Abstract
Social networks like Twitter are increasingly important in the creation of new ways of communication. They have also become useful tools for social and linguistic research due to the massive amounts of public textual data available. This is particularly important for less resourced languages, as it allows to apply current natural language processing techniques to large amounts of unstructured data. In this work, we study the linguistic and social aspects of young and adult people’s behaviour based on their tweets’ contents and the social relations that arise from them. With this objective in mind, we have gathered over 10 million tweets from more than 8000 users. First, we classified each user in terms of its life stage (young/adult) according to the writing style of their tweets. Second, we applied topic modelling techniques to the personal tweets to find the most popular topics according to life stages. Third, we established the relations and communities that emerge based on the retweets. We conclude that using large amounts of unstructured data provided by Twitter facilitates social research using computational techniques such as natural language processing, giving the opportunity both to segment communities based on demographic characteristics and to discover how they interact or relate to them.
1. Introduction
In the last few years, Twitter has become one of the most used social networks, creating new ways of consuming information but also of communicating and creating both leisure- and work-related explicit relationships. Furthermore, such relationships may be formed implicitly via the information we shared with our followers via retweets. Furthermore, Twitter has become a source of spontaneously generated textual data for many human languages, including less resourced languages such as Basque [1,2]. Thus, this data is becoming more and more useful for doing social research [3,4,5] which may complement traditional methods traditionally used in sociology. Furthermore, Twitter allows to obtain massive amounts of textual data to apply modern techniques of natural language processing (NLP) based on machine and deep learning, for tasks such as automatic analysis of opinions (opinion mining or sentiment analysis) [4,6], named entity recognition and lexical normalization [5], fake news and rumour detection [7], among others.
Taking the concept of liquid society [8] as a starting point, in this paper we present a multidisciplinary work that aims to contribute novel insights in social research by using and investigating techniques from natural language processing. Thus, the objective of this work is to provide a detailed social and demographic-based view of the most important topics and relationships that are formed between the members of a specific community, namely, the community of Basque Twitter users classified by life stage (young and adult). By “Basque Twitter users” we refer to those users that are geolocalized in the area of the Basque Country (cultural) and that write at least the 20% of their tweets using the Basque language. This analysis will be entirely based on the automatically collected tweets.
More specifically, the work presented in this paper will consist of the following steps. First, we will identify the relevant Basque Twitter users. Second, a large corpus of tweets will be extracted using the identified users’ timelines. Third, we will classify users in terms of life stage (adult/young) by classifying the writing style of the tweets in their timelines as formal or informal. This is due to the fact that we do not have metadata information about the users’ age, which means that we have to somehow try to infer the life stage based on features about writing style. Five different classification methods will be investigated, including the use of machine learning techniques based on both feature-based and neural network architectures. We will use the best classifier to label the large corpus of Basque tweets by their writing style thereby classifying their users in terms of young or adult. In the final step, this classification will be used to investigate the most relevant topics among users of Twitter writing in Basque as well as for researching the social relations that emerge between each user type (young or adult). The final result will be a comprehensive, automatically obtained, sociological picture of the most important aspects within the community of Basque users of Twitter.
The main contributions of this work are the following. First, we collect and publish a corpus of 6 M tweets written in Basque and a manually annotated gold-standard of 1000 tweets in terms of the writing style, namely, formal or informal. Both corpora are made available to facilitate both NLP and social research in Basque (https://github.com/ixa-ehu/heldugazte-corpus), a less resourced high-inflected language. Second, we investigate the classification of Basque tweets as formal or informal using five different approaches including novel NLP techniques based on word embeddings, contextual character embeddings and neural networks. We believe that our work is the most comprehensive experimentation for the detection of users’ age both in terms of number of users and NLP techniques used. An interesting insight from this part is the fact that, contrary to common views, the neural approach [9] obtains very competitive results despite being trained on a very small dataset. We believe that is due mostly to the combination of character-based contextual embeddings with static word embeddings. Third, the models of the best system will be made publicly available to facilitate their use and reproducibility of results (https://github.com/ixa-ehu/ixa-pipe-doc). Fourth, we perform the largest investigation of social relationships in terms of age stages for Basque communities based on an automatically classified corpus of almost 8000 users and six million tweets. Finally, we believe that this work shows how to make it possible to do meaningful and large scale social and NLP research for less resourced languages using texts from social media. For us, this work is just the beginning.
The rest of the paper is as follows. Next, we present the related work. Section 3 describes the process to collect our corpus while Section 4 contains the experiments performed for the classification of users by life stage. We use the obtained results to annotate our corpus and perform topic detection in Section 5. Section 6 analyzes the relations and communities of Twitter users extracted from the data and we offer some concluding remarks in Section 7.
2. Related Work
Analyzing demographic characteristics in social media is receiving increasing attention in the area of social media mining [3,10]. The popularity of Twitter has in fact benefited such approaches as it is possible now to mine spontaneous contributions and opinions of users about any kind of topic in many languages, including less resourced languages. Both social and linguistic aspects are important for our work as we will try to perform social and demographic analysis via large scale linguistic processing of tweets. The main techniques used here are those related to topic modelling, the study of social relationships and text processing or NLP.
With respect to topic modelling, many different approaches have tried to extract common information contained in large amounts of tweets scattered through the network, such as topic extraction with respect to an event and their related tweets [11], real-time classification of twitter trends [12] or to compare the content of Twitter with traditional news media [13]. Applying topic modelling to tweets, like for other tasks, requires some pre-processing to make the task appropriate for such short texts or documents [14].
In relation to the study of the social relationships that are generated within the network, closer to us are those studies that have aimed to identify communities of users based on their retweets. Among these, one can find studies about political polarization [15], political affiliation detection [16] or even studies about identifying communities in movements for independence [17]. In these studies, based on the retweets made by the user, it is shown that the identification of communities or groups is quite feasible. In this paper we will use similar methodologies to the ones mentioned here with the objective of uncovering latent communities.
The use of Twitter is very popular in NLP, where tweets are used for many tasks such as mining opinions about specific products or topics [4,18], analyzing stance detection and fake news [6,17] or in more low level NLP tasks such as POS tagging [19], Named Entity Recognition [5], normalization [20] and language identification [21]. Previous NLP work is relevant to us as we will work with tweets to perform text classification with the aim of labelling tweets according to their writing style (conventional-informal or formal).
Of particular interest to us is the body of work performed with the objective of age or life stage detection for Twitter users. Table 1 lists the most relevant work on this task. Most of them create their own datasets with manually annotated data to learn life stages or age ranges. As it can be seen the number of users varies from 300 to 3000. It is also important to mention that the best performing systems are those that use at most two [22,23] or three [10,24] labels denoting the life stages for the classification task.

Table 1.
Most relevant systems for age detection in Twitter.
For the task of age detection, most of previous works use both the text and the metadata provided by the Twitter API, most importantly, the age of each user. Previous work is based on logistic regression [10,24] and support vector machines [22,23,25]. Best results in this area have obtained around 86 word accuracy [24] for three age or life stages, although others scored well below that, most of them ranging around 74–80 word accuracy. These comparatively lower scores make it more difficult to perform meaningful social and demographic research using such automatic classifiers. Therefore, an important contribution of this work will be to strive in providing good performing classifiers for Basque tweets but also with the aim of developing robust and general enough models to be applicable for different text classification tasks across different languages.
3. Extracting a Large Corpus of Tweets from Basque Users
As we have already commented in the introduction, Twitter allows to obtain relatively large datasets also for less resourced languages. Before starting to collect the data for our work, we defined the community of users that will be the subject (or, in other words, the universe) of our study. In our case the choice was quite simple, namely, we wanted to use tweets from every Twitter user that publishes tweets in Basque. The task of identifying such users was facilitated thanks to UMAP, a platform that monitors every tweet written in Basque. More specifically, UMAP includes a list of users who publish at least 20% of their tweets in Basque (https://umap.eus/). We used such a source to obtain an initial list of 8189 users.
The Twitter API was used via the tweepy package, choosing the timeline extraction mode to gather the last 3200 available tweets of each of the 8189 users in our sample. The data collection was performed during the days 30 and 31 of May 2018, gathering, after discarding some users due to API errors, more than 10 million (multilingual) tweets from 7980 users. We call this data the large corpus. Next, we classify the tweets by language using the metadata provided by the Twitter API, identifying those that are written in Basque. The result is a dataset of around six million tweets that we refer to as the Heldugazte corpus, which we split into personal tweets and retweets. The main statistics of the Heldugazte corpus are provided by Table 2 (The corpus is publicly available at https://github.com/ixa-ehu/heldugazte-corpus.).

