Figure 7b). However, when synthetic noise was added from the 3rd loop, the DR estimate started to diverge with accumulating errors (Figure 7c); while the SLAM trajectory recovered from the erroneous state owing to the information from artificial landmarks.
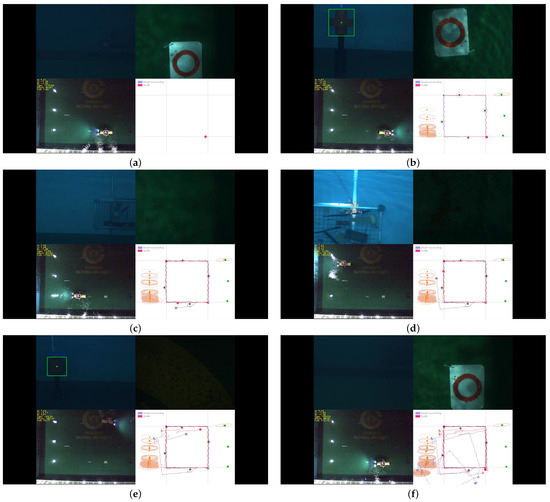
Figure 7.
Estimated robot paths (solid lines in blue: DR, red: SLAM) and mapped landmarks (circles in green: geometric, gray: tag-type, orange: feature-type). Subfigures (a–f) represent sequential snapshots of the results during the AUV’s trajectory following.
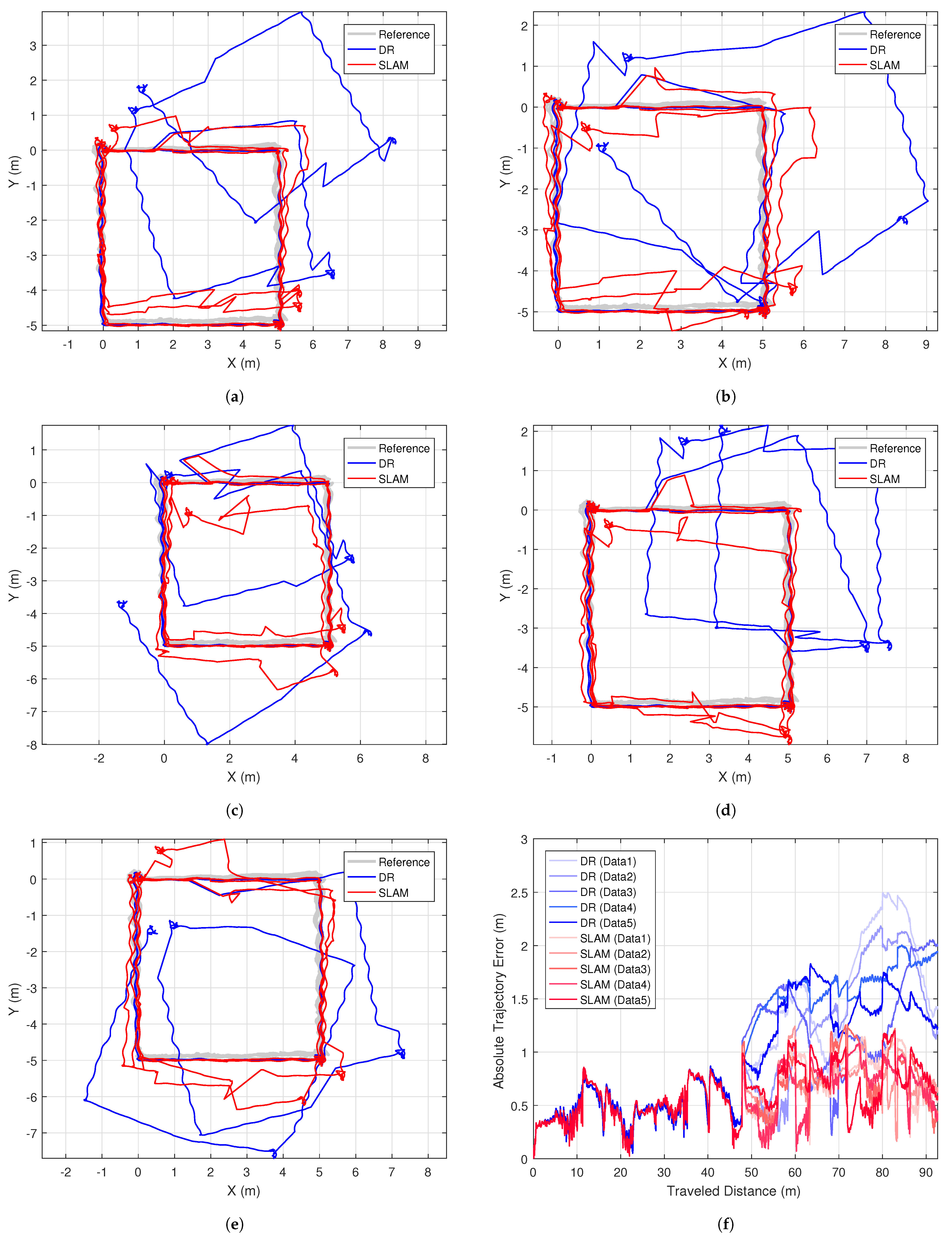
Results for all 5 datasets are shown in Figure 8. We applied different random noises for each dataset. Estimated trajectories and the absolute trajectory errors in Figure 8f support the superiority of the proposed SLAM method, which maintained the bounded errors throughout the entire trajectories. Table 1 summarizes absolute trajectory errors for DR and SLAM. The RMSE of the SLAM trajectory was 0.67 m for 92 m paths. This improved the positioning error of DR by 41.2%. Similarly, the maximum error was reduced by 43.6% when we used the SLAM.
