Abstract
In the last decade, innovative beach nourishment strategies have been developed, driven by the increased worldwide interest in environmentally friendly coastal protection measures. In this context, the massive nourishment project of the Netherlands, known as Sand Engine, begun in 2011, has been hailed as a successful means of beach protection. Continuous monitoring, field campaigns, and numerical modeling have shown that the great volume of sand deployed is gradually transported by the waves and currents along the coastline, avoiding the need for repeated invasive, small scale beach replenishments. A very small, bell-shaped Sand Engine was designed to protect the beachfront at a tourist resort near Puerto Morelos, Mexico. To estimate the morphological response of the beach and the functioning of the micro Sand Engine as a sand reservoir, XBeach numerical modelling was applied to the project. The micro Sand Engine is seen to be a sustainable and eco-friendly coastal protection measure, especially applicable when a large nourishment project is not viable. Maintenance work for the nourishment is cost and time effective, and any negative impacts to sensitive ecosystems nearby can be detected and controlled quickly.
1. Introduction
International interest in environmentally friendly strategies to protect beaches and dunes against erosion has led to an increasing preference for soft methods over hard engineering [1,2,3,4]. Of these soft methods, artificial beach nourishment has been recognized as particularly effective in curbing erosion, as it does not cause harmful effects to nearby areas [5].
Traditional beach nourishments, where the sand is placed directly ono the dry beach and dunes, is being superseded by large-scale shoreface nourishment, where the sand is placed between the low water line and the dry beach; it may be less expensive and provide recreational areas more quickly than the earlier mode.
Numerical models have been developed to better understand and optimize shoreface beach nourishment projects. Variations within the one-line shoreline models include that presented by [6], which calculates the shoreline evolution following a beach nourishment project, and considers the effect of using sediment with different characteristics than the native sediment; and the application of the numerical model GENESIS to the long-term simulation of shoreline change following a beach nourishment project in China [7]. Additionally, an analytical model and a One Line model were developed to compare beach performance with measured data in three beach projects in Florida [8]. A wave-sediment transport numerical model based on the higher order Boussinesq equations was developed by [9], which can calculate both cross-shore and planform morphology evolution. For the evaluation of shoreface nourishments specifically, [10] examined the development of a shoreface nourishment off Sylt Island, using a numerical model to simulate the hydro and local sediment transport processes, and the validity of XBeach numerical model was presented to predict the erosion of 19 shoreface nourishments at different sections of the Dutch coast [11]. Cross-shore transport (for shore-normal waves) governed the first-year erosion rates of the beach nourishment and alongshore transport only contributed about 15% to 40%, most erosion being produced under energetic wave conditions, and mild to moderate waves propagating without breaking over the nourishment [11].
In [12,13], high energy events, especially the first storm, sediment grain size, project extent, and longshore transport gradients have been reported as important factors in the first-year response of shoreface beach nourishments in a micro-tidal environment on the Florida Gulf Coast.
Improvements in alongshore sediment transport physics and in the knowledge on mechanical properties of sediment and placement, besides wave climatology forcing during the project, would lead to better prediction of project evolution [14]. The behavior of shoreface nourishment is not well understood [11] and it may be less effective if large beach nourishments are carried out in places where the possible beach response has not been previously well documented [14]. That is the case for many sand beaches in developing countries.
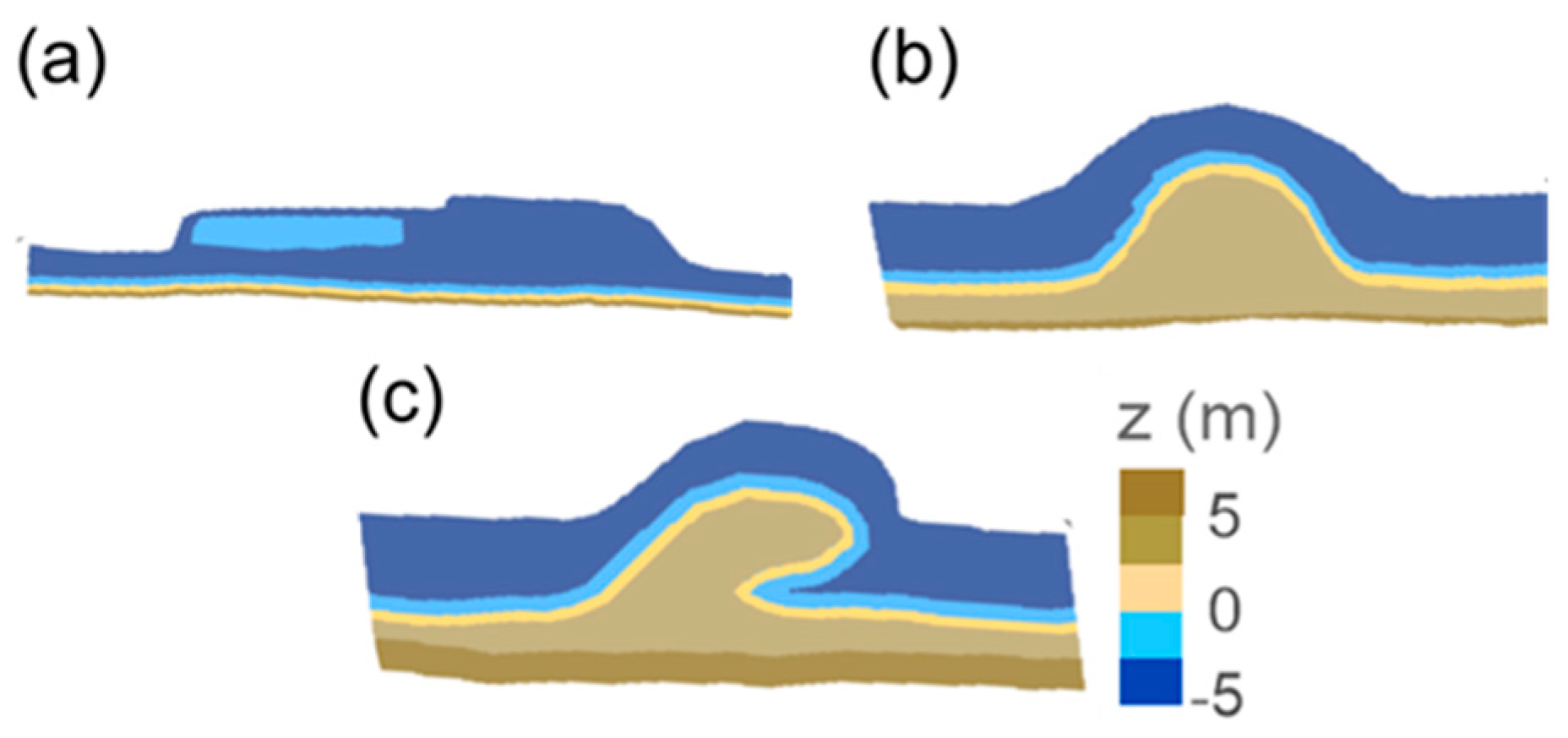
Modern coastal engineering requires sustainable coastal zone development that is compatible with the natural environment [15,16], thus Building with Nature (BwN) approaches are increasingly sought. In 1990, the Dutch government stated that beach nourishment was the preferred option in adapting to climate change. In consequence, an innovative large scale “sandscaping” beach nourishment project was begun in the Netherlands, using the so-called ‘Sand Motor’, ‘Zandmotor’, or ‘Sand Engine’ strategy [17,18,19,20]. An enormous volume of sand, approximately 20 Mm3 (~10,000 m3/m), was put onto the beach face between Ter Heijde and Kijkduin, in South Holland, from the low water mark to a distance of several kilometers off the coast, 20 m deep. The natural re-distribution of sediments to the nearby beaches and dunes is taking place through the action of wind, waves, and currents over several years [17]. The main objectives of this innovative BwN solution [17,19,21] were the creation of recreational areas that were environmentally safe. The project uses the local hydrodynamics in order to induce sedimentation through natural beach processes, rather than mechanical means, which can produce unfavorably steep beach slopes or bury marine organisms in the sand. Several Sand Engine designs were discussed before the pilot project was untaken in 2011, such as Full beach face nourishment, Peninsula or bell-shaped nourishment and the Hook configuration, which was eventually selected, Figure 1. This design was recommended for South Holland in the EIA (Environmental Impact Assessment, 2010), based on costs, safety, environmental and recreational criteria [17].
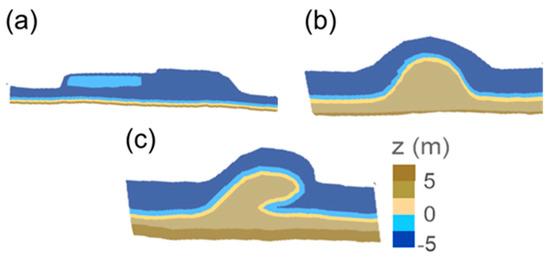
Figure 1.
Three types of Sand Engine design (after [15]: (a) beach face nourishment; (b) bell-shaped nourishment; (c) hook-shaped nourishment.
Systematic field monitoring combined with numerical modelling, on a monthly and yearly basis, allows the processes and mechanisms that govern the dynamic of the Sand Engine to be forecasted, in the short and long term. The computation of the Delft3D model showed similar morphological behaviors for the three alternative designs described above, in the long term (20–50 years), with a nourishment lifetime of some twenty years [17]. The longshore sediment transport rate was the key parameter in defining how fast the Sand Engine shape would be eroded and the sediment be spread along the beach [22]. The numerical results show the greatest changes occur in the six months after construction, a moderate evolution in the following 12 months and asymptotic stabilization after the first year, as the slope and the new coastline reached an almost stable shape [22,23].
The results of the Defl3D model showed wave forcing to be the most important process in the initial morphological changes induced by the Sand Engine (accounting in the first year for 75% of the total volume lost) [24]. A linear beach face evolution was found; the duration of a storm event had greater effect than the magnitude of the maximum waves during a storm. This suggests that less energetic wave episodes, with a high probability of occurrence, were also important in the Sand Engine response in the first year [24,25].
The tidal range was found to be the second most important factor contributing to the morphological behavior of the Sand Engine; 17% of volumetric sediment loss was due to this, while less than 5 % of the total erosion was caused by surge, wind, and horizontal tidal forcing [24]. The combination of energetic wave conditions, strong winds, and high storm surge levels can lead to high sediment transport rates and therefore intense erosion [26]. The majority (~70%–72%) of the sediment lost from the Sand Engine was found to accrete in adjacent coastal sections and dunes, and this alongshore spread was strongly related to incident waves [23,24,27]. On the other hand, small wave heights produced mainly cross-shore sediment transport [23].
Similar estimations were also obtained from the application of other numerical models, such as the MIKE21FM shoreline model [28].
Several field monitoring techniques were used to validate the numerical results: (1) aerial photographs were used for observations [19], (2) remote sensing methods and in-situ measurements of the spatial and temporal variability of the Sand Engine [29], (3) field campaigns to measure water levels inside the hook-shaped lagoon [30], (4) a six-week campaign in the autumn of 2014 monitored the spatial variations in aeolian sediment transport [31], and (5) new methods of automated shoreline detection from satellite images [32].
