Structures in Shallow Marine Sediments Associated with Gas and Fluid Migration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
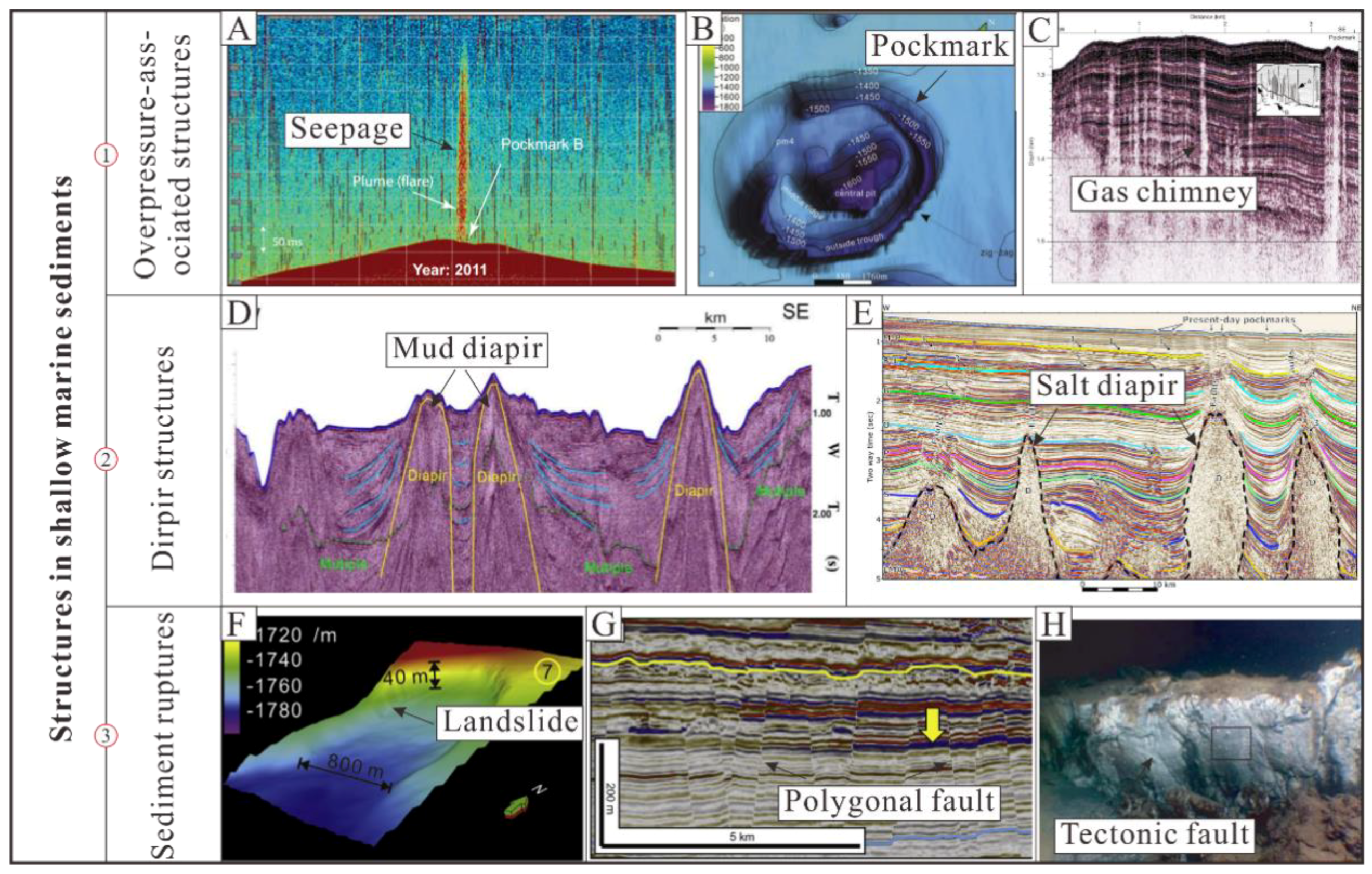
2. The Classification of the Structures
3. Overpressure-Associated Structure
3.1. Seepage
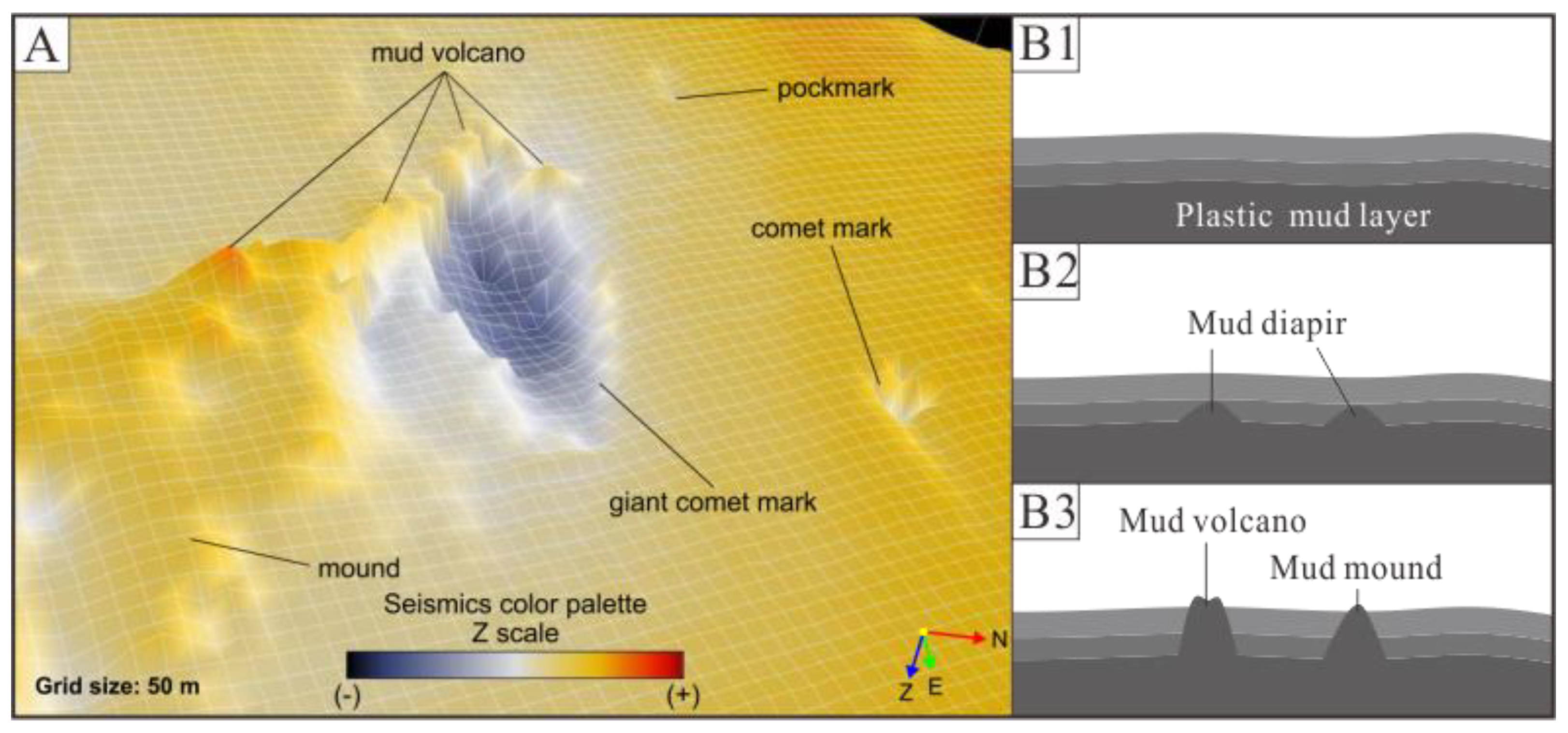
3.2. Pockmarks
3.3. Gas Chimney
4. Diapir Structures
4.1. Mud Diapirs
4.2. Salt Diapirs
5. Sediment Ruptures
5.1. Landslides
5.2. Polygonal Faults
5.3. Tectonic Faults
6. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berton, F.; Vesely, F.F. Origin of buried, bottom current-related comet marks and associated submarine bedforms from a Paleogene continental margin, southeastern Brazil. Mar. Geol. 2018, 395, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhova, N.; Semiletov, I.; Gustafsson, O.; Sergienko, V.; Lobkovsky, L.; Dudarev, O.; Tumskoy, V.; Grigoriev, M.; Mazurov, A.; Salyuk, A.; et al. Current rates and mechanisms of subsea permafrost degradation in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Völker, D.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Li, C.; Qin, Z. Three dimensional seismic studies of deep-water hazard-related features on the northern slope of South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, R.; Hiromatsu, M.; Sato, M. Fluid flow and Evolution of gas hydrate mounds of Joetsu Basin, Eastern Margin of Japan Sea: Constraints from high-resolution geophysical survey by AUV. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Gas Hydrate, Edinburgh, UK, 17–21 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-C.; Hsu, S.-K.; Wang, Y.; Chung, S.-H.; Chen, P.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Liu, C.-S.; Lin, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-W. Distribution and characters of the mud diapirs and mud volcanoes off southwest Taiwan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 92, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Dan, C.; Imbert, P. Insights into the permeability of polygonal faults from their intersection geometries with Linear Chimneys: A case study from the Lower Congo Basin. Carnets Geol. 2016, 16, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, J.; Qin, X.; Qiu, H.; Wu, N.; Lu, H.; Xie, W.; Lu, J.; Peng, F.; Xu, Z.; et al. The first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea. China Geol. 2018, 1, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, E.D. Fundamental principles and applications of natural gas hydrates. Nature 2003, 426, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Seo, Y.-T.; Lee, J.-W.; Moudrakovski, I.; Ripmeester, J.A.; Chapman, N.R.; Coffin, R.B.; Gardner, G.; Pohlman, J. Complex gas hydrate from the Cascadia margin. Nature 2007, 445, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Fang, Y.; Lu, H.; Lu, H.; Lu, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, S. Distribution and characteristics of natural gas hydrates in the Shenhu Sea Area, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; He, Y. Characteristics and dynamics of gas hydrate systems in the northwestern South China Sea—Results of the fifth gas hydrate drilling expedition. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 110, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wei, J.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, W. Complex gas hydrate system in a gas chimney, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 104, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C.; Feseker, T.; Treude, T.; Krastel, S.; Liebetrau, V.; Niemann, H.; Bertics, V.J.; Dumke, I.; Dünnbier, K.; Ferré, B. Temporal constraints on hydrate-controlled methane seepage off Svalbard. Science 2014, 343, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biastoch, A.; Treude, T.; Rüpke, L.H.; Riebesell, U.; Roth, C.; Burwicz, E.B.; Park, W.; Latif, M.; Böning, C.W.; Madec, G. Rising Arctic Ocean temperatures cause gas hydrate destabilization and ocean acidification. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boudreau, B.P.; Luo, Y.; Meysman, F.J.; Middelburg, J.J.; Dickens, G.R. Gas hydrate dissociation prolongs acidification of the Anthropocene oceans. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9337–9344A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skarke, A.; Ruppel, C.; Kodis, M.; Brothers, D.; Lobecker, E. Widespread methane leakage from the sea floor on the northern US Atlantic margin. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.-C.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.-S.; Berndt, C.; Chi, W.-C. Seismic analysis of the gas hydrate system at Pointer Ridge offshore SW Taiwan. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 105, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, J.; Su, P.; Wei, J.; Gong, Y.; Lin, L.; Liang, J.; Huang, W. Distribution and characteristics of mud diapirs, gas chimneys, and bottom simulating reflectors associated with hydrocarbon migration and gas hydrate accumulation in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern slope of the South China Sea. Geol. J. 2019, 54, 3556–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Davies, R.J.; Mathias, S.A.; Yang, J.; Hobbs, R.; Wilson, M. Gas venting that bypasses the feather edge of marine hydrate, offshore Mauritania. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 88, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenau, S.; Spieß, V.; Pape, T.; Fekete, N. Controlling mechanisms of giant deep water pockmarks in the Lower Congo Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 83, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, K.; Xu, T.; Shang, S.; Wei, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Tian, H. Numerical Modeling of Gas Migration and Hydrate Formation in Heterogeneous Marine Sediments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Qian, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Su, P.; Liang, J.; Jin, J.; Luan, Z.; Chen, D. Geophysical evidence for gas hydrate accumulation related to methane seepage in the Taixinan Basin, South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 168, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luan, X.; Lyu, F.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Yang, T.; Yao, G. Seismic evidence and formation mechanism of gas hydrates in the Zhongjiannan Basin, Western margin of the South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 84, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carreño, N.; García-Gil, S. The Holocene gas system of the Ría de Vigo (NW Spain): Factors controlling the location of gas accumulations, seeps and pockmarks. Mar. Geol. 2013, 344, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.H.; Dillon, W.P.; Pecher, I.A. Trapping and migration of methane associated with the gas hydrate stability zone at the Blake Ridge Diapir: New insights from seismic data. Mar. Geol. 2000, 164, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastras, G.; Canals, M.; Urgeles, R.; Hughes-Clarke, J.E.; Acosta, J. Shallow slides and pockmark swarms in the Eivissa Channel, western Mediterranean Sea. Sedimentology 2004, 51, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alrefaee, H.A.; Gosh, S.; Abdel-Fattah, M.I. 3D seismic characterization of the polygonal fault systems and its impact on fluid flow migration: An example from the Northern Carnarvon Basin, Australia. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, L.; Polonia, A.; Bianco, F.D.; Favali, P.; Marinaro, G.; Etiope, G. Cold seeps, active faults and the earthquake cycle along the North Anatolian Fault system in the Sea of Marmara (NE Turkey). Boll. di Geofis. Teor. ed Appl. 2012, 53, 371–384. [Google Scholar]
