A Data-Driven Approach to Set-Theoretic Model Predictive Control for Nonlinear Systems †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Manuscript Contribution
2. Notations, Definitions, and Problem Formulation
Problem Formulation
- MPC Problem—Given the nonlinear system (4), a sequence of regions and an initial state compute at each time instant t and on the basis of the current state a control strategy, compatible with (5), such that there exists a finite time instant so that is achieved while a performance index is minimized.
3. Background
| Algorithm 1 Set-theoretic Model Predictive Control (ST-MPC) Algorithm |
| Input: |
| Output: |
| 1: Compute |
| 2: if then |
| 3: else |
| 4: end if |
| 5: Apply |
| 6: Goto Step 1; |
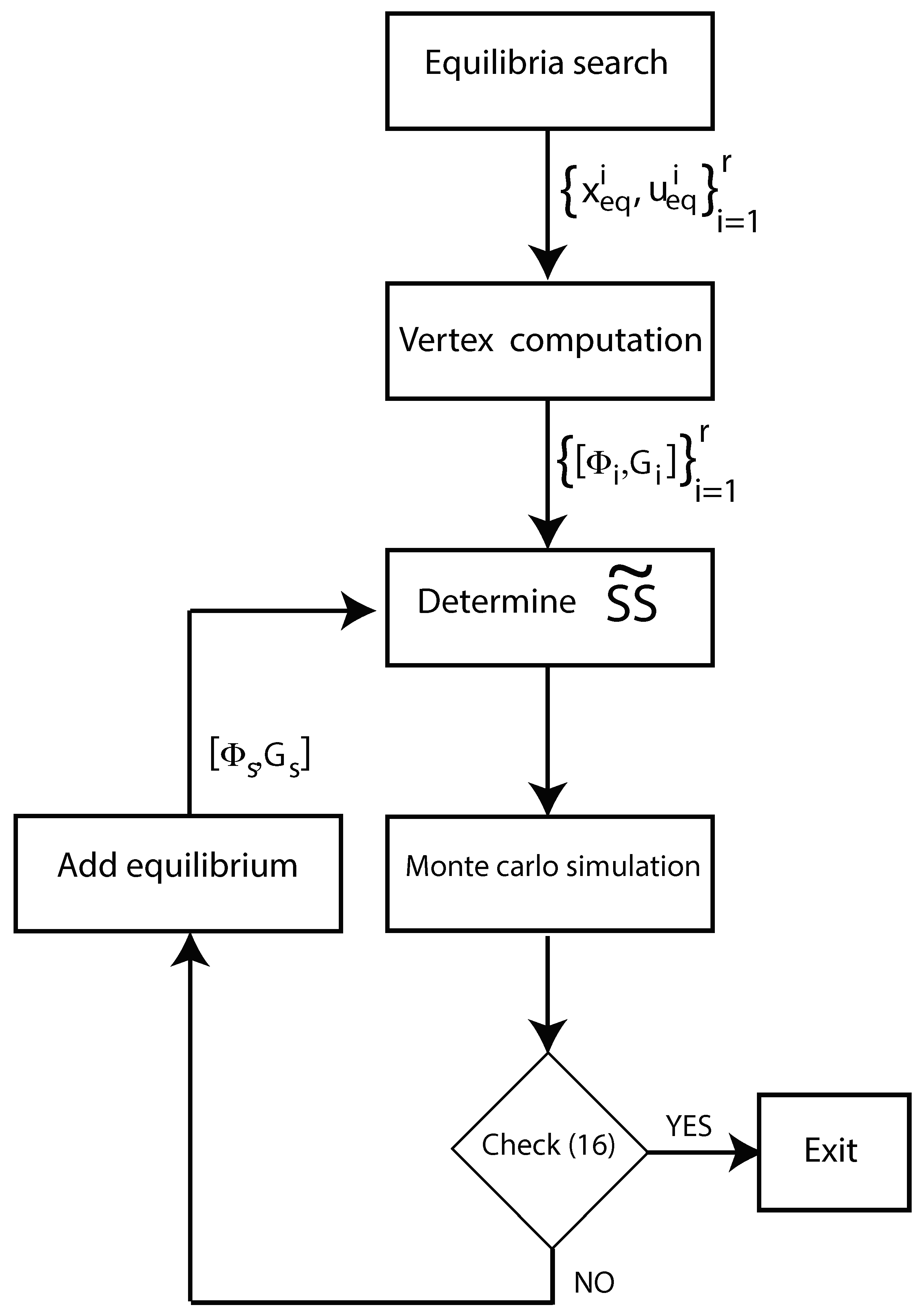
4. A Data-Driven Low-Demand Algorithm
4.1. Stabilizing Control and Positively Invariant Set
4.2. Polytopic Embedding and Data-Set Machine Learning-Based Algorithm
