Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things: A Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Comparison with Other Surveys
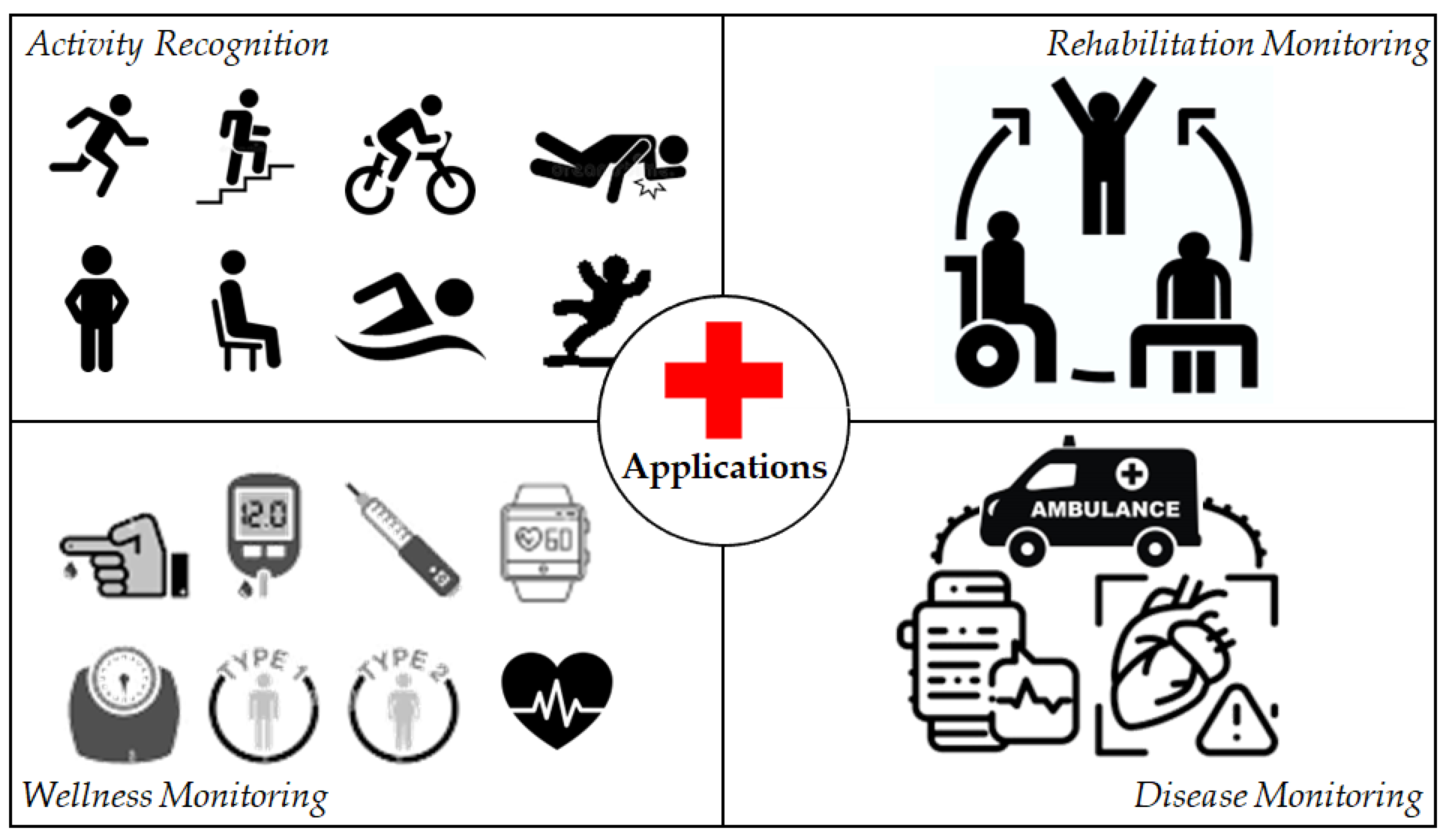
3. Applications of Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things
3.1. Activity Recognition
3.2. Rehabilitation Monitoring
3.3. Wellness Monitoring
3.4. Disease Monitoring
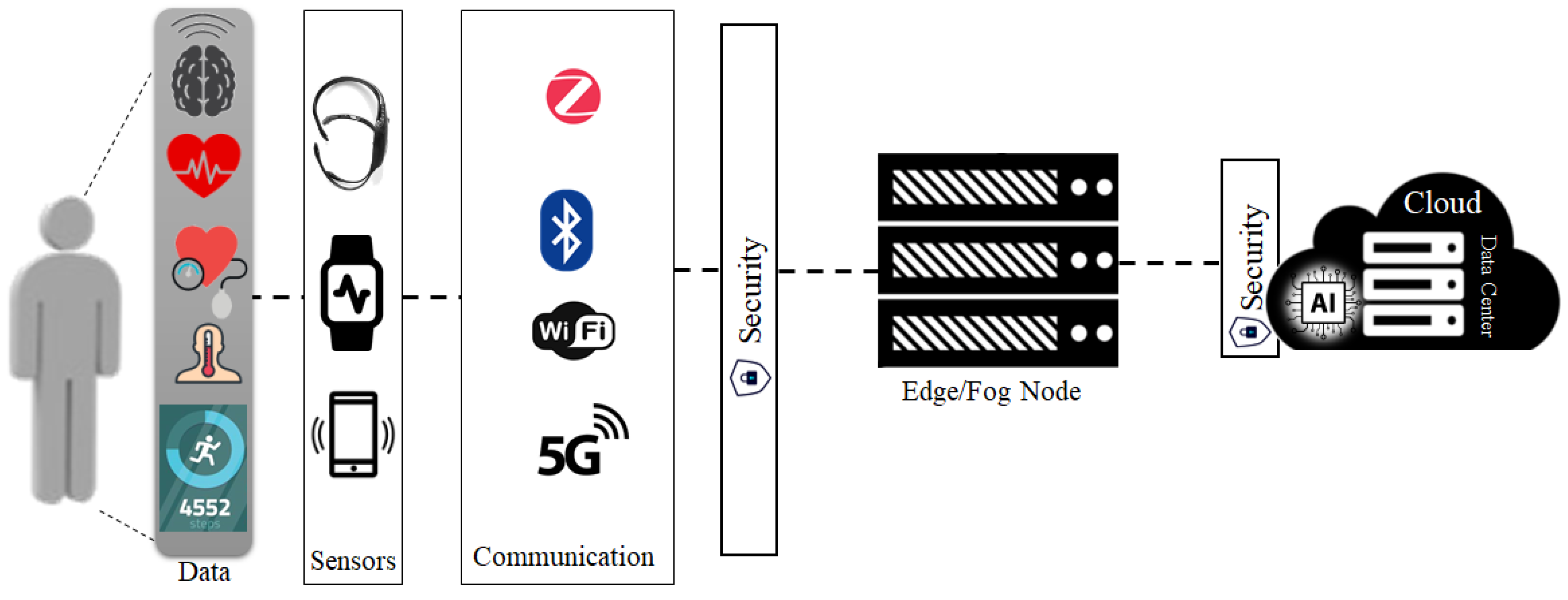
4. Key Components in the Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things
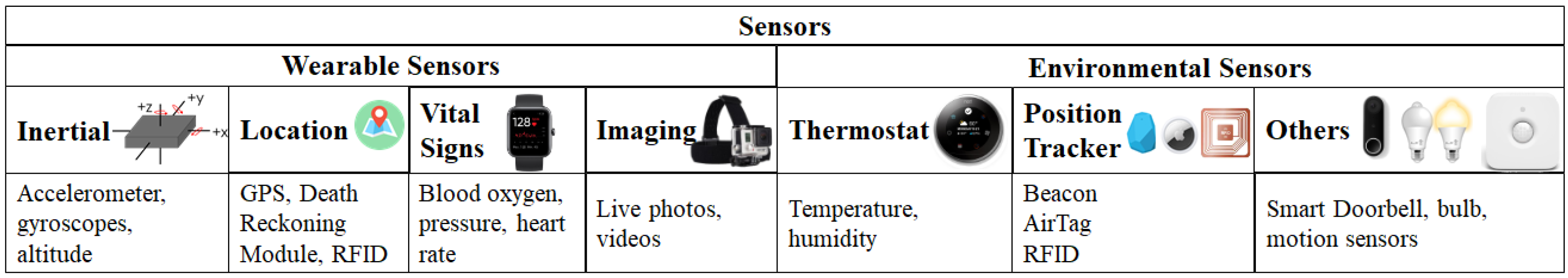
4.1. Sensors
4.2. Communication
4.2.1. Wireless Sensor Networks and Smart Body Area Networks
4.2.2. Cellular Technologies
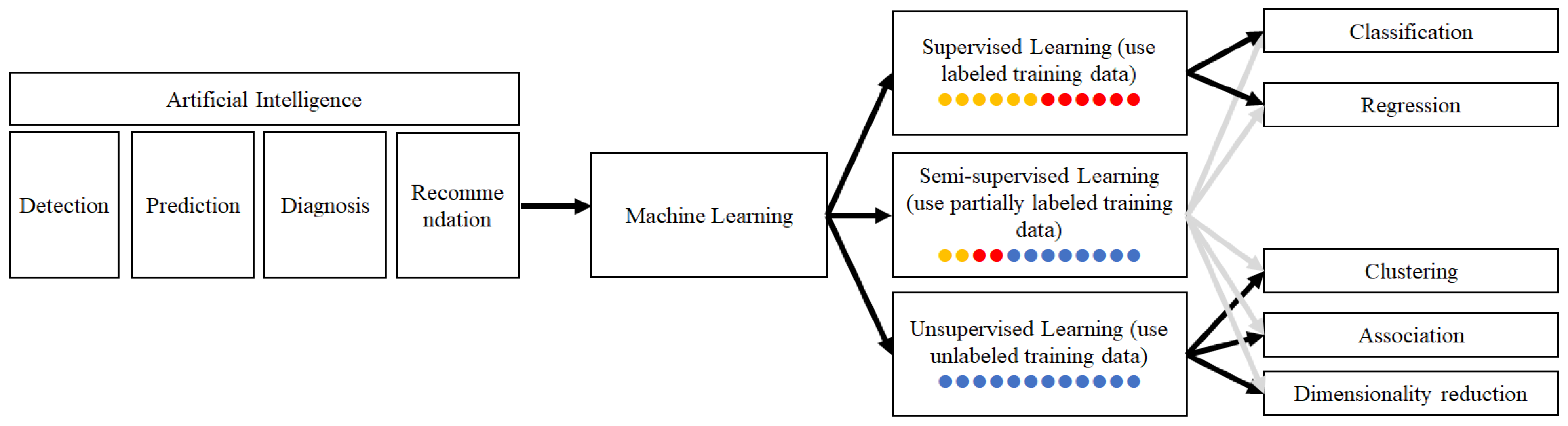
4.3. Artificial Intelligence
4.3.1. Activity Detection
4.3.2. Disease Diagnosis
4.3.3. Disease Prediction
4.3.4. Medical Decision Recommendation
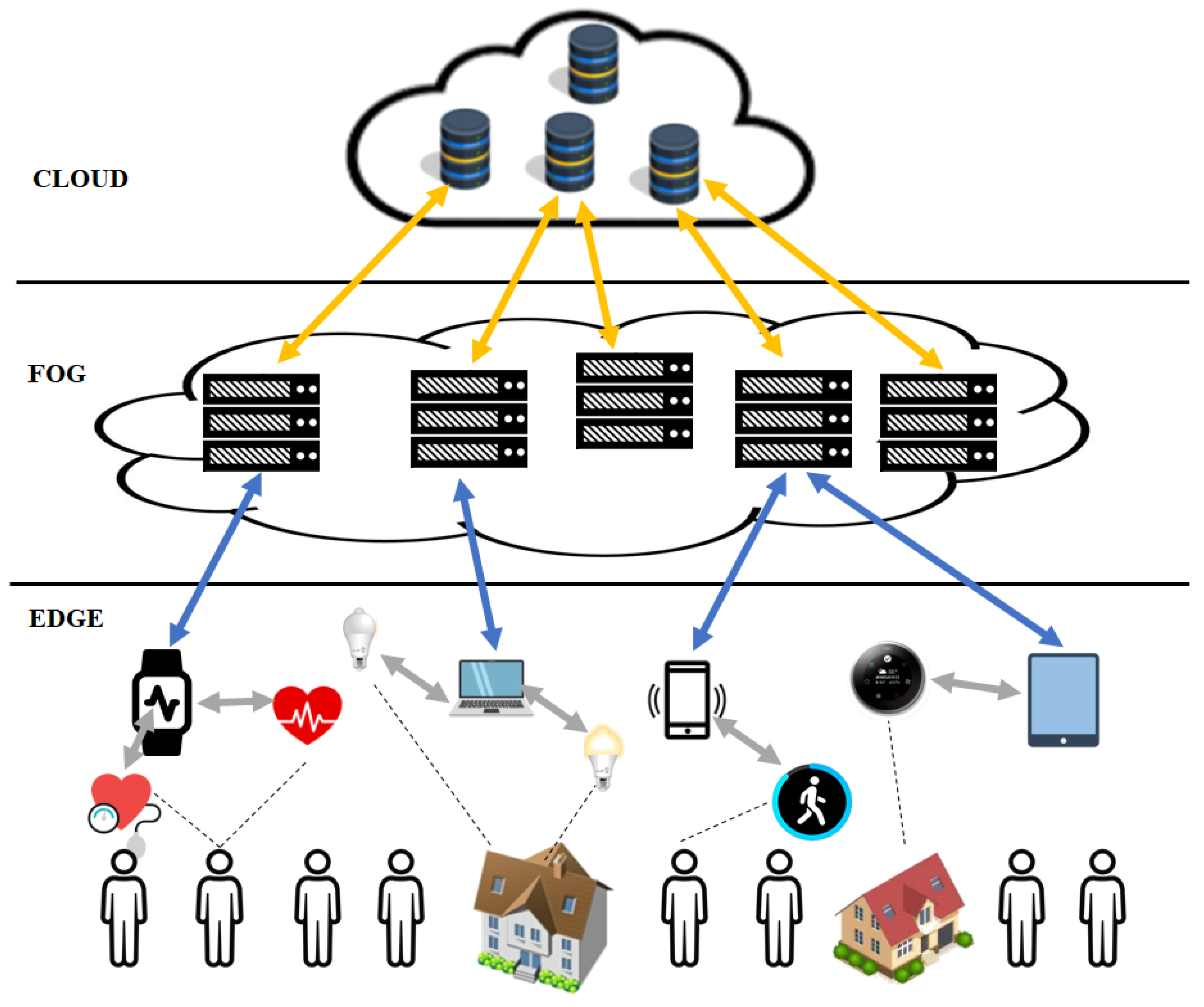
4.4. Cloud Computing Infrastructure
4.5. Security
5. Existing Challenges
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isravel, D.P.; Silas, S. A comprehensive review on the emerging IoT-cloud based technologies for smart healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 6–7 March 2020; pp. 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Yang, P.; Min, G.; Amft, O.; Dong, F.; Xu, L. Advanced internet of things for personalised healthcare systems: A survey. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2017, 41, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Malik, H.; Khan, M.I.; Pardy, T.; Kuusik, A.; le Moullec, Y. A survey on the roles of communication technologies in IoT-based personalized healthcare applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 36611–36631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, Y.; Parvati, V.K.; Biradar, S.R. Survey of smart healthcare systems using internet of things (IoT). In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Communication, Computing and Internet of Things (IC3IoT), Chennai, India, 15–17 February 2018; pp. 508–513. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, H.; Arji, G.; Shahmoradi, L.; Safdari, R.; Nilashi, M.; Alizadeh, M. The application of internet of things in healthcare: A systematic literature review and classification. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2019, 18, 837–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajini, N.H. A comprehensive survey on internet of things based healthcare services and its applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 27–29 March 2019; pp. 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Habibzadeh, H.; Dinesh, K.; Shishvan, O.R.; Boggio-Dandry, A.; Sharma, G.; Soyata, T. A survey of healthcare internet of things (HIoT): A clinical perspective. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usak, M.; Kubiatko, M.; Shabbir, M.S.; Viktorovna Dudnik, O.; Jermsittiparsert, K.; Rajabion, L. Health care service delivery based on the internet of things: A systematic and comprehensive study. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2020, 33, e4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanvijay, M.M.; Patil, S.C. Internet of things: A survey of enabling technologies in healthcare and its applications. Comput. Netw. 2019, 153, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, M.A.; Gures, E.; Shayea, I. A Survey on IoT Smart Healthcare: Emerging Technologies, Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends. arXiv 2021, arXiv:CoRR/2109.02042. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Song, Z.; Yan, S. STAP: Spatial-Temporal Attention-Aware Pooling for Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Nguyen, C.D.; Moulin, P. RGBD-camera based get-up event detection for hospital fall prevention. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 1405–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Ni, L.M. WiFall: Device-free fall detection by wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2017, 16, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Yao, L.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Falkner, N.; Li, X.; Gu, T. Tagfall: Towards unobstructive fine-grained fall detection based on UHF passive RFID tags. In Proceedings of the 12th EAI nternational Conference Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking, and Services, Coimbra, Portugal, 22–24 July 2015; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.Z.; Soylu, A. Human activity recognition using wearable sensors, discriminant analysis, and long short-term memory-based neural structured learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Tao, X.; Lu, J. Recognizing multiuser activities using wireless body sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2011, 10, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, H. Indoor human activity recognition based on ambient radar with signal processing and machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Teasell, R.; Meyer, M.J.; McClure, A.; Pan, C.; Murie-Fernandez, M.; Foley, N.; Salter, K. Stroke rehabilitation: An international perspective. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2009, 16, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3 Ways to Avoid a Second Stroke. 2022. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/stroke/3-ways-to-avoid-a-second-stroke (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Standen, P.; Threapleton, K.; Richardson, A.; Connell, L.; Brown, D.; Battersby, S.; Platts, F.; Burton, A. A low cost virtual reality system for home based rehabilitation of the arm following stroke: A randomised controlled feasibility trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, M.; Hoda, Y.; Hafidh, B.; El Saddik, A. Predicting muscle forces measurements from kinematics data using Kinect in stroke rehabilitation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 1885–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobin, M.; Anastassova, M.; Boukallel, M.; Ammi, M. SyMPATHy: Smart glass for monitoring and guiding stroke patients in a home-based context. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGCHI Symposium on Engineering Interactive Computing Systems, Brussels, Belgium, 21–24 June 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- National Diabetes Statistics Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Al-Taee, M.A.; Al-Nuaimy, W.; Muhsin, Z.J.; Al-Ataby, A. Robot assistant in management of diabetes in children based on the internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fioravanti, A.; Fico, G.; Salvi, D.; García-Betances, R.I.; Arredondo, M.T. Automatic messaging for improving patients engagement in diabetes management: An exploratory study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiya, K.; Koyama, A. Design and implementation of meal information collection system using IoT wireless tags. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th International Conference on Complex, Intelligent, and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS), Fukuoka, Japan, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hypertension Cascade: Hypertension Prevalence, Treatment and Control Estimates among U.S. Adults Aged 18 Years and Older Applying the Criteria from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association’s 2017 Hypertension Guideline—NHANES 2015–2018external Icon; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021.