- Gamberi, F.; Rovere, M. Mud diapirs, mud volcanoes and fluid flow in the rear of the Calabrian Arc Orogenic Wedge (southeastern Tyrrhenian sea). Basin Res. 2010, 22, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertz, M.; Beaumont, C.; Shimeld, J.W.; Ings, S.J.; Gradmann, S. An investigation of salt tectonic structural styles in the Scotian Basin, offshore Atlantic Canada: 1. Comparison of observations with geometrically simple numerical models. Tectonics 2010, 29, TC4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendeville, B.C. Salt tectonics driven by sediment progradation: Part I—Mechanics and kinematics. AAPG Bull. 2005, 89, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zoubi, A.; Uri, S. Salt diapirs in the Dead Sea basin and their relationship to Quaternary extensional tectonics. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2001, 18, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.K.; Weitemeyer, K.A.; Bünz, S.; Minshull, T.A.; Westbrook, G.K.; Ker, S.; Sinha, M.C. Variations in pockmark composition at the Vestnesa Ridge: Insights from marine controlled source electromagnetic and seismic data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2017, 18, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, W.T.; Gettrust, J.F.; Chapman, N.R.; Spence, G.D.; Hyndman, R.D. Decreased stability of methane hydrates in marine sediments owing to phase-boundary roughness. Nature 2002, 420, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Liu, C.-S.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chang, J.-H.; Ko, C.-C.; Chiu, S.-D.; Chen, S.-C. Diapiric activities and intraslope basin development offshore of SW Taiwan: A case study of the Lower Fangliao Basin gas hydrate prospect. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 149, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mahiques, M.M.; Schattner, U.; Lazar, M.; Sumida, P.Y.; Souza, L.A. An extensive pockmark field on the upper Atlantic margin of Southeast Brazil: Spatial analysis and its relationship with salt diapirism. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turrini, L.; Jackson, C.A.L.; Thompson, P. Seal rock deformation by polygonal faulting, offshore Uruguay. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 86, 892–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo, R.; Pondard, N.; Meyer, B.; Uçarkus, G.; Lépinay, B.M.D.; Malavieille, J.; Dominguez, S.; Gustcher, M.A.; Schmidt, S.; Beck, C. Submarine fault scarps in the Sea of Marmara pull-apart (North Anatolian Fault): Implications for seismic hazard in Istanbul. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2013, 6, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Lerche, I. Modelling abnormal pressure development in sandstone/shale basins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1996, 13, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, C.; Cartwright, J. Messinian evaporites and fluid flow. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Balushi, A.N.; Neumaier, M.; Fraser, A.J.; Jackson, C.A. The impact of the Messinian salinity crisis on the petroleum system of the Eastern Mediterranean: A critical assessment using 2D petroleum system modelling. Pet. Geosci. 2016, 22, 357–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, C.; Kirkham, C.; Cartwright, J.; Hodgson, N.; Rodriguez, K. Seismic indicators of focused fluid flow and cross-evaporitic seepage in the Eastern Mediterranean. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 88, 472–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkham, C.; Cartwright, J.; Hermanrud, C.; Jebsen, C. The genesis of mud volcano conduits through thick evaporite sequences. Basin Res. 2018, 30, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontakiotis, G.; Karakitsios, V.; Maravelis, A.G.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Agiadi, K.; Antonarakou, A.; Pasadakis, N.; Zelilidis, A. Integrated isotopic and organic geochemical constraints on the depositional controls and source rock quality of the Neogene Kalamaki sedimentary successions (Zakynthos Island, Ionian Sea). Mediterr. Geosci. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontakiotis, G.; Moforis, L.; Karakitsios, V.; Antonarakou, A. Sedimentary Facies Analysis, Reservoir Characteristics and Paleogeography Significance of the Early Jurassic to Eocene Carbonates in Epirus (Ionian Zone, Western Greece). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontakiotis, G.; Karakitsios, V.; Cornée, J.-J.; Moissette, P.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Pasadakis, N.; Koskeridou, E.; Manoutsoglou, E.; Drinia, H.; Antonarakou, A. Preliminary results based on geochemical sedimentary constraints on the hydrocarbon potential and depositional environment of a Messinian sub-salt mixed siliciclastic-carbonate succession onshore Crete (Plouti section, eastern Mediterranean). Mediterr. Geosci. Rev. 2020, 2, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, A.R. Review of submarine cold seep plumbing systems: Leakage to seepage and venting. Terra Nova 2012, 24, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Chen, D. Authigenic carbonates from an active cold seep of the northern South China Sea: New insights into fluid sources and past seepage activity. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 122, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Birgel, D.; Peckmann, J.; Roberts, H.H.; Joye, S.B.; Sassen, R.; Liu, X.-L.; Hinrichs, K.-U.; Chen, D. Time integrated variation of sources of fluids and seepage dynamics archived in authigenic carbonates from Gulf of Mexico Gas Hydrate Seafloor Observatory. Chem. Geol. 2014, 385, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchley, G.J.; Klaeschen, D.; Planert, L.; Bialas, J.; Berndt, C.; Papenberg, C.; Hensen, C.; Hornbach, M.J.; Krastel, S.; Brueckmann, W. The impact of fluid advection on gas hydrate stability: Investigations at sites of methane seepage offshore Costa Rica. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 401, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchley, G.J.; Berndt, C.; Geiger, S.; Klaeschen, D.; Papenberg, C.; Klaucke, I.; Hornbach, M.J.; Bangs, N.L.B.; Maier, C. Drivers of focused fluid flow and methane seepage at south Hydrate Ridge, offshore Oregon, USA. Geology 2013, 41, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeth, J.; Primio, R.D.; Horsfield, B.; Schaefer, R.G.; Shannon, P.M.; Bailey, W.R.; Henriet, J.P. Hydrocarbon seepage and carbonate mound formation: A basin modelling study from the Porcupine Basin (offshore Ireland). J. Pet. Geol. 2010, 28, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaucke, I.; Weinrebe, W.; Petersen, C.J.; Bowden, D. Temporal variability of gas seeps offshore New Zealand: Multi-frequency geoacoustic imaging of the Wairarapa area, Hikurangi margin. Mar. Geol. 2010, 272, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klaucke, I.; Sahling, H.; Weinrebe, W.; Blinova, V.; Bürk, D.; Lursmanashvili, N.; Bohrmann, G. Acoustic investigation of cold seeps offshore Georgia, eastern Black Sea. Mar. Geol. 2006, 231, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustoft, S.; Bünz, S.; Mienert, J.; Chand, S. Gas hydrate reservoir and active methane-venting province in sediments on <20 Ma young oceanic crust in the Fram Strait, offshore NW-Svalbard. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, H.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.A.; Fu, J.; Cao, J. Chemical and Structural Characteristics of Gas Hydrates from the Haima Cold Seeps in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. On the self-sealing nature of marine seeps. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryon, M.D.; Brown, K.M.; Torres, M.E. Fluid and chemical flux in and out of sediments hosting methane hydrate deposits on Hydrate Ridge, OR, II: Hydrological processes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 201, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasiotis, T.; Papatheodorou, G.; Ferentinos, G. A string of large and deep gas-induced depressions (pockmarks) offshore Killini peninsula, western Greece. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2002, 22, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dando, P.R. Ecology of a North Sea pockmark with an active methane seep. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 1991, 70, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fader, G.B.J. Gas-related sedimentary features from the eastern Canadian continental shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1991, 11, 1123–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, A.; Svensen, H.H.; Forsberg, C.F.; Linge, H.; Lauritzen, S.-E.; Haflidason, H.; Hammer, Ø.; Planke, S.; Tjelta, T.I. A climatic trigger for the giant Troll pockmark field in the northern North Sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 464, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Prunelé, A.; Ruffine, L.; Riboulot, V.; Peters, C.A.; Croguennec, C.; Guyader, V.; Pape, T.; Bollinger, C.; Bayon, G.; Caprais, J.-C.; et al. Focused hydrocarbon-migration in shallow sediments of a pockmark cluster in the Niger Delta (Off Nigeria). Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2017, 18, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chand, S.; Crémière, A.; Lepland, A.; Thorsnes, T.; Brunstad, H.; Stoddart, D. Long-term fluid expulsion revealed by carbonate crusts and pockmarks connected to subsurface gas anomalies and palaeo-channels in the central North Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 37, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gay, A.; Lopez, M.; Cochonat, P.; Séranne, M.; Levaché, D.; Sermondadaz, G. Isolated seafloor pockmarks linked to BSRs, fluid chimneys, polygonal faults and stacked Oligocene–Miocene turbiditic palaeochannels in the Lower Congo Basin. Mar. Geol. 2006, 226, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroot, B.M.; Klaver, G.T.; Schüttenhelm, R.T.E. Surface and subsurface expressions of gas seepage to the seabed—Examples from the Southern North Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldens, P.; Schmidt, M.; Mücke, I.; Augustin, N.; Al-Farawati, R.; Orif, M.; Faber, E. Expelled subsalt fluids form a pockmark field in the eastern Red Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 36, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, L.; Woodside, J. Deep sea pockmark environments in the eastern Mediterranean. Mar. Geol. 2003, 195, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodside, J.M.; Volgin, A.V. Brine pools associated with Mediterranean Ridge mud diapirs: An interpretation of echo-free patches in deep tow sidescan sonar data. Mar. Geol. 1996, 132, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascle, J.; Mary, F.; Praeg, D.; Brosolo, L.; Camera, L.; Ceramicola, S.; Dupré, S. Distribution and geological control of mud volcanoes and other fluid/free gas seepage features in the Mediterranean Sea and nearby Gulf of Cadiz. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2014, 34, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, J.L.; Brown, K.M. Fracture networks and hydrate distribution at Hydrate Ridge, Oregon. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 245, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryon, M.D.; Brown, K.M.; Torres, M.E.; Tréhu, A.M.; McManus, J.; Collier, R.W.J.G. Measurements of transience and downward fluid flow near episodic methane gas vents, Hydrate Ridge, Cascadia. Geology 1999, 27, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tréhu, A.M.; Long, P.E.; Torres, M.E.; Bohrmann, G.; Rack, F.R.; Collett, T.S.; Goldberg, D.S.; Milkov, A.V.; Riedel, M.; Schultheiss, P.; et al. Three-dimensional distribution of gas hydrate beneath southern Hydrate Ridge: Constraints from ODP Leg 204. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 222, 845–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, P.; Suess, E.; Torres, M.; Martens, V.; Rugh, W.D.; Ziebis, W.; Kulm, L.D. In situ measurement of fluid flow from cold seeps at active continental margins. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1994, 41, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, T.; Kakuwa, Y.; Yasudomi, Y.; Itaki, T.; Motoyama, I.; Tomiyama, T.; Machiyama, H.; Katayama, H.; Okitsu, O.; Morita, S. Formation of pockmarks and submarine canyons associated with dissociation of gas hydrates on the Joetsu Knoll, eastern margin of the Sea of Japan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 90, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Judd, A.G.; King, L.H. Characteristic features of pockmarks on the North Sea Floor and Scotian Shelf. Sedimentology 2010, 31, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. Do carbonate reefs form due to fluid seepage? Terra Nova 2010, 2, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Svensen, H.; Forsberg, C.F.; Johansen, H.; Fichler, C.; Fosså, J.H.; Jonsson, R.; Rueslåtten, H. Complex pockmarks with carbonate-ridges off mid-Norway: Products of sediment degassing. Mar. Geol. 2005, 218, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Cartwright, J.A.; Imbert, P. Vertical evolution of fluid venting structures in relation to gas flux, in the Neogene-Quaternary of the Lower Congo Basin, Offshore Angola. Mar. Geol. 2012, 332–334, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, I.R.; Guinasso, N.L., Jr.; Sassen, R.; Brooks, J.M.; Lee, L.; Scott, K.T. Gas hydrate that breaches the sea floor on the continental slope of the Gulf of Mexico. Geology 1994, 22, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurauter, T.W.; Roberts, H.H. Three generations of mud volcanoes on the Louisiana continental slope. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1994, 14, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Suess, E.; Huang, Y.; Wu, N.; Bohrmann, G.; Su, X.; Eisenhauer, A.; Rehder, G.; Fang, Y. Jiulong methane reef: Microbial mediation of seep carbonates in the South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2008, 249, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, W.W.; Macdonald, I.R.; Hou, R. Geophysical signatures of mud mounds at hydrocarbon seeps on the Louisiana continental slope, northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Geol. 2003, 198, 97–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboulot, V.; Sultan, N.; Imbert, P.; Ker, S. Initiation of gas-hydrate pockmark in deep-water Nigeria: Geo-mechanical analysis and modelling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 434, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzini, A.; Svensen, H.H.; Planke, S.; Forsberg, C.F.; Tjelta, T.I. Pockmarks and methanogenic carbonates above the giant Troll gas field in the Norwegian North Sea. Mar. Geol. 2016, 373, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.L.; Sauer, S.; Panieri, G.; Ambrose, W.G.; James, R.H.; Plaza-Faverola, A.; Schneider, A. Removal of methane through hydrological, microbial, and geochemical processes in the shallow sediments of pockmarks along eastern Vestnesa Ridge (Svalbard). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöthen, K.; Kasten, S. Reconstructing changes in seep activity by means of pore water and solid phase Sr/Ca and Mg/Ca ratios in pockmark sediments of the Northern Congo Fan. Mar. Geol. 2011, 287, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Chen, D.; Peckmann, J.; Bohrmann, G. Authigenic carbonates from methane seeps of the northern Congo fan: Microbial formation mechanism. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Suess, E.; Liebetrau, V.; Eisenhauer, A.; Huang, Y. Past methane release events and environmental conditions at the upper continental slope of the South China Sea: Constraints by seep carbonates. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 103, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panieri, G.; Bünz, S.; Fornari, D.J.; Escartin, J.; Serov, P.; Jansson, P.; Torres, M.E.; Johnson, J.E.; Hong, W.; Sauer, S.; et al. An integrated view of the methane system in the pockmarks at Vestnesa Ridge, 79°N. Mar. Geol. 2017, 390, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sassen, R.; Roberts, H.H.; Aharon, P.; Larkin, J. Chemosynthetic bacterial mats at cold hydrocarbon seeps, Gulf of Mexico continental slope. Org. Geochem. 1993, 20, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, D. Hydrocarbon-Induced Alteration of Soils and Sediments. AAPG Mem. 1996, 66, 71–89. [Google Scholar]
- King, L.H. Pockmarks on the Scotian Shelf. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1970, 81, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.; Magalhães, V.H.; Terrinha, P.; Ribeiro, C.; Madureira, P.; Pinheiro, L.M.; Benazzouz, O.; Kim, J.H.; Duarte, H. Identification and characterization of fluid escape structures (pockmarks) in the Estremadura Spur, West Iberian Margin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 82, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forwick, M.; Baeten, N.J.; Vorren, T.O. Pockmarks in Spitsbergen fjords. Nor. J. Geol. 2009, 89, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, P.K. Formation of pockmarks by pore-water escape. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1985, 5, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Gardner, J.V.; Judd, A.G. The significance of pockmarks to understanding fluid flow processes and geohazards. Geofluids 2010, 2, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, K.; Holler, P.; Herbst, G.; Bratek, A.; Ahmerkamp, S.; Neumann, A.; Bartholoma, A.; van Beusekom, J.E.E.; Holtappels, M.; Winter, C. Abrupt emergence of a large pockmark field in the German Bight, southeastern North Sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallobre, C.; Loncke, L.; Bassetti, M.