| Algorithm 2 Iterative Machine Learning (IML) Algorithm |
| 1: Find via an exhaustive search on the space |
| 2: Perturb the equilibrium inputs and generate the persistently exciting input sequence comply with (18); |
| 3: Apply Formulas (15)–(17) and obtain the data-based open-loop realization |
| 4: Compute the convex hull
|
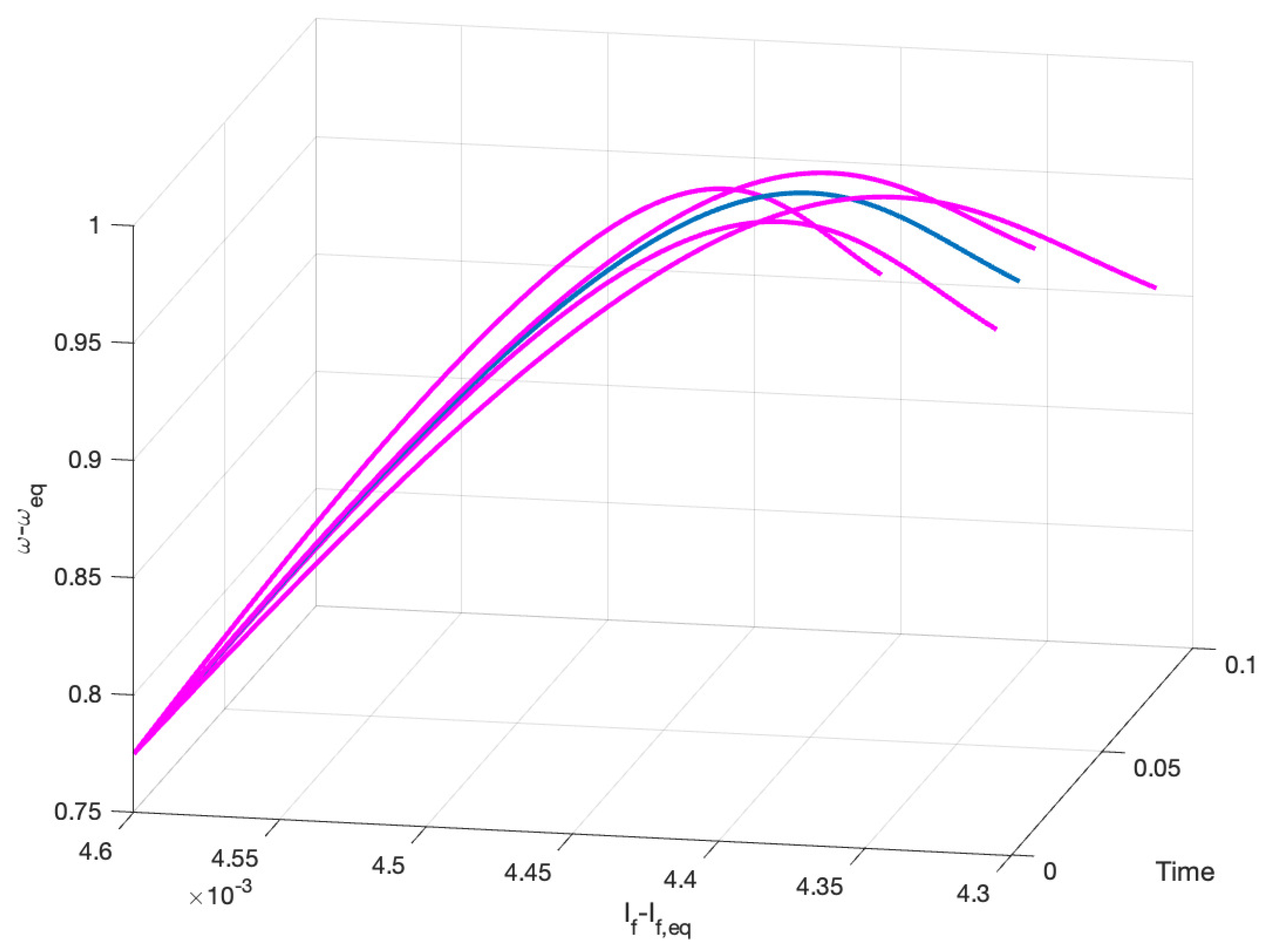
| 5: Perform Monte carlo simulations: compute sequences of state trajectories and verify |
| 6: if YES then Exit; |
| 7: else |
| 8: Find a new equilibrium |
| 9: end if |
| 10: Goto Step 4 and update |
5. Illustrative Examples
- Algorithm 1
- −
- Yalmip parser (available at the following: https://yalmip.github.io/download/ (accessed on 20 May 2024))/MOSEK © Optimization package (LMI procedures).
- −
- MATLAB Reinforcement Learning toolbox © and the MATLAB Deep learning toolbox © (Algorithm 2).
- fmincon MATLAB Optimization Toolbox © function used for the NMPC competitor.