- Janjua, G.; Guldenring, D.; Finlay, D.; McLaughlin, J. Wireless chest wearable vital sign monitoring platform for hypertension. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 821–824. [Google Scholar]
- Iakovakis, D.; Hadjileontiadis, L. Standing hypotension prediction based on smartwatch heart rate variability data: A novel approach. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services, Florence, Italy, 6–9 September 2016; pp. 1109–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying Cause of Death, 1999–2018; CDC WONDER Online Database; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018.
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Aparicio, H.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2021 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e254–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiranyaz, S.; Ince, T.; Gabbouj, M. Personalized monitoring and advance warning system for cardiac arrhythmias. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmier, J.K.; Ong, K.L.; Fonarow, G.C. Cost-effectiveness of remote cardiac monitoring with the cardioMEMS heart failure system. Clin. Cardiol. 2017, 40, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Li, S. An automatic cardiac arrhythmia classification system with wearable electrocardiogram. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 16529–16538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, S.; Page, A.; Kantarci, B.; Soyata, T. Machine learning in cardiac health monitoring and decision support. IEEE Comput. Mag. 2016, 49, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arppana, A.R.; Reshmma, N.K.; Raghu, G.; Mathew, N.; Nair, H.R.; Aneesh, R.P. Real Time Heart Beat Monitoring Using Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2021 Seventh International Conference on Bio Signals, Images, and Instrumentation (ICBSII), Chennai, India, 25–27 March 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.S.; Saatchi, R.; Elphick, H.; Burke, D. Real-time vision based respiration monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2010 7th International Symposium Communication Systems Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), Porto, Portugal, 20–22 July 2010; pp. 770–774. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.G.; Fernandes, D.; Branco, S.; Monteiro, J.L.; Cabral, J.; Catarino, A.P.; Rocha, A.M. A smart wearable system for sudden infant death syndrome monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference Industrial Technology (ICIT), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–17 March 2016; pp. 1920–1925. [Google Scholar]
- Raji, A.; Devi, P.K.; Jeyaseeli, P.G.; Balaganesh, N. Respiratory monitoring system for asthma patients based on IoT. In Proceedings of the 2016 Online Int. Conf. Green Engineering and Technologies (IC-GET), Coimbatore, India, 19 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Why Do We Need Sleep? 2022. Available online: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works/why-do-we-need-sleep (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chén, O.Y.; de Vos, M. SeqSleepNet: End-to-End Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Network for Sequence-to-Sequence Automatic Sleep Staging. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, A.; Alqurashi, R.; Raghebi, Z.; Banaei-Kashani, F.; Halbower, A.C.; Vu, T. A lightweight and inexpensive in-ear sensing system for automatic whole-night sleep stage monitoring. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Embedded Network Sensor Systems CD-ROM, Stanford, CA, USA, 14–16 November 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 230–244. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Pathak, P.H.; Zeng, Y.; Liran, X.; Mohapatra, P. Vital sign and sleep monitoring using millimeter wave. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. (TOSN) 2017, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.; Jaimes, L.G.; Labrador, M.A. mStress: A mobile recommender system for just-in-time interventions for stress. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th IEEE Annu. Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- McWhorter, J.; Brown, L.; Khansa, L. A wearable health monitoring system for posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Inspired Cogn. Archit. 2017, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.C.T.; Montoro, G.; Gomez, J. The potential of smartwatches for emotional self-regulation of people with autism spectrum disorder, BIOSTEC 2016. In Proceedings of the 9th Internationl Joint Conference Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies: Health Infornation, Rome, Italy, 21–23 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oti, O.; Azimi, I.; Anzanpour, A.; Rahmani, A.M.; Axelin, A.; Liljeberg, P. IoT-Based Healthcare System for Real-Time Maternal Stress Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems and Engineering Technologies (CHASE), Washington, DC, USA, 26–28 September 2018; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/aging/aginginfo/alzheimers.htm (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Ishii, H.; Kimino, K.; Aljehani, M.; Ohe, N.; Inoue, M. An early detection system for dementia using the M2M/IoT platform. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 96, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamamizu, K.; Tokunaga, S.; Saiki, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yasuda, K. Towards person-centered anomaly detection and support system for home dementia care. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (HCI International), Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–22 July 2016; pp. 274–285. [Google Scholar]