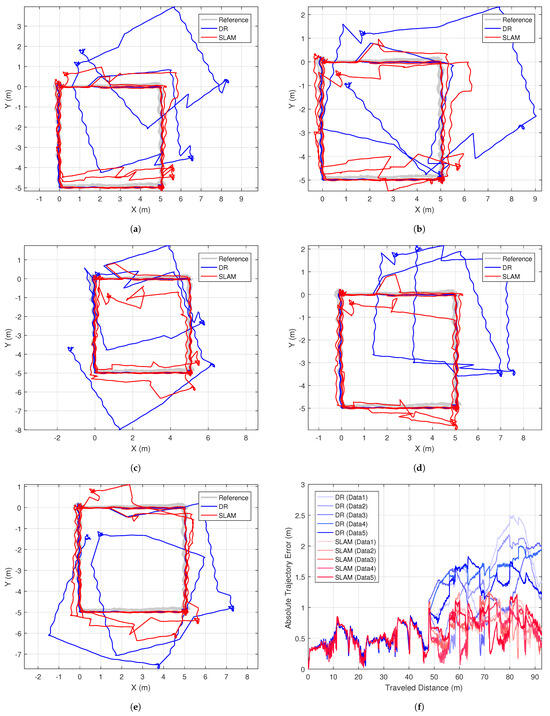
Figure 8.
Resulting AUV trajectories (a–e) and summary of estimation errors (f) from five different random noise datasets.

Table 1.
Summary of Absolute Trajectory Errors.
4.3. Discussions
We can verify how each type of landmark contributes to the reduction of position error by examining the ’jumps’ in the AUV trajectories. This analysis is possible because the layout of the landmarks in the experimental setup typically allows for the detection of one type of landmark at a time. It is clear that tag-type landmarks contribute significantly to pose correction, as illustrated in Figure 7c. The influence of a cylindrical landmark is also evident in Figure 7e, where the green circle in the lower right subplot indicates the detected landmark, causing the SLAM pose to jump onto the correct path. The contribution of object-clustered landmarks is harder to explain explicitly; however, we can infer their impact from the fact that the SLAM paths near the object panels exhibit the smallest errors in all cases, as shown in Figure 8.
While the experimental results are promising, there are limitations to consider. The validation was conducted in a controlled basin environment, meaning that the visibility of landmarks may be more challenging in real-world field conditions. To address this issue, deep learning-based image enhancement techniques [30] or multi-modal markers [31] that can be detected by both optical and sonar cameras could be utilized.