In this paper, experiences from the Sand Engine project were applied for a beach in Mexico with more than ten years of continuous monitoring. This nourishment aims to improve beach conditions by natural processes. This beach seems to be promising for the long-term sediment dispersal of a micro Sand Engine project. A natural accumulation of sand very close to the breakwater of the marina has been observed in the past, which can be used as a sand budget for periodic reloading of the Sand Engine.
2. Study Area
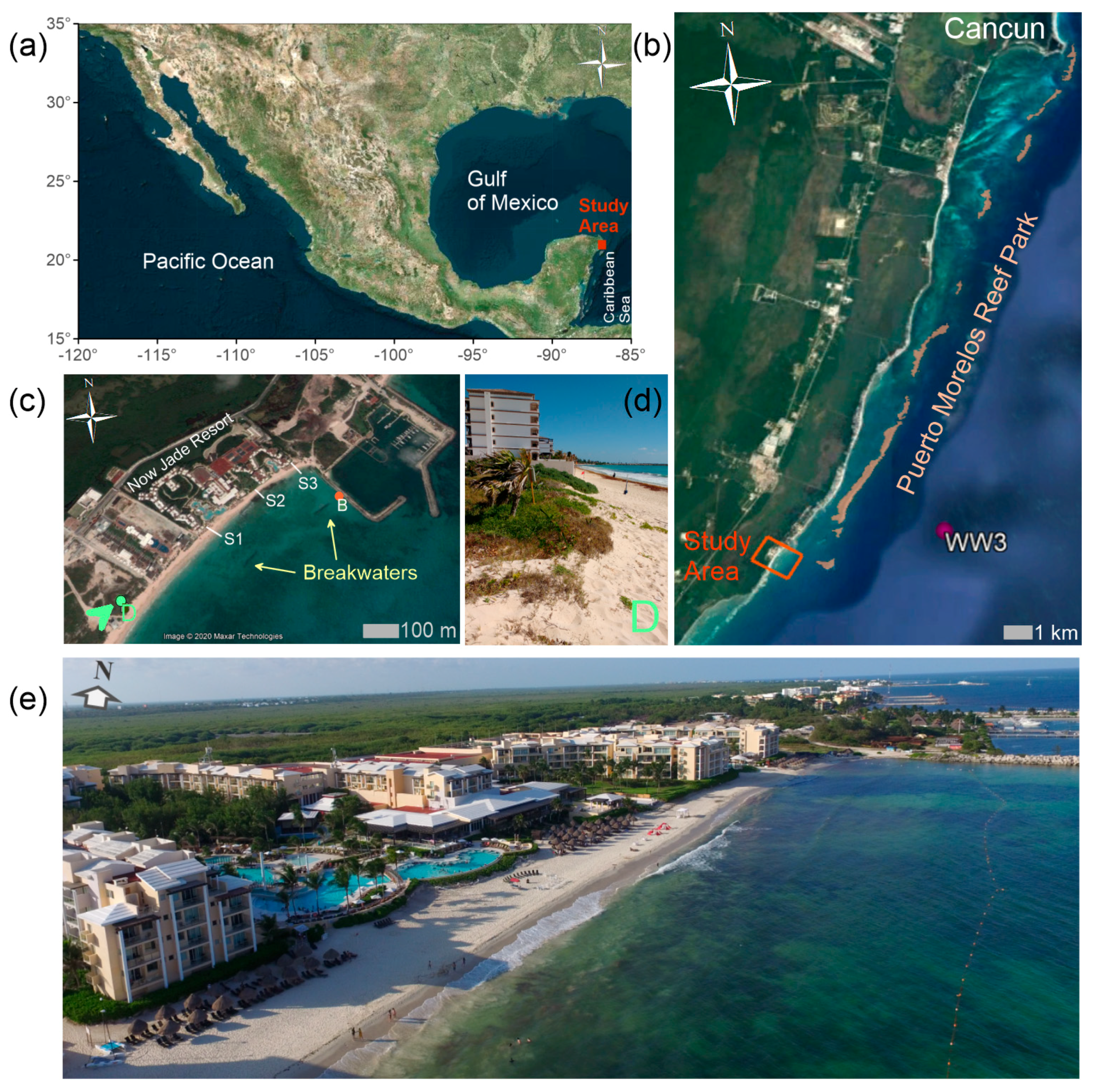
The study area is near Puerto Morelos, in the NE of the Yucatan peninsula, in the state of Quintana Roo, on the Mexican Caribbean, 30 km south of the famous tourist destination of Cancun (Figure 2). The coastal stretch of the study area is the beach front of the Now Jade Riviera Cancun Resort, which is around 400 m in length (see Figure 2c,e). To the north, the area is limited by the Puerto Morelos marina. A considerable mangrove extension is the main land cover behind the shoreline.

Figure 2.
The study area: (a) general location; (b) Coast at Puerto Morelos; (c) aerial view of the Now Jade resort; (d) existing dunes, 250 m south of the study area, taken 26 April, 2017; (e) aerial view, taken 12 August 2019.
The climate of the region is tropical, with two main seasons, winter and summer, in terms of wind patterns and air temperature. Winter (from November to March or April) is characterized by the passages of cold fronts, locally known as ‘Nortes’, with a wind direction from the northeast from October to February, though with the presence of winds from the north and the southeast following the cold fronts. In summer, the frequent storms and tropical cyclones define the patterns [33]. 90% of the records at buoy 42056 (NDBC-NOAA) show a relatively small significant wave height (<1 m) and small wave periods (<8 s), and thus the predominance of locally generated seas [34]. The fine sand is the results of this wave climate, but under hurricane conditions the beaches are very vulnerable to dramatic erosion processes. The beach is composed of medium carbonate sand of biogenic origin, with a mean sediment size of ~0.258 mm.
The beach is microtidal, predominantly semi-diurnal, with a mean tidal range of ~0.17 m, with spring and neap tidal ranges of 0.32 and 0.07 m, respectively [33]. Under extreme storm conditions, the storm surge is considered the most important threat. During hurricane Wilma, in October 2005 it reached 2.5 m at the beach (0.5 m in deep water) [34].
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Beach Evolution from Satellite Images and Fied Data
Ten satellite images taken from Google Earth (0.5-m resolution) were used to analyze the evolution of the hotel construction and the dry beach changes in the study area, in the period from 2004 to 2017. Topographic surveys were also carried out on 30 October 2012 and 26 April 2017 using a LEICA 3D scanner with 1–2 mm of precision, for the analysis of the beach evolution. Cross-shore profiles started at the limit of the hotel and extended to the submerged beach at a depth of 0.3 m. Nearshore bathymetric data were acquired using a double-frequency echosounder and complemented with 4 m resolution bathymetric data available from the National Biodiversity information system (http://www.conabio.gob.mx/informacion/gis).
3.2. Offshore Wave Data and Numerical Model Description
3.2.1. Offshore Wave Data
Hindcast data from the WAVEWATCH III model (WW3) provided the wave database for 1 February 2005 to 1 June 2019. Times series of wave data, composed of sea states at 3 h intervals, were supplied at 60 m depth, 4.5 km offshore, with coordinates 20.8333° N 86.8333° W (see Figure 2b). A storm was defined as an event with a significant wave height exceeding 1.6 m [35].
3.2.2. Numerical Model Description
The XBeach [36] numerical model was used to estimate the wave and current fields as well as the morphological evolution of the nourishment for six scenarios. The wave conditions were modelled using a Jonswap wave-spectrum with 30-h simulations, when morphological convergence was found.
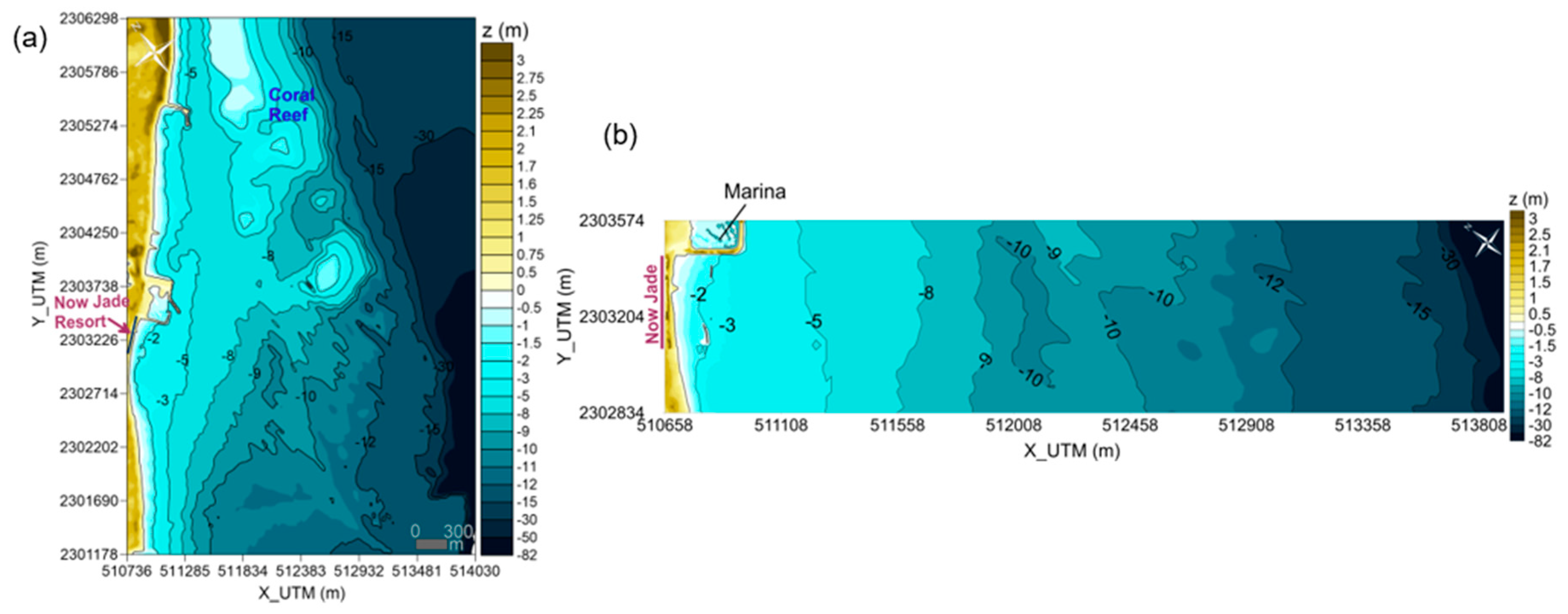
Two sets of rectangular meshes were constructed to incorporate the bathymetric and topographic data into the model, from deep water to the inland limit of the study area of the Now Jade resort. The general mesh includes part of the coral reef and surrounding area, in order to avoid the possible effects of the nourishment to the ecosystem and adjacent beaches (Figure 3a). Secondly, a higher resolution mesh was constructed for a more accurate simulation of the processes directly induced by the project (Figure 3b). Squared, 8 m long cells were used for the numerical modelling in the general mesh; whilst a cell size varying from 15 to 1 m was selected for the computation of the fine grid mesh. The study on the general mesh was carried out through the comparison of the results for two different seabed configurations with and without the micro-Sand Engine.