-A.; Giresse, P.; Bayon, G.; Buscail, R.; de Madron, X.D.; Bourrin, F.; Vanhaesebroucke, M.; Sotin, C. Description of a contourite depositional system on the Demerara Plateau: Results from geophysical data and sediment cores. Mar. Geol. 2016, 378, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nickel, J.C.; Primio, R.D.; Kai, M.; Stoddart, D.; Kallmeyer, J. Characterization of microbial activity in pockmark fields of the SW-Barents Sea. Mar. Geol. 2012, 332–334, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Weering, T.; Jansen, J.; Eisma, D. Acoustic reflection profiles of the Norwegian Channel between Oslo and Bergen. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1973, 6, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attias, E.; Weitemeyer, K.; Minshull, T.A.; Best, A.I.; Sinha, M.; Jegen-Kulcsar, M.; Hölz, S.; Berndt, C. Controlled-source electromagnetic and seismic delineation of subseafloor fluid flow structures in a gas hydrate province, offshore Norway. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 206, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cathles, L.M.; Su, Z.; Chen, D. The physics of gas chimney and pockmark formation, with implications for assessment of seafloor hazards and gas sequestration. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D.; Papatheodorou, G.; Ferentinos, G.; Masson, M. Active seepage in two contrasting pockmark fields in the Patras and Corinth gulfs, Greece. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2003, 23, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, A.; Baltzer, A.; Reynaud, M.; Ehrhold, A.; Fournier, J.; Cordier, C.; Clouet, H.; Migeon, S. Space-time evolution of a large field of pockmarks in the Bay of Concarneau (NW Brittany). Bull. Soc. géol. Fr. 2017, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostanin, I.; Anka, Z.; di Primio, R. Role of Faults in Hydrocarbon Leakage in the Hammerfest Basin, SW Barents Sea: Insights from Seismic Data and Numerical Modelling. Geosciences 2017, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilcher, R.; Argent, J. Mega-pockmarks and linear pockmark trains on the West African continental margin. Mar. Geol. 2007, 244, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattner, U.; Lazar, M.; Souza, L.A.P.; Brink, U.T.; Mahiques, M.M. Pockmark asymmetry and seafloor currents in the Santos Basin offshore Brazil. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 36, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, M.T.; Monteys, X.; O’Reilly, S.S.; Lilley, M.K.S.; Scott, G.A.; Hart, K.M.; McCarron, S.G.; Kelleher, B.P. Occurrence, characteristics and formation mechanisms of methane generated micro-pockmarks in Dunmanus Bay, Ireland. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 103, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovland, M. Characteristics of pockmarks in the Norwegian Trench. Mar. Geol. 1981, 39, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauber, R.M.; Grant, L.O.; Feng, D.; Snider, J.B. The Characteristics and Distribution of Cloud Water over the Mountains of Northern Colorado during Wintertime Storms. Part I: Temporal Variations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chand, S.; Mienert, J.; Andreassen, K.; Knies, J.; Plassen, L.; Fotland, B. Gas hydrate stability zone modelling in areas of salt tectonics and pockmarks of the Barents Sea suggests an active hydrocarbon venting system. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2008, 25, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinert, J.; Lewis, K.B.; Bialas, J.; Pecher, I.A.; Rowden, A.; Bowden, D.A.; De Batist, M.; Linke, P. Methane seepage along the Hikurangi Margin, New Zealand: Overview of studies in 2006 and 2007 and new evidence from visual, bathymetric and hydroacoustic investigations. Mar. Geol. 2010, 272, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. Pockmarks and the Recent geology of the central section of the Norwegian Trench. Mar. Geol. 1982, 47, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. Gas-induced erosion features in the North Sea. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1984, 9, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. Large pockmarks, gas-charged sediments and possible clay diapirs in the Skagerrak. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1991, 8, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Vasshus, S.; Heggland, R. Pockmarks in the Norwegian Trench—some new observations. In Proceedings of the Conference on Gas in Marine Sediments, Varna, Bulgaria, 5–10 September 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, A. Pockmarks in the UK Sector of the North Sea. UK Department of Trade and Industry Strategic Environmental Assessment Technical Report; University of Sunderland: Sunderland, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ondréas, H.; Olu, K.; Fouquet, Y.; Charlou, J.L.; Gay, A.; Dennielou, B.; Donval, J.P.; Fifis, A.; Nadalig, T.; Cochonat, P.; et al. ROV study of a giant pockmark on the Gabon continental margin. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2005, 25, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoumi, S.; Reuning, L.; Back, S.; Sandrin, A.; Kukla, P.A. Buried pockmarks on the Top Chalk surface of the Danish North Sea and their potential significance for interpreting palaeocirculation patterns. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 103, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovland, M. The formation of pockmarks and their potential influence on offshore construction. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshu 1989, 1987, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza-Faverola, A.; Bünz, S.; Johnson, J.E.; Chand, S.; Knies, J.; Mienert, J.; Franek, P. Role of tectonic stress in seepage evolution along the gas hydrate-charged Vestnesa Ridge, Fram Strait. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maia, A.R.; Cartwright, J.; Andersen, E. Shallow plumbing systems inferred from spatial analysis of pockmark arrays. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, N.; Cochonat, P.; Foucher, J.P.; Mienert, J. Effect of gas hydrates melting on seafloor slope instability. Mar. Geol. 2004, 213, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romeyn, R. Processing and Interpretation of the Svyatogor 2016 High-Resolution P-Cable 3D Seismic Dataset. Investigating the Dynamics of a Sub-Seabed Gas Hydrate System with a Potential Abiotic Methane Source. Master’s Thesis, UiT Norges arktiske universitet, Tromsø, Norway, 1 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Heeschen, K.U.; Tréhu, A.M.; Collier, R.W.; Suess, E.; Rehder, G. Distribution and height of methane bubble plumes on the Cascadia Margin characterized by acoustic imaging. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heggland, R. Gas seepage as an indicator of deeper prospective reservoirs. A study based on exploration 3D seismic data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1998, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bøe, R.; Rise, L.; Ottesen, D. Elongate depressions on the southern slope of the Norwegian Trench (Skagerrak): Morphology and evolution. Mar. Geol. 1998, 146, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. Elongated depressions associated with pockmarks in the Western Slope of the Norwegian Trench. Mar. Geol. 1983, 51, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, K.; Martera, M.D.; Noguera, A.M. Gas Chimneys in the Nile Delta Slope and Gas Fields Occurrence. In Proceedings of the EAGE Conference on Geology and Petroleum Geology of the Mediterranean and Circum-Mediterranean Basins, St. Julians, Malta, 1–4 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, J.M.; Cox, H.B.; Bryant, W.R.; Ii, M.C.K.; Mann, R.G.; Mcdonald, T.J. Association of gas hydrates and oil seepage in the Gulf of Mexico. Org. Geochem. 1986, 10, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, C.K.; Iii, W.U.; Holbrook, W.S.; Hill, T.M.; Keaten, R.; Mienert, J.; Haflidason, H.; Johnson, J.E.; Winters, W.J.; Lorenson, T.D. Origin of pockmarks and chimney structures on the flanks of the Storegga Slide, offshore Norway. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2008, 28, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, K.J.; Huuse, M. ‘Bulls-eye’ pockmarks and polygonal faulting in the Lower Congo Basin: Relative timing and implications for fluid expulsion during shallow burial. Mar. Geol. 2011, 279, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.; Tseng, W.; Liu, C. Distribution of gassy sediments and mud volcanoes offshore southwestern Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2006, 17, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gay, A.; Lopez, M.; Berndt, C.; Séranne, M. Geological controls on focused fluid flow associated with seafloor seeps in the Lower Congo Basin. Mar. Geol. 2007, 244, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, R.D.; Ewing, J.; Bryan, G.M. Anomalous wave velocities in sediments containing gas hydrates. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 2090–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cita, M.B. Prometheus mud breccia, an example of shale diapirism in the eastern Mediterranean Ridge. Ann. Geol. Pays Hell. 1981, 30, 543–570. [Google Scholar]