5. Conclusions
In this study, visual SLAM for AUVs using artificial landmarks has been investigated. Three types of artificial landmarks were proposed to be used with forward and down-looking cameras available in our AUV. We implemented a conventional EKF-based SLAM framework incorporating a kinematic model of the AUV and landmark observation models. We obtained experimental data from the tests conducted in a basin and validated the performance of the proposed method for the persistent localization scenario. We expect our method to be applied in the area of long-term AUV operations, such as valve-turning in deep-sea platforms or manipulation of nuclear waste in nuclear power plants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.J. and H.-T.C.; methodology, J.J. and Y.L; software, J.J., Y.L. and H.-T.C.; validation, J.J., Y.L. and H.-T.C.; formal analysis, J.J.; investigation, J.J. and Y.L.; resources, H.-T.C.; data curation, J.J. and Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.J.; writing—review and editing, J.J.; visualization, J.J.; supervision, J.J. and H.-T.C.; project administration, J.J. and H.-T.C.; funding acquisition, J.J. and H.-T.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by research fund of Chungnam National University.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Paull, L.; Saeedi, S.; Seto, M.; Li, H. AUV Navigation and Localization: A Review. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 39, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ji, D.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Xu, W. Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Navigation: A review. Ocean Eng. 2023, 273, 113861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteba, J.; Cieślak, P.; Palomeras, N.; Ridao, P. Sparus Docking Station: A current aware docking station system for a non-holonomic AUV. J. Field Robot. 2024, 41, 1765–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, J.; Gómez-Espinosa, A.; Cuan-Urquizo, E.; García-Valdovinos, L.G.; Salgado-Jiménez, T.; Cabello, J.A.E. Autonomous Underwater Vehicles: Localization, Navigation, and Communication for Collaborative Missions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandt, M.; Gade, K.; Jalving, B. Integrating DGPS-USBL position measurements with inertial navigation in the HUGIN 3000 AUV. In Proceedings of the 8th Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 28–30 May 2001; pp. 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xie, G.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S. USV-AUV Collaboration Framework for Underwater Tasks under Extreme Sea Conditions. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025—2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey, J.C.; Whitcomb, L.L. Preliminary field experience with the DVLNAV integrated navigation system for oceanographic submersibles. Control. Eng. Pract. 2004, 12, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Dai, Z.; Ran, C. Underwater Adaptive Height-Constraint Algorithm Based on SINS/LBL Tightly Coupled. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, G.; Kim, D.; Myung, H.; Choi, H.T. Vision-based object detection and tracking for autonomous navigation of underwater robots. Ocean Eng. 2012, 48, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, D.; Myung, H.; Choi, H.T. Artificial landmark-based underwater localization for AUVs using weighted template matching. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2014, 7, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Choi, H.T. Experimental results on EKF-based underwater localization algorithm using artificial landmark and imaging sonar. In Proceedings of the 2014 Oceans—St. John’s, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 14–19 September 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, S.; Burgard, W.; Fox, D. Probabilistic Robotics; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Madrigal, J.A.; Claraco, J.L.B. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping for Mobile Robots: Introduction and Methods; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Macario Barros, A.; Michel, M.; Moline, Y.; Corre, G.; Carrel, F. A Comprehensive Survey of Visual SLAM Algorithms. Robotics 2022, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.B.; Newman, P.; Dissanayake, G.; Durrant-Whyte, H. Autonomous underwater simultaneous localisation and map building. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 2, pp. 1793–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, C.; Singh, H. A self-consistent bathymetric mapping algorithm. J. Field Robot. 2007, 24, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, D.; Ridao, P.; Tardós, J.D.; Neira, J. Underwater SLAM in man-made structured environments. J. Field Robot. 2008, 25, 898–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ko, H.L. UKF-Based Inverted Ultra-Short Baseline SLAM With Current Compensation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 67329–67337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Feng, D.; Li, Y.; Tian, Q. Research on simultaneous localization and mapping for AUV by an improved method: Variance reduction FastSLAM with simulated annealing. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Cong, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, Z. Active Bathymetric SLAM for autonomous underwater exploration. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2023, 130, 103439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, D.; Myung, H.; Choi, H.T. AUV SLAM using forward/downward looking cameras and artificial landmarks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Underwater Technology (UT), Busan, Korea, 21–24 February 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E. AprilTag: A robust and flexible visual fiducial system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 3400–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Gool, L.V. Surf: Speeded up robust features. In Proceedings of the European conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Leutenegger, S.; Chli, M.; Siegwart, R.Y. BRISK: Binary robust invariant scalable keypoints. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2548–2555. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhou, X. LoFTR: Detector-Free Local Feature Matching With Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8922–8931. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, L.; Bai, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, S.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. ASLFeat: Learning Local Features of Accurate Shape and Localization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sarlin, P.E.; DeTone, D.; Malisiewicz, T.; Rabinovich, A. SuperGlue: Learning Feature Matching With Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Kang, G.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y. Joint-ID: Transformer-Based Joint Image Enhancement and Depth Estimation for Underwater Environments. IEEE Sensors J. 2024, 24, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Jung, J.; Kim, T.; Choi, H.T. Underwater robot exploration and identification using dual imaging sonar: Basin test. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Underwater Technology (UT), Busan, Korea, 21–24 February 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).