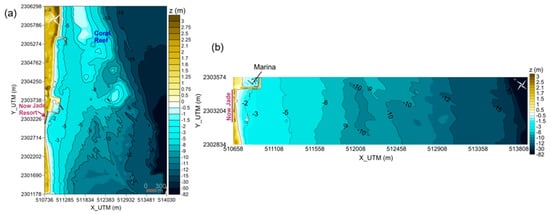
Figure 3.
Bathymetric data within the domain of the simulation grid meshes for XBeach model: (a) general mesh; (b) detailed mesh.
4. Results
4.1. Beach Evolution & Diagnosis
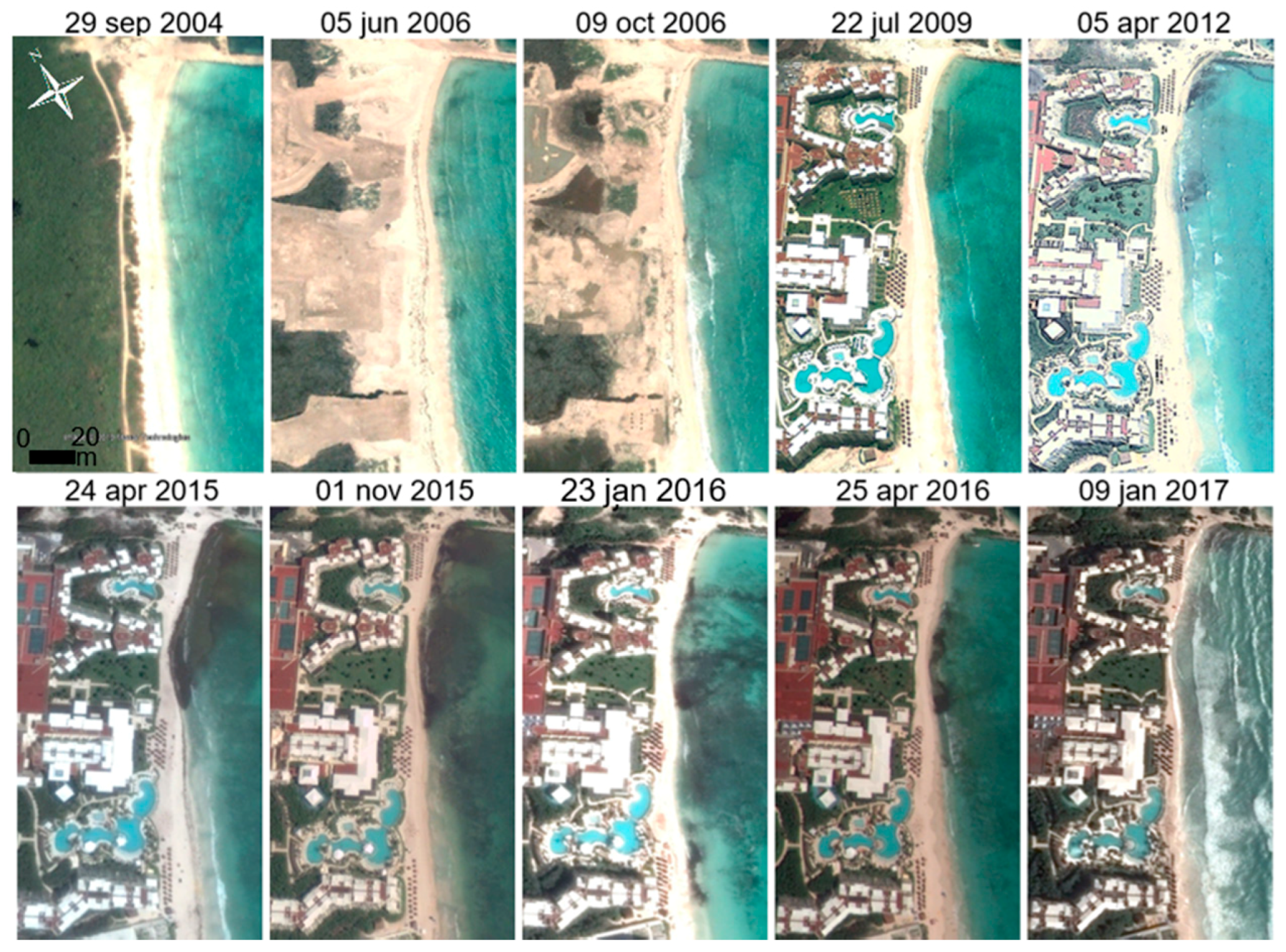
The evolution of the dry beach and the construction works of the hotel is illustrated in satellite images from 2004 to 2017 (Figure 4). Of note are a small dune extending longitudinally along the coast before the hotel was built (see image from 2004 in Figure 4 and the dune in Figure 2d), and the reduced width of the dry beach in the northern half of the study area at various dates in the period.

Figure 4.
Evolution of the dry beach from 2004 to 2017 (Source: Google Earth).
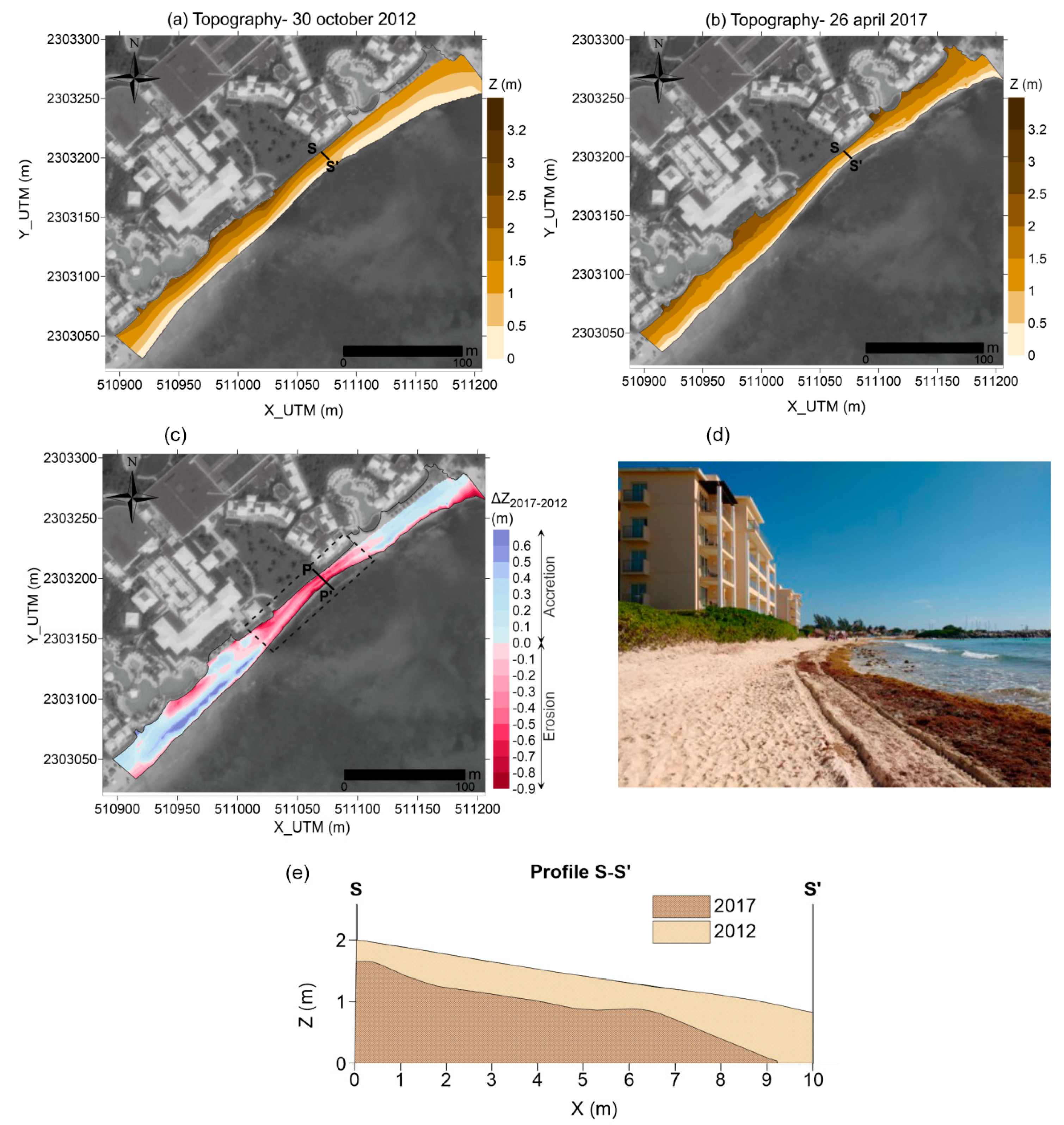
The quantification of the total sediment balance given by topographic surveys (LEICA 3D scanner with 1–2 mm resolution) on 30 October 2012 (Figure 5a) and 26 April 2017 (Figure 5b) gave a total loss of 77 m3, with a maximum value of 516 m3 in the central area of the beach (highlighted by a rectangle in Figure 5c). Approximately 7 m in width and 0.9 m in elevation were lost in the most critical beach section (section P-P’ in Figure 5c,d), located 130 m from the northern end of the beach, reaching a minimum width of 9 m. The gain of sediment observed (in blue in Figure 5c), principally in the southern area, was related to the protection offered by two submerged breakwaters, constructed in 2010 and 2012 at 2 m depth, of 60 and 45 m long in the south and north, respectively, of the beach [37] (Figure 2c). Despite the protection of these structures, chronic erosion was still produced on the beach in subsequent years, especially in spring (April), as shown in the satellite images from 2015 to 2017 (Figure 4). This situation frequently leads to a beach state that is less desirable for recreational use by tourists in the high-season (personal communication with the hotel manager), and increases the flooding risk under the dominant wave climate of the region.
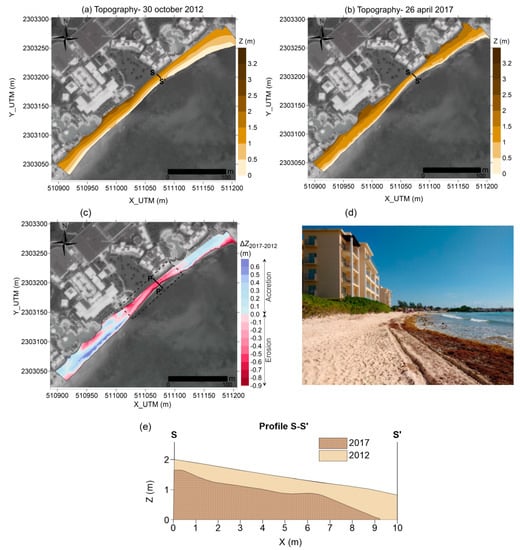
Figure 5.