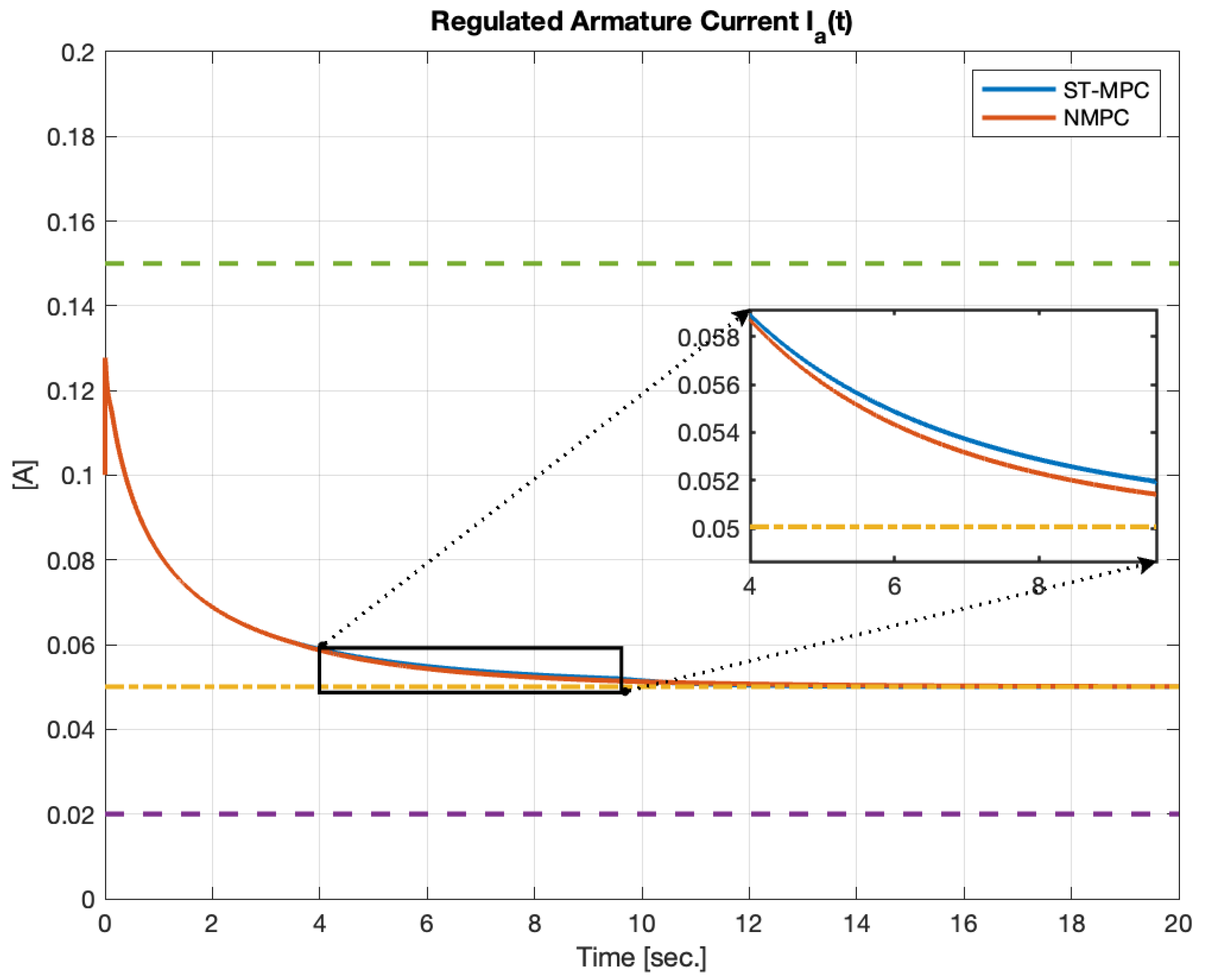
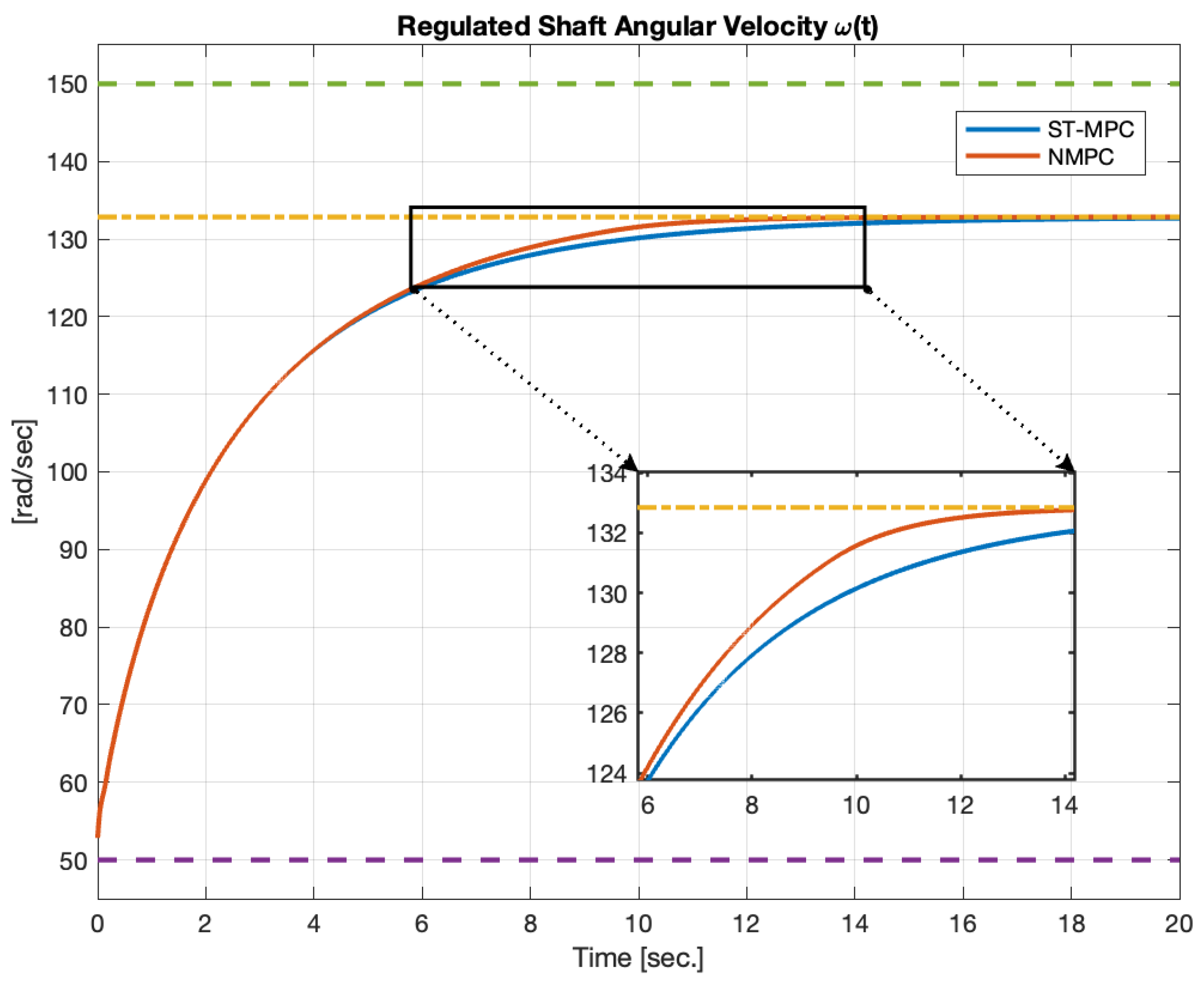
5.1. DC Motor
- and are the field and armature currents, and and are the related voltages;
- is the shaft rotor angular speed;
- is the shaft rotor torque load;