Table 2.
Characteristics of the Heldugazte corpus.
4. Classifying Users by Age Stage
In this section we present our work to classify Basque Twitter users as young or adult by analyzing their tweets’ writing style. As we have seen in Section 2, previous work includes automatic approaches to infer demographic characteristics in the context of social networks and media, the most common being those related with genre and age [26]. Our objective of developing a classifier to characterizing Basque Twitter users according to two stages of life (young/adult) is therefore placed within that research line.
Furthermore, Section 2 also shows that most of previous work addresses the problem of classifying age stages using supervised machine learning techniques. This implies that some training data must be annotated according to the age or age stage of each user. Moreover, state of the art results indicate that classifying by age stages allows one to obtain better results than when the problem is formulated in terms of age ranges [24]. This seems to be due to the fact that shared experiences are easier to relate along time by using age stages rather than age ranges [3,27]. Therefore, in this work we decided to focus on classifying users in terms of two general age stages, namely, young and adult.
However, this decision encountered an early methodological problem. In order to annotate tweets written in Basque according to the age stages of their authors it is obviously necessary to have available some data providing such information. Unfortunately, for the large majority of users from which we mined tweets this information is not available. Thus, our decision to overcome this problem consisted of focusing on the information available on the tweets themselves by taking into account writing style features. After all, most of the previous work widely uses writing style based features in order to classify users in terms of age stages [10,22,23,24].
It has been suggested that adults tend to use more conventional language [24] whereas for young people it is more common to display repetitions and out of vocabulary words [10,22,28]. Generalizing on this idea, we will assume that writing style changes according to the age of the Twitter user. In other words, we will consider that adult writing style is more formal whereas young people’s style can be seen as more informal. Therefore, we will be classifying users as young/adult by classifying their tweets in terms of formal or informal language.
4.1. Experimental Framework
Following the setting established above, we addressed the problem of classifying each tweet as formal or informal by means of several approaches. First, we applied a statistical method based on perplexity [29]. Second, we experimented with several supervised methodologies: (i) a baseline method using sparse, one-hot word representations [30]; (ii) a feature-based method using word representations as continuous word vectors, namely, word embeddings, on top of the baseline developed in (i) [31,32,33]; (iii) an off-the-shelf system which uses clustering features for representing the documents [34,35] and (iv), a deep learning approach leveraging character contextual word embeddings and a neural network architecture [9].
We developed a classifier with each of the methods listed above and evaluate it on a held-out, gold-standard dataset manually annotated at tweet level for the categories of formal and informal. The method that obtained the best results in the experiments was then used to annotate personal tweets of the six million Heldugazte corpus (see Table 2) thereby classifying their authors as young or adult. In this sense, users were classified according to the writing style of the tweets in their timelines.
In the rest of this section we will describe the process of manual annotation of the training and evaluation data. After that, we describe the configuration settings of each of the systems used or implemented for the experiments.
4.1.1. The Heldugazte Gold Standard Corpus
In order to focus on learning to classify tweets according to writing style, we decided to clean the tweets keeping only those words that contained alphanumeric characters. Thus, we removed emoticons, hashtags, users’ names (@) and URL links. Furthermore, we only considered those tweets that contained more than four tokens. We then randomly selected 1000 tweets sent from personal accounts from the 6 million tweet dataset collected as described in Section 3. One annotator manually labeled every tweet as formal or informal.
To manually label the tweets, a qualitative methodology was followed: all those tweets that contained out of vocabulary words or colloquial expressions were classified as informal. This methodology has been motivated by previous work on classifying formal and colloquial tweets [36]. Table 3 shows the main features of our manually annotated dataset. For the experiments described in the next five subsections, we split the gold standard corpus in three sets, leaving 65% for training and 35% for testing (the Heldugazte gold-standard corpus is publicly available at https://github.com/ixa-ehu/heldugazte-corpus). In the following we present two examples of the type of tweets we classify in this work. In both cases it can be seen the differences in writing style. Thus, in the informal tweets appear dialectal and/or slang forms (ein, examin, bau, det), whereas the formal tweet displays quite a standard Basque grammar.

Table 3.
The Heldugazte gold standard corpus.
- (1)
- Informal tweet: “inoizz ezdet ein mateko examin bau au baino okerro” (Informal: This is worst exam I have ever done.).
- (2)
- Formal tweet: “killian jornet fenomenoa da zegamaaizkorri irabazi du beste behin non dago mendizale gazte honen muga” (Formal: Killian Jornet is a phenomenon he won the Zegama-Aizkorri again. Where is this mountaineer’s limit?).
4.1.2. Perplexity-Based Distance
Perplexity is a widely-used evaluation metric for language models built with n-grams extracted from text corpora [37]. Furthermore, it has been used for specific tasks, namely, to classify between formal and colloquial tweets [36] or for language identification between similar languages [29]. Both works inspired our approach to classifying tweets as formal or informal using perplexity. The former showed that perplexity could be useful to indirectly detect out-of-vocabulary words in tweets [36]. More importantly for us, the latter formally proposed the concept of perplexity-based distance between two languages.
A perplexity-based distance between two languages is established by “comparing the n-grams of a text in one language with the n-gram language model trained for the other language. Then, the perplexity of a test text T in language L2, given the language model LM of language L1, can be used to define the distance, between L1 and L2” [29]. According to this definition, low perplexity indicates close proximity between languages L2 and L1.
In order to classify tweets as formal or informal, we calculated the perplexity-based distance between a tweet with respect to a character-based seven-gram language model. If the perplexity-based distance between each tweet and the character-based n-gram language model is low, then we will classify it as formal and vice versa. Of course, for this approach to work we need to establish a threshold so that if the perplexity-based distance is lower than the threshold the tweet is labeled as formal and if higher, as informal.
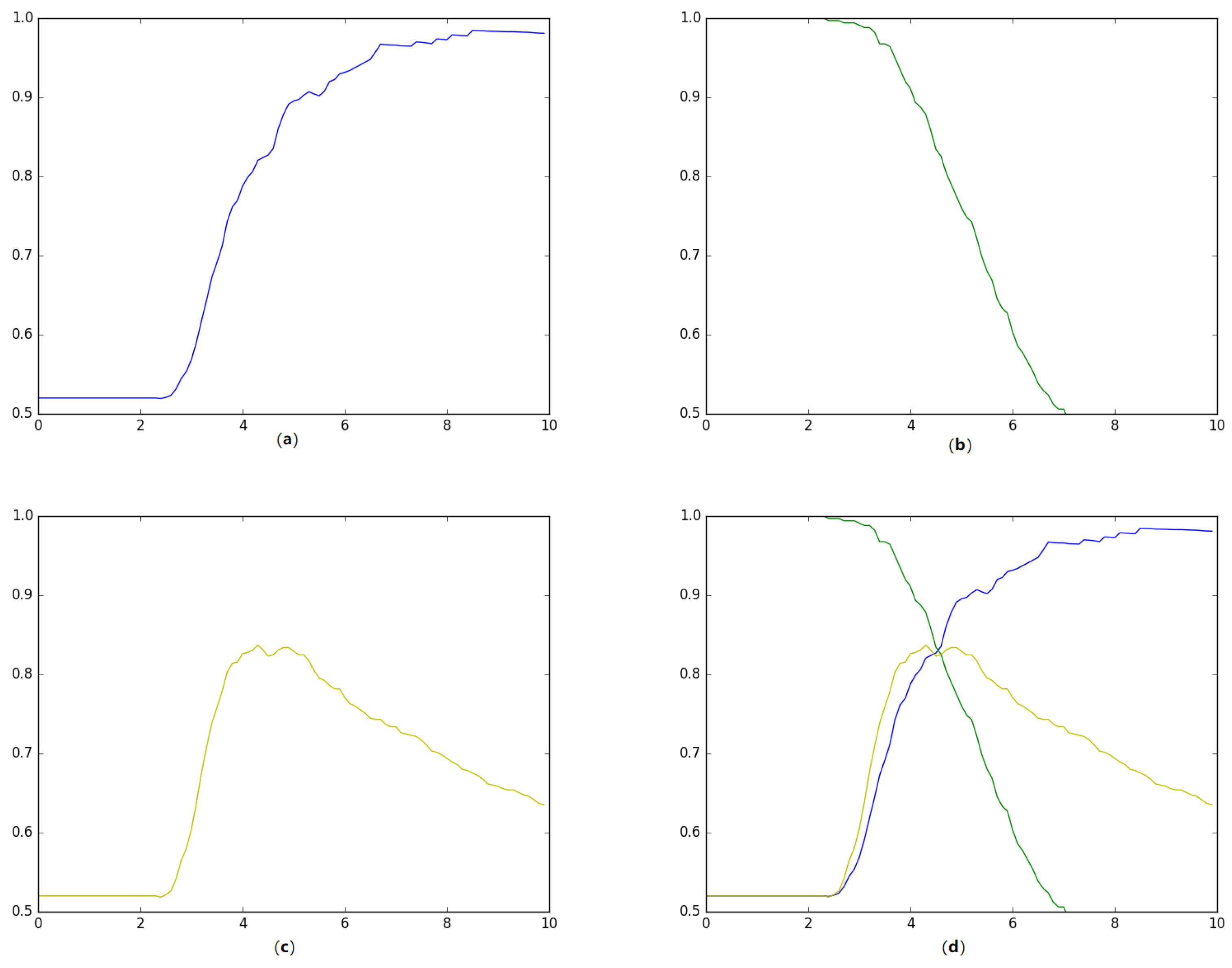
Our method to calculate such threshold proceeds in the following manner. First, we built a seven-gram character-based language model using the data from a corpus composed of texts from the Basque Egunkaria and Berria newspapers. Second, we took the tweets in the training set (65% of the dataset) and classify each of them according to the perplexity-based distance with respect to the language model. We tried every value in the [0, 10] range with an increment of 0.1 as threshold. Third, we computed precision, recall and accuracy comparing the prediction of the threshold according to the perplexity value with respect to the gold-standard labels in the training data. Finally, the threshold chosen will be the value in which all the three metrics converge. As shown by Figure 1, we found out that the best threshold value was around 4.4. We will use this value in order to evaluate this approach in Section 4.2.
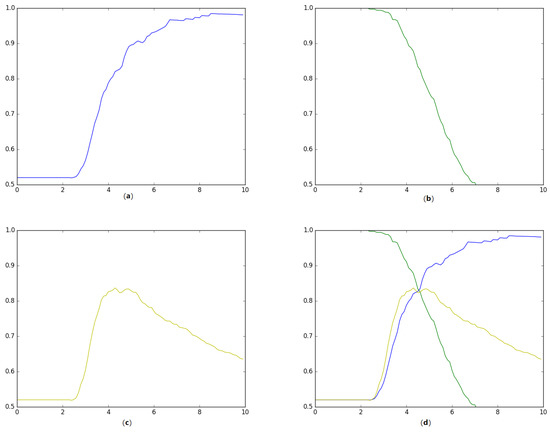
Figure 1.
Finding the optimal threshold value (d) on the training data using precision (a), recall (b) and Accuracy (c) curves.
Table 4 displays the results of classifying the tweets in the training data using perplexity-based distance with threshold value at 4.4. The obtained overall accuracy using 4.4 as threshold was 0.831.