Results of the topographic surveys with a LEICA 3D scanner: (a) 30 October 2012; (b) 26 April 2017; (c) variation of the elevation within the period; (d) view of the beach section most eroded in 2017 (section P-P’ in Figure 5c); (e) Transverse profile S-S’ to show the sediment lost in the dry beach section most affected.
4.2. The Micro Sand Engine Project
Given the importance of taking measures to protect the coastal zone and preserving the environment in the study area, the innovative strategy called Micro-Sand Engine was proposed. The concept is based on massive Sand Engine nourishment, but on a very small spatial scale. The novel solution is intended to work in fragile areas. A small, artificial beach nourishment would be quick and easy to perform, and cost effective. It also avoids the intense sediment movement of traditional beach nourishment programs and thus prevents damage to the surrounding ecosystems (coral reef in this case). In turn, the natural distribution of the sand beach nourishment will be deposited in accordance with the natural shape and slope of the natural beach.
The project is complemented by building a small coastal dune, designed to provide a sand reservoir and thus strengthen the beach profile.
Design of the Micro Sand Engine and Sand Dune
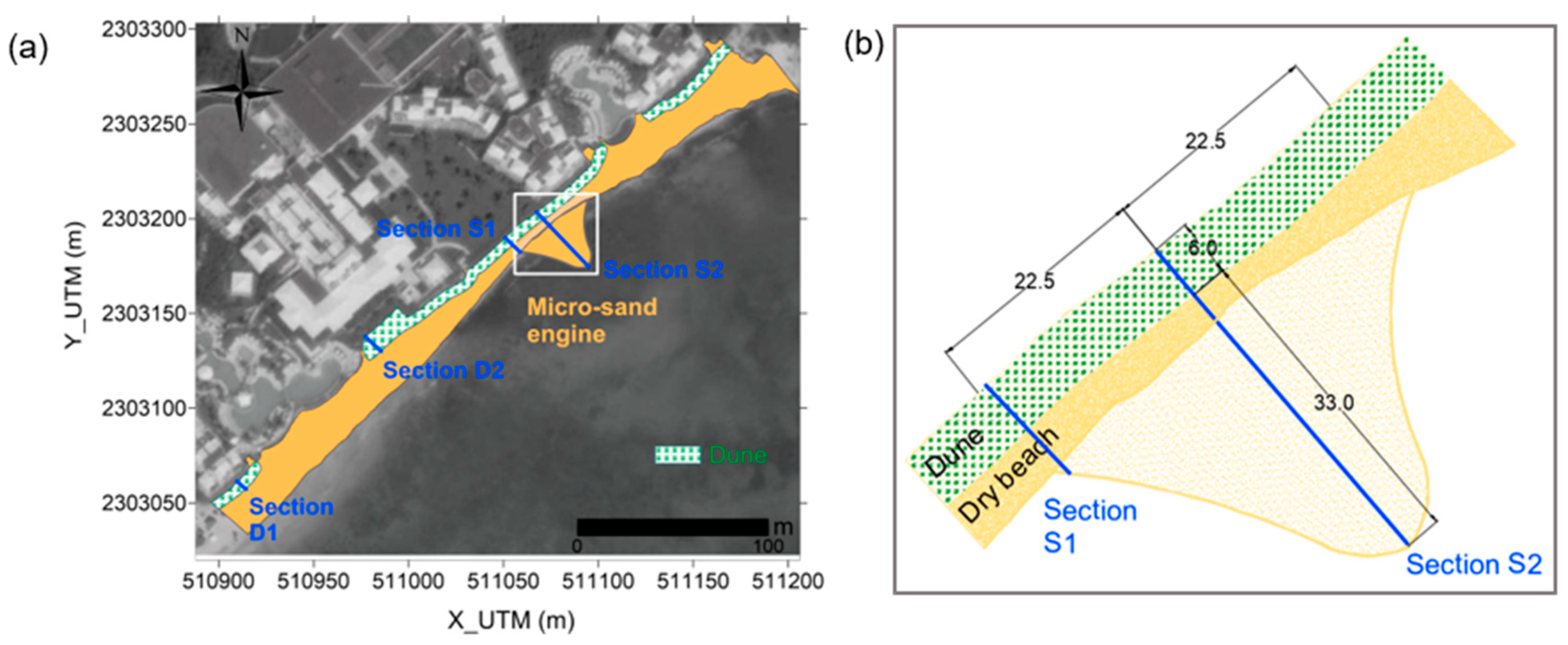
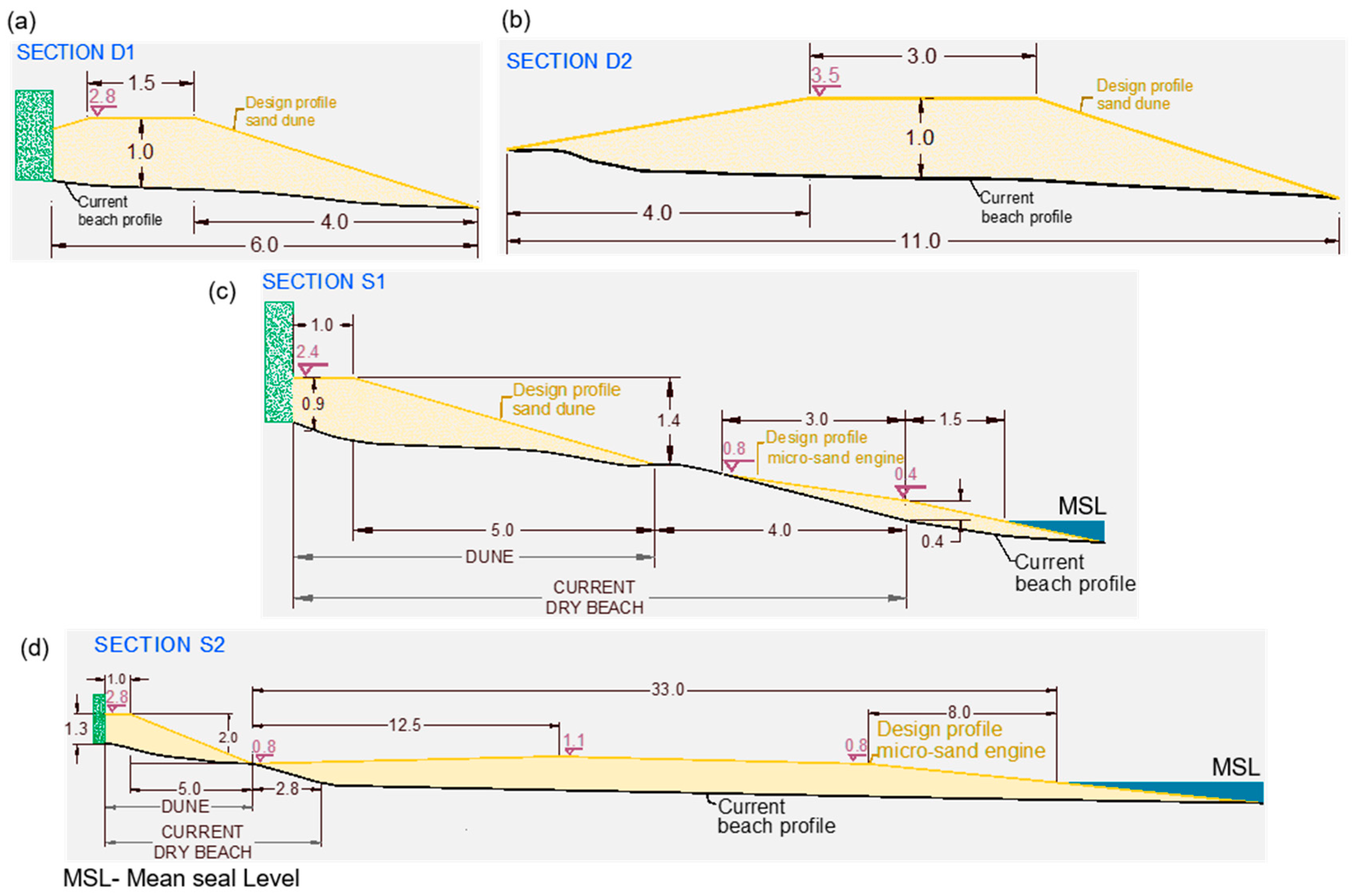
Although the ‘hook’ was the preferred Sand Engine shape, the ease of construction and the small dimensions of the beach led to the ‘bell-shape’ being used in the study area. The salient dimensions are 33 m long in transversal direction (reaching 0.5 m depth), and 45 m alongshore, covering the beach section most affected by erosion (Figure 6). A maximum elevation of 0.8–1.1 m above the mean sea level was defined for the micro Sand Engine, considering the historical beach evolution (see ‘Section S1’ and ‘Section S2’ in Figure 7).
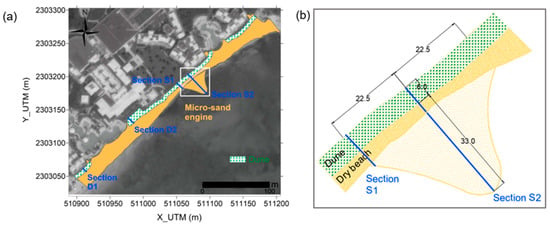
Figure 6.
Aerial view of the coastal protection strategy, taking the beach of 26 April 2017 as a baseline: (a) the micro Sand Engine and the dune; (b) detail of the micro-Sand Engine shape (dimensions in meters).

Figure 7.
Beach profile designs: (a,b) coastal dune; (c,d) micro Sand Engine.
The coastal dune extends along almost all the hotel beachfront, with the exception of the area in front of the swimming pools, due to their higher elevation and for the aesthetic perception of the hotel guests. It is shown as a dotted green rectangle in Figure 6a. The shape and size of the dune sections are shown in the transversal profiles of Figure 7: 1 m high and 6 m wide for almost all the dune (Section D1 of Figure 7a) and a wider dune (11 m width) distributed in a length of 30 m, taking advantage of a wider beach section to create a larger sand reservoir (Section D2 of Figure 7b).
The sediment source for the project, as mentioned previously, is very close to the breakwater alongside the marina (B, in red, Figure 2c). It is important to note that the shoal formed there is 150 m from the shore; far enough offshore for it not to travel naturally to the beach, but close enough to easily be pumped to the micro Sand Engine, from a depth of around 2–2.5 m. A sediment compatibility analysis was performed to validate the characteristics of the borrowed sediment as filling material. Seven sediment samples were taken at different locations along three transverse beach profiles (Sections S1, S2, and S3 in Figure 2c). The grain size of the borrowed sediment was slightly finer than the native sample at the micro Sand Engine site (Section S2 of Figure 2c), with a D50 of 0.220 mm vs. 0.267 mm, but appropriate considering a overfill factor of 1.3. A total nourishment volume of 2443 m3 would be required for the project, of which 964 m3 would be used for the micro Sand Engine and 1479 m3 for the dune sections.
