An Approach to Optimize the Efficiency of an Air Turbine of an Oscillating Water Column Based on Adaptive Model Predictive Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
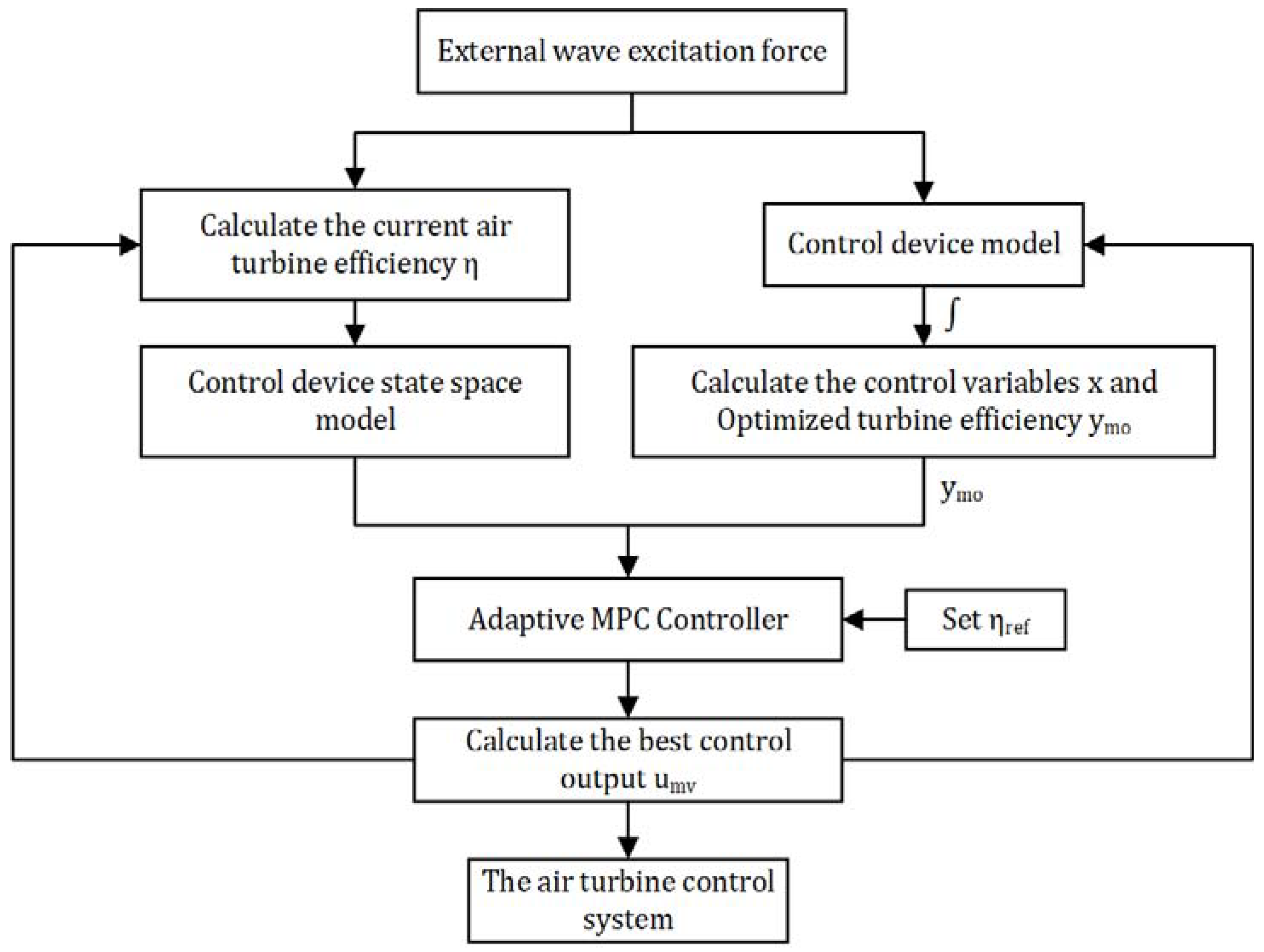
2. Principle of Adaptive Model Predictive Control
2.1. The Principle of Model Predictive Control
2.2. The Proposed Adaptive Model Predict Control for BBDB OWC