Table 4.
Results of the perplexity-based approach on the training set.
4.1.3. Supervised Baseline
The first baseline applying supervised machine learning was done to test various learning algorithms using the gold standard dataset described in Section 4.1.1. More specifically, we simply applied a bag of words representation which represented each document (tweet) according to the word frequencies in each document. The result is a very sparse word representation where the dimension of the vector representing each word is equal to the number of words in the corpus. In this setting, we apply six of the most common machine learning algorithms with default parameters using the scikit-learn library [30]. Table 5 reports their performance by means of five-fold cross validation on the training data.

Table 5.
Bag of words results via five-fold cross-validation on the training set. Best result in bold.
As it can be seen, the best performing algorithms in this baseline setting were logistic regression and SVM. This is not surprising given the ability of SVM to perform well with very few labeled data. Next, we decided to experiment with a less-sparse representation of the tweets by means of pre-trained word embeddings and the SVM classifier.
4.1.4. Pre-Trained Word Embeddings
Distributed word representations or word embeddings are widely used nowadays in natural language processing. Several techniques have been proposed in order to obtain word embeddings, most of them based on the hypothesis that the meaning of a word is defined by the context in which it appears [31,32]. Thus, obtaining word embeddings usually requires large quantities of good quality training data which makes it difficult when experimenting with less resourced languages such as Basque. However, FastText provides pre-trained models for many languages, including Basque [33] by using the common crawl data (http://commoncrawl.org). The Basque model they distribute is trained on both common crawl and Wikipedia using CBOW with position-weights, in 300 dimension, with character n-grams of length 5, a window of size 5 and 10 negatives (https://fasttext.cc).
For this experiment, we mapped the words in the corpus to their real vector representation in the FastText model and average all the vectors with respect to the vocabulary. We optimized the C hyperparameter using accuracy and evaluated by five-fold cross-validation on the training data. Table 6 reports the detailed results of the five-fold cross-validation using C as hyperparameter.

Table 6.
Support vector machine (SVM) (rbf and FastText embeddings) results via five-fold cross-validation on the training set.
4.1.5. IXA Pipes
The document classification system included in the IXA pipes tools, ixa-pipe-doc, aims to establish a simple and shallow feature set, avoiding any linguistic motivated features, with the objective of removing any reliance on costly extra gold annotations and/or cascading errors if automatic annotations are used. The underlying motivation was to obtain robust models to facilitate the development of document classification systems for several languages, datasets and domains while obtaining state of the art results.
The ixa-pipe-doc, as a component of IXA pipes, includes a simple method to combine various types of clustering features induced over different data sources or corpora. This method has already obtained state of the art results in several tasks such as newswire named entity recognition [34] and opinion target extraction [35], both in out-of-domain and in-domain evaluations and for several languages, including Basque. Clusters of words provide denser document representations. Although still a one-hot vector representation, the dimensions of the representation gets reduced to the number of clustering classes used. This is done by mapping the words in the document to the words in each of the clustering lexicons [38].
We will use the three types of simple clustering features based on unigram matching that ixa-pipe-doc implements: (i) Brown [39] clusters, taking the 4th, 8th, 12th and 20th node in the path; (ii) Clark [40] clusters and, (iii) Word2vec [31] clusters, based on K-means applied over the extracted word vectors using the skip-gram algorithm. The implementation of the clustering features looks for the cluster class of the incoming token in one or more of the clustering lexicons induced following the three methods listed above. If found, then we add the class as feature. The Brown clusters only apply to the token related features, which are duplicated (More details, including examples of the features are provided in Agerri and Rigau [34,35]).
For the experiments, we used pre-trained clusters using the Elhuyar Web Corpus [41] and from a 600 M word corpus obtained from crawling local news sites (local news corpus). The number of clusters trained with each algorithm and data source was the following: 100–800 clusters using the Clark and Word2vec methods, and 1000, 2000 and 3200 classes with the Brown algorithm. The best combination of features was obtained by performing every possible permutation between them in a five-fold cross validation setting using the gold standard training data. Following this methodology, the best configuration consisted of the features listed in Table 7 (we did not use any local or lexicon-based features, just the clustering representations).

Table 7.
Source data and number of clusters used with ixa-pipe-doc system. EWC: Elhuyar Web Corpus. LNC: local news corpus.
Table 8 provides the results per class using ixa-pipe-doc. As it can be seen, they are the best results obtained so far both in terms of accuracy (0.887) and F1 measure.

Table 8.
The ixa-pipe-doc results via five-fold cross-validation on the training set.
4.1.6. Flair
Flair refers to both a deep learning toolkit based on neural networks and to a specific type of character-based contextual word embeddings [9]. Unlike static word embeddings such as those of Word2vec [31], Glove [32] or FastText [33], contextual embeddings allow one to obtain word representations in a vector space taking into account the sense of the word given the context in which it appears. Thus, while a polysemous word would be given a unique real valued representation in the FastText pre-trained word embedding model used in Section 4.1.4, Flair embeddings will aim to provide different representations depending on the contextual meaning of the word. Another important difference is that flair embeddings are not word-based, they are trained by modeling words as sequences of characters.
Flair embeddings have been successfully applied to sequence labelling tasks obtaining best results for a number of public benchmarks [9]. In this paper, we apply the Flair toolkit to train document classification systems for classifying tweets as formal or informal. Flair provides a recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture (Cho et al., 2014) to represent documents, modelling text as a sequence of characters passed to the RNN which at each point in the sequence is trained to predict the next character [9]. We used this architecture to train document classification systems using several pre-trained word embedding models: flair contextual embeddings for Basque, character embeddings and the FastText Basque embeddings used previously. The flair contextual embeddings for Basque were trained on various sources and it contains around 249M words. We performed five-fold cross-validation on the training data obtaining the best results with a combination of the flair and the FastText embeddings, obtaining 0.808 in word accuracy. Table 9 reports on the final cross-validation results for each label.

Table 9.
Flair results via five-fold cross-validation on the training set.
4.2. Experimental Results
In order to finish our experiments, we used the full training set for the systems that obtained best cross-validation results and evaluated them on the gold standard test set. Thus, we tested the following systems: the SVM model with FastText word embeddings, the perplexity-based distance method, ixa-pipe-doc and Flair. Table 10 reports the final results of our experiments to obtain a good classifier of Basque tweets according to writing style (formal/informal).

Table 10.
Final evaluation results on the test set. Best results in bold.
It should be noticed that we did not implement any specific features for the experiments with our gold standard data. The main reason is that we wanted to avoid including any features that might cause overfitting to the training data. By doing so, we were aiming to develop general, robust classifiers that hopefully will be equally competitive for other languages, text genres and tasks. We believe that the strong results obtained by the IXA pipes and the Flair system, despite the lack of any specific tuning to the data, show the generalization power of using combined word representations. Furthermore, it is particularly interesting the fact that the neural network architecture provided by flair performed so well with such a small training data. Our hypothesis is that, being the dataset so small, there are not so many out of vocabulary words.
We believe that the developed classifiers are good enough to use them to classify the personal tweets in the six million Heldugazte corpus in terms of the formal and informal classes. We decide to use the IXA pipes model due to the results obtained and its lower requirements in terms of memory and computing power (Flair requires longer time and a GPU for training and tagging).
4.3. Labelling the Large Corpus
The young/adult classifier developed in the previous section will allow us to compare the main features of those two life stages by taking into account the topics that appear on users’ tweets and the relations that arise between them. After training the best performing model of ixa-pipe-doc described in Section 4.1.5 and evaluated in Section 4.2 on the 1000 tweets of the full gold-standard corpus, we proceed to tag the personal tweets in the Heldugazte corpus (see Table 2). We only used for classification the (multilingual) timelines of those users which contained at least 10 tweets written in the Basque language, namely, 7.087 users out of the 7.980 that we crawled in Section 3.
Given that the classifier labels each tweet as formal or informal, we decided, after some qualitative error analysis, that those users whose timelines in which more than 45% of the tweets are labelled as informal be considered as young, and adult otherwise. Thus, after classifying users in terms of young and adult, we obtained 5508 which were adult users and 1579 labelled as young users, applying the obtained label to every tweet and retweet of each user’s timeline, namely, to every tweet in the Large Corpus. Details of the tagging results are displayed in Table 11. Even though the resulting classification is quite unbalanced that is not a problem because we will perform our analysis of each type of user independently.