The monitoring program of the project includes a monthly survey of beach profiles to determine the necessity of a new beach nourishment.
The morphological evolution of the micro Sand Engine, which is expected to be constructed in 2020, was assessed numerically, for the mild and energetic wave conditions typical of the area. The results are presented in Section 4.3.2.
4.3. Modeling the Morphological Response of the Micro Sand Engine
4.3.1. Modeled Wave Scenarios
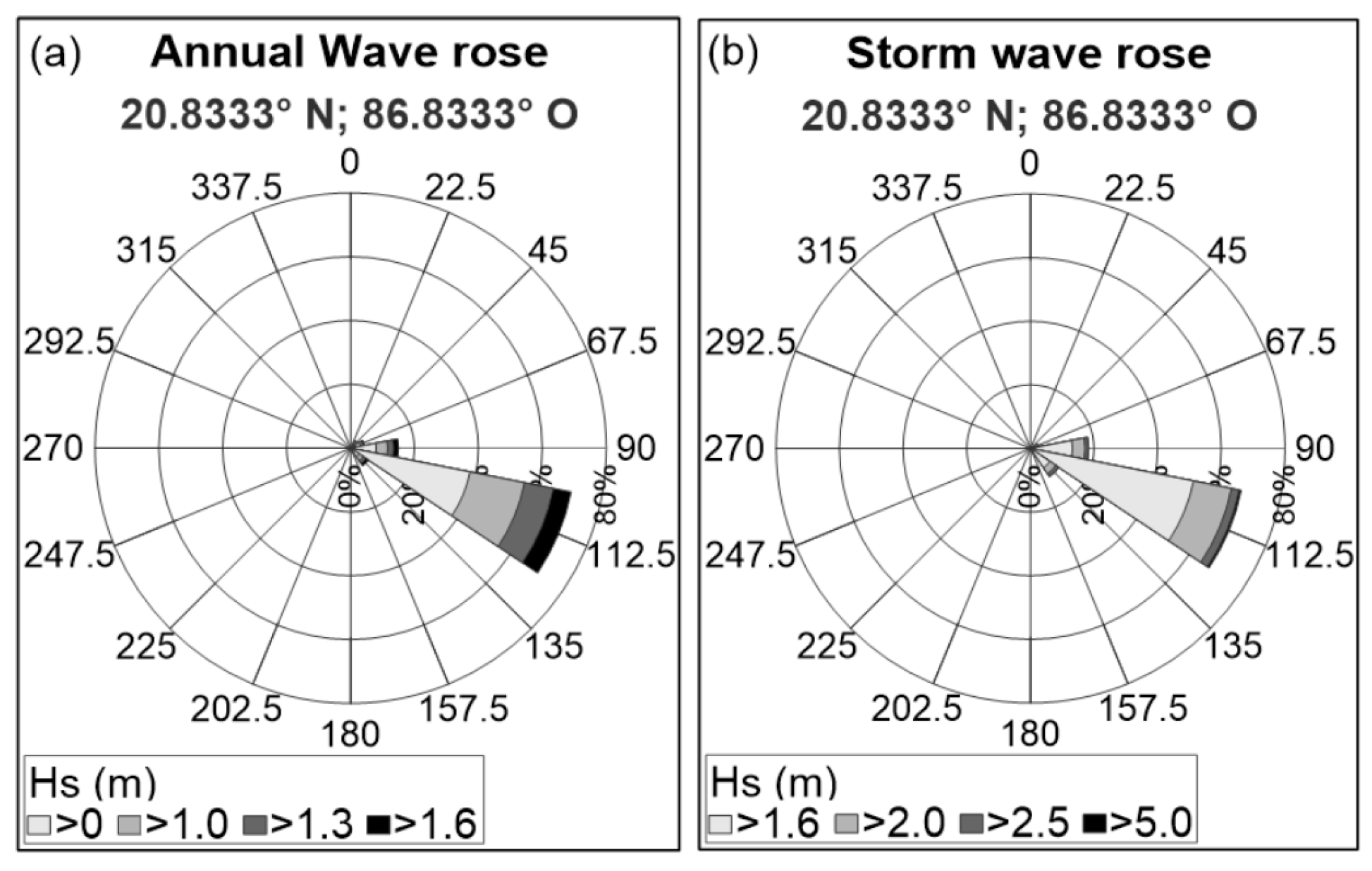
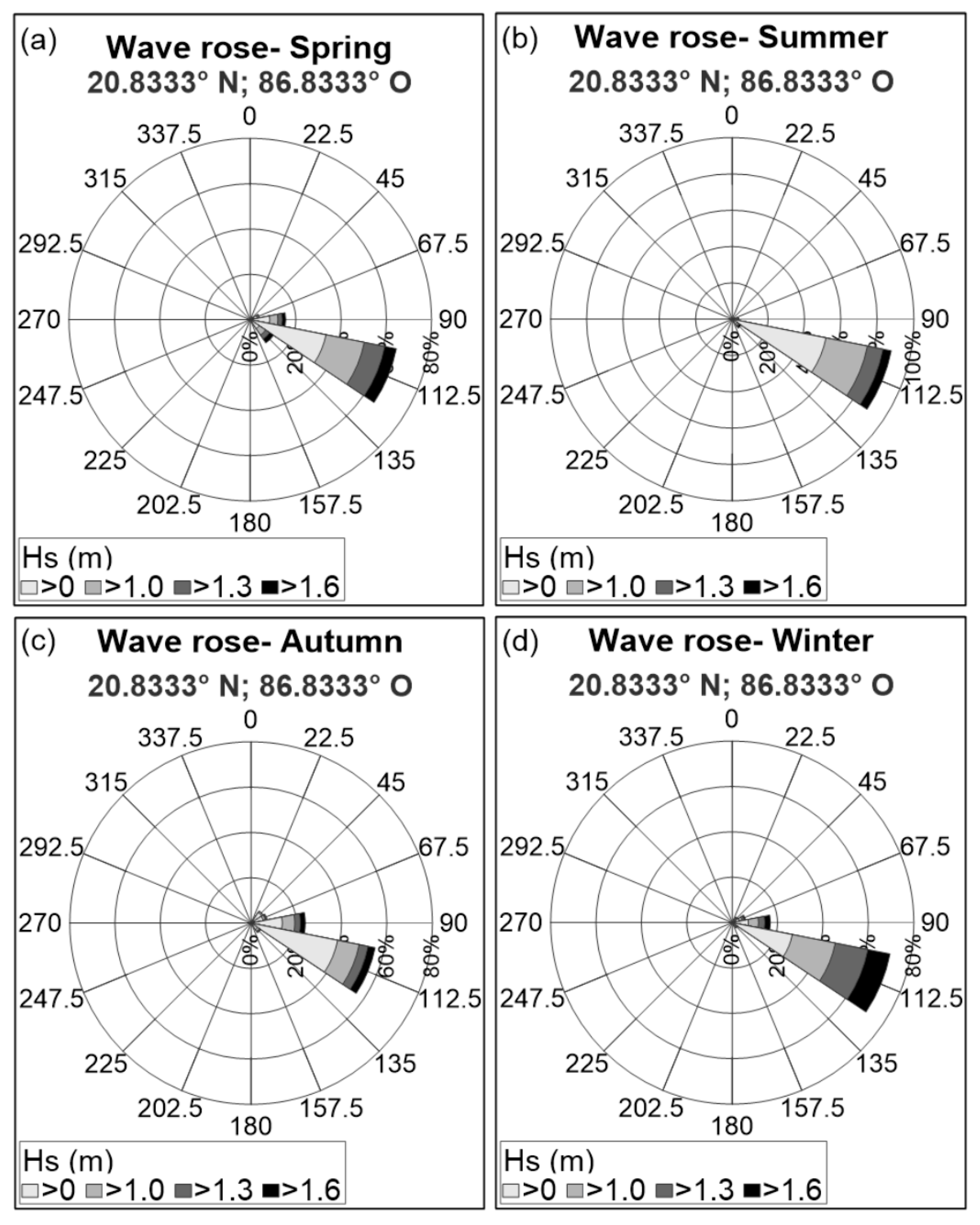
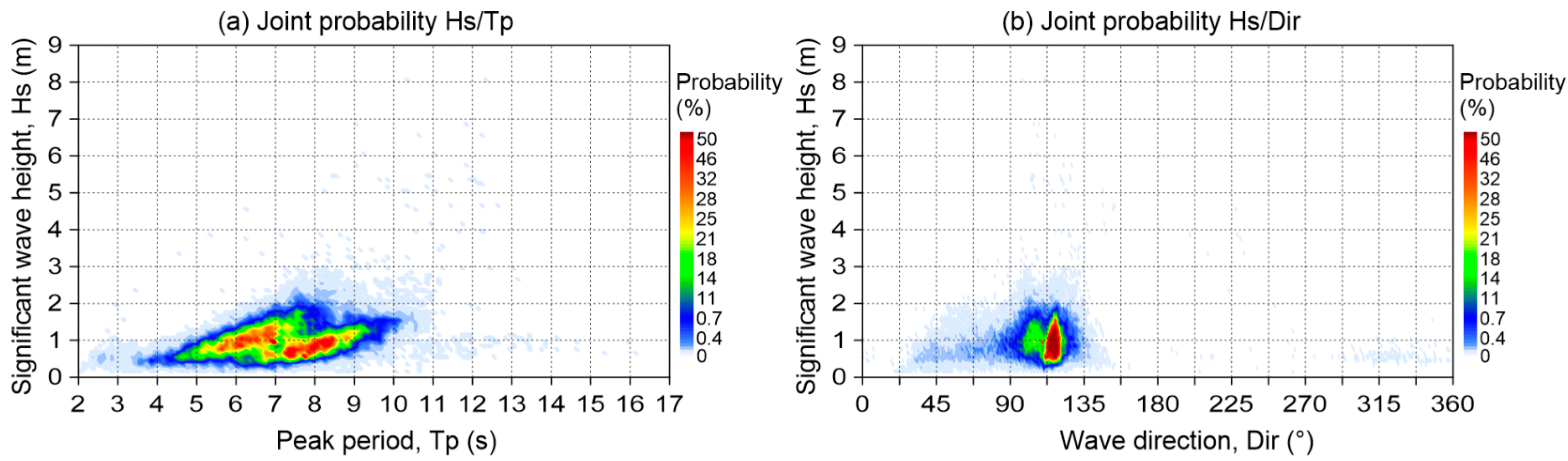
The wave roses presented in Figure 8 and Figure 9 and the joint probability of Hs (significant wave height), Tp (peak period), and Dir (wave direction), in Figure 10, show calm conditions that dominate throughout the year, with a significant wave height of less than 1.6 m, coming from the east-southeast direction (Figure 8a and Figure 10b), and peak periods of 6 to 8 s (Figure 10a). In storm conditions, waves from the east to the southeast sectors were frequent, with peak periods of 7 to 10 s (Figure 8b and Figure 10), though also with a prevalence of those in the east-southeast. In the seasonal wave roses (Figure 9), storm waves from the north-northeast are also present in Autumn due to ‘Nortes’, though with very a low frequency of occurrence.