3. The Construction of the Control State Space Model
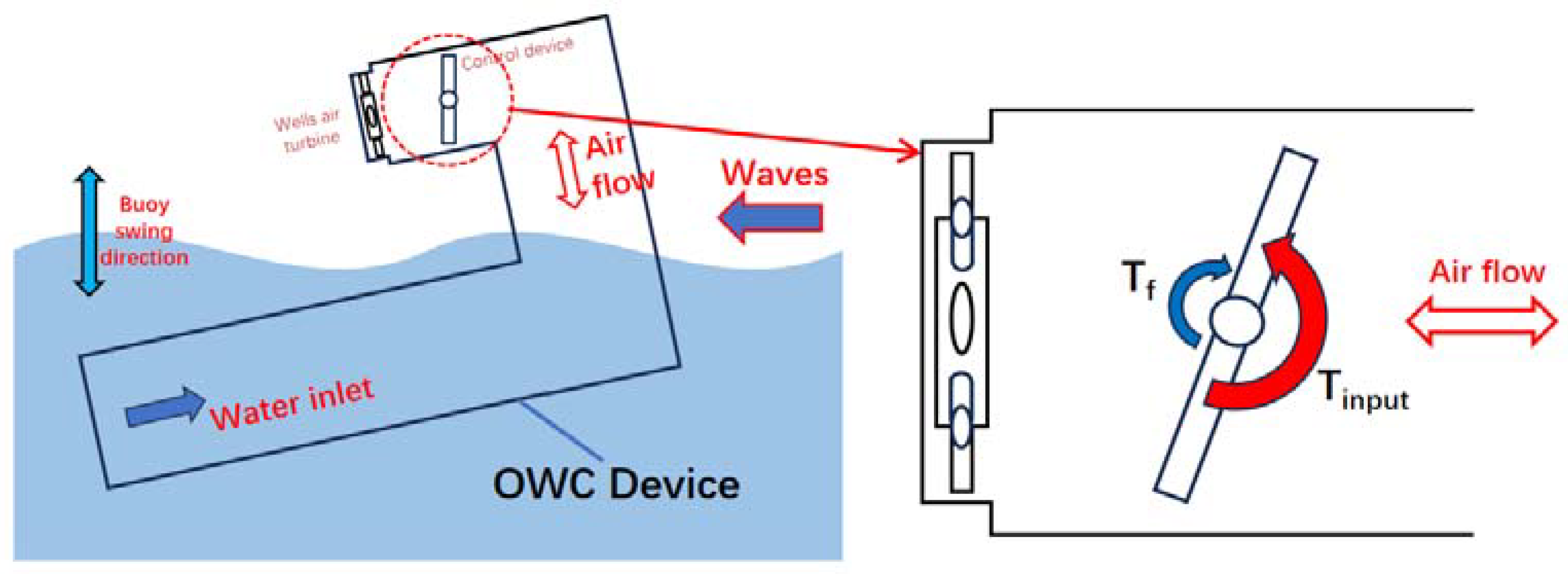
3.1. Principle of the Control System
3.2. Parameter Analysis of the Control Device
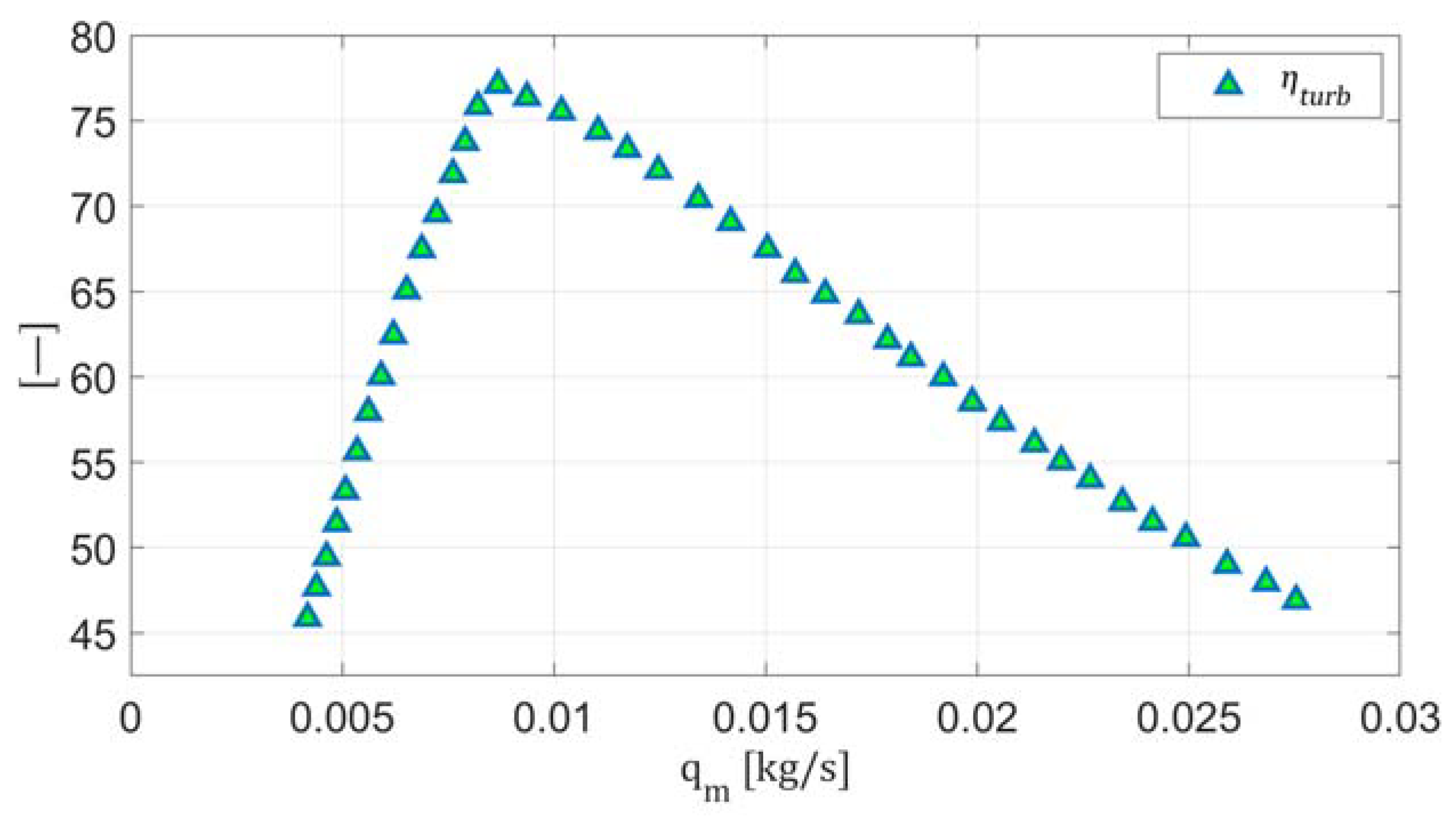
3.3. Parameter Analysis of the Air Turbine
4. Construction of Control Models
4.1. Linearization of Nonlinear Models