- , , which are the field resistance/inductance, and , , which are the armature resistance/inductance;
- , , which are the inertia and friction coefficient;
- , which is the motor torque constant.
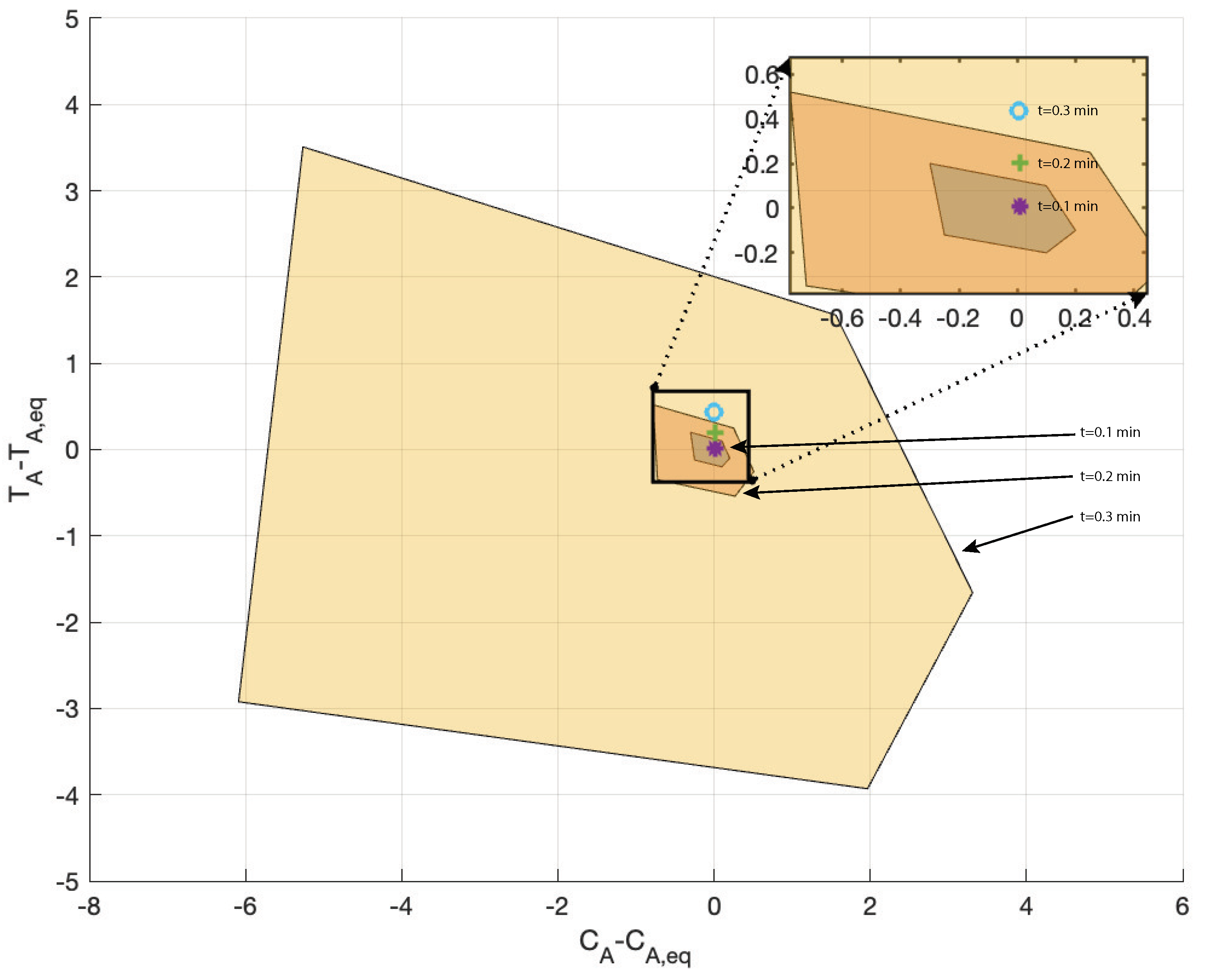