- Szeles, J.; Kubota, N. Location monitoring support application in smart phones for elderly people, using suitable interface design. In Proceedings of the International Conference Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Yantai, China, 22–25 October 2016; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson’s Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.parkinson.org/Understanding-Parkinsons/Statistics (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Huntington’s Disease. 2022. Available online: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/huntingtons-disease (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Dinesh, K.; Xiong, M.; Adams, J.; Dorsey, R.; Sharma, G. Signal analysis for detecting motor symptoms in Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease using multiple body-affixed sensors: A pilot study. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Western New York Image and Signal Processing Workshop (WNYISPW), Rochester, NY, USA, 18 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.; Dinesh, K.; Xiong, M.; Tarolli, C.; Sharma, S.; Sheth, N.; Aranyosi, A.J.; Zhu, W.; Goldenthal, S.; Biglan, K.; et al. Multiple wearable sensors in Parkinson and Huntington disease individuals: A pilot study in clinic and at home. Digit. Biomark. 2017, 1, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristopher, F.; Ophir, F.; Sean, M.; Gholam, M. Real-time Streaming of Gait Assessment for Parkinson’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Jerusalem, Israel, 8–12 March 2021; pp. 1081–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Moncada-Torres, A.; Leuenberger, K.; Gonzenbach, R.; Luft, A.; Gassert, R. Activity classification based on inertial and barometric pressure sensors at different anatomical locations. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 1245–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Bosch, S.; Incel, O.; Scholten, H.; Havinga, P. A Survey of Online Activity Recognition Using Mobile Phones. Sensors 2015, 15, 2059–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, T.; Anantakrishnan, N.S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Duttagupta, S.P. Impact of Ambulation in Wearable-ECG. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensley, D.; Silverman, M. Peak Flow Monitoring for Guided Self-management A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulling, A.; Ward, J.A.; Gellersen, H. Multimodal recognition of reading activity in transit using body-worn sensors. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. 2012, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, F.; Kuo, C.; Cheng, H.; Buthpitiya, S.; Collins, P.; Griss, M. Activity-aware Mental Stress Detection Using Physiological Sensors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mobile Computing, Applications, and Services, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–12 October 2012; Volume 76, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, E.; Kapur, N.; Williams, L.; Hodges, S.; Watson, P.; Smyth, G.; Srinivasan, J.; Smith, R.; Wilson, B.; Wood, K. The use of a wearable camera, SenseCam, as a pictorial diary to improve autobiographical memory in a patient with limbic encephalitis: A preliminary report. Eur. Rehabil. 2016, 2011, 582–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, A.R.; Caprani, N.; Conaire, C.Ó.; Kalnikaite, V.; Gurrin, C.; Smeaton, A.F.; Connor, N.E.O. Computers in Human Behavior Passively recognising human activities through lifelogging. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, C.; Kohno, R. Wireless Sensing System for Healthcare Monitoring Thermal Physiological State and Recognizing Behavior. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Broadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications, Barcelona, Spain, 26–28 October 2011; pp. 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Sixsmith, A.; Johnson, N. A smart sensor to detect the falls of the elderly. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2004, 3, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, H.; Hee, S.; Ha, K.; Chul, H.; Chung, W.; Young, J.; Chang, Y.; Hyun, D. Ubiquitous healthcare service using Zigbee and mobile phone for elderly patients. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2008, 8, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Wu, W.; Moniri, M.; Chibelushi, C.C. Efficient object localization using sparsely distributed passive RFID tags. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5914–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafferty, J.; Member, C.N.-I.; Member, L.C.-I.; Qi, J.; Dutton, R.; Zirk, A.; Boye, L.T.; Kohn, M.; Hellman, R. NFC based provisioning of instructional videos to assist with instrumental activities of daily living. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 4131–4134. [Google Scholar]
- Bouten, C.V.; Koekkoek, K.T.; Verduin, M.; Kodde, R.; Janssen, J.D. A triaxial accelerometer and portable data processing unit for the assessment of daily physical activity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1997, 44, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dejnabadi, H.; Jolles, B.M.; Aminian, K. A new approach to accurate measurement of uniaxial joint angles based on a combination of accelerometers and gyroscopes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Fox, D.; Kautz, H. Hierarchical Conditional Random Fields for GPS-Based Activity Recognition. Star 2007, 28, 487–506. [Google Scholar]