4.2. Discretization of Linear Models
4.3. Predictive Model
5. Simulation Results and Analysis
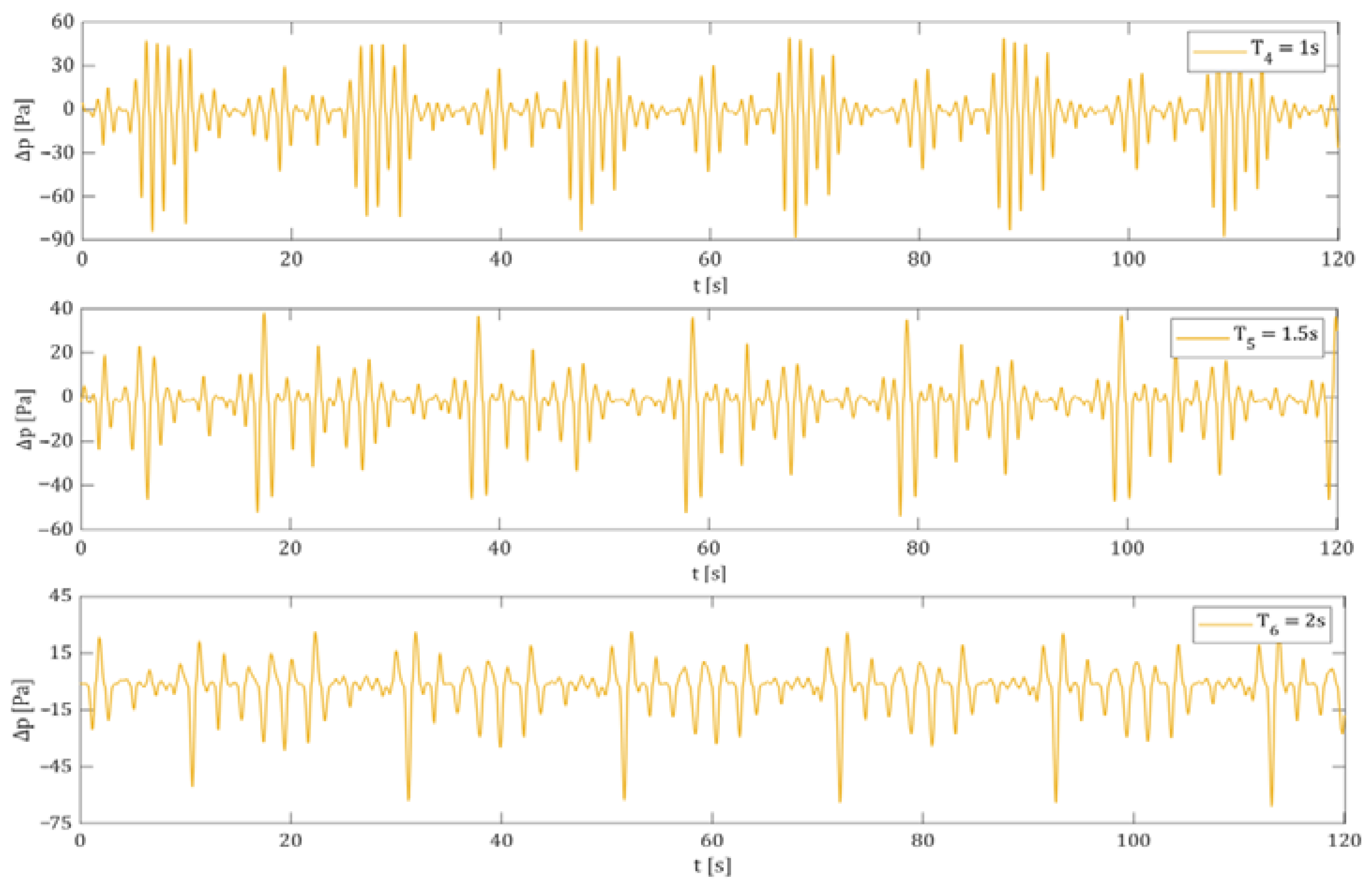
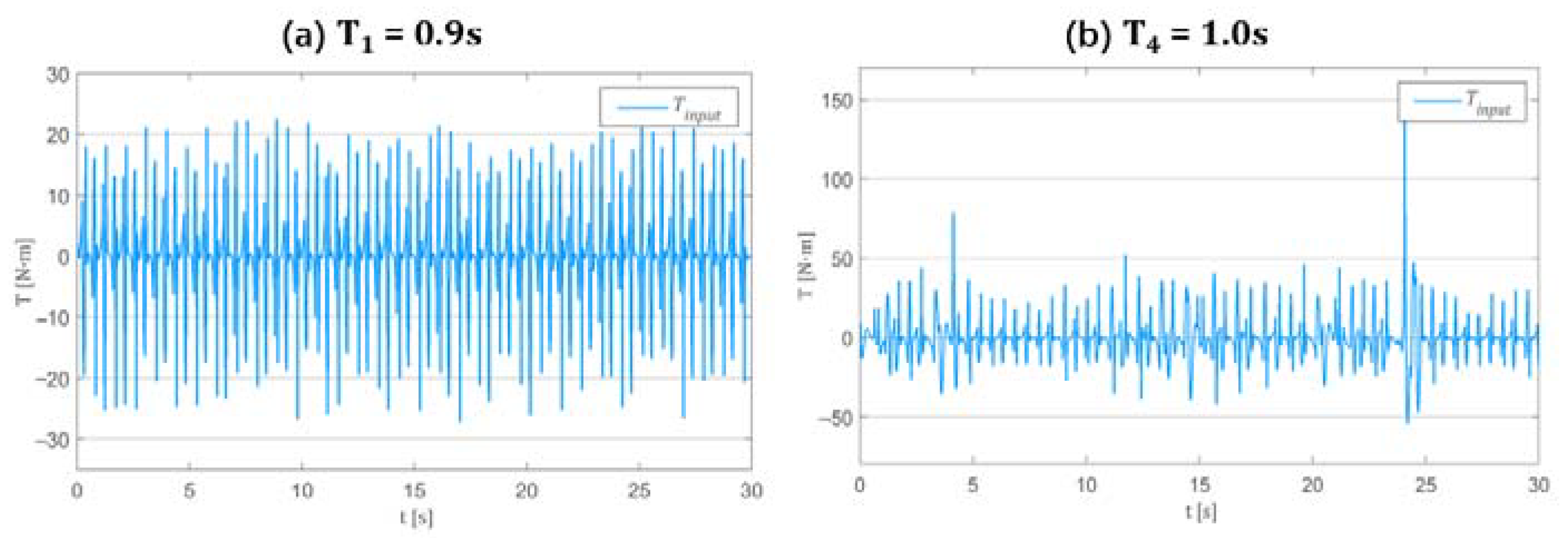
5.1. Experimental Conditions
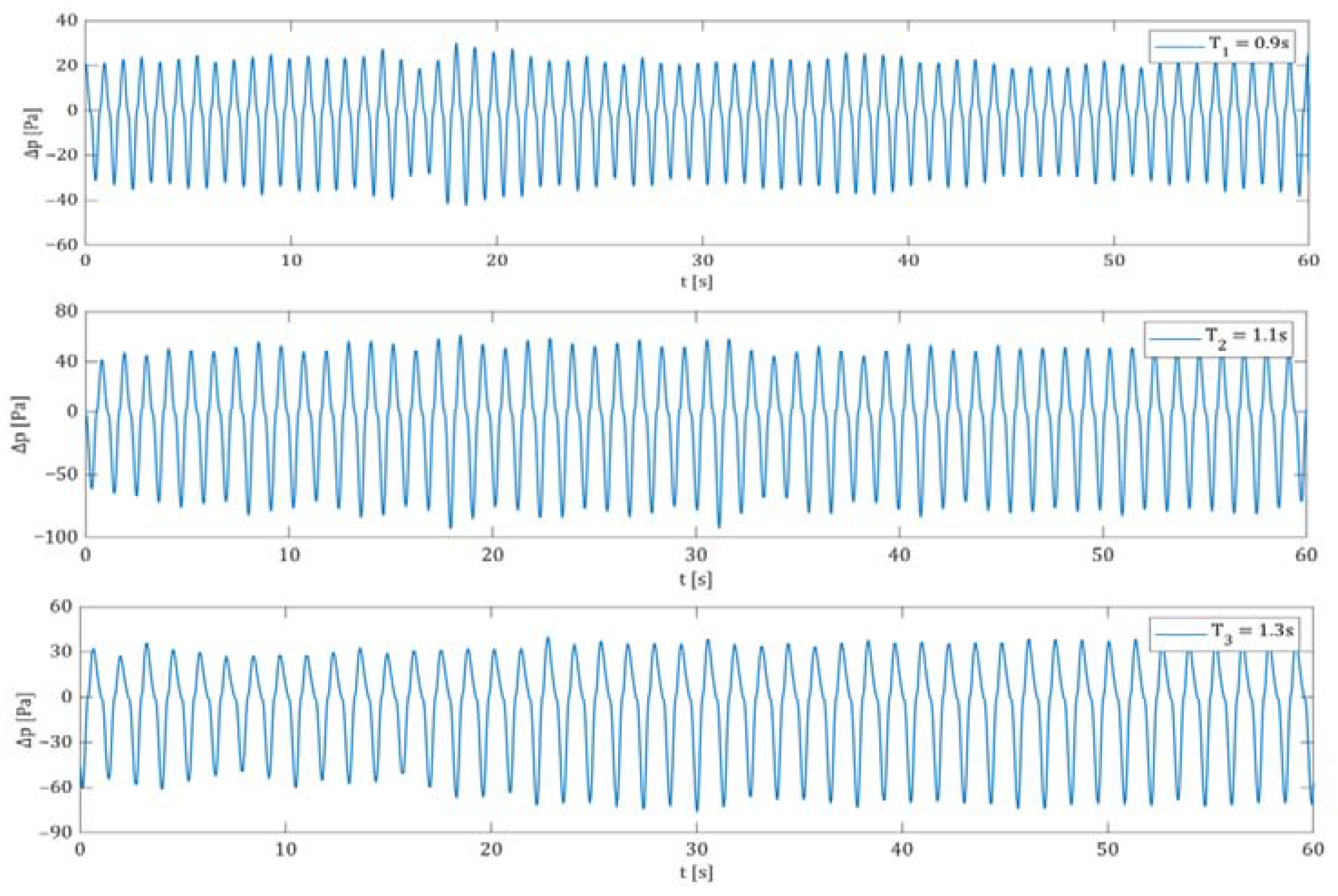
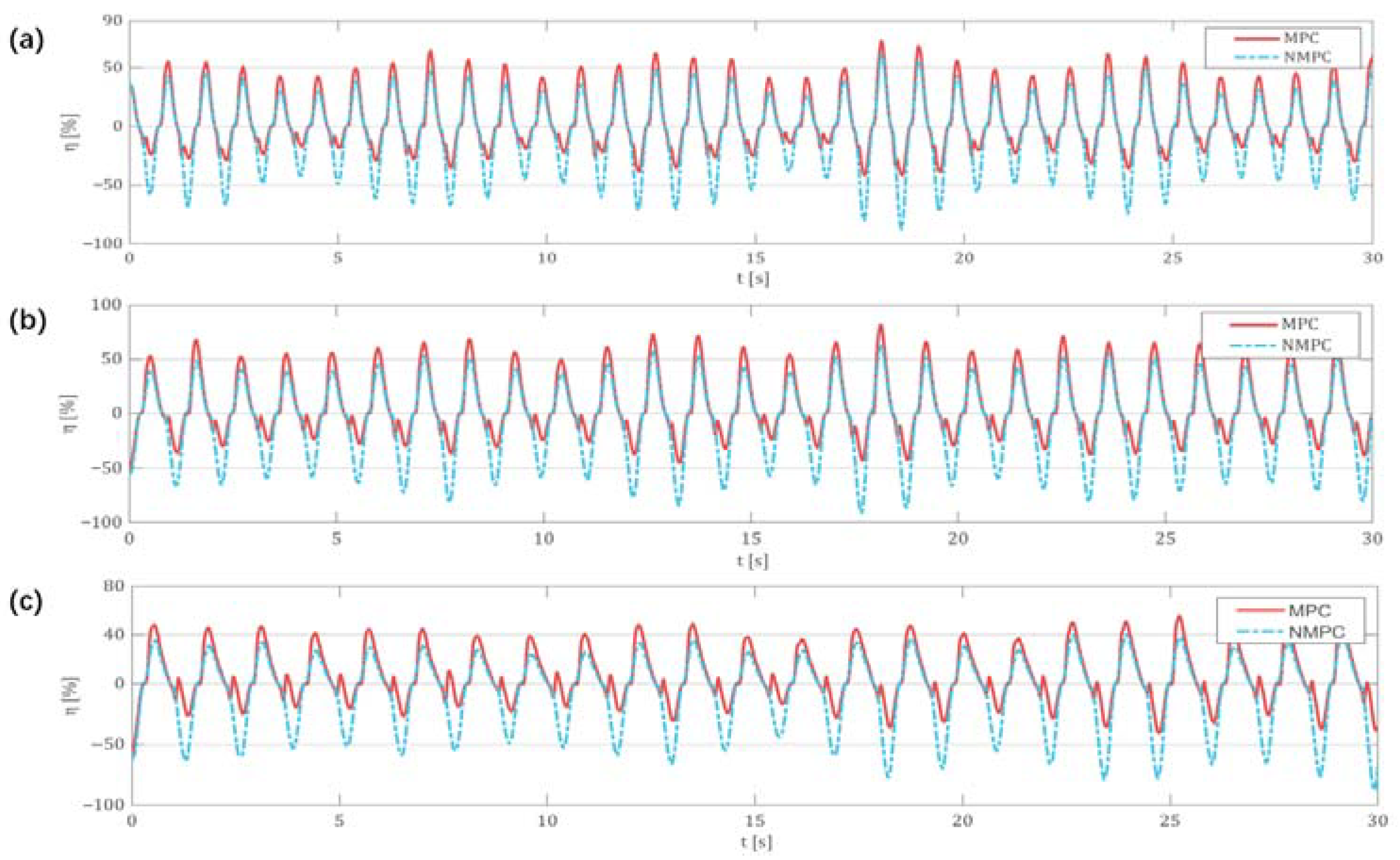
5.2. Simulation Results of Regular Wave Conditions
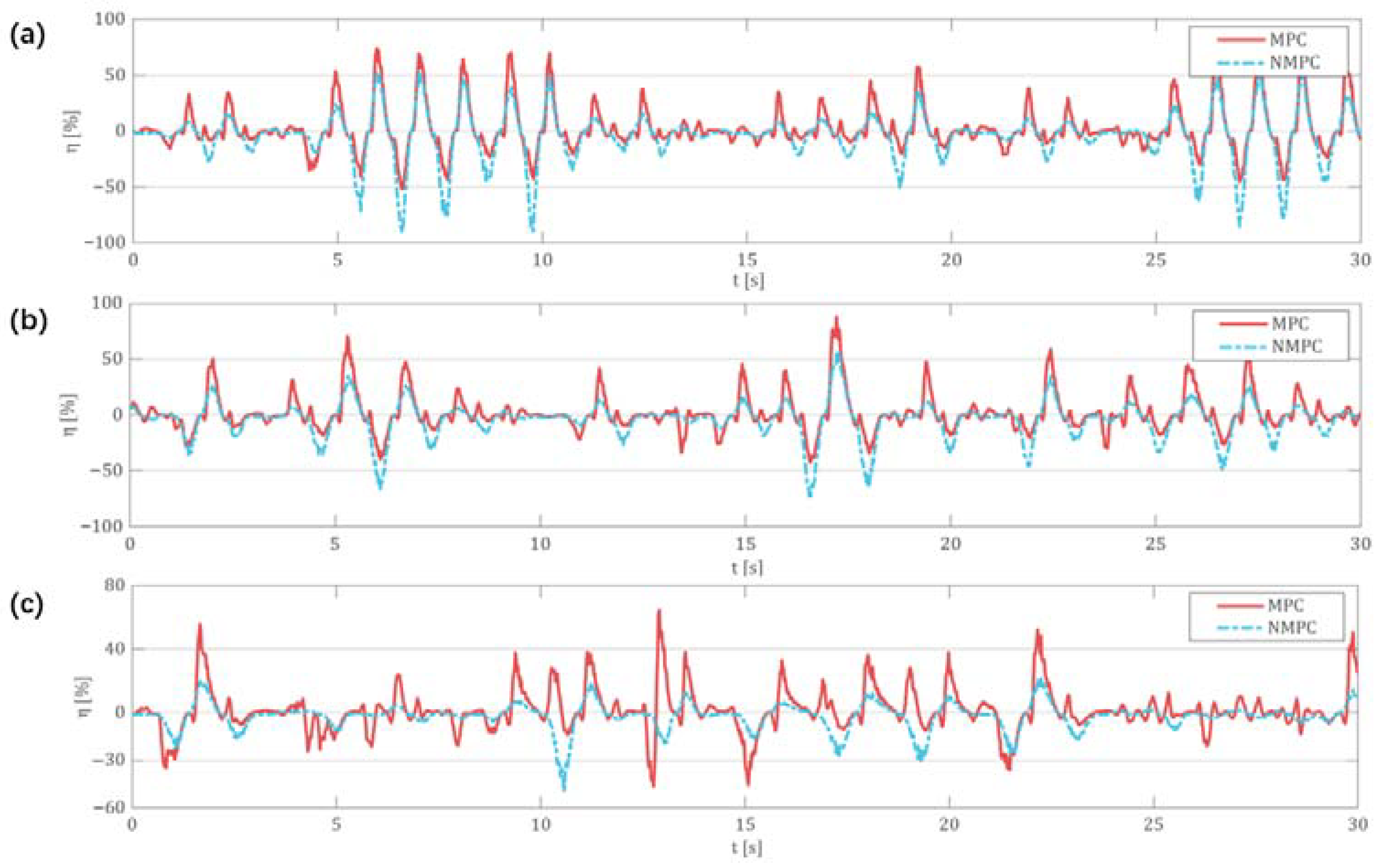
5.3. Simulation Results of Irregular Wave Conditions
5.4. Discussion
- (1)
- AMPC model errors. These may arise from (i) the linearization of the original nonlinear model and (ii) discrepancies between predicted and actual outputs.
- (2)
- Control system errors in the physical model. The rotating damping shaft is prone to rust formation due to prolonged water exposure, leading to torque regulation inaccuracies.
- (3)
- Energy losses in the air turbine. These include losses due to air resistance and mechanical inefficiencies.
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- MPC-optimized turbine efficiency shows slight improvement in regular waves. Under wave periods of 0.9 s, 1.1 s and 1.3 s, the turbine efficiency is increased by 15.1%, 16.2% and 14.0% respectively.
- (2)
- MPC is effective for short-period irregular waves but becomes unstable as the wave period increases. The standard deviations of efficiency fluctuations under irregular wave conditions with periods of 1.5 s and 2.0 s were measured as 4.929 and 8.134, respectively.