Figure 8.
Wave roses: (a) annual; (b) storm conditions.
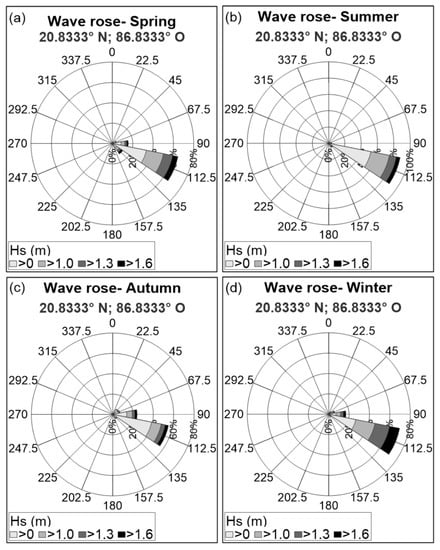
Figure 9.
Seasonal wave roses: (a) Spring; (b) Summer; (c) Autumn; (d) Winter.

Figure 10.
Joint probaility Hs, Tp, Dir: (a) Hs/Tp; (b) Hs/Dir.
The seasonal wave roses show the storms typical of the area: (1) waves from the east-northeast, in autumn and winter, due to cold fronts; (2) frequent eastern storms throughout the year, except in the summer; (3) storms producing waves from the east-southeast (more frequent in spring and winter) and southeast (principally in spring) (Figure 9).
Two wave scenarios were chosen as representative of calm, or non-storm, wave conditions: Hs= 1 m and peak period, Tp, of 8 s coming from the east and the east-southeast. To analyze the effects of typical storms of the region, four simulation scenarios of the most energetic waves were modelled (see Table 1). These scenarios did not consider hurricanes, since after the passage of these extraordinary wave and wind phenomena, substantial reconstruction work on the Sand Engine and the dune would be required. Sea level variation was not taken into account for the simulation scenarios due to the negligible astronomical tide and storm surge values of typical storms.

Table 1.
Definition of the numerical simulation wave scenarios.
4.3.2. Model Results
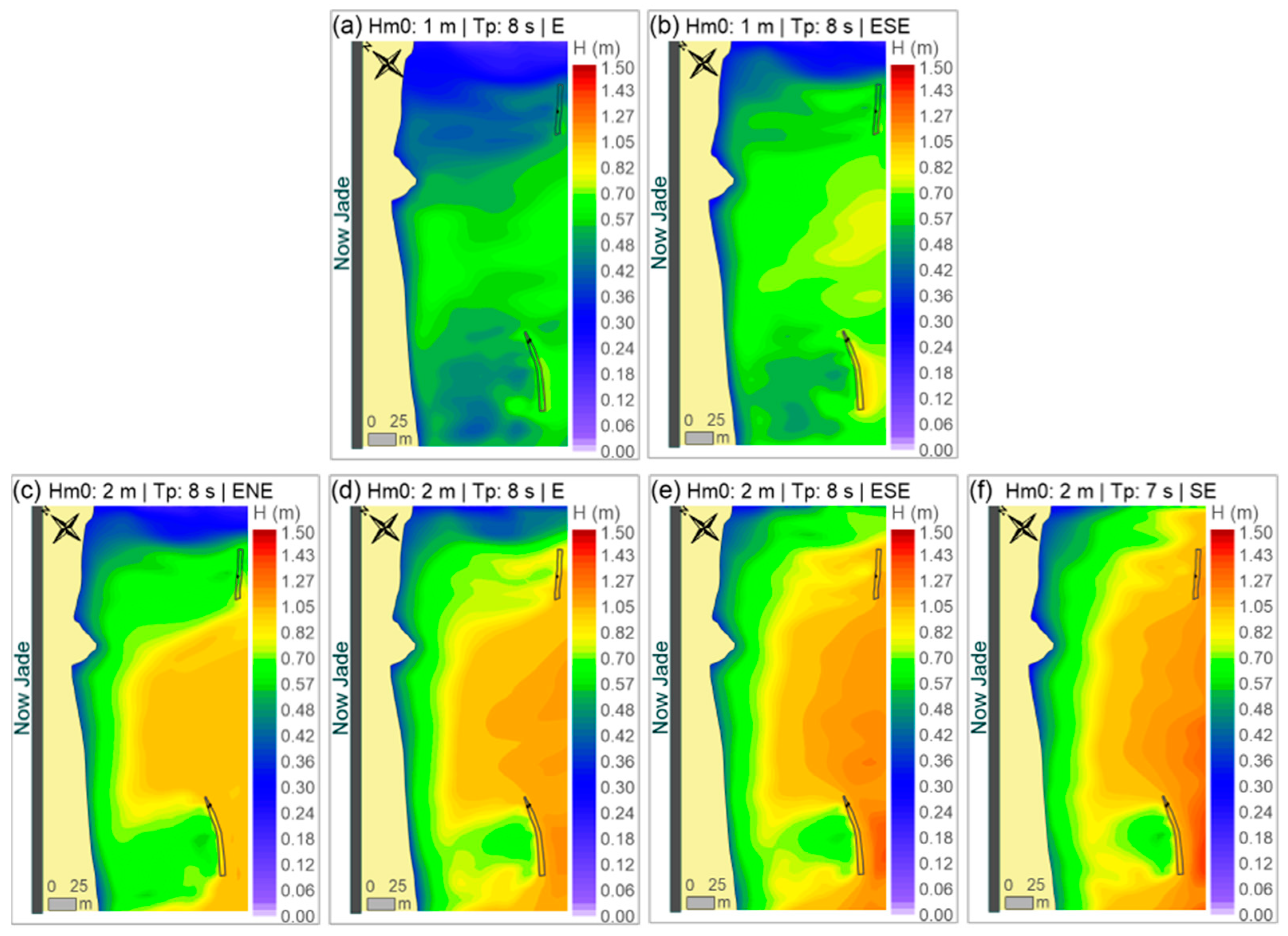
Using the general area grid, the numerical modeling predicted changes in the beach morphology only limited to the area of the nourishment. No effects were seen for nearby beaches or the coral reef. This is as expected, given the small scale of the project and the northward constraint to sediment movement of the marina. The fine grid mesh calculations show relatively high waves (~1 m) that reach the area in storm and even calm wave conditions. In particular, waves coming from the east-southeast and southeast directions seem to be the worst cases (Figure 11).

Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of wave heights for the scenarios simulated: (a,b) non-storm wave conditions; (c–f) storm wave conditions.
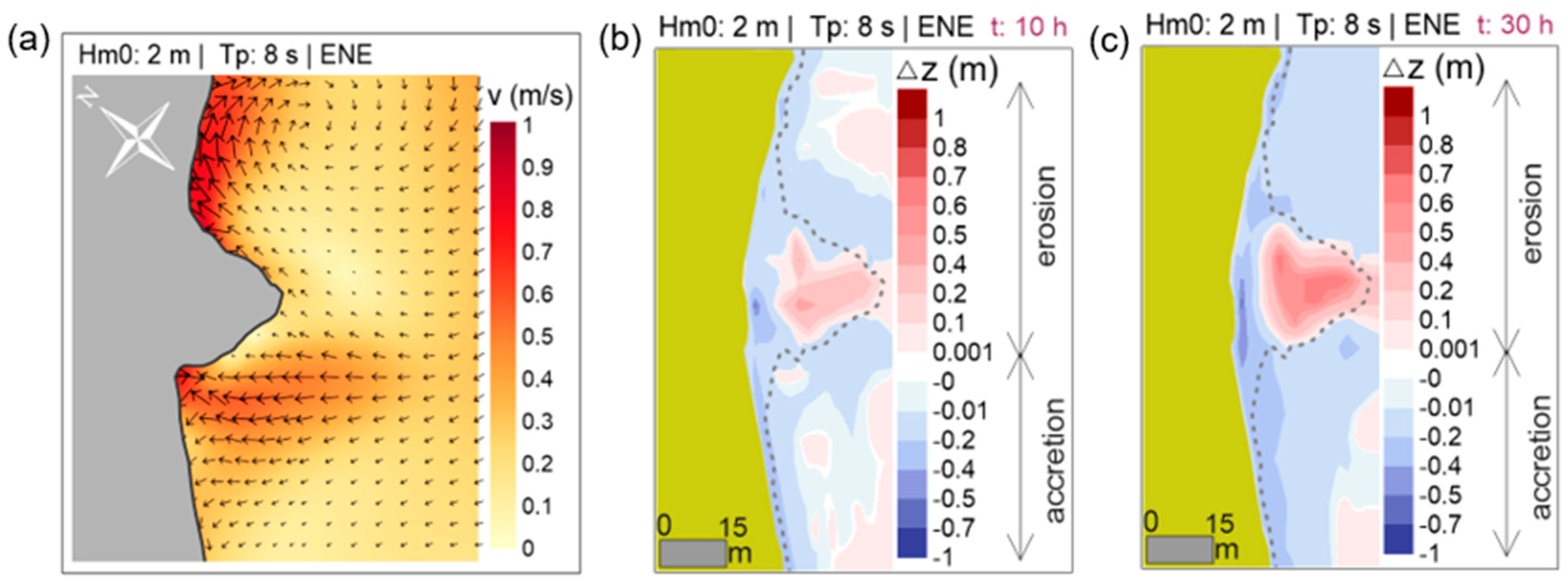
The marine processes redistribute the sediment along the beach, according to the wave energy and wave-induced currents that impact the Sand Engine. An example of the current field around the Sand Engine in its initial condition for a ‘Norte’ storm can be seen in Figure 12a. The morphological change due to these conditions after 10 h has been drawn in Figure 12b, and in Figure 12c, after 30 h. The computed sediment transport will benefit the narrowest beach sections of the hotel beachfront.

Figure 12.
Current field and morphological change of the micro Sand Engine for a ‘Norte’ storm (blue: accretion; red: erosion): (a) circulation of wave currents; (b) morphological change after 10 h of simulation; (c) morphological change after 30 h of simulation.
Figure 12 clearly shows that as the Sand Engine erodes, the adjacent beach areas benefit from the sediment distribution. In turn, the whole beachfront is expected to rise in elevation, improving its stability. Once the sand from the Sand Engine has been totally distributed, strong sea states could damage the beach, hence the need to reconstruct it periodically (it is foreseen that reloading the Sand Engine will be necessary every year, or once every two years).