Table 11.
Classifying tweets in large corpus in terms of age stage (young/adult).
4.3.1. Analyzing Adult Twitter Users
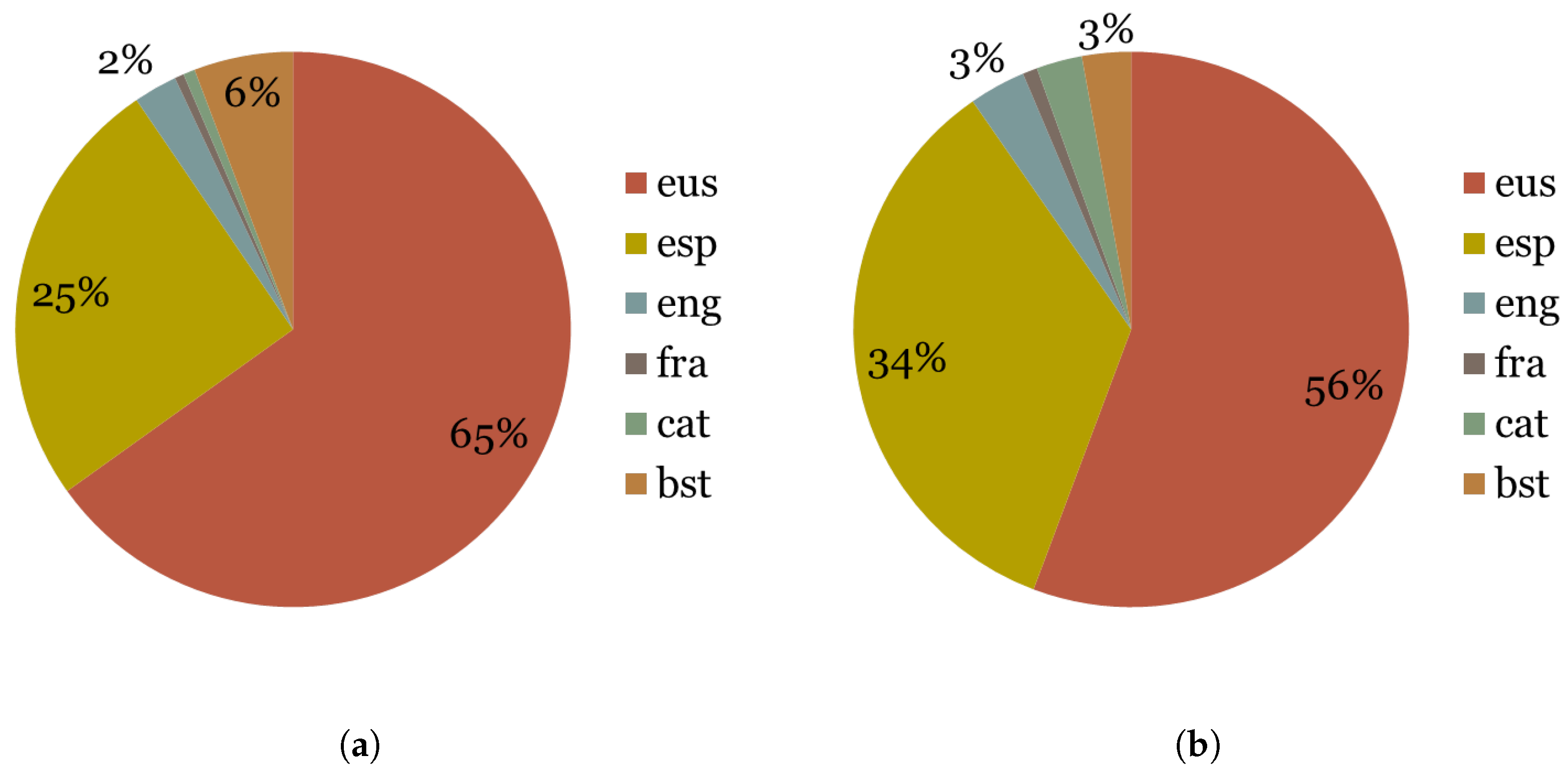
The first issue that arises when looking at the adults’ tweets is that more than half of them are actually retweets. This shows that there is a disposition to share information as much as to generate it. Furthermore, Figure 2 shows that Basque is the most used language, Spanish being the second. Finally, it is also interesting the fact that the use of Spanish increases for the retweets which probably reflects the fact that publicly available and shareable information in Spanish is much larger than in Basque.
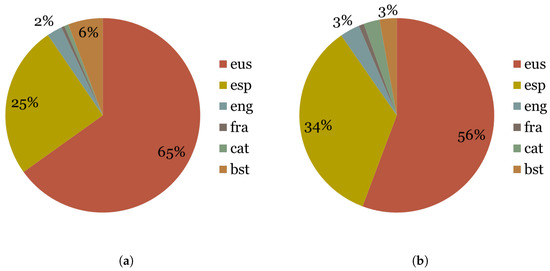
Figure 2.
Adults in the large corpus: 5508 users. (a) Adult personal tweets. (b) Adult retweets.
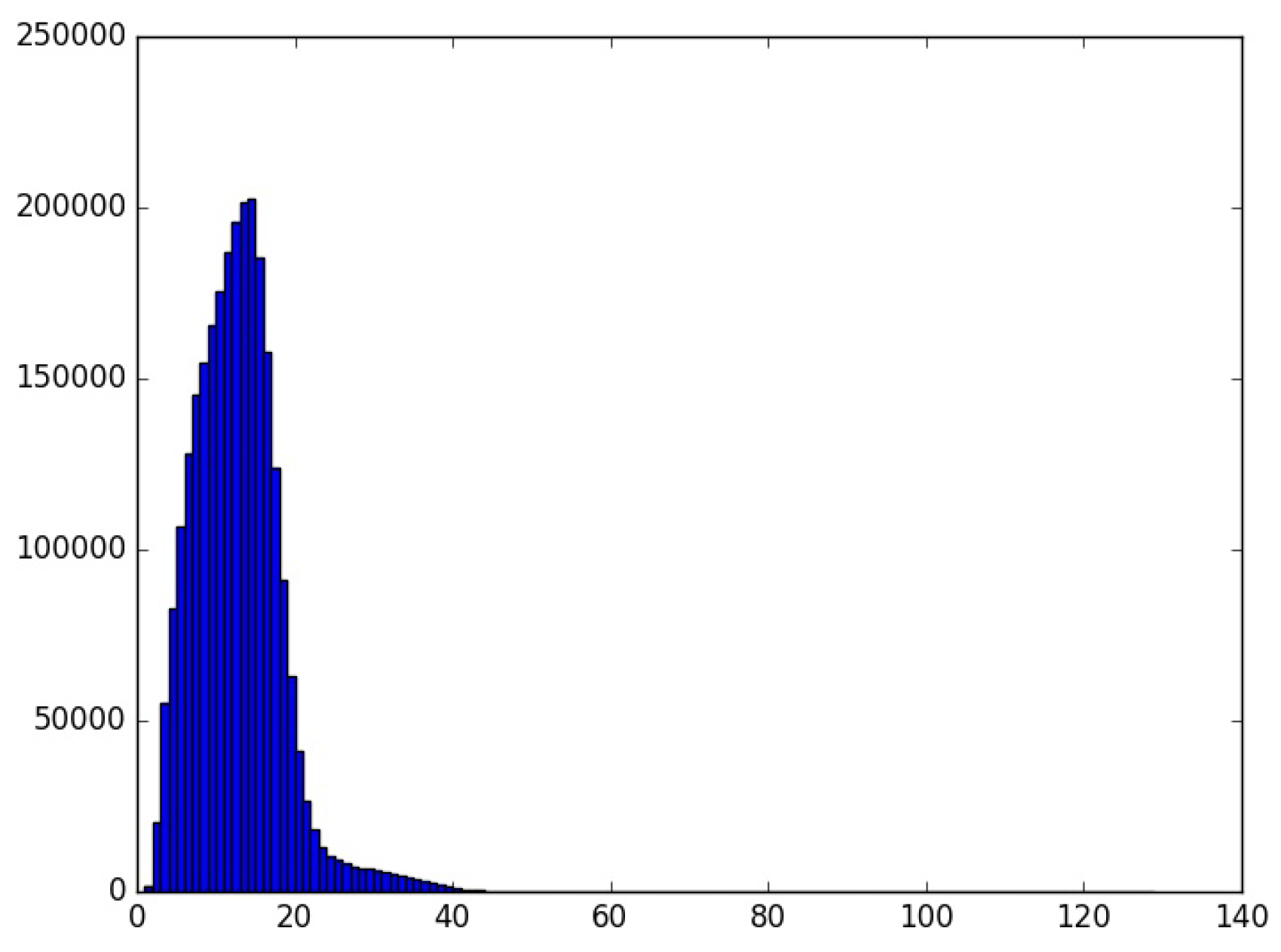
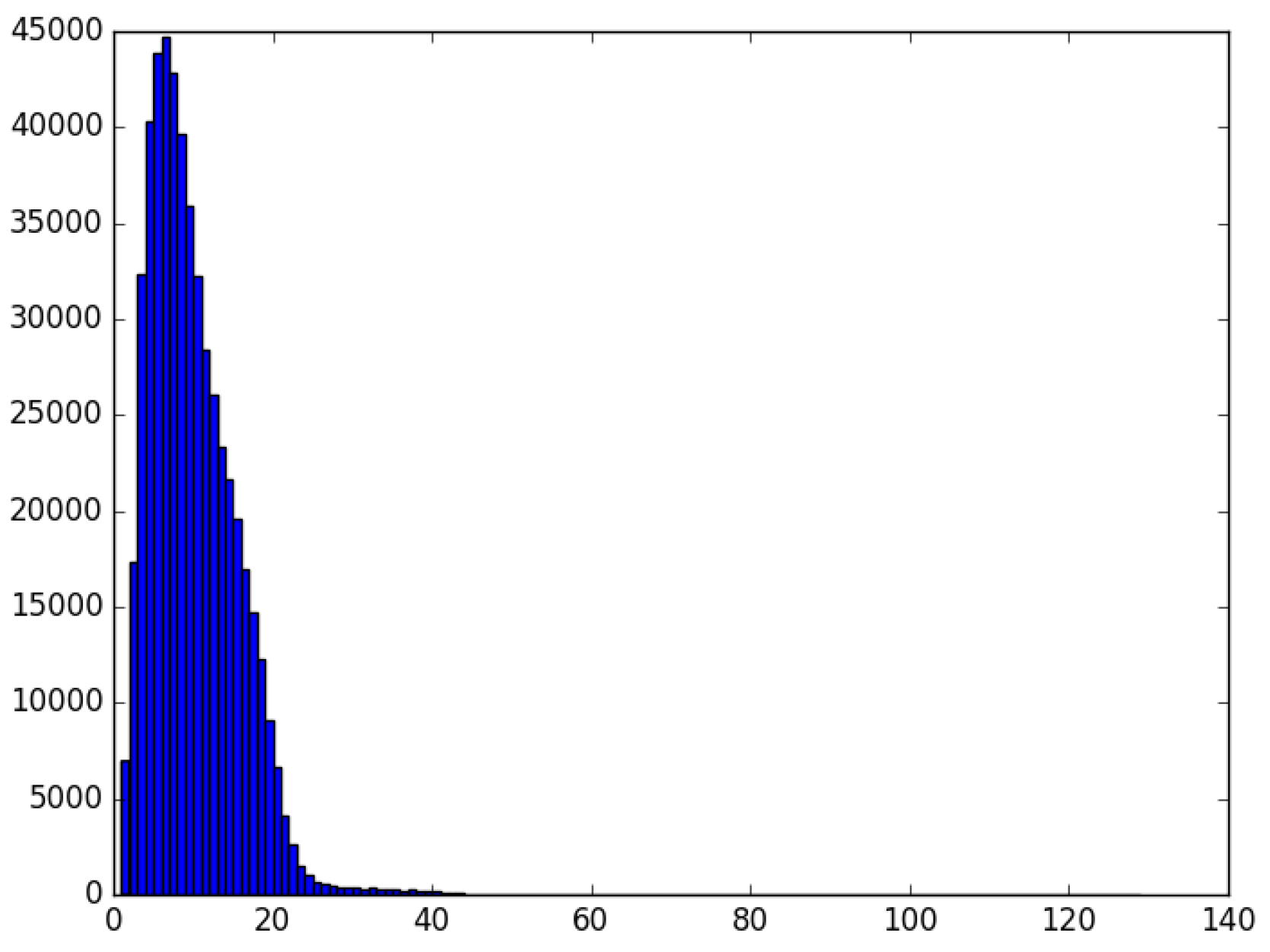
If we take a look at the tweets written only in Basque, we find that 2,634,534 tweets have been published, containing more than 32 million tokens. Figure 3 shows their distribution according to their length in tokens. The average tweet contains 12 tokens. Standard deviation with respect to the average was 5.65. Furthermore, median corresponds to 12, mode being 14 token (more than 200,000 tweets).
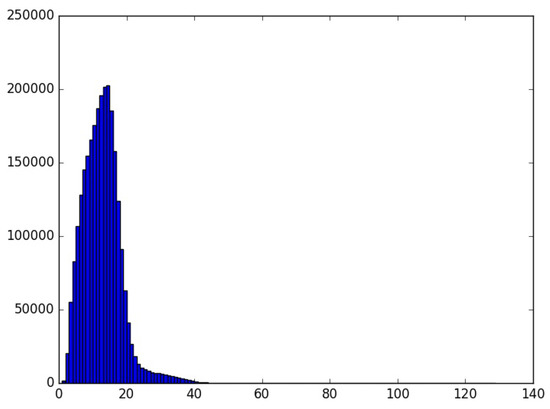
Figure 3.
Distribution of Basque tweets published by adults.
4.3.2. Analyzing Young Twitter Users
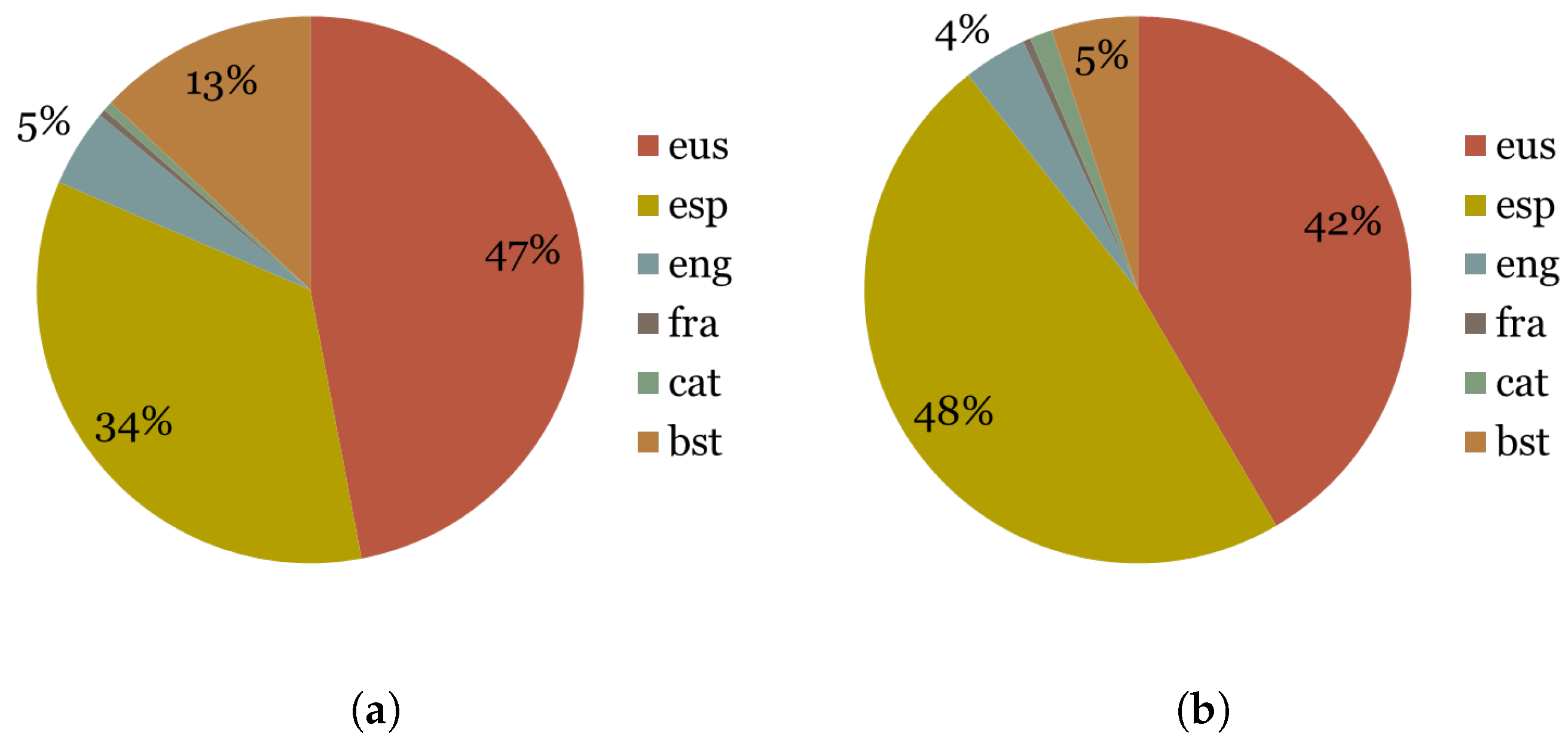
The young users corpus contains just one quarter in size with respect to the corpus of adult users. In this case, it can be seen that there were fewer retweets (963,668) than original personal tweets (1,128,124). It is perhaps more noticeable the fact that the use of Basque is less common between young users: 18% lower for tweets and 24% lower for retweets. As it is expected, the use of Spanish is higher between young users, reaching 47% for retweets and 34% for personal tweets. The data in Figure 4 shows that Basque is less used between young users of Twitter.
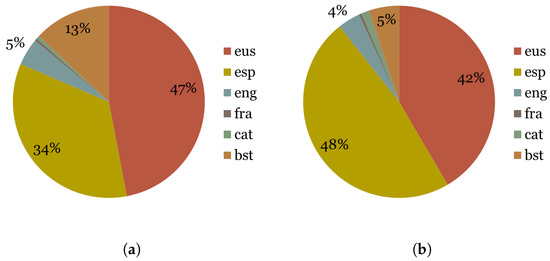
Figure 4.
Young users in large corpus: 1579 users. (a) Young personal tweets. (b) Young retweets.
If we take a look at the tweets written only in Basque, we find that 530,226 personal tweets have been published, containing more than five million tokens. Figure 5 shows their distribution according to their length in tokens. The average tweet contains nine tokens, whereas the standard deviation with respect to the average is 5.49. Furthermore, median corresponds to eight, mode being six token (around 45,000 tweets). In general, it is noticeable the fact that young users published much shorter tweets than adults.
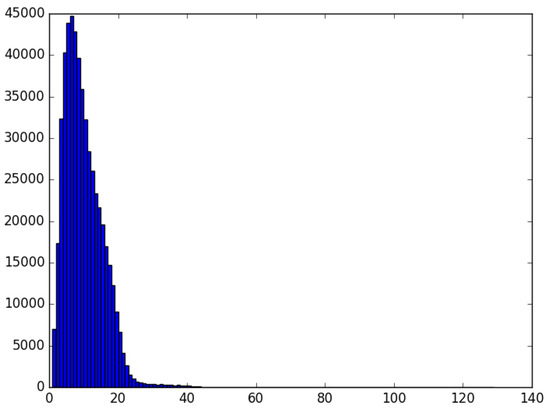
Figure 5.
Distribution of Basque tweets published by young users.