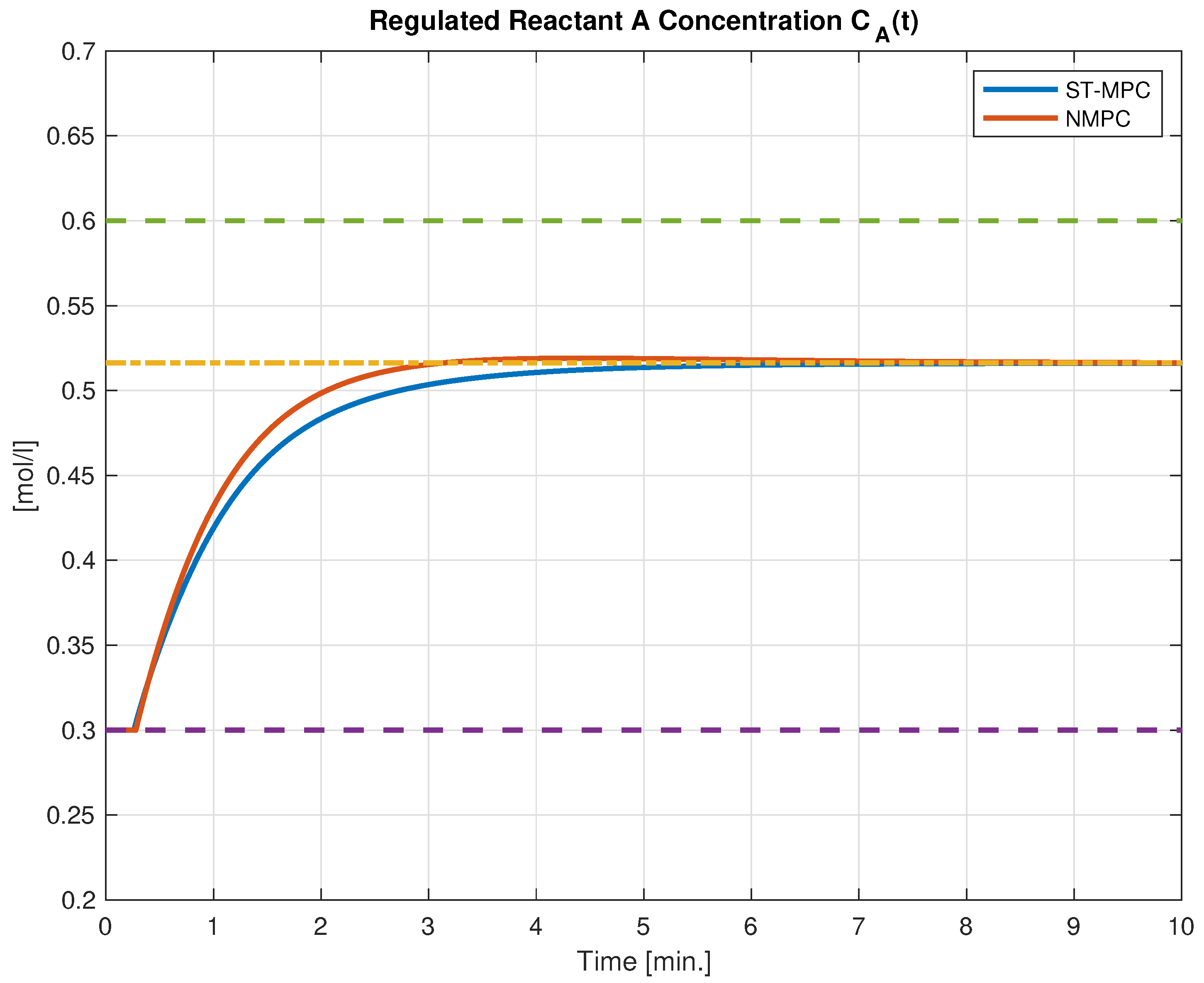
5.2. Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor
- is the concentration of A in the reactor;
- is the reactor temperature;
- is the temperature of the coolant stream.