- Cita, M.B. The Mediterranean Ridge as an accretionary prism in collisional context. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1990, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cita, M.B.; Woodside, J.M.; Ivanov, M.; Kidd, R.B.; Limonov, A.F. Fluid venting, mud volcanoes and mud diapirs in the Mediterranean Ridge. Rend. Lincei 1994, 5, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somoza, L. Seabed morphology and hydrocarbon seepage in the Gulf of Cádiz mud volcano area: Acoustic imagery, multibeam and ultra-high resolution seismic data. Mar. Geol. 2003, 195, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopf, A.J. Global methane emission through mud volcanoes and its past and present impact on the Earth’s climate. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2003, 92, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, A.J. Significance of Mud Volcanism. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 2-1–2-52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitrov, L.I. Mud volcanoes—The most important pathway for degassing deeply buried sediments. Earth Sci. Rev. 2002, 59, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, H.D. Relation of Methane Generation to Undercompacted Shales, Shale Diapirs, and Mud Volcanoes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1974, 58, 661–673. [Google Scholar]
- Milkov, A.V. Worldwide distribution of submarine mud volcanoes and associated gas hydrates. Mar. Geol. 2000, 167, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Sahling, H.; Feseker, T.; Rendle-Bühring, R.; Wei, J.; Wintersteller, P.; Marcon, Y.; Pape, T.; Römer, M.; Bohrmann, G. Morphology and activity of the Helgoland Mud Volcano in the Sorokin Trough, northern Black Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 99, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wei, J.; Liu, S.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Meng, D.; Liu, B. Characteristics and formation mechanism of seafloor domes on the north-eastern continental slope of the South China Sea. Geol. J. 2018, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Hill, A.; Stokes, D. The structure and geomorphology of the Dashgil mud volcano, Azerbaijan. Geomorphology 1997, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planke, S.; Svensen, H.; Hovland, M.; Banks, D.A.; Jamtveit, B. Mud and fluid migration in active mud volcanoes in Azerbaijan. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2003, 23, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, C.; Ayyadurai, V.; Nainar, R. Mud volcanoes show gas hydrate potential in India’s Andaman Islands. Oil Gas J. 2015, 113, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, G.; Judd, A. Mud volcanoes of Italy. Geol. J. 2004, 39, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, A.; Svensen, H.; Akhmanov, G.G.; Aloisi, G.; Planke, S.; Malthe-Sørenssen, A.; Istadi, B. Triggering and dynamic evolution of the LUSI mud volcano, Indonesia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 261, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. Hydrocarbon Seeps in Northern Marine Waters: Their Occurrence and Effects. Palaios 1992, 7, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupré, S.; Buffet, G.; Mascle, J.; Foucher, J.P.; Gauger, S.; Boetius, A.; Marfia, C. High-resolution mapping of large gas emitting mud volcanoes on the Egyptian continental margin (Nile Deep Sea Fan) by AUV surveys. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2009, 29, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shyu, C.T.; Hsu, S.K.; Liu, C.S. Heat flows off Southwest Taiwan: Measurements over mud diapirs and estimated from bottom simulating reflectors. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1998, 9, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, R.H.; Westbrook, G.K. Mud diapirism in front of the Barbados accretionary wedge: The influence of fracture zones and North America–South America plate motions. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2001, 18, 591–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.A.; Davies, R.J. Structure and emplacement of mud volcano systems in the South Caspian Basin. Appl. Psychol. 2006, 90, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouriak, S.; Vanneste, M.; Saoutkine, A. Inferred gas hydrates and clay diapirs near the Storegga Slide on the southern edge of the Vøring Plateau, offshore Norway. Mar. Geol. 2000, 163, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusi, N.; Kenyon, N.H. Distribution of mud diapirism and other geological structures from long-range sidescan sonar (GLORIA) data, in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Geol. 1996, 132, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisi, J.; Wallmann, K.; Haese, R.; Saliège, J.-F. Chemical, biological and hydrological controls on the 14C content of cold seep carbonate crusts: Numerical modeling and implications for convection at cold seeps. Chem. Geol. 2004, 213, 359–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmer, L.; Ings, S.J.; Medvedev, S.; Beaumont, C. Salt tectonics driven by differential sediment loading: Stability analysis and finite-element experiments. Basin Res. 2015, 16, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudec, M.R.; Jackson, M.P.A. Terra infirma: Understanding salt tectonics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2007, 82, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakitsios, V.; Rigakis, N.; Bakopoulos, I. Migration and trapping of the Ionian series hydrocarbons (Epirus, NW Greece). Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2001, 34, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar, J.A.; Knapp, J.H.; Knapp, C.C.; Pyles, D.R. Salt tectonics and Pliocene stratigraphic framework at MC-118, Gulf of Mexico: An integrated approach with application to deep-water confined structures in salt basins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 50, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradmann, S.; Hübscher, C.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Gajewski, D.; Netzeband, G. Salt tectonics off northern Israel. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, M.J.R.; Gawthorpe, R.L. Submarine channels controlled by salt tectonics: Examples from 3D seismic data offshore Angola. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2006, 23, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohriak, W.; Taiwani, M. Evolution of the Angolan Passive Margin, West Africa, With Emphasis on Post-Salt Structural Styles; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 129–149. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, S.A.; Coward, M.P. Synthesis of salt tectonics in the southern North Sea, UK. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1995, 12, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, P.G.; Bishop, D.J.; Hood, D.N. Development of salt-related structures in the Central North Sea: Results from section balancing. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1996, 100, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.; Brun, J.P.; Fort, X.; Cloetingh, S.; Ben-Avraham, Z. Salt tectonics in pull-apart basins with application to the Dead Sea Basin. Tectonophysics 2008, 449, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, A.; Gaullier, V.; Vendeville, B.C.; Odonne, F. Influence of differential compaction above basement steps on salt tectonics in the Ligurian-Provençal Basin, northwest Mediterranean. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudec, M.R.; Jackson, M.P.A. Structural segmentation, inversion, and salt tectonics on a passive margin: Evolution of the Inner Kwanza Basin, Angola. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2002, 115, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.D.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Shulman, H. Fault and salt tectonics in the southern Dead Sea basin. Tectonophysics 2002, 346, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmer, L.; Beaumont, C.; Ings, S.J. Dynamic modelling of passive margin salt tectonics: Effects of water loading, sediment properties and sedimentation patterns. Basin Res. 2010, 17, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, J.P.; Fort, X. Compressional salt tectonics (Angolan margin). Tectonophysics 2004, 382, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, X. Salt tectonics on the Angolan margin, synsedimentary deformation process. AAPG Bull. 2004, 88, 1523–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, M.G.; Peel, F.J.; Vendeville, B.C.; Gaullier, V. Salt tectonics at passive margins: Geology versus models—Discussion. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 37, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, J.-P.; Fort, X. Salt tectonics at passive margins: Geology versus models. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1123–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncke, L.; Mascle, J.; Parties, F.S. Mud volcanoes, gas chimneys, pockmarks and mounds in the Nile deep-sea fan (Eastern Mediterranean): Geophysical evidences. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 669–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.A. Implications of passive salt diapir kinematics for reservoir segmentation by radial and concentric faults. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2006, 23, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urlaub, M.; Talling, P.J.; Zervos, A.; Masson, D. What causes large submarine landslides on low gradient (<2°) continental slopes with slow (∼0.15 m/kyr) sediment accumulation? J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 6722–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Cheng, S.; Li, Q.; Shan, H.; Lu, J.A.; Shen, Z.; Liu, X.; Jia, Y. Giant Submarine Landslide in the South China Sea: Evidence, Causes, and Implications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hesthammer, J.; Fossen, H. Evolution and geometries of gravitational collapse structures with examples from the StatfJord Field, northern North Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1999, 16, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G. The landslide problem. J. Palaeogeogr. 2015, 4, 109–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loon, A.J.V.; Brodzikowski, K. Problems and progress in the research on soft-sediment deformations. Sediment. Geol. 1987, 50, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, M.A.; Lee, H.J.; Locat, J. Submarine landslides. Rev. Geophys. 1996, 34, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locat, J.; Lee, H.J. Submarine landslides: Advances and challenges. Can. Geotech. J. 2002, 39, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, D.G.; Harbitz, C.B.; Wynn, R.B.; Pedersen, G.; Løvholt, F. Submarine landslides: Processes, triggers and hazard prediction. Philos. Trans. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 364, 2009–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, E.L.; Talling, P.J.; Urlaub, M.; Hunt, J.E.; Clare, M.A.; Challenor, P. Are large submarine landslides temporally random or do uncertainties in available age constraints make it impossible to tell? Mar. Geol. 2015, 369, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanneste, M.; Sultan, N.; Garziglia, S.; Forsberg, C.F.; L’Heureux, J.S. Seafloor instabilities and sediment deformation processes: The need for integrated, multi-disciplinary investigations. Mar. Geol. 2014, 352, 183–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Graham, S.; Pang, X.; Mchargue, T. Characteristics of migrating submarine canyons from the middle Miocene to present: Implications for paleoceanographic circulation, northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhong, G.; Wang, L.; Kuang, Z. Characteristics and occurrence of submarine canyon-associated landslides in the middle of the northern continental slope, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 57, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, S.G.; Li, Q.P.; Wang, D.W.; Fu, S.Y. Architecture and development of a multi-stage Baiyun submarine slide complex in the Pearl River Canyon, northern South China Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2014, 34, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, P.; Bohoyo, F.; Galindo-Zaldívar, J.; Pérez, L.F.; Hernández-Molina, F.J.; Maldonado, A.; García, M.; Medialdea, T. Mass transport processes in the southern Scotia Sea: Evidence of paleoearthquakes. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 123, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournadour, E.; Mulder, T.; Borgomano, J.; Hanquiez, V.; Ducassou, E.; Gillet, H. Origin and architecture of a Mass Transport Complex on the northwest slope of Little Bahama Bank (Bahamas): Relations between off-bank transport, bottom current sedimentation and submarine landslides. Sediment. Geol. 2015, 317, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Strasser, M.; Preu, B.; Hanebuth, T.J.J.; Krastel, S.; Kopf, A. New constraints on oceanographic vs. seismic control on submarine landslide initiation: A geotechnical approach off Uruguay and northern Argentina. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2014, 34, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urgeles, R.; Camerlenghi, A. Submarine landslides of the Mediterranean Sea: Trigger mechanisms, dynamics, and frequency-magnitude distribution. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2013, 118, 2600–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultan, N.; Cochonat, P.; Canals, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Dennielou, B.; Haflidason, H.; Laberg, J.S.; Long, D.; Mienert, J.; Trincardi, F. Triggering mechanisms of slope instability processes and sediment failures on continental margins: A geotechnical approach. Mar. Geol. 2004, 213, 291–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryn, P.; Berg, K.; Forsberg, C.F.; Solheim, A.; Kvalstad, T.J. Explaining the Storegga Slide. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvalstad, T.J.; Andresen, L.; Forsberg, C.F.; Berg, K.; Bryn, P.; Wangen, M. The Storegga slide: Evaluation of triggering sources and slide mechanics. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Reuven, E.; Aharonov, E. Submarine landslides and fault scarps along the eastern Mediterranean Israeli continental-slope. Mar. Geol. 2015, 369, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chough, S.; Yoon, S. Slope-stability change from late pleistocene to holocene in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Japan Sea). Sediment. Geol. 1996, 104, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, S.; Völker, D.; Zhao, F.; Mi, L.; Kopf, A. Morphology, seismic characterization and sediment dynamics of the Baiyun Slide Complex on the northern South China Sea margin. J. Geol. Soc. 2014, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C.; Costa, S.; Canals, M.; Camerlenghi, A.; Mol, B.D.; Saunders, M. Repeated slope failure linked to fluid migration: The Ana submarine landslide complex, Eivissa Channel, Western Mediterranean Sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 319–320, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Bao, Y. The mechanism of shallow submarine landslides triggered by storm surge. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Guo, L. Experiment and Analysis of Submarine Landslide Model Caused by Elevated Pore Pressure. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAdoo, B.G.; Pratson, L.F.; Orange, D.L. Submarine landslide geomorphology, US continental slope. Mar. Geol. 2000, 169, 103–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, J. Diagenetically induced shear failure of fine-grained sediments and the development of polygonal fault systems. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1593–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colón, S.; Audemard, F.A.; Beck, C.; Avila, J.; Padrón, C.; De Batist, M.; Paolini, M.; Leal, A.F.; Van Welden, A. The 1900 Mw 7.6 earthquake offshore north–central Venezuela: Is La Tortuga or San Sebastián the source fault? Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 67, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulty, N.R. Polygonal fault networks in fine-grained sediments—An alternative to the syneresis mechanism. First Break 2001, 19, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewksbury, B.J.; Hogan, J.P.; Kattenhorn, S.A.; Mehrtens, C.J.; Tarabees, E.A. Polygonal faults in chalk: Insights from extensive exposures of the Khoman Formation, Western Desert, Egypt. Geology 2014, 42, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C.; Bünz, S.; Mienert, J. Polygonal fault systems on the mid-Norwegian margin: A long-term source for fluid flow. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 216, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartwright, J.; James, D.; Bolton, A. The genesis of polygonal fault systems: A review. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 216, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, J.; Lonergan, L. Seismic expression of layer-bound fault systems of the Eromanga and North Sea Basins. Explor. Geophys. 1997, 28, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, J.A. Episodic basin-wide hydrofracturing of overpressured Early Cenozoic mudrock sequences in the North Sea Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1994, 11, 587–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, J.A. Episodic basin-wide fluid expulsion from geopressured shale sequences in the North Sea basin. Geology 1994, 22, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, J.A.; Lonergan, L. Volumetric contraction during the compaction of mudrocks: A mechanism for the development of regional-scale polygonal fault systems. Basin Res. 1996, 8, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, J.A.; Dewhurst, D.N. Layer-bound compaction faults in fine-grained sediments. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1998, 110, 1242–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, A.; de Lépinay, B.M.; Ratzov, G.; Jean-Frédéric, L.; Lallemand, S.; Garanti Scientific Team. Seafloor giant polygons associated with underlying polygonal faults in the Caribbean Sea, west off Granada. In Proceedings of the International Meeting of Sedimentologists, Toulouse, France, 10–12 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goulty, N.R. Mechanics of layer-bound polygonal faulting in fine-grained sediments. J. Geol. Soc. 2002, 159, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.A.L.; Carruthers, D.T.; Mahlo, S.N.; Briggs, O. Can polygonal faults help locate deep-water reservoirs? AAPG Bull. 2014, 98, 1717–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostanin, I.; Anka, Z.; di Primio, R.; Bernal, A. Identification of a large Upper Cretaceous polygonal fault network in the Hammerfest basin: Implications on the reactivation of regional faulting and gas leakage dynamics, SW Barents Sea. Mar. Geol. 2012, 332, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebeck, H.; Tenthorey, E.; Consoli, C.; Nicol, A. Polygonal faulting and seal integrity in the Bonaparte Basin, Australia. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 60, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.A.; Cartwright, J.A.; Imbert, P. Perturbation of polygonal fault propagation by buried pockmarks and the implications for the development of polygonal fault systems. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 65, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, D.; Groshong, R.H. Conical faults apparent in a 3D seismic image. Interpretation 2014, 2, T1–T11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, D.; Gay, A.; Baudon, C.; Berndt, C.; Soliva, R.; Planke, S.; Mourgues, R.; Lacaze, S.; Pauget, F.; Mangue, M.; et al. High-resolution architecture of a polygonal fault interval inferred from geomodel applied to 3D seismic data from the Gjallar Ridge, Vøring Basin, Offshore Norway. Mar. Geol. 2012, 332, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonergan, L.; Cartwright, J.; Jolly, R. The geometry of polygonal fault systems in Tertiary mudrocks of the North Sea. J. Struct. Geol. 1998, 20, 529–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, T.; Magee, C.; Jackson, C.A.L.; Huuse, M.; Taylor, K.G. Kinematics of Polygonal Fault Systems: Observations from the Northern North Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriet, J.P.; Batist, M.D.; Verschuren, M. Early fracturing of Palaeogene clays, southernmost North Sea relevance to mechanisms of primary hydrocarbon migration. Gener. Accumul. Prod. Eur. Hydrocarb. Eur. Assoc. Pet. Geosci. Spec. Publ. 1991, 1, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, W.G.; Mcclay, K.R. Analogue sandbox modelling of Miocene extensional faulting in the Outer Moray Firth. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1993, 71, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, J.A.; Gabrielsen, R.H.; Reksnes, P.A.; Nysæther, E. Development of intraformational (Oligocene–Miocene) faults in the northern North Sea: Influence of remote stresses and doming of Fennoscandia. J. Struct. Geol. 1999, 21, 1457–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhurst, D.N.; Cartwright, J.A.; Lonergan, L. The development of polygonal fault systems by syneresis of colloidal sediments. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1999, 16, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.C.; Naim, F.; Mohanty, S. Seismic expression of polygonal fault systems: An example from North Sea, Dutch Offshore. In Proceedings of the Spg/seg 2016 International Geophysical Conference, Beijing, China, 20–22 April 2016; p. 556. [Google Scholar]
- Kulikowski, D.; Amrouch, K.; Cooke, D.; Gray, M.E. Basement structural architecture and hydrocarbon conduit potential of polygonal faults in the Cooper-Eromanga Basin, Australia. Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 66, 366–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, A.; Walsh, J.J.; Watterson, J.; Nell, P.A.R.; Bretan, P. The geometry, growth and linkage of faults within a polygonal fault system from South Australia. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 216, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watterson, J.; Walsh, J.; Nicol, A.; Nell, P.A.R.; Bretan, P.G. Geometry and origin of a polygonal fault system. J. Geol. Soc. 2000, 157, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Leng, J.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and genesis of the polygonal fault system in southern slope of the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 70, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pu, R.; Fan, X.; Li, B. Characteristics and Genesis of the Polygonal Fault System in Beijiao Sag of the Qiongdongnan Basin, the Northern South China Sea. Geotecton. Et Metallog. 2017, 41, 817–828. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, S.; Lü, F.; Yuan, S. Polygonal faults and their implications for hydrocarbon reservoirs in the southern Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 39, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Yao, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, G. Geophysical signatures associated with fluid flow and gas hydrate occurrence in a tectonically quiescent sequence, Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Geofluids 2010, 10, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Wu, S.G.; Wang, D.W.; Ma, Y.B.; Yao, G.S.; Gong, Y.H. The role of polygonal faults in fluid migration and gas hydrate reservoir forming in Southeast Hainan Basin. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2010, 45, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Fuliang, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q. Characteristics of Polygonal Faults Distribution and Analysis of Its Controlling Factors in Southern Xisha Offshore, South China Sea. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2017, 22, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Gay, A.; Lopez, M.; Cochonat, P.; Sermondadaz, G. Polygonal faults-furrows system related to early stages of compaction—upper Miocene to recent sediments of the Lower Congo Basin. Basin Res. 2004, 16, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, G.; Lu, H.; Lu, J.A.; Hou, G.; Gong, Y. Polygonal fault in marine sediments and its impact on gas hydrate occurrence. Geol. China 2020, 47, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, J.A.; Dewhurst, D.N. Compaction by syneresis: A mechanism for the development of polygonal fault systems in ultra-fine grained sediments. Ann. Geophys. 1998, 16, 266. [Google Scholar]