5. Topics
The aim of this section is to detect the most frequent topics of Twitter users writing in Basque. In order to do so, we start with the personal tweets of users classified as adults and young in the previous section using the classifier developed in Section 4.1.5. As shown by Table 11, more than three million personal tweets in Basque were obtained. On the one hand, 2,634,534 personal tweets will be used to predict adult topics and, on the other hand, 530,226 personal tweets for young users. We will apply topic modelling via latent dirichlet allocation (LDA) [42] in order to infer relevant topics per type of user from unstructured data. Specifically, we used the implementation of LDA provided by the gensim package [43].
Topic modeling is a commonly used tool in the field of text mining. With this technique, words are grouped or clustered according to their context, thereby generating more general contents or concepts via the clustered words and allowing to identify general topics from specific words. We apply this technique to identify the main subjects that appear in the Basque users’ tweets. In order words, LDA makes it possible to classify events that are observable in latent or hidden clusters. This is possible thanks to the many hidden features, such as the similarity of words.
Before applying LDA, we need to structured the documents in our dataset. It is difficult to directly apply LDA to our data due to the short length of tweets. Thus, we decide to group the tweets by user, namely, we will create one document per user where the document will contain every tweet published by that person [13,14]. Additionally, and considering that Basque is an agglutinative language, we decided to lemmatize the documents to reduce the number of terms that needed to be modelled. For this pre-processing step, the IXA pipes Basque lemmatizer was used [44].
LDA requires us to choose a number of topics beforehand. After several tests, 20 topics were used for the adults documents and 12 for the young ones. The different in topics is coherent with the number of tweets for each of user type. Although there is not a fixed correct number of topics, this choice affects the interpretability of the LDA results [45,46]. Thus, it is interesting to achieve the most dispersed possible model so that the overlap between topics is kept to a minimum. Furthermore, the resulting topics should correlate with social reality which is latent in the real data.
The results of applying LDA are displayed using LDAvis [47], which offers an easy interpretation of each topic. As it is customary, the identity or meaning of the topic is determined by the words of which it is composed [45]. Thus, Table 12 shows the topics obtained for the adult users whereas Table 13 lists the topics for the young users.