- and the model parameters are , , , ; ; ; , , , (see [38] for details on the meanings of these parameters). The resulting nonlinear model is then characterized by a two-state variable model in the form
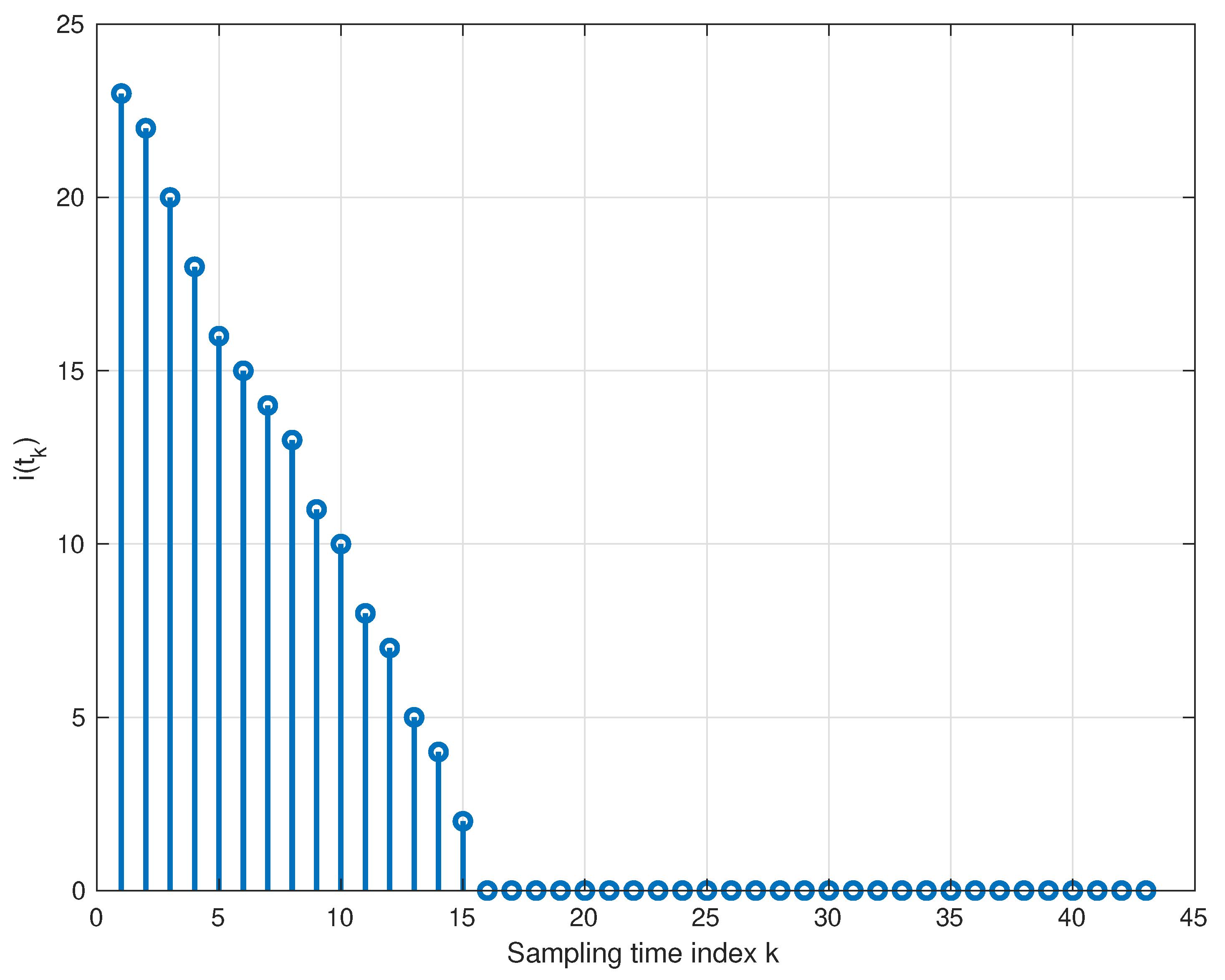
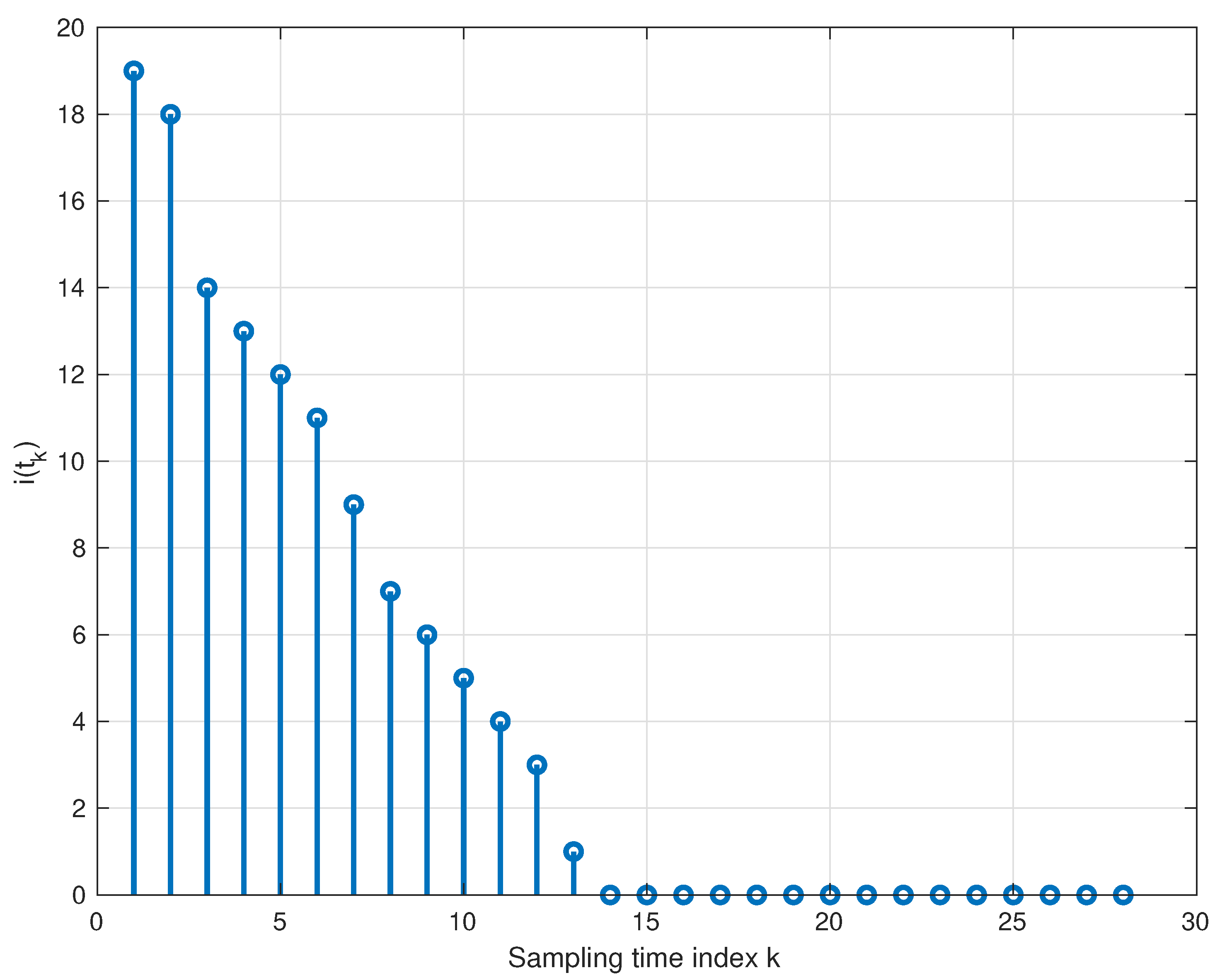
5.3. Computational Burdens
- When , it results in a trivial matrix-vector multiplication;
- When , it requires the solution of a quadratic programming problem (QP) with linear constraints whose computational complexity is ( is the optimization problem dimension size) [39].
6. Conclusions and Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawlings, J.; Mayne, D.; Diehl, M. Model Predictive Control: Theory, Computation, and Design; Nob Hill Publishing: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.S.; Wang, Z. From model-based control to data-driven control: Survey, classification and perspective. Inf. Sci. 2013, 235, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Waarde, H.J.; Eising, J.; Trentelman, H.L.; Camlibel, M.K. Data Informativity: A New Perspective on Data-Driven Analysis and Control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 65, 4753–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörfler, F.; Coulson, J.; Markovsky, I. Bridging Direct and Indirect Data-Driven Control Formulations via Regularizations and Relaxations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Pasqualetti, F. On Direct vs. Indirect Data-Driven Predictive Control. In Proceedings of the 2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Austin, TX, USA, 14–17 December 2021; pp. 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, P.; Breschi, V.; Lazar, M. Handbook of linear data-driven predictive control: Theory, implementation and design. Annu. Rev. Control 2023, 56, 100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formentin, S.; van Heusden, K.; Karimi, A. Model-based and data-driven model-reference control: A comparative analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC), Zurich, Switzerland, 17–19 July 2013; pp. 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Bonis, I.; Theodoropoulos, C. Data-driven model reduction-based nonlinear MPC for large-scale distributed parameter systems. J. Process. Control 2015, 35, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Qiao, J. Knowledge-Data-Driven Model Predictive Control for a Class of Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 4492–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, P.; Berktold, M.; Müller, D. Real-life data-driven model predictive control for building energy systems comparing different machine learning models. Energy Build. 2024, 305, 113895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Nair, S.H.; Borrelli, F. Scalable Multi-modal Model Predictive Control via Duality-based Interaction Predictions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:cs.RO/2402.01116. [Google Scholar]