- Honeywell Introduces DRM 4000 Dead Reckoning Module. 2022. Available online: https://www.fierceelectronics.com/components/honeywell-introduces-drm-4000-dead-reckoning-module (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Sangwan, R.S.; Qiu, R.G.; Member, S.K.; Jessen, D. Using RFID Tags for Tracking Patients, Charts and Medical Equipment within an Integrated Health Delivery Network. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Networking, Sensing and Control, Tucson, AZ, USA, 19–22 March 2005; pp. 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, R.; Galway, L.; Nugent, C.; Jamison, C.; Gawley, R.; McCullagh, P.; Zhang, H.; Black, N. A Platform for Self-Management Supported by Assistive, Rehabilitation and Telecare Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2011 5th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (PervasiveHealth) and Workshops, Dublin, Ireland, 23–26 May 2011; pp. 458–460. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Marcos, A.; Azkune, G.; Arganda-Carreras, I. Egocentric Vision-based Action Recognition: A survey. Neurocomputing 2022, 472, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nest Thermostat. 2022. Available online: https://nest.com/thermostats/ (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Estimote Beacon. 2022. Available online: https://estimote.com/ (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- AirTag. 2022. Available online: https://www.apple.com/airtag (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Smart Doorbell. 2022. Available online: https://ring.com/doorbell-cameras (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Smart Bulbs. 2022. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/smart-bulbs (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- de Toledo, P.; Sanchis, A. Activity Recognition Using Hybrid Generative/Discriminative Models on Home Environments Using Binary Sensors. Sensors 2013, 13, 5460–5477. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, M.; Khan, I.H. Internet of Things (IoT) enabled healthcare helps to take the challenges of COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2021, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullo, S.L.; Sinha, G.R. Advances in Smart Environment Monitoring Systems Using IoT and Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart Body Area Network (SmartBAN). Enhanced Ultra-Low Power Physical Layer. document ETSI TS 103 326 V1.1.1. ETSI TC 2015, 13, V1. [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen, M.; Mucchi, L.; Girod-Genet, M.; Paso, T.; Farserotu, J.; Tanaka, H.; Anzai, D.; Pierucci, L.; Khan, R.; Alam, M.M.; et al. ETSI SmartBAN Architecture: The Global Vision for Smart Body Area Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 150611–150625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabayashi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Sakakibara, K. Integrated Performance Evaluation of the Smart Body Area Networks Physical Layer for Future Medical and Healthcare IoT. Sensors 2018, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Xiong, X.; Zheng, K.; Xu, R.; Xiang, W.; Chatzimisios, P. Low power wide area machine-to-machine networks: Key techniques and prototype. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Mishra, P.; Wang, K.-C. 5G-IoT Architecture for Next Generation Smart Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th 5G World Forum (5GWF), Montreal, QC, Canada, 13–15 October 2021; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Juneja, P.K.; Sharma, S.; Garg, U. Future Aspect of 5G-IoT Architecture in Smart Healthcare System. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 6–8 May 2021; pp. 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.T.; Jin, Q. Deep learning-enhanced human activity recognition for internet of healthcare things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6429–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xue, K.; Zhang, K. Current status and future trends of clinical diagnoses via image-based deep learning. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7556–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battineni, G.; Sagaro, G.G.; Chinatalapudi, N.; Amenta, F. Applications of Machine Learning Predictive Models in the Chronic Disease Diagnosis. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wynants, L.; Van Calster, B.; Collins, G.S.; Riley, R.D.; Heinze, G.; Schuit, E.; Bonten, M.M.J.; Dahly, D.L.; Damen, J.A.; Debray, T.P.A.; et al. Prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19: Systematic review and critical appraisal. BMJ 2020, 369, m1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoabi, Y.; Deri-Rozov, S.; Shomron, N. Machine learning-based prediction of COVID-19 diagnosis based on symptoms. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.-W.; Zang, G.-Y.; Pu, J. The primary use of artificial intelligence in cardiovascular diseases: What kind of potential role does artificial intelligence play in future medicine? J. Geriatr. Cardiol. JGC 2019, 16, 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Almustafa, K.M. Prediction of heart disease and classifiers’ sensitivity analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, S.; Thomas, J.; John, S.-T.; Mac Aonghusa, P.; Shawe-Taylor, J.; Kelly, M.P.; Deleris, L.A.; Finnerty, A.N.; Marques, M.M.; Norris, E.; et al. The Human Behavior-Change Project: Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning for evidence synthesis and interpretation. Implement. Sci. 2017, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asthana, S.; Megahed, A.; Strong, R. A Recommendation System for Proactive Health Monitoring Using IoT and Wearable Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on AI & Mobile Services (AIMS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Monteiro, E.; Silva, L.B.; Sierra, A.P.; Oliveira, J.L. A Recommender System to Help Discovering Cohorts in Rare Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rochester, MN, USA, 28–30 July 2020; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seda, P.E.; Ilias, M.; Andreas, M.; Alexander, F.; Tran, T.N.T. Recommender Systems for IoT Enabled m-Health Applications. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations, Rhodes, Greece, 25–27 May 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.P. An Introduction to Dew Computing: Definition, Concept and Implications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazerolghaem, A.; Yaghmaee, M.H.; Leon-Garcia, A. Green Cloud Multimedia Networking: NFV/SDN Based Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2020, 4, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroui, M.; Nour, B.; Moungla, H.; Cherif, M.A.; Afifi, H. Mohsen Guizanie. Edge and fog computing for IoT: A survey on current research activities & future directions. Comput. Commun. 2021, 180, 210–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Hanzo, L. A Survey on Wireless Security: Technical Challenges, Recent Advances, and Future Trends. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1727–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, T.; Jin, H.; Nahrstedt, K. WritingHacker: Audio based eavesdropping of handwriting via mobile devices. In Proceedings of the UbiComp 2016—Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Heidelberg, Germany, 12 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Jin, H.; Nahrstedt, K. Mobile Devices based Eavesdropping of Handwriting. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 19, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.C. Yoshua Bengio: Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanas, A.; Patsakis, C.; Conti, M.; Vlachos, I.S.; Ramos, V.; Falcone, F.; Postolache, O.; Perez-martinez, P.A.; Pietro, R.D.; Perrea, D.N.; et al. Smart health: A context-aware health paradigm within smart cities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Deng, R.H. Security and Privacy in Smart Health: Efficient Policy-Hiding Attribute-Based Access Control. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 2130–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzis, K.; Jones, R.; Despotou, G. The challenges of balancing safety and security in implantable medical devices. In Unifying the Applications and Foundations of Biomedical and Health Informatics; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, G.M.; Mehmood, Q.; Khan, C.B.A. Adoption of lamport signature scheme to implement digital signatures in IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), Sukkur, Pakistan, 3–4 March 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- AboBakr, A.; Azer, M.A. IoT ethics challenges and legal issues. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Systems (ICCES), Cairo, Egypt, 19–20 December 2017; pp. 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, A.M.; Travagnin, M. A Secure Quantum Communications Infrastructure for Europe; JRC Technical Papers; JRC: Ispra, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vidakis, K.; Mavrogiorgou, A.; Kiourtis, A.; Kyriazis, D. A comparative study of short-range wireless communication technologies for health information exchange. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical, Communication, and Computer Engineering (ICECCE), Istanbul, Turkey, 12–13 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Koufos, K.; EI Haloui, K.; Dianati, M.; Higgins, M.; Elmirghani, J.; Imran, M.A.; Tafazolli, R. Trends in Intelligent Communication Systems: Review of Standards, Major Research Projects, and Identification of Research Gaps. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2021, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.T.; Le, K.; Hoang, T.; Le, H.; Nguyen, T.V.; Cheung, N.M. Simultaneous feature aggregating and hashing for compact binary code learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4954–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Surveys | Survey Comparison | Review of Applica-tions | Key Components | Challenges | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Devices/Sensors | Commu-nication | Artificial Intelligence | Cloud Computing | Security and Privacy | ||||
| Qi et al. [2] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Alam et al. [3] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Shaikh et al. [4] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Ahmadi et al. [5] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Rajin [6] | ✓ | |||||||
| Habibzadeh et al. [7] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Usak [8] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Dhanvijay and Patil [9] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Ali Tunc et al. [10] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Ours | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phung, K.A.; Kirbas, C.; Dereci, L.; Nguyen, T.V. Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things: A Survey. Information 2022, 13, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13080360
Phung KA, Kirbas C, Dereci L, Nguyen TV. Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things: A Survey. Information. 2022; 13(8):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13080360
Chicago/Turabian StylePhung, Kim Anh, Cemil Kirbas, Leyla Dereci, and Tam V. Nguyen. 2022. "Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things: A Survey" Information 13, no. 8: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13080360
APA StylePhung, K. A., Kirbas, C., Dereci, L., & Nguyen, T. V. (2022). Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things: A Survey. Information, 13(8), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13080360