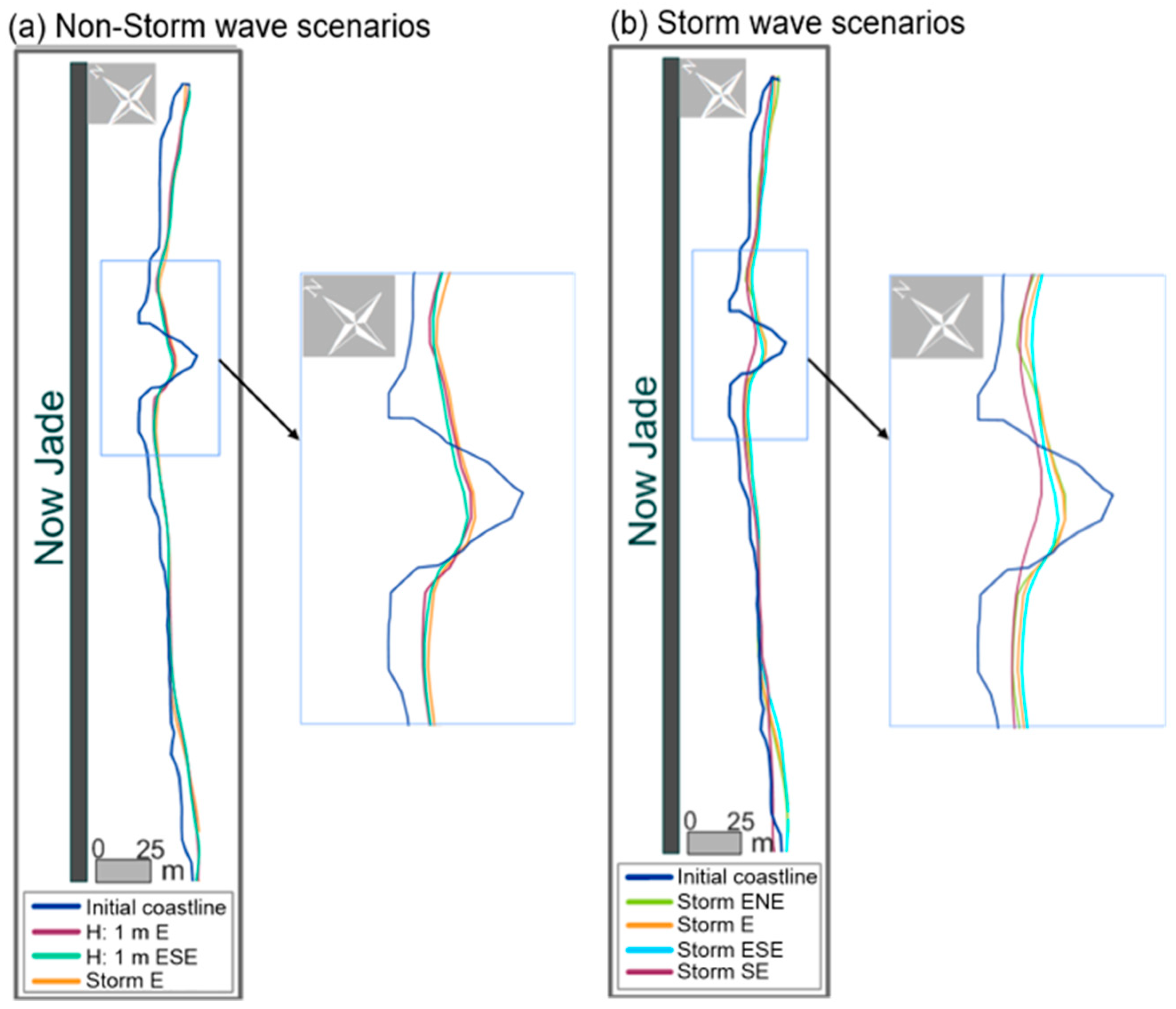
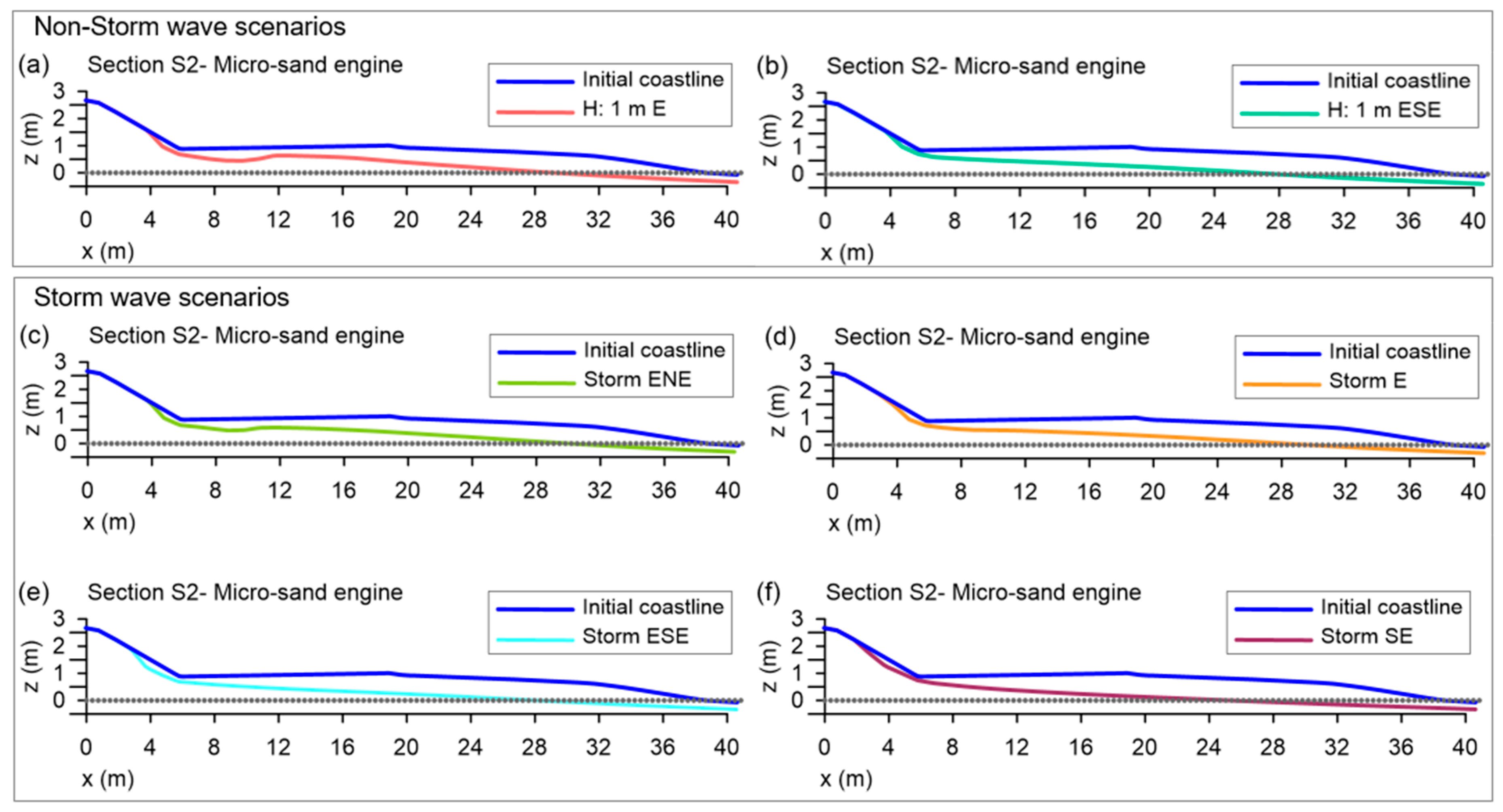
The degree of beach changes was more important with waves coming from the east-northeast, east, east-southeast, and southeast, respectively. It is interesting to note that the micro Sand Engine is eroded rapidly, but that the shape of the coastline becomes stable, keeping a small sand salient. Figure 13 shows that even for storm conditions (Figure 13b), the stable salient is present. Obviously, after the occurrence of several different sea states, particularly very intense ones, the salient will be removed and the beach will have to be reloaded. It is expected that maintenance of the Sand Engine will be needed annually, or biannually. Figure 14 shows the beach profile for Section S2 (Figure 7d). The final elevation of the profile is seen to be similar in calm and storm conditions, confirming that the salient remnant is stable and the beach is likely to remain sound for a determined time span.

Figure 13.
Coastline changes for the simulated scenarios (t: 30 h): (a) non-storm wave conditions; (b) storm scenarios.
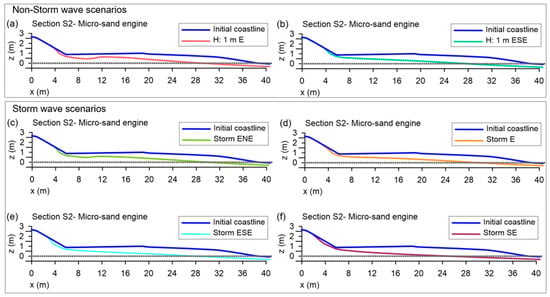
Figure 14.
Variations in elevations of the transverse profiles, defined by the symmetry axis of the micro Sand Engine, (Section S2 in Figure 7d) (t: 30 h): (a,b) non-storm wave conditions; (c–f) storm scenarios.
The computed morphological development of the project shows how the beach slope becomes milder, which is preferable for tourist activities, as the sand spreads north and south, (Figure 12b,c). As the sand of the nourishment is deposited onshore, the dry beach increases in the sections adjacent to the micro-Sand Engine, by a similar magnitude for the six wave directions, once stability is reached (Figure 13).
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Beach nourishment has been recognized as the preferred coastal protection alternative for more than 30 years [38]. Undoubtedly, the successes of mega-nourishments encourage the implementation of other large-scale projects [39]. Huge beach fills also offer benefits such as long useful lives and reduced maintenance frequency. These engineering works consume time, space, and require the management of heavy machinery both in the sea and on land. These requirements are not always feasible in recreational beaches, where the work must be planned to interrupt as little as possible tourist activities, or even be carried out alongside these. In such cases, the work should entail the least invasive activities possible and use equipment which is as light as possible. Unfortunately, little research has yet focused on understanding tourism in the context of the coastal environment, [40] nor on the impact on tourism of coastal protection activities. The micro Sand Engine proposed here is compatible with the needs of the tourism industry, as it can be performed quickly and with relatively small machines.
The micro Sand Engine performance was computed using the XBeach model. The Xbeach has shown good results in estimating coastal morphodynamics related to beach fills [41,42]. The results obtained in this work show quite a dynamic bell-shaped feature that rapidly cedes sand to its surrounding area. It has to be noted that the Xbeach model is known to overestimate erosion [43]; this means that the results of the micro Sand Engine fall on the safe side. Several other methods and models exist for the prediction of beach nourishment evolution [6,44,45]. Many of these models have shown good results, but as they were calibrated with measured data, their use is restricted to specific sites. Whenever a micro Sand Engine is constructed, a monitoring program is needed; then the numerical modelling could also be refined.
The analysis carried out in this paper shows that the Sand Engine strategy, carried out on a very small scale in Mexico, is an effective, economic, and sustainable measure for beach protection. Some of the benefits of the massive Sand Engine project, such as the environmental services of recreational functions of the beach, or its functioning as a sand reservoir to provide long-term coastal protection are also assumed to occur through this project.