- Vinod, D.; Singh, D.; Saikrishna, P.S. Data-Driven MPC for a Fog-Cloud Platform with AI-Inferencing in Mobile-Robotics. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 99589–99606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; He, A.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Jin, X. Data-Driven Model Predictive Control for Roll-to-Roll Process Register Error. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Additive Manufacturing Conference, International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 19–20 October 2022; p. V001T03A006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, T.V.; Sotoudeh, S.M.; HomChaudhuri, B. Data-Driven Prediction and Predictive Control Methods for Eco-Driving in Production Vehicles. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, S.L.; Proctor, J.L.; Kutz, J.N. Discovering governing equations from data by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3932–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prag, K.; Woolway, M.; Celik, T. Toward Data-Driven Optimal Control: A Systematic Review of the Landscape. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 32190–32212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalti, M.; Lopez, V.G.; Berberich, J.; Allgöwer, F.; Müller, M.A. Data-driven nonlinear predictive control for feedback linearizable systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.; Reinhardt, D.; Kordabad, A.B.; Gros, S. Model-Free Data-Driven Predictive Control Using Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Marina Bay Sands, Singapore, 13–15 December 2023; pp. 4046–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Xi, Y.; Gan, Z. Synthesis of model predictive control based on data-driven learning. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2019, 63, 189204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortino, G.; Savaglio, C.; Spezzano, G.; Zhou, M. Internet of Things as System of Systems: A Review of Methodologies, Frameworks, Platforms, and Tools. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Djenouri, Y.; Srivastava, G.; Djenouri, D.; Lin, J.C.W.; Fortino, G. Deep learning for pedestrian collective behavior analysis in smart cities: A model of group trajectory outlier detection. Inf. Fusion 2021, 65, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, J.; Lygeros, J.; Dörfler, F. Data-Enabled Predictive Control: In the Shallows of the DeePC. In Proceedings of the 2019 18th European Control Conference (ECC), Naples, Italy, 25–28 June 2019; pp. 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongard, J.; Berberich, J.; Köhler, J.; Allgöwer, F. Robust Stability Analysis of a Simple Data-Driven Model Predictive Control Approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 2625–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, J.C.; Rapisarda, P.; Markovsky, I.; De Moor, B.L. A note on persistency of excitation. Syst. Control Lett. 2005, 54, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Persis, C.; Tesi, P. Formulas for Data-Driven Control: Stabilization, Optimality, and Robustness. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 65, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovsky, I. Data-Driven Simulation of Generalized Bilinear Systems via Linear Time-Invariant Embedding. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, F.; Franzè, G.; Pupo, F.; Fortino, G. Set-theoretic receding horizon control for nonlinear systems: A data-driven approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE EUROCON 2023—20th International Conference on Smart Technologies, Torino, Italy, 6–8 July 2023; pp. 