Table 12.
Topics of adult users. Whenever necessary, English translation is provided below each row of representative words.

Table 13.
Topics of young users. Whenever necessary, English translation is provided below each row of representative words.
The topics from adult users show that they mostly talk about politics, social, cultural and linguistic (Basque language-related) issues. It is also interesting to notice that public institutions also appear in the social network, such as Basque Country regional offices from Gipuzkoa, Bizkaia or Nafarroa. However, if we look at the topics most common between young users (Table 13) we can see that they are mostly related to everyday affairs (chatting between friends, expressing feelings and emotions with respect to something, etc.). In some cases, they talk about everyday issues using their local Basque dialect (e.g., Gipuzkera and Bizkaiera). Additionaly, sports (athletic club, rowing) are also a recurring theme among young people. Thus, comparing the two different age stages, it should be noted that young people use Twitter for more day-to-day activities among friends or among contacts within the network. In the case of adults, it is clear that there is more political and social content.
6. Relations
In this section we will study the relations that appear between Basque users of Twitter. As in the previous section, the starting point will be the retweets of users classified as adult or young using the classifier developed in Section 4.1.5. The number of retweets for each type of users are reported in Table 11. Specifically, 2,421,058 retweets will be used to study the relations that are created between adult users. With respect to young users, the corpus consists of 400,448 retweets. The overall objective is to uncover the most important relations formed between users by studying the links between their retweets and comparing the different behaviour and relations of young and adult users.
First, we created a giant graph using the data (retweets) for each type of user. To build the graph, two features extracted from each retweet were used: (i) who retweets and (ii) who has been retweeted. Thus, the data source will be the source and the target of each retweet. Based on these two characteristics, the two graphs were created using the gephi program [48].
Once the graphs were created, we proceed as follows: first, we divided each graph into subgroups using the modularity algorithm [49]. Second, we gave the network a spatial structure by using the ForceAtlas2 algorithm [50], ordering the nodes according to the community to which they belong. Finally, the identity of each subgroup or community was defined, using the most important nodes of the created subgroups. By doing so it can be seen how the communities within each graph are structured.
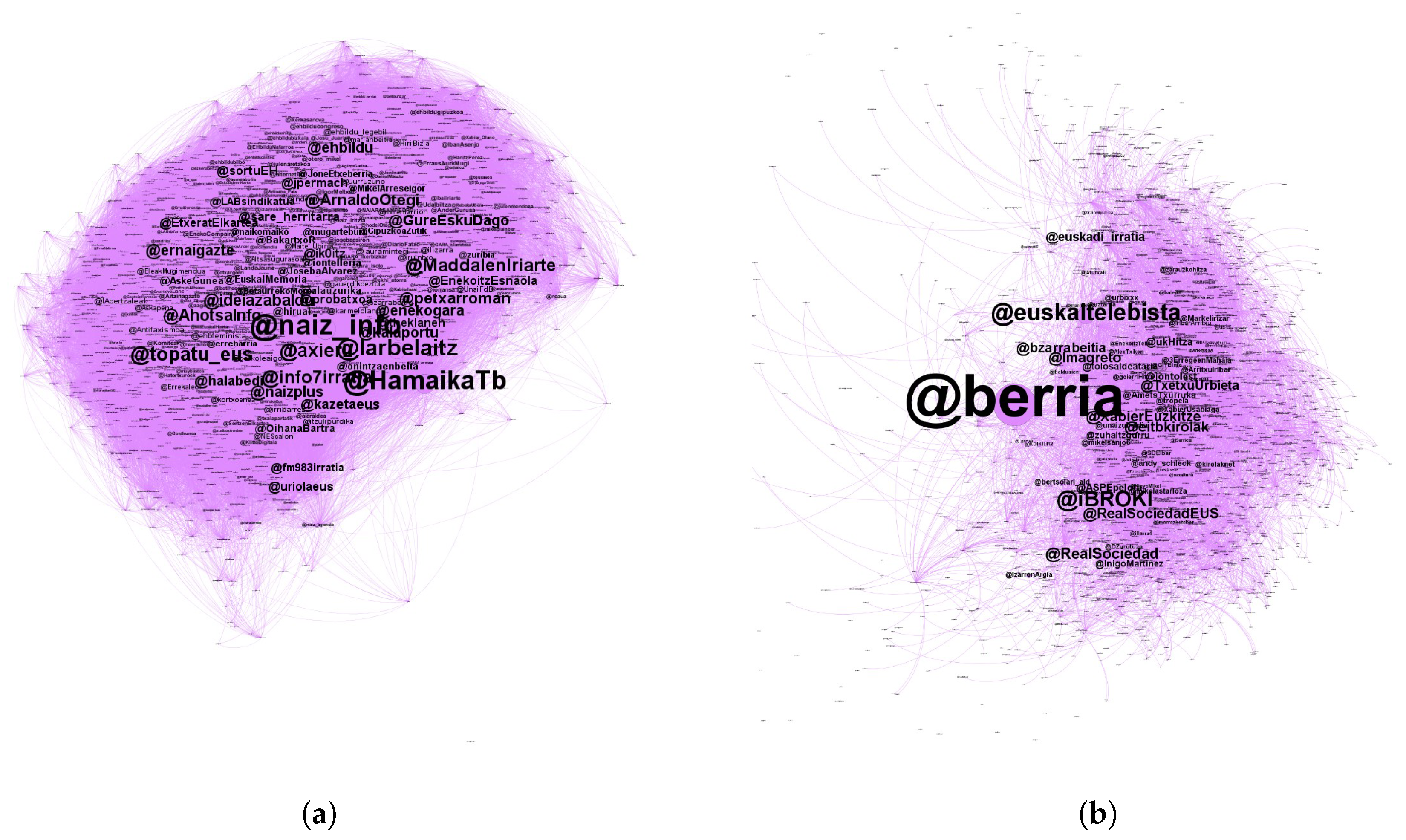
Thus, in the adult graph we identified 33,277 nodes whereas 24,987 nodes were identified among the young users. Once the two independent network graphs, one for young users and another one for adults, were created, we split each network into subgroups to analyze how the communities or subgroups inside each one are formed. The subgroups are defined based on their most important nodes. The aim is to uncover, via their retweets, the relations that are created between the Basque users of Twitter. As an example of the graphs obtained, Figure 6 displays the two most important subgroups within the adult and young graphs, respectively.
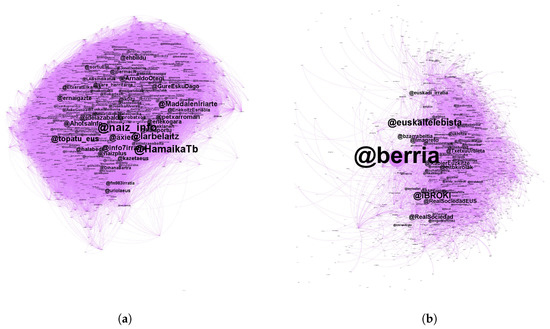
Figure 6.
Example graphs of the two most important subgroups within the adult and young graphs. (a) Most important community (nationalist left) in the adult graph. (b) Most important community (sports) in the young graph.
6.1. Relationships in the Adult Graph
Table 14 shows the five main subgroups derived from the graph of adult users. Each of the subgroups displays a common characteristic, namely, that all of them have a direct relation with topics or issues related to the Basque Country. Thus, it can be seen that for adult users Basque language is used to talk mostly about Basque issues, highlighting politics (Separatist left) and current affairs (news). In other words, the main function is to talk about politics and social issues but with a clear focus on the Basque community itself (rather than on international affairs). In the following we describe the main characteristics of each of the subgroups contained in the graph of adult users.