- Gay, A. Are polygonal faults the keystone for better understanding the timing of fluid migration in sedimentary basins? EPJ Web Conf. 2017, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, D.M.; Shimeld, J.W.; Williamson, M.A.; Lykke-Andersen, H. Development of a major polygonal fault system in Upper Cretaceous chalk and Cenozoic mudrocks of the Sable Subbasin, Canadian Atlantic margin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonergan, L.; Cartwright, J.; Laver, R.; Staffurth, J. Polygonal faulting in the Tertiary of the central North Sea: Implications for reservoir geology. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1998, 127, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Santamarina, J.C.; Cartwright, J.A. Contraction-driven shear failure in compacting uncemented sediments. Geology 2008, 36, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Santamarina, J.C.; Cartwright, J.A. Displacement field in contraction-driven faults. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulty, N.R. Geomechanics of polygonal fault systems: A review. Pet. Geosci. 2009, 14, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettermann, M.; Urai, J.L.; Vrolijk, P.J. Evolution of structure and permeability of normal faults with clay smear: Insights from water-saturated sandbox models and numerical simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustoft, S.; Mienert, J.; Bünz, S.; Nouzé, H. High-resolution 3D-seismic data indicate focussed fluid migration pathways above polygonal fault systems of the mid-Norwegian margin. Mar. Geol. 2007, 245, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Wu, S.; Völker, D.; Dong, D.; Shi, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, L. Tectonically induced, deep-burial paleo-collapses in the Zhujiang Miocene carbonate platform in the northern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2015, 364, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C. Focused fluid flow in passive continental margins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2005, 363, 2855–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo, R.; Meyer, B.; Navarro, S.; King, G.; Barka, A. Asymmetric slip partitioning in the Sea of Marmara pull-apart: A clue to propagation processes of the North Anatolian Fault? Terra Nova 2010, 14, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Déverchère, J.; Yelles, K.; Domzig, A.; Lépinay, B.M.D.; Bouillin, J.P.; Gaullier, V.; Bracène, R.; Calais, E.; Savoye, B.; Kherroubi, A. Active thrust faulting offshore Boumerdes, Algeria, and its relations to the 2003 Mw 6.9 earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McHugh, C.M.G.; Seeber, L.; Cormier, M.-H.; Dutton, J.; Cagatay, N.; Polonia, A.; Ryan, W.B.F.; Gorur, N. Submarine earthquake geology along the North Anatolia Fault in the Marmara Sea, Turkey: A model for transform basin sedimentation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 248, 661–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlides, S.; Tsapanos, T.; Zouros, N.; Sboras, S.; Koravos, G.; Chatzipetros, A. Using active fault data for assessing seismic hazard: A case study from NE Aegean sea, Greece. In Proceedings of the Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering Satellite Conference: XVIIth International Conference on Soil Mechanics & Geotechnical Engineering, Alexandria, Egypt, 2–3 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, K.M.; Tryon, M.D.; Deshon, H.R.; Dorman, L.R.M.; Schwartz, S.Y. Correlated transient fluid pulsing and seismic tremor in the Costa Rica subduction zone. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 238, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barın, B.; Okay, S.; Çifçi, G.; Dondurur, D.; Cormier, M.H.; Sorlien, C.; Meriç İlkimen, E. The central branch of the North Anatolian Fault In The Southern Marmara Sea: Evidence for a distributed, Holocene-active fault system. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 12–17 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier, N.; Birgel, D.; Lopezgarcia, P.; Taphanel, M.H.; Bouloubassi, I. Evidence for microbial methane oxidation at cold seeps along the main active fault in the Marmara Sea. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 2–7 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zitter, T.A.C.; Henry, P.; Aloisi, G.; Delaygue, G.; Çagatay, M.N.; De, L.B.; Al, S.M.; Fornacciari, F.; Tesmer, M.; Pekdeger, A. Cold seeps along the main Marmara Fault in the Sea of Marmara (Turkey). Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2008, 55, 552–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Géli, L.; Henry, P.; Zitter, T.; Dupré, S.; Tryon, M.; Çağatay, M.N.; Lépinay, B.M.D.; Pichon, X.L.; Şengör, A.M.C.; Görür, N. Gas emissions and active tectonics within the submerged section of the North Anatolian Fault zone in the Sea of Marmara. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 274, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuşçu, İ.; Okamura, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Gökaşan, E.; Awata, Y.; Tur, H.; Şimşek, M.; Keçer, M. Seafloor gas seeps and sediment failures triggered by the August 17, 1999 earthquake in the Eastern part of the Gulf of İzmit, Sea of Marmara, NW Turkey. Mar. Geol. 2005, 215, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pichon, X.; Şengör, A.M.C.; Demirbağ, E.; Rangin, C.; İmren, C.; Armijo, R.; Görür, N.; Çağatay, N.; Mercier de Lepinay, B.; Meyer, B.; et al. The active Main Marmara Fault. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 192, 595–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Kaşlılar-Özcan, A.; İmren, C.; Boztepe-Güney, A.; Demirbağ, E.; Kuşçu, İ. Active faults and evolving strike-slip basins in the Marmara Sea, northwest Turkey: A multichannel seismic reflection study. Tectonophysics 2000, 321, 189–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Demirbağ, E.; Kurt, H.; Okay, N.; Kuşçu, İ. An active, deep marine strike-slip basin along the North Anatolian fault in Turkey. Tectonics 1999, 18, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Marchese, F.; Savini, A.; Bistacchi, A. Active normal fault network of the Apulian Ridge (Eastern Mediterranean Sea) imaged by multibeam bathymetry and seismic data. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bistacchi, A.; Pellegrini, C.; Savini, A.; Marchese, F. 3D modelling of the active normal fault network in the Apulian Ridge (Eastern Mediterranean Sea): Integration of seismic and bathymetric data with implicit surface methods. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Taymaz, T.; Jackson, J.; Mckenzie, D. Active tectonics of the north and central Aegean Sea. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 106, 433–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Tsutsumi, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Arato, H. Active right-lateral strike-slip fault zone along the southern margin of the Japan Sea. Tectonophysics 2002, 351, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, P.; Lallemant, S.; Nakamura, K.I.; Tsunogai, U.; Mazzotti, S.; Kobayashi, K. Surface expression of fluid venting at the toe of the Nankai wedge and implications for flow paths. Mar. Geol. 2002, 187, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, X.L.; Kobayashi, K.; Crew, K.N.S. Fluid venting activity within the eastern Nankai trough accretionary wedge: A summary of the 1989 Kaiko-Nankai results. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 109, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, G.; Zhan, L.; Lu, H.; Hou, G. Structures in Shallow Marine Sediments Associated with Gas and Fluid Migration. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040396
Ma G, Zhan L, Lu H, Hou G. Structures in Shallow Marine Sediments Associated with Gas and Fluid Migration. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(4):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040396
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Gongzheng, Linsen Zhan, Hailong Lu, and Guiting Hou. 2021. "Structures in Shallow Marine Sediments Associated with Gas and Fluid Migration" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 4: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040396
APA StyleMa, G., Zhan, L., Lu, H., & Hou, G. (2021). Structures in Shallow Marine Sediments Associated with Gas and Fluid Migration. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(4), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040396