The changes induced by this type of nourishment, concentrated in space and time, are expected to also show benefits in the damaged ecosystems nearby. Given the small spatial scale, with depths of less than 1 m with a mild beach slope, many of the disadvantages of traditional shoreface replenishments are expected to be avoided with the implementation of this project.
The XBeach numerical modeling showed that, under typical wave climate conditions of the region, the bell-shape micro Sand Engine in Puerto Morelos will redistribute the sediment along the beach at different speeds, depending on the direction and magnitude of the incident waves, which vary in frequency according to the seasons. The numerical results and the satellite images show that the most critical beach state was in spring, related to the higher frequency of storms from the east-southeast and southeast.
To validate the functioning of this protection measure, which will be greatly affected by other ecosystem restoration work, monitoring will be necessary. However, it is clear that the response of the micro Sand Engine is very dynamic.
The findings of this paper are encouraging for increased use of eco-friendly practices for coastal protection. The bell-shaped Sand Engine can be applied anywhere, worldwide, where small nourishments are required and maintenance work is feasible. It is hoped that this innovative solution can be a useful beach conservation strategy in places where limited sediment is available and where tourist activities have to be disrupted as little as possible.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E. and E.M.; methodology, M.E. and E.M.; software, M.E. and E.M.; validation, E.M. and R.S.; formal analysis, M.E.; investigation, E.M. and R.S.; resources, R.S.; data curation, M.E. and R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E.; writing—review and editing, E.M. and R.S.; visualization, M.E.; supervision, E.M. and R.S.; project administration, E.M. and R.S.; funding acquisition, R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by Promociones Marina Morelos S de RL de CV under contract 182017.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Now Jade Riviera Cancun Resort, for providing data and access to its facilities, especially to Eduardo Solla and Pablo Lucena.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- McKenna, J.; MacLeod, M.; Power, J.; Cooper, A. Rural Beach Management: A Good Practice Guide; Donegal County Council, Lifford, Co.: Donegal, Ireland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Buisson, P.; Rousset, A.; ANCORIM; Massey, J. ANCORIM—Overview of Soft Coastal Protection Solutions; BRGM/ONF: Bordeaux, France, 2012; 56p. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, G.; Abecasis, M.; Catena, M.M. Inland & Maritime Waterways & Ports. Proceedings of the Technical Sessions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gianou, K. Soft Shoreline Stabilization: Shoreline Master Program Planning and Implementation Guidance; Shorelands and Environmental Assistance Program, Washington Department of Ecology: Olympia, WA, USA, 2014; Publication No. 14-06-009. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Vu, M.T.; Nguyen, T.V. Evaluation of Beach Nourishment Performance in Ba Lang Beach Using Numerical Modelling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts, Singapore, 25–28 September 2019; pp. 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R.G.; Yoo, C.H. Beach-nourishment performance predictions. J. Waterw. Port. C-ASCE 1992, 118, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, P. Performance evaluation of a beach nourishment project at West Beach in Beidaihe, China. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 769–783. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, T.L., Jr.; Cheng, J.; Wang, R.; Manausa, M. Modeling of three beach fill projects. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karambas, T.V.; Samaras, A.G. Soft shore protection methods: The use of advanced numerical models in the evaluation of beach nourishment. Ocean Eng. 2014, 92, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, B.; Weilbeer, H. Numerical Modeling of Shoreface Nourishments in the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea. Coast. Struct. 2019, 2019, 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, B.J.; Walstra, D.J.R.; Radermacher, M.; de Schipper, M.A.; Ruessink, B.G. Observations and modelling of shoreface nourishment behaviour. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Roberts, T.M.; Elko, N.A.; Beck, T.M. Factors controlling the first year performance of eight adjacent beach nourishment projects, west-central Florida, USA. In Proceedings of the ICCE 2008: 31st International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 31 August–5 September 2008; pp. 2532–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.M.; Wang, P. Four-year performance and associated controlling factors of several beach nourishment projects along three adjacent barrier islands, west-central Florida, USA. Coast. Eng. 2012, 70, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, O.; Astrup, S.K. Project Building with Nature (EU-InterReg); Ministry of Environment and Food of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Waterman, R.E. Integrated Coastal Policy Via Building with Nature. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Vriend, H.J.; van Koningsveld, M.; Aarninkhof, S.G.; de Vries, M.B.; Baptist, M.J. Sustainable hydraulic engineering through building with nature. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, J.P.; Tonnon, P.K. Sand Engine: Background and design of a mega-nourishment pilot in the Netherlands. In Proceedings of the ICCE 2010: 32nd Conference on Coastal Engineering, Shanghai, China, 30 June–5 July 2010; Volume 30, pp. 3805–3814. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, J.P.M.; Stive, M.J. Zandmotor (Sand Motor): Building with nature. In Proceedings of the 25th ICID European Regional Conference, Integrated Water Management for Multiple Land Use in Flat Coastal Areas, Groningen, The Netherlands, 16–20 May 2011. Paper III-21. ICID. [Google Scholar]
- Stive, M.J.F.; De Schipper, M.A.; Luijendijk, A.P.; Ranasinghe, R.W.M.R.J.B.; Van Thiel De Vries, J.S.M.; Aarninkhof, S.; Marx, S. The Sand Engine: A solution for vulnerable deltas in the 21st century? In Proceedings of the Coastal Dynamics 2013: 7th International Conference on Coastal Dynamics, Arcachon, France, 24–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Slobbe, E.; de Vriend, H.J.; Aarninkhof, S.; Lulofs, K.; de Vries, M.; Dircke, P. Building with Nature: In search of resilient storm surge protection strategies. Nat. Hazards. 2013, 66, 1461–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.P.; van Oudenhoven, A. The Sand Motor: A Nature-Based Response to Climate Change. Findings and Reflections of the Interdisciplinary Research Program Naturecoast; TU Delft Publishers: Delft, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kaji, A.O. Assessment of the Variables Influencing Sediment Transport at the Sand Motor. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Schipper, M.A.; de Vries, S.; Ruessink, G.; de Zeeuw, R.C.; Rutten, J.; van Gelder-Maas, C.; Stive, M.J. Initial spreading of a mega feeder nourishment: Observations of the Sand Engine pilot project. Coast. Eng. 2016, 111, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.P.; Ranasinghe, R.; de Schipper, M.A.; Huisman, B.A.; Swinkels, C.M.; Walstra, D.J.; Stive, M.J. The initial morphological response of the Sand Engine: A process-based modelling study. Coast. Eng. 2017, 119, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.P.; Huisman, B.J.A.; De Schipper, M.A. Impact of a storm on the first-year evolution of the Sand Engine. In Proceedings of the Coastal Sediments, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kaji, A.O.; Luijendijk, A.P.; Van Thiel de Vries, J.S.M.; De Schipper, M.A.; Stive, M.J.F. Effect of different forcing processes on the longshore sediment transport at the Sand Motor, the Netherlands. In Proceedings of the ICCE 2014: 34th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Seoul, Korea, 15–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- De Schipper, M.A.; De Vries, S.; De Zeeuw, R.C.; Rutten, J.; Ruessink, B.G.; Aarninkhof, S.G.J.; Gelder-Maas, V. Morphological development of a mega-nourishment; first observations at the Sand Engine. In Proceedings of the ICCE 2014: 34th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Seoul, Korea, 15–20 June 2014; Volume 34, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kaergaard, K.; Droenen, N. A Hybrid Shoreline Model for the Sand Engine: Comparison with Observations and Long Term Predictions. In Proceedings of the The Proceedings of the Coastal Sediments, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wengrove, M.E.; Henriquez, M.; De Schipper, M.A.; Holman, R.; Stive, M.J.F. Monitoring morphology of the Sand Engine leeside using Argus’ cBathy. In Proceedings of the Coastal Dynamics 2013: 7th International Conference on Coastal Dynamics, Arcachon, France, 24–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, S.; Radermacher, M.; De Schipper, M.A.; Stive, M.J.F. Tidal dynamics in the Sand Motor lagoon. In Proceedings of the E-proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hoonhout, B.; de Vries, S. Field measurements on spatial variations in aeolian sediment availability at the Sand Motor mega nourishment. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenaars, G.; de Vries, S.; Luijendijk, A.P.; de Boer, W.P.; Reniers, A.J. On the accuracy of automated shoreline detection derived from satellite imagery: A case study of the Sand Motor mega-scale nourishment. Coast. Eng. 2018, 133, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, C.; Candela, J.; Iglesias-Prieto, R.; Sheinbaum, J.; López, M.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J. On the circulation in the Puerto Morelos fringing reef lagoon. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño-Tapia, I.; Enriquez, C.; Silva-Casarín, R.; Mendoza-Baldwin, E.; Mancera, E.E.; Ruiz-Rentaría, F. Comparative morphodynamics between exposed and reef protected beaches under hurrricane conditions. In Proceedings of the ICCE 2014: 34th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Seoul, Korea, 15–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.; Ruíz, G.; Posada, G.; Pérez, D.; Rivillas, G.; Espinal, J.; Mendoza, E. Atlas de Clima Marítimo de la Vertiente Atlántica Mexicana; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Mexico City, Mexico, 2008. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Roelvink, D.; van Dongeren, A.; McCall, R.; Hoonhout, B.; van Rooijen, A.; van Geer, P. XBeach Manual. Model Description and Reference Guide to Functionalities; UNESCO-IHE Institute of Water Education and Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.; Mendoza, E.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Martínez, M.L.; Escalante, E. An artificial reef improves coastal protection and provides a base for coral recovery. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 75, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.G. Additional Sediment Input to the Nearshore Region. Shore Beach 1997, 55, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.M.; Phelps, J.J.C.; Barkwith, A.; Hurst, M.D.; Ellis, M.A.; Plater, A.J. The effectiveness of beach mega-nourishment, assessed over three management epochs. J. Environ. 2016, 184, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, Y.L.; Osleeb, J. Determinants of coastal tourism: A case study of Florida beach counties. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.J.; Esteves, L.S.; Rochford, L.A. Modelling storm responses on a high-energy coastline with XBeach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2015, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffini, G.; Briganti, R.; Alsina, J.M.; Brocchini, M.; Dodd, N.; McCall, R. Numerical Modeling of Flow and Bed Evolution of Bichromatic Wave Groups on an Intermediate Beach Using Nonhydrostatic XBeach. J. Waterw Port C-ASCE 2020, 146, 04019034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.M.; Oumeraci, H. Effect of beach slope and grain-stabilization on coastal sediment transport: An attempt to overcome the erosion overestimation by XBeach. Coast. Eng. 2017, 121, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, P.A.; Dean, R.G. Assessment and prediction of beach-nourishment evolution. J. Waterw Port. C-ASCE 1995, 121, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedet, L.; Finkl, C.W.; Campbell, T.; Klein, A. Predicting the effect of beach nourishment and cross-shore sediment variation on beach morphodynamic assessment. Coast. Eng. 2004, 51, 839–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).