Table 14.
Most important nodes for the subgroups in the graph of adult users.
- Nationalist left (27.92%): this subgroup is made up of nodes with a specific political orientation, mostly related to members of the Nationalist Left. In addition to the users that appear in the first column of Table 14, there are also many important nodes that refer to specific users (@ArnaldoOtegi, @jpermach, @JosebaAlvarez…) or institutions (@sortuEH, @LAB…) of the Nationalist Left. This is the main group, joined by more than a quarter of all nodes that corresponds to the relationship of a certain political orientation.
- News (23.77%): this group, related to news, consists of almost a quarter of all users. Most of the nodes of this subgroup are related to the media, specially several users related to the Basque public television (EITB).
- Basque language (15.34%): in the third subgroup, there are topics related to the Basque language, such as communication media in Basque (@zuzeu, @Gaztezulo, @ArabakoALEA), associations for the promotion of the Basque language (@AEK_eus, @EHEbizi…) as well as several individuals related to the Basque language (@KikeAmonarriz, @KoldoTellitu, @MertxeMugika).
- Music and GED (13.56%): in the fourth subgroup there is a special phenomenon, since it brings together two different groups in the same subgroup. The first one is related to music, since we can appreciate different users related to the music scene (@EsneBeltza, @ZuriHidalgo, @ZeEsatek, @40minuturock, @hesiantaldea, @ItzrrSemeak…). The second one is related to the users of the social movement “Gure Esku Dago” (@GoierrikoGED, @GEDTolosaldea, @GureEskuDagoDon…).
- Basque tweeters (13.10%): in this last subgroup we can find popular Basque users of Twitter, which are important within the Basque community due to their large number of followers or retweets.
6.2. Relationships in the Young Graph
The subgroups in the graph of young users (see Table 15) display both similarities and differences with respect to the adult graph.

Table 15.
Most important nodes for the subgroups in the graph of young users.
Focusing on the similarities, Basque language, Nationalist left and News are important subgroups in both graphs. These common subgroups can be related to politics and immediacy, which are basic characteristics of identity in Twitter. With respect to the differences, it noticeable that subgroups related to leisure take a more central stage, such as sports and music. Moreover, it is worth pointing out that young Basque users take Twitter as a channel to comment on everyday issues. Finally, the main topics in each of the subgroups within the young users graphs are listed in the following:
- Sports (21.61%): this subgroup, which includes most of the nodes which are considered roles models for the youths, is related to sports. The group is be made up of sports teams or organizations (@RealSociety, @RealSociedadEUS, @ASPEpelota, @SDEibar…), as well as its athletes (@InigoMartinez, @AmetsTxurruka, @XabierUsabiaga, @Markelirizar…). However, the most important nodes are sports journalists (@iBROKI, @XabierEuzkitze, @Imagreto, @bzarrabeitia, @TxetxuUbieta…) and the media (@berria, @euskaltelebista, @eitbkirolak, @euskadi_irratia…). Once again, it can be clearly seen that the newspapers and TV media are the most important nodes.
- Basque language (20.70%): a fifth of all the nodes are in this subgroup. The most important ones are those directly related to the Basque language (@EsaldiakEuskara, @euskarazEH, @Bertsotan, @bertsolaritza, @Euskeraz_Bizi…). In the adult graph it was also found a community related to this topic, although the most important nodes are markedly different.
- Nationalist left (17.12%): this third group, composed of nodes related to the nationalist left, is perhaps the most similar in both adult and young graphs. For example, media (@naiz_info, @topatu_eus, @inform7irratia, @naizplus…), organizations (@ernaigazte, @ehbildu, @sortuEH…) and individuals (@ArnaldoOtegi, @lauramintegi…) related to the nationalist left, appear in both subgroups.
- News (14.92%): as in the previous subgroup, this community is also very similar for both young and adult users. The most important nodes correspond to general news Basque media (@argia, @HamaikaTb, @eitb Albums, @zuzeu, @Gaztezulo).
- music (11.35%): In this final subgroup, although quite heterogeneous, it can be said that the most important nodes are related to music. Among these, the music related media (@gaztea, @DidaGaztea), music bands (@berritxarrak, @muguruzafm, @Glaukomaband), as well as record companies (@BagaBigaeus) are the main nodes.
To finish this section, Table 16 offers an overview of the main subgroups per type of user. Both graphs create communities related to political and social issues, although it is more important for the graph of young users. Moreover, in both types of users Basque language is an important subgroup and it shows that users write in Basque mostly about issues or topics directly related to the Basque Country. The main difference between both types of users is the importance of the sports subgroup which is not present in the graph of adult users. This shows the influence of sports celebrities as role models among young people.