- (3)
- The MPC adaptive model optimizes turbine efficiency under most conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Li, J.; Pan, S.; Yao, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, Z. Assessment of Wind and Wave Energy in China Seas under Climate Change Based on CMIP6 Climate Model. Energy 2024, 310, 133207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Shao, H.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, G.; Dai, S.; Wang, L.; Mao, X.Z. Spatiotemporal Distribution, Evolution, and Complementarity of Wind and Waves in China’s Offshore Waters and Its Implications for the Development of Green Energy. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 312, 118567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zheng, C.; Li, L.; Dai, Y.; Esteban, M.D.; López-Gutiérrez, J.S.; Qu, X.; Zhang, X. Wave Energy Assessment Related to Wave Energy Convertors in the Coastal Waters of China. Energy 2020, 202, 117741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Jun, D.; Ze, S. Low-Frequency Energy Capture and Water Wave Attenuation of a Hybrid WEC-Breakwater with Nonlinear Stiffness. Renew. Energy 2022, 196, 1029–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, D.W.; Lin, C.C.; Tzang, S.Y. Parametric Design Methodology for Maximizing Energy Capture of a Bottom-Hinged Flap-Type WEC with Medium Wave Resources. Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falnes, J. A Review of Wave-Energy Extraction. Mar. Struct. 2007, 20, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, A.F.d.O. Wave Energy Utilization: A Review of the Technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 899–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagath Kumara, K.D.R. A Top-Mounted, Chain-Driven, Bidirectional Point Absorber Type Wave Energy Convertor. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 1360–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Fu, L.; Dai, S.; Collu, M.; Cui, L.; Yuan, Z.; Incecik, A. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Hybrid WEC-Breakwater System Combining an Oscillating Water Column and an Oscillating Buoy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, A.F.O.; Henriques, J.C.C. Oscillating-Water-Column Wave Energy Converters and Air Turbines: A Review. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 1391–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, T.; Ghisu, T.; Parks, G.; Cambuli, F.; Puddu, P. Optimization of Blade Profiles for the Wells Turbine. Ocean Eng. 2018, 169, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, P.; Rhee, S.H.; Samad, A. Numerical Optimization of Wells Turbine for Wave Energy Extraction. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2017, 9, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenu, B.; Henriques, J.C.C.; Glorioso, M.; Gato, L.M.C.; Bonfanti, M. Real-Time Wells Turbine Simulation on an Oscillating-Water-Column Wave Energy Converter Physical Model. Appl. Energy 2024, 376, 124121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elatife, K.; El Marjani, A. Design Optimization and Analysis of a Compact Twin Radial Impulse Turbine for Wave Energy Conversion. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’zoughi, F.; Bouallègue, S.; Garrido, A.J.; Garrido, I.; Ayadi, M. Stalling-Free Control Strategies for Oscillating-Water-Column-Based Wave Power Generation Plants. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’zoughi, F.; Lekube, J.; Garrido, A.J.; De La Sen, M.; Garrido, I. Machine Learning-Based Diagnosis in Wave Power Plants for Cost Reduction Using Real Measured Experimental Data: Mutriku Wave Power Plant. Ocean Eng. 2024, 293, 116619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Purwar, S.; Kishor, N. Maximizing Output Power in Oscillating Water Column Wave Power Plants: An Optimization Based MPPT Algorithm. Technologies 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Purwar, S.; Kishor, N. Event-Triggered Nonlinear Control of OWC Ocean Wave Energy Plant. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, M.; Ringwood, J.V. Wave-to-Wire Efficiency Maximisation for Oscillating-Water-Column Systems. IFAC-Pap. 2023, 56, 10886–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faedo, N.; Olaya, S.; Ringwood, J.V. Optimal Control, MPC and MPC-like Algorithms for Wave Energy Systems: An Overview. IFAC J. Syst. Control. 2017, 1, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, S.R.; Zhao, G.W.; Dai, S.S.; He, F.; Yuan, Z.M. Model Predictive Control of Wave Energy Converters. Ocean Eng. 2024, 301, 117430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, T.; Tao, J.; Sharma, S.