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, D.; Casavola, A.; Franzè, G.; Mosca, E. An ellipsoidal off-line MPC scheme for uncertain polytopic discrete-time systems. Automatica 2008, 44, 3113–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, D.; Casavola, A.; Mosca, E. Constrained predictive control of nonlinear plants via polytopic linear system embedding. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2000, 10, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; El Ghaoui, L.; Feron, E.; Balakrishnan, V. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory; SIAM Studies in Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Magni, L.; De Nicolao, G.; Scattolini, R.; Allgöwer, F. Robust model predictive control for nonlinear discrete-time systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2003, 13, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchini, F.; Miani, S. Set-Theoretic Methods in Control, 1st ed.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzhanski, A.; Valyi, I. Ellipsoidal Calculus for Estimation and Control; Systems & Control: Foundations & Applications; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kočvara, M.; Stingl, M. PENNON: A code for convex nonlinear and semidefinite programming. Optim. Methods Softw. 2003, 18, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall Press: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jampani, R.; Xu, F.; Wu, M.; Perez, L.L.; Jermaine, C.; Haas, P.J. MCDB: A monte carlo approach to managing uncertain data. In Proceedings of the SIGMOD ’08 2008 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, New York, NY, USA, 9–12 June 2008; pp. 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S.; Pekarek, S. Analysis of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems; IEEE Press Series on Power and Energy Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pipino, H.A.; Cappelletti, C.A.; Adam, E.J. Adaptive multi-model predictive control applied to continuous stirred tank reactor. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2021, 145, 107195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tal, A.; Nemirovski, A. Lectures on Modern Convex Optimization; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M. Efficient nonlinear model predictive control algorithms. Annu. Rev. Control 2004, 28, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannini, F.; Famularo, D. A Data-Driven Approach to Set-Theoretic Model Predictive Control for Nonlinear Systems. Information 2024, 15, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15070369
Giannini F, Famularo D. A Data-Driven Approach to Set-Theoretic Model Predictive Control for Nonlinear Systems. Information. 2024; 15(7):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15070369
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannini, Francesco, and Domenico Famularo. 2024. "A Data-Driven Approach to Set-Theoretic Model Predictive Control for Nonlinear Systems" Information 15, no. 7: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15070369
APA StyleGiannini, F., & Famularo, D. (2024). A Data-Driven Approach to Set-Theoretic Model Predictive Control for Nonlinear Systems. Information, 15(7), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15070369