Table 16.
Communities in each graph of users.
7. Conclusions and Future Work
This paper presents an approach to social research of speakers of a less resourced language based on applying Natural Language Processing and topic detection techniques to a large dataset of tweets written in Basque. The collected dataset consists of more than six million tweets from almost 8000 users. This demonstrates that Twitter is a valuable source of spontaneously generated textual data for research on language use and for the discovering of latent social interactions.
Furthermore, we present a comparison of five different approaches to classify Twitter users by life stage, namely, whether they are adult or young people. As age-related information was not present in the collected data, we decided to focus instead on classifying tweets by writing style, assuming that most of the informal tweets are written by young people and vice versa. In order to develop our classifiers, we manually annotated 1000 tweets with the labels formal and informal, and experimented with modern feature-based and deep learning techniques for text classification based on vector-based word representations (word embeddings), clustering features and neural networks. We believe that we provide one of the most competitive approaches for age (or life stage) detection. In our view, our approach is robust enough to be usable across tasks, languages and datasets.
Using the best classifier we automatically tagged the personal tweets contained in the six million corpus, classifying a user’s timeline as young if more than 45% of the tweets were classified as informal, and as adult otherwise. This allowed us to classify almost 8000 Basque Twitter users by their life stage, allowing to obtain meaningful insights with respect to the most important topics per life stage. Moreover, by using the information provided by the users’ retweets, it also facilitated the uncovering of the most important relationships formed within the social network, helping to understand better the differences in social behaviour between young and adult Basque users of Twitter.
More specifically, it was found out that most Basque young users use Twitter to communicate with people close to them about everyday aspects of life, whereas for adults the most important topics were those related with politics and social issues. Furthermore, we were able to characterize quite clearly the different communities that get implicitly formed within the network. Thus, although there are certain similarities, one clear difference was the fact that young people form communities around sport celebrities (footballers and so on) and media.
Future work will include the use of cross-lingual embeddings to improve results with the neural network system, researching methods to obtain the relationship graphs (semi)-automatically and add a temporal dimension to the analysis perform in this paper, so we can see how relations and topics change over time.
We publicly distribute the data collected as well as the best classifiers developed to help promoting both sociological and linguistic processing research in a less resourced high-inflected language such as Basque and about Basque speakers. We believe that the work presented in this paper is applicable to other languages around the world.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.F.d.L., R.A. and I.A.; methodology, J.F.d.L., R.A. and I.A.; software, J.F.d.L., R.A. and I.A.; formal analysis, J.F.d.L., R.A., I.A.; data curation, J.F.d.L. and R.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A. and J.F.d.L.; writing—review and editing, R.A.; supervision, R.A. and I.A.
Funding
The second author is funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO/FEDER, UE), under the project CROSSTEXT (TIN2015-72646-EXP) and the Ramon y Cajal Fellowship RYC-2017-23647. He also acknowledges the support of the BBVA Big Data 2018 “BigKnowledge for Text Mining (BigKnowledge)” project.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of NVIDIA Corporation with the donation of the Titan V GPU used for this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cunliffe, D. Minority Languages and Social Media. In The Palgrave Handbook of Minority Languages and Communities; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 451–480. [Google Scholar]
- Leivada, E.; D’Alessandro, R.; Grohmann, K.K. Eliciting big data from small, young, or non-standard languages: 10 experimental challenges. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.; Doğruöz, A.S.; Rosé, C.P.; de Jong, F. Computational sociolinguistics: A survey. Comput. Linguist. 2016, 42, 537–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, S.; Farra, N.; Nakov, P. SemEval-2017 task 4: Sentiment analysis in Twitter. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–4 August 2017; pp. 502–518. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, T.; de Marneffe, M.C.; Han, B.; Kim, Y.B.; Ritter, A.; Xu, W. Shared tasks of the 2015 workshop on noisy user-generated text: Twitter lexical normalization and named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Noisy User-generated Text, Beijing, China, 31 July 2015; pp. 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.; Kiritchenko, S.; Sobhani, P.; Zhu, X.; Cherry, C. SemEval-2016 task 6: Detecting stance in Tweets. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2016). Association for Computational Linguistics, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2016; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Derczynski, L.; Bontcheva, K.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R.; Hoi, G.W.S.; Zubiaga, A. SemEval-2017 task 8: RumourEval: Determining rumour veracity and support for rumours. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–4 August 2017; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bauman, Z. Liquid Modernity; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Akbik, A.; Blythe, D.; Vollgraf, R. Contextual string embeddings for sequence labeling. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 1638–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan-Lopez, A.A.; Kim, A.E.; Chew, R.F.; Ruddle, P. Predicting age groups of Twitter users based on language and metadata features. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; John, A.; Wang, F.; Kambhampati, S. Et-lda: Joint topic modeling for aligning events and their twitter feedback. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–26 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zubiaga, A.; Spina, D.; Martínez, R.; Fresno, V. Real-time classification of twitter trends. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2015, 66, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.X.; Jiang, J.; Weng, J.; He, J.; Lim, E.P.; Yan, H.; Li, X. Comparing twitter and traditional media using topic models. In European Conference on Information Retrieval; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 338–349. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, L.; Davison, B.D. Empirical study of topic modeling in twitter. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Social Media Analytics, Washington, DC, USA, 25–28 July 2010; pp. 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Conover, M.D.; Ratkiewicz, J.; Francisco, M.; Gonçalves, B.; Menczer, F.; Flammini, A. Political polarization on twitter. In Proceedings of the Fifth International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Barcelona, Spain, 17–21 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pennacchiotti, M.; Popescu, A.M. Democrats, republicans and starbucks afficionados: User classification in twitter. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 August 2011; pp. 430–438. [Google Scholar]
- Zubiaga, A.; Wang, B.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R. Stance classification of social media users in independence movements. Catalonia 2017, 2, 10–960. [Google Scholar]
- Villena Román, J.; Lana Serrano, S.; Martínez Cámara, E.; González Cristóbal, J.C. Tass-Workshop on Sentiment Analysis at SEPLN; The Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing: Jaén, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ritter, A.; Clark, S.; Etzioni, O. Named entity recognition in tweets: An experimental study. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Edinburgh, UK, 27–31 July 2011; pp. 1524–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Alegria, I.; Aranberri, N.; Comas, P.R.; Fresno, V.; Gamallo, P.; Padró, L.; San Vicente, I.; Turmo, J.; Zubiaga, A. TweetNorm: A benchmark for lexical normalization of Spanish tweets. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2015, 49, 883–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiaga, A.; San Vicente, I.; Gamallo, P.; Pichel, J.R.; Alegria, I.; Aranberri, N.; Ezeiza, A.; Fresno, V. Tweetlid: A benchmark for tweet language identification. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2016, 50, 729–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.; Yarowsky, D.; Shreevats, A.; Gupta, M. Classifying latent user attributes in twitter. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Search and Mining User-Generated Contents, Toronto, ON, Canada, 26–30 October 2010; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Al Zamal, F.; Liu, W.; Ruths, D. Homophily and latent attribute inference: Inferring latent attributes of Twitter users from neighbors. ICWSM 2012, 270, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Gravel, R.; Trieschnigg, D.; Meder, T. “How old do you think I am?” A study of language and age in Twitter. In Proceedings of the Seventh International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media ICWSM, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–11 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt, J.; Farnadi, G.; Vasudevan, G.; Moens, M.F.; Davalos, S.; Teredesai, A.; De Cock, M. Age and gender identification in social media. In Proceedings of the CLEF 2014 Evaluation Labs, Sheffield, UK, 15–18 September 2014; pp. 1129–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Cesare, N.; Grant, C.; Nsoesie, E.O. Detection of user demographics on social media: A review of methods and recommendations for best practices. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1702.01807. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, P. Age as a sociolinguistic variable. In The Handbook of Sociolinguistics; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 151–167. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, S.; McKeown, K. Age prediction in blogs: A study of style, content, and online behavior in pre-and post-social media generations. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Portland, OR, USA, 19–24 June 2011; Association for Computational Linguistics: Portland, OR, USA, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 763–772. [Google Scholar]
- Gamallo, P.; Pichel, J.R.; Alegria, I. From language identification to language distance. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 484, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; Association for Computational Linguistics: Doha, Qatar, 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Grave, E.; Bojanowski, P.; Puhrsch, C.; Joulin, A. Advances in Pre-Training Distributed Word Representations. In Proceedings of the 11th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Agerri, R.; Rigau, G. Robust multilingual Named Entity Recognition with shallow semi-supervised features. Artif. Intell. 2016, 238, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerri, R.; Rigau, G. Language independent sequence labelling for Opinion Target Extraction. Artif. Intell. 2019, 268, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Bermúdez, M. An analysis of twitter corpora and the differences between formal and colloquial tweets. In Proceedings of the Tweet Translation Workshop 2015, Alicante, Spain, 5 September 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.F.; Goodman, J. An empirical study of smoothing techniques for language modeling. Comput. Speech Lang. 1999, 13, 359–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turian, J.; Ratinov, L.A.; Bengio, Y. Word representations: A simple and general method for semi-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Uppsala, Sweden, 11–16 July 2010; Association for Computational Linguistics: Uppsala, Sweden, 2010; pp. 384–394. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.F.; Desouza, P.V.; Mercer, R.L.; Pietra, V.J.D.; Lai, J.C. Class-based n-gram models of natural language. Comput. Linguist. 1992, 18, 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A. Combining distributional and morphological information for part of speech induction. In Proceedings of the Tenth Conference on European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Budapest, Hungary, 12–17 April 2003; Association for Computational Linguistics: Budapest, Hungary, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Leturia, I. Evaluating different methods for automatically collecting large general corpora for Basque from the web. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference onComputational Linguistics COLING, Mumbai, India, 8–15 December 2012; pp. 1553–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Rehurek, R.; Sojka, P. Software framework for topic modelling with large corpora. In Proceedings of the LREC 2010 Workshop on New Challenges for NLP Frameworks, Citeseer, Valletta, Malta, 22 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Agerri, R.; Bermudez, J.; Rigau, G. IXA pipeline: Efficient and ready to use multilingual NLP tools. LREC 2014, 2014, 3823–3828. [Google Scholar]
- Binkley, D.; Heinz, D.; Lawrie, D.; Overfelt, J. Understanding LDA in source code analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Program Comprehension, Hyderabad, India, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Steyvers, M.; Griffiths, T. Probabilistic Topic Models in Latent Semantic Analysis: A Road to Meaning; Landauer, T., Mc Namara, D., Dennis, S., Kintsch, W., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sievert, C.; Shirley, K. LDAvis: A method for visualizing and interpreting topics. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Interactive Language Learning, Visualization, and Interfaces, Baltimore, MD, USA, 27 June 2014; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. ICWSM 2009, 8, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacomy, M.; Venturini, T.; Heymann, S.; Bastian, M. ForceAtlas2, a continuous graph layout algorithm for handy network visualization designed for the Gephi software. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).