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Dong, X.; Shi, H. Model Predictive Control of a Single-Buoy Wave Energy Converter with Coupled Constraints and Model Adaptation. Ocean Eng. 2025, 315, 119887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Chen, Y.; Ringwood, J.V. Computationally-Efficient Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of Wave Energy Converters with Imperfect Wave Excitation Previews. Ocean Eng. 2025, 319, 120125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Gai, N.; Stansby, P.; Li, G. Linear Non-Causal Optimal Control of an Attenuator Type Wave Energy Converter M4. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Li, G. Linear Optimal Noncausal Control of Wave Energy Converters. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2019, 27, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, K.U.; Magaña, M.E.; Sawodny, O. Model Predictive Control of a Nonlinear 2-Body Point Absorber Wave Energy Converter With Estimated State Feedback. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, F.; Moghaddam, R.K. Power Maximization of a Point Absorber Wave Energy Converter Using Improved Model Predictive Control. China Ocean Eng. 2017, 31, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetinger, D.; Magana, M.E.; Sawodny, O. Decentralized Model Predictive Control for Wave Energy Converter Arrays. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ted, K.A. Brekken on Model Predictive Control for a Point Absorber Wave Energy Converter. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE PES Trondheim PowerTech: The Power of Technology for a Sustainable Society, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway, 19–23 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011. ISBN 9781424484171. [Google Scholar]
- Bracco, G.; Canale, M.; Cerone, V. Energy harvesting optimization of an Inertial Sea Wave Energy Converter through Model Predictive Control. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 15th International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), Edinburgh, Scotland, 16–19 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. ISBN 9781728111643. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, A.C.M.; Sheng, W.; Lightbody, G. An Analysis of the Potential Benefits of Centralised Predictive Control for Optimal Electrical Power Generation from Wave Energy Arrays. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, J.C.C.; Portillo, J.C.C.; Sheng, W.; Gato, L.M.C.; Falcão, A.F.O. Dynamics and Control of Air Turbines in Oscillating-Water-Column Wave Energy Converters: Analyses and Case Study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xue, G. Cooperative Model Predictive Control for Wave Energy Converter Arrays. Renew. Energy 2023, 219, 119441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Du, Z.; Tu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liang, B.; Chen, X.; Cao, G.; Xiao, S.; Yang, S. Experimental Study of a Backward Bent Duct Buoy Wave Energy Converter: Effects of the Air Chamber and Center of Gravity Height. Ocean Eng. 2024, 313, 119447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
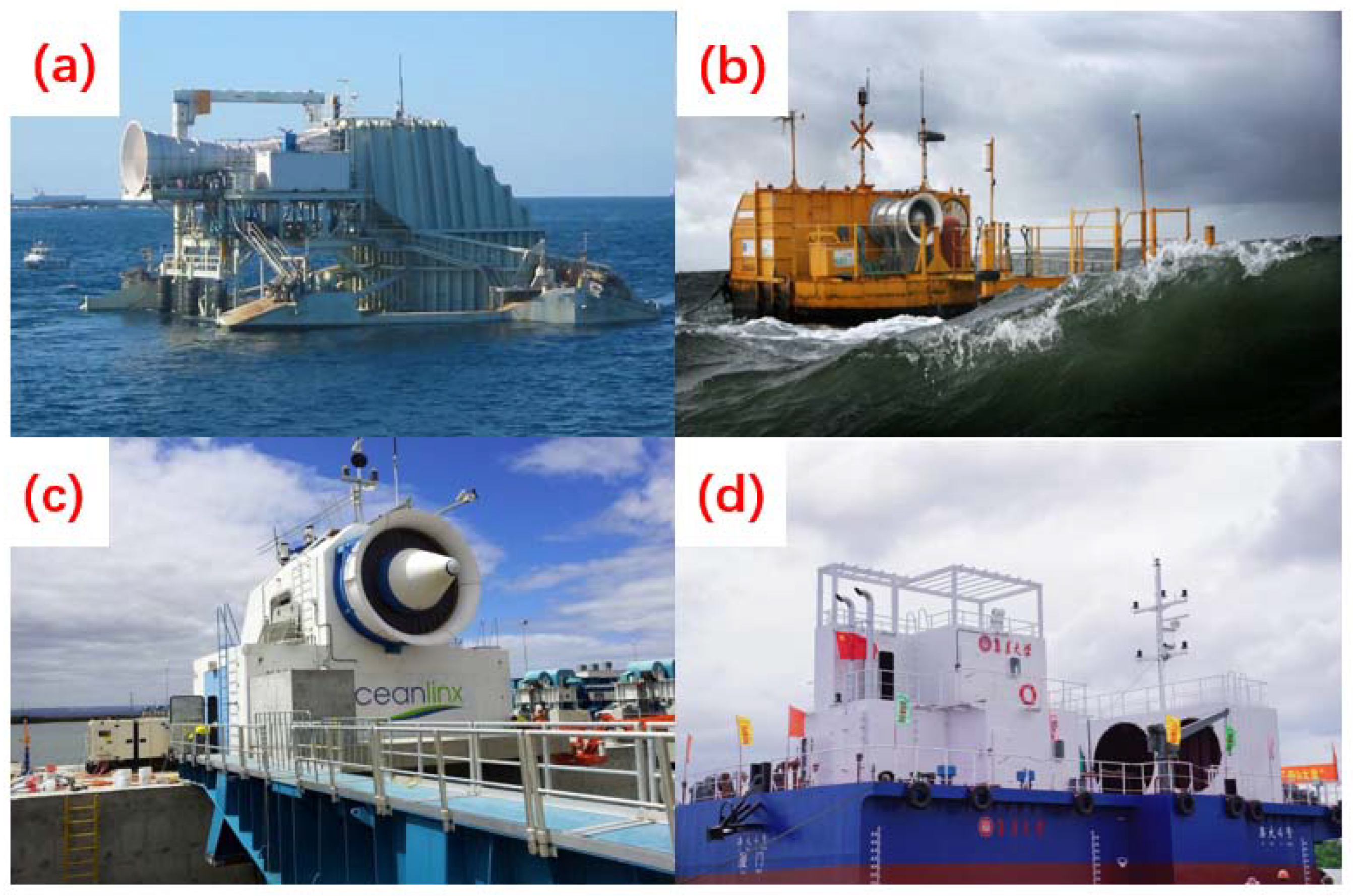



| Wave Form | Cycle | Sampling Frequency | Wave Height |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular wave | |||
| Irregular wave |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Dong, W.; Fan, J.; Yang, S.; Du, Z.; Tu, Y.; Li, C.; Lin, B. An Approach to Optimize the Efficiency of an Air Turbine of an Oscillating Water Column Based on Adaptive Model Predictive Control. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050831
Huang Y, Dong W, Fan J, Yang S, Du Z, Tu Y, Li C, Lin B. An Approach to Optimize the Efficiency of an Air Turbine of an Oscillating Water Column Based on Adaptive Model Predictive Control. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050831
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yan, Weixun Dong, Jianyu Fan, Shaohui Yang, Zhichang Du, Yongqiang Tu, Chenglong Li, and Beichen Lin. 2025. "An Approach to Optimize the Efficiency of an Air Turbine of an Oscillating Water Column Based on Adaptive Model Predictive Control" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050831
APA StyleHuang, Y., Dong, W., Fan, J., Yang, S., Du, Z., Tu, Y., Li, C., & Lin, B. (2025). An Approach to Optimize the Efficiency of an Air Turbine of an Oscillating Water Column Based on Adaptive Model Predictive Control. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050831






